Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 172-182.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-148
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
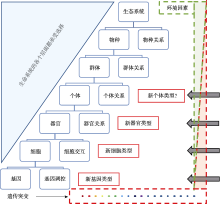
Theoretical thinking from gene evolution to cell type evolution
- 1. Chinese Institute for Brain Research, Beijing 102206, China
2. Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
-
Received:2024-05-23Revised:2024-08-17Online:2025-02-20Published:2024-08-19 -
Contact:Li Zhang E-mail:zhangli@cibr.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(32170642);National Natural Science Foundation of China(32370682)
Cite this article
Li Zhang, Chuanyun Li. Theoretical thinking from gene evolution to cell type evolution[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(2): 172-182.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | Lewontin RC. The units of selection. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1970, 1: 1-18. |
| [2] | Wray NR, Visscher PM. Estimating trait heritability. Nat Educ, 2008, 1(1): 29. |
| [3] | Griffith F. The significance of pneumococcal types. J Hyg (Lond), 1928, 27(2): 113-159. |
| [4] | Watson JD, Crick FH. Molecular structure of nucleic acids: a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Am J Psychiatry, 2003, 160(4): 623-624. |
| [5] | Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Mural RJ, Sutton GG, Smith HO, Yandell M, Evans CA, Holt RA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides P, Ballew RM, Huson DH, Wortman JR, Zhang Q, Kodira CD, Zheng XH, Chen L, Skupski M, Subramanian G, Thomas PD, Zhang J, Gabor Miklos GL, Nelson C, Broder S, Clark AG, Nadeau J, McKusick VA, Zinder N, Levine AJ, Roberts RJ, Simon M, Slayman C, Hunkapiller M, Bolanos R, Delcher A, Dew I, Fasulo D, Flanigan M, Florea L, Halpern A, Hannenhalli S, Kravitz S, Levy S, Mobarry C, Reinert K, Remington K, Abu-Threideh J, Beasley E, Biddick K, Bonazzi V, Brandon R, Cargill M, Chandramouliswaran I, Charlab R, Chaturvedi K, Deng Z, Di Francesco V, Dunn P, Eilbeck K, Evangelista C, Gabrielian AE, Gan W, Ge W, Gong F, Gu Z, Guan P, Heiman TJ, Higgins ME, Ji RR, Ke Z, Ketchum KA, Lai Z, Lei Y, Li Z, Li J, Liang Y, Lin X, Lu F, Merkulov GV, Milshina N, Moore HM, Naik AK, Narayan VA, Neelam B, Nusskern D, Rusch DB, Salzberg S, Shao W, Shue B, Sun J, Wang Z, Wang A, Wang X, Wang J, Wei M, Wides R, Xiao C, Yan C, Yao A, Ye J, Zhan M, Zhang W, Zhang H, Zhao Q, Zheng L, Zhong F, Zhong W, Zhu S, Zhao S, Gilbert D, Baumhueter S, Spier G, Carter C, Cravchik A, Woodage T, Ali F, An H, Awe A, Baldwin D, Baden H, Barnstead M, Barrow I, Beeson K, Busam D, Carver A, Center A, Cheng ML, Curry L, Danaher S, Davenport L, Desilets R, Dietz S, Dodson K, Doup L, Ferriera S, Garg N, Gluecksmann A, Hart B, Haynes J, Haynes C, Heiner C, Hladun S, Hostin D, Houck J, Howland T, Ibegwam C, Johnson J, Kalush F, Kline L, Koduru S, Love A, Mann F, May D, McCawley S, McIntosh T, McMullen I, Moy M, Moy L, Murphy B, Nelson K, Pfannkoch C, Pratts E, Puri V, Qureshi H, Reardon M, Rodriguez R, Rogers YH, Romblad D, Ruhfel B, Scott R, Sitter C, Smallwood M, Stewart E, Strong R, Suh E, Thomas R, Tint NN, Tse S, Vech C, Wang G, Wetter