Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 101-132.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-223
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
The formation, maintenance, and loss of island biodiversity
Cong Liu1( ), Yangqing Luo2, Yujing Yan3, Yangheshan Yang4, Di Zeng5, Yuhao Zhao4, Xingfeng Si4(
), Yangqing Luo2, Yujing Yan3, Yangheshan Yang4, Di Zeng5, Yuhao Zhao4, Xingfeng Si4( )
)
- 1. Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA
2. Ministry of Education Key Laboratory for Biodiversity Science and Ecological Engineering, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200438, China
3. Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, Harvard Arboretum, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA
4. Center for Global Change and Ecological Forecasting, Zhejiang Zhoushan Island Ecosystem Observation and Research Station, Institute of Eco-Chongming, Zhejiang Tiantong Forest Ecosystem National Observation and Research Station, School of Ecological and Environmental Sciences, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
5. College of Forestry and Biotechnology, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou 311300, China
-
Received:2024-08-05Revised:2024-09-20Online:2025-01-20Published:2024-11-18 -
Contact:Xingfeng Si E-mail:congliu@g.harvard.edu;sixf@des.ecnu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(32311520284);National Natural Science Foundation of China(32101268);National Natural Science Foundation of China(32101278)
Cite this article
Cong Liu, Yangqing Luo, Yujing Yan, Yangheshan Yang, Di Zeng, Yuhao Zhao, Xingfeng Si. The formation, maintenance, and loss of island biodiversity[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(1): 101-132.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | Russell JC, Kaiser-Bunbury CN. Consequences of multispecies introductions on island ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol, Evol Syst, 2019, 50(1): 169-190. |
| [2] |
Gillespie RG, Roderick GK. Arthropods on islands: colonization, speciation, and conservation. Annu Rev Entomol, 2002, 47: 595-632.
pmid: 11729086 |
| [3] |
Gillespie RG, Baldwin BG, Waters JM, Fraser CI, Nikula R, Roderick GK. Long-distance dispersal: a framework for hypothesis testing. Trends Ecol Evol, 2012, 27(1): 47-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2011.08.009 pmid: 22014977 |
| [4] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO. The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1967. |
| [5] | Gillespie RG, Baldwin BG. Island biogeography of remote archipelagoes. In: Losos JB, Ricklefs RE, eds. The Theory of Island Biogeography Revisited. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2010, 358-387. |
| [6] | Whittaker RJ, Fernández-Palacios JM, Matthews TJ, Borregaard MK, Triantis KA. Island biogeography: taking the long view of nature’s laboratories. Science, 2017, 357(6354): eaam8326. |
| [7] | Gillespie G. Ecological release. In: Gillespie RG, Clague D, eds. Encyclopedia of Islands. Oakland: University of California Press, 2009, 251-253. |
| [8] | Darwin CR. On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. 1st edn. London: John Murray, 1859. |
| [9] | Lomolino MV, Riddle BR, Whittaker RJ. Biogeography. 5th edn. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates, 2017. |
| [10] | Whittaker RJ, Fernández-Palacios JM. Island Biogeography:Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation. 2nd edn. New York: Oxford University Press, 2007. |
| [11] | Sarnat EM, Economo EP. The Ants of Fiji. 1st edn. Oakland: University of California Press, 2012. |
| [12] | Gressitt JL. Relative faunal disharmony of insects on Pacific islands. In: Asahina S, eds. Entomological Essays to Commemorate the Retirement of Professor K. Yasumatsu. Tokyo: Hokuryukan Publishing Co., Ltd., 1971, 15-24. |
| [13] | Wilson EO, Taylor RW. The ants of Polynesia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Pac Insects Monogr, 1967, (14): 1-109. |
| [14] | Wallace AR. The World of Life:A Manifestation of Creative Power, Directive Mind, and Ultimate Purpose. New York: Moffat Yard & Company, 1911. |
| [15] | Hirao T, Kubota Y, Murakami M. Geographical patterns of butterfly species diversity in the subtropical Ryukyu Islands: the importance of a unidirectional filter between two source islands. J Biogeogr, 2015, 42(8): 1418-1430. |
| [16] | Economo EP, Klimov P, Sarnat EM, Guénard B, Weiser MD, Lecroq B, Knowles LL. Global phylogenetic structure of the hyperdiverse ant genus Pheidole reveals the repeated evolution of macroecological patterns. Proc Biol Sci B, 2015, 282(1798): 20141416. |
| [17] | Wilson EO. Adaptive shift and dispersal in a tropical ant fauna. Evolution, 1959, 13(1): 122-144. |
| [18] | Wilson EO. The nature of the taxon cycle in the Melanesian ant fauna. Am Nat, 1961, 95(882): 169-193. |
| [19] | Economo EP, Sarnat EM. Revisiting the ants of Melanesia and the taxon cycle: historical and human-mediated invasions of a tropical archipelago. Am Nat, 2012, 180(1): E1-E16. |
| [20] | Liu C, Sarnat EM, Friedman NR, Garcia FH, Darwell C, Booher D, Kubota Y, Mikheyev AS, Economo EP. Colonize, radiate, decline: unraveling the dynamics of island community assembly with Fijian trap-jaw ants. Evolution, 2020, 74(6): 1082-1097. |
| [21] | Yan ER, Si XF, Zhang J, Chen XY. Edward O. Wilson and the theory of island biogeography. Biodiversity Sci, 2022, 30(1): 22024. |
|
阎恩荣, 斯幸峰, 张健, 陈小勇. E. O.威尔逊与岛屿生物地理学理论. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 22024.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2022024 |
|
| [22] | Warren BH, Baudin R, Franck A, Hugel S, Strasberg D. Predicting where a radiation will occur: acoustic and molecular surveys reveal overlooked diversity in Indian Ocean island crickets (Mogoplistinae: Ornebius). PLoS One, 2016, 11(2): e0148971. |
| [23] | Schluter D. Ecological character displacement in adaptive radiation. Am Nat, 2000, 156(S4): 4-16. |
| [24] |
Shaw KL, Gillespie RG. Comparative phylogeography of oceanic archipelagos: hotspots for inferences of evolutionary process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(29): 7986-7993.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601078113 pmid: 27432948 |
| [25] | Jorgensen TH, Olesen JM. Adaptive radiation of island plants: evidence from Aeonium (Crassulaceae) of the Canary Islands. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Sys, 2001, 4(1): 29-42. |
| [26] | Formenti G, Theissinger K, Fernandes C, Bista I, Bombarely A, Bleidorn C, Ciofi C, Crottini A, Godoy JA, Höglund J, Mouton A, Oomen RA, Paez S, Palsbøll PJ, Pampoulie C, Ruiz-López MJ, Svardal H, Theofanopoulou C, de Vries J, Waldvogel AM, Zhang GJ, Mazzoni CJ, Jarvis ED, Bálint M, European Reference Genome Atlas (ERGA) Consortium. The era of reference genomes in conservation genomics. Trends Ecol Evol, 2022, 37(3): 197-202. |
| [27] | Kautt AF, Kratochwil CF, Nater A, Machado-Schiaffino G, Olave M, Henning F, Torres-Dowdall J, Härer A, Hulsey CD, Franchini P, Pippel M, Myers EW, Meyer A. Contrasting signatures of genomic divergence during sympatric speciation. Nature, 2020, 588(7836): 106-111. |
| [28] |
Cerca J, Petersen B, Lazaro-Guevara JM, Rivera-Colón A, Birkeland S, Vizueta J, Li S, Li Q, Loureiro J, Kosawang C, Díaz PJ, Rivas-Torres G, Fernández- Mazuecos M, Vargas P, McCauley RA, Petersen G, Santos-Bay L, Wales N, Catchen JM, Machado D, Nowak MD, Suh A, Sinha NR, Nielsen LR, Nielsen LR, Seberg O, Gilbert MTP, Leebens-Mack JH, Rieseberg LH, Martin MD. The genomic basis of the plant island syndrome in Darwin’s giant daisies. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 3729.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31280-w pmid: 35764640 |
| [29] |
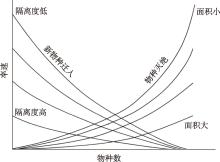
Stuessy TF, Takayama K, López-Sepúlveda P, Crawford DJ. Interpretation of patterns of genetic variation in endemic plant species of oceanic islands. Bot J Linn Soc, 2014, 174(3): 276-288.
pmid: 26074627 |
| [30] | Feiner N. Accumulation of transposable elements in Hox gene clusters during adaptive radiation of Anolis lizards. Proc Biol Sci B, 2016, 283(1840): 20161555. |
| [31] |
Cerca J, Cotoras DD, Bieker VC, De-Kayne R, Vargas P, Fernández-Mazuecos M, López-Delgado J, White O, Stervander M, Geneva AJ, Guevara Andino JE, Meier JI, Roeble L, Brée B, Patiño J, Guayasamin JM, de Lourdes Torres M, Valdebenito H, Castañeda MDR, Chaves JA, Díaz PJ, Valente L, Knope ML, Price JP, Rieseberg LH, Baldwin BG, Emerson BC, Rivas-Torres G, Gillespie R, Martin MD. Evolutionary genomics of oceanic island radiations. Trends Ecol Evol, 2023, 38(7): 631-642.
