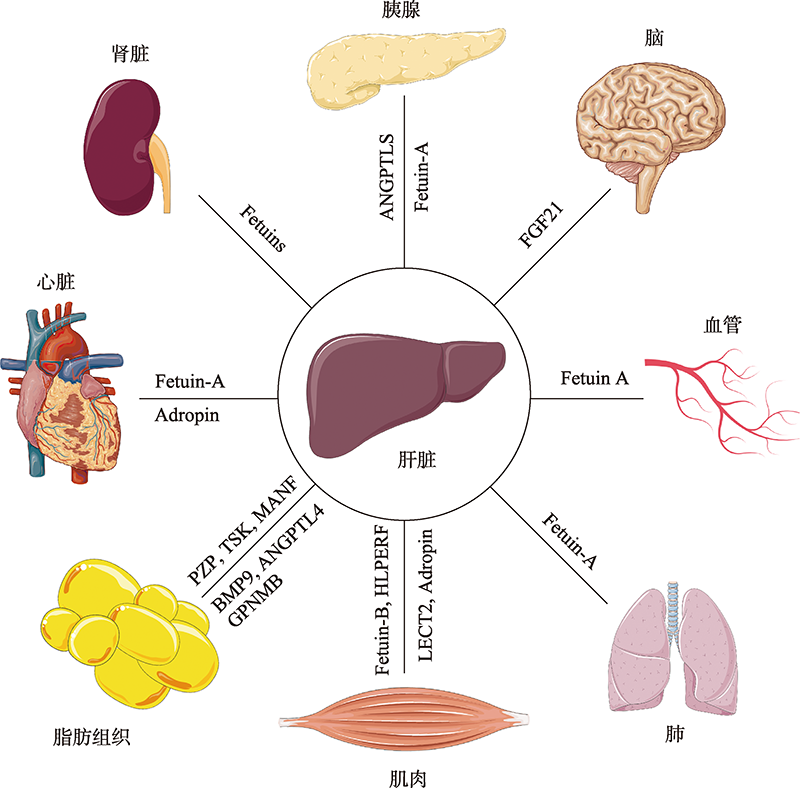
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 853-866.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-218
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Interaction between hepatokines and metabolic diseases
Jiaqi Liang( ), Chang Liu, Wenxiang Zhang, Siyu Chen(
), Chang Liu, Wenxiang Zhang, Siyu Chen( )
)
- College of Life Sciences, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 211198, China
-
Received:2022-06-27Revised:2022-09-06Online:2022-10-20Published:2022-09-20 -
Contact:Chen Siyu E-mail:3221030939@stu.cpu.edu.cn;siyuchen@cpu.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of China(31800992);the Natural Science Foundation of JiangSu(BK20180554)
Cite this article
Jiaqi Liang, Chang Liu, Wenxiang Zhang, Siyu Chen. Interaction between hepatokines and metabolic diseases[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 853-866.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Main characteristics of the hepatokines"
| 肝脏分泌因子 | 分子量大小(kDa) | 主要表达组织/器官 | 受体 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGF21 | 23 | 肝脏、胰腺和脂肪组织 | KLB、FGFR1C | [ |
| ANGPTL3 | 70 | 肝脏 | integrin αvβ3 | [ |
| ANGPTL4 | 45 | 肝脏和脂肪组织 | 未知 | |
| ANGPTL8 | 22 | 肝脏和脂肪组织 | PirB | [ |
| Vanin-1 | 70 | 肝脏、肾脏和大肠 | 未知 | [ |
| Fetuin-A | 46 | 肝脏 | TLR4、IR | [ |
| Fetuin-B | 42 | 肝脏 | 未知 | |
| GPNMB | 115 | 肝脏、皮肤和脂肪组织 | integrin α5β1、NRP-1、VEGFR | [ |
| Adropin | 5 | 肝脏和脑 | GPR19 | [ |
| Tsukushi | 40 | 肝脏、脑、眼和骨 | 未知 | |
| LECT2 | 16 | 肝脏 | Tie1、VEGFR2、MET、CD209,、CD209a | [ |
| Hepassocin | 36 | 肝脏 | LAG3 | [ |
| MANF | 18 | 肝脏、脑、唾液腺和睾丸 | NPTN | [ |
| BMP9 | 47 | 肝脏 | GRP78、ALK1、ALK2、ALK3、ALK6、BMPRII、ActRIIA、ActRIIB | [ |
| PZP | 164 | 肝脏、肺、子宫内膜和睾丸 | TGF-β | [ |
| [1] |
Saklayen MG. The global epidemic of the metabolic syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep, 2018, 20(2): 12.
doi: 10.1007/s11906-018-0812-z pmid: 29480368 |
| [2] |
Kuang H, Lin JD. Gpnmb: expanding the code for liver-fat communication. Nat Metab, 2019, 1(5): 507-508.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0069-0 pmid: 32694853 |
| [3] |
Kilkenny DM, Rocheleau JV. The FGF21 receptor signaling complex: Klothoβ, fgfr1c, and other regulatory interactions. Vitam Horm, 2016, 101: 17-58.
doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2016.02.008 pmid: 27125737 |
| [4] |
Jiang S, Qiu GH, Zhu N, Hu ZY, Liao DF, Qin L. ANGPTL3: a novel biomarker and promising therapeutic target. J Drug Target, 2019, 27(8): 876-884.
doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2019.1566342 pmid: 30615486 |
| [5] |
Chen SY, Feng MY, Zhang SY, Dong ZW, Wang YF, Zhang WX, Liu C. ANGPTL 8 mediates food-driven resetting of hepatic circadian clock in mice. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 3518.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11513-1 pmid: 31388006 |
| [6] |
Bartucci R, Salvati A, Olinga P, Boersma YL. Vanin 1: Its physiological function and role in diseases. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(16): 3891.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20163891 |
| [7] |
Sardana O, Goyal R, Bedi O. Molecular and pathobiological involvement of fetuin-A in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Inflammopharmacology, 2021, 29(4): 1061-1074.
doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00837-4 pmid: 34185201 |
| [8] |
Stefan N, Häring HU. The role of hepatokines in metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2013, 9(3): 144-152.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2012.258 pmid: 23337953 |
| [9] |
Taya M, Hammes SR. Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB) and cancer: a novel potential therapeutic target. Steroids, 2018, 133: 102-107.
doi: S0039-128X(17)30193-9 pmid: 29097143 |
| [10] |
Stein LM, Yosten GLC, Samson WK.Adropin acts in brain to inhibit water drinking: potential interaction with the orphan g protein-coupled receptor, gpr19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2016, 310(6): R476-R480.
doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00511.2015 |
| [11] |
Xie Y, Fan KW, Guan SX, Hu Y, Gao Y, Zhou WJ. Lect2: A pleiotropic and promising hepatokine, from bench to bedside. J Cell Mol Med, 2022, 26(13): 3598-3607.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17407 pmid: 35656863 |
| [12] |
Liu XH, Qi LW, Alolga RN, Liu Q. Implication of the hepatokine, fibrinogen-like protein 1 in liver diseases, metabolic disorders and cancer: the need to harness its full potential. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(1): 292-300.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66834 |
| [13] |
Yagi T, Asada R, Kanekura K, Eesmaa A, Lindahl M, Saarma M, Urano F. Neuroplastin modulates anti- inflammatory effects of manf. iScience, 2020, 23(12): 101810.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101810 |
| [14] |
Yang S, Li SH, Li XJ. Manf: a new player in the control of energy homeostasis, and beyond. Front Physiol, 2018, 9: 1725.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01725 pmid: 30555354 |
| [15] | Lin J, Jiang XX, Dong M, Liu XM, Shen QW, Huang YY, Zhang HL, Ye RC, Zhou HQ, Yan CL, Yuan SL, Wu XN, Chen L, Wang YF, He M, Tao Y, Zhang ZY, Jin WZ. Hepatokine pregnancy zone protein governs the diet- induced thermogenesis through activating brown adipose tissue. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2021, 8(21): e2101991. |
| [16] |
Jiang QQ, Liu BB, Xu KS. New insights into BMP9 signaling in liver diseases. Mol Cell Biochem, 2021, 476(10): 3591-3600.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04182-6 |
| [17] |
Kumar R, Kuligina E, Sokolenko A, Siddiqui Q, Gardi N, Gupta S, Varma AK, Hasan SK. Genetic ablation of pregnancy zone protein promotes breast cancer progression by activating TGF-β/SMAD signaling. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 185(2): 317-330.
doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05958-y |
| [18] |
Philip A, Bostedt L, Stigbrand T, O'Connor-McCourt MD. Binding of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) to pregnancy zone protein (PZP). Comparison to the TGF-beta-alpha 2-macroglobulin interaction. Eur J Biochem, 1994, 221(2): 687-693.
pmid: 7513640 |
| [19] |
Mossahebi-Mohammadi M, Quan MY, Zhang JS, Li XK. FGF signaling pathway: a key regulator of stem cell pluripotency. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 79.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00079 pmid: 32133359 |
| [20] |
Savchenko E, Teku GN, Boza-Serrano A, Russ K, Berns M, Deierborg T, Lamas NJ, Wichterle H, Rothstein J, Henderson CE, Vihinen M, Roybon L. FGF family members differentially regulate maturation and proliferation of stem cell-derived astrocytes. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 9610.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46110-1 pmid: 31270389 |
| [21] |
Wang J, Xiang B, Dolinsky VW, Kardami E, Cattini PA. Cardiac FGF-16 expression supports cardiomyocyte survival and increases resistance to doxorubicin cytotoxicity. DNA Cell Biol, 2018, 37(11): 866-877.
doi: 10.1089/dna.2018.4362 pmid: 30230915 |
| [22] |
Blitz E, Matsuda H, Guenther S, Morikawa T, Kubota Y, Zada D, Lerer-Goldshtein T, Stainier DYR, Appelbaum L. Thyroid hormones regulate goblet cell differentiation and FGF19-FGFR4 signaling. Endocrinology, 2021, 162(5): bqab047.
doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab047 |
| [23] |
Farooq M, Khan AW, Kim MS, Choi S. The role of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling in tissue repair and regeneration. Cells, 2021, 10(11): 3242.
doi: 10.3390/cells10113242 |
| [24] |
Geng LL, Lam KSL, Xu AM. The therapeutic potential of FGF21 in metabolic diseases: from bench to clinic. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2020, 16(11): 654-667.
doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0386-0 |
| [25] |
Morton GJ, Kaiyala KJ, Foster-Schubert KE, Cummings DE, Schwartz MW. Carbohydrate feeding dissociates the postprandial FGF19 response from circulating bile acid levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2014, 99(2): E241-E245.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3129 |
| [26] |
Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo GZ, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA, Gerard RD, Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab, 2005, 2(4): 217-225.
pmid: 16213224 |
| [27] |
Yoshiko Y, Wang H, Minamizaki T, Ijuin C, Yamamoto R, Suemune S, Kozai K, Tanne K, Aubin JE, Maeda N.Mineralized tissue cells are a principal source of FGF23. Bone, 2007, 40(6): 1565-1573.
pmid: 17350357 |
| [28] |
Quarles LD. Skeletal secretion of FGF-23 regulates phosphate and vitamin d metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2012, 8(5): 276-286.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.218 pmid: 22249518 |
| [29] |
Tezze C, Romanello V, Sandri M. fgf 21 as modulator of metabolism in health and disease. Front Physiol, 2019, 10: 419.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00419 pmid: 31057418 |
| [30] |
Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2000, 1492(1): 203-206.
pmid: 10858549 |
| [31] |
Markan KR, Naber MC, Ameka MK, Anderegg MD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA, Mohammadi M, Potthoff MJ. Circulating FGF 21 is liver derived and enhances glucose uptake during refeeding and overfeeding. Diabetes, 2014, 63(12): 4057-4063.
doi: 10.2337/db14-0595 |
| [32] | Xu S, Dai J, Tong Y. Research progress of FGF21 and disease treatment. Pharm Biotechnol, 2022, 29(2): 209-216. |
| 徐赛, 戴佳, 童玥. FGF21与疾病治疗的研究进展. 药物生物技术, 2022, 29(2): 209-216. | |
| [33] |
Keinicke H, Sun G, Mentzel CMJ, Fredholm M, John LM, Andersen B, Raun K, Kjaergaard M. FGF 21 regulates hepatic metabolic pathways to improve steatosis and inflammation. Endocr Connect, 2020, 9(8): 755-768.
doi: 10.1530/EC-20-0152 pmid: 32688339 |
| [34] |
Guo C, Zhao L, Li YY, Deng X, Yuan GY. Relationship between FGF21 and drug or nondrug therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(1): 55-67.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.29879 |
| [35] |
Gao Y, Zhang W, Zeng LQ, Bai H, Li J, Zhou J, Zhou GY, Fang CW, Wang F, Qin XJ. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy. Redox Biol, 2020, 36: 101635.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101635 |
| [36] |
Xu J, Stanislaus S, Chinookoswong N, Lau YY, Hager T, Patel J, Ge HF, Weiszmann J, Lu SC, Graham M, Busby J, Hecht R, Li YS, Li Y, Lindberg R, Véniant MM. Acute glucose-lowering and insulin-sensitizing action of FGF21 in insulin-resistant mouse models—association with liver and adipose tissue effects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2009, 297(5): E1105-E1114.
doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00348.2009 |
| [37] |
Wang N, Sun B, Guo HN, Jing YY, Ruan Q, Wang MJ, Mi Y, Chen H, Song L, Cui W. Association of elevated plasma FGF21 and activated FGF21 signaling in visceral white adipose tissue and improved insulin sensitivity in gestational diabetes mellitus subtype: a case-control study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12: 795520.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.795520 |
| [38] |
Schlein C, Talukdar S, Heine M, Fischer AW, Krott LM, Nilsson SK, Brenner MB, Heeren J, Scheja L. FGF 21 lowers plasma triglycerides by accelerating lipoprotein catabolism in white and brown adipose tissues. Cell Metab, 2016, 23(3): 441-453.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.01.006 pmid: 26853749 |
| [39] |
Cuevas-Ramos D, Mehta R, Aguilar-Salinas CA. Fibroblast growth factor 21 and browning of white adipose tissue. Front Physiol, 2019, 10: 37.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00037 pmid: 30804796 |
| [40] |
Owen BM, Ding XS, Morgan DA, Coate KC, Bookout AL, Rahmouni K, Kliewer SA, Mangelsdorf DJ. FGF 21 acts centrally to induce sympathetic nerve activity, energy expenditure, and weight loss. Cell Metab, 2014, 20(4): 670-677.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.07.012 pmid: 25130400 |
| [41] |
Bao LC, Yin J, Gao W, Wang Q, Yao WB, Gao XD. A long-acting FGF21 alleviates hepatic steatosis and inflamemation in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis partly through an FGF21-adiponectin-IL17A pathway. Br J Pharmacol, 2018, 175(16): 3379-3393.
doi: 10.1111/bph.14383 |
| [42] |
Carbone C, Piro G, Fassan M, Tamburrino A, Mina MM, Zanotto M, Chiao PJ, Bassi C, Scarpa A, Tortora G, Melisi D. An angiopoietin-like protein 2 autocrine signaling promotes EMT during pancreatic ductal carcinogenesis. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(15): 13822-13834.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2635 pmid: 25360865 |
| [43] |
Abu-Farha M, Sriraman D, Cherian P, AlKhairi I, Elkum N, Behbehani K, Abubaker J. Circulating ANGPTL8/betatrophin is increased in obesity and reduced after exercise training. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0147367.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147367 |
| [44] |
Chen HA, Kuo TC, Tseng CF, Ma JT, Yang ST, Yen CJ, Yang CY, Sung SY, Su JL. Angiopoietin-like protein 1 antagonizes MET receptor activity to repress sorafenib resistance and cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 2016, 64(5): 1637-1651.
