Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (6): 625-635.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-307
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and progress of proximity labeling technology in the study of protein-protein interactions
Xinru Xu1( ), Benhua Qiu2,3(
), Benhua Qiu2,3( ), Xiumin Yan1(
), Xiumin Yan1( )
)
- 1. Ministry of Education-Shanghai Key Laboratory of Children’s Environmental Health, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200092, China
2. Key Laboratory of Multi-Cell Systems, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2024-11-18Revised:2024-12-23Online:2025-06-20Published:2025-01-10 -
Contact:Xiumin Yan E-mail:9894678@sjtu.edu.cn;qiubenhua2018@sibcb.ac.cn;yanx@shsmu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(32470724)
Cite this article
Xinru Xu, Benhua Qiu, Xiumin Yan. Application and progress of proximity labeling technology in the study of protein-protein interactions[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(6): 625-635.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
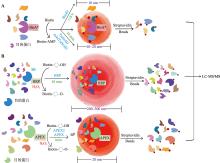
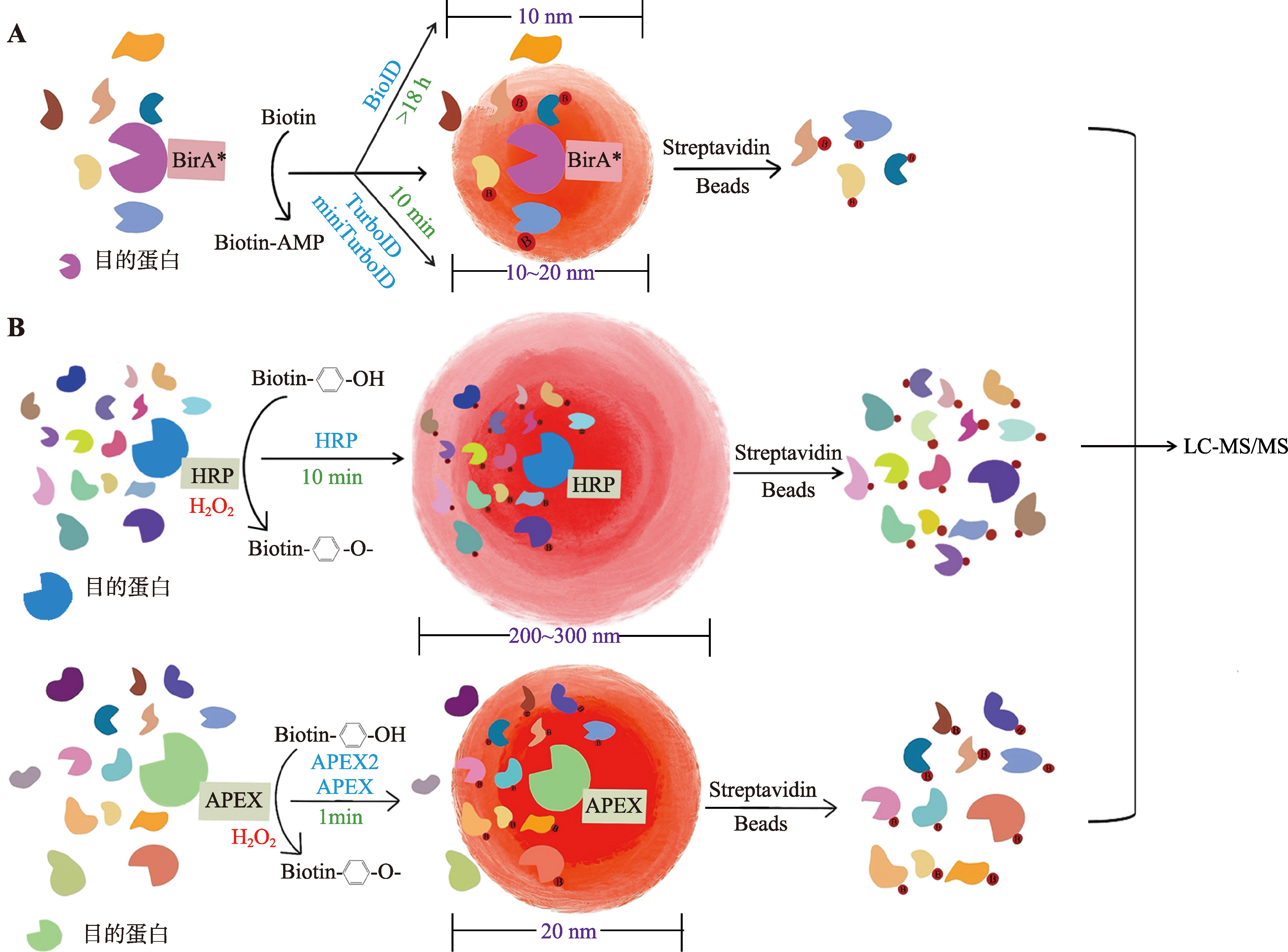
Table 1
Comparison of two proximity labeling techniques"
| 方法 | 基于生物素连接酶的邻近标记技术 | 基于过氧化物酶的邻近标记技术 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioID | TurboID | miniTurboID | HRP | APEX | APEX2 | |
| 分子量大小 | 35 kDa | 35 kDa | 28 kDa | 44 kDa | 27 kDa | 27 kDa |
| 特点 | BirA来自大肠杆菌,BioID基于BirA的R118G突变体(BirA*) | 改良型BirA*,通过15个点突变提高催化效率,标记范围约为10~20 nm,标记时间为10 min | TurboID的改良版本,删除了N端区域并只携带有13个点突变,小分子量减少对目标蛋白功能和定位的干扰 | 酶催化活性受pH值的影响,在不同的细胞区室中酶催化活性有所不同 | APX是一种植物酶,经过工程化改造的APEX,催化活性高 | APEX的A134P突变体,具有更高的催化活性和稳定性 |
