Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 335-345.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-006
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Genetic polymorphisms of 66 InDel loci in the Chinese Han population
Xueqian Wang1,2( ), Qingzhen Zhang2, Peng Cheng2, Tingting Dong2, Weiguo Li1(
), Qingzhen Zhang2, Peng Cheng2, Tingting Dong2, Weiguo Li1( ), Zhe Zhou2(
), Zhe Zhou2( ), Shengqi Wang2(
), Shengqi Wang2( )
)
- 1. College of Life Sciences, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang 453007, China
2. Beijing institute of Radiation Medicine, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing 100850, China
-
Received:2022-01-06Revised:2022-03-15Online:2022-04-20Published:2022-03-24 -
Contact:Li Weiguo,Zhou Zhe,Wang Shengqi E-mail:Wangxqer0122@163.com;liwg0618@htu.edu.cn;zhouzhe@bmi.ac.cn;sqwang@bmi.ac.cn
Cite this article
Xueqian Wang, Qingzhen Zhang, Peng Cheng, Tingting Dong, Weiguo Li, Zhe Zhou, Shengqi Wang. Genetic polymorphisms of 66 InDel loci in the Chinese Han population[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(4): 335-345.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
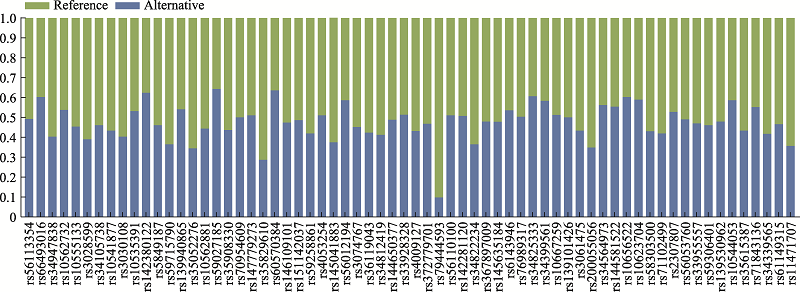
Table 1
The genetic information of 66 InDel loci and the genotyping result of positive control DNA sample"
| rs#1) | 物理位置2) | 突变基因座信息3) (参考基因Ref/突变基因Alt) | 目的片段 长度(bp) | 9947A | 9948 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs56113354 | chr1:45018875~45018876 | -/ATTA | 176 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs66493016 | chr1:62247127~62247132 | GCTTTC/- | 155 | 1,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs34947838 | chr1:84607676~84607677 | TT/- | 165 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs10562732 | chr1:112154318~112154321 | TACA/- | 168 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs10555133 | chr1:160678978~160678979 | AA/- | 161 | 1,1 | 2,2 | |
| rs3028599 | chr1:175158983~175158984 | -/GAGAGA | 172 | 2,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs34105738 | chr1:200039007~200039008 | -/AT | 151 | 2,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs10541877 | chr2:51510007~51510008 | CT/- | 161 | 1,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs3030108 | chr2:207819130~207819131 | -/AA | 176 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs10535391 | chr2:234910112~234910114 | ATT/- | 174 | 2,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs142380122 | chr3:830142~830149 | TATTTTTA/- | 179 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs5849187 | chr3:57111346~57111347 | -/AG | 152 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs59715790 | chr3:125227757~125227758 | -/AG | 178 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs139940865 | chr3:151246716~151246717 | -/CT | 168 | 1,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs35052276 | chr4:56498033~56498034 | AT/- | 155 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs10562881 | chr4:90225051~90225052 | AT/- | 180 | 1,1 | 1,1 | |