doi: 10.1002/hep.28773 |
| [45] |
Conklin D, Gilbertson D, Taft DW, Maurer MF, Whitmore TE, Smith DL, Walker KM, Chen LH, Wattler S, Nehls M, Lewis KB. Identification of a mammalian angiopoietin-related protein expressed specifically in liver. Genomics, 1999, 62(3): 477-482.
doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.6041 pmid: 10644446 |
| [46] |
Kersten S. Physiological regulation of lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1841(7): 919-933.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.03.013 pmid: 24721265 |
| [47] |
Wang Y, Gusarova V, Banfi S, Gromada J, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH. Inactivation of ANGPTL3 reduces hepatic VLDL-triglyceride secretion. J Lipid Res, 2015, 56(7): 1296-1307.
doi: 10.1194/jlr.M054882 pmid: 25954050 |
| [48] |
Gusarova V, Alexa CA, Wang Y, Rafique A, Kim JH, Buckler D, Mintah IJ, Shihanian LM, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH, Xin YR, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Yancopoulos GD, Gromada J. ANGPTL 3 blockade with a human monoclonal antibody reduces plasma lipids in dyslipidemic mice and monkeys. J Lipid Res, 2015, 56(7): 1308-1317.
doi: 10.1194/jlr.M054890 pmid: 25964512 |
| [49] |
Robciuc MR, Maranghi M, Lahikainen A, Rader D, Bensadoun A, Öörni K, Metso J, Minicocci I, Ciociola E, Ceci F, Montali A, Arca M, Ehnholm C, Jauhiainen M. ANGPTL 3 deficiency is associated with increased insulin sensitivity, lipoprotein lipase activity, and decreased serum free fatty acids. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2013, 33(7): 1706-1713.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301397 pmid: 23661675 |
| [50] |
Stitziel NO, Khera AV, Wang X, Bierhals AJ, Vourakis AC, Sperry AE, Natarajan P, Klarin D, Emdin CA, Zekavat SM, Nomura A, Erdmann J, Schunkert H, Samani NJ, Kraus WE, Shah SH, Yu B, Boerwinkle E, Rader DJ, Gupta N, Frossard PM, Rasheed A, Danesh J, Lander ES, Gabriel S, Saleheen D, Musunuru K, Kathiresan S, PROMIS and Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium Investigators. ANGPTL3 deficiency and protection against coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2017, 69(16): 2054-2063.
doi: S0735-1097(17)30703-9 pmid: 28385496 |
| [51] |
Dewey FE, Gusarova V, Dunbar RL, O'Dushlaine C, Schurmann C, Gottesman O, McCarthy S, Van Hout CV, Bruse S, Dansky HM, Leader JB, Murray MF, Ritchie MD, Kirchner HL, Habegger L, Lopez A, Penn J, Zhao A, Shao WP, Stahl N, Murphy AJ, Hamon S, Bouzelmat A, Zhang R, Shumel B, Pordy R, Gipe D, Herman GA, Sheu WHH, Lee IT, Liang KW, Guo XQ, Rotter JI, Chen YDI, Kraus WE, Shah SH, Damrauer S, Small A, Rader DJ, Wulff AB, Nordestgaard BG, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, van den Hoek AM, Princen HMG, Ledbetter DH, Carey DJ, Overton JD, Reid JG, Sasiela WJ, Banerjee P, Shuldiner AR, Borecki IB, Teslovich TM, Yancopoulos GD, Mellis SJ, Gromada J, Baras A. Genetic and pharmacologic inactivation of ANGPTL3 and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(3): 211-221.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1612790 |
| [52] |
Raal FJ, Rosenson RS, Reeskamp LF, Hovingh GK, Kastelein JJP, Rubba P, Ali S, Banerjee P, Chan KC, Gipe DA, Khilla N, Pordy R, Weinreich DM, Yancopoulos GD, Zhang Y, Gaudet D, Investigators EH. Evinacumab for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(8): 711-720.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004215 |
| [53] |
McQueen AE, Kanamaluru D, Yan K, Gray NE, Wu L, Li ML, Chang A, Hasan A, Stifler D, Koliwad SK, Wang JC. The c-terminal fibrinogen-like domain of angiopoietin-like 4 stimulates adipose tissue lipolysis and promotes energy expenditure. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(39): 16122-16134.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.803973 pmid: 28842503 |
| [54] |
Zhu PC, Goh YY, Chin HFA, Kersten S, Tan NS. Angiopoietin-like 4: a decade of research. Biosci Rep, 2012, 32(3): 211-219.
