Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (12): 1287-1299.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.25-055
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances in functional mechanisms of genomic G-quadruplex structures in transcriptional regulation
Zhenzhen He1,2( ), Xiaofeng Chen2, Yue Hou2, Tie-Lin Yang2, Bo Yang1(
), Xiaofeng Chen2, Yue Hou2, Tie-Lin Yang2, Bo Yang1( ), Yan Guo2(
), Yan Guo2( )
)
1. Department of Orthopaedics ,Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University Xi'an 710069, China 2. Key Laboratory of Biomedical Information Engineering of Ministry of Education ,School of Life Science and Technology, Xi'an Jiaotong University Xi'an 710049, China
-
Received:2025-02-24Revised:2025-04-08Online:2025-12-20Published:2025-06-03 -
Contact:Bo Yang, Yan Guo E-mail:hezz1121@stu.xjtu.edu.cn;yangbo1981911@126.com;guoyan253@xjtu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(32370653)
Cite this article
Zhenzhen He, Xiaofeng Chen, Yue Hou, Tie-Lin Yang, Bo Yang, Yan Guo. Advances in functional mechanisms of genomic G-quadruplex structures in transcriptional regulation[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(12): 1287-1299.
share this article
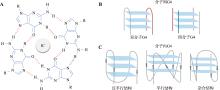
Table 1
Common approaches for identification and detection of G-quadruplex (G4) in genomes"
| 检测对象 | 技术 | 优点 | 限制 | 应用举例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体外DNA序列 | 生物物理方法 | 能够依据热稳定性、紫外吸收峰等物理性质确定未知序列在体外能否折叠成G4并确定其构象 | 检测通量低,只能在体外检测 | 圆二色光谱[ 紫外熔融[ |
| 生物化学方法 | 以单核苷酸分辨率确定长链DNA序列中G4的位置 | 具有细胞毒性,活性受限于溶剂可及性和局部离子环境 | DMS foot printing[ | |
| 全基因组 | 计算预测 | 根据给定的核酸基序可以预测基因组潜在的G4形成序列 | 预测仅限于基因组序列,无法纳入三维分子间G4及排除因染色质结构无法形成的G4 | QGRS mapper[ G4 Hunter[ |
| 聚合酶链终止法 结合二代测序 | 结合二代测序可以全面检测细胞中潜在G4,获得基因组G4图谱 | 使用提取后的DNA序列进行实验,检测结果不能代表细胞生理状态下的G4图谱 | G4-seq[ | |
| 依赖G4抗体的染 色质免疫共沉淀 | 使用特异性抗体与固定后染色质(G4 ChIP-seq)或天然细胞(G4 CUT & Tag)中G4互作检测全基因组范围存在的G4,可用于研究细胞因素对G4形成动态的影响 | 需要ChIP级别的抗体,该法会受到批次效应影响,影响可重复性。 | BG4 ChIP-seq[ BG4 CUT&Tag[ | |
| 活细胞G4动态表征 | 荧光稳定小分子 配体 | 允许在活细胞中观察单个G4的动态形成,不影响G4折叠动力学 | 荧光配体对细胞环境中pH、离子环境的变化以及光照敏感,可能会影响荧光的持续观测 | SiR-PyPDS[ |
| [1] |
Hänsel-Hertsch R, Di Antonio M, Balasubramanian S. DNA G-quadruplexes in the human genome: detection, functions and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18(5): 279-284.
pmid: 28225080 |
| [2] |
Kawauchi K, Urano R, Kinoshita N, Kuwamoto S, Torii T, Hashimoto Y, Taniguchi S, Tsuruta M, Miyoshi D. Photosensitizers based on G-quadruplex ligand for cancer photodynamic therapy. Genes, 2020, 11(11): 1340.
pmid: 33198362 |
| [3] |
Sundquist WI, Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature, 1989, 342(6251): 825-829.
pmid: 2601741 |
| [4] |
Zahler AM, Williamson JR, Cech TR, Prescott DM. Inhibition of telomerase by G-quartet DNA structures. Nature, 1991, 350(6320): 718-720.
pmid: 2023635 |
| [5] |
Siddiqui-Jain A, Grand CL, Bearss DJ, Hurley LH. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(18): 11593-11598.
