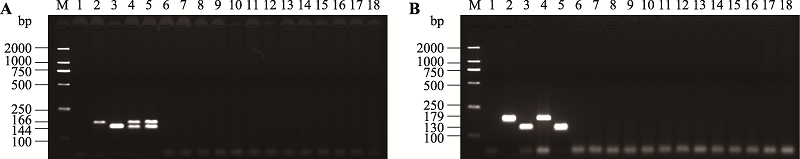
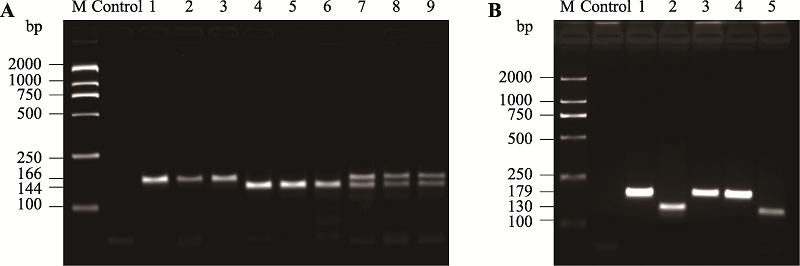
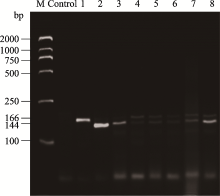
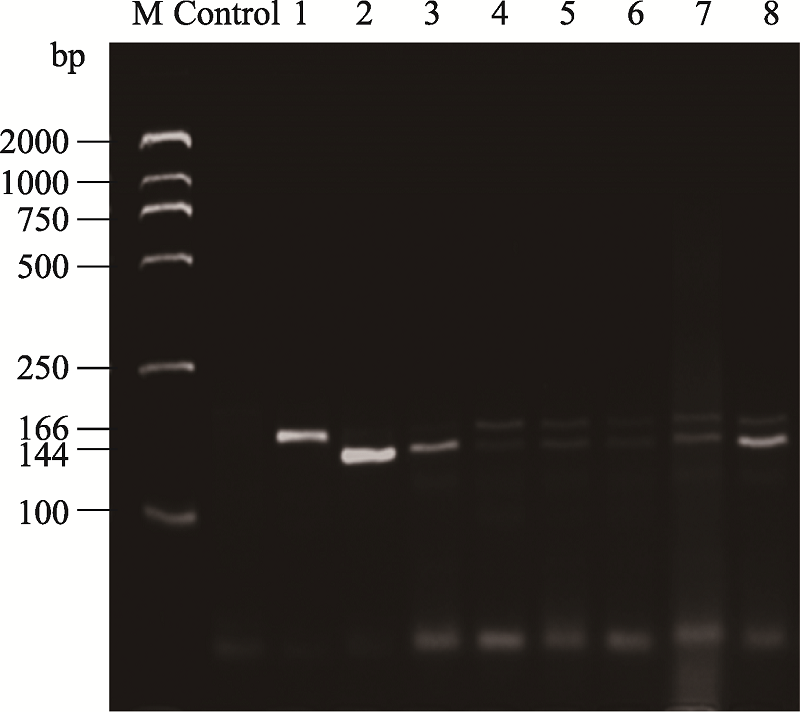
| [1] |
丁立威 . 阿胶产供销趋势分析. 中国现代中药, 2014,16(4):329-332, 335.
|
| [2] |
李杰, 王玉斌 . 我国驴业发展现状、问题及对策. 中国畜牧杂志, 2019,55(5):159-162.
|
| [3] |
Huang SQ, Zhang W, Peng Y . Studies on identification of furs of Equus Asinus L. Strait Pharm J, 2016,28(4):50-53.
|
|
黄世琼, 张伟, 彭娅 . 驴皮的真伪鉴别. 海峡药学, 2016,28(4):50-53.
|
| [4] |
Tian JS, Shi BY, Zhang FS, Li XW, Geng WH, Yang Y, Liu HL, Qin XM . Establishment of RAPD for analysis on furs of Equus asinus and discrimination from Equus caballus orientalis. Chin Tradit Herb Drug, 2013,44(3):354-358.
|
|
田俊生, 史碧云, 张福生, 李晓伟, 耿伟华, 杨永, 刘会来, 秦雪梅 . 驴皮药材RAPD分析方法建立及其与伪品马皮的鉴别. 中草药, 2013,44(03):354-358.
|
| [5] |
Wang XL, Pan J, Wang S, Wan JF, Bao Z, Jie XJ, You JH, Jie FS, Shi XM. Identification of the raw material of ejiao using the CytB gene PCR-RFLP method. Perio Ocean Univ China, 2006, 36(4): 645-648.
|
|
汪小龙, 潘洁, 王师, 万俊芬, 包振, 解锡军, 尤金花, 解福生, 师秀梅 . 细胞色素B基因 PCR-RFLP鉴定阿胶原料. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2006,36(4):645-648.
|
| [6] |
Zhang H, Sun HX, Xu N, Huang JF, Sun PC . Study on Semi-nested Multiplex PCR Identification Method of Gelatin. Food Res Dev, 2016,37(17):103-106.
|
|
张慧, 孙海新, 许娜, 黄金发, 孙丕春 . 阿胶的半巢式-多重PCR鉴别方法研究. 食品研究与开发, 2016,37(17):103-106.
|
| [7] |
Kumeta Y, Maruyama T, Asama H, Yamamoto Y, Hakamatsuka T, Goda Y . Species identification of Asini Corii Collas (donkey glue) by PCR amplification of cytochrome b gene. J Nat Med, 2014,68(1):181-185.
doi: 10.1007/s11418-013-0790-z
pmid: 23807625
|
| [8] |
Zuo HL, Zhao J, Wang YT, Xia ZN, Hu YJ, Yang FQ . Identification of the adulterated Asini Corii Colla with cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene-based polymerase chain reaction. Pharmacognosy Res, 2017,9(4):313-318.
doi: 10.4103/pr.pr_33_17
pmid: 29263623
|
| [9] |
Zhang WJ, Cui SH, Cheng XL, Wei F, Ma SC . An optimized TaqMan real-time PCR method for authentication of ASINI CORII COLLA (donkey-hide gelatin). J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2019,170:196-203.
pmid: 30928895
|
| [10] |
Liu YY, Zhang QF, Bian RR, Chen J, Bu X . The detection of donkeys, horses, hinny and mule hides derived materials in ass-hide gelatin products by multiple fluorescent quantitative PCR. J Pharma Res, 2016,35(10):569-574, 578.
|
|
刘艳艳, 张全芳, 卞如如, 陈杰, 步讯 . 利用多重荧光定量PCR检测阿胶原料驴、马、驴骡和马骡皮张的源性. 药学研究, 2016,35(10):569-574, 578.
|
| [11] |
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T . Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989.
|
| [12] |
Chen JW, Shao N, Zhang YC, Zhu YS, Yang LT, Tao SC, Lu DR . A visual multiplex PCR microchip with easy sample loading. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017,39(6):525-534.
|
|
陈建伟, 邵宁, 张雨晨, 朱元首, 杨立桃, 陶生策, 卢大儒 . 一种载样简单的多重可视化PCR微芯片. 遗传, 2017,39(6):525-534.
|
 ), Wenjun Wang, Ming Fu, Guoqiang Xu, Xiang Zhou, Bang Liu(
), Wenjun Wang, Ming Fu, Guoqiang Xu, Xiang Zhou, Bang Liu( )
)