| rs59027185 | chr4:107185571~107185581 | CTCACAAAAGT/- | 157 | 2,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs35908330 | chr4:154092802~154092804 | ATA/- | 180 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs70954609 | chr5:19843605~19843609 | AAGTT/- | 171 | 2,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs147779273 | chr5:118725106~118725107 | AG/- | 179 | 2,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs35829610 | chr5:131823862~131823863 | -/TG | 171 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs60570384 | chr5:170837222~170837223 | -/AG | 178 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs146109101 | chr6:25420796~25420798 | CGA/- | 180 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs151142037 | chr6:62835920~62835930 | GCAGGGTAGAG/- | 165 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs59258861 | chr6:82184508~82184509 | AC/- | 174 | 2,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs4053254 | chr6:127484851~127484852 | -/AT | 180 | 2,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs145041883 | chr6:156295757~156295759 | ATG/- | 170 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs56012194 | chr7:34013472~34013473 | TT/- | 169 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs3074767 | chr7:106542693~106542694 | TT/- | 167 | 1,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs36119043 | chr7:137772061~137772062 | CT/- | 169 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs34812419 | chr7:151669590~151669591 | -/TT | 165 | 1,1 | 2,2 | |
| rs144650377 | chr8:605792~605793 | TC/- | 150 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs33928328 | chr8:33345203~33345205 | GTG/- | 164 | 2,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs4009127 | chr8:69001469~69001470 | TT/- | 153 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs372779701 | chr8:87918722~87918723 | AT/- | 179 | 1,1 | 2,2 | |
| rs79444593 | chr8:108392362~108392363 | -/CT | 152 | 1,1 | 1,1 | |
| rs56110100 | chr9:94516336~94516338 | GAC/- | 154 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs142281120 | chr9:115167202~115167203 | AG/- | 156 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs34822234 | chr10:3177604~3177605 | CA/- | 150 | 1,1 | 1,1 | |
| rs367897009 | chr10:27693664~27693665 | -/TGACCTCA | 172 | 2,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs145635184 | chr10:45607159~45607160 | -/GG | 176 | 2,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs6143946 | chr10:63754553~63754554 | -/TGATATAAGCACAGAATT | 158 | 2,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs76989317 | chr10:114144063~114144064 | TT/- | 163 | 2,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs34825333 | chr11:3889423~3889424 | AA/- | 170 | 1,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs34399561 | chr11:72500114~72500115 | AC/- | 160 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs10667259 | chr11:94222748~94222749 | -/AA | 166 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs139101426 | chr11:129108689~129108695 | CATAATT/- | 153 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs3061475 | chr12:21597614~21597616 | AGG/- | 153 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs200055056 | chr12:49463362~49463374 | CCTCCACTCTTCC/- | 155 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs34564973 | chr12:63157978~63157979 | -/CAG | 160 | 2,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs144581522 | chr12:104293761~104293762 | CT/- | 169 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs10656522 | chr12:119567037~119567038 | -/AA | 151 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs10623704 | chr12:129659763~129659764 | -/AA | 165 | 1,1 | 1,2 | |