pmid: 12195017 |
| [6] |
D’Aria F, Pagano B, Petraccone L, Giancola C. KRAS promoter G-quadruplexes from sequences of different length: a physicochemical study. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(1): 448.
pmid: 33466280 |
| [7] |
Rigo R, Sissi C. Characterization of G4-G4 crosstalk in the c-KIT promoter region. Biochem, 2017, 56(33): 4309-4312.
pmid: 28763217 |
| [8] |
Agrawal P, Hatzakis E, Guo KX, Carver M, Yang DZ. Solution structure of the major G-quadruplex formed in the human VEGF promoter in K+: insights into loop interactions of the parallel G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41(22): 10584-10592.
pmid: 24005038 |
| [9] |
Wang WM, Li DD, Xu QQ, Cheng JH, Yu ZW, Li GY, Qiao SY, Pan JS, Wang H, Shi JM, Zheng TS, Sui GC. G-quadruplexes promote the motility in MAZ phase- separated condensates to activate CCND1 expression and contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 1045.
pmid: 38316778 |
| [10] |
Kosiol N, Juranek S, Brossart P, Heine A, Paeschke K. G-quadruplexes: a promising target for cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 40.
pmid: 33632214 |
| [11] |
Sen D, Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature, 1988, 334(6180): 364-366.
pmid: 3393228 |
| [12] |
Lago S, Nadai M, Cernilogar FM, Kazerani M, Domíniguez Moreno H, Schotta G, Richter SN. Promoter G-quadruplexes and transcription factors cooperate to shape the cell type-specific transcriptome. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 3885.
pmid: 34162892 |
| [13] |
Guiblet WM, DeGiorgio M, Cheng XH, Chiaromonte F, Eckert KA, Huang YF, Makova KD. Selection and thermostability suggest G-quadruplexes are novel functional elements of the human genome. Genome Res, 2021, 31(7): 1136-1149.
pmid: 34187812 |
| [14] |
Puig Lombardi E, Londoño-Vallejo A. A guide to computational methods for G-quadruplex prediction. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(1): 1-15.
pmid: 31754698 |
| [15] |
Chambers VS, Marsico G, Boutell JM, Di Antonio M, Smith GP, Balasubramanian S. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nat Biotechnol, 2015, 33(8): 877-881.
pmid: 26192317 |
| [16] |
Williamson JR, Raghuraman MK, Cech TR. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell, 1989, 59(5): 871-880.
pmid: 2590943 |
| [17] |
Hänsel-Hertsch R, Spiegel J, Marsico G, Tannahill D, Balasubramanian S. Genome-wide mapping of endogenous G-quadruplex DNA structures by chromatin immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing. Nat Protoc, 2018, 13(3): 551-564.
pmid: 29470465 |
| [18] |
Lyu J, Shao R, Kwong Yung PY, Elsässer SJ. Genome- wide mapping of G-quadruplex structures with CUT&Tag. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 50(3): e13.
pmid: 34792172 |
| [19] |
Liew D, Lim ZW, Yong EH. Machine learning-based prediction of DNA G-quadruplex folding topology with G4ShapePredictor. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 24238.
pmid: 39414858 |
| [20] |
Rocher V, Genais M, Nassereddine E, Mourad R. DeepG4: a deep learning approach to predict cell-type specific active G-quadruplex regions. PLoS Comput Biol, 2021, 17(8): e1009308.
pmid: 34383754 |
| [21] |
Paramasivan S, Rujan I, Bolton PH. Circular dichroism of quadruplex DNAs: applications to structure, cation effects and ligand binding. Methods, 2007, 43(4): 324-331.
pmid: 17967702 |
| [22] |
Mergny JL, Lacroix L. UV melting of G-quadruplexes. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem, 2009, Chapter 17: 17.1.1-17.1.15.
pmid: 19488970 |
| [23] |
Kikin O, D’Antonio L, Bagga PS. QGRS Mapper: a web-based server for predicting G-quadruplexes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res, 2006, 34(Web Server issue): W676-W682.
pmid: 16845096 |
| [24] |
Bedrat A, Lacroix L, Mergny JL. Re-evaluation of G-quadruplex propensity with G4Hunter. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44(4): 1746-1759.
