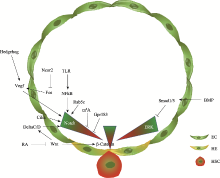
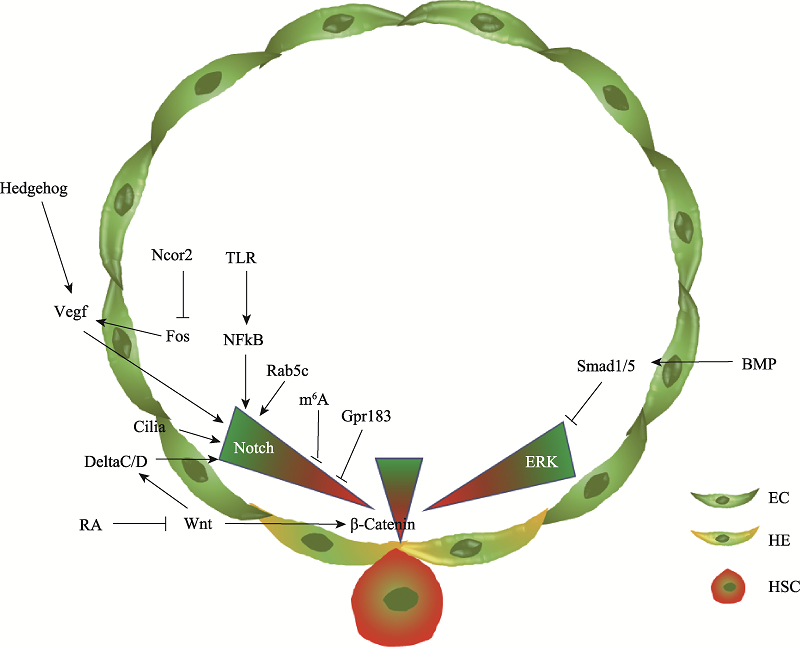
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 295-307.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-026
• Special Section: Excellent Doctoral Thesis • Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory signaling pathways in hematopoietic stem cell development
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
2. Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA;
-
Received:2021-01-20Revised:2021-03-01Online:2021-04-20Published:2021-04-20 -
Contact:Liu Feng E-mail:liuf@ioz.ac.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China Nos(2018YFA0800200);Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China Nos(2018YFA080100);the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, China No(XDA16010207);the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos)(32030032);the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos)(31830061)
Cite this article
Chunxia Zhang, Feng Liu. Regulatory signaling pathways in hematopoietic stem cell development[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(4): 295-307.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Orkin SH, Zon LI. Hematopoiesis: an evolving paradigm for stem cell biology. Cell, 2008,132(4):631-644.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.025 pmid: 18295580 |
| [2] |
Choi K, Kennedy M, Kazarov A, Papadimitriou JC, Keller G. A common precursor for hematopoietic and endothelial cells. Development, 1998,125(4):725-732.
pmid: 9435292 |
| [3] |
Palis J, Robertson S, Kennedy M, Wall C, Keller G. Development of erythroid and myeloid progenitors in the yolk sac and embryo proper of the mouse. Development, 1999,126(22):5073-5084.
pmid: 10529424 |
| [4] |
Chen MJ, Li Y, De Obaldia ME, Yang Q, Yzaguirre AD, Yamada-Inagawa T, Vink CS, Bhandoola A, Dzierzak E, Speck NA. Erythroid/myeloid progenitors and hematopoietic stem cells originate from distinct populations of endothelial cells. Cell Stem Cell, 2011,9(6):541-552.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.10.003 |
| [5] |
McGrath KE, Frame JM, Fegan KH, Bowen JR, Conway SJ, Catherman SC, Kingsley PD, Koniski AD, Palis J. Distinct sources of hematopoietic progenitors emerge before HSCs and provide functional blood cells in the mammalian embryo. Cell Rep, 2015,11(12):1892-1904.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.05.036 pmid: 26095363 |
| [6] |
Schulz C, Gomez Perdiguero E, Chorro L, Szabo-Rogers H, Cagnard N, Kierdorf K, Prinz M, Wu BS, Jacobsen SEW, Pollard JW, Frampton J, Liu KJ, Geissmann F. A lineage of myeloid cells independent of Myb and hematopoietic stem cells. Science, 2012,336(6077):86-90.