| 是否需要H2O2 | 否 | 是 | ||||
| 反应底物 | Biotin | Biotin-phenol | ||||
| 反应时间 | 18~24 h | 10 min | 10 min | 5~10 min | ≤1 min | ≤1 min |
| 标记范围 | 10 nm | 10~20 nm | 10~20 nm | 200~300 nm | 20 nm | 20 nm |
| 背景噪音 | 中等 | 中等 | 低 | 高 | 中等 | 中等 |
| 应用 | 用于识别邻近蛋白,适合研究细胞内相互作用 | 捕获瞬时和动态蛋白质相互作用,应用于多种模式生物 | 用于标记邻近蛋白,但应用受到细胞环境限制 | 用于空间蛋白质组和蛋白质相互作用研究以及电镜成像 | ||
| [1] |
Omranian S, Nikoloski Z, Grimm DG. Computational identification of protein complexes from network interactions: present state, challenges, and the way forward. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2022, 20: 2699-2712.
pmid: 35685359 |
| [2] |
Wang TW, Yang NN, Liang C, Xu HJ, An YF, Xiao S, Zheng MY, Liu L, Wang GZ, Nie L. Detecting protein- protein interaction based on protein fragment complementation assay. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2020, 21(6): 598-610.
pmid: 32053071 |
| [3] |
Wang S, Wu RX, Lu JQ, Jiang YJ, Huang T, Cai YD. Protein-protein interaction networks as miners of biological discovery. Proteomics, 2022, 22(15-16): e2100190.
pmid: 35567424 |
| [4] |
Jia XY, Lin LS, Guo SQ, Zhou LL, Jin GW, Dong JY, Xiao JM, Xie XQ, Li YM, He SC, Wei ZY, Yu C. CLASP- mediated competitive binding in protein condensates directs microtubule growth. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 6509.
pmid: 39095354 |
| [5] |
Dikic I, Schulman BA. An expanded lexicon for the ubiquitin code. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2023, 24(4): 273-287.
pmid: 36284179 |
| [6] |
Shkel O, Kharkivska Y, Kim YK, Lee JS. Proximity labeling techniques: a multi-omics toolbox. Chem Asian J, 2022, 17(2): e202101240.
