Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 810-818.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-128
• Genetic Resource • Previous Articles
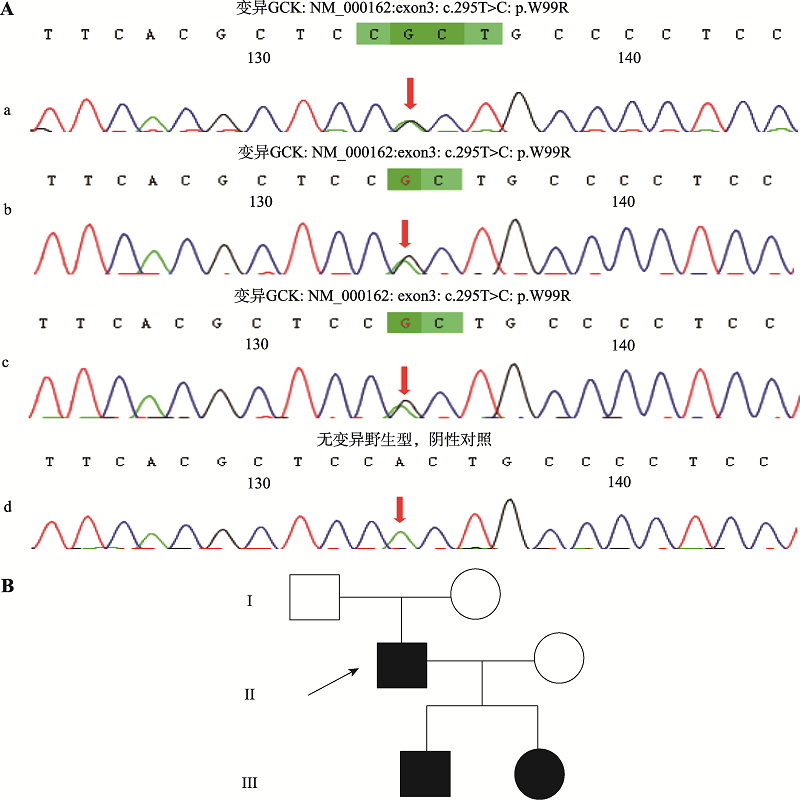
Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of a case of hypoglycemia caused by glucokinase gene mutation
Luyang Li( ), Sunqiang Liu, Yun Shi, Chengcheng Zhao, Hongwen Zhou, Xuqin Zheng(
), Sunqiang Liu, Yun Shi, Chengcheng Zhao, Hongwen Zhou, Xuqin Zheng( )
)
- Department of Endocrinology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
-
Received:2022-04-27Revised:2022-06-20Online:2022-09-20Published:2022-08-12 -
Contact:Zheng Xuqin E-mail:liluyang6986@163.com;zhengxuqin@njmu.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China No(2019YFA0802701);2021 School Level Education Research Project of Nanjing Medical University No(2021YJSLX009)
Cite this article
Luyang Li, Sunqiang Liu, Yun Shi, Chengcheng Zhao, Hongwen Zhou, Xuqin Zheng. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of a case of hypoglycemia caused by glucokinase gene mutation[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 810-818.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 2
Simultaneous glucose, insulin, C-peptide, ACTH, cortisol, growth hormone and glucagon in hunger test"
| 项目 | 饥饿试验前 | 饥饿试验9 h | 饥饿试验14 ha |
|---|---|---|---|
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 2.8 | 1.55 | 2.55 |
| 胰岛素(pmol/L) | 99.7 | 65.5 | 58.7 |
| C肽(pmol/L) | 982.0 | 651.4 | 557.9 |
| 胰岛素释放指数 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.18 |
| 皮质醇(nmol/L) | 465.0 | 372.0 | 187.0 |
| ACTH(pg/mL) | 52.7 | 31.2 | 20.4 |
| 生长激素(ng/mL) | 2.992 | - | 0.141 |
| 胰高血糖素(pg/mL) | 421.4 | - | 204.0 |
Table 3
Clinical and functional characterizations of naturally occurring GCK-CHI mutations"
| 氨基酸 变异位点 | 核苷酸 突变位点 | GSIR的预测 阈值(mmol/L, 野生型为5) | S0.5 (mmol/L, 野生型 为7.63) | 相对野生型 的活动指数 (无单位) | 症状特点 | 二氮嗪 反应性 | 有无发生 超重或者 远期T2DM | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S64Y | c.191C>A | 1.4 | 1.5 | 22.4 | 出生即被诊断为低血糖,但程度较轻 | 是 | 无 | [ |
| T65I | c.194C>T | 3.1 | 1.7 | 9.81 | 低血糖程度较轻,且婴儿出生体重没有增加 | 是 | 无 | [ |
| G68V | c.203G>T | 1.9 | 1.9 | 16 | 低血糖和相关症状的严重程度异质 | 是 | 有 | [ |
| K90R | c.269A>G | NA | 4.8 | 1.6 | 无症状的空腹低血糖 | NA | 有 | [ |
| V91L | c.271C>G | 0.96 | 1.7 | 24 | 新生儿严重低血糖 | 是 | 无 | [ |
| W99C | c.297G>T | NA | 3.5 | 11.6 | 症状较温和且较晚发病 | 是 | 无 | [ |
| W99L | c.296G>T | 2.2 | 2.9 | 8.9 | 低血糖出现较迟,需用药物及连续葡萄糖治疗 | 部分 | 无 | [ |
| W99R | c.295T>C | 2.8 | 4.9 | 6.36 | 程度不一和更难治疗的低血糖以及偶发的酮症 | 部分 | 无 | [ |
| T103S | c.308C>G | 2.9 | 3.3 | 8.4 | 症状较温和 | 是 | 无 | [ |
| N180D | c.538A>G | NA | NA | NA | 反复发作的中度永久性低血糖 | 部分 | 有 | [ |
| M197I | c.591G>T | 3.5 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 低血糖程度较轻,通常是无症状的 | 是 | 无 | [ |
| M197T | c.590T>C | NA | 4.1 | 2.9 | 轻度低血糖,可伴部分肾上腺皮质功能不全 | NA | 无 | [ |
| M197V | c.589A>G | NA | 2.6 | 4.7 | 可有发作性四肢僵直伴意识不清 | 部分 | 有 | [ |
| I211F | NA | NA | NA | NA | 体细胞突变,仅在一个功能亢进的胰岛中发现 | NA | 无 | [ |
| Y214C | c.641A>G | 0.8 | 1.2 | 130 | 难以控制的致命性低血糖,引起智力低下、癫痫甚至早逝 | 否 | 无 | [ |
| V389L | c.1165C>G | 2.9 | 3.5 | 6.0 | 低血糖出现迟,频繁进食可缓解 | 部分 | 有 | [ |
| E442K | NA | 4.14 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 儿童和成年生活中相对轻微的低血糖症状 | 是 | 无 | [ |
| V452L | c.1354G>C | 1.9 | 2.6 | 10.8 | 间歇性、严重程度不一的新生儿高血糖 | 是 | 有 | [ |
