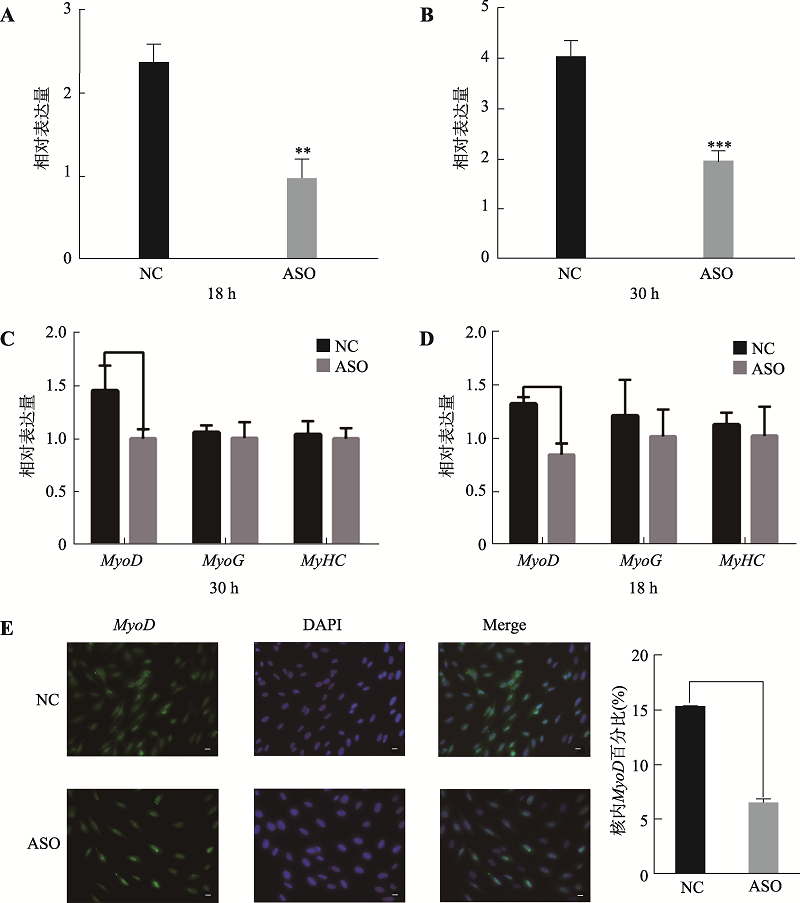
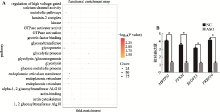
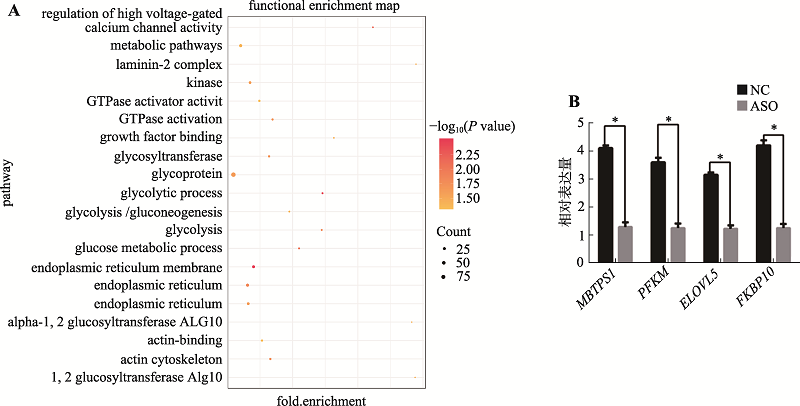
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2019, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (12): 1119-1128.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-146
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
The effect of lncRNA TCONS_00815878 on differentiation of porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells
Ziying Huang1, Long Li1, Qianqian Li1, Xiangdong Liu1,2, Changchun Li1,2( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Agricultural Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction, Ministry of Education, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
2. Guangxi Yangxiang Co., Ltd. Production Center, Guigang 537131, China
-
Received:2019-05-21Revised:2019-11-19Online:2019-12-20Published:2019-12-05 -
Contact:Li Changchun E-mail:lichangchun@mail.hzau.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No(31872322);Central University Innovation Research Fund No(2662017PY030)
Cite this article
Ziying Huang, Long Li, Qianqian Li, Xiangdong Liu, Changchun Li. The effect of lncRNA TCONS_00815878 on differentiation of porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(12): 1119-1128.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Sequences of primers used in this study"
| 目的基因 | 引物序列( 5′→3′) | 复性温度(℃) | 产物大小(bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCONS_00815878 | F: ACACCCTTTCCCAAAATCAA | 56 | 93 |
| R: GCAGACTGTCCAAATCTACCCT | |||
| PFKM | F: GAGAGCGTTTCCATGATGCTTC | 60 | 221 |
| R: AATCAAAGAGGGTGCCATCCAT | |||
| ELOVL5 | F: ATATGAAGATCATCCGCGTGCT | 60 | 59 |
| R: GTGATCTGGTGGTTGTTCTTGC | |||
| MBTPS1 | F: CCTCAACAGTGGTGGAATACGA | 60 | 179 |
| R: TTGGGATGATCTTCAAGCGTCA | |||
| MyoD | F: GGCTGCCCAAGGTGGAAATC | 60 | 170 |
| R: TGCGTCTGAGTCACCGCTGTAG | |||
| MyoG | F: ATGAGACATCCCCCTACTTCTACCA | 60 | 160 |