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2023.02.003 pmid: 36870806 |
| [32] | Parent CE, Caccone A, Petren K. Colonization and diversification of Galápagos terrestrial fauna: a phylogenetic and biogeographical synthesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 2008, 363(1508): 3347-3361. |
| [33] | Grant PR, Grant BR. Speciation and hybridization in island birds. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B: Biol Sci, 1996, 351(1341): 765-772. |
| [34] | Grant PR, Grant BR, Petren K. Hybridization in the recent past. Am Nat, 2005, 166(1): 56-67. |
| [35] | James HF. The osteology and phylogeny of the Hawaiian finch radiation (Fringillidae: Drepanidini), including extinct taxa. Zool J Linn Soc, 2004, 141(2): 207-255. |
| [36] | Wilson EO. The Diversity of Life. New York: WW Norton & Company, 1999. |
| [37] | O’Grady P, DeSalle R. Out of Hawaii: the origin and biogeography of the genus Scaptomyza (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Biol Letters, 2008, 4(2): 195-199. |
| [38] |
Bennett GM, O’Grady PM. Host-plants shape insect diversity: phylogeny, origin, and species diversity of native Hawaiian leafhoppers (Cicadellidae: Nesophrosyne). Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2012, 65(2): 705-717.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2012.07.024 pmid: 22884527 |
| [39] |
Gillespie RG. Island time and the interplay between ecology and evolution in species diversification. Evol Appl, 2016, 9(1): 53-73.
doi: 10.1111/eva.12302 pmid: 27087839 |
| [40] | Carlquist S, Baldwin BG, Carr GD. Tarweeds & Silverswords: Evolution of the Madiinae (Asteraceae). St. Louis: Missouri Botanical Garden Press, 2003. |
| [41] | Givnish TJ, Millam KC, Mast AR, Paterson TB, Theim TJ, Hipp AL, Henss JM, Smith JF, Wood KR, Sytsma KJ. Origin, adaptive radiation and diversification of the Hawaiian lobeliads (Asterales: Campanulaceae). ProcBiol Sci, 2009, 276(1656): 407-416. |
| [42] | Losos JB. Lizards in an Evolutionary Tree:Ecology and Adaptive Radiation of Anoles. 1st edn. Oakland: University of California Press, 2011. |
| [43] | Brawand D, Wagner CE, Li YI, Malinsky M, Keller I, Fan SH, Simakov O, Ng AY, Lim ZW, Bezault E, Turner-Maier J, Johnson J, Alcazar R, Noh HJ, Russell P, Aken B, Alföldi J, Amemiya C, Azzouzi N, Baroiller J-F, Barloy-Hubler F, Berlin A, Bloomquist R, Carleton KL, Conte MA, D'Cotta H, Eshel O, Gaffney L, Galibert F, Gante HF, Gnerre S, Greuter L, Guyon R, Haddad NS, Haerty W, Harris RM, Hofmann HA, Hourlier T, Hulata G, Jaffe DB, Lara M, Lee AP, MacCallum I, Mwaiko S, Nikaido M, Nishihara H, Ozouf-Costaz C, Penman DJ, Przybylski D, Rakotomanga M, Renn SCP, Ribeiro FJ, Ron M, Salzburger W, Sanchez-Pulido L, Santos ME, Searle S, Sharpe T, Swofford R, Tan FJ, Williams L, Young S, Yin SY, Okada N, Kocher TD, Miska EA, Lander ES, Venkatesh B, Fernald RD, Meyer A, Ponting CP, Streelman JT, Lindblad-Toh K, Seehausen O, Di Palma F. The genomic substrate for adaptive radiation in African cichlid fish. Nature, 2014, 513(7518): 375-381. |
| [44] | Punzo F. Studies on the natural history, ecology, and behavior of Pepsis cerberus and P. Mexicana (Hymenoptera: Pompilidae) from Big Bend National Park, Texas. J N Y Entomol, 2005, 113(1): 84-95. |
| [45] | Gould SJ. Wonderful Life:The Burgess Shale and the Nature of History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1990. |
| [46] | Darlington PJ. Carabidae of mountains and islands: data on the evolution of isolated faunas, and on atrophy of wings. Ecol Monogr, 1943, 13(1): 37-61. |
| [47] | Roff DA. The evolution of flightlessness in insects. Ecol Monogr, 1990, 60(4): 389-421. |
| [48] | Vogler AP, Timmermans MJTN. Speciation: don't fly and diversify? Curr Biol, 2012, 22(8): R284-R286. |
| [49] | Darwin C. The Life and Letters of Charles Darwin, Including an Autobiographical Chapter. Vol. 1. London: John Murray, 1887. |
| [50] | Carlquist SJ. Island Life:A Natural History of the Islands of the World. New York: Natural History Press, 1965. |
| [51] | Van Valen L. Pattern and the balance of nature. Evol Theor, 1973, 1(1): 31-49. |
| [52] | Reyes-Agüero JA, Aguirre R JR, Valiente-Banuet A. Reproductive biology of Opuntia: a review. J Arid Environ, 2006, 64(4): 549-585. |
| [53] | Baldwin BG, Robichaux RH. Historical biogeography and ecology of the Hawaiian silversword alliance (Asteraceae):new molecular phylogenetic perspectives. In: Wagner WL, Funk VA, eds. Hawaiian Biogeography: Evolution on a Hot Spot Archipelago. Washington, D.C: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1995, 259-287. |
| [54] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO. An equilibrium theory of insular zoogeography. Evolution, 1963, 17(4): 373-387. |
| [55] | Johnson DL. Problems in the land vertebrate zoogeography of certain islands and the swimming powers of elephants. J Biogeogr, 1980, 7(4): 383-398. |
| [56] | Lomolino MV. The target area hypothesis: the influence of island area on immigration rates of non-volant mammals. Oikos, 1990, 57(3): 297-300. |
| [57] | Brown JH, Kodric-Brown A. Turnover rates in insular biogeography: effect of immigration on extinction. Ecology, 1977, 58(2): 445-449. |
| [58] | Losos JB, Ricklefs RE. The Theory of Island Biogeography Revisited. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2010. |
| [59] | Whittaker RJ, Fernández-Palacios JM, Matthews TJ. Island Biogeography:Geo-environmental Dynamics, Ecology, Evolution, Human Impact, and Conservation. New York: Oxford University Press, 2023. |
| [60] | Matthews TJ, Triantis KA, Whittaker RJ. The Species- Area Relationship:Theory and Application. London: Cambridge University Press, 2021. |
| [61] | Matthews TJ, Guilhaumon F, Triantis KA, Borregaard MK, Whittaker RJ. On the form of species-area relationships in habitat islands and true islands. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2016, 25(7): 847-858. |
| [62] | Zhou HN, Zhao YH, Zeng D, Liu J, Jin TH, Ding P. Spatial patterns and influencing factors of ground ant species diversity on the land-bridge islands in the Thousand Island Lake, China. Biodiversity Sci, 2019, 27(10): 1101-1111. |
|
周浩楠, 赵郁豪, 曾頔, 刘娟, 金挺浩, 丁平. 千岛湖陆桥岛屿地表蚂蚁群落物种多样性空间格局及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1101-1111.
