Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (4): 306-318.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-253
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
A DNA typing panel of 201 genetic markers for degraded samples: development and validation
Wei Han( ), Qingzhen Zhang, Jing Yang(
), Qingzhen Zhang, Jing Yang( ), Zhe Zhou(
), Zhe Zhou( )
)
- Bioinformatics Center of Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing 100850, China
-
Received:2023-12-05Revised:2024-01-30Online:2024-04-20Published:2024-01-31 -
Contact:Jing Yang, Zhe Zhou E-mail:651430459@qq.com;jingyang0511@163.com;zhouzhe@bmi.ac.cn
Cite this article
Wei Han, Qingzhen Zhang, Jing Yang, Zhe Zhou. A DNA typing panel of 201 genetic markers for degraded samples: development and validation[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(4): 306-318.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
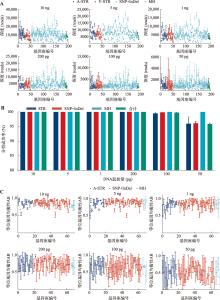
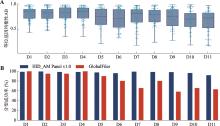
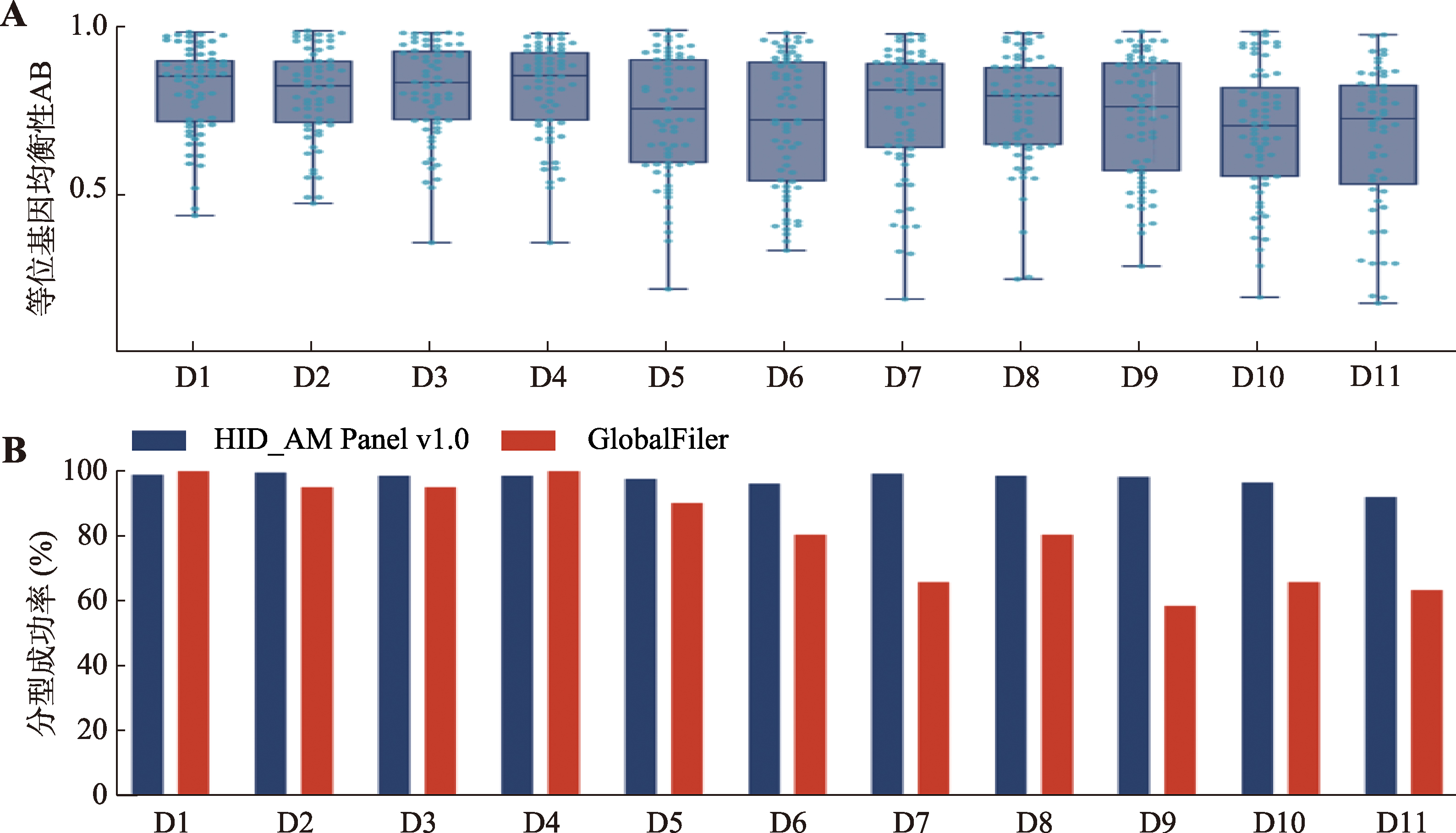
Concentrations of large amplicon, small amplicon, Y chromosome amplicon, degradation index (DI) and genotyping success rate of genetic markers in mock degraded samples"
| 样本名称 | 大片段(pg/μL) | 小片段(pg/μL) | Y片段(pg/μL) | 降解指数 DI | STR分型成功率(%) | SNP+InDel分型成功率(%) | MH分型成功率(%) | 全部遗传标记分型成功率(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0.44 | 0.80 | 1.32 | 1.84 | 98.51 | 99.11 | 100 | 98.97 |
