Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 881-898.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-238
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
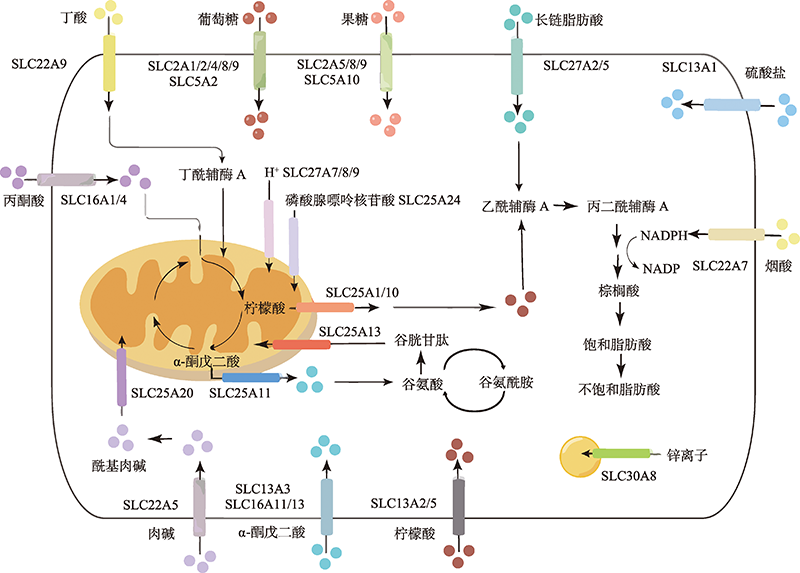
Progress of solute carrier SLC family in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Zhiquan Tang( ), Li Shi, Jing Xiong(
), Li Shi, Jing Xiong( )
)
- School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
-
Received:2022-07-16Revised:2022-09-22Online:2022-10-20Published:2022-09-30 -
Contact:Xiong Jing E-mail:1350312679@qq.com;jxiong@cpu.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(82070883);the National Natural Science Foundation of China(82273982);the National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province(BK20221525);and the Scientific Research Foundation for High-level Faculty, China Pharmaceutical University
Cite this article
Zhiquan Tang, Li Shi, Jing Xiong. Progress of solute carrier SLC family in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 881-898.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
The cellular localization, physiological functions and expression of the SLC family members related to NAFLD"
| 基因名称 | 别称 | 定位 | 生理功能 | 表达情况 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slc2a1 | Glut1 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外葡萄糖进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc2a2 | Glut2 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外葡萄糖进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc2a4 | Glut4 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外葡萄糖进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc2a5 | Glut5 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外果糖进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc2a8 | Glut8 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外葡萄糖和果糖进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc2a9 | Glut9/Uratv1 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外尿酸、葡萄糖和果糖进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc5a2 | Sglt2 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外葡萄糖进入细胞内 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc5a10 | Sglt5 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外果糖进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc13a1 | Nas1 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外硫酸盐进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc13a2 | Nadc1 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外柠檬酸盐进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc13a3 | Nadc3 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外α-酮戊二酸盐进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc13a5 | Nact | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外琥珀酸进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc16a1 | Mct1 | 细胞膜 | 促进细胞内单羧酸盐外排 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc16a4 | Mct4 | 细胞膜 | 转运细胞膜外单羧酸盐进入细胞内 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc16a10 | Mct10 | 细胞膜 | 促进细胞内芳香族氨基酸外排 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc16a11 | Mct11 | 内质网 细胞膜 | 转运单羧酸盐进出细胞 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc16a13 | Mct13 | 细胞膜 | 转运乳酸进入细胞内 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc22a5 | Octn2 | 细胞膜 | 转运肉碱进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc22a7 | Oat2 | 细胞膜 | 转运cGMP、烟酸和烟酰胺进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc22a9 | Oat4 | 细胞膜 | 转运丁酸进入细胞内 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc22a12 | Oat4l/Urat1 | 细胞膜 | 转运尿酸盐进入细胞内 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc25a1 | Ctp | 线粒体 | 促进柠檬酸盐从线粒体转运到细胞浆 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc25a7 | Ucp1 | 线粒体 | 促进长链脂肪酸从线粒体内膜到外膜的转移及质子从线粒体外膜到内膜的转移 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc25a8 | Ucp2 | 线粒体 | 同Ucp1 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc25a9 | Ucp3 | 线粒体 | 同Ucp1 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc25a10 | Dic | 线粒体 | 促进柠檬酸盐、琥珀酸盐从线粒体转运到细胞浆 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc25a11 | Ogc | 线粒体 | 促进α-酮戊二酸盐从线粒体转运到细胞浆及谷胱甘肽从细胞浆转运到线粒体 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc25a13 | Agc2 | 线粒体 | 促进天冬氨酸从线粒体转运到细胞浆及谷胱甘肽从细胞浆转运到线粒体 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc25a20 | Cac | 线粒体 | 促进游离肉碱从线粒体转运到细胞浆及酰基肉碱从细胞浆转运到线粒体 | ↓ | [ |
| Slc25a24 | Apc1 | 线粒体 | 促进线粒体内膜上磷酸盐和核苷酸的转运 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc27a2 | Fatp2 | 细胞膜 | 转运长链脂肪酸进入细胞内 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc27a5 | Fatp5 | 细胞膜 | 转运长链脂肪酸进入细胞内 | ↑ | [ |
| Slc30a8 | Znt8 | 细胞膜 | 促进胰岛素分泌颗粒膜上锌离子外排 | ↓ | [ |
Table 2
Natural products or drugs partially mediated by SLC for the treatment of NAFLD"
| 靶点 | 药物 | 作用 | 表型 | 机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC2A2 | 丁酸盐 GW501516 瑞舒伐他汀 | ↑ | 减轻肝脏炎症和脂肪变性 | 抑制Toll样受体和NF-κB激活 | [ |
| 减少肝细胞肿胀和炎细胞浸润 | 激活PPARδ | [ | |||
| 减轻肝脏脂肪变性 | 抑制HMG-CoA还原酶 | [ | |||
| SLC2A4 | 乳酸 | ↑ | 改善胰岛素抵抗 | 激活GPR81 | [ |
| 淫羊藿苷 | 减少脂质积累和细胞凋亡 | 激活AMPKα1-PGC-1α | [ | ||
| 二甲双胍 | 降低肝脏氧化应激和体重 | [ | |||
| 硝酸芬替康唑 | 抑制肝脏炎症反应 | [ | |||
| SLC2A5 | 洋甘菊提取物 | ↑ | 减轻肝脏脂肪变性 | 抑制CHREBP | [ |
| SLC5A2 | 恩格列净 | ↓ | 降低血糖和肝脏脂肪含量 | 抑制葡萄糖重吸收 | [ |
| SLC13A5 | PF-06649298 | ↑ | 降低血糖和肝脏脂肪含量 | 抑制转运体活性 | [ |
| 姜黄素 | 减少肝脏脂肪累积和氧化应激 | 抑制促炎巨噬细胞活化 | [ | ||
| SLC22A5 | L-肉碱 | ↑ | 降低肝脏脂肪含量和炎症损伤 | 促进脂肪酸氧化 | [ |
| SLC22A7 | PF-06835919 | ↑ | 降低肝脏脂肪含量和体重 | 抑制己糖激酶 | [ |
| SLC25A7 | Linifanib | ↑ | 减轻肝脏氧化应激和炎症 | 抑制STAT3 | [ |
| SLC54A1 | MSDC-0602K | ↑ | 减轻肝脏炎症 | 增加胰岛素敏感性 | [ |
| [1] |
Samson SL, Garber AJ. Metabolic syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am, 2014, 43(1): 1-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.09.009 |
| [2] |
Lemieux I, Després JP. Metabolic syndrome: past, present and future. Nutrients, 2020, 12(11): 3501.