pmid: 26792894 |
| [25] |
Di Antonio M, Ponjavic A, Radzevičius A, Ranasinghe RT, Catalano M, Zhang XY, Shen JZ, Needham LM, Lee SF, Klenerman D, Balasubramanian S. Single-molecule visualization of DNA G-quadruplex formation in live cells. Nat Chem, 2020, 12(9): 832-837.
pmid: 32690897 |
| [26] |
Monsen RC, Trent JO, Chaires JB. G-quadruplex DNA: a longer story. Acc Chem Res, 2022, 55(22): 3242-3252.
pmid: 36282946 |
| [27] |
Lane AN, Chaires JB, Gray RD, Trent JO. Stability and kinetics of G-quadruplex structures. Nucleic Acids Res, 2008, 36(17): 5482-5515.
pmid: 18718931 |
| [28] |
Burge S, Parkinson GN, Hazel P, Todd AK, Neidle S. Quadruplex DNA: sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res, 2006, 34(19): 5402-5415.
pmid: 17012276 |
| [29] |
Ma Y, Iida K, Nagasawa K. Topologies of G-quadruplex: biological functions and regulation by ligands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 531(1): 3-17.
pmid: 31948752 |
| [30] |
Jana J, Weisz K. Thermodynamic stability of G-quadruplexes: impact of sequence and environment. ChemBioChem, 2021, 22(19): 2848-2856.
pmid: 33844423 |
| [31] |
Wu F, Niu KK, Cui Y, Li CC, Lyu M, Ren YD, Chen YF, Deng HM, Huang LH, Zheng SC, Liu L, Wang J, Song QS, Xiang H, Feng QL. Genome-wide analysis of DNA G-quadruplex motifs across 37 species provides insights into G4 evolution. Commun Biol, 2021, 4(1): 98.
pmid: 33483610 |
| [32] |
Li Z, Qian SH, Wang F, Mohamed HI, Yang GF, Chen ZX, Wei DG. G-quadruplexes in genomes of viruses infecting eukaryotes or prokaryotes are under different selection pressures from hosts. J Genet Genomics, 2022, 49(1): 20-29.
pmid: 34601118 |
| [33] |
Nakata M, Kosaka N, Kawauchi K, Miyoshi D. Quantitative effects of the loop region on topology, thermodynamics, and cation binding of DNA G-quadruplexes. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(32): 35028-35036.
pmid: 39157113 |
| [34] |
Zhang ZH, Qian SH, Wei DG, Chen ZX. In vivo dynamics and regulation of DNA G-quadruplex structures in mammals. Cell Biosci, 2023, 13(1): 117.
pmid: 37381029 |
| [35] |
Chen YW, Agrawal P, Brown RV, Hatzakis E, Hurley L, Yang DZ. The major G-quadruplex formed in the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor β promoter adopts a novel broken-strand structure in K+ solution. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134(32): 13220-13223.
pmid: 22866911 |
| [36] |
Hänsel-Hertsch R, Simeone A, Shea A, Hui WWI, Zyner KG, Marsico G, Rueda OM, Bruna A, Martin A, Zhang XY, Adhikari S, Tannahill D, Caldas C, Balasubramanian S. Landscape of G-quadruplex DNA structural regions in breast cancer. Nat Genet, 2020, 52(9): 878-883.
pmid: 32747825 |
| [37] |
Hänsel-Hertsch R, Beraldi D, Lensing SV, Marsico G, Zyner K, Parry A, Di Antonio M, Pike J, Kimura H, Narita M, Tannahill D, Balasubramanian S. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat Genet, 2016, 48(10): 1267-1272.
pmid: 27618450 |
| [38] |
Hanna R, Flamier A, Barabino A, Bernier G. G-quadruplexes originating from evolutionary conserved L1 elements interfere with neuronal gene expression in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1828.
pmid: 33758195 |
| [39] |
Shen JZ, Varshney D, Simeone A, Zhang XY, Adhikari S, Tannahill D, Balasubramanian S. Promoter G-quadruplex folding precedes transcription and is controlled by chromatin. Genome Biol, 2021, 22(1): 143.
pmid: 33962653 |
| [40] |
Fleming AM, Burrows CJ. Interplay of guanine oxidation and G-quadruplex folding in gene promoters. J Am Chem Soc, 2020, 142(3): 1115-1136.
pmid: 31880930 |
| [41] |
Liu Y, Zhu XT, Wang KJ, Zhang B, Qiu SY. The cellular functions and molecular mechanisms of G-quadruplex unwinding helicases in humans. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8: 783889.