doi: 10.1042/BSR20110102 |
| [55] |
Robal T, Larsson M, Martin M, Olivecrona G, Lookene A. Fatty acids bind tightly to the N-terminal domain of angiopoietin-like protein 4 and modulate its interaction with lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(35): 29739-29752.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.303529 pmid: 22773878 |
| [56] |
Mandard S, Zandbergen F, van Straten E, Wahli W, Kuipers F, Müller M, Kersten S. The fasting-induced adipose factor/angiopoietin-like protein 4 is physically associated with lipoproteins and governs plasma lipid levels and adiposity. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(2): 934-944.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506519200 pmid: 16272564 |
| [57] |
Xu AM, Lam MC, Chan KW, Wang Y, Zhang JL, Hoo RLC, Xu JY, Chen BY, Chow WS, Tso AWK, Lam KSL. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 decreases blood glucose and improves glucose tolerance but induces hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(17): 6086-6091.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408452102 |
| [58] |
Singh AK, Aryal B, Chaube B, Rotllan N, Varela L, Horvath TL, Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C. Brown adipose tissue derived ANGPTL4 controls glucose and lipid metabolism and regulates thermogenesis. Mol Metab, 2018, 11: 59-69.
doi: S2212-8778(18)30227-8 pmid: 29627378 |
| [59] |
Aryal B, Singh AK, Zhang XB, Varela L, Rotllan N, Goedeke L, Chaube B, Camporez JP, Vatner DF, Horvath TL, Shulman GI, Suárez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C. Absence of ANGPTL4 in adipose tissue improves glucose tolerance and attenuates atherogenesis. JCI Insight, 2018, 3(6): e97918.
doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.97918 |
| [60] |
Li YC, Teng CB. Angiopoietin-like proteins 3, 4 and 8: Regulating lipid metabolism and providing new hope for metabolic syndrome. J Drug Target, 2014, 22(8): 679-687.
doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2014.928715 pmid: 24960069 |
| [61] |
Vatner DF, Goedeke L, Camporez JPG, Lyu K, Nasiri AR, Zhang DY, Bhanot S, Murray SF, Still CD, Gerhard GS, Shulman GI, Samuel VT. ANGPTL 8 antisense oligonucleotide improves adipose lipid metabolism and prevents diet-induced nafld and hepatic insulin resistance in rodents. Diabetologia, 2018, 61(6): 1435-1446.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4579-1 pmid: 29497783 |
| [62] |
Zheng JK, Umikawa M, Cui CH, Li JY, Chen XL, Zhang CZ, Huynh H, Kang XL, Silvany R, Wan X, Ye JX, CantóAP, Chen SH, Wang HY, Ward ES, Zhang CC. Inhibitory receptors bind ANGPTLs and support blood stem cells and leukaemia development. Nature, 2012, 485(7400): 656-660.
doi: 10.1038/nature11095 |
| [63] |
Kersten S. New insights into angiopoietin-like proteins in lipid metabolism and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr Opin Lipidol, 2019, 30(3): 205-211.
doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000600 pmid: 30893111 |
| [64] |
Catalano-Iniesta L, Sánchez Robledo V, Iglesias-Osma MC, Galán Albiñana A, Carrero S, Blanco EJ, Carretero- Hernández M, Carretero J, García-Barrado MJ. Evidences for expression and location of ANGPTL8 in human adipose tissue. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(2): 512.
doi: 10.3390/jcm9020512 |
| [65] |
Espes D, Lau J, Carlsson PO. Increased circulating levels of betatrophin in individuals with long-standing type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia, 2014, 57(1): 50-53.
pmid: 24078058 |
| [66] |
Zhang R. Lipasin, a novel nutritionally-regulated liver- enriched factor that regulates serum triglyceride levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 424(4): 786-792.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.038 |
| [67] |
Dang FB, Wu R, Wang PF, Wu YT, Azam MS, Xu Q, Chen YQ, Liu Y. Fasting and feeding signals control the oscillatory expression of ANGPTL8 to modulate lipid metabolism. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 36926.
doi: 10.1038/srep36926 pmid: 27845381 |
| [68] |
Rommelaere S, Millet V, Gensollen T, Bourges C, Eeckhoute J, Hennuyer N, Baugé E, Chasson L, Cacciatore I, Staels B, Pitari G, Galland F, Naquet P. Pparalpha regulates the production of serum vanin-1 by liver. FEBS Lett, 2013, 587(22): 3742-3748.
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.09.046 pmid: 24140347 |
| [69] |
Chen SY, Zhang WX, Tang CQ, Tang XL, Liu L, Liu C. Vanin-1 is a key activator for hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetes, 2014, 63(6): 2073-2085.
doi: 10.2337/db13-0788 pmid: 24550194 |
| [70] | Chen SY, Zhang WX, Sun C, Song MM, Liu S, Xu MY, Zhang XJ, Liu L, Liu C. Systemic nanoparticle-mediated delivery of pantetheinase vanin-1 regulates lipolysis and adiposity in abdominal white adipose tissue. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2021, 8(12): e2101789. |
| [71] | van Diepen JA, Jansen PA, Ballak DB, Hijmans A, Hooiveld GJ, Rommelaere S, Galland F, Naquet P, Rutjes FPJT, Mensink RP, Schrauwen P, Tack CJ, Netea MG, Kersten S, Schalkwijk J, Stienstra R. PPAR-alpha dependent regulation of vanin-1 mediates hepatic lipid metabolism. J Hepatol, 2014, 61(2): 366-372. |
| [72] |
Ferreira DW, Goedken MJ, Rommelaere S, Chasson L, Galland F, Naquet P, Manautou JE. Enhanced hepatotoxicity by acetaminophen in vanin-1 knockout mice is associated with deficient proliferative and immune responses. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016, 1862(4): 662-669.