doi: 10.3390/nu12113501 |
| [3] |
Povsic M, Wong OY, Perry R, Bottomley J. A structured literature review of the epidemiology and disease burden of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Adv Ther, 2019, 36(7): 1574-1594.
doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-00960-3 pmid: 31065991 |
| [4] |
Zhou JH, Zhou F, Wang WX, Zhang XJ, Ji YX, Zhang P, She ZG, Zhu LH, Cai JJ, Li HL.Epidemiological features of NAFLD from 1999 to 2018 in China. Hepatology, 2020, 71(5): 1851-1864.
doi: 10.1002/hep.31150 pmid: 32012320 |
| [5] |
Mundi MS, Velapati S, Patel J, Kellogg TA, Abu Dayyeh BK, Hurt RT. Evolution of NAFLD and its management. Nutr Clin Pract, 2020, 35(1): 72-84.
doi: 10.1002/ncp.10449 pmid: 31840865 |
| [6] |
Sonveaux P, Maechler P, Martinou JC. Channels and transporters in cell metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016, 1863(10): 2359-2361.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.06.001 pmid: 27263487 |
| [7] |
Rieg T, Vallon V. Development of SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetologia, 2018, 61(10): 2079-2086.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4654-7 pmid: 30132033 |
| [8] |
Sivaprakasam S, Bhutia YD, Yang SP, Ganapathy V. Short-chain fatty acid transporters: role in colonic homeostasis. Compr Physiol, 2017, 8(1): 299-314.
doi: 10.1002/cphy.c170014 pmid: 29357130 |
| [9] |
Zhang Y, Zhang YP, Sun K, Meng ZY, Chen LG. The SLC transporter in nutrient and metabolic sensing, regulation, and drug development. J Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 11(1): 1-13.
doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy052 pmid: 30239845 |
| [10] | Chitturi S, Wong VWS, Chan WK, Wong GLH, Wong SKH, Sollano J, Ni YH, Liu CJ, Lin YC, Lesmana LA, Kim SU, Hashimoto E, Hamaguchi M, Goh KL, Fan JG, Duseja A, Dan YY, Chawla Y, Farrell G, Chan HLY. The Asia-Pacific working party on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease guidelines 2017-Part 2: Management and special groups. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33(1): 86-98. |
| [11] |
Chadt A, Al-Hasani H. Glucose transporters in adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle in metabolic health and disease. Pflugers Arch, 2020, 472(9): 1273-1298.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02417-x |
| [12] |
Vallon V, Platt KA, Cunard R, Schroth J, Whaley J, Thomson SC, Koepsell H, Rieg T. SGLT2 mediates glucose reabsorption in the early proximal tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011, 22(1): 104-112.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010030246 pmid: 20616166 |
| [13] |
Olson AL, Pessin JE. Structure, function, and regulation of the mammalian facilitative glucose transporter gene family. Annu Rev Nutr, 1996, 16: 235-256.
pmid: 8839927 |
| [14] |
Heilig CW, Saunders T, Brosius FC, Moley K, Heilig K, Baggs R, Guo LR, Conner D. Glucose transporter-1- deficient mice exhibit impaired development and deformities that are similar to diabetic embryopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(26): 15613-15618.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2536196100 |
| [15] |
Vazquez-Chantada M, Gonzalez-Lahera A, Martinez- Arranz I, Garcia-Monzon C, Regueiro MM, Garcia- Rodriguez JL, Schlangen KA, Mendibil I, Rodriguez- Ezpeleta N, Lozano JJ, Banasik K, Justesen JM, Joergensen T, Witte DR, Lauritzen T, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Veyrie N, Clement K, Tordjman J, Tran A, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Buque X, Aspichueta P, Echevarria-Uraga JJ, Martin-Duce A, Caballeria J, Gual P, Castro A, Mato JM, Martinez-Chantar ML, Aransay AM. Solute carrier family 2 member 1 is involved in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology, 2013, 57(2): 505-514.
doi: 10.1002/hep.26052 pmid: 22961556 |
| [16] |
Uldry M, Ibberson M, Hosokawa M, Thorens B. GLUT2 is a high affinity glucosamine transporter. FEBS Lett, 2002, 524(1-3): 199-203.
pmid: 12135767 |
| [17] |
Su RC, Lad A, Breidenbach JD, Blomquist TM, Gunning WT, Dube P, Kleinhenz AL, Malhotra D, Haller ST, Kennedy DJ. Hyperglycemia induces key genetic and phenotypic changes in human liver epithelial HepG2 cells which parallel the Leprdb/J mouse model of non- alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). PLoS One, 2019, 14(12): e0225604.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225604 |
| [18] |
Wallberg-Henriksson H, Zierath JR. GLUT4: a key player regulating glucose homeostasis? Insights from transgenic and knockout mice (review). Mol Membr Biol, 2001, 18(3): 205-211.
