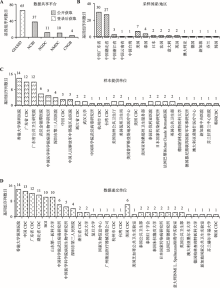
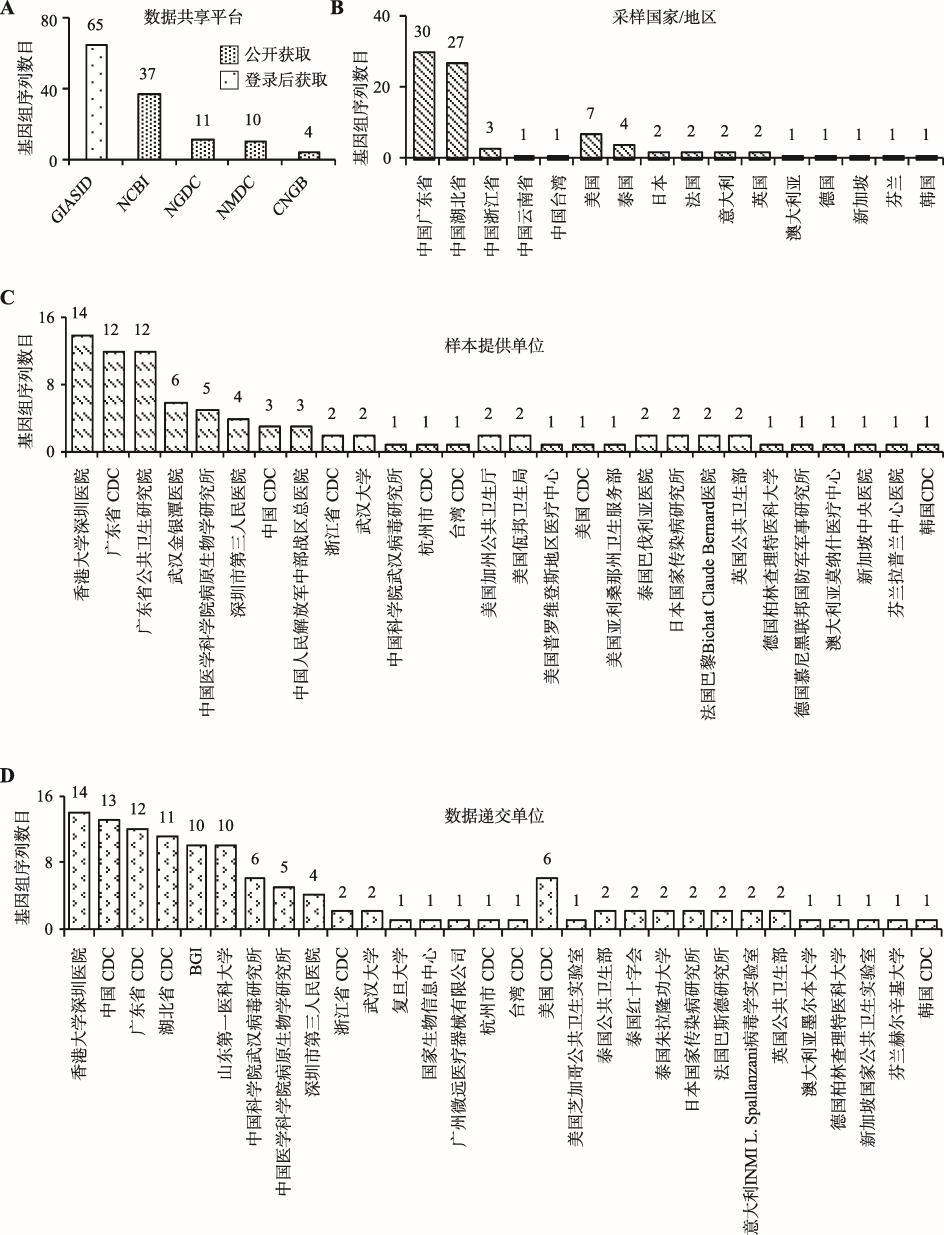
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 212-221.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-030
• Resource and Platform • Previous Articles Next Articles
The 2019 novel coronavirus resource
Wenming Zhao1,2,3( ), Shuhui Song1,2(
), Shuhui Song1,2( ), Meili Chen1,2(
), Meili Chen1,2( ), Dong Zou1,2(
), Dong Zou1,2( ), Lina Ma1,2(
), Lina Ma1,2( ), Yingke Ma1,2, Rujiao Li1,2, Lili Hao1,2, Cuiping Li1,2, Dongmei Tian1,2, Bixia Tang1,2, Yanqing Wang1,2, Junwei Zhu1,2, Huanxin Chen1,2, Zhang Zhang1,2,3, Yongbiao Xue1,3(
), Yingke Ma1,2, Rujiao Li1,2, Lili Hao1,2, Cuiping Li1,2, Dongmei Tian1,2, Bixia Tang1,2, Yanqing Wang1,2, Junwei Zhu1,2, Huanxin Chen1,2, Zhang Zhang1,2,3, Yongbiao Xue1,3( ), Yiming Bao1,2,3(
), Yiming Bao1,2,3( )
)
- 1. China National Center for Bioinformation & National Genomics Data Center, Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China;
2. CAS Key Laboratory of Genome Sciences and Information, Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2020-01-31Revised:2020-02-07Online:2020-02-20Published:2020-02-08 -
Supported by:the National Key Research & Development Program of China(2016YFE0206600);the National Key Research & Development Program of China(2017YFC1201202);13th Five-year Informatization Plan of CAS(XXH13505-05);Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chines Academy of Sciences (CAS)(XDA19050302);Capacity building project of genome science data center of Chinese Academy of Sciences(0202);Key Technology Talent Program of the CAS, The Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Cite this article
Wenming Zhao, Shuhui Song, Meili Chen, Dong Zou, Lina Ma, Yingke Ma, Rujiao Li, Lili Hao, Cuiping Li, Dongmei Tian, Bixia Tang, Yanqing Wang, Junwei Zhu, Huanxin Chen, Zhang Zhang, Yongbiao Xue, Yiming Bao. The 2019 novel coronavirus resource[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(2): 212-221.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table S1
"
| Virus Isolate Name | Accession ID | Data Source | Related ID | Host | Sample Collection Date | Location | Nuc.Completeness | Originating Lab | Submitting Lab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BetaCoV/USA/WA1-F6/2020 | EPI_ISL_407215 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-25 | USA / Washington | Complete | WA State Department of Health | Pathogen Discovery, Respiratory Viruses Branch, Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Dieases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Korea/KCDC03/2020 | EPI_ISL_407193 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-25 | Korea / Gyeonggi-do | Complete | Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (KCDC) Center for Laboratory Control of Infectious Diseases Division of Viral Diseases | Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (KCDC) Center for Laboratory Control of Infectious Diseases Division of Viral Diseases | |
| BetaCoV/Japan/AI/I-004/2020 | EPI_ISL_407084 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-25 | Japan / Aichi | Complete | Department of Virology III, National Institute of Infectious Diseases | Pathogen Genomics Center, National Institute of Infectious Diseases | |
| BetaCoV/USA/WA1-A12/2020 | EPI_ISL_407214 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-25 | USA / Washington | Complete | WA State Department of Health | Pathogen Discovery, Respiratory Viruses Branch, Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Dieases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Singapore/1/2020 | EPI_ISL_406973 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-23 | Singapore | Complete | Singapore General Hospital | National Public Health Laboratory | |
| BetaCoV/England/02/2020 | EPI_ISL_407073 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-29 | England | Complete | Respiratory Virus Unit, Microbiology Services Colindale, Public Health England | Respiratory Virus Unit, Microbiology Services Colindale, Public Health England | |
| BetaCoV/England/01/2020 | EPI_ISL_407071 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-29 | England | Complete | Respiratory Virus Unit, Microbiology Services Colindale, Public Health England | Respiratory Virus Unit, Microbiology Services Colindale, Public Health England | |
| BetaCoV/Finland/1/2020 | EPI_ISL_407079 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-29 | Finland / Lapland | Partial/scaffold level | Lapland Central Hospital | Department of Virology, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland | |
| BetaCoV/Hangzhou/HZ-1/2020 | EPI_ISL_406970 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-20 | China / Zhejiang / Hangzhou | Complete | Hangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Microbiology Lab | Hangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Microbiology Lab | |
| 2019 nCoV/Italy-INMI1 | MT008022 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406959 | Human | 2020-01 | Italy / Rome | Partial/gene level | Virology Laboratory, INMI L. Spallanzani | |
| 2019 nCoV/Italy-INMI2 | MT008023 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406960 | Human | 2020-01 | Italy / Rome | Partial/gene level | Virology Laboratory, INMI L. Spallanzani | |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH19002/2019 | NMDC60013002-05 | NMDC | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention; BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd | ||
