Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 153-160.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-262
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress in RNA interference against the infection of mosquito-borne viruses
Yong Wei( ), Yulan He, Xueli Zheng(
), Yulan He, Xueli Zheng( )
)
- Department of Pathogen Biology, School of Public Health, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China
-
Received:2019-10-15Revised:2019-12-14Online:2020-01-02Published:2020-01-07 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31630011);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China(2017A030313625);Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou City(201804020084)
Cite this article
Yong Wei, Yulan He, Xueli Zheng. Research progress in RNA interference against the infection of mosquito-borne viruses[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(2): 153-160.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Gubler DJ . Human arbovirus infections worldwide. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2001,951:13-24.
doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb02681.x pmid: 11797771 |
| [2] |
Beckham JD, Tyler KL . Arbovirus infections. Continuum (Minneap Minn), 2015,21:1599-1611.
doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000240 pmid: 26633778 |
| [3] |
Laureti M, Narayanan D, Rodriguez-Andres J, Fazakerley JK, Kedzierski L . Flavivirus receptors: diversity, identity, and cell entry. Front Immunol, 2018,9:2180.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02180 pmid: 30319635 |
| [4] |
Lim EXY, Lee WS, Madzokere ET, Herrero LJ . Mosquitoes as suitable vectors for alphaviruses. Viruses, 2018,10(2):E84.
doi: 10.3390/v10020084 pmid: 29443908 |
| [5] | Wuerth JD, Weber F . Phleboviruses and the type I interferon response. Viruses, 2016,8(6):174. |
| [6] |
Dash AP, Bhatia R, Sunyoto T, Mourya DT . Emerging and re-emerging arboviral diseases in Southeast Asia. J Vector Borne Dis, 2013,50(2):77-84.
pmid: 23995308 |
| [7] |
Lowe R, Barcellos C, Brasil P, Cruz OG, Honório NA, Kuper H, Carvalho MS . The Zika virus epidemic in Brazil: From discovery to future implications. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2018,15(1):96.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph15010096 pmid: 29315224 |
| [8] |
Weaver SC, Costa F, Garcia-Blanco MA, Ko AI, Ribeiro GS, Saade G, Shi PY, Vasilakis N . Zika virus: History, emergence, biology, and prospects for control. Antiviral Res, 2016,130:69-80.
doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.03.010 pmid: 26996139 |
| [9] |
Pang T, Mak TK, Gubler DJ . Prevention and control of dengue-the light at the end of the tunnel. Lancet Infect Dis, 2017,17(3):e79-e87.
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30471-6 pmid: 28185870 |
| [10] |
Xi ZY, Ramirez JL, Dimopoulos G . The Aedes aegypti toll pathway controls dengue virus infection. PLoS Pathog, 2008,4(7):e1000098.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000098 pmid: 18604274 |
| [11] |
Souza-Neto JA, Sim S, Dimopoulos G . An evolutionary conserved function of the JAK-STAT pathway in anti- dengue defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009,106(42):17841-17846.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905006106 pmid: 19805194 |
| [12] | Liu XM, Yuan ML . Progress in innate immunity-related genes in insects. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018,40(6):451-466. |
| 刘小民, 袁明龙 . 昆虫天然免疫相关基因研究进展. 遗传, 2018,40(6):451-466. | |
| [13] |
Ding SW, Voinnet O . Antiviral immunity directed by small RNAs. Cell, 2007,130(3):413-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.039 pmid: 17693253 |
| [14] |
Nandety RS, Kuo YW, Nouri S, Falk BW . Emerging strategies for RNA interference (RNAi) applications in insects. Bioengineered, 2015,6(1):8-19.
doi: 10.4161/21655979.2014.979701 pmid: 25424593 |
| [15] |
Lee WS, Webster JA, Madzokere ET, Stephenson EB, Herrero LJ . Mosquito antiviral defense mechanisms: a delicate balance between innate immunity and persistent viral infection. Parasit Vectors, 2019,12(1):165.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3433-8 pmid: 30975197 |
| [16] |
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC . Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 1998,391(6669):806-811.
doi: 10.1038/35888 pmid: 9486653 |
| [17] |
Saleh MC , Tassetto M, van Rij RP, Goic B, Gausson V, Berry B, Jacquier C, Antoniewski C, Andino R. Antiviral immunity in Drosophila requires systemic RNA interference spread. Nature, 2009,458(7236):346-350.