pmid: 34912850 |
| [42] |
Teng XC, Dai YC, Li K, Wu YC, Hou HW, Li JH. LiveG4ID-Seq for profiling the dynamic landscape of chromatin G-quadruplexes during cell cycle in living cells. Small Methods, 2023, 7(4): 2201487.
pmid: 36739600 |
| [43] |
Lejault P, Mitteaux J, Sperti FR, Monchaud D. How to untie G-quadruplex knots and why? Cell Chem Biol, 2021, 28(4): 436-455.
pmid: 33596431 |
| [44] |
Shu HL, Zhang RX, Xiao K, Yang J, Sun X. G-quadruplex-binding proteins: promising targets for drug design. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(5): 648.
pmid: 35625576 |
| [45] |
Zhang RX, Wang YQ, Wang C, Sun X, Mergny JL. G-quadruplexes as pivotal components of cis-regulatory elements in the human genome. BMC Biol, 2024, 22(1): 177.
pmid: 39183303 |
| [46] |
Raiber EA, Kranaster R, Lam E, Nikan M, Balasubramanian S. A non-canonical DNA structure is a binding motif for the transcription factor SP1 in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012, 40(4): 1499-1508.
pmid: 22021377 |
| [47] |
González V, Guo KX, Hurley L, Sun D. Identification and characterization of nucleolin as a c-myc G-quadruplex- binding protein. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(35): 23622-23635.
pmid: 19581307 |
| [48] |
Xiao CM, Li YP, Liu YS, Dong RF, He XY, Lin Q, Zang X, Wang KB, Xia YZ, Kong LY. Overcoming cancer persister cells by stabilizing the ATF4 promoter G-quadruplex. Adv Sci, 2024, 11(35): e2401748.
pmid: 38994891 |
| [49] |
Garcia IE, Kirchner A, Melidis L, de Cesaris Araujo Tavares R, Dhir S, Simeone A, Yu ZT, Madden SK, Hermann R, Tannahill D, Balasubramanian S. G-quadruplex DNA structure is a positive regulator of MYC transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2024, 121(7): e2320240121.
pmid: 38315865 |
| [50] |
Pavlova II, Tsvetkov VB, Isaakova EA, Severov VV, Khomyakova EA, Lacis IA, Lazarev VN, Lagarkova MA, Pozmogova GE, Varizhuk AM. Transcription-facilitating histone chaperons interact with genomic and synthetic G4 structures. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 160: 1144-1157.
pmid: 32454109 |
| [51] |
Lamonica JM, Deng WL, Kadauke S, Campbell AE, Gamsjaeger R, Wang HX, Cheng Y, Billin AN, Hardison RC, Mackay JP, Blobel GA. Bromodomain protein Brd3 associates with acetylated GATA1 to promote its chromatin occupancy at erythroid target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(22): E159-E168.
pmid: 21536911 |
| [52] |
Liano D, Chowdhury S, Di Antonio M. Cockayne syndrome B protein selectively resolves and interact with intermolecular DNA G-quadruplex structures. J Am Chem Soc, 2021, 143(49): 20988-21002.
pmid: 34855372 |
| [53] |
Gao Z, Yuan J, He XM, Wang HD, Wang YS. Phase separation modulates the formation and stabilities of DNA Guanine quadruplex. JACS Au, 2023, 3(6): 1650-1657.