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH19008/2019 | NMDC60013002-06 | NMDC | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention; BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd | ||
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/YS8011/2020 | NMDC60013002-07 | NMDC | Human | 2020-1-7 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention; BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd | ||
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH19001/2019 | NMDC60013002-08 | NMDC | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention; BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd | ||
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH19004/2020 | NMDC60013002-09 | NMDC | Human | 2020-1-1 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention; BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd | ||
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH19005/2019 | NMDC60013002-10 | NMDC | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention; BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd | ||
| BetaCoV/Germany/BavPat1/2020 | EPI_ISL_406862 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-28 | Germany / Bavaria / Munich | Complete | Charité Universit?tsmedizin Berlin, Institute of Virology; Institut für Mikrobiologie der Bundeswehr, Munich | Charité Universit?tsmedizin Berlin, Institute of Virology | |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH-01/2019 | NMDC60013002-01 | NMDC | LR757998, EPI_ISL_406798, CNA0007332 | Human | 2019-12-26 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | General Hospital of Central Theater Command of People's Liberation Army of China | BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd; China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH-02/2019 | NMDC60013002-02 | NMDC | LR757997, CNA0007333 | Human | 2019-12-31 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Partial/scaffold level | BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd; China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH-03/2019 | NMDC60013002-03 | NMDC | LR757996, EPI_ISL_406800, CNA0007334 | Human | 2020-1-1 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | General Hospital of Central Theater Command of People's Liberation Army of China | BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd; China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/WH-04/2019 | NMDC60013002-04 | NMDC | LR757995, EPI_ISL_406801, CNA0007335 | Human | 2020-1-5 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | General Hospital of Central Theater Command of People's Liberation Army of China | BGI PathoGenesis Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd; China CDC; Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences; Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| BetaCoV/Australia/VIC01/2020 | MT007544 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406844 | Human | 2020-1-25 | Australia / Victoria / Clayton | Complete | Monash Medical Centre | Department of Microbiology and Immunology, The University of Melbourne at The Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity |
| WIV02 | GWHABKK00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_402127, MN996527 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China/ Hubei / Wuhan | Complete | Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital | CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety and Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| WIV04 | GWHABKL00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_402124, MN996528 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei / Wuhan | Complete | Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital | CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety and Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| WIV05 | GWHABKM00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_402128, MN996529 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei / Wuhan | Complete | Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital | CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety and Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| WIV06 | GWHABKN00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_402129, MN996530 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei / Wuhan | Complete | Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital | CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety and Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| WIV07 | GWHABKO00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_402130, MN996531 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei / Wuhan | Complete | Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital | CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety and Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| TG13 | GWHABKP00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_402131, MN996532 | Rhinolophus affinis | 2013-7-24 | China / Yunnan / Pu'er | Complete | Wuhan Institute of Virology | CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety and Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF174/2020 | EPI_ISL_406531 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-22 | China / Guangdong Province | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Guangzhou/20SF206/2020 | EPI_ISL_406533 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-22 | China / Guangdong Province / Guangzhou City | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Foshan/20SF207/2020 | EPI_ISL_406534 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-22 | China / Guangdong Province | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Foshan/20SF210/2020 | EPI_ISL_406535 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-22 | China / Guangdong Province | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Foshan/20SF211/2020 | EPI_ISL_406536 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-22 | China / Guangdong Province | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF201/2020 | EPI_ISL_406538 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-23 | China / Guangdong Province | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention;Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Shenzhen/SZTH-001/2020 | EPI_ISL_406592 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-13 | China/ Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Immunity, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Disease, Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | |
| BetaCoV/Shenzhen/SZTH-003/2020 | EPI_ISL_406594 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-16 | China/ Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Immunity, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Disease, Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Immunity, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Disease, Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | |
| BetaCoV/Shenzhen/SZTH-004/2020 | EPI_ISL_406595 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-16 | China/ Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Immunity, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Disease, Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Immunity, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Disease, Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | |
| BetaCoV/Shenzhen/SZTH-002/2020 | EPI_ISL_406593 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-13 | China/ Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Immunity, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Disease, Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Immunity, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Disease, Shenzhen Third People's Hospital | |
| BetaCoV/France/IDF0373/2020 | EPI_ISL_406597 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-23 | France / Ile-de-France / Paris | Complete | Department of Infectious and Tropical Diseases, Bichat Claude Bernard Hospital, Paris | National Reference Center for Viruses of Respiratory Infections, Institut Pasteur, Paris | |
| BetaCoV/France/IDF0372/2020 | EPI_ISL_406596 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-23 | France / Ile-de-France / Paris | Complete | Department of Infectious and Tropical Diseases, Bichat Claude Bernard Hospital, Paris | National Reference Center for Viruses of Respiratory Infections, Institut Pasteur, Paris | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-001_2020 | MN938387 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-001_2020 | MN938385 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-002b_2020 | MN938388 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-004_2020 | MN938389 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-004_2020 | MN938386 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-005_2020 | MN938390 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-007a_2020 | MN975266 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-007a_2020 | MN975263 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-007b_2020 | MN975264 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-007b_2020 | MN975267 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-007c_2020 | MN975268 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-007c_2020 | MN975265 | GenBank | Human | 2020-01 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Partial/gene level | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | |
| SI200040-SP | MN970003 | GenBank | Human | 2020-1-8 | Thailand | Partial/gene level | Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University | ||
| SI200121-SP | MN970004 | GenBank | Human | 2020-1-13 | Thailand | Partial/gene level | Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University | ||
| BetaCoV/Taiwan/2/2020 | EPI_ISL_406031 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-23 | Taiwan/Kaohsiung City | Complete | Centers for Disease Control (Taiwan) | Centers for Disease Control (Taiwan) | |
| 2019-nCoV/USA-CA1/2020 | MN994467 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406034 | Human | 2020-1-23 | USA / California / Los Angeles | Complete | California Department of Public Health | Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| 2019-nCoV/USA-CA2/2020 | MN994468 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406036 | Human | 2020-1-22 | USA / California / Orange County | Complete | California Department of Public Health | Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| 2019-nCoV/USA-AZ1/2020 | MN997409 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406223 | Human | 2020-1-22 | USA / Arizona / Phoenix | Complete | Arizona Department of Health Services | Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| 2019-nCoV WHU01 | MN988668 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406716 | Human | 2020-1-2 | China / Hubei / Wuhan | Complete | State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan University | State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan University |
| 2019-nCoV WHU02 | MN988669 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406717 | Human | 2020-1-2 | China / Hubei / Wuhan | Complete | State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan University | State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan University |