J, Williams S, Williams M, Windsor S, Winn-Deen E, Wolfe K, Zaveri J, Zaveri K, Abril JF, Guigó R, Campbell MJ, Sjolander KV, Karlak B, Kejariwal A, Mi H, Lazareva B, Hatton T, Narechania A, Diemer K, Muruganujan A, Guo N, Sato S, Bafna V, Istrail S, Lippert R, Schwartz R, Walenz B, Yooseph S, Allen D, Basu A, Baxendale J, Blick L, Caminha M, Carnes-Stine J, Caulk P, Chiang YH, Coyne M, Dahlke C, Deslattes Mays A, Dombroski M, Donnelly M, Ely D, Esparham S, Fosler C, Gire H, Glanowski S, Glasser K, Glodek A, Gorokhov M, Graham K, Gropman B, Harris M, Heil J, Henderson S, Hoover J, Jennings D, Jordan C, Jordan J, Kasha J, Kagan L, Kraft C, Levitsky A, Lewis M, Liu X, Lopez J, Ma D, Majoros W, McDaniel J, Murphy S, Newman M, Nguyen T, Nguyen N, Nodell M, Pan S, Peck J, Peterson M, Rowe W, Sanders R, Scott J, Simpson M, Smith T, Sprague A, Stockwell T, Turner R, Venter E, Wang M, Wen M, Wu D, Wu M, Xia A, Zandieh A, Zhu X. The sequence of the human genome. Science, 2001, 291(5507): 1304-1351. |
| [6] | Eddy SR. The C-value paradox, junk DNA and ENCODE. Curr Biol, 2012, 22(21): R898-R899. |
| [7] |
Carroll SB. Endless forms: the evolution of gene regulation and morphological diversity. Cell, 2000, 101(6): 577-580.
pmid: 10892643 |
| [8] |
Chen SD, Krinsky BH, Long MY. New genes as drivers of phenotypic evolution. Nat Rev Genet, 2013, 14(9): 645-660.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3521 pmid: 23949544 |
| [9] | Chen SD, Zhang YE, Long MY. New genes in Drosophila quickly become essential. Science, 2010, 330(6011): 1682-1685. |
| [10] | Darwin CR. On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. London: John Murray, 1859. |
| [11] |
Jacob F. Evolution and tinkering. Science, 1977, 196(4295): 1161-1166.
doi: 10.1126/science.860134 pmid: 860134 |
| [12] | Ohno S. Evolution by Gene Duplication. New York: Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, 1970. |
| [13] |
Wang W, Zhang J, Alvarez C, Llopart A, Long M. The origin of the Jingwei gene and the complex modular structure of its parental gene, yellow emperor, in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol, 2000, 17(9): 1294-1301.
pmid: 10958846 |
| [14] |
VanKuren NW, Long MY. Gene duplicates resolving sexual conflict rapidly evolved essential gametogenesis functions. Nat Ecol Evol, 2018, 2(4): 705-712.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-018-0471-0 pmid: 29459709 |
| [15] |
Zhou Q, Zhang GJ, Zhang Y, Xu SY, Zhao RP, Zhan ZB, Li X, Ding Y, Yang S, Wang W. On the origin of new genes in Drosophila. Genome Res, 2008, 18(9): 1446-1455.
doi: 10.1101/gr.076588.108 pmid: 18550802 |
| [16] |
Zhang YE, Vibranovski MD, Krinsky BH, Long MY. Age-dependent chromosomal distribution of male-biased genes in Drosophila. Genome Res, 2010, 20(11): 1526-1533.
doi: 10.1101/gr.107334.110 pmid: 20798392 |
| [17] | Zhang YE, Landback P, Vibranovski MD, Long MY. Accelerated recruitment of new brain development genes into the human genome. PLoS Biol, 2011, 9(10): e1001179. |
| [18] |
Domazet-Loso T, Brajković J, Tautz D. A phylostratigraphy approach to uncover the genomic history of major adaptations in metazoan lineages. Trends Genet, 2007, 23(11): 533-539.