doi: S0925-4439(16)30027-8 pmid: 26850476 |
| [73] |
Icer MA, Yıldıran H. Effects of fetuin-A with diverse functions and multiple mechanisms on human health. Clin Biochem, 2021, 88: 1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.11.004 pmid: 33245873 |
| [74] |
Olivier E, Soury E, Ruminy P, Husson A, Parmentier F, Daveau M, Salier JP. Fetuin-B, a second member of the fetuin family in mammals. Biochem J, 2000, 350(Pt 2): 589-597.
doi: 10.1042/bj3500589 |
| [75] |
Brown WM, Saunders NR, Møllgård K, Dziegielewska KM. Fetuin——an old friend revisited. Bioessays, 1992, 14(11): 749-755.
pmid: 1285422 |
| [76] |
Icer MA, Yıldıran H. Effects of nutritional status on serum fetuin-A level. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2020, 60(11): 1938-1946.
doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1631751 pmid: 31232084 |
| [77] | Chung HS, Lee HJ, Hwang SY, Choi JH, Yoo HJ, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Choi DS, Baik SH, Choi KM. Relationship of circulating fetuin-A levels with body size and metabolic phenotypes. Int J Endocrinol, 2018, 2018: 7918714. |
| [78] |
Sujana C, Huth C, Zierer A, Meesters S, Sudduth-Klinger J, Koenig W, Herder C, Peters A, Thorand B. Association of fetuin-A with incident type 2 diabetes: results from the monica/kora augsburg study and a systematic meta- analysis. Eur J Endocrinol, 2018, 178(4): 389-398.
doi: 10.1530/EJE-17-1053 |
| [79] |
Guo VY, Cao B, Cai CY, Cheng KKY, Cheung BMY. Fetuin-A levels and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol, 2018, 55(1): 87-98.
doi: 10.1007/s00592-017-1068-9 pmid: 29127490 |
| [80] |
Trepanowski JF, Mey J, Varady KA. Fetuin-A: a novel link between obesity and related complications. Int J Obes (Lond), 2015, 39(5): 734-741.
doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.203 |
| [81] |
Mathews ST, Singh GP, Ranalletta M, Cintron VJ, Qiang XL, Goustin AS, Jen KLC, Charron MJ, Jahnen-Dechent W, Grunberger G. Improved insulin sensitivity and resistance to weight gain in mice null for the ahsg gene. Diabetes, 2002, 51(8): 2450-2458.
doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.8.2450 pmid: 12145157 |
| [82] |
Shi J, Fan JG, Su Q, Yang Z. Cytokines and abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2019, 10: 703.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00703 |
| [83] |
Li LN, Spranger L, Stobäus N, Beer F, Decker AM, Wernicke C, Brachs S, Brachs M, Spranger J, Mai K. Fetuin-B, a potential link of liver-adipose tissue cross talk during diet-induced weight loss-weight maintenance. Nutr Diabetes, 2021, 11(1): 31.
doi: 10.1038/s41387-021-00174-z pmid: 34611132 |
| [84] |
Meex RC, Hoy AJ, Morris A, Brown RD, Lo JCY, Burke M, Goode RJA, Kingwell BA, Kraakman MJ, Febbraio MA, Greve JW, Rensen SS, Molloy MP, Lancaster GI, Bruce CR, Watt MJ. Fetuin B is a secreted hepatocyte factor linking steatosis to impaired glucose metabolism. Cell Metab, 2015, 22(6): 1078-1089.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.09.023 pmid: 26603189 |
| [85] |
Weterman MA, Ajubi N, van Dinter IM, Degen WG, van Muijen GN, Ruitter DJ, Bloemers HP. Nmb, a novel gene, is expressed in low-metastatic human melanoma cell lines and xenografts. Int J Cancer, 1995, 60(1): 73-81.
pmid: 7814155 |
| [86] |
van der Lienden MJC, Gaspar P, Boot R, Aerts JMFG, van Eijk M. Glycoprotein non-metastatic protein B: an emerging biomarker for lysosomal dysfunction in macrophages. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 20(1): 66.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20010066 |
| [87] |
Abdelmagid SM, Barbe MF, Rico MC, Salihoglu S, Arango-Hisijara I, Selim AH, Anderson MG, Owen TA, Popoff SN, Safadi FF. Osteoactivin, an anabolic factor that regulates osteoblast differentiation and function. Exp Cell Res, 2008, 314(13): 2334-2351.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.02.006 pmid: 18555216 |
| [88] |
Rose AAN, Annis MG, Dong ZF, Pepin F, Hallett M, Park M, Siegel PM. ADAM10 releases a soluble form of the gpnmb/osteoactivin extracellular domain with angiogenic properties. PLoS One, 2010, 5(8): e12093.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012093 |
| [89] |
Ripoll VM, Irvine KM, Ravasi T, Sweet MJ, Hume DA. Gpnmb is induced in macrophages by IFN-gamma and lipopolysaccharide and acts as a feedback regulator of proinflammatory responses. J Immunol, 2007, 178(10): 6557-6566.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.10.6557 pmid: 17475886 |
| [90] |
Gong XM, Li YF, Luo J, Wang JQ, Wei J, Wang JQ, Xiao T, Xie C, Hong J, Ning G, Shi XJ, Li BL, Qi W, Song BL. Gpnmb secreted from liver promotes lipogenesis in white adipose tissue and aggravates obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Metab, 2019, 1(5): 570-583.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0065-4 |
| [91] |
Katayama A, Nakatsuka A, Eguchi J, Murakami K, Teshigawara S, Kanzaki M, Nunoue T, Hida K, Wada N, Yasunaka T, Ikeda F, Takaki A, Yamamoto K, Kiyonari H, Makino H, Wada J. Beneficial impact of GPNMB and its significance as a biomarker in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 16920.