pmid: 11681787 |
| [19] |
Bryant NJ, Gould GW. Insulin stimulated GLUT4 translocation—Size is not everything! Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2020, 65: 28-34.
doi: S0955-0674(20)30029-6 pmid: 32182545 |
| [20] |
Preitner F, Bonny O, Laverrière A, Rotman S, Firsov D, Da Costa A, Metref S, Thorens B. Glut9 is a major regulator of urate homeostasis and its genetic inactivation induces hyperuricosuria and urate nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(36): 15501-15506.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904411106 |
| [21] |
Xie D, Zhao HR, Lu JM, He FR, Liu WD, Yu W, Wang Q, Hisatome I, Yamamoto T, Koyama H, Cheng JD. High uric acid induces liver fat accumulation via ROS/JNK/AP-1 signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2021, 320(6): E1032-E1043.
doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00518.2020 |
| [22] |
Soret PA, Magusto J, Housset C, Gautheron J. In vitro and in vivo models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a critical appraisal. J Clin Med, 2020, 10(1): 36.
doi: 10.3390/jcm10010036 |
| [23] |
Shiba K, Tsuchiya K, Komiya C, Miyachi Y, Mori K, Shimazu N, Yamaguchi S, Ogasawara N, Katoh M, Itoh M, Suganami T, Ogawa Y. Canagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, attenuates the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in a mouse model of human NASH. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 2362.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19658-7 pmid: 29402900 |
| [24] |
Han T, Fan YJ, Gao J, Fatima M, Zhang YL, Ding YM, Bai L, Wang CX. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin depressed adiposity and ameliorated hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet induced obese mice. Adipocyte, 2021, 10(1): 446-455.
doi: 10.1080/21623945.2021.1979277 pmid: 34550043 |
| [25] |
Meng ZY, Liu XH, Li T, Fang T, Cheng Y, Han LP, Sun B, Chen LM. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin negatively regulates IL-17/IL-23 axis-mediated inflammatory responses in T2DM with NAFLD via the AMPK/mTOR/ autophagy pathway. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 94: 107492.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107492 |
| [26] |
Androutsakos T, Nasiri-Ansari N, Bakasis AD, Kyrou I, Efstathopoulos E, Randeva HS, Kassi E. SGLT-2 inhibitors in NAFLD: expanding their role beyond diabetes and cardioprotection. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(6): 3107.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23063107 |
| [27] |
Lim JS, Mietus-Snyder M, Valente A, Schwarz JM, Lustig RH. The role of fructose in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and the metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 7(5): 251-264.
doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.41 pmid: 20368739 |
| [28] | Basaranoglu M, Basaranoglu G, Bugianesi E. Carbohydrate intake and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: fructose as a weapon of mass destruction. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2015, 4(2): 109-116. |
| [29] |
Herman MA, Birnbaum MJ. Molecular aspects of fructose metabolism and metabolic disease. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(12): 2329-2354.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.09.010 pmid: 34619074 |
| [30] |
DeBosch BJ, Chen Zj, Saben JL, Finck BN, Moley KH. Glucose transporter8 (GLUT8) mediates fructose- induced de novo lipogenesis and macrosteatosis. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(16): 10989-10998.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.527002 |
| [31] |
DeBosch BJ, Chen Zj, Finck BN, Chi M, Moley KH. Glucose transporter-8 (GLUT8) mediates glucose intolerance and dyslipidemia in high-fructose diet-fed male mice. Mol Endocrinol, 2013, 27(11): 1887-1896.
doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1137 pmid: 24030250 |
| [32] |
Hyer MM, Dyer SK, Kloster A, Adrees A, Taetzsch T, Feaster J, Valdez G, Neigh GN. Sex modifies the consequences of extended fructose consumption on liver health, motor function, and physiological damage in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2019, 317(6): R903-R911.
doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00046.2019 |
| [33] |
Novelle MG, Bravo SB, Deshons M, Iglesias C, García-Vence M, Annells R, da Silva Lima N, Nogueiras R, Fernandez-Rojo MA, Diéguez C, Romero-Picó A. Impact of liver-specific GLUT8 silencing on fructose- induced inflammation and omega oxidation. iScience, 2021, 24(2): 102071.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102071 |
| [34] |
Fukuzawa T, Fukazawa M, Ueda O, Shimada H, Kito A, Kakefuda M, Kawase Y, Wada NA, Goto C, Fukushima N, Jishage KI, Honda K, King GL, Kawabe Y. SGLT5 reabsorbs fructose in the kidney but its deficiency paradoxically exacerbates hepatic steatosis induced by fructose. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e56681.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056681 |
| [35] |
Pajor AM. Molecular properties of the SLC13 family of dicarboxylate and sulfate transporters. Pflugers Arch, 2006, 451(5): 597-605.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-005-1487-2 |
| [36] |
Bergeron MJ, Clémençon B, Hediger MA, Markovich D. SLC13 family of Na+-coupled di- and tri-carboxylate/ sulfate transporters. Mol Aspects Med, 2013, 34(2-3): 299-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.001 pmid: 23506872 |
| [37] |
Markovich D, Murer H. The SLC13 gene family of sodium sulphate/carboxylate cotransporters. Pflugers Arch, 2004, 447(5): 594-602.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1128-6 |
| [38] |
Monchi M. Citrate pathophysiology and metabolism. Transfus Apher Sci, 2017, 56(1): 28-30.
doi: S1473-0502(16)30199-9 pmid: 28073690 |
| [39] |
Williams NC, O'Neill LAJ. A role for the Krebs cycle intermediate citrate in metabolic reprogramming in innate immunity and inflammation. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 141.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00141 pmid: 29459863 |
| [40] |
Le JM, Fu Y, Han QQ, Wei XD, Ji HL, Chen YF, Wang QY, Pi PX, Li JL, Lin XJ, Zhang XY, Zhang Y, Ye JP. Restoration of mRNA expression of solute carrier proteins in liver of diet-induced obese mice by metformin. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12: 720784.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.720784 |
| [41] |
Hagos Y, Schley G, Schödel J, Krick W, Burckhardt G, Willam C, Burckhardt BC. α-Ketoglutarate-related inhibitors of HIF prolyl hydroxylases are substrates of renal organic anion transporters 1 (OAT1) and 4 (OAT4). Pflugers Arch, 2012, 464(4): 367-374.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1140-9 |
| [42] |
Lin ZH, Cai FF, Lin N, Ye JL, Zheng QQ, Ding GS. Effects of glutamine on oxidative stress and nuclear factor-κB expression in the livers of rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp Ther Med, 2014, 7(2): 365-370.