| R: GTCCCCAGCCCCTTATCTTCC | |||
| Pax7 | F: GGAGTACAAGAGGGAGAACCC | 60 | 122 |
| R: TTCTGAGCACGCGGCTAATC | |||
| Myf5 | F: GAATGCCATCCGCTACAT | 60 | 125 |
| R: AACTGCTGCTCTTTCTGG | |||
| MyHC | F: GTTCAGAGAAAGGCATCCCAAA | 60 | 135 |
| R: GAGAGTGACCGACACCACAAGTG | |||
| FKBP10 | F: ATGTGTCCTGGAGAGAGAAGGA | 60 | 209 |
| R: AATCAAAGAGGGTGCCATCCAT | |||
| 18S rRNA | F: TCCCGACGTGACTGCTC | 60 | 133 |
| R: GGTGACAGCGGGGTGG |
Supplementary Table 1
List of target genes"
| 基因名称 | 基因名称 | 基因名称 | 基因名称 | 基因名称 | 基因名称 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARFGAP3 | ADGRL4 | POLR3K | SLC25A26 | LAMC2 | ARHGEF10 |
| IFT27 | PGM1 | KCTD5 | MITF | INTS7 | PLXNA3 |
| PRPF40B | KIF2C | ADRA2B | GXYLT2 | LPGAT1 | REEP1 |
| IGFBP6 | SMOC2 | MAP4K4 | PPARG | HHAT | TECTA |
| NCKAP1L | CNKSR3 | TBC1D8 | GK5 | MGAT5 | SLC16A3 |
| STAT2 | NT5DC1 | CHST10 | P2RY14 | ADGRA2 | ADAMTS2 |
| BAZ2A | SNAP91 | ANKRD23 | SENP5 | HERC2 | ELOVL5 |
| RASSF8 | PSTPIP2 | SMYD1 | PARP14 | SCN3A | CES3 |
| KCNJ8 | CTIF | TMSB10 | CD47 | CALCRL | KDM4B |
| P3H3 | ZNF106 | DOK1 | OTC | TFPI | BBS9 |
| GAPDH | TYRO3 | DGUOK | ATP6AP2 | TMEFF2 | MPI |
| TNFRSF1A | RPAP1 | PREB | SLC9A7 | PLCL1 | PPIP5K2 |
| CRACR2A | ATP10A | NBAS | WDR45 | CARF | GREB1 |
| ITFG2 | ZNF516 | CD38 | SYNJ2 | PARD3B | PTPN6 |
| BID | SERPINB2 | KLHL2 | PGK1 | BARD1 | PXDC1 |
| SLC22A23 | DPP8 | GUCY1B1 | ZMAT1 | CYP27A1 | KDSR |
| SERPINB1 | ARF6 | SLC4A4 | ELF4 | PRKAG3 | ST6GAL1 |
| JARID2 | KANK1 | ARHGAP10 | ENOX2 | GPC1 | NOA1 |
| PHF1 | NPR2 | ANXA5 | FMR1 | HDLBP | IGFBP5 |
| VEGFA | TMEM8B | STPG2 | TMEM185A | SNED1 | SRPK2 |
| ZXDC | ZCCHC7 | MAPK10 | RENBP | NEB | SLC25A40 |
| TMEM266 | FKTN | PAQR3 | NADSYN1 | CAV2 | SCAP |
| LINGO1 | OLFML2A | FGF9 | BRMS1 | DBNL | ACSM5 |
| EDC3 | DNM1 | EBPL | EHBP1L1 | ZNF282 | PADI2 |
| AKAP5 | EXD3 | PHF11 | MAP4K2 | CDK3 | DCUN1D2 |
| GALNT16 | FBXL6 | MPHOSPH8 | MARK2 | GALK1 | CARHSP1 |