| rs58303500 | chr13:25442008~25442010 | CAT/- | 154 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs71102499 | chr13:64606780~64606781 | -/AA | 180 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs2307807 | chr13:77083474~77083477 | TGTT/- | 162 | 2,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs56053760 | chr13:95418135~95418144 | GCAATCAACT/- | 156 | 1,1 | 1,1 | |
| rs33955557 | chr14:55227708~55227717 | TGAAAGTGTT/- | 164 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs59306401 | chr14:69752162~69752163 | AT/- | 156 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs139530962 | chr14:85881796~85881797 | AG/- | 176 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs10544053 | chr15:33782138~33782141 | CTTA/- | 174 | 1,2 | 1,1 | |
| rs35615387 | chr15:81105775~81105776 | CT/- | 175 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs71843136 | chr17:2917277~2917278 | AG/- | 177 | 1,2 | 2,2 | |
| rs34339565 | chr18:1326066~1326067 | -/AT | 177 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs61149315 | chr20:35053964~35053965 | -/AT | 172 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| rs11471707 | chr20:51686268~51686269 | -/AA | 168 | 2,2 | 1,2 | |
Table 2
The forensic parameters of 66 InDel loci (n=251)"
| rs# | Ref | Alt | PHWE | Ho | He | DP | PIC | TPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs56113354 | 0.508 | 0.492 | 0.871 | 0.506 | 0.500 | 0.622 | 0.375 | 1.012 |
| rs66493016 | 0.398 | 0.602 | 0.233 | 0.518 | 0.479 | 0.595 | 0.364 | 1.037 |
| rs34947838 | 0.596 | 0.404 | 0.985 | 0.482 | 0.482 | 0.615 | 0.366 | 0.965 |
| rs10562732 | 0.462 | 0.538 | 0.897 | 0.494 | 0.497 | 0.625 | 0.374 | 0.988 |
| rs10555133 | 0.546 | 0.454 | 0.930 | 0.494 | 0.496 | 0.624 | 0.373 | 0.988 |
| rs3028599 | 0.610 | 0.390 | 0.971 | 0.478 | 0.476 | 0.611 | 0.363 | 0.958 |
| rs34105738 | 0.540 | 0.460 | 0.205 | 0.538 | 0.497 | 0.601 | 0.373 | 1.082 |
| rs10541877 | 0.566 | 0.434 | 0.481 | 0.470 | 0.491 | 0.630 | 0.371 | 0.944 |
| rs3030108 | 0.596 | 0.404 | 0.214 | 0.522 | 0.482 | 0.595 | 0.366 | 1.046 |
| rs10535391 | 0.468 | 0.532 | 0.635 | 0.514 | 0.498 | 0.616 | 0.374 | 1.029 |
| rs142380122 | 0.376 | 0.624 | 0.381 | 0.498 | 0.469 | 0.595 | 0.359 | 0.996 |
| rs5849187 | 0.540 | 0.460 | 0.078 | 0.442 | 0.497 | 0.646 | 0.373 | 0.896 |
| rs59715790 | 0.635 | 0.365 | 0.754 | 0.474 | 0.463 | 0.600 | 0.356 | 0.951 |
| rs139940865 | 0.460 | 0.540 | 0.805 | 0.490 | 0.497 | 0.627 | 0.373 | 0.980 |
| rs35052276 | 0.655 | 0.345 | 0.667 | 0.466 | 0.452 | 0.592 | 0.350 | 0.937 |
| rs10562881 | 0.556 | 0.444 | 0.364 | 0.466 | 0.494 | 0.634 | 0.372 | 0.937 |
| rs59027185 | 0.357 | 0.643 | 0.224 | 0.498 | 0.459 | 0.585 | 0.354 | 0.996 |
| rs35908330 | 0.564 | 0.436 | 0.154 | 0.538 | 0.492 | 0.596 | 0.371 | 1.082 |
| rs70954609 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.549 | 0.482 | 0.500 | 0.633 | 0.375 | 0.965 |