pmid: 37388701 |
| [54] |
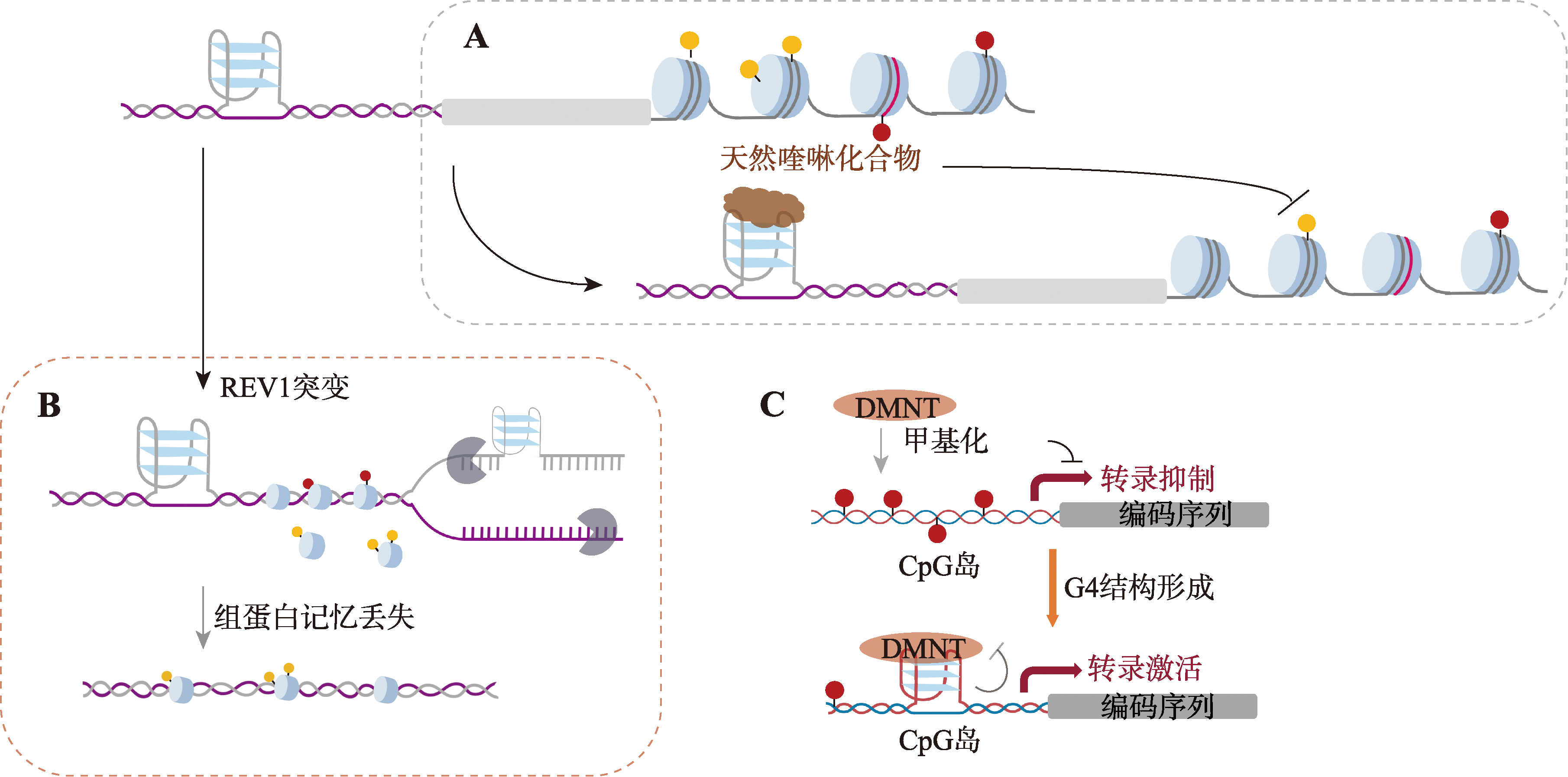
Li CH, Yin ZN, Xiao RJ, Huang BL, Cui YL, Wang HH, Xiang Y, Wang LR, Lei LY, Ye JQ, Li TY, Zhong YQ, Guo FT, Xia YC, Fang PP, Liang KW. G-quadruplexes sense natural porphyrin metabolites for regulation of gene transcription and chromatin landscapes. Genome Biol, 2022, 23(1): 259.
pmid: 36522639 |
| [55] |
Schiavone D, Guilbaud G, Murat P, Papadopoulou C, Sarkies P, Prioleau MN, Balasubramanian S, Sale JE. Determinants of G quadruplex-induced epigenetic instability in REV1-deficient cells. EMBO J, 2014, 33(21): 2507-2520.
pmid: 25190518 |
| [56] |
Saha D, Singh A, Hussain T, Srivastava V, Sengupta S, Kar A, Dhapola P, Dhople V, Ummanni R, Chowdhury S. Epigenetic suppression of human telomerase (hTERT) is mediated by the metastasis suppressor NME2 in a G-quadruplex-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(37): 15205-15215.