pmid: 34850572 |
| [7] |
Brückner A, Polge C, Lentze N, Auerbach D, Schlattner U. Yeast two-hybrid, a powerful tool for systems biology. Int J Mol Sci, 2009, 10(6): 2763-2788.
pmid: 19582228 |
| [8] |
Tang ZY, Takahashi Y. Analysis of protein-protein interaction by Co-IP in human cells. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1794: 289-296.
pmid: 29855966 |
| [9] |
Chapman-Smith A, Cronan JE JR. Molecular biology of biotin attachment to proteins. J Nutr, 1999, 129(2S Suppl): 477S-484S.
pmid: 10064313 |
| [10] |
Xu YF, Fan XQ, Hu Y. In vivo interactome profiling by enzyme-catalyzed proximity labeling. Cell Biosci, 2021, 11(1): 27.
pmid: 33514425 |
| [11] |
Bosch JA, Chen CL, Perrimon N. Proximity-dependent labeling methods for proteomic profiling in living cells: an update. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol, 2021, 10(1): e392.
pmid: 32909689 |
| [12] |
Branon TC, Bosch JA, Sanchez AD, Udeshi ND, Svinkina T, Carr SA, Feldman JL, Perrimon N, Ting AY. Efficient proximity labeling in living cells and organisms with TurboID. Nat Biotechnol, 2018, 36(9): 880-887.
pmid: 30125270 |
| [13] |
Guo JY, Guo S, Lu S, Gong J, Wang L, Ding LQ, Chen QJ, Liu W. The development of proximity labeling technology and its applications in mammals, plants, and microorganisms. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 269.
pmid: 37777761 |
| [14] |
Qin W, Cho KF, Cavanagh PE, Ting AY. Deciphering molecular interactions by proximity labeling. Nat Methods, 2021, 18(2): 133-143.
pmid: 33432242 |
| [15] |
Roux KJ, Kim DI, Raida M, Burke B. A promiscuous biotin ligase fusion protein identifies proximal and interacting proteins in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol, 2012, 196(6): 801-810.
pmid: 22412018 |
| [16] |
Wang YK, Qin W. Revealing protein trafficking by proximity labeling-based proteomics. Bioorg Chem, 2024, 143: 107041.
pmid: 38134520 |
| [17] |
Hung V, Lam SS, Udeshi ND, Svinkina T, Guzman G, Mootha VK, Carr SA, Ting AY. Proteomic mapping of cytosol-facing outer mitochondrial and ER membranes in living human cells by proximity biotinylation. eLife, 2017, 6: e24463.
pmid: 28441135 |
| [18] |
Yang R, Meyer AS, Droujinine IA, Udeshi ND, Hu YH, Guo JJ, McMahon JA, Carey DK, Xu C, Fang Q, Sha JH, Qin SS, Rocco D, Wohlschlegel J, Ting AY, Carr SA, Perrimon N, McMahon AP. A genetic model for in vivo proximity labelling of the mammalian secretome. Open Biol, 2022, 12(8): 220149.
pmid: 35946312 |
| [19] |
Jamilloux Y, Lagrange B, Di Micco A, Bourdonnay E, Provost A, Tallant R, Henry T, Martinon F. A proximity- dependent biotinylation (BioID) approach flags the p62/sequestosome-1 protein as a caspase-1 substrate. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293(32): 12563-12575.
pmid: 29929983 |
| [20] |
Hollstein LS, Schmitt K, Valerius O, Stahlhut G, Pöggeler S. Establishment of in vivo proximity labeling with biotin using TurboID in the filamentous fungus sordaria macrospora. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 17727.
pmid: 36272986 |
| [21] |
Dani N, Herbst RH, McCabe C, Green GS, Kaiser K, Head JP, Cui J, Shipley FB, Jang A, Dionne D, Nguyen L, Rodman C, Riesenfeld SJ, Prochazka J, Prochazkova M, Sedlacek R, Zhang F, Bryja V, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Habib N, Regev A, Lehtinen MK. A cellular and spatial map of the choroid plexus across brain ventricles and ages. Cell, 2021, 184(11): 3056-3074.e21.