doi: 10.1038/nature07712 pmid: 19204732 |
| [18] |
Puglise JM, Estep AS, Becnel JJ . Expression profiles and RNAi silencing of inhibitor of apoptosis transcripts in Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol, 2016,53(2):304-314.
doi: 10.1093/jme/tjv191 pmid: 26659858 |
| [19] |
Kang S, Hong YS . RNA interference in infectious tropical diseases. Korean J Parasitol, 2008,46(1):1-15.
doi: 10.3347/kjp.2008.46.1.1 pmid: 18344671 |
| [20] |
Gandhi NS, Tekade RK, Chougule MB . Nanocarrier mediated delivery of siRNA/miRNA in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for cancer therapy: current progress and advances. J Control Release, 2014,194:238-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.001 pmid: 25204288 |
| [21] | Zheng WH, Lin ZQ, Zhuo M, Du HL, Wang XN . Research progress on influenza antiviral small RNAs. Hereditas (Beijing), 2012,34(5):526-532. |
| 郑维豪, 林志强, 卓敏, 杜红丽, 王小宁 . 抗流感病毒小RNAs研究进展. 遗传, 2012,34(5):526-532. | |
| [22] |
Galiana-Arnoux D, Dostert C, Schneemann A, Hoffmann JA, Imler JL . Essential function in vivo for Dicer-2 in host defense against RNA viruses in drosophila. Nat Immunol, 2006,7(6):590-597.
doi: 10.1038/ni1335 pmid: 16554838 |
| [23] |
Wang XH, Aliyari R, Li WX, Li HW, Kim K, Carthew R, Atkinson P, Ding SW . RNA interference directs innate immunity against viruses in adult Drosophila. Science, 2006,312(5772):452-454.
doi: 10.1126/science.1125694 pmid: 16556799 |
| [24] |
Matranga C, Tomari Y, Shin C, Bartel DP, Zamore PD . Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell, 2005,123(4):607-620.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.044 pmid: 16271386 |
| [25] |
Miyoshi K, Tsukumo H, Nagami T, Siomi H, Siomi MC . Slicer function of Drosophila argonautes and its involvement in RISC formation. Genes Dev, 2005,19(23):2837-2848.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1370605 pmid: 16287716 |
| [26] |
Li WX, Li H, Lu R, Li F, Dus M, Atkinson P, Brydon EW, Johnson KL, García-Sastre A, Ball LA, Palese P, Ding SW . Interferon antagonist proteins of influenza and vaccinia viruses are suppressors of RNA silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004,101(5):1350-1355.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308308100 pmid: 14745017 |
| [27] |
Sánchez-Vargas I, Scott JC, Poole-Smith BK, Franz AW, Barbosa-Solomieu V, Wilusz J, Olson KE, Blair CD . Dengue virus type 2 infections of Aedes aegypti are modulated by the mosquito's RNA interference pathway. PLoS Pathog, 2009,5(2):e1000299.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000299 pmid: 19214215 |
| [28] |
Khoo CC, Piper J, Sanchez-Vargas I, Olson KE, Franz AW . The RNA interference pathway affects midgut infection- and escape barriers for Sindbis virus in Aedes aegypti. BMC Microbiol, 2010,10:130.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-130 pmid: 20426860 |
| [29] |
Basu S, Aryan A, Overcash JM, Samuel GH, Anderson MA, Dahlem TJ, Myles KM, Adelman ZN . Silencing of end-joining repair for efficient site-specific gene insertion after TALEN/CRISPR mutagenesis in Aedes aegypti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015,112(13):4038-4043.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502370112 pmid: 25775608 |
| [30] |
Samuel GH, Wiley MR, Badawi A, Adelman ZN, Myles KM . Yellow fever virus capsid protein is a potent suppressor of RNA silencing that binds double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016,113(48):13863-13868.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600544113 pmid: 27849599 |
| [31] |
Keene KM, Foy BD, Sanchez-Vargas I, Beaty BJ, Blair CD, Olson KE . RNA interference acts as a natural antiviral response to O'nyong-nyong virus (Alphavirus; Togaviridae) infection of Anopheles gambiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004,101(49):17240-17245.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406983101 pmid: 15583140 |
| [32] |
Brackney DE, Beane JE, Ebel GD . RNAi targeting of West Nile virus in mosquito midguts promotes virus diversification. PLoS Pathog, 2009,5(7):e1000502.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000502 pmid: 19578437 |
| [33] |
Myles KM, Morazzani EM, Adelman ZN . Origins of alphavirus-derived small RNAs in mosquitoes. RNA Biol, 2009,6(4):387-391.