| IFT43 | MYC | DNAH10 | DTX4 | TANC2 | B4GALT2 |
| VASH1 | NCOA2 | TMEM120B | KBTBD4 | FKBP10 | CTC1 |
| IRF2BPL | SCYL3 | PPTC7 | ABTB2 | TBKBP1 | LMAN2L |
| SETD3 | F5 | ACAD10 | LMO2 | TSPOAP1 | CASP10 |
| WDR20 | PBX1 | HSPB8 | MPPED2 | ABR | STK36 |
| MBTPS1 | CD84 | NOS1 | TEAD1 | ANKFY1 | BDKRB2 |
| THAP11 | SLAMF8 | MIF | SCAMP4 | SMTNL2 | MED31 |
| SLC9A5 | SYT11 | LZTR1 | ANKRD24 | ENO3 | CENPH |
| YIF1B | CERS2 | DGCR2 | CHAF1A | BCL6B | PANK4 |
| ARHGEF1 | FMO5 | SIPA1L2 | PNPLA6 | MYH8 | ESYT3 |
| IRF2BP1 | ZNF697 | ARID5B | ZNF608 | SLC5A10 | OBSL1 |
| PLEKHA4 | TTF2 | SPOCK2 | PDLIM4 | ARHGAP23 | CASP8 |
| BCAT2 | CTTNBP2NL | CEP55 | IL5 | PFKM | FLYWCH1 |
| BAX | ARHGAP29 | TBC1D12 | TRPC7 | OXTR | VPS37C |
| CACNG6 | GLMN | SORBS1 | FZD4 | KCNA5 | PARVA |
| PUSL1 | TGFBR3 | ZDHHC6 | ARHGAP42 | CEP19 | PHACTR4 |
| MMEL1 | GBP2 | EIF3A | HINFP | DUS2 | RASIP1 |
| CLCN6 | HSPA12B | PPP1R12B | SORL1 | DIS3L2 | OLFM1 |
| NPPA | TTI1 | RPP25L | NTM | HS6ST1 | CCDC112 |
| VPS13D | KCNB1 | CACNB2 | PRELP | STK38L | HS1BP3 |
| DHRS3 | GUSB | CREM | SRI | WDR73 | AHR |
| FHAD1 | CTF1 | TRAK1 | CALCR | IL20RB | TBC1D23 |
| HMGN2 | SETD1A | PTH1R | CROT | CALM3 | LYSMD4 |
| EPB41 | REXO5 | TEX264 | PHTF2 | WDR4 | PDIK1L |
| CLSPN | ZNF174 | NISCH | LAMB1 | NFIA | |
| MOCOS | RHBDF1 | GLT8D1 | KIAA1614 | TIA1 |
| [1] |
Groenen MAM, Archibald AL, Uenishi H, Tuggle CK, Takeuchi Y, Rothschild MF, Rogel-Gaillard C, Park C, Milan D, Megens HJ, Li ST, Larkin DM, Kim H, Frantz LAF, Caccamo M, Ahn H, Aken BL, Anselmo A, Anthon C, Auvil L, Badaoui B, Beattie CW, Bendixen C, Berman D, Blecha F, Blomberg J, Bolund L, Bosse M, Botti S, Bujie Z, Bystrom M, Capitanu B, Silva DC, Chardon P, Chen C, Cheng R, Choi SH, Chow W, Clark RC, Clee C, Crooijmans RPMA, Dawson HD, Dehais P, De Sapio F, Dibbits B, Drou N, Du ZQ, Eversole K, Fadista J, Fairley S, Faraut T, Faulkner GJ, Fowler KE, Fredholm M, Fritz E, Gilbert JGR, Giuffra E, Gorodkin