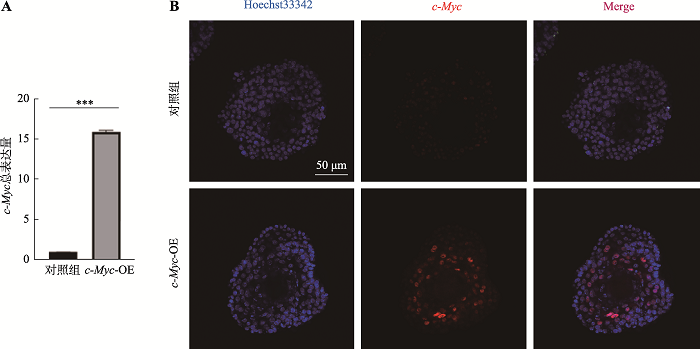
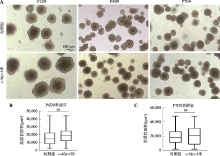
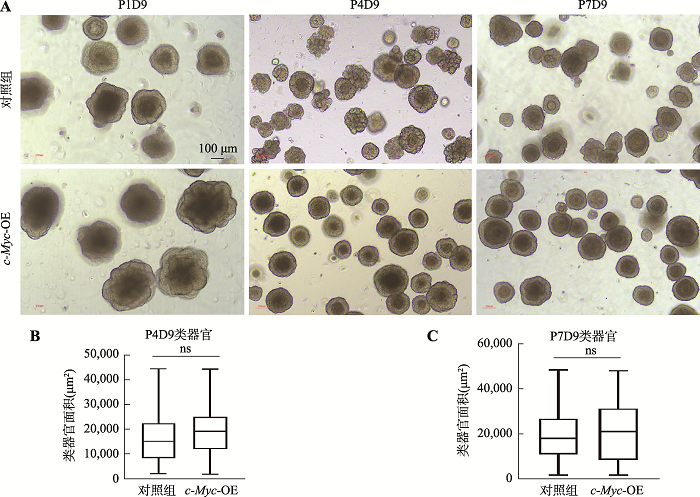
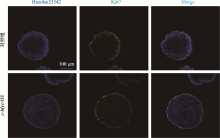
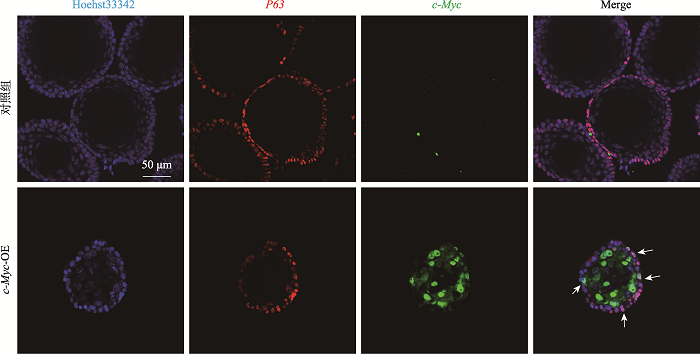
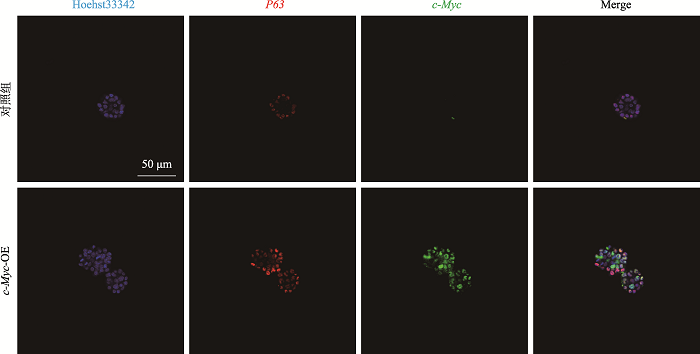
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 601-614.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-010
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
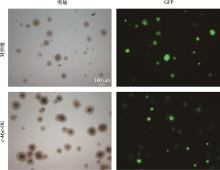
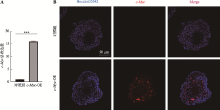
Using esophagus organoid to explore the role of c-Myc in esophageal cancer initiation
Youhong Chen1( ), Wenhao Yang1,2, Chao Ni1(
), Wenhao Yang1,2, Chao Ni1( )
)
- 1. School of Life Sciences Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2. Department of Pediatrics, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China
-
Received:2021-01-08Revised:2021-04-06Online:2021-06-20Published:2021-04-25 -
Contact:Ni Chao E-mail:15216686231@163.com;chaoni@fudan.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No(31900581)
Cite this article
Youhong Chen, Wenhao Yang, Chao Ni. Using esophagus organoid to explore the role of c-Myc in esophageal cancer initiation[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(6): 601-614.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
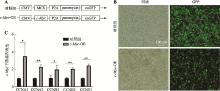
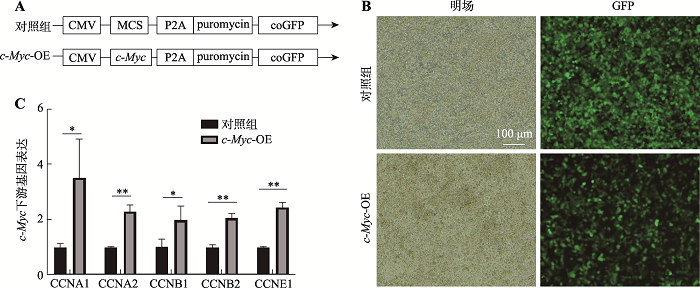
Table 1
Primers used in qPCR"
| 基因名称 | 上游引物(5′→3′) | 下游引物(5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| c-Myc-总 | CCCTCCACTCGGAAGGACTA | CGTTGTGTGTTCGCCTCTTG |
| h-CCNA1 | GAGGTCCCGATGCTTGTCAG | GTTAGCAGCCCTAGCACTGTC |
| h-CCNA2 | CGCTGGCGGTACTGAAGTC | GAGGAACGGTGACATGCTCAT |
| h-CCNB1 | AATAAGGCGAAGATCAACATGGC | TTTGTTACCAATGTCCCCAAGAG |
| h-CCNB2 | TGCTCTGCAAAATCGAGGACA | GCCAATCCACTAGGATGGCA |
| h-CCNE1 | GCCAGCCTTGGGACAATAATG | CTTGCACGTTGAGTTTGGGT |
| h-GAPDH | TGACTTCAACAGCGACACCCA | CACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAA |
| m-CCNA1 | GCCCGACGTGGATGAGTTT | AGGAGGAATTGGTTGGTGGTT |
| m-CCNA2 | CAGCATGAGGGCGATCCTT | GCAGGGTCTCATTCTGTAGTTTATATTCT |
| m-CCNB1 | AATAAGGCGAAGATCAACATGGC | TTTGTTACCAATGTCCCCAAGAG |
| m-CCNB2 | GCCAAGAGCCATGTGACTATC | CAGAGCTGGTACTTTGGTGTTC |
| m-CCNE1 | CACCACTGAGTGCTCCAGAA | CTGTTGGCTGACAGTGGAGA |
| m-CDK4 | GTGGCTGAAATTGGTGTCGG | TAACAAGGCCACCTCACGAA |
| m-ODC | AGATCACCGGCGTAATCAAC | TCCATAGACGCCATCATTCA |
| m-NAMPT | TCGGTTCTGGTGGCGCTTTGCTAC | AAGTTCCCCGCTGGTGTCCTATGT |
| m-MTA1 | CGCTCAAGTCCTACCTGGAG | TGGTACCGGTTTCCTACTCG |
| m-LDHA | TGTGGCAGACTTGGCTGAGA | CTGAGGAAGACATCCTCATTGATTC |
| m-NRF1 | CCACGTTGGATGAGTACACG | CTGAGCCTGGGTCATTTTGT |
| m-HMGCR | CTGAGGAAGACATCCTCATTGATTC | CCTGGACTGGAAACGGATATAG |
| m-Sox2 | GGT TACCTCTTCCTCCCACTC CAG | TCACATGTGCGACAGGGGCAG |
| m-KRT17 | ACCATCCGCCAGTTTACCTC | CTACCCAGGCCACTAGCTGA |
| m-Trp63 | TGCCATGCCTGTCTACAAG | GCTGTTCCCTTCTACTCGAATC |
