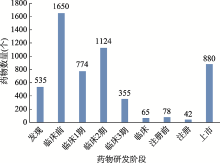
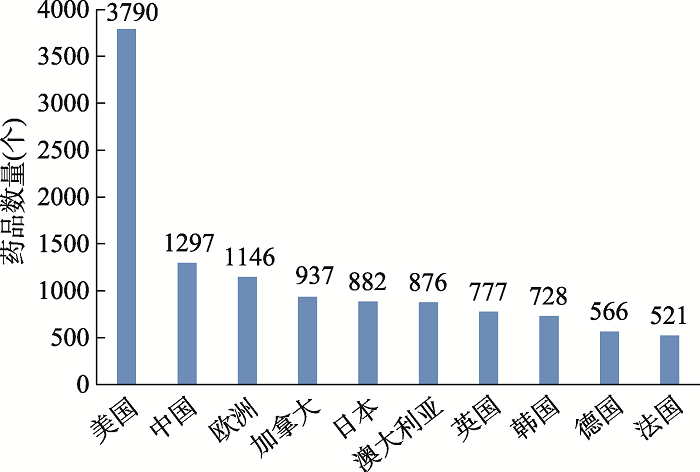
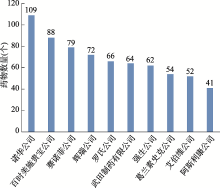
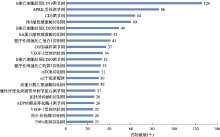
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 531-544.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-030
• Research Trends • Previous Articles Next Articles
Current status and future perspectives of rare disease research
Caihong He1,3( ), Wanzi Jiang2(
), Wanzi Jiang2( ), Liwen Zhang1, Meihua Ruan1, Hongwen Zhou2(
), Liwen Zhang1, Meihua Ruan1, Hongwen Zhou2( ), Jianrong Yu1,3(
), Jianrong Yu1,3( )
)
- 1. Shanghai Information Center for Life Sciences, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China
2. Department of Endocrinology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029,China
3. Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-01-25Revised:2021-03-01Online:2021-06-20Published:2021-04-20 -
Contact:Zhou Hongwen,Yu Jianrong E-mail:hecaihong2019@sibs.ac.cn;1995jwz@sina.com;drhongwenzhou@njmu.edu.cn;yjianrong@sibs.ac.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China No(2018YFA0506904);the National Natural Science F oundation of China No(L1924031)
Cite this article
Caihong He, Wanzi Jiang, Liwen Zhang, Meihua Ruan, Hongwen Zhou, Jianrong Yu. Current status and future perspectives of rare disease research[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(6): 531-544.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Regulations on rare diseases and orphan drugs issued by major countries"
| 时间 | 出台的政策法案 |
|---|---|
| 1982年 | 美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)设立孤儿药研发办公室 |
| 1983年 | 美国颁布《孤儿药法案》,并于1984年、1985年、1988年、2007年进行了修订 |
| 1983年 | 美国国立卫生研究院成立罕见病研究办公室 |
| 1991年 | 新加坡颁布《罕见病药物特许令》 |
| 1993年 | 日本修改药事法,增加孤儿药的认定标准和受理当局,厚生劳务省制定相关法规,出台《罕见病用药管理制度》 |
| 1998年 | 澳大利亚颁布了《罕见病药物纲要》 |
| 1999年 | 欧盟颁布《欧洲联盟罕见疾病行动方案》 |
| 2000年 | 欧洲医药局(EMA)实施孤儿药法规(Regulation(EC) No 141/2000),鼓励制药企业开展孤儿药的研究、开发和上市,为欧洲各国孤儿药法规的制定提供关键性的法律框架 |
| 2000年 | EMA设立孤儿药委员会,对孤儿药采取集中式审评程序进行上市审评审批 |
| 2002年 | 美国《罕见病法案》(Rare Diseases Act)出台 |
Table 2
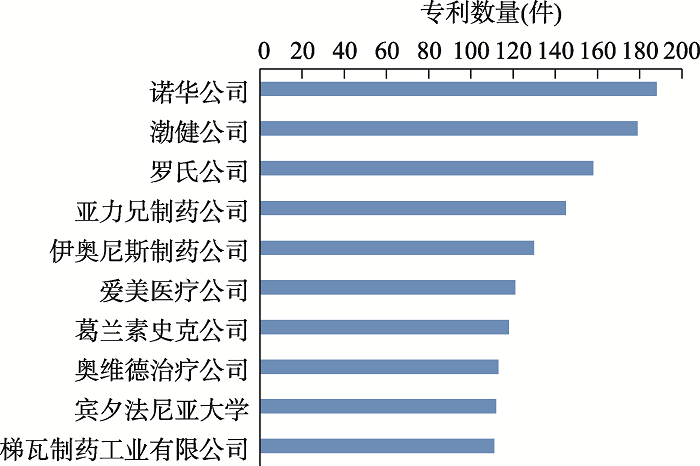
Top 10 international and Chinese institutions in the field of rare diseases by publication volume, 2015-2019"
| 国际Top 10机构发文情况 | 中国Top 10机构发文情况 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 机构 | 发文量/篇 | 机构 | 发文量/篇 |
| 哈佛医学院 | 1267 | 中国医学科学院北京协和医学院 | 685 |
| 伦敦大学学院 | 1374 | 上海交通大学 | 559 |
| 宾夕法尼亚大学 | 1314 | 首都医科大学 | 545 |
| 梅奥诊所医学中心 | 1288 | 中国科学院 | 502 |
| 多伦多大学 | 1236 | 复旦大学 | 447 |
| 约翰斯·霍普金斯大学 | 1202 | 中南大学 | 440 |
| 加利福尼亚大学旧金山分校 | 1162 | 中山大学 | 407 |
| 密歇根大学 | 967 | 浙江大学 | 381 |
| 华盛顿大学 | 943 | 四川大学 | 372 |
| 米兰大学 | 920 | 北京大学 | 354 |
| [1] | Li TT, Dai G, Zhang F. Comparative analysis on the research progress of rare diseases in domestic and abroad. Chin Pharm J, 2017,52(6):506-512. |
| 李彤彤, 戴罡, 张方. 国内外罕见病领域研究进展对比分析. 中国药学杂志, 2017,52(6):506-512. | |