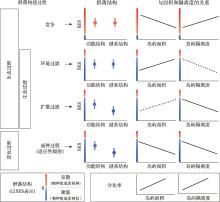
doi: 10.17520/biods.2019213 |
|
| [63] | Si XF, Jin TH, Li WD, Ren P, Wu Q, Zeng D, Zhang X, Zhao YH, Zhu C, Ding P. TIL20: A review of island biogeography and habitat fragmentation studies on subtropical reservoir islands of Thousand Island Lake, China. Zool Res Divers Conserv, 2024, 1(2): 89-105. |
| [64] |
Zeng D, Swihart RK, Zhao YH, Si XF, Ding P. Cascading effects of forested area and isolation on seed dispersal effectiveness of rodents on subtropical islands. J Ecol, 2019, 107(3): 1506-1517.
doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.13122 |
| [65] | Wang YP, Bao YX, Yu MJ, Xu GF, Ding P. Biodiversity research: nestedness for different reasons: the distributions of birds, lizards and small mammals on islands of an inundated lake. Divers Distrib, 2010, 16(5): 862-873. |
| [66] | Lomolino MV. Ecology’s most general, yet protean pattern: the species-area relationship. J Biogeogr, 2000, 27(1): 17-26. |
| [67] | Niering WA. Terrestrial ecology of Kapingamarangi Atoll, Caroline Islands. Ecol Monogr, 1963, 33(2): 131-160. |
| [68] | Triantis KA, Vardinoyannis K, Tsolaki EP, Botsaris I, Lika K, Mylonas M. Re-approaching the small island effect. J Biogeogr, 2006, 33(5): 914-923. |
| [69] |
Whitehead DR, Jones CE. Small islands and the equilibrium theory of insular biogeography. Evolution, 1969, 23(1): 171-179.
doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1969.tb03503.x pmid: 28562965 |
| [70] | Gao D, Wang YP. A review of the small-island effect detection methods and method advancement. Biodiversity Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23299. |
|
高德, 王彦平. 小岛屿效应检测方法研究进展. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23299.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2023299 |
|
| [71] | Rosenzweig ML. Species Diversity in Space and Time. London: Cambridge University Press, 1995. |
| [72] |
Kreft H, Jetz W, Mutke J, Kier G, Barthlott W. Global diversity of island floras from a macroecological perspective. Ecol Lett, 2008, 11(2): 116-127.
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01129.x pmid: 18036182 |
| [73] |
Gilpin ME. The role of stepping-stone islands. Theor Popul Biol, 1980, 17(2): 247-253.
pmid: 7404443 |
| [74] |
Díaz-Pérez A, Sequeira M, Santos-Guerra A, Catalán P. Multiple colonizations, in situ speciation, and volcanism- associated stepping-stone dispersals shaped the phylogeography of the Macaronesian red fescues (Festuca L., Gramineae). Syst Biol, 2008, 57(5): 732-749.
doi: 10.1080/10635150802302450 pmid: 18853360 |
| [75] | Garb JE, Gillespie RG. Island hopping across the central pacific: mitochondrial DNA detects sequential colonization of the Austral Islands by crab spiders (Araneae: Thomisidae). J Biogeogr, 2006, 33(2): 201-220. |
| [76] | Borges PAV, Hortal J. Time, area and isolation: factors driving the diversification of Azorean arthropods. J Biogeogr, 2009, 36(1): 178-191. |
| [77] | Chandra AK, Raghavan P, Ruzzo WL, Smolensky R, Tiwari P. The electrical resistance of a graph captures its commute and cover times. Comput Complex, 1996, 6: 312-340. |
| [78] | Etherington TR, Perry GL. Visualising continuous intra- landscape isolation with uncertainty using least-cost modelling based catchment areas: common brushtail possums in the Auckland isthmus. Int J Geogr Inf Sci, 2016, 30(1): 36-50. |
| [79] | Weigelt P, Kreft H. Quantifying island isolation - insights from global patterns of insular plant species richness. Ecography, 2013, 36(4): 417-429. |
| [80] | Weigelt P, Jetz W, Kreft H. Bioclimatic and physical characterization of the world’s islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(38): 15307. |
| [81] | Flantua SGA, Payne D, Borregaard MK, Beierkuhnlein CB, Steinbauer MJ, Dullinger S, Essl F, Irl SDH, Kienle D, Kreft H, Lenzner B, Norder SJ, Rijsdijk KF, Rumpf SB, Weigelt P, Field R. Snapshot isolation and isolation history challenge the analogy between mountains and islands used to understand endemism. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2020, 29(10): 1651-1673. |
| [82] | Wang DR, Zhao YH, Tang SP, Liu XX, Li WD, Han P, Zeng D, Yang YHS, Wei GP, Kang Y, Si XF. Nearby large islands diminish biodiversity of the focal island by a negative target effect. J Anim Ecol, 2023, 92(2): 492-502. |
| [83] | Diamond JM. Assembly of species communities. In: Cody M, Diamond J, eds. Ecology and Evolution of Communities. Cambridge, USA: Harvard University Press, 1975, 342-444. |
| [84] | Walker D, West RG. Studies in the Vegetational History of the British Isles. London: Cambridge University Press, 1970. |
| [85] | Connor EF, Simberloff D. The assembly of species communities: chance or competition? Ecology, 1979, 60(6): 1132-1140. |
| [86] | Simberloff D. Using island biogeographic distributions to determine if colonization is stochastic. Am Nat, 1978, 112(986): 713-726. |
| [87] | Diamond JM, Gilpin ME. Biogeographic umbilici and the origin of the Philippine avifauna. Oikos, 1983, 41(3): 307-321. |
| [88] |
Gilpin ME, Diamond JM. Factors contributing to non-randomness in species co-occurrences on islands. Oecologia, 1982, 52(1): 75-84.
doi: 10.1007/BF00349014 pmid: 28310111 |
| [89] | Sanderson JG, Diamond JM, Pimm SL. Pairwise co-existence of Bismarck and Solomon landbird species. Evol Ecol Res, 2009, 11(5): 771-786. |
| [90] |
Diamond J, Pimm SL, Sanderson JG. The checkered history of checkerboard distributions: comment. Ecology, 2015, 96(12): 3386-3388.
pmid: 26909443 |
| [91] | Patterson BD, Atmar W. Nested subsets and the structure of insular mammalian faunas and archipelagos. Biol J Linn Soc, 1986, 28(1-2): 65-82. |
| [92] | Wright DH, Patterson BD, Mikkelson GM, Cutler A, Atmar W. A comparative analysis of nested subset patterns of species composition. Oecologia, 1998, 113(1): 1-20. |
| [93] | Darlington PJ. Zoogeography: The Geographical Distribution of Animals. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1957. |
| [94] | Andrén H. Can one use nested subset pattern to reject the random sample hypothesis? Examples from boreal bird communities. Oikos, 1994, 70(3): 489-491. |
| [95] | Cutler AH. Nested biotas and biological conservation: metrics, mechanisms, and meaning of nestedness. Landscape Urban Plan, 1994, 28(1): 73-82. |
| [96] | Higgins CL, Willig MR, Strauss RE. The role of stochastic processes in producing nested patterns of species distributions. Oikos, 2006, 114(1): 159-167. |
| [97] |
Calmé S, Desrochers A. Nested bird and micro-habitat assemblages in a peatland archipelago. Oecologia, 1999, 118(3): 361-370.
doi: 10.1007/s004420050737 pmid: 28307280 |
| [98] | Wang YP, Zhang MC, Zhan CX. A review on the nested distribution pattern (nestedness): Analysis methods, mechanisms and conservation implications. Biodiversity Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23314. |
|
王彦平, 张敏楚, 詹成修. 嵌套分布格局研究进展: 分析方法, 影响机制及保护应用. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23314.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2023314 |
|
| [99] | Wang YP, Wang X, Ding P. Nestedness of snake assemblages on islands of an inundated lake. Curr Zool, 2012, 58(6): 828-836. |
| [100] | Zhang MC, Tang CN, Zhang Q, Zhan CX, Chen CW, Wang YP. Selective extinction and habitat nestedness are the main drivers of lizard nestedness in the Zhoushan Archipelago. Curr Zool, 2024, 70(2): 244-252. |
| [101] | Xu AC, Han XF, Zhang XM, Millien V, Wang YP. Nestedness of butterfly assemblages in the Zhoushan Archipelago, China: area effects, life-history traits and conservation implications. Biodivers Conserv, 2017, 26(6): 1375-1392. |
| [102] | Millien V, Zhan CX, Li YX, Wang J, Wang YP. A global assessment of nested patterns in insular mammal assemblages. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2024, 33(9): e13885. |
| [103] |
Kraft NJB, Valencia R, Ackerly DD. Functional traits and niche-based tree community assembly in an Amazonian forest. Science, 2008, 322(5901): 580.
doi: 10.1126/science.1160662 pmid: 18948539 |
| [104] | Wiens JJ, Graham CH. Niche conservatism: Integrating evolution, ecology, and conservation biology. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Sys, 2005, 36(1): 519-539. |
| [105] |
Kozak KH, Wiens J. Does niche conservatism promote speciation? A case study in North American salamanders. Evolution, 2006, 60(12): 2604-2621.
pmid: 17263120 |
| [106] |
Emerson BC, Gillespie RG. Phylogenetic analysis of community assembly and structure over space and time. Trends Ecol Evol, 2008, 23(11): 619-630.