| rs147779273 | 0.490 | 0.510 | 0.071 | 0.558 | 0.500 | 0.591 | 0.375 | 1.131 |
| rs35829610 | 0.713 | 0.287 | 0.513 | 0.430 | 0.409 | 0.562 | 0.325 | 0.878 |
| rs60570384 | 0.365 | 0.635 | 0.952 | 0.466 | 0.463 | 0.604 | 0.356 | 0.937 |
| rs146109101 | 0.526 | 0.474 | 0.028 | 0.430 | 0.499 | 0.651 | 0.374 | 0.878 |
| rs151142037 | 0.514 | 0.486 | 0.965 | 0.502 | 0.500 | 0.624 | 0.375 | 1.004 |
| rs59258861 | 0.580 | 0.420 | 0.144 | 0.442 | 0.487 | 0.636 | 0.369 | 0.896 |
| rs4053254 | 0.490 | 0.510 | 0.970 | 0.502 | 0.500 | 0.624 | 0.375 | 1.004 |
| rs145041883 | 0.626 | 0.375 | 0.435 | 0.494 | 0.469 | 0.596 | 0.359 | 0.988 |
| rs56012194 | 0.414 | 0.586 | 0.204 | 0.446 | 0.485 | 0.633 | 0.368 | 0.903 |
| rs3074767 | 0.548 | 0.452 | 0.649 | 0.482 | 0.495 | 0.629 | 0.373 | 0.965 |
| rs36119043 | 0.576 | 0.424 | 0.074 | 0.546 | 0.489 | 0.587 | 0.369 | 1.101 |
| rs34812419 | 0.588 | 0.412 | 0.911 | 0.482 | 0.485 | 0.618 | 0.367 | 0.965 |
| rs144650377 | 0.512 | 0.488 | 0.153 | 0.546 | 0.500 | 0.599 | 0.375 | 1.101 |
| rs33928328 | 0.486 | 0.514 | 0.835 | 0.494 | 0.500 | 0.628 | 0.375 | 0.988 |
| rs4009127 | 0.568 | 0.432 | 0.955 | 0.490 | 0.491 | 0.621 | 0.370 | 0.980 |
| rs372779701 | 0.532 | 0.468 | 0.122 | 0.450 | 0.498 | 0.644 | 0.374 | 0.909 |
| rs79444593 | 0.902 | 0.098 | 0.123 | 0.139 | 0.176 | 0.286 | 0.161 | 0.581 |
| rs56110100 | 0.490 | 0.510 | 0.772 | 0.510 | 0.500 | 0.620 | 0.375 | 1.020 |
| rs142281120 | 0.492 | 0.508 | 0.871 | 0.506 | 0.500 | 0.622 | 0.375 | 1.012 |
| rs34822234 | 0.635 | 0.365 | 0.228 | 0.426 | 0.463 | 0.617 | 0.356 | 0.872 |
| rs367897009 | 0.520 | 0.480 | 0.747 | 0.490 | 0.499 | 0.629 | 0.375 | 0.980 |
| rs145635184 | 0.522 | 0.478 | 0.413 | 0.526 | 0.499 | 0.610 | 0.375 | 1.055 |
| rs6143946 | 0.464 | 0.536 | 0.811 | 0.506 | 0.497 | 0.619 | 0.374 | 1.012 |
| rs76989317 | 0.496 | 0.504 | 0.874 | 0.506 | 0.500 | 0.622 | 0.375 | 1.012 |
| rs34825333 | 0.394 | 0.606 | 0.626 | 0.494 | 0.478 | 0.606 | 0.364 | 0.988 |
| rs34399561 | 0.416 | 0.584 | 0.244 | 0.450 | 0.486 | 0.632 | 0.368 | 0.909 |
| rs10667259 | 0.488 | 0.512 | 0.868 | 0.506 | 0.500 | 0.622 | 0.375 | 1.012 |
| rs139101426 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.508 | 0.522 | 0.500 | 0.613 | 0.375 | 1.046 |
| rs3061475 | 0.566 | 0.434 | 0.001 | 0.390 | 0.491 | 0.653 | 0.371 | 0.820 |
| rs200055056 | 0.651 | 0.349 | 0.094 | 0.402 | 0.454 | 0.614 | 0.351 | 0.837 |
| rs34564973 | 0.438 | 0.562 | 0.081 | 0.438 | 0.492 | 0.643 | 0.371 | 0.890 |
| rs144581522 | 0.446 | 0.554 | 0.588 | 0.478 | 0.494 | 0.629 | 0.372 | 0.958 |
| rs10656522 | 0.398 | 0.602 | 0.407 | 0.454 | 0.479 | 0.624 | 0.364 | 0.916 |
| rs10623704 | 0.410 | 0.590 | 0.971 | 0.486 | 0.484 | 0.616 | 0.367 | 0.973 |
| rs58303500 | 0.570 | 0.430 | 0.503 | 0.470 | 0.490 | 0.629 | 0.370 | 0.944 |
| rs71102499 | 0.580 | 0.420 | 0.087 | 0.434 | 0.487 | 0.639 | 0.369 | 0.884 |
| rs2307807 | 0.472 | 0.528 | 0.048 | 0.562 | 0.498 | 0.587 | 0.374 | 1.141 |
| rs56053760 | 0.510 | 0.490 | 0.640 | 0.486 | 0.500 | 0.631 | 0.375 | 0.973 |
| rs33955557 | 0.530 | 0.470 | 0.677 | 0.486 | 0.498 | 0.630 | 0.374 | 0.973 |
| rs59306401 | 0.540 | 0.460 | 0.310 | 0.530 | 0.497 | 0.606 | 0.373 | 1.064 |