| [2] | Veeramachaneni V. Data analysis in rare disease diagnostics. J Indian I Sci, 2020 Oct; 100(4):733-751. doi: 10.1007/s41745-020-00189-y. |
| [3] | 张钟艺. 罕见病的现状分析及相关政策解读. ( 2017-0-23) [2021-01-15]. https://www.sohu.com/a/199656205_803087. |
| [4] | 人民日报海外版. 应对罕见病, 中国在行动. (2020-11-03)[ 2021-01-15]. 应对罕见病, 中国在行动. (2020-11-03) [2021-01-15].http://www.xinhuanet.com/politics/2020-11/03/c_1126689473.htm . |
| [5] | 人民日报海外版. 罕见病, 你了解多少?(2019-03-09)[ 2021-01-16]. . 罕见病, 你了解多少?(2019-03-09) [2021-01-16].http://www.xinhuanet.com/politics/2019-03/09/c_1124211779.htm . |
| [6] | Burr CW, McCarthy DJ. An atypical case of multiple sclerosis. J Nerv Ment Dis, 1900,27(12):634-642. doi: 10.1097/00005053-190012000-00003. |
| [7] | Bonar AB. A case of primary progressive muscular dystrophy of the facio scapulo humeral type of landouzy and dejerine. J Nerv Ment Dis, 1900,27(10):547-550. doi: 10.1097/00005053-190010000-00009. |
| [8] | Yi BX, Wang GP, Ji HH, Wu XM. Improving Chinese innovation system of new drug according to 30-year history of U.S.Orphan Drug Act. Chin J New Drug, 2014,23(10):1107-1114. |
| 易八贤, 王广平, 姬海红, 吴晓明. 美国孤儿药法案30年历程与我国新药创新制度体系完善. 中国新药杂志, 2014,23(10):1107-1114. | |
| [9] | Ji XW, Liang JB, Ji SM. Research status in treatment of rare diseases. Chin J Clin Pharm, 2019,35(3):305-308. |
| 冀希炜, 梁家彬, 季双敏. 罕见病治疗国内外的研究现状. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2019,35(3):305-308. | |
| [10] | Mao YS, Gao Y, Du T. Comparative study on orphan drug policies of US, Japan and Europe. Prog Pharm Sci s, 2016,40(6):429-436. |
| 毛元圣, 高翼, 杜涛. 各国孤儿药政策对比分析. 药学进展, 2016,40(6):429-436. | |
| [11] | Liu YC, Dong JP. Research on the status quo of management of rare diseases and orphan medicines in the European Union. Chin Pharm J, 2012,47(5):395-398. |
| 刘玉聪, 董江萍. 欧盟罕见病及孤儿药管理现状的研究. 中国药学杂志, 2012,47(5):395-398. | |
| [12] | Nahm M, Lim SM, Kim YE, Park J, Noh MY, Lee S, Roh JE, Hwang SM, Park CK, Kim YH, Lim G, Lee J, Oh KW, Ki CS, Kim SH. ANXA11 mutations in ALS cause dysregulation of calcium homeostasis and stress granule dynamics. Sci Transl Med, 2020 Oct 21; 12(566): eaax3993. |
| [13] | Gómez P, Londral ARM., Gómez A, Palacios D, Rodellar V (2018). Monitoring ALS from speech articulation kinematics. Neural Comput Appl, 2020,32(20):15801-15812. doi: 10.1007/s00521-018-3538-6 |
| [14] | Lew DS, Mazzoni F, Finnemann SC. Microglia inhibition delays retinal degeneration due to MerTK phagocytosis receptor deficiency. Front Immunol, 2020,11:1463. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01463. |
| [15] | Appiah VA, Pesewu GA, Kotey FCN, Boakye AN, Duodu S, Tette EMA, Nyarko MY, Donkor ES. Staphylococcus aureus Nasal olonization among children with sickle cell disease at the children's hospital, Accra: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Antibiotic Resistance. Pathogens, 2020,9(5):329. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050329. |