| ins454A | c.1361-364 insCGG | 1.1 | 1.1 | 26 | 难以控制的致命性低血糖 | 否 | 无 | [ |
| V455L | c.1363G>C | NA | 2.4 | NA | 在婴儿期食欲旺盛,发展为严重肥胖 | NA | 有 | [ |
| V455M | c.1363C>A | NA | 2.9 | 5.2 | 低血糖程度较轻 | 是 | 有 | [ |
| A456V | c.1367C>T | 1.5 | 2.5 | 37.9 | 无症状低血糖 | 是 | 有 | [ |
| [1] | Steele AM, Shields BM, Wensley KJ, Colclough K, Ellard S, Hattersley AT . Prevalence of vascular complications among patients with glucokinase mutations and prolonged, mild hyperglycemia. JAMA, 2014,311(3):279-286. |
| [2] | Kavvoura FK, Raimondo A, Thanabalasingham G, Barrett A, Webster AL, Shears D, Mann NP, Ellard S, Gloyn AL, Owen KR . Reclassification of diabetes etiology in a family with multiple diabetes phenotypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2014,99(6):E1067-E1071. |
| [3] | Gϋemes M, Rahman SA, Kapoor RR, Flanagan S, Houghton JAL, Misra S, Oliver N, Dattani MT, Shah P . Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in children and adolescents: Recent advances in understanding of pathophysiology and management. Rev Endocr Metab Disord, 2020,21(4):577-597. |
| [4] | Osbak KK, Colclough K, Saint-Martin C, Beer NL, Bellanné-Chantelot C, Ellard S, Gloyn AL . Update on mutations in glucokinase (GCK), which cause maturity- onset diabetes of the young, permanent neonatal diabetes, and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Hum Mutat, 2009,30(11):1512-1526. |
| [5] | Sims K . Congenital hyperinsulinism. Neoreviews, 2021,22(4):e230-e240. |
| [6] | Aynsley-Green A, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Gough MH, Keeling J, Ashcroft SJ, Turner RC, Baum JD . Nesidioblastosis of the pancreas: definition of the syndrome and the management of the severe neonatal hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. Arch Dis Child, 1981,56(7):496-508. |
| [7] | Arnoux JB, Verkarre V, Saint-Martin C, Montravers F, Brassier A, Valayannopoulos V, Brunelle F, Fournet JC, Robert JJ, Aigrain Y, Bellanné-Chantelot C, De Lonlay P . Congenital hyperinsulinism: current trends in diagnosis and therapy. Orphanet J Dis, 2011,6:63. |
| [8] | Glaser B, Kesavan P, Heyman M, Davis E, Cuesta A, Buchs A, Stanley CA, Thornton PS, Permutt MA, Matschinsky M, Herold KC . Familial hyperinsulinism caused by an activating glucokinase mutation. N Engl J Med, 1998,338(4):226-230. |
| [9] | Langer S, Waterstradt R, Hillebrand G, Santer R, Baltrusch S . The novel GCK variant p.Val455Leu associated with hyperinsulinism is susceptible to allosteric activation and is conducive to weight gain and the development of diabetes. Diabetologia, 2021,64(12):2687-2700. |
| [10] | Ping F, Wang ZX, Xiao XH . Clinical and enzymatic phenotypes in congenital hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia due to glucokinase-activating mutations: a report of two cases and a brief overview of the literature. J Diabetes Investig, 2019,10(6):1454-1462. |
| [11] | Christesen HBT, Tribble ND, Molven A, Siddiqui J, Sandal T, Brusgaard K, Ellard S, Njølstad PR, Alm J, Brock Jacobsen B, Hussain K, Gloyn AL . Activating glucokinase (GCK) mutations as a cause of medically responsive congenital hyperinsulinism: prevalence in children and characterisation of a novel GCK mutation. Eur J Endocrinol, 2008,159(1):27-34. |