doi: 10.1126/science.1219179 pmid: 22442384 |
| [7] |
Gomez Perdiguero E, Klapproth K, Schulz C, Busch K, Azzoni E, Crozet L, Garner H, Trouillet C, de Bruijn MF, Geissmann F, Rodewald HR. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature, 2015,518(7540):547-551.
doi: 10.1038/nature13989 pmid: 25470051 |
| [8] |
Böiers C, Carrelha J, Lutteropp M, Luc S, Green JCA, Azzoni E, Woll PS, Mead AJ, Hultquist A, Swiers G, Perdiguero EG, Macaulay IC, Melchiori L, Luis TC, Kharazi S, Bouriez-Jones T, Deng QL, Ponten A, Atkinson D, Jensen CT, Sitnicka E, Geissmann F, Godin I, Sandberg R, de Bruijn MFTR, Jacobsen SEW. Lymphomyeloid contribution of an immune-restricted progenitor emerging prior to definitive hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell, 2013,13(5):535-548.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.08.012 |
| [9] |
Müller AM, Medvinsky A, Strouboulis J, Grosveld F, Dzierzak E. Development of hematopoietic stem cell activity in the mouse embryo. Immunity, 1994,1(4):291-301.
doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90081-7 pmid: 7889417 |
| [10] |
Gekas C, Dieterlen-Lievre F, Orkin SH, Mikkola HKA. The placenta is a niche for hematopoietic stem cells. Dev Cell, 2005,8(3):365-375.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.12.016 pmid: 15737932 |
| [11] |
Boisset JC, van Cappellen W, Andrieu-Soler C, Galjart N, Dzierzak E, Robin C. In vivo imaging of haematopoietic cells emerging from the mouse aortic endothelium. Nature, 2010,464(7285):116-120.
doi: 10.1038/nature08764 pmid: 20154729 |
| [12] |
Chen AT, Zon LI. Zebrafish blood stem cells. J Cell Biochem, 2009,108(1):35-42.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.22251 pmid: 19565566 |
| [13] |
Detrich HW, Kieran MW, Chan FY, Barone LM, Yee K, Rundstadler JA, Pratt S, Ransom D, Zon LI. Intraembryonic hematopoietic cell migration during vertebrate development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1995,92(23):10713-10717.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10713 pmid: 7479870 |
| [14] |
Bertrand JY, Kim AD, Violette EP, Stachura DL, Cisson JL, Traver D. Definitive hematopoiesis initiates through a committed erythromyeloid progenitor in the zebrafish embryo. Development, 2007,134(23):4147-4156.
doi: 10.1242/dev.012385 pmid: 17959717 |
| [15] |
Kissa K, Herbomel P. Blood stem cells emerge from aortic endothelium by a novel type of cell transition. Nature, 2010,464(7285):112-115.
doi: 10.1038/nature08761 pmid: 20154732 |
| [16] |
Patterson LJ, Gering M, Patient R. Scl is required for dorsal aorta as well as blood formation in zebrafish embryos. Blood, 2005,105(9):3502-3511.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3547 pmid: 15644413 |
| [17] |
Ren X, Gomez GA, Zhang B, Lin S. Scl isoforms act downstream of etsrp to specify angioblasts and definitive hematopoietic stem cells. Blood, 2010,115(26):5338-5346.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-244640 pmid: 20185582 |
| [18] |
Zhen FH, Lan YH, Yan B, Zhang WQ, Wen ZL. Hemogenic endothelium specification and hematopoietic stem cell maintenance employ distinct Scl isoforms. Development, 2013,140(19):3977-3985.