pmid: 33932339 |
| [22] |
Brown MC, Benson TE. Transneuronal labeling of cochlear nucleus neurons by HRP-labeled auditory nerve fibers and olivocochlear branches in mice. J Comp Neurol, 1992, 321(4): 645-665.
pmid: 1380524 |
| [23] |
Han S, Udeshi ND, Deerinck TJ, Svinkina T, Ellisman MH, Carr SA, Ting AY. Proximity biotinylation as a method for mapping proteins associated with mtDNA in living cells. Cell Chem Biol, 2017, 24(3): 404-414.
pmid: 28238724 |
| [24] |
Go CD, Knight JDR, Rajasekharan A, Rathod B, Hesketh GG, Abe KT, Youn JY, Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Zhang H, Zhu LY, Popiel E, Lambert JP, Coyaud É, Cheung SWT, Rajendran D, Wong CJ, Antonicka H, Pelletier L, Palazzo AF, Shoubridge EA, Raught B, Gingras AC. A proximity-dependent biotinylation map of a human cell. Nature, 2021, 595(7865): 120-124.
pmid: 34079125 |
| [25] |
Jablonska Z. Proximity-based labelling for proteomic mapping. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2024, 21(8): 521.
pmid: 38898320 |
| [26] |
Buoncristiani MR, Howard PK, Otsuka AJ. DNA-binding and enzymatic domains of the bifunctional biotin operon repressor (BirA) of Escherichia coli. Gene, 1986, 44(2-3): 255-261.
pmid: 3536662 |
| [27] |
Choi-Rhee E, Schulman H, Cronan JE. Promiscuous protein biotinylation by Escherichia coli biotin protein ligase. Protein Sci, 2004, 13(11): 3043-3050.
pmid: 15459338 |
| [28] |
Chen I, Howarth M, Lin WY, Ting AY. Site-specific labeling of cell surface proteins with biophysical probes using biotin ligase. Nat Methods, 2005, 2(2): 99-104.
pmid: 15782206 |
| [29] |
Kim DI, Birendra KC, Zhu WH, Motamedchaboki K, Doye V, Roux KJ. Probing nuclear pore complex architecture with proximity-dependent biotinylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(24): E2453-E2461.
pmid: 24927568 |
| [30] |
Stevens LM, Zhang Y, Volnov Y, Chen G, Stein DS. Isolation of secreted proteins from Drosophila ovaries and embryos through in vivo BirA-mediated biotinylation. PLoS One, 2019, 14(10): e0219878.
pmid: 31658274 |
| [31] |
Alwash M, Gariépy J. Labeling cell surface receptors with ligand.BirA* bispecifics. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, 2022, 5(2): 62-69.
pmid: 36742360 |
| [32] |
Kanzler CR, Donohue M, Dowdle ME, Sheets MD. TurboID functions as an efficient biotin ligase for BioID applications in Xenopus embryos. Dev Biol, 2022, 492: 133-138.
pmid: 36270327 |
| [33] |
May DG, Scott KL, Campos AR, Roux KJ. Comparative application of BioID and TurboID for protein- proximity biotinylation. Cells, 2020, 9(5): 1070.
pmid: 32344865 |
| [34] |
Cheng LC, Zhang X, Abhinav K, Nguyen JA, Baboo S, Martinez-Bartolomé S, Branon TC, Ting AY, Loose E, Yates JR 3rd, Gerace L. Shared and distinctive neighborhoods of Emerin and Lamin B receptor revealed by proximity labeling and quantitative proteomics. J Proteome Res, 2022, 21(9): 2197-2210.
pmid: 35972904 |
| [35] |
Cho KF, Branon TC, Udeshi ND, Myers SA, Carr SA, Ting AY. Proximity labeling in mammalian cells with TurboID and split-TurboID. Nat Protoc, 2020, 15(12): 3971-3999.
pmid: 33139955 |
| [36] |
Li YY, Zhang YL, Dinesh-Kumar SP. TurboID-based proximity labeling: a method to decipher protein-protein interactions in plants. Methods Mol Biol, 2024, 2724: 257-272.
