Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (6): 636-649.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-282
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Progress on the role of eicosanoids in insect immunity
Yimin Zhao1( ), Ruixuan Li1(
), Ruixuan Li1( ), Ziyi Qin1, Yong Wang1,2(
), Ziyi Qin1, Yong Wang1,2( )
)
- 1. College of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang 110866, China
2. Insect Resource Innovation Center for Professional Technology of Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110866, China
-
Received:2024-09-26Revised:2024-12-22Online:2025-06-20Published:2025-02-13 -
Contact:Yong Wang E-mail:zhaoyimin19991007@163.com;lirx0412@163.com;yongwang216@163.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31902213);Earmarked Fund for China Agricultural Research System(CARS-18);Major Science and Technology Projects of Liaoning Province(2024JH1/11700009)
Cite this article
Yimin Zhao, Ruixuan Li, Ziyi Qin, Yong Wang. Progress on the role of eicosanoids in insect immunity[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(6): 636-649.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Common eicosanoids species and their structures"
| 通用名称 | 系统命名及NCBI化合物编号 | 化学结构 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PGG2 (C20H32O6) | (5Z,9α,11α,13E,15S)-9,11-Epidioxy-15-hydroperoxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid PubChem CID: 5280883 | 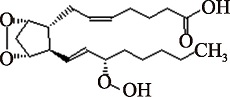 | [ |
| PGH2 (C20H32O5) | (5Z,13E,15S)-9alpha,11alpha-epidioxy-15-hydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate PubChem CID: 445049 | 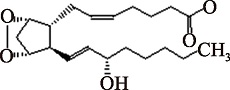 | [ |
| PGD2 (C20H32O5) | (5Z,9α,13E,15S)-9,15-Dihydroxy-11-oxoprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid PubChem CID: 448457 | 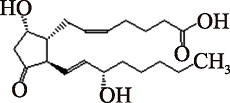 | [ |
| PGJ2 (C20H30O4) | (5Z,13E,15S)-15-hydroxy-11-oxoprosta-5,9,13-trien-1-oic acid PubChem CID: 5280884 | 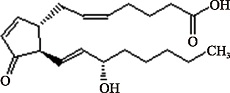 | [ |
| 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 (C20H28O3) | (5Z,12E,14E)-11-oxoprosta-5,9,12,14-tetraen-1-oic acid PubChem CID: 5311211 | 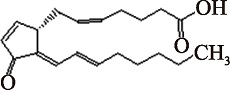 | [ |
| PGE2 (C20H32O5) | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-11alpha,15-Dihydroxy-9-oxoprosta-5,13-dienoate PubChem CID: 5280360 | 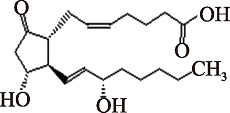 | [ |
| PGF2α (C20H34O5) | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-9alpha,11alpha,15-Trihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate PubChem CID: 5280363 | 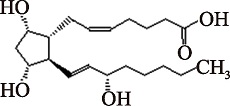 | [ |
| PGA2 (C20H30O4) | 9-oxo-15S-hydroxy-prosta-5Z,10,13E-trien-1-oic acid PubChem CID: 5280880 | 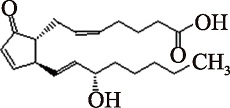 | [ |
| PGB2 (C20H30O4) | (5Z,13E,15S)-15-Hydroxy-9-oxoprosta-5,8(12),13-trien-1-oic acid PubChem CID: 5280881 | 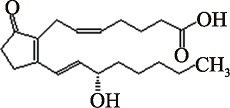 | [ |
| PGI2 (C20H32O5) | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-6,9alpha-Epoxy-11alpha,15-dihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate PubChem CID: 5282411 | 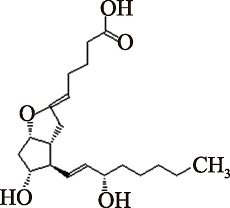 | [ |
| PGE1 (C20H34O5) | (13E)-(15S)-11alpha,15-Dihydroxy-9-oxoprost-13-enoate PubChem CID: 5280723 | 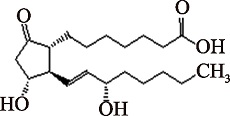 | [ |
| LTA4 (C20H30O3) | (7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-(5S,6S)-5,6-Epoxyeicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid PubChem CID: 5280383 | 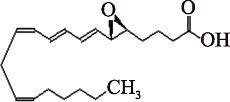 | [ |