| m-GATA4 | CCCTACCCAGCCTACATGG | ACATATCGAGATTGGGGTGTCT |
| m-GATA6 | AAAGCTTGCTCCGGTAACAG | TCTCCCACTGCAGACATCAC |
| m-VEGFA | GGAGAGACTTCGAGGAGCACTT | GGCGATTTAGCAGCAGATATAAGAA |
| m-GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
| [1] | Lin YS, Totsuka Y, Shan BE, Wang CC, Wei WQ, Qiao YL, Kikuchi S, Inoue M, Tanaka H, He YT. Esophageal cancer in high-risk areas of China: research progress and challenges. Ann Epidemiol, 2017,27(3):215-221. |
| [2] | Huang FL, Yu SJ. Esophageal cancer: risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J Surg, 2018,41(3):210-215. |
| [3] | Sethi NS, Kikuchi O, Duronio GN, Stachler MD, McFarland JM, Ferrer-Luna R, Zhang YX, Bao CY, Bronson R, Patil D, Sanchez-Vega F, Liu JB, Sicinska E, Lazaro JB, Ligon KL, Beroukhim R, Bass AJ. Early TP53 alterations engage environmental exposures to promote gastric premalignancy in an integrative mouse model. Nat Genet, 2020,52(2):219-230. |
| [4] | Testa U, Castelli G, Pelosi E. Esophageal cancer: genomic and molecular characterization, stem cell compartment and clonal evolution. Medicines (Basel), 2017,4(3):67. |
| [5] | di Pietro M, Canto MI, Fitzgerald RC. Endoscopic management of early adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: screening, diagnosis, and therapy. Gastroenterology, 2018,154(2):421-436. |
| [6] | Talukdar FR, di Pietro M, Secrier M, Moehler M, Goepfert K, Lima SSC, Pinto LFR, Hendricks D, Parker MI, Herceg Z. Molecular landscape of esophageal cancer: implications for early detection and personalized therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2018,1434(1):342-359. |
| [7] | Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, Analysis Working Group: Asan University, BC Cancer Agency, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Broad Institute, Brown University, Case Western Reserve University, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Duke University, Greater Poland Cancer Centre, Harvard Medical School, Institute for Systems Biology, KU Leuven, Mayo Clinic, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, National Cancer Institute, Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Stanford University, University of Alabama, University of Michigan, University of North Carolina, University of Pittsburgh, University of Rochester, University of Southern California, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, University of Washington, Van Andel Research Institute, Vanderbilt University, Washington University, Genome Sequencing Center: Broad Institute, Washington University in St. Louis, Genome Characterization Centers: BC Cancer Agency, Broad Institute, Harvard Medical School, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins University, University of North Carolina, University of Southern California Epigenome Center, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Van Andel Research