| [12] | Gloyn AL, Noordam K, Willemsen MAAP, Ellard S, Lam WWK, Campbell IW, Midgley P, Shiota C, Buettger C, Magnuson MA, Matschinsky FM, Hattersley AT . Insights into the biochemical and genetic basis of glucokinase activation from naturally occurring hypoglycemia mutations. Diabetes, 2003,52(9):2433-2440. |
| [13] | Wabitsch M, Lahr G, Van De Bunt M, Marchant C, Lindner M, Von Puttkamer J, Fenneberg A, Debatin KM, Klein R, Ellard S, Clark A, Gloyn AL. Heterogeneity in disease severity in a family with a novel G68V GCK activating mutation causing persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia of infancy. Diabet Med, 2007,24(12):1393-1399. |
| [14] | Kassem S, Bhandari S, Rodríguez-Bada P, Motaghedi R, Heyman M, García-Gimeno MA, Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Sanz P, Maclaren NK, Rahier J, Glaser B, Cuesta-Muñoz AL . Large islets, beta-cell proliferation, and a glucokinase mutation. N Engl J Med, 2010,362(14):1348-1350. |
| [15] | Martínez R, Gutierrez-Nogués Á, Fernández-Ramos C, Velayos T, Vela A, Spanish Congenital Hyperinsulinism Group, Navas M-Á, Castaño L. Heterogeneity in phenotype of hyperinsulinism caused by activating glucokinase mutations: a novel mutation and its functional characterization. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2017,86(6):778-783. |
| [16] | Sayed S, Langdon DR, Odili S, Chen P, Buettger C, Schiffman AB, Suchi M, Taub R, Grimsby J, Matschinsky FM, Stanley CA . Extremes of clinical and enzymatic phenotypes in children with hyperinsulinism caused by glucokinase activating mutations. Diabetes, 2009,58(6):1419-1427. |
| [17] | Gilis-Januszewska A, Bogusławska A, Kowalik A, Rzepka E, Soczówka K, Przybylik-Mazurek E, Głowa B, Hubalewska-Dydejczyk A . Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in three generations of a family with glucokinase activating mutation, c.295T>C (p.Trp99Arg). Genes (Basel), 2021,12(10):1566. |
| [18] | Beer NL, Van De Bunt M, Colclough K, Lukacs C, Arundel P, Chik CL, Grimsby J, Ellard S, Gloyn AL, . Discovery of a novel site regulating glucokinase activity following characterization of a new mutation causing hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in humans. J Biol Chem, 2011,286(21):19118-19126. |
| [19] | Jannin A, Espiard S, Douillard C, Pasquier F, Bellanné-Chantelot C, Vantyghem MC . Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia without insulinoma: think of activating glucokinase mutation. Presse Med, 2018,47(6):595-597. |
| [20] | Morishita K, Kyo C, Yonemoto T, Kosugi R, Ogawa T, Inoue T . Asymptomatic congenital hyperinsulinism due to a glucokinase-activating mutation, treated as adrenal insufficiency for twelve years. Case Rep Endocrinol, 2017,2017:4709262. |
| [21] | Henquin JC, Sempoux C, Marchandise J, Godecharles S, Guiot Y, Nenquin M, Rahier J . Congenital hyperinsulinism caused by hexokinase I expression or glucokinase- activating mutation in a subset of β-cells. Diabetes, 2013,62(5):1689-1696. |
| [22] | Cuesta-Muñoz AL, Huopio H, Otonkoski T, Gomez- Zumaquero JM, Näntö-Salonen K, Rahier J, López- Enriquez S, García-Gimeno MA, Sanz P, Soriguer FC, Laakso M . Severe persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia due to a de novo glucokinase mutation. Diabetes, 2004,53(8):2164-2168. |
| [23] | Challis BG, Harris J, Sleigh A, Isaac I, Orme SM, Seevaratnam N, Dhatariya K, Simpson HL, Semple RK . Familial adult onset hyperinsulinism due to an activating glucokinase mutation: implications for pharmacological glucokinase activation. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2014,81(6):855-861. |