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2008.07.005 pmid: 18823678 |
| [107] |
Gillespie R. Community assembly through adaptive radiation in Hawaiian spiders. Science, 2004, 303(5656): 356-359.
doi: 10.1126/science.1091875 pmid: 14726588 |
| [108] |
Ottaviani G, Keppel G, Götzenberger L, Harrison S, Øpedal OH, Conti L, Liancourt P, Klimešová J, Silveira FAO, Jiménez-Alfaro B, Negoita L, Doležal J, Hájek M, Ibanez T, Méndez-Castro FE, Chytrý M. Linking plant functional ecology to island biogeography. Trends Plant Sci, 2020, 25(4): 329-339.
doi: S1360-1385(19)30347-4 pmid: 31953170 |
| [109] |
Whittaker RJ, Rigal F, Borges PAV, Cardoso P, Terzopoulou S, Casanoves F, Pla L, Guilhaumon F, Ladle RJ, Triantis KA. Functional biogeography of oceanic islands and the scaling of functional diversity in the Azores. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(38): 13709-13714.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218036111 pmid: 25225395 |
| [110] |
Si XF, Cadotte MW, Zeng D, Baselga A, Zhao YH, Li JQ, Wu YR, Wang SY, Ding P. Functional and phylogenetic structure of island bird communities. J Anim Ecol, 2017, 86(3): 532-542.
doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.12650 pmid: 28191629 |
| [111] |
Cadotte MW, Albert CH, Walker SC. The ecology of differences: assessing community assembly with trait and evolutionary distances. Ecol Lett, 2013, 16(10): 1234-1244.
doi: 10.1111/ele.12161 pmid: 23910526 |
| [112] | Zhao YH, Dunn RR, Zhou HN, Si XF, Ding P. Island area, not isolation, drives taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional diversity of ants on land-bridge islands. J Biogeogr, 2020, 47(8): 1627-1637. |
| [113] | Zhang AY, Cadotte MW, Wu DH, Yu MJ. What drives phylogenetic and trait clustering on islands? Landscape Ecol, 2023, 38(5): 1339-1350. |
| [114] |
Mayfield MM, Levine JM. Opposing effects of competitive exclusion on the phylogenetic structure of communities. Ecol Lett, 2010, 13(9): 1085-1093.
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01509.x pmid: 20576030 |
| [115] |
Schrader J, Craven D, Sattler C, Cámara-Leret R, Moeljono S, Kreft H. Life-history dimensions indicate non-random assembly processes in tropical island tree communities. Ecography, 2021, 44(3): 469-480.
doi: 10.1111/ecog.05363 |
| [116] | Schrader J, Westoby M, Wright IJ, Kreft H. Disentangling direct and indirect effects of island area on plant functional trait distributions. J Biogeogr, 2021, 48(8): 2098-2110. |
| [117] | Weigelt P, Daniel Kissling W, Kisel Y, Fritz SA, Karger DN, Kessler M, Lehtonen S, Svenning J-C, Kreft H. Global patterns and drivers of phylogenetic structure in island floras. Sci Rep, 2015, 5(1): 12213. |
| [118] |
Si XF, Cadotte MW, Davies TJ, Antonelli A, Ding P, Svenning J-C, Faurby S. Phylogenetic and functional clustering illustrate the roles of adaptive radiation and dispersal filtering in jointly shaping late-Quaternary mammal assemblages on oceanic islands. Ecol Lett, 2022, 25(5): 1250-1262.
doi: 10.1111/ele.13997 pmid: 35275608 |
| [119] | Johnston AS. Predicting emergent animal biodiversity patterns across multiple scales. Glob Change Biol, 2024, 30(7): e17397. |
| [120] |
Kraft NJ, Comita LS, Chase JM, Sanders NJ, Swenson NG, Crist TO, Stegen JC, Vellend M, Boyle B, Anderson MJ. Disentangling the drivers of β diversity along latitudinal and elevational gradients. Science, 2011, 333(6050): 1755-1758.
doi: 10.1126/science.1208584 pmid: 21940897 |
| [121] | González-Caro S, Duivenvoorden JF, Balslev H, Cavelier J, Grández C, Macía MJ, Romero-Saltos H, Sánchez M, Valencia R, Duque Á. Scale-dependent drivers of the phylogenetic structure and similarity of tree communities in northwestern Amazonia. J Ecol, 2021, 109(2): 888-899. |
| [122] | Yang J, Zhang GC, Ci XQ, Swenson NG, Cao M, Sha Lq, Li J, Baskin CC, Slik JF, Lin LX, Poorter L. Functional and phylogenetic assembly in a Chinese tropical tree community across size classes, spatial scales and habitats. Funct Ecol, 2014, 28(2): 520-529. |
| [123] | Donoso DA. Assembly mechanisms shaping tropical litter ant communities. Ecography, 2014, 37(5): 490-499. |
| [124] | Zhao YH, Mendenhall CD, Matthews TJ, Wang DR, Li WD, Liu XX, Tang SP, Han P, Wei GP, Kang Y, Wu CX, Wang R, Zeng D, Frishkoff LO, Si XF. Land-use change interacts with island biogeography to alter bird community assembly. Proc Biol Sci B, 2024, 291(2018): 20232245. |
| [125] |
Wisz MS, Pottier J, Kissling WD, Pellissier L, Lenoir J, Damgaard CF, Dormann CF, Forchhammer MC, Grytnes J-A, Guisan A, Heikkinen RK, Høye TT, Kühn I, Luoto M, Maiorano L, Nilsson M-C, Normand S, Öckinger E, Schmidt NM, Termansen M, Timmermann A, Wardle DA, Aastrup P, Svenning J-C. The role of biotic interactions in shaping distributions and realised assemblages of species: implications for species distribution modelling. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2013, 88(1): 15-30.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2012.00235.x pmid: 22686347 |
| [126] |
Taylor A, Weigelt P, König C, Zotz G, Kreft H. Island disharmony revisited using orchids as a model group. New Phytol, 2019, 223(2): 597-606.
doi: 10.1111/nph.15776 pmid: 30848492 |
| [127] | Burns KC. Are there general patterns in plant defence against megaherbivores? Biol J Linn Soc, 2014, 111(1): 38-48. |
| [128] |
Sugiura S, Abe T, Makino S. Loss of extrafloral nectary on an oceanic island plant and its consequences for herbivory. Am J Bot, 2006, 93(3): 491-495.
doi: 10.3732/ajb.93.3.491 pmid: 21646208 |
| [129] | Bascompte J. Mutualistic networks. Front Ecol Environ, 2009, 7(8): 429-436. |
| [130] | Li HD, Wu XW, Xiao ZS. Assembly, ecosystem functions, and stability in species interaction networks. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2021, 45(10): 1049-1063. |
|
李海东, 吴新卫, 肖治术. 种间互作网络的结构、生态系统功能及稳定性机制研究. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(10): 1049-1063.