| 2019-nCoV/USA-WA1/2020 | MN985325 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_404895 | Human | 2020-1-19 | USA / Washington / Snohomish County | Complete | Providence Regional Medical Center | Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| 2019-nCoV/USA-IL1/2020 | MN988713 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_404253 | Human | 2020-1-21 | USA / Illinois /Chicago | Complete | Pathogen Discovery, Respiratory Viruses Branch, Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Dieases Control and Prevention | IL Department of Public Health Chicago Laboratory |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IPBCAMS-WH-01/2019 | GWHABKF00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_402123 | Human | 2019-12-23 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College; Vision Medicals Co., Ltd |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IPBCAMS-WH-02/2019 | GWHABKG00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_403931 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IPBCAMS-WH-03/2019 | GWHABKH00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_403930 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IPBCAMS-WH-04/2019 | GWHABKI00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_403929 | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IPBCAMS-WH-05/2020 | GWHABKJ00000000 | Genome Warehouse | EPI_ISL_403928 | Human | 2020-1-1 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College; China National Center for Bioinformation |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-002a_2020 | MN938384 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_406030 | Human | 2020-1 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Complete | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital |
| 2019-nCoV_HKU-SZ-005b_2020 | MN975262 | GenBank | EPI_ISL_405839 | Human | 2020-1 | China / Guangdong / Shenzhen | Complete | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital | University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF040/2020 | EPI_ISL_403937 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-18 | China / Guangdong Province / Zhuhai City | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF028/2020 | EPI_ISL_403936 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-17 | China / Guangdong Province / Zhuhai City | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF025/2020 | EPI_ISL_403935 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-15 | China / Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF014/2020 | EPI_ISL_403934 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-15 | China / Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF013/2020 | EPI_ISL_403933 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-15 | China / Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Guangdong/20SF012/2020 | EPI_ISL_403932 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-14 | China / Guangdong Province / Shenzhen City | Complete | Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention; Guangdong Provincial Institute of Public Health | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Zhejiang/WZ-01/2020 | EPI_ISL_404227 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-16 | China / Zhejiang Province | Complete | Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention | Department of Microbiology, Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Zhejiang/WZ-02/2020 | EPI_ISL_404228 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-17 | China / Zhejiang Province | Complete | Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention | Department of Microbiology, Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/HBCDC-HB-01/2019 | EPI_ISL_402132 | GISAID | Human | 2019-12-30 | China/Hubei Province | Complete | Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital | Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention | |
| BetaCoV/Nonthaburi/74/2020 | EPI_ISL_403963 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-13 | Thailand/ Nonthaburi Province | Complete | Bamrasnaradura Hospital | Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand; Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases - Health Science Centre; Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand | |
| BetaCoV/Nonthaburi/61/2020 | EPI_ISL_403962 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-8 | Thailand/ Nonthaburi Province | Complete | Bamrasnaradura Hospital | Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand; Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases - Health Science Centre; Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand | |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IVDC-HB-04/2020 | EPI_ISL_402120 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-1 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IVDC-HB-01/2019 | EPI_ISL_402119 | GISAID | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | |
| BetaCoV/Wuhan/IVDC-HB-05/2019 | EPI_ISL_402121 | GISAID | Human | 2019-12-30 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | |
| BetaCoV/Kanagawa/1/2020 | EPI_ISL_402126 | GISAID | Human | 2020-1-14 | Kanagawa Prefecture / Japan | Partial | Dept. of Virology III, National Institute of Infectious Diseases | Dept. of Virology III, National Institute of Infectious Diseases | |
| Wuhan-Hu-1 | MN908947 | GenBank | NC_045512 | Human | 2019-12 | China / Hubei Province / Wuhan City | Complete | Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center & School of Public Health, Fudan University, Shanghai, China | |