pmid: 37987912 |
| [37] |
Cygan AM, Jean Beltran PM, Mendoza AG, Branon TC, Ting AY, Carr SA, Boothroyd JC. Proximity-labeling reveals novel host and parasite proteins at the toxoplasma parasitophorous vacuole membrane. mBio, 2021, 12(6): e0026021.
pmid: 34749525 |
| [38] |
Pirayeshfard L, Luo S, Githaka JM, Saini A, Touret N, Goping IS, Julien O. Comparing the BAD protein interactomes in 2D and 3D cell culture using proximity labeling. J Proteome Res, 2024, 23(8): 3433-3443.
pmid: 38959414 |
| [39] |
Mair A, Xu SL, Branon TC, Ting AY, Bergmann DC. Proximity labeling of protein complexes and cell-type- specific organellar proteomes in Arabidopsis enabled by TurboID. eLife, 2019, 8: e47864.
pmid: 31535972 |
| [40] |
Liu W, Long YF, Bao YF, Li Y, Deng MX, Yang XY, Zhu H, Su YT. Efficient TurboID-based proximity labelling method for identifying terminal sialic acid glycosylation in living cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2022, 54(12): 1841-1853.
pmid: 36789692 |
| [41] |
Hopkins C, Gibson A, Stinchcombe J, Futter C. Chimeric molecules employing horseradish peroxidase as reporter enzyme for protein localization in the electron microscope. Methods Enzymol, 2000, 327: 35-45.
pmid: 11044972 |
| [42] |
Loh KH, Stawski PS, Draycott AS, Udeshi ND, Lehrman EK, Wilton DK, Svinkina T, Deerinck TJ, Ellisman MH, Stevens B, Carr SA, Ting AY. Proteomic analysis of unbounded cellular compartments: synaptic clefts. Cell, 2016, 166(5): 1295-1307.e21.
pmid: 27565350 |
| [43] |
Veitch NC. Horseradish peroxidase: a modern view of a classic enzyme. Phytochemistry, 2004, 65(3): 249-259.
pmid: 14751298 |
| [44] |
Henriksen A, Smith AT, Gajhede M. The structures of the horseradish peroxidase C-ferulic acid complex and the ternary complex with cyanide suggest how peroxidases oxidize small phenolic substrates. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274(49): 35005-35011.
pmid: 10574977 |
| [45] |
Yuan F, Li Y, Zhou XY, Meng PY, Zou P. Spatially resolved mapping of proteome turnover dynamics with subcellular precision. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 7217.
pmid: 37940635 |
| [46] |
Martell JD, Deerinck TJ, Sanca Y, Poulos TL, Mootha VK, Sosinsky GE, Ellisman MH, Ting AY. Engineered ascorbate peroxidase as a genetically encoded reporter for electron microscopy. Nat Biotechnol, 2012, 30(11): 1143-1148.
pmid: 23086203 |
| [47] |
Karpinski S, Escobar C, Karpinska B, Creissen G, Mullineaux PM. Photosynthetic electron transport regulates the expression of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase genes in Arabidopsis during excess light stress. Plant Cell, 1997, 9(4): 627-640.
pmid: 9144965 |
| [48] |
Li SC. Novel insight into functions of ascorbate peroxidase in higher plants: more than a simple antioxidant enzyme. Redox Biol, 2023, 64: 102789.
pmid: 37352686 |
| [49] |
Sharp KH, Mewies M, Moody PCE, Raven EL. Crystal structure of the ascorbate peroxidase-ascorbate complex. Nat Struct Biol, 2003, 10(4): 303-307.
pmid: 12640445 |
| [50] |
Raven EL, Lad L, Sharp KH, Mewies M, Moody PCE. Defining substrate specificity and catalytic mechanism in ascorbate peroxidase. Biochem Soc Symp, 2004, (71): 27-38.
pmid: 15777010 |
| [51] |
Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Samson R, Gingras AC. Proximity dependent biotinylation: key enzymes and adaptation to proteomics approaches. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2020, 19(5): 757-773.