pmid: 24396406 |
| [43] |
Li YL, Chen D, Xu CM, Zhao Q, Ma YG, Zhao SL, Chen CY. Glycolipid metabolism and liver transcriptomic analysis of the therapeutic effects of pressed degreased walnut meal extracts on type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Food Funct, 2020, 11(6): 5538-5552.
doi: 10.1039/d0fo00670j pmid: 32515761 |
| [44] |
Aragonès G, Auguet T, Berlanga A, Guiu-Jurado E, Martinez S, Armengol S, Sabench F, Ras R, Hernandez M, Aguilar C, Colom J, Sirvent JJ, Del Castillo D, Richart C. Increased circulating levels of alpha- ketoglutarate in morbidly obese women with non- alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0154601.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154601 |
| [45] | Inoue K, Zhuang LN, Maddox DM, Smith SB, Ganapathy V. Human NaCT, the ortholog of Drosophila Indy, as a novel target for lithium action. Biochem J, 2003, 374(1). |
| [46] |
Birkenfeld AL, Lee HY, Guebre-Egziabher F, Alves TC, Jurczak MJ, Jornayvaz FR, Zhang DY, Hsiao JJ, Martin-Montalvo A, Fischer-Rosinsky A, Spranger J, Pfeiffer AF, Jordan J, Fromm MF, König J, Lieske S, Carmean CM, Frederick DW, Weismann D, Knauf F, Irusta PM, De Cabo R, Helfand SL, Samuel VT, Shulman GI. Deletion of the mammalian INDY homolog mimics aspects of dietary restriction and protects against adiposity and insulin resistance in mice. Cell Metab, 2011, 14(2): 184-195.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.009 pmid: 21803289 |
| [47] |
Hu T, Huang WL, Li ZH, Kane MA, Zhang L, Huang SM, Wang HB. Comparative proteomic analysis of SLC13A5 knockdown reveals elevated ketogenesis and enhanced cellular toxic response to chemotherapeutic agents in HepG2 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2020, 402: 115117.
doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115117 |
| [48] |
Dawson PA, Gardiner B, Grimmond S, Markovich D. Transcriptional profile reveals altered hepatic lipid and cholesterol metabolism in hyposulfatemic NaS1 null mice. Physiol Genomics, 2006, 26(2): 116-124.
pmid: 16621889 |
| [49] |
Felmlee MA, Jones RS, Rodriguez-Cruz V, Follman KE, Morris ME.Monocarboxylate transporters(SLC16): function, regulation, and role in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev, 2020, 72(2): 466-485.
doi: 10.1124/pr.119.018762 |
| [50] |
Halestrap AP, Wilson MC. The monocarboxylate transporter family—role and regulation. IUBMB Life, 2012, 64(2): 109-119.
doi: 10.1002/iub.572 pmid: 22162139 |
| [51] |
Martini T, Ripperger JA, Chavan R, Stumpe M, Netzahualcoyotzi C, Pellerin L, Albrecht U. The hepatic monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) contributes to the regulation of food anticipation in mice. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 665476.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.665476 |
| [52] |
Droździk M, Szeląg-Pieniek S, Grzegółkowska J, Łapczuk-Romańska J, Post M, Domagała P, Miętkiewski J, Oswald S, Kurzawski M. Monocarboxylate transporter1 (MCT1) in liver pathology. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(5): 1606.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21051606 |
| [53] |
Lokman FE, Seman NA, Ismail AAS, Yaacob NA, Mustafa N, Khir ASM, Hussein Z, Wan Mohamud WN. Gene expression profiling in ethnic Malays with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with and without diabetic nephropathy. J Nephrol, 2011, 24(6): 778-789.
doi: 10.5301/JN.2011.6382 pmid: 21360476 |
| [54] |
Granja SC, Longatto-Filho A, de Campos PB, Oliveira CP, Stefano JT, Martins-Filho SN, Chagas AL, Herman P, D'Albuquerque LC, Reis Alvares-da-Silva M, Carrilho FJ, Baltazar F, Alves VAF. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma: immunohistochemical assessment of markers of cancer cell metabolism. Pathobiology, 2022, 89(3): 157-165.
doi: 10.1159/000521034 |
| [55] |
Mariotta L, Ramadan T, Singer D, Guetg A, Herzog B, Stoeger C, Palacín M, Lahoutte T, Camargo SMR, Verrey F. T-type amino acid transporter TAT1 (Slc16a10) is essential for extracellular aromatic amino acid homeostasis control. J Physiol, 2012, 590(24): 6413-6424.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.239574 |
| [56] |
Lake AD, Novak P, Shipkova P, Aranibar N, Robertson DG, Reily MD, Lehman-McKeeman LD, Vaillancourt RR, Cherrington NJ. Branched chain amino acid metabolism profiles in progressive human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Amino Acids, 2015, 47(3): 603-615.
doi: 10.1007/s00726-014-1894-9 pmid: 25534430 |
| [57] |
Gaggini M, Carli F, Rosso C, Buzzigoli E, Marietti M, Della Latta V, Ciociaro D, Abate ML, Gambino R, Cassader M, Bugianesi E, Gastaldelli A. Altered amino acid concentrations in NAFLD: Impact of obesity and insulin resistance. Hepatology, 2018, 67(1): 145-158.
doi: 10.1002/hep.29465 pmid: 28802074 |
| [58] |
Lebeaupin C, Vallée D, Hazari Y, Hetz C, Chevet E, Bailly-Maitre B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(4): 927-947.
doi: S0168-8278(18)32161-5 pmid: 29940269 |
| [59] |
Rusu V, Hoch E, Mercader JM, Tenen DE, Gymrek M, Hartigan CR, DeRan M, von Grotthuss M, Fontanillas P, Spooner A, Guzman G, Deik AA, Pierce KA, Dennis C, Clish CB, Carr SA, Wagner BK, Schenone M, Ng MCY, Chen BH, MEDIA Consortium, SIGMA T2D Consortium, Centeno-Cruz F, Zerrweck C, Orozco L, Altshuler DM, Schreiber SL, Florez JC, Jacobs SBR, Lander ES. Type 2 diabetes variants disrupt function of SLC16A11 through two distinct mechanisms. Cell, 2017, 170(1): 199-212.e20.