Table S2
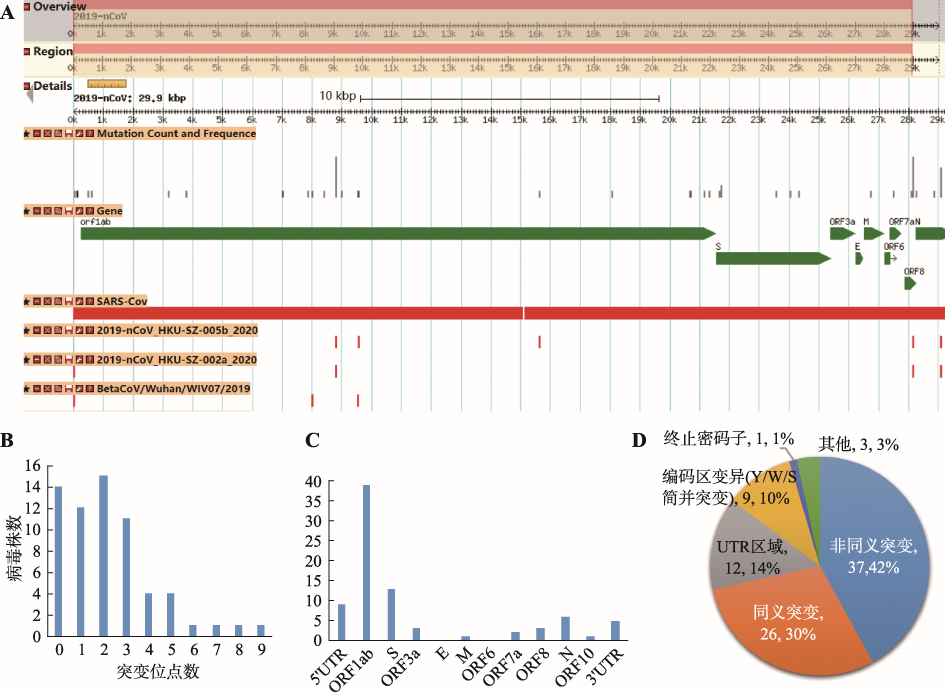
Genome variants and annotations"
| 基因组位置 | 基因/区域名称 | 变异病毒株数 | 碱基变化及病毒株数 | 变异注释类型 | 蛋白名称.位置.氨基酸变化 | 基因名.CDS位置.序列变化 | 效应类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-nCoV_16 | 5'UTR | 1 | C->T:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_31 | 5'UTR | 1 | A->G:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_104 | 5'UTR | 1 | T->A:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_111 | 5'UTR | 1 | T->C:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_112 | 5'UTR | 1 | T->G:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_119 | 5'UTR | 1 | C->G:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_120 | 5'UTR | 1 | T->C:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_124 | 5'UTR | 1 | G->A:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_241 | 5'UTR | 1 | C->T:1 | upstream_gene_variant | QHD43415.1 | gene-orf1ab | MODIFIER;DISTANCE=25 |
| 2019-nCoV_358 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | TGGAGACTCCGTGGAGGAGGTCTTA->T:1 | inframe_deletion | QHD43415.1:p.32-39GDSVEEVL>- | gene-orf1ab:c.94-117GGAGACTCCGTGGAGGAGGTCTTA>- | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_490 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->W:1 | coding_sequence_variant | QHD43415.1:p.75- | gene-orf1ab:c.225gaT>gaW | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_583 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.106V | gene-orf1ab:c.318gtC>gtT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_709 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->A:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.148E | gene-orf1ab:c.444gaG>gaA | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_1548 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->A:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.428S>N | gene-orf1ab:c.1283aGc>aAc | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_1912 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.549S | gene-orf1ab:c.1647tcC>tcT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_3037 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.924F | gene-orf1ab:c.2772ttC>ttT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_3177 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->Y:1 | coding_sequence_variant | QHD43415.1:p.971- | gene-orf1ab:c.2912cCt>cYt | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_3778 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | A->G:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.1171T | gene-orf1ab:c.3513acA>acG | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_4402 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->C:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.1379L | gene-orf1ab:c.4137ctT>ctC | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_5062 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.1599L>F | gene-orf1ab:c.4797ttG>ttT | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_6846 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->C:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2194M>T | gene-orf1ab:c.6581aTg>aCg | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_6968 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->A:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2235L>I | gene-orf1ab:c.6703Cta>Ata | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_6996 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->C:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2244I>T | gene-orf1ab:c.6731aTc>aCc | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_7016 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->A:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2251G>S | gene-orf1ab:c.6751Ggt>Agt | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_7866 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2534G>V | gene-orf1ab:c.7601gGt>gTt | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_8001 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | A->C:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2579D>A | gene-orf1ab:c.7736gAt>gCt | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_8388 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | A->G:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2708N>S | gene-orf1ab:c.8123aAc>aGc | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_8782 | gene-orf1ab | 16 | C->T:15;C->Y:1 | synonymous_variant;coding_sequence_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2839S;QHD43415.1:p.2839- | gene-orf1ab:c.8517agC>agT;gene-orf1ab:c.8517agC>agY | LOW;MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_8987 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->A:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.2908F>I | gene-orf1ab:c.8722Ttt>Att | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_9534 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.3090T>I | gene-orf1ab:c.9269aCt>aTt | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_9561 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.3099S>L | gene-orf1ab:c.9296tCa>tTa | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_11083 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.3606L>F | gene-orf1ab:c.10818ttG>ttT | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_11707 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | A->G:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.3814L | gene-orf1ab:c.11442ttA>ttG | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_11764 