| D2 | 0.24 | 0.71 | 1.18 | 2.93 | 98.51 | 100 | 100 | 99.66 |
| D3 | 0.14 | 0.70 | 1.03 | 4.84 | 97.01 | 99.11 | 100 | 98.63 |
| D4 | 0.31 | 0.86 | 1.29 | 2.72 | 97.01 | 99.11 | 100 | 98.63 |
| D5 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 0.94 | 10.45 | 95.52 | 98.22 | 100 | 97.6 |
| D6 | 0.04 | 0.65 | 0.99 | 15.78 | 92.54 | 97.33 | 100 | 96.23 |
| D7 | 0.02 | 0.40 | 0.74 | 16.66 | 97.01 | 100 | 100 | 99.32 |
| D8 | 0.03 | 0.51 | 0.80 | 20.35 | 97.01 | 99.11 | 100 | 98.63 |
| D9 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.69 | 37.61 | 97.01 | 98.67 | 100 | 98.29 |
| D10 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 82.78 | 91.04 | 98.22 | 100 | 96.58 |
| D11 | 0.00 | 0.49 | 0.62 | 401.02 | 83.58 | 95.56 | 87.5 | 92.12 |
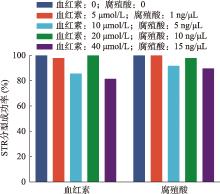
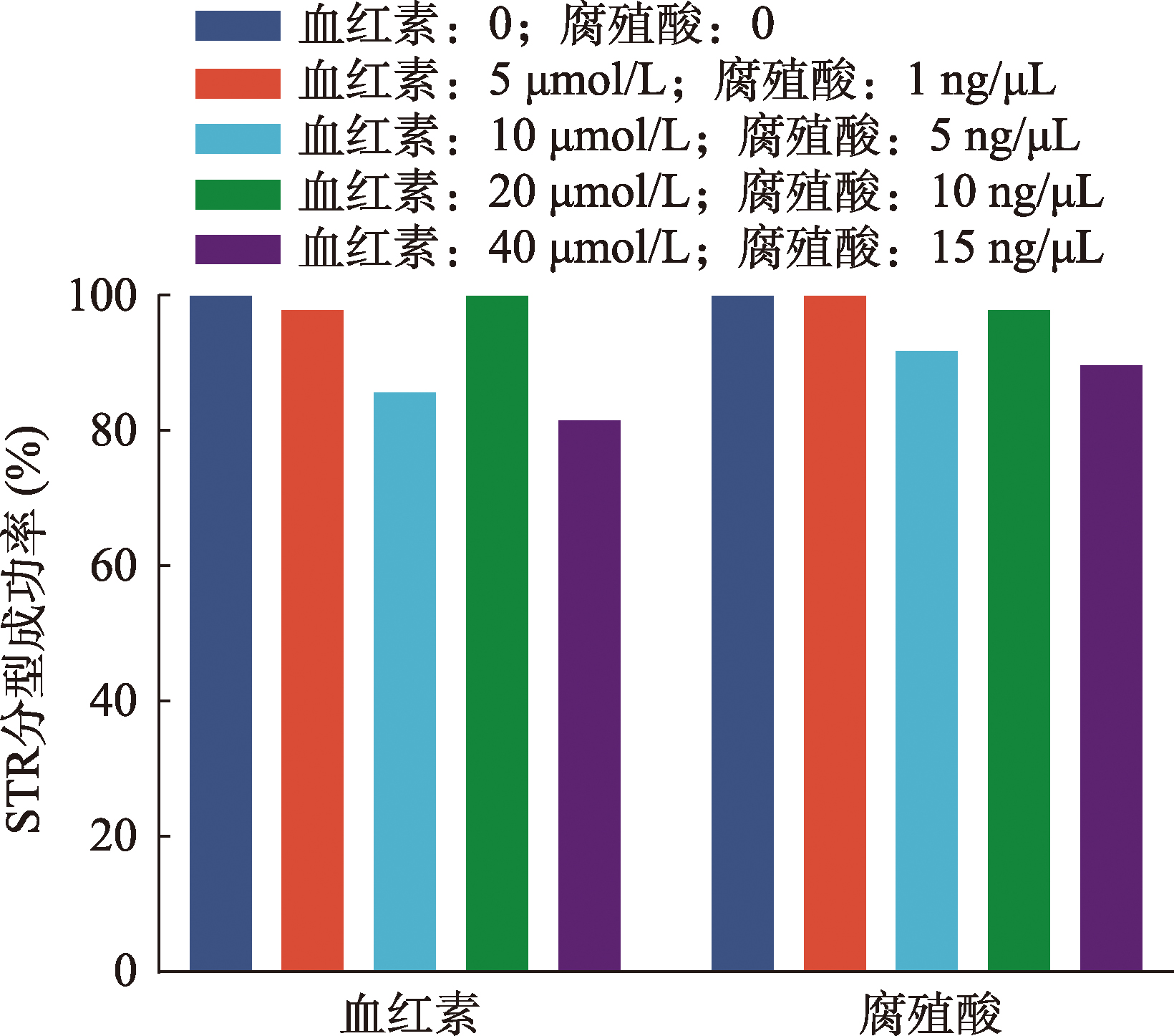
Table 2
The loci typed incorrectly after adding different concentrations of hematin, indigo blue or humic acid"
| 样品名 | 分型错误STR | 分型错误SNP | 分型错误InDel | 分型错误MH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 血红素-空白 | / | / | / | / |
| 血红素-5 µmol/L | CSF1PO | / | / | / |
| 血红素-10 µmol/L | CSF1PO 、D7S820、D9S1122、DYS437、DYS392、DYS448、DYS438 | / | rs3032356 | / |
| 血红素-20 µmol/L | / | / | / | / |
| 血红素-40 µmol/L | D17S974、D19S433、D3S1358、D7S820、DYS481、DYS19、DYS643、Y_GATA_H4、DYS389II | / | / | / |
| 血红素-80 µmol/L | × | × | × | × |