pmid: 32127388 |
| [52] |
Hung V, Udeshi ND, Lam SS, Loh KH, Cox KJ, Pedram K, Carr SA, Ting AY. Spatially resolved proteomic mapping in living cells with the engineered peroxidase APEX2. Nat Protoc, 2016, 11(3): 456-475.
pmid: 26866790 |
| [53] |
Lam SS, Martell JD, Kamer KJ, Deerinck TJ, Ellisman MH, Mootha VK, Ting AY. Directed evolution of APEX2 for electron microscopy and proximity labeling. Nat Methods, 2015, 12(1): 51-54.
pmid: 25419960 |
| [54] |
Han YS, Branon T C, Martell JD, Boassa D, Shechner D, Ellisman MH, Ting A. Directed evolution of split APEX2 peroxidase. ACS Chem Biol, 2019, 14(4): 619-635.
pmid: 30848125 |
| [55] |
Martell JD, Deerinck TJ, Lam SS, Ellisman MH, Ting AY. Electron microscopy using the genetically encoded APEX2 tag in cultured mammalian cells. Nat Protoc, 2017, 12(9): 1792-1816.
pmid: 28796234 |
| [56] |
Golas S, Chory EJ. Proximity labeling of endogenous protein interactions enabled by directed evolution. Trends Biotechnol, 2023, 41(3): 301-303.
pmid: 36710130 |
| [57] |
Hung V, Zou P, Rhee HW, Udeshi ND, Cracan V, Svinkina T, Carr SA, Mootha VK, Ting AY. Proteomic mapping of the human mitochondrial intermembrane space in live cells via ratiometric APEX tagging. Mol Cell, 2014, 55(2): 332-341.
pmid: 25002142 |
| [58] |
Hwang J, Espenshade PJ. Proximity-dependent biotin labelling in yeast using the engineered ascorbate peroxidase APEX2. Biochem J, 2016, 473(16): 2463-2469.
pmid: 27274088 |
| [59] |
Singer-Krüger B, Fröhlich T, Franz-Wachtel M, Nalpas N, Macek B, Jansen RP. APEX2-mediated proximity labeling resolves protein networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. FEBS J, 2020, 287(2): 325-344.
pmid: 31323700 |
| [60] |
Mathew B, Bathla S, Williams KR, Nairn AC. Deciphering spatial protein-protein interactions in brain using proximity labeling. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2022, 21(11): 100422.
pmid: 36198386 |
| [61] |
Milione RR, Schell BB, Douglas CJ, Seath CP. Creative approaches using proximity labeling to gain new biological insights. Trends Biochem Sci, 2024, 49(3): 224-235.
pmid: 38160064 |
| [62] |
Roux KJ, Kim DI, Burke B, May DG. BioID: a screen for protein-protein interactions. Curr Protoc Protein Sci, 2018, 91: 19.23.1-19.23.15.
pmid: 29516480 |
| [63] |
Zhang T, Fassl A, Vaites LP, Fu SP, Sicinski P, Paulo JA, Gygi SP. Interrogating kinase-substrate relationships with proximity labeling and phosphorylation enrichment. J Proteome Res, 2022, 21(2): 494-506.
pmid: 35044772 |
| [64] |
Niinae T, Imami K, Sugiyama N, Ishihama Y. Identification of endogenous kinase substrates by proximity labeling combined with kinase perturbation and phosphorylation motifs. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2021, 20: 100119.
pmid: 34186244 |
| [65] |
Ubersax JA, Ferrell JE JR. Mechanisms of specificity in protein phosphorylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 8(7): 530-541.
pmid: 17585314 |
| [66] | Deng XY, Jiang Y, He FC. Technique progress in the study of protein/peptide phosphorylation. Hereditas (Beijing), 2007, 29(10): 1163-1166. |
| 邓新宇, 姜颖, 贺福初. 磷酸化蛋白质及多肽相关研究的技术进展. 遗传, 2007, 29(10): 1163-1166. | |
| [67] |
Dang T, Yu J, Cao ZH, Zhang BJ, Li SS, Xin Y, Yang LY, Lou RH, Zhuang M, Shui WQ. Endogenous cell membrane interactome mapping for the GLP-1 receptor in different cell types. Nat Chem Biol, 2024.