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->A:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.3833N>K | gene-orf1ab:c.11499aaT>aaA | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_15324 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.5020N | gene-orf1ab:c.15060aaC>aaT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_15607 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->C:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.5115L | gene-orf1ab:c.15343Tta>Cta | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_16188 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.5308W>C | gene-orf1ab:c.15924tgG>tgT | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_17000 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.5579T>I | gene-orf1ab:c.16736aCa>aTa | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_17373 | gene-orf1ab | 2 | C->T:2 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.5703A | gene-orf1ab:c.17109gcC>gcT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_18060 | gene-orf1ab | 3 | C->T:3 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.5932L | gene-orf1ab:c.17796ctC>ctT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_18488 | gene-orf1ab | 2 | T->C:2 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.6075I>T | gene-orf1ab:c.18224aTa>aCa | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_18512 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | C->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.6083P>L | gene-orf1ab:c.18248cCt>cTt | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_19065 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | T->C:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.6267P | gene-orf1ab:c.18801ccT>ccC | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_19959 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | A->C:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.6565E>D | gene-orf1ab:c.19695gaA>gaC | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_20670 | gene-orf1ab | 2 | G->A:2 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.6802A | gene-orf1ab:c.20406gcG>gcA | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_20679 | gene-orf1ab | 2 | G->A:2 | synonymous_variant | QHD43415.1:p.6805P | gene-orf1ab:c.20415ccG>ccA | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_21137 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | A->G:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.6958K>R | gene-orf1ab:c.20873aAg>aGg | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_21316 | gene-orf1ab | 1 | G->A:1 | missense_variant | QHD43415.1:p.7018D>N | gene-orf1ab:c.21052Gat>Aat | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_21656 | gene-S | 1 | T->A:1 | missense_variant | QHD43416.1:p.32F>I | gene-S:c.94Ttc>Atc | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_21707 | gene-S | 3 | C->T:3 | missense_variant | QHD43416.1:p.49H>Y | gene-S:c.145Cat>Tat | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_22303 | gene-S | 1 | T->G:1 | missense_variant | QHD43416.1:p.247S>R | gene-S:c.741agT>agG | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_22586 | gene-S | 1 | T->Y:1 | coding_sequence_variant | QHD43416.1:p.342- | gene-S:c.1024Ttt>Ytt | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_22622 | gene-S | 1 | A->G:1 | missense_variant | QHD43416.1:p.354N>D | gene-S:c.1060Aac>Gac | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_22652 | gene-S | 1 | G->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43416.1:p.364D>Y | gene-S:c.1090Gat>Tat | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_22661 | gene-S | 2 | G->T:2 | missense_variant | QHD43416.1:p.367V>F | gene-S:c.1099Gtc>Ttc | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_23403 | gene-S | 1 | A->G:1 | missense_variant | QHD43416.1:p.614D>G | gene-S:c.1841gAt>gGt | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_23569 | gene-S | 2 | T->C:2 | synonymous_variant | QHD43416.1:p.669G | gene-S:c.2007ggT>ggC | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_23605 | gene-S | 2 | T->G:2 | synonymous_variant | QHD43416.1:p.681P | gene-S:c.2043ccT>ccG | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_24034 | gene-S | 2 | C->T:1;C->Y:1 | synonymous_variant;coding_sequence_variant | QHD43416.1:p.824N;QHD43416.1:p.824- | gene-S:c.2472aaC>aaT;gene-S:c.2472aaC>aaY | LOW;MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_24325 | gene-S | 2 | A->G:2 | synonymous_variant | QHD43416.1:p.921K | gene-S:c.2763aaA>aaG | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_25060 | gene-S | 1 | A->G:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43416.1:p.1166L | gene-S:c.3498ttA>ttG | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_25645 | gene-ORF3a | 1 | T->C:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43417.1:p.85L | gene-ORF3a:c.253Ttg>Ctg | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_25964 | gene-ORF3a | 1 | A->G:1 | missense_variant | QHD43417.1:p.191E>G | gene-ORF3a:c.572gAa>gGa | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_26144 | gene-ORF3a | 5 | G->T:5 | missense_variant | QHD43417.1:p.251G>V | gene-ORF3a:c.752gGt>gTt | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_26729 | gene-M | 2 | T->C:1;T->Y:1 | synonymous_variant;coding_sequence_variant | QHD43419.1:p.69A;QHD43419.1:p.69- | gene-M:c.207gcT>gcC;gene-M:c.207gcT>gcY | LOW;MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_27493 | gene-ORF7a | 2 | C->T:2 | missense_variant | QHD43421.1:p.34P>S | gene-ORF7a:c.100Cct>Tct | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_27577 | gene-ORF7a | 1 | C->T:1 | stop_gained | QHD43421.1:p.62Q>* | gene-ORF7a:c.184Caa>Taa | HIGH |
