| [1] |
Mehta A, Haber JE. Sources of DNA double-strand breaks and models of recombinational DNA repair. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2014, 6(9):a016428.
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016428
|
| [2] |
Huang M, Yang YR, Sun XY, Zhang T, Guo CX. RAD51 regulates REV1 recruitment to DNA double-strand break sites. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(11):1007-1014.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-176
pmid: 30465533
|
|
黄敏, 杨业然, 孙晓艳, 张婷, 郭彩霞. RAD51调控REV1参与DNA双链断裂修复. 遗传, 2018, 40(11):1007-1014.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-176
pmid: 30465533
|
| [3] |
Thadathil N, Hori R, Xiao JF, Khan MM. DNA double- strand breaks: a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases. Chromosome Res, 2019, 27(4):345-364.
doi: 10.1007/s10577-019-09617-x
pmid: 31707536
|
| [4] |
Dai YX, Zhang F, Wang LG, Shan S, Gong ZH, Zhou Z. Structural basis for shieldin complex subunit 3-mediated recruitment of the checkpoint protein REV7 during DNA double-strand break repair. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295(1):250-262.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011464
|
| [5] |
Shrivastav M, De Haro LP, Nickoloff JA. Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Cell Res, 2008, 18(1):134-147.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.111
pmid: 18157161
|
| [6] |
Gong Y, Handa N, Kowalczykowski SC, de Lange T. PHF11 promotes DSB resection, ATR signaling, and HR. Genes Dev, 2017, 31(1):46-58.
doi: 10.1101/gad.291807.116
|
| [7] |
Whelan DR, Lee WTC, Marks F, Kong YT, Yin YD, Rothenberg E. Super-resolution visualization of distinct stalled and broken replication fork structures. PLoS Genet, 2020, 16(12):e1009256.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009256
|
| [8] |
Liu SJ, Hua Y, Wang JN, Li LY, Yuan JJ, Zhang B, Wang ZY, Ji JG, Kong DC. RNA polymerase III is required for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. Cell, 2021, 184(5): 1314-1329.e1310.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.048
|
| [9] |
Limbo O, Porter-Goff ME, Rhind N, Russell P. Mre11 nuclease activity and Ctp1 regulate Chk1 activation by Rad3ATR and Tel1ATM checkpoint kinases at double-strand breaks. Mol Cell Biol, 2011, 31(3):573-583.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.00994-10
|
| [10] |
Sato H, Niimi A, Yasuhara T, Permata TBM, Hagiwara Y, Isono M, Nuryadi E, Sekine R, Oike T, Kakoti S, Yoshimoto Y, Held KD, Suzuki Y, Kono K, Miyagawa K, Nakano T, Shibata A. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1):1751.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01883-9
|
| [11] |
Zofall M, Grewal SI. HULC, a histone H2B ubiquitinating complex, modulates heterochromatin independent of histone methylation in fission yeast. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(19):14065-14072.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700292200
|
| [12] |
Deng ZH, Ai HS, Lu CP, Li JB. The Bre1/Rad6 machinery: writing the central histone ubiquitin mark on H2B and beyond. Chromosome Res, 2020, 28(3-4):247-258.
doi: 10.1007/s10577-020-09640-3
|
| [13] |
So CC, Ramachandran S, Martin A. E3 ubiquitin ligases RNF20 and RNF40 are required for double-stranded break (DSB) repair: evidence for monoubiquitination of histone H2B lysine 120 as a novel axis of DSB signaling and repair. Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 39(8):e00488-e00518.
|
| [14] |
In S, Kim YI, Lee JE, Kim J. RNF20/40-mediated eEF1BδL monoubiquitylation stimulates transcription of heat shock-responsive genes. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(6):2840-2855.
|
| [15] |
Scherer S, Davis RW. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1979, 76(10):4951-4955.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951
|
| [16] |
Rai SK, Atwood-Moore A, Levin HL. High-frequency lithium acetate transformation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1721:167-177.
|
| [17] |
Forsburg SL, Rhind N. Basic methods for fission yeast. Yeast, 2006, 23(3):173-183.