| rs139530962 | 0.520 | 0.480 | 0.663 | 0.514 | 0.499 | 0.617 | 0.375 | 1.029 |
| rs10544053 | 0.414 | 0.586 | 0.453 | 0.510 | 0.485 | 0.605 | 0.368 | 1.020 |
| rs35615387 | 0.566 | 0.434 | 0.842 | 0.486 | 0.491 | 0.623 | 0.371 | 0.973 |
| rs71843136 | 0.448 | 0.552 | 0.940 | 0.498 | 0.495 | 0.621 | 0.372 | 0.996 |
| rs34339565 | 0.582 | 0.418 | 0.479 | 0.510 | 0.487 | 0.607 | 0.368 | 1.020 |
| rs61149315 | 0.534 | 0.466 | 0.172 | 0.542 | 0.498 | 0.599 | 0.374 | 1.091 |
| rs11471707 | 0.643 | 0.357 | 0.287 | 0.426 | 0.459 | 0.613 | 0.354 | 0.872 |
| TDP | 0.999 999 999 999 999 999 999 999 999 428 18 | |||||||
Table 3
The ability of exclusion in trios and ability of exclusion in duos of 66 InDel loci (n=251)"
| rs# | PEduo | PEtrio | rs# | PEduo | PEtrio | rs# | PEduo | PEtrio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs56113354 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs146109101 | 0.124 | 0.281 | rs34399561 | 0.118 | 0.277 |
| rs66493016 | 0.115 | 0.275 | rs151142037 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs10667259 | 0.125 | 0.281 |
| rs34947838 | 0.116 | 0.276 | rs59258861 | 0.119 | 0.277 | rs139101426 | 0.125 | 0.281 |
| rs10562732 | 0.124 | 0.280 | rs4053254 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs3061475 | 0.121 | 0.279 |
| rs10555133 | 0.123 | 0.280 | rs145041883 | 0.110 | 0.271 | rs200055056 | 0.103 | 0.267 |
| rs3028599 | 0.113 | 0.274 | rs56012194 | 0.118 | 0.277 | rs34564973 | 0.121 | 0.279 |
| rs34105738 | 0.123 | 0.280 | rs3074767 | 0.123 | 0.280 | rs144581522 | 0.122 | 0.279 |
| rs10541877 | 0.121 | 0.279 | rs36119043 | 0.119 | 0.278 | rs10656522 | 0.115 | 0.275 |
| rs3030108 | 0.116 | 0.276 | rs34812419 | 0.117 | 0.276 | rs10623704 | 0.117 | 0.276 |
| rs10535391 | 0.124 | 0.281 | rs144650377 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs58303500 | 0.120 | 0.278 |
| rs142380122 | 0.110 | 0.272 | rs33928328 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs71102499 | 0.119 | 0.277 |
| rs5849187 | 0.123 | 0.280 | rs4009127 | 0.121 | 0.278 | rs2307807 | 0.124 | 0.281 |
| rs59715790 | 0.107 | 0.270 | rs372779701 | 0.124 | 0.281 | rs56053760 | 0.125 | 0.281 |
| rs139940865 | 0.123 | 0.280 | rs79444593 | 0.016 | 0.142 | rs33955557 | 0.124 | 0.281 |
| rs35052276 | 0.102 | 0.266 | rs56110100 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs59306401 | 0.123 | 0.280 |
| rs10562881 | 0.122 | 0.279 | rs142281120 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs139530962 | 0.125 | 0.281 |
| rs59027185 | 0.105 | 0.268 | rs34822234 | 0.107 | 0.270 | rs10544053 | 0.118 | 0.277 |
| rs35908330 | 0.121 | 0.279 | rs367897009 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs35615387 | 0.121 | 0.279 |
| rs70954609 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs145635184 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs71843136 | 0.122 | 0.280 |
| rs147779273 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs6143946 | 0.124 | 0.280 | rs34339565 | 0.118 | 0.277 |
| rs35829610 | 0.084 | 0.251 | rs76989317 | 0.125 | 0.281 | rs61149315 | 0.124 | 0.281 |
| rs60570384 | 0.107 | 0.270 | rs34825333 | 0.114 | 0.274 | rs11471707 | 0.105 | 0.268 |
| CPEduo | 0.999 739 | |||||||
| CPEtrio | 0.999 999 999 417 | |||||||
Table 4