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2019.0159 |
|
| [131] | Traveset A, Tur C, Trøjelsgaard K, Heleno R, Castro- Urgal R, Olesen JM, Santos AMP. Global patterns of mainland and insular pollination networks. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2016, 25(7): 880-890. |
| [132] | Ren P, Didham RK, Murphy MV, Zeng D, Si XF, Ding P. Forest edges increase pollinator network robustness to extinction with declining area. Nat Ecol Evol, 2023, 7(3): 393-404. |
| [133] | Li WD, Zhu C, Grass I, Vázquez DP, Wang DR, Zhao YH, Zeng D, Kang Y, Ding P, Si XF. Plant-frugivore network simplification under habitat fragmentation leaves a small core of interacting generalists. Commun Biol, 2022, 5(1): 1-10. |
| [134] |
Zhu C, Dalsgaard B, Li WD, Gonçalves F, Vollstädt MGR, Ren P, Zhang X, Shao JJ, Ding P, Si XF. Generalist and topologically central avian frugivores promote plant invasion unequally across land-bridge islands. Ecology, 2024, 105(2): e4216.
doi: 10.1002/ecy.4216 pmid: 38037487 |
| [135] | Stubbs WJ, Wilson JB. Evidence for limiting similarity in a sand dune community. J Ecol, 2004, 92(4): 557-567. |
| [136] | Grant PR, Grant BR. How and Why Species Multiply:The Radiation of Darwin's Finches. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2008. |
| [137] | Losos JB. Seeing the forest for the trees: the limitations of phylogenies in comparative biology. (American Society of Naturalists Address). Am Nat, 2011, 177(6): 709-727. |
| [138] | Silvertown J. The ghost of competition past in the phylogeny of island endemic plants. J Ecol, 2004, 92(1): 168-173. |
| [139] |
Cadotte MW, Carboni M, Si XF, Tatsumi S. Do traits and phylogeny support congruent community diversity patterns and assembly inferences? J Ecol, 2019, 107(5): 2065-2077.
doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.13247 |
| [140] | Burns KC. Evolution in Isolation:The Search for an Island Syndrome in Plants. London: Cambridge University Press, 2019. |
| [141] | Moreira X, Castagneyrol B, García-Verdugo C, Abdala-Roberts L. A meta-analysis of insularity effects on herbivory and plant defences. J Biogeogr, 2021, 48(2): 386-393. |
| [142] | Cubas J, Irl SDH, Villafuerte R, Bello-Rodríguez V, Rodríguez-Luengo JL, del Arco M, Martín-Esquivel JL, González-Mancebo JM. Endemic plant species are more palatable to introduced herbivores than non-endemics. Proc Biol Sci B, 2019, 286(1900): 20190136. |
| [143] | Holt RD. Toward a trophic island biogeography. In: Losos JB, Ricklefs RE, eds. The Theory of Island Biogeography Revisited. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2010, 143-185. |
| [144] |
Piovia-Scott J, Spiller DA, Schoener TW. Effects of experimental seaweed deposition on lizard and ant predation in an island food web. Science, 2011, 331(6016): 461-463.
doi: 10.1126/science.1200282 pmid: 21273487 |
| [145] | Zhang X, Dalsgaard B, Staab M, Zhu C, Zhao YH, Gonçalves F, Ren P, Cai C, Qiao GX, Ding P, Si XF. Habitat fragmentation increases specialization of multi-trophic interactions by high species turnover. Proc Biol Sci B, 2023, 290(2009): 20231372. |
| [146] | Baker HG. Self-compatibility and establishment after ‘long-distance' dispersal. Evolution, 1955, 9(3): 347-349. |
| [147] | Chamorro S, Heleno R, Olesen JM, McMullen CK, Traveset A. Pollination patterns and plant breeding systems in the Galapagos: a review. Ann Bot, 2012, 110(7): 1489-1501. |
| [148] | Bernardello G. A survey of floral traits, breeding systems, floral visitors, and pollination systems of the angiosperms of the Juan Fernández Islands (Chile). Bot Rev, 2001, 67(3): 255-308. |
| [149] | Patiño J, Bisang I, Hedenäs L, Dirkse G, Bjarnason ÁH, Ah-Peng C, Vanderpoorten A. Baker's law and the island syndromes in bryophytes. J Ecol, 2013, 101(5): 1245-1255. |
| [150] |
Grossenbacher DL, Brandvain Y, Auld JR, Burd M, Cheptou PO, Conner JK, Grant AG, Hovick SM, Pannell JR, Pauw A, Petanidou T, Randle AM, Rubio de Casas R, Vamosi J, Winn A, Igic B, Busch JW, Kalisz S, Goldberg EE. Self-compatibility is over-represented on islands. New Phytol, 2017, 215(1): 469-478.
doi: 10.1111/nph.14534 pmid: 28382619 |
| [151] | Crawford Daniel J, Archibald Jenny K, Stoermer D, Mort Mark E, Kelly John K, Santos-Guerra A. A test of baker’s Law: breeding systems and the radiation of tolpis (Asteraceae) in the Canary islands. Int J Plant Sci, 2008, 169(6): 782-791. |
| [152] | Olesen JM, Valido A. Lizards as pollinators and seed dispersers: an island phenomenon. Trends Ecol Evol, 2003, 18(4): 177-181. |
| [153] |
Delavaux CS, Weigelt P, Dawson W, Duchicela J, Essl F, van Kleunen M, König C, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Stein A, Winter M, Schultz P, Kreft H, Bever JD. Mycorrhizal fungi influence global plant biogeography. Nat Ecol Evol, 2019, 3(3): 424-429.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-019-0823-4 pmid: 30804519 |
| [154] | Keeler KH. Extrafloral nectaries on plants in communities without ants: Hawaii. Oikos, 1985, 44(3): 407-414. |
| [155] | Nogales M, Heleno R, Rumeu B, González-Castro A, Traveset A, Vargas P, Olesen JM. Seed-dispersal networks on the Canaries and the Galápagos archipelagos: interaction modules as biogeographical entities. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2016, 25(7): 912-922. |
| [156] | Wardle DA. Islands as model systems for understanding how species affect ecosystem properties. J Biogeogr, 2002, 29(5-6): 583-591. |
| [157] | Hagan JG, Vanschoenwinkel B, Gamfeldt L. We should not necessarily expect positive relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in observational field data. Ecol Lett, 2021, 24(12): 2537-2548. |
| [158] | Tolmos ML, Guerrero-Ramirez NR, Ameztegui A, Barajas Barbosa MP, Craven D, Kreft H. Biogeographic context mediates multifaceted diversity-productivity relationships in island and mainland forests. J Ecol, 2024, 112(4): 800-816. |
| [159] | Wardle DA, Zackrisson O. Effects of species and functional group loss on island ecosystem properties. Nature, 2005, 435(7043): 806-810. |
| [160] | Zemp DC, Guerrero-Ramirez N, Brambach F, Darras K, Grass I, Potapov A, Röll A, Arimond I, Ballauff J, Behling H, Berkelmann D, Biagioni S, Buchori D, Craven D, Daniel R, Gailing O, Ellsäßer F, Fardiansah R, Hennings N, Irawan B, Khokthong W, Krashevska V, Krause A, Kückes J, Li K, Lorenz H, Maraun M, Merk MS, Moura CCM, Mulyani YA, Paterno GB, Pebrianti HD, Polle A, Prameswari DA, Sachsenmaier L, Scheu S, Schneider D, Setiajiati F, Setyaningsih CA, Sundawati L, Tscharntke T, Wollni M, Hölscher D, Kreft H. Tree islands enhance biodiversity and functioning in oil palm landscapes. Nature, 2023, 618(7964): 316-321. |
| [161] |
Wroe S, Field J, Grayson DK. Megafaunal extinction: climate, humans and assumptions. Trends Ecol Evol, 2006, 21(2): 61-62.
pmid: 16701473 |
| [162] | Fernández-Palacios JM, Kreft H, Irl SDH, Norder S, Ah-Peng C, Borges PAV, Burns KC, de Nascimento L, Meyer J-Y, Montes E, Drake D. Scientists’ warning-- The outstanding biodiversity of islands is in peril. Glob Ecol Conserv, 2021, 31: e01847. |
| [163] | Louys J, Braje TJ, Chang C-H, Cosgrove R, Fitzpatrick SM, Fujita M, Hawkins S, Ingicco T, Kawamura A, MacPhee RDE, McDowell MC, Meijer HJM, Piper PJ, Roberts P, Simmons AH, van den Bergh G, van der Geer A, Kealy S, O’Connor S. No evidence for widespread island extinctions after Pleistocene hominin arrival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(20): e2023005118. |
| [164] |
Leclerc C, Courchamp F, Bellard C. Insular threat associations within taxa worldwide. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 6393.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24733-0 pmid: 29686360 |
| [165] | Tershy BR, Shen K-W, Newton KM, Holmes ND, Croll DA. The importance of islands for the protection of biological and linguistic diversity. BioScience, 2015, 65(6): 592-597. |
| [166] |
Anderson SH, Kelly D, Ladley JJ, Molloy S, Terry J. Cascading effects of bird functional extinction reduce pollination and plant density. Science, 2011, 331(6020): 1068-1071.