pmid: 16498704
|
| [18] |
Osman F, Fortunato EA, Subramani S. Double-strand break-induced mitotic intrachromosomal recombination in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics, 1996, 142(2):341-357.
doi: 10.1093/genetics/142.2.341
pmid: 8852835
|
| [19] |
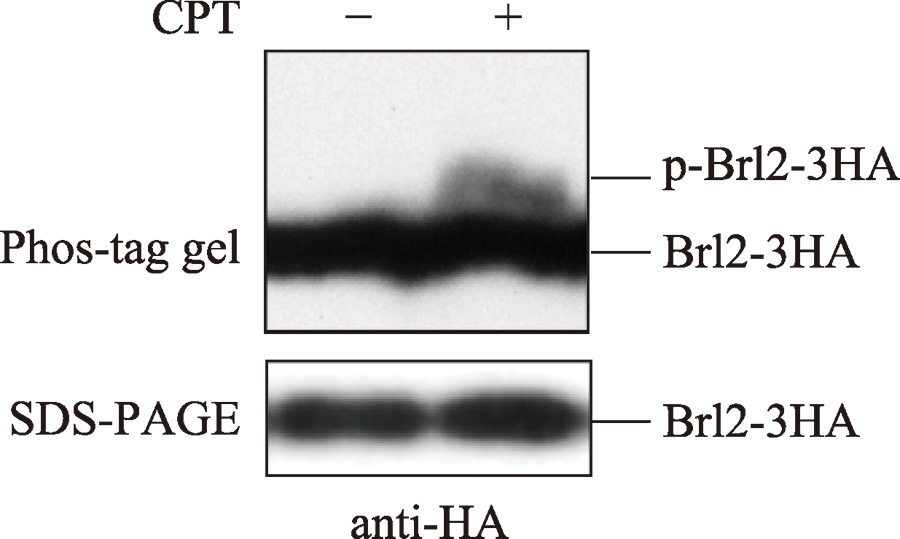
Nagy Z, Comer S, Smolenski A. Analysis of protein phosphorylation using Phos-tag gels. Curr Protoc Protein Sci, 2018, 93(1):e64.
doi: 10.1002/cpps.64
|
| [20] |
Moyal L, Lerenthal Y, Gana-Weisz M, Mass G, So S, Wang SY, Eppink B, Chung YM, Shalev G, Shema E, Shkedy D, Smorodinsky NI, van Vliet N, Kuster B, Mann M, Ciechanover A, Dahm-Daphi J, Kanaar R, Hu MC, Chen DJ, Oren M, Shiloh Y. Requirement of ATM-dependent monoubiquitylation of histone H2B for timely repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Mol Cell, 2011, 41(5):529-542.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.02.015
|
| [21] |
Nakamura K, Kato A, Kobayashi J, Yanagihara H, Sakamoto S, Oliveira DVNP, Shimada M, Tauchi H, Suzuki H, Tashiro S, Zou L, Komatsu K. Regulation of homologous recombination by RNF20-dependent H2B ubiquitination. Mol Cell, 2011, 41(5):515-528.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.02.002
pmid: 21362548
|
| [22] |
Zheng SH, Li D, Lu Z, Liu GX, Wang M, Xing PY, Wang M, Dong Y, Wang XJ, Li JY, Zhang SM, Peng HY, Ira G, Li GH, Chen XF. Bre1-dependent H2B ubiquitination promotes homologous recombination by stimulating histone eviction at DNA breaks. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(21):11326-11339.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gky918
|
| [23] |
Zukowski A, Johnson AM. The interplay of histone H2B ubiquitination with budding and fission yeast heterochromatin. Curr Genet, 2018, 64(4):799-806.
doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0812-1
pmid: 29464330
|
| [24] |
Marsh DJ, Ma Y, Dickson KA. Histone monoubiquitination in chromatin remodelling: focus on the histone H2B interactome and cancer. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12(11):3462.
doi: 10.3390/cancers12113462
|
 ), Feiran Chang2, Sijie Liu2, Fei Wu2, Daochun Kong2
), Feiran Chang2, Sijie Liu2, Fei Wu2, Daochun Kong2