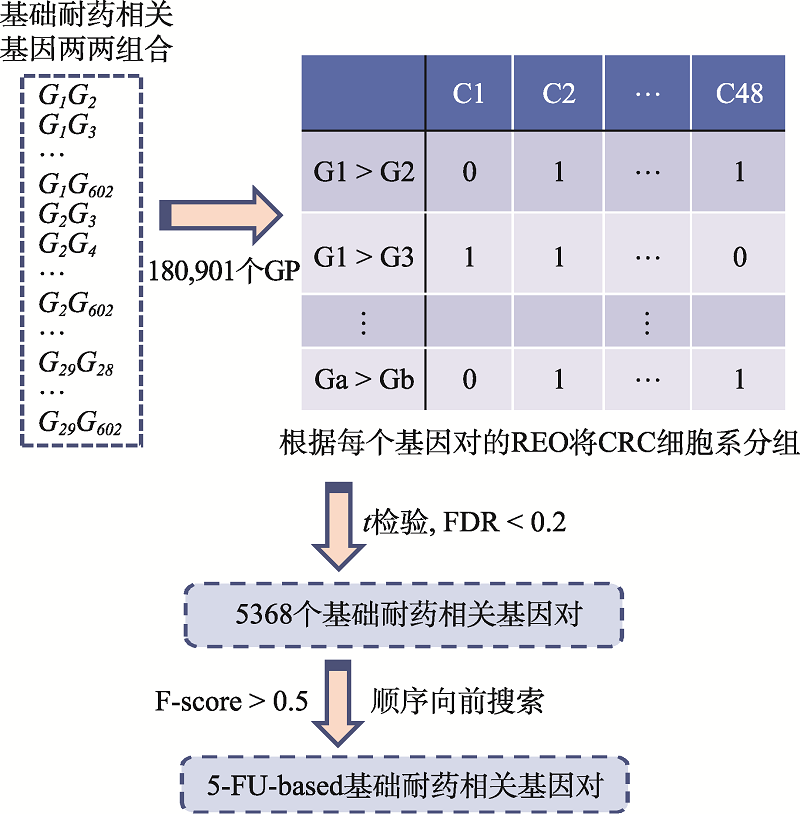
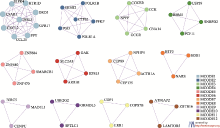
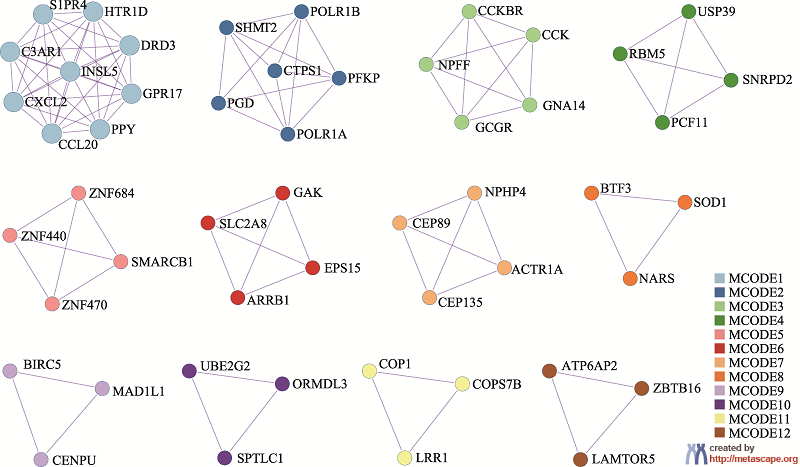
| [1] |
Geeleher P, Cox NJ, Huang RS . Cancer biomarker discovery is improved by accounting for variability in general levels of drug sensitivity in pre-clinical models. Genome Biol, 2016,17(1):190.
|
| [2] |
Zhang CY, Feng YX, Li P, Fu SB . Study on the relationship between the resistance to MTX and the transport protein superfamily of ATP-binding cassette that induces multiple drug resistance. Hereditas(Beijing), 2006,28(10):1201-1205.
|
|
张春玉, 冯源熙, 李璞, 傅松滨 . 介导多药耐药的ABC转运蛋白超家族与MTX耐药性的关系研究. 遗传, 2006,28(10):1201-1205.
|
| [3] |
Guo Q, Cao H, Qi X, Li H, Ye P, Wang Z, Wang D, Sun M . Research progress in reversal of tumor multi-drug resistance via natural products. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2017,17(11):1466-1476.
|
| [4] |
Li ST, Lu XR, Chi P, Pan J . Identification of HOXB8 and KLK11 expression levels as potential biomarkers to predict the effects of FOLFOX4 chemotherapy. Future Oncol, 2013,9(5):727-736.
|
| [5] |
Criscitiello C, Bayar MA, Curigliano G, Symmans FW, Desmedt C, Bonnefoi H, Sinn B, Pruneri G, Vicier C, Pierga JY, Denkert C, Loibl S, Sotiriou C, Michiels S, André F . A gene signature to predict high tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and outcome in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol, 2018,29(1):162-169.