The comparison of identification performance in different systems"
| 体系 | TDP | CPE(trio) |
|---|---|---|
| 66-plex InDels | 0.999 999 999 999 999 999 999 999 999 428 18 | 0.999 999 999 417 |
| Investigator® DIPplex[ | 0.999 999 926 31 | 0.997 806 392 |
| AGCU InDel 50[ | 0.999 999 999 999 999 999 8 | 0.999 732 16 |
| DNA Typer 21™[ | 0.999 999 999 999 999 999 999 998 85 | 0.999 999 996 |
| [1] | Song F, Lang M, Li LY, Luo HB, Hou YP. Forensic features and genetic background exploration of a new 47-autosomal InDel panel in five representative Han populations residing in Northern China. Mol Genet Genomic Med, 2020, 8(5):e1224. |
| [2] |
Pan XY, Liu CH, Du WA, Chen L, Han XL, Yang XY, Li Y, Liu C. Genetic polymorphism and forensic application of 47 autosomal InDel loci in 5 Chinese ethnic groups. J Foren Med, 2020, 36(4):531-537.
doi: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2020.04.019 pmid: 33047539 |
|
潘习勇, 刘长晖, 杜蔚安, 陈玲, 韩晓龙, 杨幸怡, 李越, 刘超. 47个常染色体InDel位点在中国5个民族中的遗传多态性及法医学应用. 法医学杂志, 2020, 36(4):531-537.
doi: 10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2020.04.019 pmid: 33047539 |
|
| [3] | Zhang XR, Shen CM, Jin XY, Guo YX, Xie T, Zhu BF. Developmental validations of a self-developed 39 AIM- InDel panel and its forensic efficiency evaluations in the Shaanxi Han population. Int J Legal Med, 2021, 135(4):1359-1367. |
| [4] |
Jin XY, Wei YY, He YF, Guo YX, Mei T, Meng HT, Zhang YD, Kong TT, Zhu BF. Genetic polymorphisms of 30 InDel loci in Ewenki ethnic group from Inner Mongolia. J Foren Med, 2017, 33(3): 271-276+280.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.03.012 pmid: 29230993 |
|
靳小业, 魏媛媛, 贺永锋, 郭瑜鑫, 梅婷, 孟昊天, 张玉党, 孔婷婷, 朱波峰. 内蒙古鄂温克族人群30个 InDel位点遗传多态性. 法医学杂志, 2017, 33(3): 271-276+280.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.03.012 pmid: 29230993 |
|
| [5] |
Tozzo P, Delicati A, Frigo AC, Caenazzo L. Comparison of the allelic alterations between InDel and STR markers in tumoral tissues used for forensic purposes. Medicina, 2021, 57(3):226.
doi: 10.3390/medicina57030226 |
| [6] | Hong L, Wang XG, Liu SJ, Zhang YM, Ou XL, Chen Y, Chen WH, Sun HY. Genetic polymorphisms of 30 InDel loci in Guangdong Han population. J Sun Yat-sen Univ Med Sci, 2013, 34(2):299-304. |
| 洪丽, 王小广, 刘素娟, 张胤鸣, 欧雪玲, 陈勇, 陈维红, 孙宏钰. 30个插入/缺失多态性位点在中国广东汉族人群中的遗传多态性. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2013, 34(2):299-304. | |
| [7] |
Bai RF, Jiang LZ, Zhang Z, Shi MS. Genetic polymorphism and forensic application of 30 InDel loci of Han population in Beijin. Hereditas (Beijing), 2013, 35(12):1368-1376.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2013.01368 |
|
百茹峰, 姜立喆, 张中, 石美森. 北京汉族群体30个常染色体InDel位点群体遗传学及法医学研究. 遗传, 2013, 35(12):1368-1376.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2013.01368 |
|
| [8] | Liu YJ, Hu M, Shi MS, Li XB. Analysis on the genetic polymorphisms of 30 InDel loci in Gelao and Miao ethnic population in Guizhou. Lab Med Clin, 2021, 18(15): 2162-2168+2172. |
| 刘亚举, 胡萌, 石美森, 李学博. 贵州仡佬族和苗族人群30个插入/缺失位点遗传多态性分析. 检验医学与临床, 2021, 18(15): 2162-2168+2172. | |
| [9] |
Haidar M, Alsaleh H, Haddrill PR. Population genetics of 30 insertion/deletion polymorphisms in the Kuwaiti population. Int J Legal Med, 2020, 134(3):985-986.