| 2019-nCoV_28077 | gene-ORF8 | 2 | G->S:1;G->C:1 | coding_sequence_variant;missense_variant | QHD43422.1:p.62-;QHD43422.1:p.62V>L | gene-ORF8:c.184Gtg>Stg;gene-ORF8:c.184Gtg>Ctg | MODIFIER;MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_28144 | gene-ORF8 | 16 | T->C:15;T->Y:1 | missense_variant;coding_sequence_variant | QHD43422.1:p.84L>S;QHD43422.1:p.84- | gene-ORF8:c.251tTa>tCa;gene-ORF8:c.251tTa>tYa | MODERATE;MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_28253 | gene-ORF8 | 2 | C->T:2 | synonymous_variant | QHD43422.1:p.120F | gene-ORF8:c.360ttC>ttT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_28291 | gene-N | 1 | C->T:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43423.2:p.6P | gene-N:c.18ccC>ccT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_28716 | gene-N | 1 | C->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43423.2:p.148T>I | gene-N:c.443aCc>aTc | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_28792 | gene-N | 1 | A->T:1 | synonymous_variant | QHD43423.2:p.173A | gene-N:c.519gcA>gcT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_28854 | gene-N | 3 | C->T:2;C->Y:1 | missense_variant;coding_sequence_variant | QHD43423.2:p.194S>L;QHD43423.2:p.194- | gene-N:c.581tCa>tTa;gene-N:c.581tCa>tYa | MODERATE;MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_29095 | gene-N | 7 | C->T:7 | synonymous_variant | QHD43423.2:p.274F | gene-N:c.822ttC>ttT | LOW |
| 2019-nCoV_29303 | gene-N | 1 | C->T:1 | missense_variant | QHD43423.2:p.344P>S | gene-N:c.1030Cca>Tca | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_29596 | gene-ORF10 | 1 | A->G:1 | missense_variant | QHI42199.1:p.13I>M | gene-ORF10:c.39atA>atG | MODERATE |
| 2019-nCoV_29749 | 3'UTR | 1 | ACGATCGAGTG->A:1 | downstream_gene_variant | QHI42199.1 | gene-ORF10 | MODIFIER;DISTANCE=76 |
| 2019-nCoV_29854 | 3'UTR | 1 | C->T:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_29856 | 3'UTR | 1 | T->A:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_29868 | 3'UTR | 1 | GA->G:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| 2019-nCoV_29877 | 3'UTR | 1 | A->T:1 | intergenic_variant | - | - | MODIFIER |
| [1] | WHO. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019, 2020. |
| [2] |
Xu XT, Chen P, Wang JF, Feng JN, Zhou H, Li X, Zhong W, Hao P . Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission. Sci China Life Sci, 2020, doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1637-5.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1637-5 pmid: 32009228 |
| [3] | Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang RD, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Zheng XS, Zhao K, Chen QJ, Deng F, Liu LL, Yan B, Zhan FX, Wang YY, Xiao GF, Shi ZL . Discovery of a novel coronavirus associated with the recent pneumonia outbreak in humans and its potential bat origin. bioRxiv, 2020, doi: 10.1101/2020.01.22.914952. |
| [4] | Ji W, Wang W, Zhao XF, Zai JJ, Li XG . Homologous recombination within the spike glycoprotein of the newly identified coronavirus may boost cross-species transmission from snake to human. J Med Virol, 2020, doi: 10.1002/jmv.25682. |
| [5] | Dong N, Yang XM, Ye LW, Chen KC, Chan EWC, Yang MS, Chen S . Genomic and protein structure modelling analysis depicts the origin and infectivity of 2019-nCoV, a new coronavirus which caused a pneumonia outbreak in Wuhan, China. bioRxiv, 2020, doi: 10.1101/2020.01.20. 913368. |
| [6] |
Benvenuto D, Giovanetti M, Ciccozzi A, Spoto S, Angeletti S, Ciccozzi M . The 2019-new Coronavirus epidemic: evidence for virus evolution. J Med Virol, 2020, doi: 10.1101/2020.01.24.915157.
doi: 10.1002/jmv.25688 pmid: 31994738 |
| [7] | Chen JY, Shi JS, Qiu DA, Liu C, Li X, Zhao Q, Ruan JS, Gao S . Bioinformatics analysis of the Wuhan 2019 human coronavirus genome. Chin J Bio, 2020, doi: 10.12113/ 202001007. |
| 陈嘉源, 施劲松, 丘栋安, 刘畅, 李鑫, 赵强, 阮吉寿, 高山 . 武汉2019冠状病毒基因组的生物信息学分析. 生物信息学, 2020, doi: 10.12113/202001007. | |
| [8] |
Heymann DL . Data sharing and outbreaks: best practice exemplified. Lancet, 2020, doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30184-7.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30184-7 pmid: 31986258 |
| [9] | Munster VJ , Koopmans M, van Doremalen N, van Riel D, de Wit E. A novel coronavirus emerging in China - key questions for impact assessment. N Engl J Med, 2020, doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2000929. |
| [10] |
Sayers EW, Beck J, Brister JR, Bolton EE, Canese K, Comeau DC, Funk K, Ketter A, Kim S, Kimchi A, Kitts PA, Kuznetsov A, Lathrop S, Lu Z , McGarvey K, Madden TL, Murphy TD, O'Leary N, Phan L, Schneider VA, Thibaud-Nissen F, Trawick BW, Pruitt KD, Ostell J. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020,48:D9-D16.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz899 pmid: 31602479 |
| [11] |
Shu YL , McCauley J. GISAID: Global initiative on sharing all influenza data-from vision to reality. Euro Surveill, 2017,22(13):30494.
doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.13.30494 pmid: 28382917 |
| [12] |
Wang B, Liu F, Zhang EC, Wo CL, Chen J, Qian PY, Lu HR, Zeng WJ, Chen T, Wei JP, Wan Q, Wang R, Xu X . The China National GeneBank—owned by all, completed by all and shared by all. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019,41(8):761-772.
doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(92)90041-4 pmid: 1447427 |
|
王博, 刘芳, 张二春, 沃晨亮, 陈振家, 钱璞毅, 卢浩荣, 曾文君, 陈泰, 危金普, 万仟, 王韧, 徐讯 . 国家基因库: 共有、共为、共享. 遗传, 2019,41(8):761-72.
doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(92)90041-4 pmid: 1447427 |
|
| [13] |
Wu LH, Sun QL, Desmeth P, Sugawara H, Xu ZH , McCluskey K, Smith D, Alexander V, Lima N, Ohkuma M, Robert V, Zhou YG, Li JH, Fan GM, Ingsriswang S, Ozerskaya S, Ma JC. World data centre for microorganisms: an information infrastructure to explore and utilize preserved microbial strains worldwide. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017,45(D1):D611-D618.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw903 pmid: 28053166 |
| [14] |
Zhang Z, Bao Y, Zhao W, Xiao J, Chen R, Zhang G, Li Y, Zhao G, Pervaiz N, Li R, Gao F, Zhi X, Lu Y, Liu L, He S, Li Q, Yuan C, Ma L, Xiao Y, Wang J, Hao Y, Wang Q, Shang Y, Zhang Y, Yuan N, Song S, Tian F, Sun L, Teng Y, Sun X, Chen H, Xue Y, Zhang Q, Teng X, Huang Z, Wang H, Zhu T, Zhang C, Ma Y, Zhang X, Lin S, Gao Y, Zhou J, Guo J, Liu X, Kang H, Tian D, Gao G, Ling Y, Xu S, Wang P, Zhou H, Niu Y, Ruan C, Lv D, Dong L, Zhu Q, Abbasi AA, Tang Q, Li H, Yao L, Chen M, Gao Q, Cao R, Guo Y, Zhai S, Shi S, Guo AY, Shireen H, Miao YR, Jin JP, Qian Q, Wang Y, Cao J, Duan G, Ning Z, Yu L, Li Z, Du Q, Wu W, Zhou Q, Hu H, Wang G, Wu S, Li CY, Zhao F, Xiong Z, Wang C, Gong Z, Zeng J, Yuan L, Xia X, Sun M, Batool F, Xue H, Sang J, Du Z, Wang X, Lan L, Fang S, Cui Q, Wang Z, Hao L, Liu W, Jiang Z, Zhang H, Raza RZ, Wu Y, Luo H, Zhang YE, Zhu J, Jiang M, Li M, Ying C, Li X, Li C, Zhao Y, Kang Q, Klenk HP, Zheng Y, Yang F, Tang B, Zhang P, Chen X, Zhang L, Zhao L, Tu Y, Chen T, Zou D, Zhang S, Ning W, Niu G, Guo H, Yan J, Shi Y, Sun Y, Pan M, Lu M, Ji P, Peng D, Yuan H . Database resources of the National Genomics Data Center in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020,48(D1):D24-D33.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz913 pmid: 31702008 |
| [15] |
Wang YQ, Song FH, Zhu JW, Zhang SS, Yang YD, Chen TT, Tang BX, Dong LL, Ding N, Zhang Q, Bai ZX, Dong XN, Chen HX, Sun MY, Zhai S, Sun YB, Yu L, Lan L, Xiao JF, Fang XD, Lei HX, Zhang Z, Zhao WM . GSA: genome sequence archive. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2017,15(1):14-18.
doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2017.01.001 pmid: 28387199 |
| [16] |
Zhang SS, Chen TT, Zhu JW, Zhou Q, Chen X, Wang YQ, Zhao WM . GSA: genome sequence archive. Hereditas (Beijing), 2018,40(11):1044-1047.
doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90090-4 pmid: 465538 |
|
张思思, 陈婷婷, 朱军伟, 周晴, 陈旭, 王彦青, 赵文明 . GSA: 组学原始数据归档库. 遗传, 2018,40(11):1044-1047.
doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90090-4 pmid: 465538 |
|
| [17] |
Zhang YS, Xia L, Sang J, Li M, Liu L, Li MW, Niu GY, Cao JB, Teng XF, Zhou Q, Zhang Z . The BIG Data Center’s database resources. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018,40(11):1039-1043.
doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90089-8 pmid: 465537 |
|
张源笙, 夏琳, 桑健, 李漫, 刘琳, 李萌伟, 牛广艺, 曹佳宝, 滕徐菲, 周晴, 章张 . 生命与健康大数据中心资源. 遗传, 2018,40(11):1039-1043.
doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90089-8 pmid: 465537 |
|
| [18] |
Ma YK, Bao YM . Prospects for national biological big data centers. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018,40(11):938-943.
doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90096-5 pmid: 465527 |
|
马英克, 鲍一明 . 国家级生物大数据中心展望. 遗传, 2018,40(11):938-943.
doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90096-5 pmid: 465527 |
|
| [19] |
Edgar RC . MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res, 2004,32(5):1792-1797.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340 pmid: 15034147 |
| [20] |
Bodenhofer U, Bonatesta E, Horejš-Kainrath C , Hochreiter S. msa: an R package for multiple sequence alignment. Bioinformatics, 2015,31(24):3997-3999.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv494 pmid: 26315911 |
| [21] | Donlin MJ . Using the generic genome browser(GBrowse) . Curr Protoc Bioinformatics, 2009, 28(1): 9.9.1-9.9.25. |
| [22] |
McLaren W, Gil L, Hunt SE, Riat HS, Ritchie GRS, Thormann A, Flicek P, Cunningham F . The ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome Biol, 2016,17:122.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0974-4 pmid: 27268795 |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||