J, Griffin DK, Harrow JL, Hayward A, Howe K, Hu ZL, Humphray SJ, Hunt T, Hornshøj H, Jeon JT, Jern P, Jones M, Jurka J, Kanamori H, Kapetanovic R, Kim J, Kim JH, Kim KW, Kim TK, Larson G, Lee K, Lee KT, Leggett R, Lewin HA, Li YR, Liu WS, Loveland JE, Lu Y, Lunney JK, Ma J, Madsen O, Mann K, Matthews L, McLaren S, Morozumi T, Murtaugh MP, Narayan J, Nguyen DT, Ni PX, Oh SJ, Onteru S, Panitz F, Park EW, Park HS, Pascal G, Paudel Y, Perez-Enciso M, Ramirez-Gonzalez R, Reecy JM, Zas SR, Rohrer GA, Rund L, Sang YM, Schachtschneider K, Schraiber JG, Schwartz J, Scobie L, Scott C, Searle S, Servin B, Southey BR, Sperber G, Stadler P, Sweedler JV, Tafer H, Thomsen B, Wali R, Wang J, Wang J, White S, Xu X, Yerle M, Zhang GJ, Zhang JG, Zhang J, Zhao SH, Rogers J, Churcher C, Schook LB . Analyses of pig genomes provide insight into porcine demography and evolution. Nature, 2012,491(7424):393-398.
doi: 10.1038/nature11622 |
| [2] |
Almada AE, Wagers AJ . Molecular circuitry of stem cell fate in skeletal muscle regeneration, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016,17(5):267-279.
doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.7 pmid: 26956195 |
| [3] |
Sacco A, Doyonnas R, Kraft P, Vitorovic S, Blau HM . Self-renewal and expansion of single transplanted muscle stem cells. Nature, 2008,456(7221):502-506.
doi: 10.1038/nature07384 pmid: 18806774 |
| [4] |
Allen RE, Merkel RA, Young RB . Cellular aspects of muscle growth: myogenic cell proliferation. J Anim Sci, 1979,49(1):115-127.
doi: 10.2527/jas1979.491115x pmid: 500507 |
| [5] |
Buckingham M . Myogenic progenitor cells and skeletal myogenesis in vertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2006,16(5):525-532.
doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.08.008 |
| [6] |
Jathar S, Kumar V, Srivastava J, Tripathi V . Technological developments in lncRNA biology. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017,1008:283-323.
doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5203-3_10 pmid: 28815544 |
| [7] |
Yang F, Yi F, Cao HQ, Liang ZC, Du Q . The emerging landscape of long non-coding RNAs. Hereditas(Beijing), 2014,36(5):456-468.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2014.0456 |
|
杨峰, 易凡, 曹慧青, 梁子才, 杜权 . 长链非编码RNA研究进展. 遗传, 2014,36(5):456-468.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2014.0456 |
|
| [8] |
Lu C, Huang YH . Progress in long non-coding RNAs in animals. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017,39(11):1054-1065.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-120 pmid: 29254923 |
|
路畅, 黄银花 . 动物长链非编码RNA研究进展. 遗传, 2017,39(11):1054-1065.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-120 pmid: 29254923 |
|
| [9] |
Weikard R, Demasius W, Kuehn C . Mining long noncoding RNA in livestock. Anim Genet, 2017,48(1):3-18.
doi: 10.1111/age.12493 pmid: 27615279 |
| [10] |
Li H, Feng JC, Li GL, Wang X, Li MZ, Liu HF . The effect of lnc-RAP3 on 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation in mouse. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018,40(9):758-766.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-053 pmid: 30369479 |
|
李欢, 冯晋川, 李贵林, 王讯, 李明洲, 刘海峰 . Lnc- RAP3对小鼠3T3-L1前脂肪细胞分化的影响. 遗传, 2018,40(9):758-766.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-053 pmid: 30369479 |
|
| [11] | Xie SH . Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles of muscle development in Changbai and Lantang pigs[Dissertation]. Sun Yat-Sen University, 2017. |
| 谢水华 . 长白猪和蓝塘猪肌肉发育差异miRNA和mRNA表达谱的整合分析[学位论文]. 中山大学, 2017. | |
| [12] |
Tang ZL, Wu Y, Yang YL, Yang YCT, Wang ZS, Yuan JP, Yang Y, Hua CJ, Fan XH, Niu GL, Zhang YB, Lu ZJ, Li K . Comprehensive analysis of long non-coding RNAs highlights their spatio-temporal expression patterns and evolutional conservation in Sus scrofa. Sci Rep, 2017,7:43166.
doi: 10.1038/srep43166 pmid: 28233874 |
| [13] |
Zhou ZY, Li AM, Adeola AC, Liu YH, Irwin DM, Xie HB, Zhang YP . Genome-Wide identification of long intergenic noncoding RNA genes and their potential association with domestication in pigs. Genome Biol Evol, 2014,6(6):1387-1392.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu113 pmid: 24891613 |
| [14] | Yun L, Liu JP, Zhuang ZX, Yang LQ, Zhang RL, Ye XM, Cheng JQ . Real-time RT-PCR gene expression relative quantification REST © software analysis compared with 2 (-ΔΔCT)method . J Trop Med, 2007,7(10):956-958. |
| 庾蕾, 刘建平, 庄志雄, 杨淋清, 张仁利, 叶小明, 程锦泉 . 实时RT-PCR基因表达相对定量REST ©软件分析与2 (-ΔΔCT)法比较 . 热带医学杂志, 2007,7(10):956-958. | |
| [15] |
Chen G, Shi TL, Shi LM . Characterizing and annotating the genome using RNA-seq data. Sci China Life Sci, 2017,60(2):116-125.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-0349-4 pmid: 27294835 |
| [16] |
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A, Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F, Xue C, Marinov GK, Khatun J, Williams BA, Zaleski C, Rozowsky J, Röder M, Kokocinski F, Abdelhamid RF, Alioto T, Antoshechkin I, Baer MT, Bar NS, Batut P, Bell K, Bell I, Chakrabortty S, Chen X, Chrast J, Curado J, Derrien T, Drenkow J, Dumais E, Dumais J, Duttagupta R, Falconnet E, Fastuca M, Fejes-Toth K, Ferreira P, Foissac S, Fullwood MJ, Gao H, Gonzalez D, Gordon A, Gunawardena H, Howald C, Jha S, Johnson R, Kapranov P, King B, Kingswood C, Luo OJ, Park E, Persaud K, Preall JB, Ribeca P, Risk B, Robyr D, Sammeth M, Schaffer L, See LH, Shahab A, Skancke J, Suzuki AM, Takahashi H, Tilgner H, Trout D, Walters N, Wang H, Wrobel J, Yu Y, Ruan X, Hayashizaki Y, Harrow J, Gerstein M, Hubbard T, Reymond A, Antonarakis SE, Hannon G, Giddings MC, Ruan Y, Wold B, Carninci P, Guigó R, Gingeras TR . Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature, 2012,489(7414):101-108.