Institute, Genome Data Analysis Centers: Broad Institute, Brown University, Harvard Medical School, Institute for Systems Biology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, University of California Santa Cruz, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Biospecimen Core Resource: International Genomics Consortium, Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Tissue Source Sites: Analytic Biologic Services, Asan Medical Center, Asterand Bioscience, Barretos Cancer Hospital, BioreclamationIVT, Botkin Municipal Clinic, Chonnam National University Medical School, Christiana Care Health System, Cureline, Duke University, Emory University, Erasmus University, Indiana University School of Medicine, Institute of Oncology of Moldova, International Genomics Consortium, Invidumed, Israelitisches Krankenhaus Hamburg, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, National Cancer Center Goyang, Ontario Tumour Bank, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Pusan National University Medical School, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, St. Joseph’s Hospital &Medical Center, St. Petersburg Academic University, Tayside Tissue Bank, University of Dundee, University of Kansas Medical Center, University of Michigan, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Disease Working Group, Duke University, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, National Cancer Institute, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Data Coordination Center: CSRA Inc, Project Team: National Institutes of Health. Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma. Nature, 2017,541(7636):169-175. |
| [8] | Lin DC, Dinh HQ, Xie JJ, Mayakonda A, Silva TC, Jiang YY, Ding LW, He JZ, Xu XE, Hao JJ, Wang MR, Li CQ, Xu LY, Li EM, Berman BP, Koeffler HP. Identification of distinct mutational patterns and new driver genes in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Gut, 2018,67(10):1769-1779. |
| [9] | Forbes SA, Beare D, Boutselakis H, Bamford S, Bindal N, Tate J, Cole CG, Ward S, Dawson E, Ponting L, Stefancsik R, Harsha B, Kok CY, Jia MM, Jubb H, Sondka Z, Thompson S, De T, Campbell PJ. COSMIC: somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017,45(D1):D777-D783. |
| [10] | Hoffman B, Amanullah A, Shafarenko M, Liebermann DA. The proto-oncogene c-Myc in hematopoietic development and leukemogenesis. Oncogene, 2002,21(21):3414-3421. |
| [11] | Kim EY, Kim A, Kim SK, Chang YS. MYC expression correlates with PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer, 2017,110:63-67. |
| [12] | Dolezal JM, Wang HB, Kulkarni S, Jackson L, Lu J, Ranganathan S, Goetzman ES, Bharathi SS, Beezhold K, Byersdorfer CA, Prochownik EV. Sequential adaptive changes in a c-Myc-driven model of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biol Chem, 2017,292(24):10068-10086. |