|
| [6] |
Watanabe T, Kobunai T, Yamamoto Y, Matsuda K, Ishihara S, Nozawa K, Iinuma H, Konishi T, Horie H, Ikeuchi H, Eshima K, Muto T . Gene expression signature and response to the use of leucovorin, fluorouracil and oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol, 2011,13(6):419-425.
|
| [7] |
Qi LS, Chen LB, Li Y, Qin Y, Pan RF, Zhao WY, Gu YY, Wang HW, Wang RP, Chen XQ, Guo Z . Critical limitations of prognostic signatures based on risk scores summarized from gene expression levels: a case study for resected stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Brief Bioinform, 2016,17(2):233-242.
|
| [8] |
Eddy JA, Sung J, Geman D, Price ND . Relative expression analysis for molecular cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2010,9(2):149-159.
|
| [9] |
Del Rio M, Mollevi C, Martineau P. Molecular subtypes of metastatic colorectal cancer are predictive of patient response to chemo and targeted therapies( part 1). NCBI,GEO, 2017. .
|
| [10] |
Del Rio M, Mollevi C, Martineau P . Molecular subtypes of metastatic colorectal cancer are predictive of patient response to chemo and targeted therapies(part 2). NCBI, GEO, 2017. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE72969 .
|
| [11] |
Shingo Tsuji. CRC samples for FOLFOX therapy prediction. NCBI, GEO, 2011. .
|
| [12] |
Zhou YY, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C, Chanda SK . Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems- level datasets. Nat Commun, 2019,10(1):1523.
|
| [13] |
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y . Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B, 1995,57(1):289-300.
|
| [14] |
Bader GD, Hogue CW . An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 2003,4:2.
|
| [15] |
Zhan X, Wang J, Liu Y, Peng YQ, Tan WF . GPCR-like signaling mediated by smoothened contributes to acquired chemoresistance through activating Gli. Mol Cancer, 2014,13:4.
|
| [16] |
Shigeta K, Ishii Y, Hasegawa H, Okabayashi K, Kitagawa Y . Evaluation of 5-fluorouracil metabolic enzymes as predictors of response to adjuvant chemotherapy outcomes in patients with stage II/III colorectal cancer: a decision- curve analysis. World J Surg, 2014,38(12):3248-3256.
|
| [17] |
Siegfried Z, Karni R . The role of alternative splicing in cancer drug resistance. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2018,48:16-21.
|
| [18] |
Wilding JL, Bodmer WF . Cancer cell lines for drug discovery and development. Cancer Res, 2014,74(9):2377-2384.
|
| [19] |
Daniel VC, Marchionni L, Hierman JS, Rhodes JT, Devereux WL, Rudin CM, Yung R, Parmigiani G, Dorsch M, Peacock CD, Watkins DN . A primary xenograft model of small-cell lung cancer reveals irreversible changes in gene expression imposed by culture in vitro. Cancer Res, 2009,69(8):3364-3373.
|
| [20] |
Tong M, Zheng W, Li H, Li X, Ao L, Shen Y, Liang Q, Li J, Hong G, Yan H, Cai H, Li M, Guan Q, Guo Z . Multi-omics landscapes of colorectal cancer subtypes discriminated by an individualized prognostic signature for 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Oncogenesis, 2016,5(7):e242
|
| [21] |
Hafner M, Niepel M, Subramanian K, Sorger PK . Designing drug-response experiments and quantifying their results. Curr Protoc Chem Biol, 2017,9(2):96-116.
|
| [22] |
Sartor ITS, Recamonde-Mendoza M, Ashton-Prolla P . TULP3: A potential biomarker in colorectal cancer? PLoS One, 2019,14(1):e0210762.
|
| [23] |
Zeng H, Li H, Zhao YN, Chen LY, Ma XL . Transcripto- based network analysis reveals a model of gene activation in tongue squamous cell carcinomas. Head Neck, 2019,41(12):4098-4110.
|
| [24] |
Miao ZF, Zhao TT, Wang ZN, Xu YY, Song YX, Wu JH, Xu HM . SCC-S2 is overexpressed in colon cancers and regulates cell proliferation. Tumour Biol, 2012,33(6):2099-2106.
|
| [25] |
Wang J, Gao HY, Liu GH, Gu LN, Yang C, Zhang FM, Liu TB . Tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 8 expression as a predictor of prognosis and resistance in patients with advanced ovarian cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Hum Pathol, 2018,82:239-248.
|
| [26] |
Yang W, Wu B, Ma N, Wang YF, Guo JH, Zhu J, Zhao SH . BATF2 reverses multidrug resistance of human gastric cancer cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019,55(6):445-452.
|
| [27] |
Stebbing J, Shah K, Lit LC, Gagliano T, Ditsiou A, Wang T, Wendler F, Simon T, Szabó KS, O'Hanlon T, Dean M, Roslani AC, Cheah SH, Lee SC, Giamas G, . LMTK3 confers chemo-resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene, 2018,37(23):3113-3130.
|
 )
)