pmid: 28717007 |
| [57] |
Blackledge NP, Klose R. CpG island chromatin: a platform for gene regulation. Epigenetics, 2011, 6(2): 147-152.
pmid: 20935486 |
| [58] |
Jurkowska RZ, Jurkowski TP, Jeltsch A. Structure and function of mammalian DNA methyltransferases. Chembiochem, 2011, 12(2): 206-222.
pmid: 21243710 |
| [59] |
Loiko AG, Sergeev AV, Genatullina AI, Monakhova MV, Kubareva EA, Dolinnaya NG, Gromova ES. Impact of G-quadruplex structures on methylation of model substrates by DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(18): 10226.
pmid: 36142137 |
| [60] |
Mao SQ, Ghanbarian AT, Spiegel J, Cuesta SM, Beraldi D, Antonio MD, Marsico G, Hänsel-Hertsch R, Tannahill D, Balasubramanian S. DNA G-quadruplex structures mold the DNA methylome. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2018, 25(10): 951.
pmid: 30275516 |
| [61] |
Matsumoto S, Tateishi-Karimata H, Sugimoto N. DNA methylation is regulated by both the stability and topology of G-quadruplex. Chem Commun, 2022, 58(89): 12459-12462.
pmid: 36263745 |
| [62] |
Guo HS, Vuille JA, Wittner BS, Lachtara EM, Hou Y, Lin MX, Zhao T, Raman AT, Russell HC, Reeves BA, Pleskow HM, Wu CL, Gnirke A, Meissner A, Efstathiou JA, Lee RJ, Toner M, Aryee MJ, Lawrence MS, Miyamoto DT, Maheswaran S, Haber DA. DNA hypomethylation silences anti-tumor immune genes in early prostate cancer and CTCs. Cell, 2023, 186(13): 2765-2782.e28.
pmid: 37327786 |
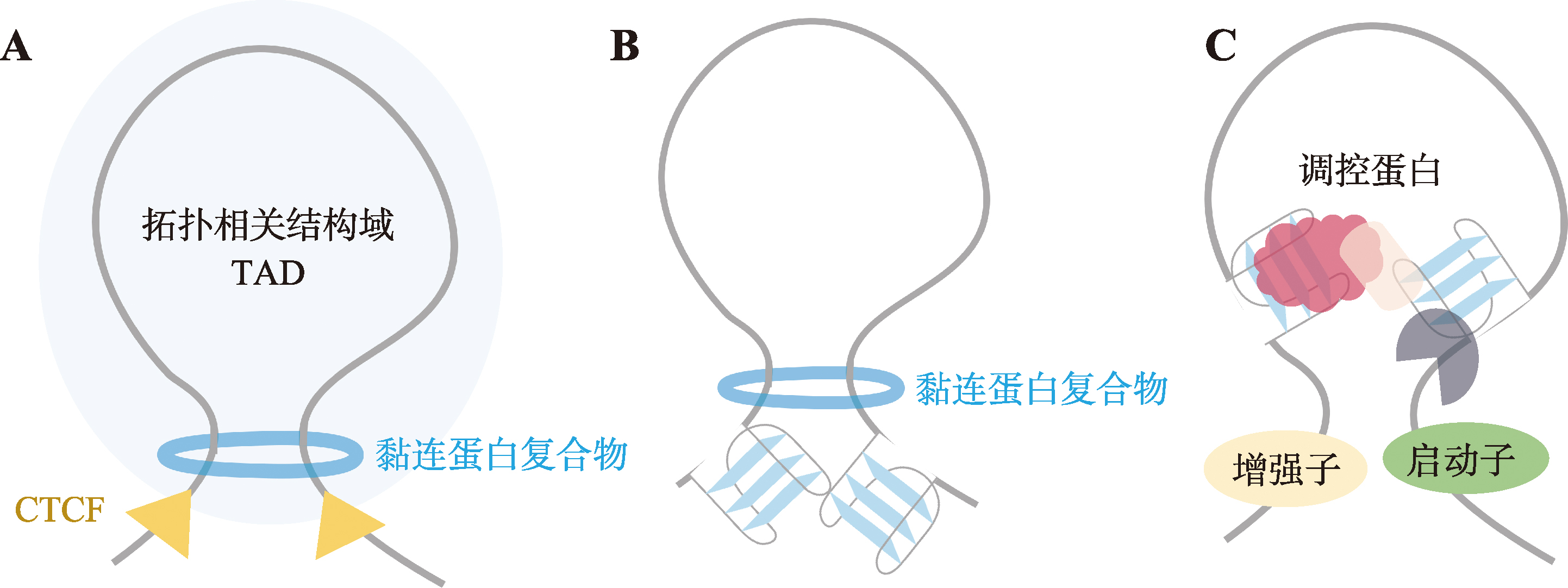
| [63] | Ning CY, He MN, Tang QZ, Zhu Q, Li MZ, Li DY. Advances in mammalian three-dimensional genome by using Hi-C technology approach. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(3): 215-233. |
| 宁椿游, 何梦楠, 唐茜子, 朱庆, 李明洲, 李地艳. 基于Hi-C技术哺乳动物三维基因组研究进展. 遗传, 2019, 41(3): 215-233. | |
| [64] |
Yuan J, He XM, Wang YS. G-quadruplex DNA contributes to RNA polymerase II-mediated 3D chromatin architecture. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(16): 8434-8446.