| 靛蓝-空白 | / | / | / | / |
| 靛蓝-2 mmol/L | D18S51、Penta D、FGA、DYS458、DYS518、DYS389II | rs1413212、rs2399332、rs717302、rs159606、rs12174864、rs1336071、rs826472、rs3780962、rs2107612、rs1295330、rs2096458、rs914165、rs747718394 | rs35771136、rs2307805、rs16660 | mh13KK-213 |
| 靛蓝-4 mmol/L | × | × | × | × |
| 腐殖酸-空白 | / | / | / | / |
| 腐殖酸-1 ng/µL | / | / | / | / |
| 腐殖酸-5 ng/µL | CSF1PO、D7S820、DYS393、DYS389I | rs1295330 | / | / |
| 腐殖酸-10 ng/µL | DYS389II | rs1295330 | / | / |
| 腐殖酸-15 ng/µL | D18S51、D21S11、Penta D、DYS518、DYS389II | rs1295330、rs2096458 | / | / |
| 腐殖酸-50 ng/µL | × | × | × | × |
| [1] |
Tahir MA, Balamurugan K, Tahir UA, Amjad M, Awin MB, Chaudhary OR, Hamby JE, Budowle B, Herrera RJ. Allelic distribution of nine short tandem repeat (STR), HLA-DQA1, and polymarker loci in an Omani sample population. Forensic Sci Int, 2000, 109(2): 81-85.
pmid: 10704812 |
| [2] |
Puers C, Hammond HA, Jin L, Caskey CT, Schumm JW. Identification of repeat sequence heterogeneity at the polymorphic short tandem repeat locus HUMTH01[AATG]n and reassignment of alleles in population analysis by using a locus-specific allelic ladder. Am J Hum Genet, 1993, 53(4): 953-958.
pmid: 8105685 |
| [3] | Gill P, Kimpton C, D'Aloja E, Andersen JF, Bar W, Brinkmann B, Holgersson S, Johnsson V, Kloosterman AD, Lareu MV. Report of the European DNA profiling group (EDNAP)--towards standardisation of short tandem repeat (STR) loci. Forensic Sci Int, 1994, 65(1): 51-59. |