doi: 10.1242/dev.097071 |
| [19] |
North TE, Goessling W, Walkley CR, Lengerke C, Kopani KR, Lord AM, Weber GJ, Bowman TV, Jang IH, Grosser T, Fitzgerald GA, Daley GQ, Orkin SH, Zon LI. Prostaglandin E2 regulates vertebrate haematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Nature, 2007,447(7147):1007-1011.
doi: 10.1038/nature05883 pmid: 17581586 |
| [20] |
Wang Q, Stacy T, Binder M, Marin-Padilla M, Sharpe AH, Speck NA. Disruption of the Cbfa2 gene causes necrosis and hemorrhaging in the central nervous system and blocks definitive hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996,93(8):3444-3449.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3444 pmid: 8622955 |
| [21] |
Chen MJ, Yokomizo T, Zeigler BM, Dzierzak E, Speck NA. Runx1 is required for the endothelial to haematopoietic cell transition but not thereafter. Nature, 2009,457(7231):887-891.
doi: 10.1038/nature07619 pmid: 19129762 |
| [22] |
Lancrin C, Mazan M, Stefanska M, Patel R, Lichtinger M, Costa G, Vargel O, Wilson NK, Möröy T, Bonifer C, Göttgens B, Kouskoff V, Lacaud G. GFI1 and GFI1B control the loss of endothelial identity of hemogenic endothelium during hematopoietic commitment. Blood, 2012,120(2):314-322.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-386094 |
| [23] |
Eich C, Arlt J, Vink CS, Solaimani Kartalaei P, Kaimakis P, Mariani SA, van der Linden R, van Cappellen WA, Dzierzak E. In vivo single cell analysis reveals Gata2 dynamics in cells transitioning to hematopoietic fate. J Exp Med, 2018,215(1):233-248.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20170807 pmid: 29217535 |
| [24] |
de Pater E, Kaimakis P, Vink CS, Yokomizo T, Yamada-Inagawa T, van der Linden R, Kartalaei PS, Camper SA, Speck N, Dzierzak E. Gata2 is required for HSC generation and survival. J Exp Med, 2013,210(13):2843-2850.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20130751 |
| [25] |
Gao X, Johnson KD, Chang YI, Boyer ME, Dewey CN, Zhang J, Bresnick EH. Gata2 cis-element is required for hematopoietic stem cell generation in the mammalian embryo. J Exp Med, 2013,210(13):2833-2842.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20130733 |
| [26] |
Patterson LJ, Gering M, Eckfeldt CE, Green AR, Verfaillie CM, Ekker SC, Patient R. The transcription factors Scl and Lmo2 act together during development of the hemangioblast in zebrafish. Blood, 2006,109(6):2389-2398.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-003087 pmid: 17090656 |
| [27] |
Butko E, Distel M, Pouget C, Weijts B, Kobayashi I, Ng K, Mosimann C, Poulain FE, McPherson A, Ni CW, Stachura DL, Del Cid N, Espín-Palazón R, Lawson ND, Dorsky R, Clements WK, Traver D. Gata2b is a restricted early regulator of hemogenic endothelium in the zebrafish embryo. Development, 2015,142(6):1050-1061.
doi: 10.1242/dev.119180 pmid: 25758220 |
| [28] |
Dobrzycki T, Mahony CB, Krecsmarik M, Koyunlar C, Rispoli R, Peulen-Zink J, Gussinklo K, Fedlaoui B, de Pater E, Patient R, Monteiro R. Deletion of a conserved Gata2 enhancer impairs haemogenic endothelium programming and adult Zebrafish haematopoiesis. Commun Biol, 2020,3(1):71.
doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0798-3 pmid: 32054973 |
| [29] |
Massagué J. TGF-β SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION. Annu Rev Biochem, 1998,67(1):753-791.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.753 |
| [30] |
Wang RN, Green J, Wang ZL, Deng YL, Qiao M, Peabody M, Zhang Q, Ye JX, Yan ZJ, Denduluri S, Idowu O, Li M, Shen C, Hu A, Haydon RC, Kang R, Mok J, Lee MJ, Luu HL, Shi LL. Bone Morphogenetic Protein(BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes Dis, 2014,1(1):87-105.
doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.07.005 pmid: 25401122 |
| [31] |
Massagué J, Seoane J, Wotton D. Smad transcription factors. Genes Dev, 2005,19(23):2783-2810.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1350705 pmid: 16322555 |
| [32] |
Hata A, Seoane J, Lagna G, Montalvo E, Hemmati- Brivanlou A, Massagué J. OAZ uses distinct DNA- and protein-binding zinc fingers in separate BMP-Smad and Olf signaling pathways. Cell, 2000,100(2):229-240.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81561-5 pmid: 10660046 |
| [33] |
Kim DW, Lassar AB. Smad-dependent recruitment of a histone deacetylase/Sin3A complex modulates the bone morphogenetic protein-dependent transcriptional repressor activity of Nkx3.2. Mol Cell Biol, 2003,23(23):8704-8717.
doi: 10.1128/mcb.23.23.8704-8717.2003 pmid: 14612411 |
| [34] |
Hata A, Lagna G, Massagué J, Hemmati-Brivanlou A. Smad6 inhibits BMP/Smad1 signaling by specifically competing with the Smad4 tumor suppressor. Genes Dev, 1998,12(2):186-197.
doi: 10.1101/gad.12.2.186 pmid: 9436979 |
| [35] |
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Morén A, Nakayama T, Christian JL, Heuchel R, Itoh S, Kawabata M, Heldin NE , Heldin CH, ten Dijke P. Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta- inducible antagonist of TGF-beta signalling. Nature, 1997,389(6651):631-635.
doi: 10.1038/39369 pmid: 9335507 |
| [36] |
Kavsak P, Rasmussen RK, Causing CG, Bonni S, Zhu H, Thomsen GH, Wrana JL. Smad7 binds to Smurf2 to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the TGF beta receptor for degradation. Mol Cell, 2000,6(6):1365-1375.
doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00134-9 pmid: 11163210 |
| [37] |
Sadlon TJ, Lewis ID, D'Andrea RJ. BMP4: its role in development of the hematopoietic system and potential as a hematopoietic growth factor. Stem Cells, 2004,22(4):457-474.
doi: 10.1634/stemcells.22-4-457 pmid: 15277693 |
| [38] |
Pyati UJ, Webb AE, Kimelman D. Transgenic zebrafish reveal stage-specific roles for Bmp signaling in ventral and posterior mesoderm development. Development, 2005,132(10):2333-2343.
doi: 10.1242/dev.01806 pmid: 15829520 |
| [39] |
Gupta S, Zhu H, Zon LI, Evans T. BMP signaling restricts hemato-vascular development from lateral mesoderm during somitogenesis. Development, 2006,133(11):2177-2187.
doi: 10.1242/dev.02386 pmid: 16672337 |
| [40] |
Wilkinson RN, Pouget C, Gering M, Russell AJ, Davies SG, Kimelman D, Patient R. Hedgehog and Bmp polarize hematopoietic stem cell emergence in the zebrafish dorsal aorta. Dev Cell, 2009,16(6):909-916.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.04.014 pmid: 19531361 |
| [41] |
Monteiro R, van Dinther M, Bakkers J, Wilkinson R, Patient R, ten Dijke P, Mummery C. Two novel type II receptors mediate BMP signalling and are required to establish left-right asymmetry in zebrafish. Dev Biol, 2008,315(1):55-71.
doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.11.038 pmid: 18222420 |
| [42] |
Durand C, Robin C, Bollerot K, Baron MH, Ottersbach K, Dzierzak E. Embryonic stromal clones reveal developmental regulators of definitive hematopoietic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007,104(52):20838-20843.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706923105 pmid: 18087045 |
| [43] |
McReynolds LJ, Gupta S, Figueroa ME, Mullins MC, Evans T. Smad1 and Smad5 differentially regulate embryonic hematopoiesis. Blood, 2007,110(12):3881-3890.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-04-085753 pmid: 17761518 |
| [44] |
Zhang CX, Lv JH, He QP, Wang SF, Gao Y, Meng AM, Yang X, Liu F. Inhibition of endothelial ERK signalling by Smad1/5 is essential for haematopoietic stem cell emergence. Nat Commun, 2014,5:3431.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms4431 pmid: 24614941 |
| [45] |
Cook BD, Liu S, Evans T. Smad1 signaling restricts hematopoietic potential after promoting hemangioblast commitment. Blood, 2011,117(24):6489-6497.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-312389 |
| [46] |
Lan Y, He WY, Li Z, Wang Y, Wang J, Gao J, Wang WL, Cheng T, Liu B, Yang X. Endothelial Smad4 restrains the transition to hematopoietic progenitors via suppression of ERK activation. Blood, 2014,123(14):2161-2171.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-09-526053 |
| [47] |
Pimanda JE, Donaldson IJ, de Bruijn MFTR, Kinston S, Knezevic K, Huckle L, Piltz S, Landry JR, Green AR, Tannahill D, Göttgens B. The SCL transcriptional network and BMP signaling pathway interact to regulate RUNX1 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007,104(3):840-845.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607196104 pmid: 17213321 |
| [48] |
Xu RH, Ault KT, Kim J, Park MJ, Hwang YS, Peng Y, Sredni D, Kung HF. Opposite effects of FGF and BMP-4 on embryonic blood formation: roles of PV.1 and GATA-2. Dev Biol, 1999,208(2):352-361.
doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9205 pmid: 10191050 |
| [49] |
Pera EM, Ikeda A, Eivers E, De Robertis EM. Integration of IGF, FGF, and anti-BMP signals via Smad1 phosphorylation in neural induction. Genes Dev, 2003,17(24):3023-3028.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1153603 pmid: 14701872 |
| [50] |
Yu PZ, Pan G, Yu J, Thomson JA. FGF2 sustains NANOG and switches the outcome of BMP4-induced human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cell Stem Cell, 2011,8(3):326-334.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.01.001 |
| [51] |
Kopan R, Ilagan MXG. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell, 2009,137(2):216-233.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.045 pmid: 19379690 |
| [52] |
Shawber CJ, Kitajewski J. Notch function in the vasculature: insights from zebrafish, mouse and man. Bioessays, 2004,26(3):225-234.
doi: 10.1002/bies.20004 pmid: 14988924 |
| [53] |
Lomeli H, Castillo-Castellanos F. Notch signaling and the emergence of hematopoietic stem cells. Dev Dyn, 2020,249(11):1302-1317.
doi: 10.1002/dvdy.230 pmid: 32996661 |
| [54] |
Butko E, Pouget C, Traver D. Complex regulation of HSC emergence by the Notch signaling pathway. Dev Biol, 2016,409(1):129-138.
doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.11.008 pmid: 26586199 |
| [55] |
Lawson ND, Scheer N, Pham VN, Kim CH, Chitnis AB, Campos-Ortega JA, Weinstein BM. Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular development. Development, 2001,128(19):3675-3683.
pmid: 11585794 |
| [56] |
Kumano K, Chiba S, Kunisato A, Sata M, Saito T, Nakagami-Yamaguchi E, Yamaguchi T, Masuda S, Shimizu K, Takahashi T, Ogawa S, Hamada Y, Hirai H. Notch1 but not Notch2 is essential for generating hematopoietic stem cells from endothelial cells. Immunity, 2003,18(5):699-711.
doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00117-1 |
| [57] |
Grego-Bessa J, Luna-Zurita L, del Monte G, Bolós V, Melgar P, Arandilla A, Garratt AN, Zang H, Mukouyama YS, Chen HY, Shou WN, Ballestar E, Esteller M, Rojas A, Pérez-Pomares JM, de la Pompa JL. Notch signaling is essential for ventricular chamber development. Dev Cell, 2007,12(3):415-429.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.12.011 pmid: 17336907 |
| [58] |
Burns CE, Traver D, Mayhall E, Shepard JL, Zon LI. Hematopoietic stem cell fate is established by the Notch- Runx pathway. Genes Dev, 2005,19(19):2331-2342.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1337005 pmid: 16166372 |
| [59] |
Robert-Moreno A, Guiu J, Ruiz-Herguido C, López ME, Inglés-Esteve J, Riera L, Tipping A, Enver T, Dzierzak E, Gridley T, Espinosa L, Bigas A. Impaired embryonic haematopoiesis yet normal arterial development in the absence of the Notch ligand Jagged1. EMBO J, 2008,27(13):1886-1895.
doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.113 pmid: 18528438 |
| [60] |
Robert-Moreno A, Espinosa L, de la Pompa JL, Bigas A. RBPjkappa-dependent Notch function regulates Gata2 and is essential for the formation of intra-embryonic hematopoietic cells. Development, 2005,132(5):1117-1126.
doi: 10.1242/dev.01660 pmid: 15689374 |
| [61] |
Guiu J, Bergen DJM, De Pater E, Islam ABMMK, Ayllón V, Gama-Norton L, Ruiz-Herguido C, González J, López-Bigas N, Menendez P, Dzierzak E, Espinosa L, Bigas A. Identification of Cdca7 as a novel Notch transcriptional target involved in hematopoietic stem cell emergence. J Exp Med, 2014,211(12):2411-2423.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20131857 |
| [62] |
Gama-Norton L, Ferrando E, Ruiz-Herguido C, Liu ZY, Guiu J, Islam ABMMK, Lee SU, Yan MH, Guidos CJ, López-Bigas N, Maeda T, Espinosa L, Kopan R, Bigas A. Notch signal strength controls cell fate in the haemogenic endothelium. Nat Commun, 2015,6:8510.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms9510 pmid: 26465397 |
| [63] |
Zhang PP, He QP, Chen DB, Liu WX, Wang L, Zhang CX, Ma DY, Li W, Liu B, Liu F. G protein-coupled receptor 183 facilitates endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition via Notch1 inhibition. Cell Res, 2015,25(10):1093-1107.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.109 pmid: 26358189 |
| [64] |
Richard C, Drevon C, Canto PY, Villain G, Bollérot K, Lempereur A, Teillet MA, Vincent C, Rosselló Castillo C, Torres M, Piwarzyk E, Speck NA, Souyri M, Jaffredo T. Endothelio-mesenchymal interaction controls runx1 expression and modulates the notch pathway to initiate aortic hematopoiesis. Dev Cell, 2013,24(6):600-611.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.02.011 pmid: 23537631 |
| [65] |
Swift MR, Weinstein BM. Arterial-venous specification during development. Circ Res, 2009,104(5):576-588.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.188805 pmid: 19286613 |
| [66] |
He QP, Zhang CX, Wang L, Zhang PP, Ma DY, Lv JH, Liu F. Inflammatory signaling regulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell emergence in vertebrates. Blood, 2015,125(7):1098-1106.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-09-601542 pmid: 25540193 |
| [67] |
Espín-Palazón R, Stachura DL, Campbell CA, García- Moreno D, Del Cid N, Kim AD, Candel S, Meseguer J, Mulero V, Traver D. Proinflammatory signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell emergence. Cell, 2014,159(5):1070-1085.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.031 |
| [68] |
Liu ZB, Tu HQ, Kang YS, Xue YY, Ma DY, Zhao CT, Li HY, Wang L, Liu F. Primary cilia regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell specification through Notch signaling in zebrafish. Nat Commun, 2019,10(1):1839.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09403-7 pmid: 31015398 |
| [69] |
Wei YL, Ma DY, Gao Y, Zhang CX, Wang L, Liu F. Ncor2 is required for hematopoietic stem cell emergence by inhibiting Fos signaling in zebrafish. Blood, 2014,124(10):1578-1585.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-541391 |
| [70] |
Zhang CX, Chen YS, Sun BF, Wang L, Yang Y, Ma DY, Lv JH, Heng J, Ding YY, Xue YY, Lu XY, Xiao W, Yang YG, Liu F. m(6)A modulates haematopoietic stem and progenitor cell specification. Nature, 2017,549(7671):273-276.