pmid: 39227725 |
| [68] | Rondón Ortiz AN, Zhang LS, Ash PEA, Basu A, Puri S, van der Spek SJ, Wang ZH, Dorrian L, Emili A, Wolozin B. Proximity labeling reveals dynamic changes in the SQSTM1 protein network. bioRxiv, 2024, doi: 10.1101/2023.12.12.571324. |
| [69] |
Paek J, Kalocsay M, Staus DP, Wingler L, Pascolutti R, Paulo JA, Gygi SP, Kruse AC. Multidimensional tracking of GPCR signaling via peroxidase-catalyzed proximity labeling. Cell, 2017, 169(2): 338-349.e11.
pmid: 28388415 |
| [70] |
Lobingier BT, Hüttenhain R, Eichel K, Miller KB, Ting AY, von Zastrow M, Krogan NJ. An approach to spatiotemporally resolve protein interaction networks in living cells. Cell, 2017, 169(2): 350-360.e12.
pmid: 28388416 |
| [71] |
Liu Q, Zheng J, Sun WP, Huo YB, Zhang LY, Hao PL, Wang HP, Zhuang M. A proximity-tagging system to identify membrane protein-protein interactions. Nat Methods, 2018, 15(9): 715-722.
pmid: 30104635 |
| [72] |
Zhang R, Anguiano M, Aarrestad IK, Chandra J, Vadde SS, Olson DE, Kim CK. Rapid, biochemical tagging of cellular activity history in vivo. bioRxiv, 2024, doi: 10.1101/2023.09.06.556431.
pmid: 38798353 |
| [73] |
Terracciano R, Preianò M, Fregola A, Pelaia C, Montalcini T, Savino R. Mapping the SARS-CoV-2-Host protein- protein interactome by affinity purification mass spectrometry and proximity-dependent biotin labeling: a rational and straightforward route to discover host-directed Anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(2): 532.
pmid: 33430309 |
| [74] |
Soto JS, Jami-Alahmadi Y, Chacon J, Moye SL, Diaz- Castro B, Wohlschlegel JA, Khakh BS. Astrocyte-neuron subproteomes and obsessive-compulsive disorder mechanisms. Nature, 2023, 616(7958): 764-773.
pmid: 37046092 |
| [75] |
Chen L, Li N, Zhang MQ, Sun MM, Bian JX, Yang B, Li ZCX, Wang JY, Li F, Shi XM, Wang Y, Yuan F, Zou P, Shan CL, Wang J. APEX2-based proximity labeling of Atox1 identifies CRIP2 as a nuclear copper-binding protein that regulates autophagy activation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2021, 60(48): 25346-25355.
pmid: 34550632 |
| [76] |
Banani SF, Lee HO, Hyman AA, Rosen MK. Biomolecular condensates: organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18(5): 285-298.
pmid: 28225081 |
| [77] |
Mick DU, Rodrigues RB, Leib RD, Adams CM, Chien AS, Gygi SP, Nachury MV. Proteomics of primary cilia by proximity labeling. Dev Cell, 2015, 35(4): 497-512.
pmid: 26585297 |
| [78] |
Chen CL, Hu Y, Udeshi ND, Lau TY, Wirtz-Peitz F, He L, Ting AY, Carr SA, Perrimon N. Proteomic mapping in live Drosophila tissues using an engineered ascorbate peroxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(39): 12093-12098.
pmid: 26362788 |
| [79] |
Le Guerroué F, Eck F, Jung J, Starzetz T, Mittelbronn M, Kaulich M, Behrends C. Autophagosomal content profiling reveals an LC3C-dependent piecemeal mitophagy pathway. Mol Cell, 2017, 68(4): 786-796.e6.