| [13] | Huang J, Jiang DX, Zhu T, Wang YQ, Wang H, Wang Q, Tan LJ, Zhu HG, Yao JX, Hou YY. Prognostic significance of c-Myc amplification in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg, 2019,107(2):436-443. |
| [14] | von Rahden BHA, Stein HJ, Puhringer-Oppermann F, Sarbia M. c-Myc amplification is frequent in esophageal adenocarcinoma and correlated with the upregulation of VEGFA expression. Neoplasia, 2006,8(9):702-707. |
| [15] | Sun LL, Wang YQ, Cen J, Ma XL, Cui L, Qiu ZX, Zhang ZT, Li H, Yang RZ, Wang CH, Chen XT, Wang L, Ye Y, Zhang HB, Pan GY, Kang JS, Ji Y, Zheng YW, Zheng S, Hui LJ. Modelling liver cancer initiation with organoids derived from directly reprogrammed human hepatocytes. Nat Cell Biol, 2019,21(8):1015-1026. |
| [16] | Clevers H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell, 2016,165(7):1586-1597. |
| [17] | Huch M, Koo BK. Modeling mouse and human development using organoid cultures. Development, 2015,142(18):3113-3125. |
| [18] | Schutgens F, Clevers H. Human organoids: tools for understanding biology and treating diseases. Annu Rev Pathol, 2020,15:211-234. |
| [19] | Trisno SL, Philo KED, McCracken KW, Catá EM, Ruiz-Torres S, Rankin SA, Han L, Nasr T, Chaturvedi P, Rothenberg ME, Mandegar MA, Wells SI, Zorn AM, Wells JM,. Esophageal organoids from human pluripotent stem cells delineate SOX2 functions during esophageal specification. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23(4): 501-515.e7. |
| [20] | Zhang YC, Yang Y, Jiang M, Huang SX, Zhang WW, Alam DA, Danopoulos S, Mori M, Chen YW, Balasubramanian R, de Sousa Lopes SMC, Serra C, Bialecka M, Kim E, Lin SJ, de Carvalho ALRT, Riccio PN, Cardoso WV, Zhang X, Snoeck HW, Que JW. 3D Modeling of esophageal development using human PSC-derived basal progenitors reveals a critical role for notch signaling. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23(4): 516-529.e5. |
| [21] | Bailey DD, Zhang YC, van Soldt BJ, Jiang M, Suresh S, Nakagawa H, Rustgi AK, Aceves SS, Cardoso WV, Que JW. Use of hPSC-derived 3D organoids and mouse genetics to define the roles of YAP in the development of the esophagus. Development, 2019, 146(23): xdev178855. |
| [22] | Fujii M, Clevers H, Sato T. Modeling human digestive diseases with CRISPR-Cas9-modified organoids. Gastroenterology, 2019,156(3):562-576. |
| [23] | DeWard AD, Cramer J, Lagasse E. Cellular heterogeneity in the mouse esophagus implicates the presence of a nonquiescent epithelial stem cell population. Cell Rep, 2014,9(2):701-711. |
| [24] | Koo BK, Sasselli V, Clevers H. Retroviral gene expression control in primary organoid cultures. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol, 2013, 27: Unit 5A.6. |
| [25] | Maru Y, Orihashi K, Hippo Y. Lentivirus-based stable gene delivery into intestinal organoids. Methods Mol Biol, 2016,1422:13-21. |