doi: 10.1126/science.1199092 pmid: 21292938 |
| [167] | Maxwell SL, Fuller RA, Brooks TM, Watson JEM. Biodiversity: the ravages of guns, nets and bulldozers. Nature, 2016, 536(7615): 143-145. |
| [168] | Russell JC, Kueffer C. Island biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Annu Rev Env Resour, 2019, 44(1): 31-60. |
| [169] | Graham NR, Gruner DS, Lim JY, Gillespie RG. Island ecology and evolution: challenges in the Anthropocene. Environ Conserv, 2017, 44(4): 323-335. |
| [170] | Menard H. Islands. New York: Scientific American Library, 1986. |
| [171] | Frankham R, Briscoe DA, Ballou JD. Introduction to Conservation Genetics. 1st edn. London: Cambridge University Press, 2002. |
| [172] |
James JE, Lanfear R, Eyre-Walker A. Molecular evolutionary consequences of island colonization. Genome Biol Evol, 2016, 8(6): 1876-1888.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw120 pmid: 27358424 |
| [173] | Pinto AV, Hansson B, Patramanis I, Morales HE, van Oosterhout C. The impact of habitat loss and population fragmentation on genomic erosion. Conserv Genet, 2024, 25(1): 49-57. |
| [174] | Lomolino MV, Sax DF, Palombo MR, van der Geer AA. Of mice and mammoths: evaluations of causal explanations for body size evolution in insular mammals. J Biogeogr, 2012, 39(5): 842-854. |
| [175] | Lomolino MV, van der Geer AA, Lyras GA, Palombo MR, Sax DF, Rozzi R. Of mice and mammoths: generality and antiquity of the island rule. J Biogeogr, 2013, 40(8): 1427-1439. |
| [176] | Li JQ, Dirzo R, Wang YP, Zeng D, Liu J, Ren P, Zhong L, Ding P. Rapid morphological change in a small mammal species after habitat fragmentation over the past half-century. Divers Distrib, 2021, 27(12): 2615-2628. |
| [177] | van de Crommenacker J, Bunbury N, Jackson HA, Nupen LJ, Wanless R, Fleischer-Dogley F, Groombridge JJ, Warren BH. Rapid loss of flight in the Aldabra white-throated rail. PLoS One, 2019, 14(12): e0226064. |
| [178] | Blumstein DT, Daniel JC. The loss of anti-predator behaviour following isolation on islands. Proc Biol Sci B, 2005, 272(1573): 1663-1668. |
| [179] | Jolly CJ, Webb JK, Phillips BL. The perils of paradise: an endangered species conserved on an island loses antipredator behaviours within 13 generations. Biol Lett, 2018, 14(6): 20180222. |
| [180] | Cooper WE, Pyron RA, Garland T Jr. Island tameness: living on islands reduces flight initiation distance. Proc Biol Sci B, 2014, 281(1777): 20133019. |
| [181] | Brock KM, Bednekoff PA, Pafilis P, Foufopoulos J. Evolution of antipredator behavior in an island lizard species, Podarcis erhardii (Reptilia: Lacertidae): the sum of all fears? Evolution, 2015, 69(1): 216-231. |
| [182] | Li BB, Belasen A, Pafilis P, Bednekoff P, Foufopoulos J. Effects of feral cats on the evolution of anti- predator behaviours in island reptiles: insights from an ancient introduction. Proc Biol Sci B, 2014, 281(1788): 20140339. |
| [183] | Lens F, Davin N, Smets E, del Arco M. Insular woodiness on the Canary Islands: a remarkable case of convergent evolution. Int J Plant Sci, 2013, 174(7): 992-1013. |
| [184] | Kavanagh PH. Herbivory and the evolution of divaricate plants: structural defences lost on an offshore island. Austral Ecol, 2015, 40(2): 206-211. |
| [185] | Ricklefs RE, Bermingham E. The concept of the taxon cycle in biogeography. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2002, 11(5): 353-361. |
| [186] | Kueffer C, Daehler CC, Torres-Santana CW, Lavergne C, Meyer JY, Otto R, Silva L. A global comparison of plant invasions on oceanic islands. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Sys, 2010, 12(2): 145-161. |
| [187] | Terzopoulou S, Rigal F, Whittaker RJ, Borges PAV, Triantis KA. Drivers of extinction: the case of Azorean beetles. Biol Lett, 2015, 11(6): 20150273. |
| [188] | Kueffer C, Drake DR, Fernández-Palacios JM. Island biology: looking towards the future. Biol Lett, 2014, 10(10): 20140719. |
| [189] |
Duncan RP, Boyer AG, Blackburn TM. Magnitude and variation of prehistoric bird extinctions in the Pacific. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(16): 6436-6441.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216511110 pmid: 23530197 |
| [190] | Matthews TJ, Wayman JP, Cardoso P, Sayol F, Hume JP, Ulrich W, Tobias JA, Soares FC, Thébaud C, Martin TE, Triantis KA. Threatened and extinct island endemic birds of the world: distribution, threats and functional diversity. J Biogeogr, 2022, 49(11): 1920-1940. |
| [191] | Foley JA, DeFries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Monfreda C, Patz JA, Prentice IC, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK. Global consequences of land use. Science, 2005, 309(5734): 570-574. |
| [192] | Goldstein JH, Caldarone G, Duarte TK, Ennaanay D, Hannahs N, Mendoza G, Polasky S, Wolny S, Daily GC. Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into land-use decisions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109(19): 7565-7570. |
| [193] | Díaz S, Settele J, Brondízio ES, Ngo HT, Agard J, Arneth A, Balvanera P, Brauman KA, Butchart SHM, Chan KMA, Garibaldi LA, Ichii K, Liu JG, Subramanian SM, Midgley GF, Miloslavich P, Molnár Z, Obura D, Pfaff A, Polasky S, Purvis A, Razzaque J, Reyers B, Chowdhury RR, Shin YJ, Visseren-Hamakers I, Willis KJ, Zayas CN. Pervasive human-driven decline of life on Earth points to the need for transformative change. Science, 2019, 366(6471): eaax3100. |
| [194] | Harper GJ, Steininger MK, Tucker CJ, Juhn D, Hawkins F. Fifty years of deforestation and forest fragmentation in Madagascar. Environ Conserv, 2007, 34(4): 325-333. |
| [195] | Lehman SM, Radespiel U, Zimmermann E. Conservation biology of the Cheirogaleidae:future research directions. In: Lehman SM, Radespiel U, Zimmermann E, eds. The Dwarf and Mouse Lemurs of Madagascar: Biology, Behavior and Conservation Biogeography of the Cheirogaleidae. London: Cambridge University Press, 2016, 520-540. |
| [196] | Heaney LR. Small mammal diversity along elevational gradients in the Philippines: an assessment of patterns and hypotheses. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2001, 10(1): 15-39. |
| [197] | Razanatsoa E, Gillson L, Virah-Sawmy M, Woodborne S. Synergy between climate and human land-use maintained open vegetation in southwest Madagascar over the last millennium. Holocene, 2021, 32(1-2): 57-69. |
| [198] | Konoshima M, Tonda T, Kamo K, Razafindrabe BHN. Assessing the immediate impact of surrounding land uses on the extents of freshwater body over time in Madagascar--a demonstrative case study of Itasy Lake. Formath, 2021, 20. |
| [199] |
Lal R. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ Int, 2003, 29(4): 437-450.
pmid: 12705941 |
| [200] | Hiradate S, Morita S, Hata K, Osawa T, Sugai K, Kachi N. Effects of soil erosion and seabird activities on chemical properties of surface soils on an oceanic island in Ogasawara Islands, Japan. Catena, 2015, 133: 495-502. |
| [201] | Foucher A, Evrard O, Rabiet L, Cerdan O, Landemaine V, Bizeul R, Chalaux-Clergue T, Marescaux J, Debortoli N, Ambroise V, Desprats J-F. Uncontrolled deforestation and population growth threaten a tropical island’s water and land resources in only 10 years. Sci Adv, 2024, 10(33): eadn5941. |
| [202] |
Grimm NB, Faeth SH, Golubiewski NE, Redman CL, Wu JG, Bai XM, Briggs JM. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science, 2008, 319(5864): 756-760.
doi: 10.1126/science.1150195 pmid: 18258902 |
| [203] | Ehrenfeld JG. Vegetation of forested wetlands in urban and suburban landscapes in New Jersey. J Torrey Bot Soc, 2005, 132(2): 262-279. |
| [204] | Liu C, Fuertes E, Tiesler CMT, Birk M, Babisch W, Bauer CP, Koletzko S, von Berg A, Hoffmann B, Heinrich J, GINIplus and LISAplus Study Groups. The associations between traffic-related air pollution and noise with blood pressure in children: results from the GINIplus and LISAplus studies. Int J Hyg Environ Health, 2014, 217(4-5): 499-505. |
| [205] | Malik DS, Sharma AK, Sharma AK, Thakur R, Sharma M. A review on impact of water pollution on freshwater fish species and their aquatic environment. In: Kumar V, eds. Advances in Environmental Pollution Management: Wastewater Impacts and Treatment Technologies. Haridwar: Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy, 2020, 10-28. |
| [206] |
Kight CR, Swaddle JP. How and why environmental noise impacts animals: an integrative, mechanistic review. Ecol Lett, 2011, 14(10): 1052-1061.