doi: S0092-8674(17)30694-3 pmid: 28666119 |
| [60] |
Deprince A, Haas JT, Staels B. Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease. Mol Metab, 2020, 42: 101092.
doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101092 |
| [61] |
Zhao YX, Feng ZH, Zhang YX, Sun YM, Chen Y, Liu X, Li S, Zhou T, Chen L, Wei Y, Ma D, Lui KO, Ying H, Chen Y, Ding Q. Gain-of-function mutations of SLC16A11 contribute to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Cell Rep, 2019, 26(4): 884-892.e4.
doi: S2211-1247(18)32075-8 pmid: 30673611 |
| [62] |
Zhang T, Qi ZT, Wang HY, Ding SZ. Adeno-associated virus-mediated knockdown of SLC16A11 improves glucose tolerance and hepatic insulin signaling in high fat diet-fed mice. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2021, 129(2): 104-111.
doi: 10.1055/a-0840-3330 |
| [63] |
Schumann T, König J, von Loeffelholz C, Vatner DF, Zhang DY, Perry RJ, Bernier M, Chami J, Henke C, Kurzbach A, El-Agroudy NN, Willmes DM, Pesta D, de Cabo R, O Sullivan JF, Simon E, Shulman GI, Hamilton BS, Birkenfeld AL. Deletion of the diabetes candidate gene Slc16a13 in mice attenuates diet-induced ectopic lipid accumulation and insulin resistance. Commun Biol, 2021, 4(1): 826.
doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02279-8 pmid: 34211098 |
| [64] |
Hirai T, Fukui Y, Motojima K. PPARalpha agonists positively and negatively regulate the expression of several nutrient/drug transporters in mouse small intestine. Biol Pharm Bull, 2007, 30(11): 2185-2190.
pmid: 17978498 |
| [65] |
Koepsell H. Organic cation transporters in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev, 2020, 72(1): 253-319.
doi: 10.1124/pr.118.015578 pmid: 31852803 |
| [66] |
Nigam SK, Bush KT, Martovetsky G, Ahn SY, Liu HC, Richard E, Bhatnagar V, Wu W. The organic anion transporter (OAT) family: a systems biology perspective. Physiol Rev, 2015, 95(1): 83-123.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00025.2013 pmid: 25540139 |
| [67] |
Pochini L, Galluccio M, Scalise M, Console L, Indiveri C. OCTN: a small transporter subfamily with great relevance to human pathophysiology, drug discovery, and diagnostics. SLAS Discov, 2019, 24(2): 89-110.
doi: 10.1177/2472555218812821 pmid: 30523710 |
| [68] |
Tamai I. Pharmacological and pathophysiological roles of carnitine/organic cation transporters (OCTNs: SLC22A4, SLC22A5 and SLC22A21). Biopharm Drug Dispos, 2013, 34(1): 29-44.
doi: 10.1002/bdd.1816 pmid: 22952014 |
| [69] |
Rinaldo P, Cowan TM, Matern D. Acylcarnitine profile analysis. Genet Med, 2008, 10(2): 151-156.
doi: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181614289 pmid: 18281923 |
| [70] |
Chapoy PR, Angelini C, Brown WJ, Stiff JE, Shug AL, Cederbaum SD. Systemic carnitine deficiency—a treatable inherited lipid-storage disease presenting as Reye's syndrome. N Engl J Med, 1980, 303(24): 1389-1394.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012113032403 |
| [71] |
Deswal S, Bijarnia-Mahay S, Manocha V, Hara K, Shigematsu Y, Saxena R, Verma IC. Primary carnitine deficiency—a rare treatable cause of cardiomyopathy and massive hepatomegaly. Indian J Pediatr, 2017, 84(1): 83-85.
doi: 10.1007/s12098-016-2227-7 |
| [72] |
Cropp CD, Komori T, Shima JE, Urban TJ, Yee SW, More SS, Giacomini KM. Organic anion transporter 2 (SLC22A7) is a facilitative transporter of cGMP. Mol Pharmacol, 2008, 73(4): 1151-1158.
doi: 10.1124/mol.107.043117 pmid: 18216183 |
| [73] |
Mathialagan S, Bi YA, Costales C, Kalgutkar AS, Rodrigues AD, Varma MVS. Nicotinic acid transport into human liver involves organic anion transporter 2 (SLC22A7). Biochem Pharmacol, 2020, 174: 113829.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113829 |
| [74] |
Dall M, Hassing AS, Treebak JT. NAD+ and NAFLD— caution, causality and careful optimism. J Physiol, 2022, 600(5): 1135-1154.
doi: 10.1113/JP280908 |
| [75] |
Shin HJ, Anzai N, Enomoto A, He X, Kim DK, Endou H, Kanai Y. Novel liver-specific organic anion transporter OAT7 that operates the exchange of sulfate conjugates for short chain fatty acid butyrate. Hepatology, 2007, 45(4): 1046-1055.
pmid: 17393504 |
| [76] |
Zhou D, Pan Q, Xin FZ, Zhang RN, He CX, Chen GY, Liu C, Chen YW, Fan JG. Sodium butyrate attenuates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice by improving gut microbiota and gastrointestinal barrier. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(1): 60-75.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.60 |
| [77] |
Klein K, Jüngst C, Mwinyi J, Stieger B, Krempler F, Patsch W, Eloranta JJ, Kullak-Ublick GA. The human organic anion transporter genes OAT5 and OAT7 are transactivated by hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α (HNF-1α). Mol Pharmacol, 2010, 78(6): 1079-1087.
doi: 10.1124/mol.110.065201 pmid: 20829431 |
| [78] | Liu F, Zhu X, Jiang XP, Li S, Lv YC. Transcriptional control by HNF-1: emerging evidence showing its role in lipid metabolism and lipid metabolism disorders. Genes Dis, 2021, 9(5): 1248-1257. |
| [79] |
Tanaka Y, Nagoshi T, Takahashi H, Oi YH, Yoshii A, Kimura H, Ito K, Kashiwagi Y, Tanaka TD, Yoshimura M. URAT1-selective inhibition ameliorates insulin resistance by attenuating diet-induced hepatic steatosis and brown adipose tissue whitening in mice. Mol Metab, 2022, 55: 101411.
doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101411 |
| [80] |
Ruprecht JJ, Kunji ERS. The SLC 25 mitochondrial carrier family: structure and mechanism. Trends Biochem Sci, 2020, 45(3): 244-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2019.11.001 |
| [81] | Kunji ERS, King MS, Ruprecht JJ, Thangaratnarajah C. The SLC25 carrier family: important transport proteins in mitochondrial physiology and pathology. Physiology (Bethesda), 2020, 35(5): 302-327. |
| [82] |
Dolce V, Scarcia P, Iacopetta D, Palmieri F. A fourth ADP/ATP carrier isoform in man: identification, bacterial expression, functional characterization and tissue distribution. FEBS Lett, 2005, 579(3): 633-637.
pmid: 15670820 |
| [83] |
Kunji ERS, Robinson AJ. Coupling of proton and substrate translocation in the transport cycle of mitochondrial carriers. Curr Opin Struct Biol, 2010, 20(4): 440-447.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.06.004 |
| [84] | Monteiro BS, Freire-Brito L, Carrageta DF, Oliveira PF, Alves MG. Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins (UCPs) as key modulators of ROS homeostasis: a crosstalk between diabesity and male infertility? Antioxidants (Basel), 2021, 10(11): 1746. |
| [85] |
Chouchani ET, Kazak L, Spiegelman BM. New advances in adaptive thermogenesis: UCP1 and beyond. Cell Metab, 2019, 29(1): 27-37.
doi: S1550-4131(18)30679-X pmid: 30503034 |
| [86] |
Mills EL, Harmon C, Jedrychowski MP, Xiao HP, Garrity R, Tran NV, Bradshaw GA, Fu A, Szpyt J, Reddy A, Prendeville H, Danial NN, Gygi SP, Lynch L, Chouchani ET. UCP1 governs liver extracellular succinate and inflammatory pathogenesis. Nat Metab, 2021, 3(5): 604-617.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00389-5 pmid: 34002097 |
| [87] |
De Munck TJI, Xu P, Vanderfeesten BLJ, Elizalde M, Masclee AAM, Nevens F, Cassiman D, Schaap FG, Jonkers DMAE, Verbeek J. The role of brown adipose tissue in the development and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: an exploratory gene expression study in mice. Horm Metab Res, 2020, 52(12): 869-876.
doi: 10.1055/a-1301-2378 pmid: 33260239 |
| [88] |
Gallardo-Montejano VI, Yang CF, Hahner L, McAfee JL, Johnson JA, Holland WL, Fernandez-Valdivia R, Bickel PE. Perilipin 5 links mitochondrial uncoupled respiration in brown fat to healthy white fat remodeling and systemic glucose tolerance. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 3320.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23601-2 pmid: 34083525 |
| [89] |
Cadenas S. Mitochondrial uncoupling, ROS generation and cardioprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg, 2018, 1859(9): 940-950.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.05.019 |
| [90] |
Seshadri N, Jonasson ME, Hunt KL, Xiang B, Cooper S, Wheeler MB, Dolinsky VW, Doucette CA. Uncoupling protein 2 regulates daily rhythms of insulin secretion capacity in MIN6 cells and isolated islets from male mice. Mol Metab, 2017, 6(7): 760-769.
doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.04.008 pmid: 28702331 |
| [91] |
Li JR, Jiang RH, Cong XL, Zhao YF. UCP2 gene polymorphisms in obesity and diabetes, and the role of UCP2 in cancer. FEBS Lett, 2019, 593(18): 2525-2534.
doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13546 pmid: 31330574 |
| [92] |
Camara Y, Mampel T, Armengol J, Villarroya F, Dejean L. UCP3 expression in liver modulates gene expression and oxidative metabolism in response to fatty acids, and sensitizes mitochondria to permeability transition. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2009, 24(3-4): 243-252.
doi: 10.1159/000233249 pmid: 19710539 |
| [93] |
Tan MJ, Mosaoa R, Graham GT, Kasprzyk-Pawelec A, Gadre S, Parasido E, Catalina-Rodriguez O, Foley P, Giaccone G, Cheema A, Kallakury B, Albanese C, Yi CL, Avantaggiati ML. Inhibition of the mitochondrial citrate carrier, Slc25a1, reverts steatosis, glucose intolerance, and inflammation in preclinical models of NAFLD/ NASH. Cell Death Differ, 2020, 27(7): 2143-2157.
doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0491-6 |
| [94] |
Unami A, Shinohara Y, Kajimoto K, Baba Y. Comparison of gene expression profiles between white and brown adipose tissues of rat by microarray analysis. Biochem Pharmacol, 2004, 67(3): 555-564.
pmid: 15037207 |
| [95] |
Mizuarai S, Miki S, Araki H, Takahashi K, Kotani H. Identification of dicarboxylate carrier Slc25a10 as malate transporter in de novo fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(37): 32434-32441.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503152200 pmid: 16027120 |
| [96] |
Lin Y, Berg AH, Iyengar P, Lam TKT, Giacca A, Combs TP, Rajala MW, Du XL, Rollman B, Li WJ, Hawkins M, Barzilai N, Rhodes CJ, Fantus IG, Brownlee M, Scherer PE. The hyperglycemia-induced inflammatory response in adipocytes: the role of reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(6): 4617-4626.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411863200 pmid: 15536073 |
| [97] |
An YA, Chen S, Deng YF, Wang ZV, Funcke JB, Shah M, Shan B, Gordillo R, Yoshino J, Klein S, Kusminski CM, Scherer PE. The mitochondrial dicarboxylate carrier prevents hepatic lipotoxicity by inhibiting white adipocyte lipolysis. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(2): 387-399.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.006 pmid: 33746082 |
| [98] |
Zhong Q, Putt DA, Xu F, Lash LH. Hepatic mitochondrial transport of glutathione: studies in isolated rat liver mitochondria and H4IIE rat hepatoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2008, 474(1): 119-127.