pmid: 18029048 |
| [19] |
Long MY, VanKuren NW, Chen SD, Vibranovski MD. New gene evolution: little did we know. Annu Rev Genet, 2013, 47: 307-333.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-111212-133301 pmid: 24050177 |
| [20] |
Tautz D, Domazet-Lošo T. The evolutionary origin of orphan genes. Nat Rev Genet, 2011, 12(10): 692-702.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3053 pmid: 21878963 |
| [21] |
Schlötterer C. Genes from scratch--the evolutionary fate of de novo genes. Trends Genet, 2015, 31(4) 215-219.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2015.02.007 pmid: 25773713 |
| [22] | Carvunis AR, Rolland T, Wapinski I, Calderwood MA, Yildirim MA, Simonis N, Charloteaux B, Hidalgo CA, Barbette J, Santhanam B, Brar GA, Weissman JS, Regev A, Thierry-Mieg N, Cusick ME, Vidal M. Proto-genes and de novo gene birth. Nature, 2012, 487(7407): 370-374. |
| [23] |
Zhao L, Saelao P, Jones CD, Begun DJ. Origin and spread of de novo genes in Drosophila melanogaster populations. Science, 2014, 343(6172): 769-772.
doi: 10.1126/science.1248286 pmid: 24457212 |
| [24] |
Moyers BA, Zhang JZ. Phylostratigraphic bias creates spurious patterns of genome evolution. Mol Biol Evol, 2015, 32(1): 258-267.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu286 pmid: 25312911 |
| [25] |
Moyers BA, Zhang JZ. Evaluating phylostratigraphic evidence for widespread de novo gene birth in genome evolution. Mol Biol Evol, 2016, 33(5): 1245-1256.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw008 pmid: 26758516 |
| [26] |
Moyers BA, Zhang JZ. Further simulations and analyses demonstrate open problems of phylostratigraphy. Genome Biol Evol, 2017, 9(6): 1519-1527.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx109 pmid: 28637261 |
| [27] |
Domazet-Lošo T, Carvunis AR, Albà MM, Šestak MS, Bakaric R, Neme R, Tautz D. No evidence for phylostratigraphic bias impacting inferences on patterns of gene emergence and evolution. Mol Biol Evol, 2017, 34(4): 843-856.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw284 pmid: 28087778 |
| [28] |
Knowles DG, McLysaght A. Recent de novo origin of human protein-coding genes. Genome Res, 2009, 19(10): 1752-1759.
doi: 10.1101/gr.095026.109 pmid: 19726446 |
| [29] | Xie C, Zhang YE, Chen JY, Liu CJ, Zhou WZ, Li Y, Zhang M, Zhang RL, Wei LP, Li CY. Hominoid-specific de novo protein-coding genes originating from long non-coding RNAs. PLoS Genet, 2012, 8(9): e1002942. |
| [30] | Murphy DN, McLysaght A. De novo origin of protein- coding genes in murine rodents. PLoS One, 2012, 7(11): e48650. |
| [31] |
Chen L, DeVries AL, Cheng CH. Evolution of antifreeze glycoprotein gene from a trypsinogen gene in Antarctic notothenioid fish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1997, 94(8): 3811-3816.
pmid: 9108060 |
| [32] | Cai J, Zhao RP, Jiang HF, Wang W. De novo origination of a new protein-coding gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics, 2008, 179(1): 487-496. |
| [33] |
Zhang L, Ren Y, Yang T, Li GW, Chen JH, Gschwend AR, Yu Y, Hou GX, Zi J, Zhou R, Wen B, Zhang JW, Chougule K, Wang MH, Copetti D, Peng ZY, Zhang CJ, Zhang Y, Ouyang YD, Wing RA, Liu SQ, Long MY. Rapid evolution of protein diversity by de novo origination in Oryza. Nat Ecol Evol, 2019, 3(4): 679-690.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-019-0822-5 pmid: 30858588 |
| [34] |
Kaessmann H. Origins, evolution, and phenotypic impact of new genes. Genome Res, 2010, 20(10): 1313-1326.