doi: 10.4161/rna.6.4.8946 pmid: 19535909 |
| [34] |
Myles KM, Wiley MR, Morazzani EM, Adelman ZN . Alphavirus-derived small RNAs modulate pathogenesis in disease vector mosquitoes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008,105(50):19938-19943.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803408105 pmid: 19047642 |
| [35] |
Schuster S, Zirkel F , Kurth A, van Cleef KWR, Drosten C, van Rij RP, Junglen S. A unique nodavirus with novel features: mosinovirus expresses two subgenomic RNAs, a capsid gene of unknown origin, and a suppressor of the antiviral RNA interference pathway. J Virol, 2014,88(22):13447-13459.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.02144-14 |
| [36] |
Szemiel AM, Failloux AB, Elliott RM . Role of Bunyamwera Orthobunyavirus NSs protein in infection of mosquito cells. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2012,6(9):e1823.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001823 pmid: 23029584 |
| [37] |
Kakumani PK, Ponia SS , S RK, Sood V, Chinnappan M, Banerjea AC, Medigeshi GR, Malhotra P, Mukherjee SK, Bhatnagar RK. Role of RNA interference (RNAi) in dengue virus replication and identification of NS4B as an RNAi suppressor. J Virol, 2013,87(16):8870-8883.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.02774-12 pmid: 23741001 |
| [38] |
Samuel GH, Wiley MR, Badawi A, Adelman ZN, Myles KM . Yellow fever virus capsid protein is a potent suppressor of RNA silencing that binds double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016,113(48):13863-13868.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600544113 pmid: 27849599 |
| [39] |
Jonas S, Izaurralde E . Towards a molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat Rev Genet, 2015,16(7):421-433.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3965 pmid: 26077373 |
| [40] |
Pedersen IM, Cheng GF, Wieland S, Volinia S, Croce CM, Chisari FV, David M . Interferon modulation of cellular microRNAs as an antiviral mechanism. Nature, 2007,449(7164):919-922.
doi: 10.1038/nature06205 pmid: 17943132 |
| [41] |
Lee YS, Nakahara K, Pham JW, Kim K, He Z, Sontheimer EJ, Carthew RW . Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell, 2004,117(1):69-81.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00261-2 pmid: 15066283 |
| [42] |
Xia MM, Shen XY, Niu CM, Xia J, Sun HY, Zheng Y . MicroRNA regulates Sertoli cell proliferation and adhesion. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018,40(9):724-732.
pmid: 369476 |
|
夏蒙蒙, 申雪沂, 牛长敏, 夏静, 孙红亚, 郑英 . MicroRNA参与调控睾丸支持细胞的增殖与粘附功能. 遗传, 2018,40(9):724-732.
pmid: 369476 |
|
| [43] |
Trobaugh DW, Klimstra WB . MicroRNA regulation of RNA virus replication and pathogenesis. Trends Mol Med, 2017,23(1):80-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.11.003 pmid: 27989642 |
| [44] |
Hussain M, Torres S, Schnettler E, Funk A, Grundhoff A, Pijlman GP, Khromykh AA, Asgari S . West Nile virus encodes a microRNA-like small RNA in the 3' untranslated region which up-regulates GATA4 mRNA and facilitates virus replication in mosquito cells. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012,40(5):2210-2223.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr848 pmid: 22080551 |
| [45] |
Hussain M, Asgari S . MicroRNA-like viral small RNA from Dengue virus 2 autoregulates its replication in mosquito cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014,111(7):2746-2751.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320123111 pmid: 24550303 |
| [46] |
Campbell CL, Harrison T, Hess AM, Ebel GD . MicroRNA levels are modulated in Aedes aegypti after exposure to Dengue-2. Insect Mol Biol, 2014,23(1):132-139.