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.03.008 pmid: 18374655 |
| [99] |
Pan GQ, Wang RB, Jia SN, Li YQ, Jiao Y, Liu N. SLC25A11 serves as a novel prognostic biomarker in liver cancer. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 9871.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66837-6 pmid: 32555317 |
| [100] |
Yuan YX, Zhu CJ, Wang YL, Sun J, Feng JL, Ma ZW, Li PL, Peng WT, Yin C, Xu GL, Xu PW, Jiang YW, Jiang QY, Shu G. α-Ketoglutaric acid ameliorates hyperglycemia in diabetes by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis via serpina1e signaling. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(18): eabn2879.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn2879 |
| [101] |
Palmieri F, Pierri CL. Mitochondrial metabolite transport. Essays Biochem, 2010, 47: 37-52.
doi: 10.1042/bse0470037 pmid: 20533899 |
| [102] |
Saheki T, Kobayashi K, Iijima M, Moriyama M, Yazaki M, Takei YI, Ikeda SI. Metabolic derangements in deficiency of citrin, a liver-type mitochondrial aspartate- glutamate carrier. Hepatol Res, 2005, 33(2): 181-184.
doi: 10.1016/j.hepres.2005.09.031 |
| [103] |
Amoedo ND, Punzi G, Obre E, Lacombe D, De Grassi A, Pierri CL, Rossignol R. AGC1/2, the mitochondrial aspartate-glutamate carriers. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016, 1863(10): 2394-2412.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.04.011 pmid: 27132995 |
| [104] |
Komatsu M, Yazaki M, Tanaka N, Sano K, Hashimoto E, Takei YI, Song YZ, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K, Saheki T, Aoyama T, Kobayashi K. Citrin deficiency as a cause of chronic liver disorder mimicking non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol, 2008, 49(5): 810-820.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.05.016 pmid: 18620775 |
| [105] |
Tonazzi A, Giangregorio N, Console L, Palmieri F, Indiveri C. The mitochondrial carnitine acyl-carnitine carrier (SLC25A20): molecular mechanisms of transport, role in redox sensing and interaction with drugs. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(4): 521.
doi: 10.3390/biom11040521 |
| [106] |
Fiermonte G, De Leonardis F, Todisco S, Palmieri L, Lasorsa FM, Palmieri F. Identification of the mitochondrial ATP-Mg/Pi transporter. Bacterial expression, reconstitution, functional characterization, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(29): 30722-30730.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400445200 pmid: 15123600 |
| [107] |
Harborne SPD, King MS, Crichton PG, Kunji ERS. Calcium regulation of the human mitochondrial ATP- Mg/Pi carrier SLC25A24 uses a locking pin mechanism. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 45383.
doi: 10.1038/srep45383 pmid: 28350015 |
| [108] |
Urano T, Shiraki M, Sasaki N, Ouchi Y, Inoue S. SLC25A24 as a novel susceptibility gene for low fat mass in humans and mice. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 100(4): E655-E663.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-2829 |
| [109] |
Black PN, DiRusso CC. Vectorial acylation: linking fatty acid transport and activation to metabolic trafficking. Novartis Found Symp, 2007, 286: 127-138.
pmid: 18269179 |
| [110] |
Stahl A, Evans JG, Pattel S, Hirsch D, Lodish HF. Insulin causes fatty acid transport protein translocation and enhanced fatty acid uptake in adipocytes. Dev Cell, 2002, 2(4): 477-488.
pmid: 11970897 |
| [111] |
Krammer J, Digel M, Ehehalt F, Stremmel W, Füllekrug J, Ehehalt R. Overexpression of CD36 and acyl-CoA synthetases FATP2, FATP4 and ACSL1 increases fatty acid uptake in human hepatoma cells. Int J Med Sci, 2011, 8(7): 599-614.
doi: 10.7150/ijms.8.599 pmid: 22022213 |
| [112] |
Falcon A, Doege H, Fluitt A, Tsang B, Watson N, Kay MA, Stahl A. FATP2 is a hepatic fatty acid transporter and peroxisomal very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2010, 299(3): E384-E393.
doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00226.2010 |
| [113] |
Doege H, Baillie RA, Ortegon AM, Tsang B, Wu QW, Punreddy S, Hirsch D, Watson N, Gimeno RE, Stahl A. Targeted deletion of FATP5 reveals multiple functions in liver metabolism: alterations in hepatic lipid homeostasis. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(4): 1245-1258.
pmid: 16618416 |
| [114] |
Hubbard B, Doege H, Punreddy S, Wu H, Huang XM, Kaushik VK, Mozell RL, Byrnes JJ, Stricker-Krongrad A, Chou CJ, Tartaglia LA, Lodish HF, Stahl A, Gimeno RE. Mice deleted for fatty acid transport protein 5 have defective bile acid conjugation and are protected from obesity. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(4): 1259-1269.
pmid: 16618417 |
| [115] |
Tamaki M, Fujitani Y, Hara A, Uchida T, Tamura Y, Takeno K, Kawaguchi M, Watanabe T, Ogihara T, Fukunaka A, Shimizu T, Mita T, Kanazawa A, Imaizumi MO, Abe T, Kiyonari H, Hojyo S, Fukada T, Kawauchi T, Nagamatsu S, Hirano T, Kawamori R, Watada H. The diabetes-susceptible gene SLC30A8/ZnT8 regulates hepatic insulin clearance. J Clin Invest, 2013, 123(10): 4513-4524.
doi: 10.1172/JCI68807 pmid: 24051378 |
| [116] |
Hardy AB, Wijesekara N, Genkin I, Prentice KJ, Bhattacharjee A, Kong D, Chimienti F, Wheeler MB.Effects of high-fat diet feeding on Znt8-null mice: differences between β-cell and global knockout of Znt8. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 302(9): E1084-E1096.
doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00448.2011 |
| [117] |
Fukunaka A, Fujitani Y. Role of zinc homeostasis in the pathogenesis of diabetes and obesity. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(2): 476.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19020476 |
| [118] |
Mattace Raso G, Simeoli R, Russo R, Iacono A, Santoro A, Paciello O, Ferrante MC, Canani RB, Calignano A, Meli R. Effects of sodium butyrate and its synthetic amide derivative on liver inflammation and glucose tolerance in an animal model of steatosis induced by high fat diet. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e68626.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068626 |
| [119] |
Li XL, Li J, Lu XL, Ma HH, Shi HT, Li H, Xie DH, Dong L, Liang CL. Treatment with PPARδ agonist alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating glucose and fatty acid metabolic enzymes in a rat model. Int J Mol Med, 2015, 36(3): 767-775.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2270 pmid: 26133486 |
| [120] |
Wikan N, Tocharus J, Sivasinprasasn S, Kongkaew A, Chaichompoo W, Suksamrarn A, Tocharus C. Capsaicinoid nonivamide improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed a high-fat diet. J Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 143(3): 188-198.