| [4] |
Zhu BF, Zhang YD, Shen CM, Du WA, Liu WJ, Meng HT, Wang HD, Yang G, Jin R, Yang CH, Yan JW, Bie XH. Developmental validation of the AGCU 21+1 STR kit: a novel multiplex assay for forensic application. Electrophoresis, 2015, 36(2): 271-276.
doi: 10.1002/elps.v36.2 |
| [5] | Hou YP. Forensic genetics. Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House, 2009: 130-131. |
| 侯一平. 法医物证学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2009: 130-131. | |
| [6] |
Gettings KB, Lai R, Johnson JL, Peck MA, Hart JA, Gordish-Dressman H, Schanfield MS, Podini DS. A 50-SNP assay for biogeographic ancestry and phenotype prediction in the U.S.population. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2014, 8(1): 101-108.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2013.07.010 |
| [7] |
Walsh S, Lindenbergh A, Zuniga SB, Sijen T, de Knijff P, Kayser M, Ballantyne KN. Developmental validation of the IrisPlex system: determination of blue and brown iris colour for forensic intelligence. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2011, 5(5): 464-471.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2010.09.008 |
| [8] |
Rajeevan H, Soundararajan U, Pakstis AJ, Kidd KK. Introducing the forensic research/reference on genetics knowledge base, FROG-kb. Investig Genet, 2012, 3(1): 18.