doi: 10.1101/gr.101386.109 pmid: 20651121 |
| [35] | Cui X, Lv Y, Chen ML, Nikoloski Z, Twell D, Zhang DB. Young genes out of the male: an insight from evolutionary age analysis of the pollen transcriptome. Mol Plant, 2015, 8(6): 935-945. |
| [36] | Witt E, Benjamin S, Svetec N, Zhao L. Testis single-cell RNA-seq reveals the dynamics of de novo gene transcription and germline mutational bias in Drosophila. eLife, 2019, 8: e47138. |
| [37] |
Levine MT, Jones CD, Kern AD, Lindfors HA, Begun DJ. Novel genes derived from noncoding DNA in Drosophila melanogaster are frequently X-linked and exhibit testis-biased expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(26): 9935-9939.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509809103 pmid: 16777968 |
| [38] | Begun DJ, Lindfors HA, Kern AD, Jones CD. Evidence for de novo evolution of testis-expressed genes in the Drosophila yakuba/Drosophila erecta clade. Genetics, 2007, 176(2): 1131-1137. |
| [39] |
Vibranovski MD, Zhang Y, Long MY. General gene movement off the X chromosome in the Drosophila genus. Genome Res, 2009, 19(5): 897-903.
doi: 10.1101/gr.088609.108 pmid: 19251740 |
| [40] |
Gubala AM, Schmitz JF, Kearns MJ, Vinh TT, Bornberg-Bauer E, Wolfner MF, Findlay GD. The goddard and saturn genes are essential for Drosophila male fertility and may have arisen de novo. Mol Biol Evol, 2017, 34(5): 1066-1082.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx057 pmid: 28104747 |
| [41] | Reinhardt JA, Wanjiru BM, Brant AT, Saelao P, Begun DJ, Jones CD. De novo ORFs in Drosophila are important to organismal fitness and evolved rapidly from previously non-coding sequences. PLoS Genet, 2013, 9(10): e1003860. |
| [42] |
Heinen TJAJ, Staubach F, Häming D, Tautz D. Emergence of a new gene from an intergenic region. Curr Biol, 2009, 19(18): 1527-1531.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.049 pmid: 19733073 |
| [43] | Xie C, Bekpen C, Künzel S, Keshavarz M, Krebs-Wheaton R, Skrabar N, Ullrich KK, Tautz D. A de novo evolved gene in the house mouse regulates female pregnancy cycles. eLife, 2019, 8: e44392. |
| [44] | Kleene KC. A possible meiotic function of the peculiar patterns of gene expression in mammalian spermatogenic cells. Mech Dev, 2001, 106(1-2): 3-23. |
| [45] |
Kleene KC. Sexual selection, genetic conflict, selfish genes, and the atypical patterns of gene expression in spermatogenic cells. Dev Biol, 2005, 277(1): 16-26.
doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.09.031 pmid: 15572136 |
| [46] | Green EW, Fedele G, Giorgini F, Kyriacou CP. A Drosophila RNAi collection is subject to dominant phenotypic effects. Nat Methods, 2014, 11(3): 222-223. |
| [47] | Kondo S, Vedanayagam J, Mohammed J, Eizadshenass S, Kan LJ, Pang N, Aradhya R, Siepel A, Steinhauer J, Lai EC. New genes often acquire male-specific functions but rarely become essential in Drosophila. Genes Dev, 2017, 31(18): 1841-1846. |
| [48] | Xia SQ, VanKuren NW, Chen CY, Zhang L, Kemkemer C, Shao Y, Jia HX, Lee U, Advani AS, Gschwend A, Vibranovski MD, Chen SD, Zhang YE, Long MY. Genomic analyses of new genes and their phenotypic effects reveal rapid evolution of essential functions in Drosophila development. PLoS Genet, 2021, 17(7): e1009654. |
| [49] |
Emerson JJ, Kaessmann H, Betrán E, Long MY. Extensive gene traffic on the mammalian X chromosome. Science, 2004, 303(5657): 537-540.
pmid: 14739461 |
| [50] |
Zhao Y, Hawes J, Popov KM, Jaskiewicz J, Shimomura Y, Crabb DW, Harris RA. Site-directed mutagenesis of phosphorylation sites of the branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem, 1994, 269(28): 18583-18587.