doi: 10.1038/nature23883 pmid: 28869969 |
| [71] |
Heng J, Lv P, Zhang YF, Cheng XJ, Wang L, Ma DY, Liu F. Rab5c-mediated endocytic trafficking regulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell development via Notch and AKT signaling. PLoS Biol, 2020,18(4):e3000696.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000696 pmid: 32275659 |
| [72] |
Steinhart Z, Angers S. Wnt signaling in development and tissue homeostasis. Development, 2018,145(11).
doi: 10.1242/dev.164988 pmid: 29724757 |
| [73] |
Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell, 2012,149(6):1192-1205.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.012 |
| [74] |
Daulat AM, Borg JP. Wnt/Planar cell polarity signaling: new opportunities for cancer treatment. Trends Cancer, 2017,3(2):113-125.
doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.01.001 pmid: 28718442 |
| [75] |
De A. Wnt/Ca 2+ signaling pathway: a brief overview . Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2011,43(10):745-756.
doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmr079 |
| [76] |
Kohn AD, Moon RT. Wnt and calcium signaling: beta-catenin-independent pathways. Cell Calcium, 2005,38(3-4):439-446.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2005.06.022 pmid: 16099039 |
| [77] |
Goessling W, North TE, Loewer S, Lord AM, Lee S, Stoick-Cooper CL, Weidinger G, Puder M, Daley GQ, Moon RT, Zon LI. Genetic interaction of PGE2 and Wnt signaling regulates developmental specification of stem cells and regeneration. Cell, 2009,136(6):1136-1147.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.015 pmid: 19303855 |
| [78] |
Lengerke C, Schmitt S, Bowman TV, Jang IH, Maouche-Chretien L, McKinney-Freeman S, Davidson AJ, Hammerschmidt M, Rentzsch F, Green JBA, Zon LI, Daley GQ. BMP and Wnt specify hematopoietic fate by activation of the Cdx-Hox pathway. Cell Stem Cell, 2008,2(1):72-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.10.022 pmid: 18371423 |
| [79] |
Ruiz-Herguido C, Guiu J, D'Altri T, Inglés-Esteve J, Dzierzak E, Espinosa L, Bigas A. Hematopoietic stem cell development requires transient Wnt/β-catenin activity. J Exp Med, 2012,209(8):1457-1468.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20120225 |
| [80] |
Chanda B, Ditadi A, Iscove NN, Keller G. Retinoic acid signaling is essential for embryonic hematopoietic stem cell development. Cell, 2013,155(1):215-227.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.055 |
| [81] |
Clements WK, Kim AD, Ong KG, Moore JC, Lawson ND, Traver D. A somitic Wnt16/Notch pathway specifies haematopoietic stem cells. Nature, 2011,474(7350):220-224.
doi: 10.1038/nature10107 pmid: 21654806 |
| [82] |
Kim AD, Melick CH, Clements WK, Stachura DL, Distel M, Panákova D, MacRae C, Mork LA, Crump JG, Traver D. Discrete Notch signaling requirements in the specification of hematopoietic stem cells. EMBO J, 2014,33(20):2363-2373.