doi: 10.1111/imb.12070 |
| [47] |
Slonchak A, Hussain M, Torres S, Asgari S, Khromykh AA . Expression of mosquito microRNA Aae-miR-2940-5p is downregulated in response to West Nile virus infection to restrict viral replication. J Virol, 2014,88(15):8457-8467.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00317-14 |
| [48] |
Su JX, Li CX, Zhang YM, Yan T, Zhu XJ, Zhao MH, Xing D, Dong YD, Guo XX, Zhao TY . Identification of microRNAs expressed in the midgut of Aedes albopictus during dengue infection. Parasit Vectors, 2017,10(1):63.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-1966-2 pmid: 28159012 |
| [49] |
Su JX, Wang G, Li CX, Xing D, Yan T, Zhu XJ, Liu QM, Wu Q, Guo XX, Zhao TY . Screening for differentially expressed miRNAs in Aedes albopictus(Diptera: Culicidae) exposed to DENV-2 and their effect on replication of DENV-2 in C6/36 cells. Parasit Vectors, 2019,12(1):44.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3261-2 pmid: 30658692 |
| [50] |
Varjak M, Maringer K, Watson M, Sreenu VB, Fredericks AC, Pondeville E, Donald CL, Sterk J, Kean J, Vazeille M, Failloux AB, Kohl A, Schnettler E . Aedes aegypti Piwi4 is a noncanonical PIWI protein involved in antiviral responses. mSphere, 2017,2(3):e00144-17.
doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00144-17 pmid: 28497119 |
| [51] |
Yin H, Lin HF . An epigenetic activation role of Piwi and a Piwi-associated piRNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature, 2007,450(7167):304-308.
doi: 10.1038/nature06263 pmid: 17952056 |
| [52] |
Kirino Y, Mourelatos Z . Mouse Piwi-interacting RNAs are 2'-O-methylated at their 3' termini. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2007,14(4):347-348.
doi: 10.1038/nsmb1218 pmid: 17384647 |
| [53] |
Liu QP, An N, Cen S, Li XY . Molecular mechanisms of genetic transposition inhibition by piRNA. Hereditas (Beijing), 2018,40(6):445-450.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-072 pmid: 29959117 |
|
刘启鹏, 安妮, 岑山, 李晓宇 . piRNA抑制基因转座的分子机制. 遗传, 2018,40(6):445-450.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-072 pmid: 29959117 |
|
| [54] |
Siomi MC, Sato K, Pezic D, Aravin AA . PIWI-interacting small RNAs: the vanguard of genome defence. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2011,12(4):246-258.
doi: 10.1038/nrm3089 pmid: 21427766 |
| [55] |
Brennecke J, Aravin AA, Stark A, Dus M, Kellis M, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ . Discrete small RNA- generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell, 2007,128(6):1089-1103.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.043 pmid: 17346786 |
| [56] |
Hayashi R, Schnabl J, Handler D, Mohn F, Ameres SL, Brennecke J . Genetic and mechanistic diversity of piRNA 3'-end formation. Nature, 2016,539(7630):588-592.
doi: 10.1038/nature20162 pmid: 27851737 |
| [57] |
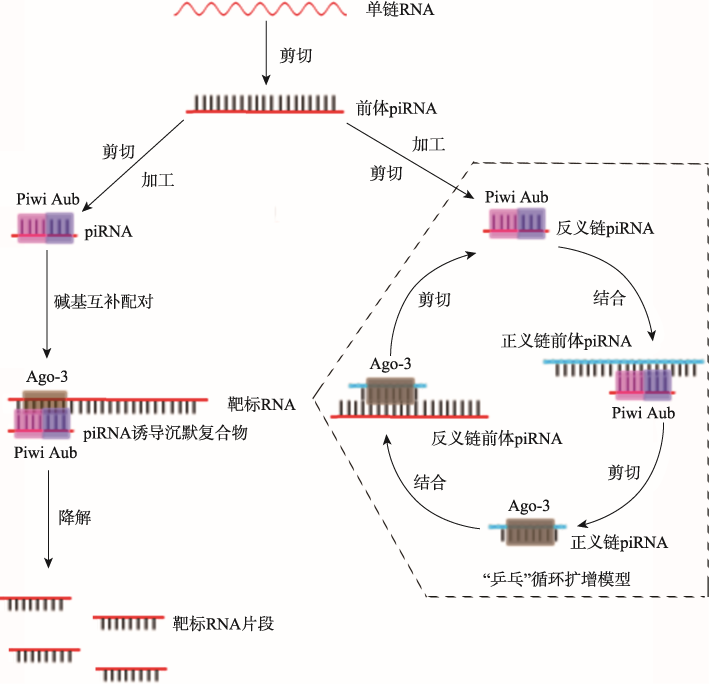
Morazzani EM, Wiley MR, Murreddu MG, Adelman ZN, Myles KM . Production of virus-derived ping-pong-dependent piRNA-like small RNAs in the mosquito soma. PLoS Pathog, 2012,8(1):e1002470.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002470 pmid: 22241995 |
| [58] |
Miesen P , Joosten J, van Rij RP. PIWIs go viral: arbovirus-derived piRNAs in vector mosquitoes. PLoS Pathog, 2016,12(12):e1006017.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006017 pmid: 28033427 |
| [59] |
Miesen P , Girardi E, van Rij RP. Distinct sets of PIWI proteins produce arbovirus and transposon-derived piRNAs in Aedes aegypti mosquito cells. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015,43(13):6545-6556.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv590 pmid: 26068474 |
| [60] |
Schnettler E, Donald CL, Human S, Watson M, Siu RW , McFarlane M, Fazakerley JK, Kohl A, Fragkoudis R. Knockdown of piRNA pathway proteins results in enhanced Semliki Forest virus production in mosquito cells. J Gen Virol, 2013,94(Pt 7):1680-1689.