pmid: 8034607 |
| [51] |
Wildman DE, Uddin M, Liu GZ, Grossman LI, Goodman M. Implications of natural selection in shaping 99.4% nonsynonymous DNA identity between humans and chimpanzees: enlarging genus Homo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(12): 7181-7188.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1232172100 pmid: 12766228 |
| [52] | An NA, Zhang J, Mo F, Luan XK, Tian L, Shen QS, Li XS, Li CQ, Zhou FQ, Zhang BY, Ji MJ, Qi JH, Zhou WZ, Ding WQ, Chen JY, Yu J, Zhang L, Shu SK, Hu BY, Li CY. De novo genes with an lncRNA origin encode unique human brain developmental functionality. Nat Ecol Evol, 2023, 7(2): 264-278. |
| [53] |
Rice WR, Chippindale AK. Sexual recombination and the power of natural selection. Science, 2001, 294(5542): 555-559.
pmid: 11641490 |
| [54] |
Boehm T, Hirano M, Holland SJ, Das S, Schorpp M, Cooper MD. Evolution of alternative adaptive immune systems in vertebrates. Annu Rev Immunol, 2018, 36: 19-42.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053028 pmid: 29144837 |
| [55] |
Böhm I, Schild H. Apoptosis: the complex scenario for a silent cell death. Mol Imaging Biol, 2003, 5(1): 2-14.
pmid: 14499155 |
| [56] | Janeway CA, Travers P, Walport M. Immunobiology:the Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science, 2001. |
| [57] |
Klein AM, Mazutis L, Akartuna I, Tallapragada N, Veres A, Li V, Peshkin L, Weitz DA, Kirschner MW. Droplet barcoding for single-cell transcriptomics applied to embryonic stem cells. Cell, 2015, 161(5): 1187-1201.
doi: S0092-8674(15)00500-0 pmid: 26000487 |
| [58] | de Magãlhaes JP, Costa J. A database of vertebrate longevity records and their relation to other life-history traits. J Evol Biol, 2009, 22(8): 1770-1774. |
| [59] | Zhang L, Park JJ, Dong MB, Arsala D, Xia SQ, Chen JH, Sosa D, Atlas JE, Long MY, Chen SD. Human gene age dating reveals an early and rapid evolutionary construction of the adaptive immune system. Genome Biol Evol, 2023, 15(5): evad081. |
| [60] |
Cooper MD, Alder MN. The evolution of adaptive immune systems. Cell, 2006, 124(4): 815-822.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.001 pmid: 16497590 |
| [61] |
Smith JJ, Timoshevskaya N, Ye CX, Holt C, Keinath MC, Parker HJ, Cook ME, Hess JE, Narum SR, Lamanna F, Kaessmann H, Timoshevskiy VA, Waterbury CKM, Saraceno C, Wiedemann LM, Robb SMC, Baker C, Eichler EE, Hockman D, Sauka-Spengler T, Yandell M, Krumlauf R, Elgar G, Amemiya CT. The sea lamprey germline genome provides insights into programmed genome rearrangement and vertebrate evolution. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(2): 270-277.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-017-0036-1 pmid: 29358652 |
| [62] | Yu DQ, Ren YD, Uesaka M, Beavan AJS, Muffato M, Shen JY, Li YX, Sato I, Wan WT, Clark JW, Keating JN, Carlisle EM, Dearden RP, Giles S, Randle E, Sansom RS, Feuda R, Fleming JF, Sugahara F, Cummins C, Patricio M, Akanni W, D'Aniello S, Bertolucci C, Irie N, Alev C, Sheng GJ, de Mendoza A, Maeso I, Irimia M, Fromm B, Peterson KJ, Das S, Hirano M, Rast JP, Cooper MD, Paps J, Pisani D, Kuratani S, Martin FJ, Wang W, Donoghue PCJ, Zhang YE, Pascual-Anaya J. Hagfish genome elucidates vertebrate whole-genome duplication events and their evolutionary consequences. Nat Ecol Evol, 2024, 8(3): 519-535. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||