pmid: 37427784 |
| [65] |
Cordero J, Swaminathan G, Rogel-Ayala DG, Rubio K, Elsherbiny A, Mahmood S, Szymanski W, Graumann J, Braun T, Günther S, Dobreva G, Barreto G. Nuclear microRNA 9 mediates G-quadruplex formation and 3D genome organization during TGF-β-induced transcription. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 10711.
pmid: 39706840 |
| [66] |
Li L, Williams P, Ren WD, Wang MY, Gao Z, Miao WL, Huang M, Song JK, Wang YS. YY1 interacts with guanine quadruplexes to regulate DNA looping and gene expression. Nat Chem Biol, 2021, 17(2): 161-168.
pmid: 33199912 |
| [67] | Zhou C, Zhou QW, Cheng S, Li GL. Research progress of CTCF in mediating 3D genome formation and regulating gene expression. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 816-821. |
| 周聪, 周强伟, 成盛, 李国亮. CTCF在介导三维基因组形成及调控基因表达中的研究进展. 遗传, 2021, 43(9): 816-821. | |
| [68] |
Tikhonova P, Pavlova I, Isaakova E, Tsvetkov V, Bogomazova A, Vedekhina T, Luzhin AV, Sultanov R, Severov V, Klimina K, Kantidze OL, Pozmogova G, Lagarkova M, Varizhuk A. DNA G-quadruplexes contribute to CTCF recruitment. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(13): 7090.
pmid: 34209337 |
| [69] |
Hou Y, Li FY, Zhang RX, Li S, Liu HD, Qin ZHS, Sun X. Integrative characterization of G-Quadruplexes in the three-dimensional chromatin structure. Epigenetics, 2019, 14(9): 894-911.
pmid: 31177910 |
| [70] |
Wang L, Gao YF, Zheng XD, Liu CF, Dong SS, Li R, Zhang GW, Wei YX, Qu HY, Li YH, Allis CD, Li GH, Li HT, Li PL. Histone modifications regulate chromatin compartmentalization by contributing to a phase separation mechanism. Mol Cell, 2019, 76(4): 646-659.e6.
pmid: 31543422 |
| [71] |
Yang QF, Wang XR, Wang YH, Wu XH, Shi RY, Wang YX, Zhu HN, Yang S, Tang YL, Li F. G4LDB 3.0:a database for discovering and studying G-quadruplex and i-motif ligands. Nucleic Acids Res, 2025, 53(D1): D91-D98.
pmid: 39319582 |
| [72] |
Xu H, Di Antonio M, McKinney S, Mathew V, Ho B, O'Neil NJ, Santos ND, Silvester J, Wei V, Garcia J, Kabeer F, Lai D, Soriano P, Banáth J, Chiu DS, Yap D, Le DD, Ye FB, Zhang AN, Thu K, Soong J, Lin SC, Tsai AHC, Osako T, Algara T, Saunders DN, Wong JS, Xian J, Bally MB, Brenton JD, Brown GW, Shah SP, Cescon D, Mak TW, Caldas C, Stirling PC, Hieter P, Balasubramanian S, Aparicio S. CX-5461 is a DNA G-quadruplex stabilizer with selective lethality in BRCA1/2 deficient tumours. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 14432.