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01664.x pmid: 21806743 |
| [207] | Wang WJ, Wu T, Li YZ, Xie SL, Han BL, Zheng H, Ouyang ZY. Urbanization Impacts on natural habitat and ecosystem services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong- Macao "Megacity". Sustainability, 2020, 12(16): 6675. |
| [208] | Savidge JA. Extinction of an island forest avifauna by an introduced snake. Ecology, 1987, 68(3): 660-668. |
| [209] | Simberloff D. Extinction-proneness of island species- causes and management implications. Raffles B Zool, 2000, 48(1): 1-9. |
| [210] | Gómez-Baggethun E, Gren Å, Barton DN, Langemeyer J, McPhearson T, O'Farrell P, Andersson E, Hamstead Z, Kremer P. Urban ecosystem services. In: Elmqvist T, eds. Urbanization, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities. New York City: Springer, 2013, 175-251. |
| [211] | Daye M, Chambers D, Roberts S. New Perspectives in Caribbean Tourism. Abingdon: Routledge, 2008. |
| [212] | McElroy JL, Pearce KB. The advantages of political affiliation: dependent and independent small-island profiles. Round Table, 2006, 95(386): 529-539. |
| [213] | Dodds R, Butler R. Overtourism: issues, realities and solutions. 1st edn. Berlin: De Gruyter Oldenbourg, 2019. |
| [214] |
Lukman KM, Uchiyama Y, Quevedo JMD, Kohsaka R. Tourism impacts on small island ecosystems: public perceptions from Karimunjawa Island, Indonesia. J Coast Conserv, 2022, 26(3): 14.
doi: 10.1007/s11852-022-00852-9 pmid: 35465221 |
| [215] | Baloch QB, Shah SN, Iqbal N, Sheeraz M, Asadullah M, Mahar S, Khan AU. Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2023, 30(3): 5917-5930. |
| [216] | Shannon G, Larson CL, Reed SE, Crooks KR, Angeloni LM. Ecological consequences of ecotourism for wildlife populations and communities. In: Blumstein DT, Blumstein DT, Geffroy B, Samia DSM, Bessa E, eds. Ecotourism’s Promise and Peril: A Biological Evaluation. New York City: Springer, 2017, 29-46. |
| [217] |
Bellard C, Bertelsmeier C, Leadley P, Thuiller W, Courchamp F. Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecol Lett, 2012, 15(4): 365-377.
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01736.x pmid: 22257223 |
| [218] |
Veron S, Mouchet M, Govaerts R, Haevermans T, Pellens R. Vulnerability to climate change of islands worldwide and its impact on the tree of life. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 14471.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51107-x pmid: 31597935 |
| [219] | Harter DE, Irl SD, Seo B, Steinbauer MJ, Gillespie R, Triantis KA, Fernández-Palacios J-M, Beierkuhnlein C. Impacts of global climate change on the floras of oceanic islands--projections, implications and current knowledge. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Sys, 2015, 17(2): 160-183. |
| [220] |
Courchamp F, Hoffmann BD, Russell JC, Leclerc C, Bellard C. Climate change, sea-level rise, and conservation: keeping island biodiversity afloat. Trends Ecol Evol, 2014, 29(3): 127-130.
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2014.01.001 pmid: 24486005 |
| [221] |
Leclerc C, Courchamp F, Bellard C. Future climate change vulnerability of endemic island mammals. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 4943.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18740-x pmid: 33009384 |
| [222] |
Rosenblad KC, Perret DL, Sax DF. Niche syndromes reveal climate-driven extinction threat to island endemic conifers. Nat Clim Change, 2019, 9(8): 627-631.
doi: 10.1038/s41558-019-0530-9 |
| [223] | Alcala AC, Bucol AA, Diesmos AC, Brown RM. Vulnerability of Philippine amphibians to climate change. Philipp J Sci, 2012, 140(1): 77-87. |
| [224] | Patiño J, Mateo RG, Zanatta F, Marquet A, Aranda SC, Borges PAV, Dirkse G, Gabriel R, Gonzalez-Mancebo JM, Guisan A, Muñoz J, Sim-Sim M, Vanderpoorten A. Climate threat on the Macaronesian endemic bryophyte flora. Sci Rep, 2016, 6(1): 29156. |
| [225] | Xiong Y, Rozzi R, Zhang YZ, Fan LQ, Zhao JD, Li DM, Yao YF, Xiao HT, Liu J, Zeng XY, Xu HL, Jiang YZ, Lei FM. Convergent evolution toward a slow pace of life predisposes insular endotherms to anthropogenic extinctions. Sci Adv, 2024, 10(28): eadm8240. |
| [226] | Bellard C, Leclerc C, Courchamp F. Impact of sea level rise on the 10 insular biodiversity hotspots. Global Ecol Biogeogr, 2014, 23(2): 203-212. |
| [227] | Seneviratne S, Nicholls N, Easterling D, Goodess CM, Kanae S, Kossin J, Luo YL, Marengo J, McInnes K, Rahimi M, Reichstein M, Sorteberg A, Vera C, Zhang XB, Rusticucci M, Semenov V, Alexander LV, Allen S, Benito G, Cavazos T, Clague J, Conway D, Della-Marta PM, Gerber M, Gong SL, Goswami BN, Hemer M, Huggel C, van den Hurk B, Kharin VV, Kitoh A, Klein Tank AMG, Li GL, Mason S, Guire WM, van Oldenborgh GJ, Orlowsky B, Smith S, Thiaw W, Velegrakis A, Yiou P, Zhang TJ, Zhou TJ, Zwiers FW. Changes in climate extremes and their impacts on the natural physical environment. In: Field CB, Barros V, Stocker TF, Qin D, Dokken DJ, Ebi KL, Mastrandrea MD, Mach KJ, Plattner GK, Allen SK, Tignor M, Midgley PM, eds. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation: A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. London: Cambridge University Press, 2012, 109-230. |
| [228] |
van Kleunen M, Essl F, Pergl J, Brundu G, Carboni M, Dullinger S, Early R, González-Moreno P, Groom QJ, Hulme PE, Kueffer C, Kühn I, Máguas C, Maurel N, Novoa A, Parepa M, Pyšek P, Seebens H, Tanner R, Touza J, Verbrugge L, Weber E, Dawson W, Kreft H, Weigelt P, Winter M, Klonner G, Talluto MV, Dehnen-Schmutz K. The changing role of ornamental horticulture in alien plant invasions. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2018, 93(3): 1421-1437.