doi: S1347-8613(20)30039-6 pmid: 32414691 |
| [121] |
Zhang Y, Lu QH, Cao HF, Zhang SR, Wang HD. Effects of GPR81 agonist on insulin resistance in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Chin J Appl Physiol, 2021, 37(4): 354-358.
doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.6055.2021.033 pmid: 34374253 |
| [122] |
Lin W, Jin Y, Hu X, Huang EJ, Zhu QH. AMPK/PGC- 1α/GLUT4-mediated effect of icariin on hyperlipidemia- induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Biochemistry (Mosc), 2021, 86(11): 1407-1417.
doi: 10.1134/S0006297921110055 |
| [123] | Yasmin T, Rahman MM, Khan F, Kabir F, Nahar K, Lasker S, Islam MD, Hossain MM, Hasan R, Rana S, Alam MA. Metformin treatment reverses high fat diet- induced non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases and dyslipidemia by stimulating multiple antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Biochem Biophys Rep, 2021, 28: 101168. |
| [124] |
Ma L, Lian YL, Tang JY, Chen FY, Gao H, Zhou Z, Hou N, Yi W. Identification of the anti-fungal drug fenticonazole nitrate as a novel PPARγ-modulating ligand with good therapeutic index: structure-based screening and biological validation. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 173: 105860.
doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105860 |
| [125] |
Zaklos-Szyda M, Pietrzyk N, Kowalska-Baron A, Nowak A, Chałaśkiewicz K, Ratajewski M, Budryn G, Koziołkiewicz M. Phenolics-rich extracts of dietary plants as regulators of fructose uptake in Caco-2 cells via GLUT5 involvement. Molecules, 2021, 26(16): 4745.
doi: 10.3390/molecules26164745 |
| [126] |
Nasykhova YA, Tonyan ZN, Mikhailova AA, Danilova MM, Glotov AS. Pharmacogenetics of type 2 diabetes- progress and prospects. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(18): 6842.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21186842 |
| [127] |
Huard K, Brown J, Jones JC, Cabral S, Futatsugi K, Gorgoglione M, Lanba A, Vera NB, Zhu YM, Yan QY, Zhou YJ, Vernochet C, Riccardi K, Wolford A, Pirman D, Niosi M, Aspnes G, Herr M, Genung NE, Magee TV, Uccello DP, Loria P, Di L, Gosset JR, Hepworth D, Rolph T, Pfefferkorn JA, Erion DM. Discovery and characterization of novel inhibitors of the sodium-coupled citrate transporter (NaCT or SLC13A5). Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 17391.
doi: 10.1038/srep17391 pmid: 26620127 |
| [128] |
Sun QS, Niu Q, Guo YT, Zhuang Y, Li XN, Liu J, Li N, Li ZY, Huang F, Qiu ZX. Regulation on citrate influx and metabolism through inhibiting SLC13A5 and ACLY: a novel mechanism mediating the therapeutic effects of curcumin on NAFLD. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69(31): 8714-8725.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03105 |
| [129] |
Savic D, Hodson L, Neubauer S, Pavlides M. The importance of the fatty acid transporter L-carnitine in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Nutrients, 2020, 12(8): 2178.
doi: 10.3390/nu12082178 |
| [130] |
Weng Y, Fonseca KR, Bi YA, Mathialagan S, Riccardi K, Tseng E, Bessire AJ, Cerny MA, Tess DA, Rodrigues AD, Kalgutkar AS, Litchfield JE, Di L, Varma MVS. Transporter-enzyme interplay in the pharmacokinetics of PF-06835919, a first-in-class ketohexokinase inhibitor for metabolic disorders and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Drug Metab Dispos, 2022, 50(9): 1312-1321.
doi: 10.1124/dmd.122.000953 |
| [131] |
Zhao ST, Chu Y, Zhang YW, Zhou YL, Jiang ZW, Wang ZQ, Mao LF, Li K, Sun W, Li P, Jia SQ, Wang CC, Xu AM, Loomes K, Tang SB, Wu DH, Hui XY, Nie T. Linifanib exerts dual anti-obesity effect by regulating adipocyte browning and formation. Life Sci, 2019, 222: 117-124.
doi: S0024-3205(19)30060-8 pmid: 30708100 |
| [132] |
Colca JR, McDonald WG, Adams WJ. MSDC-0602K, a metabolic modulator directed at the core pathology of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2018, 27(7): 631-636.
doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1494153 |
| [133] |
Gawrieh S, Noureddin M, Loo N, Mohseni R, Awasty V, Cusi K, Kowdley KV, Lai M, Schiff E, Parmar D, Patel P, Chalasani N. Saroglitazar, a PPAR-α/γ agonist, for treatment of NAFLD: a randomized controlled double- blind phase 2 trial. Hepatology, 2021, 74(4): 1809-1824.
doi: 10.1002/hep.31843 pmid: 33811367 |
| [134] |
Sven MF, Pierre B, Manal FA, Quentin MA, Elisabetta B, Vlad R, Philippe HM, Bruno S, Jean-Louis J, Pierre B, Jean-Louis A. A randomised, double-blind, placebo- controlled, multi-centre, dose-range, proof-of-concept, 24-week treatment study of lanifibranor in adult subjects with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Design of the NATIVE study. Contemp Clin Trials, 2020, 98: 106170.
doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2020.106170 |
| [135] | Bhattacharya D, Basta B, Mato JM, Craig A, Fernández-Ramos D, Lopitz-Otsoa F, Tsvirkun D, Hayardeny L, Chandar V, Schwartz RE, Villanueva A, Friedman SL. Aramchol downregulates stearoyl CoA- desaturase 1 in hepatic stellate cells to attenuate cellular fibrogenesis. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3(3): 100237. |
| [136] |
Ratziu V, de Guevara L, Safadi R, Poordad F, Fuster F, Flores-Figueroa J, Arrese M, Fracanzani AL, Ben Bashat D, Lackner K, Gorfine T, Kadosh S, Oren R, Halperin M, Hayardeny L, Loomba R, Friedman S, ARREST Investigator Study Group, Sanyal AJ. Aramchol in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Nat Med, 2021, 27(10): 1825-1835.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01495-3 pmid: 34621052 |
| [1] | Jia Zheng, Xinhua Xiao, Qian Zhang, Miao Yu, Jianping Xu, Zhixin Wang, Yijing Liu, Mingmin Li. PPARγ links maternal malnutrition and abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism in the offspring of mice [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(1): 70-76. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||