| [26] | Wei JS, Ran G, Wang X, Jiang N, Liang JQ, Lin XH, Ling C, Zhao B. Gene manipulation in liver ductal organoids by optimized recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors. J Biol Chem, 2019,294(38):14096-14104. |
| [27] | Sachs N, Papaspyropoulos A, Zomer-van Ommen DD, Heo I, Böttinger L, Klay D, Weeber F, Huelsz-Prince G, Iakobachvili N, Amatngalim GD, de Ligt J, van Hoeck A, Proost N, Viveen MC, Lyubimova A, Teeven L, Derakhshan S, Korving J, Begthel H, Dekkers JF, Kumawat K, Ramos E, van Oosterhout MF, Offerhaus GJ, Wiener DJ, Olimpio EP, Dijkstra KK, Smit EF, van der Linden M, Jaksani S, van de Ven M, Jonkers J, Rios AC, Voest EE, van Moorsel CH, van der Ent CK, Cuppen E, van Oudenaarden A, Coenjaerts FE, Meyaard L, Bont LJ, Peters PJ, Tans SJ, van Zon JS, Boj SF, Vries RG, Beekman JM, Clevers H. Long-term expanding human airway organoids for disease modeling. EMBO J, 2019,38(4):e100300. |
| [28] | Dang CV. Myc on the path to cancer. Cell, 2012,149(1):22-35. |
| [29] | Dang CV. Myc, metabolism, cell growth, and tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2013,3(8):a014217. |
| [30] | Li J, Liang Y, Lv H, Meng H, Xiong G, Guan XY, Chen XD, Bai Y, Wang K. miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit esophageal squamous cancer cell proliferation through suppression of c-Myc pathway. Gene, 2017,625:1-9. |
| [31] | McCauley HA, Wells JM. Pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids: using principles of developmental biology to grow human tissues in a dish. Development, 2017,144(6):958-962. |
| [32] | Pan XN, Chen JJ, Wang LX, Xiao RZ, Liu LL, Fang ZG, Liu QT, Long ZJ, Lin DJ. Inhibition of c-Myc overcomes cytotoxic drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia cells by promoting differentiation. PLoS One, 2014,9(8):e105381. |
| [33] | Chan JC, Hannan KM, Riddell M, Ng PY, Peck A, Lee RS, Hung S, Astle MV, Bywater M, Wall M, Poortinga G, Jastrzebski K, Sheppard KE, Hemmings BA, Hall MN, Johnstone RW, McArthur GA, Hannan RD, Pearson RB. AKT promotes rRNA synthesis and cooperates with c-Myc to stimulate ribosome biogenesis in cancer. Sci Signal, 2011, 4(188): ra56. |
| [34] | Liang MQ, Yu FQ, Chen C. C-Myc regulates PD-L1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Transl Res, 2020,12(2):379-388. |
| [35] | Hong J, Maacha S, Belkhiri A. Transcriptional upregulation of c-Myc by AXL confers epirubicin resistance in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Mol Oncol, 2018,12(12):2191-2208. |
| [36] | Rygiel AM, Milano F, Ten Kate FJ, Schaap A, Wang KK, Peppelenbosch MP, Bergman JJGHM, Krishnadath KK. Gains and amplifications of c-Myc, EGFR, and 20.q13 loci in the no dysplasia-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence of Barrett's esophagus. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2008,17(6):1380-1385. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||