doi: 10.1007/s00414-019-02180-4 pmid: 31728633 |
| [10] |
Wang MG, He GL, Gao S, Jia FQ, Zou X, Liu J, Wang SY, Ye ZW, Hou YP, Wang Z. Molecular genetic survey and forensic characterization of Chinese Mongolians via the 47 autosomal insertion/deletion marker. Genomics, 2021, 113(4):2199-2210.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.05.010 |
| [11] |
Chen L, Du W, Wu WB, Yu A, Pan XY, Feng PP, Feng CL, Li C, Xu LD, Liu CH, Liu C. Developmental validation of a novel six-dye typing system with 47 A-InDels and 2 Y-InDels. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2019, 40:64-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.02.009 |
| [12] | Wang YL, Song ZX, Gu J, Bai HR, Zhou YY, Zhang JY, Yang Y, Shi WY, Chen LQ. Forensic genetic study and application of 30 autosomal InDel loci in Chinese Mongolia population residing in Chifeng. Life Sci Res, 2019, 23(05):359-366. |
| 王亚丽, 宋振祥, 顾捷, 白慧茹, 周圆圆, 张佳怡, 杨越, 史唯一, 陈丽琴. 内蒙古赤峰地区蒙古族人群30个常染色体InDel的遗传多态性. 生命科学研究, 2019, 23(05):359-366. | |
| [13] | Wang MY, Yu H. Analysis of genetic polymorphism of 19 short tandem repeat loci in Henan Han population. Henan Med Res, 2021, 30(22):4067-4071. |
| 王美莹, 于皓. 19个短串联重复序列基因座在河南汉族人群中的遗传多态性分析. 河南医学研究, 2021, 30(22):4067-4071. | |
| [14] |
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST, McVean G, Durbin R. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(15):2156-2158.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330 pmid: 21653522 |
| [15] |
Mo SK, Ren ZL, Yang YR, Liu YC, Zhang JJ, Wu HJ, Li Z, Bo XC, Wang SQ, Yan JW, Ni M. A 472-SNP panel for pairwise kinship testing of second-degree relatives. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2018, 34:178-185.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.02.019 |
| [16] |
Qu WB, Shen ZY, Zhao DS, Yang Y, Zhang CG. MFEprimer:multiple factor evaluation of the specificity of PCR primers. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(2):276-278.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn614 |
| [17] |
Peakall R, Smouse PE. GenAlEx 6.5:genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research- an update. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(19):2537-2539.