| [16] | Moccia M, Brescia Morra V, Lanzillo R, Loperto I, Giordana R, Fumo MG, Petruzzo M, Capasso N, Triassi M, Sormani MP, Palladino R. Multiple Sclerosis in the Campania Region (South Italy): Algorithm validation and 2015-2017 prevalence. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020,17(10):3388. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103388. |
| [17] | Odashima K, Kagiyama N, Kanauchi T, Ishiguro T, Takayanagi N. Incidence and etiology of chronic pulmonary infections in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One, 2020,15(4):e0230746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230746. |
| [18] | Jung H, Kim HN, Jang Y, Park CK, Shin SH, Ha SY. Hepatic Angiosarcoma: Clinicopathologic study with a innvestigation of ROS1 gene rearrangements. In Vivo, 2020,34(3):1463-1467. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11930. |
| [19] | Carnero Contentti E, Daccach Marques V, Soto de Castillo I, Tkachuk V, Ariel B, Castillo MC, Cristiano E, Diégues Serva GB, Dos Santos AC, Finkelsteyn AM, López PA, Patrucco L, Molina O, Pettinicchi JP, Toneguzzo V, Caride A, Rojas JI. Clinical features and prognosis of late-onset neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders in a Latin American cohort. J Neurol, 2020,267(5):1260-1268. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-09699-2. |
| [20] | de Jong MC, Kors WA, Moll AC, de Graaf P, Castelijns JA, Jansen RW, Gallie B, Soliman SE, Shaikh F, Dimaras H, Kivelä TT. Screening for pineal trilateral retinoblastoma revisited: A Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology, 2020,127(5):601-607. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.10.040. |
| [21] | Binzer S, McKay KA, Brenner P, Hillert J, Manouchehrinia A. Disability worsening among persons with multiple sclerosis and depression: A Swedish cohort study. Neurology, 2019,93(24):e2216-e2223. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008617. |
| [22] | Kahraman T, Ozdogar AT, Abasiyanik Z, Ozakbas S, Multiple Sclerosis Research Group. Associations between smoking and walking, fatigue, depression, and health- related quality of life in persons with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Belg, 2020,28. doi: 10.1007/s13760-020-01341-2. |
| [23] | Chan ZYS, MacPhail AJC, Au IPH, Zhang JH, Lam BMF, Ferber R, Cheung RTH. Walking with head-mounted virtual and augmented reality devices: Effects on position control and gait biomechanics. PLoS One, 2019,14(12):e0225972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225972. |
| [24] | Lillo P, Caramelli P, Musa G, Parrao T, Hughes R, Aragon A, Valenzuela D, Cea G, Aranguiz R, Guimarães HC, Rousseff L, Gambogi LB, Mariano LI, Teixeira AL , Slachevsky A, de Souza LC. Inside minds, beneath diseases: social cognition in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis- frontotemporal spectrum disorder. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2020,91(12):1279-1282. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-324302. |