doi: 10.1111/brv.12402 pmid: 29504240 |
| [229] | Seebens H, Blackburn TM, Dyer EE, Genovesi P, Hulme PE, Jeschke JM, Pagad S, Pyšek P, van Kleunen M, Winter M, Ansong M, Arianoutsou M, Bacher S, Blasius B, Brockerhoff EG, Brundu G, Capinha C, Causton CE, Celesti-Grapow L, Dawson W, Dullinger S, Economo EP, Fuentes N, Guénard B, Jäger H, Kartesz J, Kenis M, Kühn I, Lenzner B, Liebhold AM, Mosena A, Moser D, Nentwig W, Nishino M, Pearman D, Pergl J, Rabitsch W, Rojas-Sandoval J, Roques A, Rorke S, Rossinelli S, Roy HE, Scalera R, Schindler S, Štajerová K, Tokarska-Guzik B, Walker K, Ward DF, Yamanaka T, Essl F. Global rise in emerging alien species results from increased accessibility of new source pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(10): 2264-2273. |
| [230] | Dawson W, Moser D, van Kleunen M, Kreft H, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Weigelt P, Winter M, Lenzner B, Blackburn TM, Dyer EE, Cassey P, Scrivens SL, Economo EP, Guénard B, Capinha C, Seebens H, García-Díaz P, Nentwig W, García-Berthou E, Casal C, Mandrak NE, Fuller P, Meyer C, Essl F. Global hotspots and correlates of alien species richness across taxonomic groups. Nat Ecol Evol, 2017, 1(7): 0186. |
| [231] | Li YX, Wang YP, Liu X. Half of global islands have reached critical area thresholds for undergoing rapid increases in biological invasions. Proc Biol Sci B, 2024, 291(2025): rspb20240844. |
| [232] | Keane RM, Crawley MJ. Exotic plant invasions and the enemy release hypothesis. Trends Ecol Evol, 2002, 17(4): 164-170. |
| [233] | Courchamp F, Chapuis JL, Pascal M. Mammal invaders on islands: impact, control and control impact. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2003, 78(3): 347-383. |
| [234] | Rodda GH, Sawai Y, Chiszar D, Tanaka H. Problem Snake Management:The Habu and the Brown Treesnake. Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1999. |
| [235] | Gerlach J. Icons of Evolution:Pacific Island Tree-snails of the Family Partulidae. Devon: Phelsuma Press, 2016. |
| [236] | Li YM, Ke ZW, Wang YH, Blackburn TM. Frog community responses to recent American bullfrog invasions. Curr Zool, 2011, 57(1): 83-92. |
| [237] | Liu X, Wang SP, Ke ZW, Cheng CY, Wang YH, Zhang F, Xu F, Li XP, Gao X, Jin CN, Zhu W, Yan SF, Li YM. More invaders do not result in heavier impacts: the effects of non-native bullfrogs on native anurans are mitigated by high densities of non-native crayfish. J Anim Ecol, 2018, 87(3): 850-862. |
| [238] | Nuñez MA, Hayward J, Horton TR, Amico GC, Dimarco RD, Barrios-Garcia MN, Simberloff D. Exotic mammals disperse exotic fungi that promote invasion by exotic trees. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e66832. |
| [239] |
Bellard C, Rysman JF, Leroy B, Claud C, Mace GM. A global picture of biological invasion threat on islands. Nat Ecol Evol, 2017, 1(12): 1862-1869.
doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0365-6 pmid: 29109470 |
| [240] | Thibault JC, Martin JL, Penloup A, Meyer JY. Understanding the decline and extinction of monarchs (Aves) in Polynesian Islands. Biol Conserv, 2002, 108(2): 161-174. |
| [241] | Gillham ME. Some interactions of plants, rabbits and sea-birds on South African islands. J Ecol, 1963, 51(2): 275-294. |
| [242] | Weimerskirch H, Zotier R, Jouventin P. The avifauna of the Kerguelen Islands. Emu, 1989, 89(1): 15-29. |
| [243] | Medina FM, Bonnaud E, Vidal E, Tershy BR, Zavaleta ES, Josh Donlan C, Keitt BS, Le Corre M, Horwath SV, Nogales M. A global review of the impacts of invasive cats on island endangered vertebrates. Glob Change Biol, 2011, 17(11): 3503-3510. |
| [244] | Fitzgerald BM, Turner DC. Hunting behaviour of domestic cats and their impact on prey populations. In: Turner D, Bateson P, eds. The Domestic Cat: The Biology of Its Behavior. London: Cambridge University Press, 2000, 151-175. |
| [245] | Nogales M, Medina FM. Trophic ecology of feral cats (Felis silvestris f. catus) in the main environments of an oceanic archipelago (Canary Islands): an updated approach. Mamm Biol, 2009, 74(3): 169-181. |
| [246] | Wolf S, Keitt B, Aguirre-Muñoz A, Tershy B, Palacios E, Croll D. Transboundary seabird conservation in an important North American marine ecoregion. Environ Conserv, 2006, 33(4): 294-305. |
| [247] | Traveset A, Richardson DM. Mutualistic interactions and biological invasions. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Sys, 2014, 45(1): 89-113. |
| [248] | Fricke EC, Svenning JC. Accelerating homogenization of the global plant-frugivore meta-network. Nature, 2020, 585(7823): 74-78. |
| [249] | Nogales M, Medina FM, Valido A. Indirect seed dispersal by the feral cats Felis catus in island ecosystems (Canary Islands). Ecography, 1996, 19(1): 3-6. |
| [250] | Rothschild LWRB. Extinct Birds:Exploring the Lost World of Avian Extinction. Glasgow: Good Press, 2023. |
| [251] |
Macinnis-Ng C, Mcintosh AR, Monks JM, Waipara N, White RS, Boudjelas S, Clark CD, Clearwater MJ, Curran TJ, Dickinson KJ, Nelson N, Perry GL, Richardson SJ, Stanley MC, Peltzer DA. Climate-change impacts exacerbate conservation threats in island systems: New Zealand as a case study. Front Ecol Environ, 2021, 19(4): 216-224.
doi: 10.1002/fee.2285 |
| [252] | White RSA, McHugh PA, McIntosh AR. Drought survival is a threshold function of habitat size and population density in a fish metapopulation. Glob Change Biol, 2016, 22(10): 3341-3348. |
| [253] | White RSA, Wintle BA, McHugh PA, Booker DJ, McIntosh AR. The scaling of population persistence with carrying capacity does not asymptote in populations of a fish experiencing extreme climate variability. Proc Biol Sci B, 2017, 284(1856): 20170826. |
| [254] | Rafanoharana SC, Andrianambinina FOD, Rasamuel HA, Waeber PO, Wilmé L, Ganzhorn JU. Projecting forest cover in Madagascar's protected areas to 2050 and its implications for lemur conservation. Oryx, 2024, 58(2): 155-163. |
| [255] | Nogales M, Vidal E, Medina FM, Bonnaud E, Tershy BR, Campbell KJ, Zavaleta ES. Feral cats and biodiversity conservation: the urgent prioritization of island management. BioScience, 2013, 63(10): 804-810. |
| [256] |
Tumbaga JRA, Hipolito MC, Gabriel AG. Community participation toward biodiversity conservation among protected areas in Pangasinan, Philippines. Environ Dev Sustain, 2021, 23(3): 4698-4714.
doi: 10.1007/s10668-020-00705-1 |
| [257] |
Zhong JH, Cui LL, Deng ZY, Zhang Y, Lin J, Guo G, Zhang X. Long-term effects of ecological restoration projects on ecosystem services and their spatial interactions: a case study of Hainan tropical forest park in China. Environ Manage, 2023, 73(3): 493-508.
doi: 10.1007/s00267-023-01892-z pmid: 37853251 |
| [258] | Swarts HM, Crooks KR, Willits N, Woodroffe R. Possible contemporary evolution in an endangered species, the Santa Cruz Island fox. Anim Conserv, 2009, 12(2): 120-127. |
| [259] | Borges PAV, Cardoso P, Kreft H, Whittaker RJ, Fattorini S, Emerson BC, Gil A, Gillespie RG, Matthews TJ, Santos AMC, Steinbauer MJ, Thébaud C, Ah-Peng C, Amorim IR, Aranda SC, Arroz AM, Azevedo JMN, Boieiro M, Borda-de-Água L, Carvalho JC, Elias RB, Fernández-Palacios JM, Florencio M, González- Mancebo JM, Heaney LR, Hortal J, Kueffer C, Lequette B, Martín-Esquivel JL, López H, Lamelas-López L, Marcelino J, Nunes R, Oromí P, Patiño J, Pérez AJ, Rego C, Ribeiro SP, Rigal F, Rodrigues P, Rominger AJ, Santos-Reis M, Schaefer H, Sérgio C, Serrano ARM, Sim-Sim M, Stephenson PJ, Soares AO, Strasberg D, Vanderporten A, Vieira V, Gabriel R. Global island monitoring scheme (GIMS): a proposal for the long-term coordinated survey and monitoring of native island forest biota. Biodivers Conserv, 2018, 27(10): 2567-2586. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||