doi: 10.1038/nature11233 |
| [17] |
Deniz E, Erman B . Long noncoding RNA (lincRNA), a new paradigm in gene expression control. Funct Integr Genomics, 2017,17(2-3):135-143.
doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0524-x pmid: 27681237 |
| [18] |
Jandura A, Krause HM . The new RNA world: growing evidence for long noncoding RNA functionality. Trends Genet, 2017,33(10):665-676.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.08.002 pmid: 28870653 |
| [19] |
Li YY, Chen XN, Sun H, Wang HT . Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of skeletal myogenesis and muscle diseases. Cancer Lett, 2018,417:58-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.12.015 pmid: 29253523 |
| [20] |
Flynn RA, Chang HY . Long noncoding RNAs in cell-fate programming and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell, 2014,14(6):752-761.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.05.014 |
| [21] |
Qin CY, Cai H, Qing HR, Li L, Zhang HP . Recent advances on the role of long non-coding RNA H19 in regulating mammalian muscle growth and development. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017,39(12):1150-1157.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-193 pmid: 29258985 |
|
秦辰雨, 蔡禾, 卿涵睿, 李利, 张红平 . 长链非编码RNA H19对哺乳动物肌肉生长发育的调控. 遗传, 2017,39(12):1150-1157.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-193 pmid: 29258985 |
|
| [22] | Zhou R, Wang YX, Long KR, Jiang AA, Jin L . Regulatory mechanism for lncRNAs in skeletal muscle development and progress on its research in domestic animals. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018,40(4):292-304. |
| 周瑞, 王以鑫, 龙科任, 蒋岸岸, 金龙 . LncRNA调控骨骼肌发育的分子机制及其在家养动物中的研究进展. 遗传, 2018,40(4):292-304. | |
| [23] | Li MX, Huang T, Ma LP, Liu Y, Li T, Gong HB, Qiu MY, Xie S, Sun XM . Cloning of porcine lncRNA-ENSSSCT00000018610 and its expression pattern in porcine ovarian follicles. Acta Vet Et Zootech Sin, 2018,49(9):1830-1839. |
| 李梦寻, 黄涛, 马力鹏, 刘乙, 李涛, 公红斌, 邱梅玉, 谢苏, 孙晓梅 . 猪lncRNA-ENSSSCT00000018610的克隆及其在猪卵泡中的表达. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018,49(9):1830-1839. | |
| [24] |
Picard B, Lefaucheur L, Berri C, Duclos MJ . Muscle fibre ontogenesis in farm animal species. Reprod Nutr Dev, 2002,42(5):415-431.
doi: 10.1051/rnd:2002035 pmid: 12537254 |
| [25] |
Lefaucheur L, Vigneron P . Post-natal changes in some histochemical and enzymatic characteristics of three pig muscles. Meat Sci, 1986,16(3):199-216.
doi: 10.1016/0309-1740(86)90026-4 pmid: 22054929 |
| [26] |
Zammit PS, Heslop L, Hudon V, Rosenblatt JD, Tajbakhsh S, Buckingham ME, Beauchamp JR, Partridge TA . Kinetics of myoblast proliferation show that resident satellite cells are competent to fully regenerate skeletal muscle fibers. Exp Cell Res, 2002,281(1):39-49.
doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5653 pmid: 12441128 |
| [27] |
Liao Q, Liu CN, Yuan XY, Kang SL, Miao RY, Xiao H, Zhao GG, Luo HT, Bu DC, Zhao HT, Skogerbø G, Wu ZD, Zhao Y . Large-scale prediction of long non-coding RNA functions in a coding-non-coding gene co-expression network. Nucleic Acids Res, 2011,39(9):3864-3878.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1348 pmid: 21247874 |
| [28] |
Sanoudou D, Haslett JN, Kho AT, Guo SQ, Gazda HT, Greenberg SA, Lidov HGW, Kohane IS, Kunkel LM, Beggs AH . Expression profiling reveals altered satellite cell numbers and glycolytic enzyme transcription in nemaline myopathy muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003,100(8):4666-4671.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0330960100 pmid: 12677001 |
| [29] |
Mangano KM, Sahni S, Kerstetter JE, Kenny AM, Hannan MT . Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their relation with bone and muscle health in adults. Curr Osteoporos Rep, 2013,11(3):203-212.
doi: 10.1007/s11914-013-0149-0 pmid: 23857286 |
| [30] |
Lambadiari V, Triantafyllou K, Dimitriadis GD . Insulin action in muscle and adipose tissue in type 2 diabetes: The significance of blood flow. World J Diabetes, 2015,6(4):626-633.
doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i4.626 pmid: 25987960 |
| [1] | Lingling Wu, Xiaoyu Zhang, Xiao Li, Jianjun Jin, Gongshe Yang, Xin’e Shi. miR-196b-5p promotes myoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(5): 435-446. |
| [2] | Huan Zhao, Bin Zhou. Pancreatic beta cells regeneration [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(5): 370-382. |
| [3] | Zhixin Yu, Pengyu Li, Kai Li, Shiying Miao, Linfang Wang, Wei Song. Progress on spermatogonial stem cell microenvironment [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1103-1116. |
| [4] | Liping Zou, Cheng Pan, Mengxin Wang, Lin Cui, Baoyu Han. Progress on the mechanism of hormones regulating plant flower formation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(8): 739-751. |
| [5] | Kun Du, Chuyang Mao, Anyong Ren, Xuemei Wu, Qingling Li, Tingting Chen, Shiyi Chen, Songjia Lai. Analysis of gene expression profiles at different stages during preadipocyte differentiation in rabbits [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(3): 309-320. |
| [6] | Wanyin Chen, Yidan Yan, Xiaojin Luan, Min Wang, Jie Fang. Functional analysis of CG8005 gene in Drosophila testis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(11): 1122-1132. |
| [7] | Ke Yang, Zheng Xue, Xiang Lv. Molecular mechanism of the 3D genome structure and function regulation during cell terminal differentiation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(1): 32-44. |
| [8] | Li Huan, Feng Jinchuan, Li Guilin, Wang Xun, Li Mingzhou, Liu Haifeng. The effect of lnc-RAP3 on 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation in mouse [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(9): 758-766. |
| [9] | Lan Ren,Rudan Xiao,Qian Zhang,Xiaomin Lou,Zhaojun Zhang,Xiangdong Fang. Synergistic regulation of the erythroid differentiation of K562 cells by KLF1 and KLF9 [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(11): 998-1006. |
| [10] | Man Yang,Bingjie Lu,Yuanyuan Duan,Xiaofeng Chen,Jiangang Ma,Yan Guo. Genetics association study and functional analysis on osteoporosis susceptibility gene BDNF [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(8): 726-736. |
| [11] | Yi Kang,Guijun Guan,Yunhan Hong. Insights of sex determination and differentiation from medaka as a teleost model [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(6): 441-454. |
| [12] | Zhenwei Jia. Mitochondria and pluripotent stem cells function [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(7): 603-611. |
| [13] | Jun Wu, Junhong Zhang, Menghui Huang, Minhui Zhu, Zaikang Tong. Expression analysis of miR164 and its target gene NAC1 in response to low nitrate availability in Betula luminifera [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(2): 155-162. |
| [14] | Xue Zhou, Yilan Du, Ping Jin, Fei Ma. Bioinformatic analysis of cancer-related microRNAs and their target genes [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(9): 855-864. |
| [15] | Yuntao Guo, Xiangyang Miao. MicroRNAs in the regulation of brown adipocyte differentiation [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(3): 240-249. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||