doi: 10.1038/srep16920 pmid: 26581806 |
| [92] |
Nickl B, Qadri F, Bader M. Anti-inflammatory role of GPNMB in adipose tissue of mice. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 19614.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99090-6 pmid: 34608215 |
| [93] |
Kumar KG, Trevaskis JL, Lam DD, Sutton GM, Koza RA, Chouljenko VN, Kousoulas KG, Rogers PM, Kesterson RA, Thearle M, Ferrante AW, Mynatt RL, Burris TP, Dong JZ, Halem HA, Culler MD, Heisler LK, Stephens JM, Butler AA. Identification of adropin as a secreted factor linking dietary macronutrient intake with energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Cell Metab, 2008, 8(6): 468-481.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.10.011 pmid: 19041763 |
| [94] |
Butler AA, Tam CS, Stanhope KL, Wolfe BM, Ali MR, O'Keeffe M, St-Onge MP, Ravussin E, Havel PJ. Low circulating adropin concentrations with obesity and aging correlate with risk factors for metabolic disease and increase after gastric bypass surgery in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 97(10): 3783-3791.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2194 pmid: 22872690 |
| [95] |
Chen S, Zeng K, Liu QC, Guo Z, Zhang S, Chen XR, Lin JH, Wen JP, Zhao CF, Lin XH, Gao F. Adropin deficiency worsens HFD-induced metabolic defects. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(8): e3008.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.362 |
| [96] |
Ganesh Kumar K, Zhang JY, Gao S, Rossi J, McGuinness OP, Halem HH, Culler MD, Mynatt RL, Butler AA. Adropin deficiency is associated with increased adiposity and insulin resistance. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2012, 20(7): 1394-1402.
doi: 10.1038/oby.2012.31 |
| [97] |
Xiong XL, Wang QY, Wang S, Zhang JL, Liu TY, Guo L, Yu YH, Lin JD. Mapping the molecular signatures of diet-induced NASH and its regulation by the hepatokine tsukushi. Mol Metab, 2019, 20: 128-137.
doi: S2212-8778(18)31116-5 pmid: 30595550 |
| [98] |
Wang QY, Sharma VP, Shen H, Xiao YY, Zhu Q, Xiong XL, Guo L, Jiang L, Ohta K, Li SM, Shi HF, Rui LY, Lin JD. The hepatokine tsukushi gates energy expenditure via brown fat sympathetic innervation. Nat Metab, 2019, 1(2): 251-260.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-018-0020-9 pmid: 31535079 |
| [99] |
Mouchiroud M, Camiré É, Aldow M, Caron A, Jubinville É, Turcotte L, Kaci I, Beaulieu MJ, Roy C, Labbé SM, Varin TV, Gélinas Y, Lamothe J, Trottier J, Mitchell PL, Guénard F, Festuccia WT, Joubert P, Rose CF, Karvellas CJ, Barbier O, Morissette MC, Marette A, Laplante M. The hepatokine tsukushi is released in response to NAFLD and impacts cholesterol homeostasis. JCI Insight, 2019, 4(15): e129492.
doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.129492 |
| [100] |
Yamagoe S, Yamakawa Y, Matsuo Y, Minowada J, Mizuno S, Suzuki K.Purification and primary amino acid sequence of a novel neutrophil chemotactic factor LECT2. Immunol Lett, 1996, 52(1): 9-13.
pmid: 8877413 |
| [101] |
Chikamoto K, Misu H, Takayama H, Kikuchi A, Ishii KA, Lan F, Takata N, Tajima-Shirasaki N, Takeshita Y, Tsugane H, Kaneko S, Matsugo S, Takamura T. Rapid response of the steatosis-sensing hepatokine LECT2 during diet-induced weight cycling in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 478(3): 1310-1316.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.117 |
| [102] |
Lan F, Misu H, Chikamoto K, Takayama H, Kikuchi A, Mohri K, Takata N, Hayashi H, Matsuzawa-Nagata N, Takeshita Y, Noda H, Matsumoto Y, Ota T, Nagano T, Nakagen M, Miyamoto KI, Takatsuki K, Seo T, Iwayama K, Tokuyama K, Matsugo S, Tang H, Saito Y, Yamagoe S, Kaneko S, Takamura T. LECT 2 functions as a hepatokine that links obesity to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Diabetes, 2014, 63(5): 1649-1664.
doi: 10.2337/db13-0728 pmid: 24478397 |
| [103] |
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang LF, Görgün CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature, 2002, 420(6913): 333-336.