| [24] | Barbetti F, Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Dionisi-Vici C, Toni S, Ciampalini P, Massa O, Rodriguez-Bada P, Colombo C, Lenzi L, Garcia-Gimeno MA, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Rodriguez De Fonseca F, Banin P, Aledo JC, Baixeras E, Sanz P, Cuesta-Muñoz AL. Opposite clinical phenotypes of glucokinase disease: description of a novel activating mutation and contiguous inactivating mutations in human glucokinase (GCK) gene. Mol Endocrinol, 2009,23(12):1983-1989. |
| [25] | Ajala ON, Huffman DM, Ghobrial II . Glucokinase mutation-a rare cause of recurrent hypoglycemia in adults: a case report and literature review. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect, 2016,6(5):32983. |
| [26] | Maiorana A, Manganozzi L, Barbetti F, Bernabei S, Gallo G, Cusmai R, Caviglia S, Dionisi-Vici C . Ketogenic diet in a patient with congenital hyperinsulinism: a novel approach to prevent brain damage. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2015,10:120. |
| [27] | Christesen HBT, Jacobsen BB, Odili S, Buettger C, Cuesta-Munoz A, Hansen T, Brusgaard K, Massa O, Magnuson MA, Shiota C, Matschinsky FM, Barbetti F . The second activating glucokinase mutation (A456V): implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes therapy. Diabetes, 2002,51(4):1240-1246. |
| [28] | Adzick NS, De Leon DD, States LJ, Lord K, Bhatti TR, Becker SA, Stanley CA . Surgical treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism: results from 500 pancreatectomies in neonates and children. J Pediatr Surg, 2019,54(1):27-32. |
| [29] | Ferrara C, Patel P, Becker S, Stanley CA, Kelly A . Biomarkers of insulin for the diagnosis of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in infants and children. J Pediatr, 2016,168:212-219. |
| [30] | Banerjee I, Salomon-Estebanez M, Shah P, Nicholson J, Cosgrove KE, Dunne MJ . Therapies and outcomes of congenital hyperinsulinism-induced hypoglycaemia. Diabet Med, 2019,36(1):9-21. |
| [31] | Skae M, Avatapalle HB, Banerjee I, Rigby L, Vail A, Foster P, Charalambous C, Bowden L, Padidela R, Patel L, Ehtisham S, Cosgrove KE, Dunne MJ, Clayton PE . Reduced glycemic variability in diazoxide-responsive children with congenital hyperinsulinism using supplemental omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids; a pilot trial with maxEPA(R.). Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2014,5:31. |
| [32] | De Leon DD, Stanley CA . congenital hypoglycemia disorders: new aspects of etiology, diagnosis, treatment and outcomes: highlights of the proceedings of the congenital hypoglycemia disorders symposium, Philadelphia April 2016. Pediatr Diabetes, 2017,18(1):3-9. |
| [33] | Huopio H, Otonkoski T, Vauhkonen I, Reimann F, Ashcroft FM, Laakso M . A new subtype of autosomal dominant diabetes attributable to a mutation in the gene for sulfonylurea receptor 1. Lancet, 2003,361(9354):301-307. |
| [34] | Heredia VV, Carlson TJ, Garcia E, Sun SX . Biochemical basis of glucokinase activation and the regulation by glucokinase regulatory protein in naturally occurring mutations. J Biol Chem, 2006,281(52):40201-40207. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||