pmid: 22820204 |
| [18] | Zhao F, Wu XY, Cai GQ, Xu CC. Modified-Powerstates software in forensic biostatistics. Chin J Foren Med, 2003, 18(5): 297-298+312. |
| 赵方, 伍新尧, 蔡贵庆, 许传超. Modified-Powerstates软件在法医生物统计中应用. 中国法医学杂志, 2003, 18(5): 297-298+312. | |
| [19] |
Pan M, Ju XB, Liu YT, Cui H, Gu M, Zhou HY. Genetic polymorphism of 30 InDel loci in Han population from Jiangsu province. J Foren Med, 2017, 33(6): 611-614+618.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.06.009 pmid: 29441769 |
|
潘猛, 居晓斌, 刘燕婷, 崔鹤, 顾民, 周惠英. 江苏汉族人群30个插入/缺失位点的遗传多态性. 法医学杂志, 2017, 33(6): 611-614+618.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.06.009 pmid: 29441769 |
|
| [20] | Yang X, Mu R, Cao YW, Wang X, Li CX, Cai JC, Liu HJ, Ma WH. Genetic polymorphism of 20 STR loci in Kazakh, Hui and Han population in Shihezi region of Xinjiang. Acta Laser Biol Sin, 2021, 30(4):339-347. |
| 杨秀, 牟睿, 曹雨薇, 王郗, 李春香, 蔡君成, 刘焕杰, 马温华. 新疆石河子地区哈萨克族、回族、汉族人群20个STR基因座的遗传多态性研究. 激光生物学报, 2021, 30(4):339-347. | |
| [21] | Wang W, Zhao L, Jiang L, Liu J, Huang MS, Li RR, Liu JJ, Ma Q, Wang YY, Li CX. Constructing a multiplex PCR system for personal identification by the InDel polymorphism of Chinese population. Foren Sci Technol, 2017, 42(01):1-8. |
| 王玮, 赵蕾, 江丽, 刘京, 黄美莎, 李冉冉, 刘佳佳, 马泉, 王英元, 李彩霞. 用于中国人群个体识别的InDe多重PCR系统的构建. 刑事技术, 2017, 42(01):1-8. | |
| [22] | Hou YP. Forensic genetics. Beijing: People’s medical publishing house, 2009: 72-73. |
| 侯一平. 法医物证学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2009: 72-73. | |
| [23] | Zhao SM, Zhang SH, Li CT. InDel_typer30:A multiplex PCR system for DNA identification among five Chinese populations. J Foren Med, 2010, 26(5): 343-348+356. |
| 赵书民, 张素华, 李成涛. InDel_typer30:用于中国5个主要民族DNA鉴定的多重PCR系统. 法医学杂志, 2010, 26(5): 343-348+356. | |
| [24] | Ji FQ, Teng J, Lai L, Han LL, Shen XL, Pu XD. A study on genetic polymorphisms of Han population in Fujian based on Sinofiler detection system. Int J Lab Med, 2013, 34(21): 2835-2836+2839. |
| 纪凤卿, 滕菁, 赖力, 韩丽丽, 沈晓丽, 浦晓东. 基于Sinofiler检测系统的福建汉族群体遗传多态性研究. 国际检验医学杂志, 2013, 34(21): 2835-2836+2839. |
| [1] | Zhiyong Liu, He Ren, Chong Chen, Jingjing Zhang, Xiaomeng Zhang, Yan Shi, Linyu Shi, Ying Chen, Feng Cheng, Li Jia, Man Chen, Qingwei Fan, Jiarong Zhang, Wanting Li, Mengchun Wang, Zilin Ren, Yacheng Liu, Ming Ni, Hongyu Sun, Jiangwei Yan. Actual mutational research of 19 autosomal STRs based on restricted mutation model and big data [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(10): 949-961. |
| [2] | Ming Liu, Yi Li, Yafang Yang, Yuwen Yan, Fan Liu, Caixia Li, Faming Zeng, Wenting Zhao. Human facial shape related SNP analysis in Han Chinese populations [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(7): 680-690. |
| [3] | WANG Jing, LIU Chou-Sheng, ZHANG Li-Ping, WANG Zhi-Gang, YU Fu-Qing, ZHANG Gui-Xiang, SONG Xiu-Zhu, HAN Xu, WEI Yu-Chun. Individual identification and paternity testing of bulls using microsatellite [J]. HEREDITAS, 2009, 31(3): 285-295. |
| [4] | JIA Zhen-Jun, WU Jin, LI Hui, HOU Yi-Ping, ZHANG Wei-Juan, ZHOU Xue-Ping, DENG Jian-Qiang, SHI Mei-Sen, ZHANG Ji, LI Ying-Bi. Study of Five STR Loci in A Chinese Han Population [J]. HEREDITAS, 2005, 27(3): 343-348. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||