pmid: 28211448 |
| [73] |
Qin G, Liu ZQ, Yang J, Liao XF, Zhao CQ, Ren JS, Qu XG. Targeting specific DNA G-quadruplexes with CRISPR-guided G-quadruplex-binding proteins and ligands. Nat Cell Biol, 2024, 26(7): 1212-1224.
pmid: 38961283 |
| [74] |
Liu LY, Ma TZ, Zeng YL, Liu WT, Zhang H, Mao ZW. Organic-platinum hybrids for covalent binding of G-quadruplexes: structural basis and application to cancer immunotherapy. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2023, 62(36): e202305645.
pmid: 37464955 |
| [75] |
Zhang RX, Shu HL, Wang YQ, Tao TT, Tu J, Wang C, Mergny JL, Sun X. G-quadruplex structures are key modulators of somatic structural variants in cancers. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(8): 1234-1248.
pmid: 36791413 |
| [76] |
Richl T, Kuper J, Kisker C. G-quadruplex-mediated genomic instability drives SNVs in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res, 2024, 52(5): 2198-2211.
pmid: 38407356 |
| [77] |
Wang G, Vasquez KM. Dynamic alternative DNA structures in biology and disease. Nat Rev Genet, 2022, 24(4): 211-234.
pmid: 36316397 |
| [78] |
Batra S, Allwein B, Kumar C, Devbhandari S, Brüning JG, Bahng S, Lee CM, Marians KJ, Hite RK, Remus D. G-quadruplex-stalled eukaryotic replisome structure reveals helical inchworm DNA translocation. Science, 2025, 387(6738): eadt1978.
pmid: 40048517 |
| [1] | Ying Feng, Xiaoli He, Yu Liu, Jin Wang. Mass spectrometry-based analysis of RNA and its modifications [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(8): 885-902. |
| [2] | Jiehao Lin, Tongshu Yang, Wenqing Zhang, Wei Liu. Role of different Lyl1 transcripts in zebrafish primitive hematopoiesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(5): 573-588. |
| [3] | Jialin Ren, Yize Tong, Rui Cai. Advances of m6A modification of chromatin-associated RNAs regulating chromatin accessibility and gene transcription [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(11): 1186-1196. |
| [4] | Jilong Wang, Qing Li, Tingzheng Zhan. Principle and application of self-transcribing active regulatory region sequencing in enhancer discovery research [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(8): 589-602. |
| [5] | Daiyuan Liu, Zhaohui Zhang, Xianjiang Kang. Research progress on the effect of sperm chromatin integrity on function and its detection methods [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(7): 511-529. |
| [6] | Yuan Shen, Jintao Li, Miao Yin, Qunying Lei. The roles of branched-chain amino acids metabolism in tumorigenesis and progression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(6): 438-451. |
| [7] | Zhaoran Sun, Xudong Wu. The roles and mechanisms of histone variant H2A.Z in transcriptional regulation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(4): 279-289. |
| [8] | Jiaxin Hong, Song’en Xu, Wenqing Zhang, Wei Liu. The interaction of Pu.1 and cMyb in zebrafish neutrophil development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(4): 319-332. |
| [9] | Qi Li, Zhicheng Dong, Min Liu. The carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II large subunit: simple repeats are not simple [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(12): 1028-1041. |
| [10] | Linlin You, Yu Zhang. Progress on molecular mechanisms of bacterial transcription termination [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(12): 982-994. |
| [11] | Yanni Wang, Jia Li. Processing pipelines and analytical methods for single-cell DNA methylation sequencing data [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(10): 807-819. |
| [12] | Xiufang Ou, Ying Wu, Ning Li, Lili Jiang, Bao Liu, Lei Gong. Epigenetics comprehensive experimental course based on the integration of science and education to cultivate students' ability of cutting-edge innovation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(12): 1158-1168. |
| [13] | Meng Yuan, Hui Li, Shouzhi Wang. Massively parallel reporter assay: a novel technique for analyzing the regulation of gene expression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(10): 859-873. |
| [14] | Dandan Wu, Mingkun Zhu, Zhongyan Fang, Wei Ma. Progress on molecular composition and genetic mechanism of plant B chromosomes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 772-782. |
| [15] | Fengyu Sun, Qianghua Xu. Research progress of microRNAs involved in hematopoiesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 756-771. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||