| [25] | Grothe M, Opolka M, Berneiser J, Dressel A. Testing social cognition in multiple sclerosis: Difference between emotion recognition and theory of mind and its influence on quality of life. Brain Behav, 2021,11(1):e01925. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1925. |
| [26] | Del Campo N, Phillips O, Ory-Magne F, Brefel-Courbon C, Galitzky M, Thalamas C, Narr KL, Joshi S, Singh MK, Péran P, Pavy-LeTraon A, Rascol O. Broad white matter impairment in multiple system atrophy. Hum Brain Mapp, 2020,42(2):357-366. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25227. |
| [27] | Bao ZK, Deng MX, Zou Y, Wang HZ, Liang JW, Mi YH. Case report of Langerhans cell histiocytosis in a fetus detected by magnetic resonance imaging. J Obstet Gynaecol Res, 2021,47(1):456-462. doi: 10.1111/jog.14559. |
| [28] | Iba M, Kim C, Sallin M, Kwon S, Verma A, Overk C, Rissman RA, Sen R, Sen JM, Masliah E. Neuroinflammation is associated with infiltration of T cells in Lewy body disease and α-synuclein transgenic models. J Neuroinflammation,2020, 17(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s12974- 020-01888-0. |
| [29] | Lee JD, McDonald TS, Fung JNT, Woodruff TM. Absence of receptor for advanced glycation end product (RAGE) reduces inflammation and extends survival in the hSOD1G93A mouse model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol, 2020,57(10):4143-4155. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02019-9. |
| [30] | Hauptmann J, Johann L, Marini F, Kitic M, Colombo E, Mufazalov IA, Krueger M, Karram K, Moos S, Wanke F, Kurschus FC, Klein M, Cardoso S, Strauß J, Bolisetty S, Lühder F, Schwaninger M, Binder H, Bechman I, Bopp T, Agarwal A, Soares MP, Regen T, Waisman A. Interleukin-1 promotes autoimmune neuroinflammation by suppressing endothelial heme oxygenase-1 at the blood-brain barrier. Acta Neuropathol, 2020,140(4):549-567. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02187-x. |
| [31] | Mehrpour S, Rodrigues CR, Ferreira RC, Briones MRDS, Oliveira ASB. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium in different mitochondrial haplogroups of four genes associated with neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. Arq Neuropsiquiatr, 2020,78(5):269-276. doi: 10.1590/0004-282x20200002. |
| [32] | de Roquemaurel A, Galli P, Landais A, Avendano S, Cabre P. Fingolimod for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in French West Indies, a real-world study in patients from African ancestry. J Neurol Sci, 2019,402:180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2019.05.027. |