doi: 10.1186/2041-2223-3-18 pmid: 22938150 |
| [9] |
Zaumsegel D, Rothschild MA, Schneider PM. A21 marker insertion deletion polymorphism panel to study biogeographic ancestry. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2013, 7(2): 305-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.12.007 |
| [10] | Qin CJ, Dilixiati T, Jia J, Dong H, Wei YL, Hu L, Li CX. Forensic genetics study of 30 InDel markers for forensic identification in three Chinese populations. Chin J Forensic Med, 2014, 29(4):299-303. |
| 秦翠娇, 迪力夏提·塔什, 贾竟, 董会, 魏以梁, 胡兰, 李彩霞.30个InDels在中国三个民族的遗传学调查及法医学应用. 中国法医学杂志, 2014, 29(4): 299-303. | |
| [11] | Chen BL, Feng YS, Wang Y, Zhao J, Zhang C, Kang Kl, Ye J, Wang L. Development of a 100-plex microhaplotype panel and its application on BGI-500RS and MiSeq sequencing platforms. Chin J Forensic Med, 2022, 37(6):531-537. |
| 陈邦柳, 冯耀森, 王羽, 赵杰, 张驰, 康克莱, 叶健, 王乐. 100重微单倍型复合检测体系建立及其在BGI-500RS和MiSeq测序平台的应用. 中国法医学杂志, 2022, 37(6): 531-537. | |
| [12] | Zhou J, Wang Y, Xu EP. Research progress on application of microhaplotype in forensic genetics. J Zhejiang Univ Med Sci, 2021, 50(6): 777-782. |
| 周靖, 王艳, 徐恩萍. 微单倍型在法医遗传学中的研究进展. 浙江大学学报(医学版), 2021, 43(10): 962-992. | |
| [13] | Li X, Wang HY, Cao YY, Zhu Q, Shu PY, Hou TY, Wang YT, Zhang J. Forensic genomics research on microhaplotypes. Hereditas (Beijing). 2021 Oct 20; 43(10):962-971. |
| 李茜, 王浩宇, 曹悦岩, 朱强, 舒潘寅, 侯婷芸, 王雨婷, 张霁. 微单倍型遗传标记的法医基因组学研究. 遗传, 2021, 43(10): 962-992. | |
| [14] |
Amorim A, Pereira L. Pros and cons in the use of SNPs in forensic kinship investigation: a comparative analysis with STRs. Forensic Sci Int, 2005, 150(1): 17-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2004.06.018 pmid: 15837005 |
| [15] |
Wenk RE. Testing for parentage and kinship. Curr Opin Hematol, 2004, 11(5): 357-361.
pmid: 15666661 |
| [16] | Børsting C, Morling N. Next generation sequencing and its applications in forensic genetics. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2015 18: 78-89. |
| [17] |
Daniel R, Santos C, Phillips C, Fondevila M, Carracedo A, Lareu MV, McNevin D. A SNaPshot of next generation sequencing for forensic SNP analysis. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2015, 14: 50-60.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2014.08.013 |
| [18] | Bornman DM, Hester ME, Schuetter JM, Kasoji MD, Minard-Smith A, Barden CA, Nelson SC, Godbold GD, Baker CH, Yang BY, Walther JE, Tornes IE, Yan PS, Rodriguez B, Bundschuh R, Dickens ML, Young BA, Faith SA. Short-read, high-throughput sequencing technology for STR genotyping. Biotech Rapid Dispatches, 2012, 2012: 1-6. |
| [19] |
Fan HL, Du ZM, Wang FF, Wang X, Wen SQ, Wang LX, Du PX, Liu H, Cao SP, Luo ZM, Han BB, Huang PY, Zhu BF, Qiu PM. The forensic landscape and the population genetic analyses of Hainan Li based on massively parallel sequencing DNA profiling. Int J Legal Med, 2021, 135(4): 1295-1317.
doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02590-3 pmid: 33847803 |
| [20] |
Delest A, Godfrin D, Chantrel Y, Ulus A, Vannier J, Faivre M, Hollard C, Laurent FX. Sequenced-based French population data from 169 unrelated individuals with Verogen’s ForenSeq DNA Signature Prep Kit. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2020, 47: 102304.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2020.102304 |
| [21] |
Tao RY, Qi WJ, Chen C, Zhang JY, Yang ZH, Song W, Zhang SH, Li CT. Pilot study for forensic evaluations of the Precision ID GlobalFilerTM NGS STR Panel v2 with the Ion S5TM system. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2019, 43: 102147.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.102147 |
| [22] |
Fan HL, Wang LX, Liu CH, Lu XY, Xu XD, Ru K, Qiu PM, Liu C, Wen SQ. Development and validation of a novel 133-plex forensic STR panel (52 STRs and 81 Y-STRs) using single-end 400 bp massive parallel sequencing. Int J Legal Med, 2022, 136(2): 447-464.
doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02738-1 |
| [23] |
Tao RY, Wang SY, Chen AQ, Xia RC, Zhang XC, Yang Q, Qu YL, Zhang SH, Li CT. Parallel sequencing of 87 STR and 294 SNP markers using the prototype of the SifaMPS panel on the MiSeq FGxTM system. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2021, 52: 102490.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2021.102490 |
| [24] |
Li R, Shen XF, Chen H, Peng D, Wu RG, Sun HY. Developmental validation of the MGIEasy Signature Identification Library Prep Kit, an all-in-one multiplex system for forensic applications. Int J Legal Med, 2021, 135(3): 739-753.
doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02507-0 pmid: 33523251 |
| [25] |
Silvery J, Ganschow S, Wiegand P, Tiemann C. Developmental validation of the monSTR identity panel, a forensic STR multiplex assay for massively parallel sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2020, 46: 102236.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2020.102236 |
| [26] |
Ganschow S, Silvery J, Tiemann C. Development of a multiplex forensic identity panel for massively parallel sequencing and its systematic optimization using design of experiments. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2019, 39: 32-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.11.023 |
| [27] |
Fattorini P, Previderé C, Carboni I, Marrubini G, Sorçaburu-Cigliero S, Grignani P, Bertoglio B, Vatta P, Ricci U. Performance of the ForenSeqTM DNA Signature Prep Kit on highly degraded samples. Electrophoresis, 2017, 38(8): 1163-1174.
doi: 10.1002/elps.201600290 pmid: 28078776 |
| [28] |
Zhang QZ, Zhou Z, Liu QQ, Liu LY, Shao LT, Zhang ML, Ding XR, Gao Y, Wang SQ. Evaluation of the performance of Illumina’s ForenSeq™ system on serially degraded samples. Electrophoresis, 2018, 39(21): 2674-2684.
doi: 10.1002/elps.v39.21 |
| [29] |
Sharma V, Van der Plaat DA, Liu YX, Wurmbach E. Analyzing degraded DNA and challenging samples using the ForenSeq™ DNA Signature Prep Kit. Sci Justice, 2020, 60(3): 243-252.
doi: S1355-0306(19)30153-4 pmid: 32381241 |
| [30] | Cheng F, Yan JW. Research progresses of next-generation sequencing applied in forensic DNA analysis of difficult specimens. Life Sci Res, 2018, 22(6): 511-516. |
| 程凤, 严江伟. 二代测序技术在疑难生物检材法医DNA检验的研究进展. 生命科学研究, 2018, 22(6): 511-516. | |
| [31] | SWGDAM validation guidelines for forensic DNA analysis methods(2016).https://www.swgdam.org/_files/ugd/4344b0_813b241e8944497e99b9c45b163b76bd.pdf |
| [32] |
Holt A, Wootton SC, Mulero JJ, Brzoska PM, Langit E, Green RL. Developmental validation of the Quantifiler(®) HP and Trio Kits for human DNA quantification in forensic samples. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2016, 21: 145-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.12.007 |
| [33] |
Mo SK, Ren ZL, Yang YR, Liu YC, Zhang JJ, Wu HJ, Li Z, Bo XC, Wang SQ, Yan JW, Ni M. A 472-SNP panel for pairwise kinship testing of second-degree relatives. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2018, 34: 178-185.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.02.019 |
| [34] |
Woerner AE, King JL, Budowle B.Fast STR allele identification with STRait Razor 3.0. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2017, 30: 18-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.05.008 |
| [35] |
Chang CC, Chow CC, Tellier LC, Vattikuti S, Purcell SM, Lee JJ. Second-generation PLINK: rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience, 2015, 4: 7.