doi: 10.15252/embj.201488784 |
| [83] |
Lee Y, Manegold JE, Kim AD, Pouget C, Stachura DL, Clements WK, Traver D. FGF signalling specifies haematopoietic stem cells through its regulation of somitic Notch signalling. Nat Commun, 2014,5:5583.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6583 pmid: 25428693 |
| [84] |
Genthe JR, Clements WK. R-spondin 1 is required for specification of hematopoietic stem cells through Wnt16 and Vegfa signaling pathways. Development, 2017,144(4):590-600.
doi: 10.1242/dev.139956 pmid: 28087636 |
| [1] | Yiming Gong, Xiangyu Wang, Xiaoyun He, Yufang Liu, Ping Yu, Mingxing Chu, Ran Di. Progress on the effect of FecB mutation on BMPR1B activity and BMP/SMAD pathway in sheep [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(4): 295-305. |
| [2] | Pengfei Zheng, Haibo Xie, Panpan Zhu, Chengtian Zhao. Distribution pattern of floor plate neurons in zebrafish [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 510-520. |
| [3] | Xingqi Wan, Wanzhen Wei, Shengliang Guo, Yixiao Cui, Xueying Jing, Lujie Huang, Jie Ma. Functional analysis of the long-range regulatory element of BMP2 gene [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1141-1147. |
| [4] | Tingting Jia, Lei Lei, Xinyuan Wu, Shunyou Cai, Yixuan Chen, Yu Xue. Study on the mechanism of metformin on zebrafish skeletal development and damage repair [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(1): 68-79. |
| [5] | Zhaojie Lyu, Zhihao Wang, Shuxian Lu, Peirong Liu, Jing Tian. Brachydactyly and the molecular mechanisms of digit formation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(12): 1073-1083. |
| [6] | Qingqing Fan, Feilong Meng, Ran Fang, Gaopeng Li, Xiaoli Zhao. Functions of Wnt signaling pathway in hair cell differentiation and regeneration [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(10): 897-907. |
| [7] | Min Wang,Xuan Shi,Xiang Huang,Xiaofeng Liu,Yufeng Qin,Xiaohong Liu,Yaosheng Chen,Zuyong He. Improving gene targeting efficiency on the porcine BMP15 gene mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 by using the RGS surrogate reporter system [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(1): 48-55. |
| [8] | Shan He, Lingqiang Zhang. Research progress in linear ubiquitin modification [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(9): 911-917. |
| [9] | Manli Zhang, Yanping Lu, Yali Li. Correlation between primary cilium and Wnt signaling pathway [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(3): 233-239. |
| [10] | Xiao Qiu, Rongfei Wei, Lingqiang Zhang, Fuchu He. The roles of signaling pathways in regulating kidney development [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(1): 1-7. |
| [11] | Fei Xu, Jin Zhang, Duan Ma. Crosstalk of Hippo/YAP and Wnt/β-catenin pathways [J]. HEREDITAS, 2014, 36(2): 95-102. |
| [12] | ZHENG Zhong-Zhong SHEN Jin-Qiu PAN Wei-Huai PAN Jian-Wei. Calcium sensors and their stress signaling pathways in plants [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(7): 875-884. |
| [13] | WANG Xu, XIONG Jing-Wei. Vascular endothelial cell development and underlying mechanisms [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(9): 1114-1122. |
| [14] | JIAN Guang-Hui, WANG Xi-Quan. Wnt signaling pathway and the Evo-Devo of deuterostome axis [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(7): 684-694. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yu, ZHENG Zeng-Zhang, GE Jun, ZHANG Hong-Yan, HUANG Yan-Wang, SONG Hong-Sheng. Advances on Drosophila presenilin gene [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(11): 1164-1170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||