| [33] | Zecca C, Bovis F, Novi G, Capobianco M, Lanzillo R, Frau J, Repice AM, Hakiki B, Realmuto S, Bonavita S, Curti E, Brambilla L, Mataluni G, Cavalla P, Di Sapio A, Signoriello E, Barone S, Maniscalco GT, Maietta I, Maraffi I, Boffa G, Malucchi S, Nozzolillo A, Coghe G, Mechi C, Salemi G, Gallo A, Sacco R, Cellerino M, Malentacchi M, De Angelis M, Lorefice L, Magnani E, Prestipino E, Sperli F, Brescia Morra V, Fenu G, Barilaro A, Abbadessa G, Signori A, Granella F, Amato MP, Uccelli A, Gobbi C, Sormani MP. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with rituximab: A multicentric Italian-Swiss experience. Mult Scler, 2020, 26(12):1519-1531. doi: 10.1177/1352458519872889. |
| [34] | Ebata S, Yoshizaki A, Fukasawa T, Miura S, Takahashi T, Sumida H, Asano Y, Sato S. Rituximab therapy is more effective than cyclophosphamide therapy for Japanese patients with anti-topoisomerase I-positive systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. J Dermatol, 2019,46(11):1006-1013. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15079. |
| [35] | Metzdorf J, Hobloss Z, Schlevogt S, Ayzenberg I, Stahlke S, Pedreiturria X, Haupeltshofer S, Gold R, Tönges L, Kleiter I. Fingolimod for irradiation-induced neurodegeneration. Front Neurosci, 2019,13:699. doi: 10.3389/ fnins.2019.00699. |
| [36] | Mariz S, Reese JH, Westermark K, Greene L, Goto T, Hoshino T, Llinares-Garcia J, Sepodes B. Worldwide collaboration for orphan drug designation. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2016,15(6):440-441. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.80. |
| [37] | Austin CP, Cutillo CM, Lau LPL, Jonker AH, Rath A, Julkowska D, Thomson D, Terry SF, de Montleau B, Ardigò D, Hivert V, Boycott KM, Baynam G, Kaufmann P, Taruscio D, Lochmüller H, Suematsu M, Incerti C, Draghia-Akli R, Norstedt I, Wang L, Dawkins HJS. International rare diseases research consortium (IRDiRC). future of rare diseases research 2017-2027: An IRDiRC Perspective. Clin Transl Sci, 2018,11(1):21-27. doi: 10.1111/cts.12500. |
| [38] | Tambuyzer E, Vandendriessche B, Austin CP, Brooks PJ, Larsson K, Miller Needleman KI, Valentine J, Davies K, Groft SC, Preti R, Oprea TI, Prunotto M. Therapies for rare diseases: therapeutic modalities, progress and challenges ahead. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2020,19(2):93-111. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0049-9. |
| [39] | 曾溢滔 . 曾溢滔院士谈罕见病:基因诊断、个体化医疗是发展趋势. (2015-03-13)[2021-01-18]. 曾溢滔院士谈罕见病:基因诊断、个体化医疗是发展趋势. (2015-03-13)[2021-01-18].http://www.biotech.org.cn/information/131536 . |
| [1] | Liwen Zhang, Meihua Ruan, Jialan Liu, Caihong He, Jianrong Yu. Progress on research and development in diabetes mellitus [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 824-839. |
| [2] | Wanzi Jiang, Liwen Zhang, Caihong He, Meihua Ruan, Yong Ji, Jianrong Yu, Hongwen Zhou. Progress on familial hypercholesterolemia [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(11): 1011-1022. |
| [3] | WANG Ao-Xue, CHEN Xiu-Ling. Current status and industrialization of transgenic tomatoes [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(9): 962-974. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||