doi: 10.1186/s13742-015-0047-8 pmid: 25722852 |
| [36] |
Churchill JD, Novroski NMM, King JL, Seah LH, Budowle B. Population and performance analyses of four major populations with Illumina’s FGx forensic genomics system. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2017, 30: 81-92.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.06.004 |
| [37] | Ruan XY, Wang WN, Yang YR, Xie BB, Chen J, Liu YC, Yan JW. Genetic variability and phylogenetic analysis of 39 short tandem repeat loci in Beijing Han population. Hereditas (Beijing), 2015 37(7): 683-691. |
| 阮修艳, 王伟妮, 杨雅冉, 谢兵兵, 陈婧, 刘雅诚, 严江伟. 北京汉族群体39个短串联重复序列基因座多态性及其遗传关系. 遗传, 2015, 37(7): 683-691. | |
| [38] |
Pang JB, Rao M, Chen QF, Ji AQ, Zhang C, Kang KL, Wu H, Ye J, Nie SJ, Wang L. A 124-plex microhaplotype panel based on next-generation sequencing developed for forensic applications. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 1945.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58980-x |
| [39] | Zhang YM, Yu DY, Wang Y, Yang Y, Li R, Hong L, Wan ZB, Sun HY. The pilot study of the phasing method for STR haplotype. Chin J Forensic Med, 2017, 32(1): 5-8. |
| 张胤鸣, 余丹媛, 王瑛, 杨阳, 李燃, 洪玲, 万志波, 孙宏钰. STR基因座单倍型的推断方法初探. 中国法医学杂志, 2017, 32(1): 5-8. | |
| [40] | 于昕, 唐剑频, 蒋丰慧. 6个X-STR基因座的连锁不平衡和单倍型分析. 中国法医学杂志, 2013, 28(6): 506-507. |
| [41] | Casals F, Rasal R, Anglada R, Tormo M, Bonet N, Rivas N, Vásquez P, Calafell F. A forensic population database in El Salvador: 58 STRs and 94 SNPs. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2022, 57: 102646. |
| [42] |
Elwick K, Zeng XP, King J, Budowle B, Hughes-Stamm S. Comparative tolerance of two massively parallel sequencing systems to common PCR inhibitors. Int J Legal Med, 2018, 132(4): 983-995.
doi: 10.1007/s00414-017-1693-4 pmid: 28956146 |
| [43] | Jäger AC, Alvarez ML, Davis CP, Guzmán E, Han Y, Way L, Walichiewicz P, Silva D, Pham N, Caves G, Bruand J, Schlesinger F, Pond SJK, Varlaro J, Stephens KM, Holt CL. Developmental validation of the MiSeq FGx forensic genomics system for targeted next generation sequencing in forensic DNA casework and database laboratories. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2017, 28: 52-70. |
| [44] | Allentoft ME, Collins M, Harker D, Haile J, Oskam CL, Hale ML, Campos PF, Samaniego JA, Gilbert MTP, Willerslev E, Zhang GJ, Scofield RP, Holdaway RN, Bunce M. The half-life of DNA in bone: measuring decay kinetics in 158 dated fossils. Proc Biol Sci, 2012, 279(1748): 4724-33 |
| [45] |
Yu J, Xiao C, Wei T, Pan C, Yi SH, Huang DX. Allele dropout at the STR loci TH01 and vWA and identification of two new point mutations upstream of the repeat region at the vWA locus. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2016, 23: e14-e17.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.04.006 |
| [46] |
Hendrickson BC, Leclair B, Forrest S, Ryan J, Ward BE, Petersen D, Kupferschmid TD, Scholl T. Accurate STR allele designations at the FGA and vWA loci despite primer site polymorphisms. J Forensic Sci, 2004, 49(2): 250-254.