pmid: 29149599 |
| [80] |
Bersuker K, Peterson CWH, To M, Sahl SJ, Savikhin V, Grossman EA, Nomura DK, Olzmann JA. A proximity labeling strategy provides insights into the composition and dynamics of lipid droplet proteomes. Dev Cell, 2018, 44(1): 97-112.e7.
pmid: 29275994 |
| [81] |
Qin W, Cheah JS, Xu C, Messing J, Freibaum BD, Boeynaems S, Taylor JP, Udeshi ND, Carr SA, Ting AY. Dynamic mapping of proteome trafficking within and between living cells by TransitID. Cell, 2023, 186(15): 3307-3324.e30.
pmid: 37385249 |
| [82] |
Zhou Y, Zou P. The evolving capabilities of enzyme- mediated proximity labeling. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2021, 60: 30-38.
pmid: 32801087 |
| [83] |
Rhee HW, Zou P, Udeshi ND, Martell JD, Mootha VK, Carr SA, Ting AY. Proteomic mapping of mitochondria in living cells via spatially restricted enzymatic tagging. Science, 2013, 339(6125): 1328-1331.
pmid: 23371551 |
| [84] |
Bhushan V, Nita-Lazar A. Recent advancements in subcellular proteomics: growing impact of organellar protein niches on the understanding of cell biology. J Proteome Res, 2024, 23(8): 2700-2722.
pmid: 38451675 |
| [85] |
Xue MM, Hou JJ, Wang LL, Cheng DW, Lu JZ, Zheng L, Xu T. Optimizing the fragment complementation of APEX2 for detection of specific protein-protein interactions in live cells. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 12039.
pmid: 28955036 |
| [86] |
Qiu WQ, Xu ZJ, Zhang M, Zhang DD, Fan H, Li TT, Wang QF, Liu PR, Zhu ZH, Du D, Tan MJ, Wen B, Liu Y. Determination of local chromatin interactions using a combined CRISPR and peroxidase APEX2 system. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(9): e52.
pmid: 30805613 |
| [87] |
Kaewsapsak P, Shechner DM, Mallard W, Rinn JL, Ting AY. Live-cell mapping of organelle-associated RNAs via proximity biotinylation combined with protein-RNA crosslinking. eLife, 2017, 6: e29224.
pmid: 29239719 |
| [88] |
Lu MX, Wei WC. Proximity labeling to detect RNA- protein interactions in live cells. FEBS Open Bio, 2019, 9(11): 1860-1868.
pmid: 31350943 |
| [89] |
Padrón A, Iwasaki S, Ingolia NT. Proximity RNA labeling by APEX-Seq reveals the organization of translation initiation complexes and repressive RNA granules. Mol Cell, 2019, 75(4): 875-887.e5.
pmid: 31442426 |
| [90] |
Zhou Y, Wang G, Wang PC, Li ZY, Yue TQ, Wang JB, Zou P. Expanding APEX2 substrates for proximity-dependent labeling of nucleic acids and proteins in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2019, 58(34): 11763-11767.
pmid: 31240809 |
| [91] |
Liao YC, Fernandopulle MS, Wang GZ, Choi H, Hao L, Drerup CM, Patel R, Qamar S, Nixon-Abell J, Shen Y, Meadows W, Vendruscolo M, Knowles TPJ, Nelson M, Czekalska MA, Musteikyte G, Gachechiladze MA, Stephens CA, Pasolli HA, Forrest LR, St George-Hyslop P, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Ward ME. RNA granules hitchhike on lysosomes for long-distance transport, using annexin A11 as a molecular tether. Cell, 2019, 179(1): 147-164.e20.
pmid: 31539493 |
| [92] |
Han S, Zhao BS, Myers SA, Carr SA, He C, Ting AY. RNA-protein interaction mapping via MS2- or Cas13-based APEX targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(36): 22068-22079.
pmid: 32839320 |
| [1] | WANG Ming-Qiang, WU Jin-Xia, ZHANG Yu-Hong, HAN Ning, BIAN Hong-Wu, ZHU Mu-Yuan. Recent advances in the techniques of protein-protein interaction study [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(11): 1274-1283. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||