doi: 10.1038/nature01137 |
| [104] |
Gao M, Zhan YQ, Yu M, Ge CH, Li CY, Zhang JH, Wang XH, Ge ZQ, Yang XM. Hepassocin activates the EGFR/ERK cascade and induces proliferation of l02 cells through the Src-dependent pathway. Cell Signal, 2014, 26(10): 2161-2166.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.04.013 pmid: 24768768 |
| [105] |
Wu HT, Ou HY, Hung HC, Su YC, Lu FH, Wu JS, Yang YC, Wu CL, Chang CJ. A novel hepatokine, HFREP1, plays a crucial role in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia, 2016, 59(8): 1732-1742.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3991-7 pmid: 27221093 |
| [106] |
Cheng KP, Ou HY, Hung HC, Li CH, Fan KC, Wu JS, Wu HT, Chang CJ. Unsaturated fatty acids increase the expression of hepassocin through a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-dependent pathway in HepG2 cells. Lipids, 2018, 53(9): 863-869.
doi: 10.1002/lipd.12099 |
| [107] |
Jung TW, Chung YH, Kim HC, Abd El-Aty AM, Jeong JH. Hyperlipidemia-induced hepassocin in the liver contributes to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2018, 470: 26-33.
doi: S0303-7207(17)30551-8 pmid: 29111387 |
| [108] |
Glembotski CC, Thuerauf DJ, Huang CQ, Vekich JA, Gottlieb RA, Doroudgar S. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor protects the heart from ischemic damage and is selectively secreted upon sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium depletion. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(31): 25893-25904.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.356345 pmid: 22637475 |
| [109] |
Sousa-Victor P, Neves J, Cedron-Craft W, Ventura PB, Liao CY, Riley RR, Soifer I, van Bruggen N, Kolumam GA, Villeda SA, Lamba DA, Jasper H. MANF regulates metabolic and immune homeostasis in ageing and protects against liver damage. Nat Metab, 2019, 1(2): 276-290.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-018-0023-6 pmid: 31489403 |
| [110] |
Wu T, Liu QH, Li YP, Li H, Chen L, Yang XP, Tang Q, Pu SY, Kuang JY, Li R, Huang Y, Zhang JH, Zhang ZJ, Zhou J, Huang CY, Zhang GR, Zhao YN, Zou M, Jiang W, Mo L, He JH. Feeding-induced hepatokine, MANF, ameliorates diet-induced obesity by promoting adipose browning via p38 mapk pathway. J Exp Med, 2021, 218(6): e20201203.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20201203 |
| [111] |
Jensen GS, Leon-Palmer NE, Townsend KL. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in the central regulation of energy balance and adult neural plasticity. Metabolism, 2021, 123: 154837.
doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154837 |
| [112] |
David L, Mallet C, Keramidas M, Lamandé N, Gasc JM, Dupuis-Girod S, Plauchu H, Feige JJ, Bailly S. Bone morphogenetic protein-9 is a circulating vascular quiescence factor. Circ Res, 2008, 102(8): 914-922.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.165530 pmid: 18309101 |
| [113] |
Majumdar MK, Wang E, Morris EA.BMP-2 and BMP-9 promotes chondrogenic differentiation of human multipotential mesenchymal cells and overcomes the inhibitory effect of Il-1. J Cell Physiol, 2001, 189(3): 275-284.
pmid: 11748585 |
| [114] |
Um JH, Park SY, Hur JH, Lee HY, Jeong KH, Cho Y, Lee SH, Yoon SM, Choe S, Choi CS. Bone morphogenic protein 9 is a novel thermogenic hepatokine secreted in response to cold exposure. Metabolism, 2022, 129: 155139.
doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155139 |
| [115] |
Ekelund L, Laurell CB. The pregnancy zone protein response during gestation: a metabolic challenge. Scand J Clin Lab Invest, 1994, 54(8): 623-629.
doi: 10.3109/00365519409087542 |
| [116] |
Kubes P, Jenne C. Immune responses in the liver. Annu Rev Immunol, 2018, 36: 247-277.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052415 pmid: 29328785 |
| [117] |
Adeva-Andany MM, Pérez-Felpete N, Fernández-Fernández C, Donapetry-García C, Pazos-García C. Liver glucose metabolism in humans. Biosci Rep, 2016, 36(6): e00416.
doi: 10.1042/BSR20160385 |
| [118] |
Graham MJ, Lee RG, Brandt TA, Tai LJ, Fu WX, Peralta R, Yu R, Hurh E, Paz E, McEvoy BW, Baker BF, Pham NC, Digenio A, Hughes SG, Geary RS, Witztum JL, Crooke RM, Tsimikas S. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of ANGPTL3 antisense oligonucleotides. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(3): 222-232.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1701329 |
| [119] |
Gaich G, Chien JY, Fu HD, Glass LC, Deeg MA, Holland WL, Kharitonenkov A, Bumol T, Schilske HK, Moller DE. The effects of ly2405319, an FGF21 analog, in obese human subjects with type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab, 2013, 18(3): 333-340.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.08.005 pmid: 24011069 |
| [1] | DING Hui, YUE Li-Jie, YANG Chun-Lan. Research progress in hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltrans-ferase [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(8): 948-954. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||