pmid: 15027538 |
| [47] |
Gettings KB, Aponte RA, Vallone PM, Butler JM. STR allele sequence variation: current knowledge and future issues. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2015, 18: 118-130.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.06.005 |
| [48] | You C, Zhao DQ, Liang CB, Zhou CH. Review of the PCR primer design method. Mod Agric Sci Technol, 2011, (17): 48-51. |
| 尤超, 赵大球, 梁乘榜, 周春华. PCR引物设计方法综述. 现代农业科技, 2011, (17): 48-51. |
| [1] | Mengnan Cui, Yan Guo, Yarong Wu, Guangqian Pei, Yujun Cui. Progress on the quality control technology of next generation sequencing library [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(2): 140-148. |
| [2] | Ke Zhang, Guangde Feng, Baoyun Zhang, Wei Xiang, Long Chen, Fang Yang, Mingxing Chu, Pingqing Wang. Application of epigenetic markers in molecular breeding of the swine [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016, 38(7): 634-643. |
| [3] | Fang Liu, Xiaozhen Song, Hua Xie, Xiaoli Chen. The pathogenicity of somatic mutation to common tumors and developmental malformation of the nervous system [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(3): 196-205. |
| [4] | Wenke Li, Fengyu Li, Siyao Zhang, Bin Cai, Na Zheng, Yu Nie, Dao Zhou, Qian Zhao. Automatic analysis pipeline of next-generation sequencing data [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(6): 618-624. |
| [5] | Sheng Shen, Yanchun Qu, Jun Zhang. The application of next generation sequencing on epigenetic study [J]. HEREDITAS, 2014, 36(3): 256-275. |
| [6] | Huijun Yuan, Yu Lu. Application of next generation sequencing in gene identification and genetic diagnosis of hereditary hearing loss [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(11): 1112-1120. |
| [7] | GAO Shan, ZHANG Ning, LI Bo, XU Shuo, YE Yan-Bo, RUAN Ji-Shou. Processing and analysis of ChIP-seq data [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(6): 773-783. |
| [8] | TANG Hai-Ming, CHEN Hong, ZHANG Jing, REN Jing-Yi, XU Ning. Application of next generation sequencing in microRNA detection [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(6): 784-792. |
| [9] | LIANG Ye, CHEN Shuang-Yan, LIU Gong-She. Application of next generation sequencing techniques in plant transcriptome [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(12): 1317-1326. |
| [10] | BO Xing-Hua, SHU Hai-Yang, MARJANI Sadie L.. Technological advances in single-cell genomic analyses [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(1): 17-24. |
| [11] | QIN Qiao-Beng, ZHANG Lan-Lan, LI Na-Yi, CUI Yong-Yi, XU Kai. Optimizing of cDNA preparation for next generation sequencing [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(9): 974-977. |
| [12] | . Establishment of target genomic DNA capturing system for next generation sequencing [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(12): 1296-1303. |
| [13] | HE Jun-Ping, RUAN Song-Lin, ZHU Shui-Jin, MA Hua-Sheng. Amplified consensus genetic markers and its application in plants [J]. HEREDITAS, 2009, 31(9): 913-920. |
| [14] | HOU Ning , ZHANG Yan, LU Cui-Yun, LI Yong , LI Da-Yu , JI Xu , DING Lei , SUN Xiao-Wen UP. Genetic potential analysis of Germany mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) using microsatellite markers [J]. HEREDITAS, 2007, 29(12): 1509-1518. |
| [15] | Zhang Zheng-Hai, Kang Xiang-Yang. Advances in Researches on Genetic Markers of 2n Gametes [J]. HEREDITAS, 2006, 28(1): 105-109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||