doi: 10.1099/vir.0.053850-0 pmid: 23559478 |
| [1] | Chengxian Wang, Yikang S. Rong, Min Cui. The molecular mechanism of Drosophila restricting telomeric transposons [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(3): 221-228. |
| [2] | Yan Zhu, Ming Wei, Xiao Zhou, Linhua Deng, Jian Qiu, Guo Li, Shiqiang Zhou, Hao Xie, Desheng Li, Chengdong Wang. Progress on miRNA in giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 849-857. |
| [3] | Wenquan Liang,Yu Hou,Cunyou Zhao. Schizophrenia-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms affecting microRNA function [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(8): 677-685. |
| [4] | Yakun Song,Min Zhang,Qiaochu Wang,Yuli Peng,Fangxing Jia,Chunhong Yu. Laboratory design and practice for undergraduates: Using RNAi to modulate gene expression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(7): 653-661. |
| [5] | Lin Rao, Feilong Meng, Ran Fang, Chenyi Cai, Xiaoli Zhao. Molecular mechanism of microRNA in regulating cochlear hair cell development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(11): 994-1008. |
| [6] | Xia Mengmeng,Shen Xueyi,Niu Changmin,Xia Jing,Sun Hongya,Zheng Ying. MicroRNA regulates Sertoli cell proliferation and adhesion [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(9): 724-732. |
| [7] | Hailong Liu, Yang Shen, Yang Gao, Ling Zhou, Xiaosong Han, Changzhi Zhao, Gaojuan Yang, Yilong Chen, Hui Yang, Shengsong Xie. Assessing abundance and specificity of different types of sgRNA targeting miRNA precursors [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(7): 561-571. |
| [8] | Qipeng Liu, Ni An, Shan Cen, Xiaoyu Li. Molecular mechanisms of genetic transposition inhibition by piRNA [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(6): 445-450. |
| [9] | Juan Xiao, Xun Wang, Yi Luo, Xiaokai Li, Xuewei Li. Research progress in sRNAs and functional proteins in epididymosomes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(3): 197-206. |
| [10] | Enhui Li,Xin Zhao,Ce Zhang,Wei Liu. Fragile X mental retardation protein participates in non-coding RNA pathways [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(2): 87-94. |
| [11] | Zhiheng Yuan,Yanmei Zhao. The regulatory functions of piRNA/PIWI in spermatogenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(8): 683-691. |
| [12] | Xinyun Li, Liangliang Fu, Huijun Cheng, Shuhong Zhao. Advances on microRNA in regulating mammalian skeletal muscle development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(11): 1046-1053. |
| [13] | Chendong Liu, Lu Yang, Hongzhou Pu, Qiong Yang, Wenyao Huang, Xue Zhao, Li Zhu, Shunhua Zhang. Epigenetics regulates gene expression patterns of skeletal muscle induced by physical exercise [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(10): 888-896. |
| [14] | Jun Wei,Xiujun Lu,Xiaolin Zhang,Mei Mei,Xiaoli Huang. Functions of microRNA in seed development, dormancy and germination processes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(1): 14-21. |
| [15] | Ke Zhang, Guangde Feng, Baoyun Zhang, Wei Xiang, Long Chen, Fang Yang, Mingxing Chu, Pingqing Wang. Application of epigenetic markers in molecular breeding of the swine [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016, 38(7): 634-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||