| LTB4 (C20H32O4) | (6Z,8E,10E,14Z)-(5S,12R)-5,12-Dihydroxyeicosa-6,8,10,14-tetraenoate PubChem CID: 5280492 | 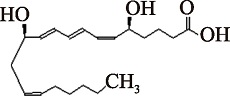 | [ |
| LXA4 (C20H32O5) | (5S,6R,7E,9E,11Z,13E,15S)-5,6,15-Trihydroxy-7,9,11,13-eicosatetraenoic acid PubChem CID: 5280914 | 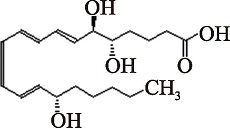 | [ |
| LXB4 (C20H32O5) | (5S,6E,8Z,10E,12E,14R,15S)-5,14,15-Trihydroxy-6,8,10,12-eicosatetraenoic acid PubChem CID: 5280915 | 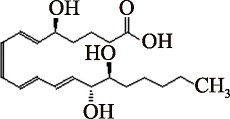 | [ |
| 5(S)-PHETE (C20H32O4) | (5S,6E,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5-Hydroperoxy-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid PubChem CID: 5280778 | 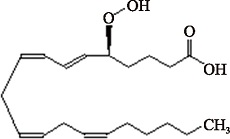 | [ |
| 5(S)-HETE (C20H32O3) | (6E,8Z,11Z,14Z)-(5S)-5-Hydroxyicosa-6,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid PubChem CID: 5280733 | 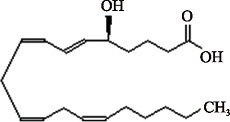 | [ |
| 5,6-EET (C20H32O3) | (8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,6-Epoxyeicosa-8,11,14-trienoic acid PubChem CID: 5283202 | 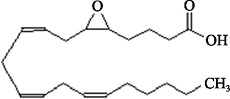 | [ |
| 8,9-EET (C20H32O3) | (5Z,11Z,14Z)-8,9-Epoxyeicosa-5,11,14-trienoic acid PubChem CID: 5283203 | 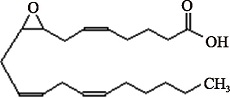 | [ |
| Hepoxilin A3 (C20H32O4) | (5Z,9E,14Z)-(11S,12S)-11,12-Epoxy-8-hydroxyeicosa-5,9,14-trienoic acid PubChem CID: 5283211 | 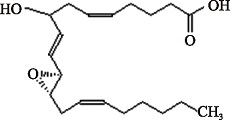 | [ |
| Hepoxilin B3 (C20H32O4) | (5Z,8Z,14Z)-(11S,12S)-11,12-Epoxy-10-hydroxyeicosa-5,8,14-trienoic acid PubChem CID: 16759353 | 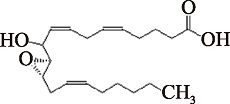 | [ |
| TXA2 (C20H32O5) | (5Z,13E)-(15S)-9alpha,11alpha-Epoxy-15-hydroxythromboxa-5,13-dienoate PubChem CID: 5280497 | 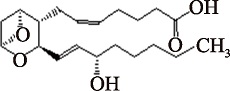 | [ |
| TXB2 (C20H34O6) | (5Z)-7-[(2R,3S,4S)-Tetrahydro-4,6-dihydroxy-2-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxy-1-octen- 1-yl]-2H-pyran-3-yl]-5-heptenoic acid PubChem CID: 5283137 | 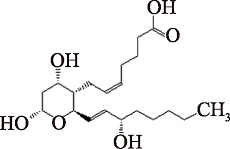 | [ |
| [1] |
Sheehan G, Farrell G, Kavanagh K. Immune priming: the secret weapon of the insect world. Virulence, 2020, 11(1): 238-246.
pmid: 32079502 |
| [2] |
Ma HX, Abbas MN, Zhang K, Hu XS, Xu M, Liang HH, Kausar S, Yang LQ, Cui HJ. 20-Hydroxyecdysone regulates the transcription of the lysozyme via Broad-Complex Z2 gene in silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev Comp Immunol, 2019, 94: 66-72.
pmid: 30716346 |
| [3] |
Stanley D, Haas E, Kim Y. Beyond cellular immunity: on the biological significance of insect hemocytes. Cells, 2023, 12(4): 599.
pmid: 36831266 |
| [4] |
Ha EM, Oh CT, Bae YS, Lee WJ. A direct role for dual oxidase in Drosophila gut immunity. Science, 2005, 310(5749): 847-850.
pmid: 16272120 |
| [5] |
Stanley D. Prostaglandins and other eicosanoids in insects: biological significance. Annu Rev Entomol, 2006, 51: 25-44.
pmid: 16332202 |
| [6] |
Feng M, Fei SG, Xia JM, Labropoulou V, Swevers L, Sun JC. Antimicrobial peptides as potential antiviral factors in insect antiviral immune response. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 2030.
pmid: 32983149 |
| [7] |
Ragland SA, Criss AK. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: Recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog, 2017, 13(9): e1006512.
pmid: 28934357 |
| [8] | Xiao HQ, Li YZ, Lin QL, Zhao MM, Liu J, Zhou Q. Advances in multiple targets mechanism of antimicrobial peptides. J Food Sci Biotechnol, 2022, 41(5): 11-19. |
| 肖怀秋, 李玉珍, 林亲录, 赵谋明, 刘军, 周全. 抗菌肽多靶点作用抑菌机理研究进展. 食品与生物技术学报, 2022, 41(5): 11-19. | |
| [9] |
Yi HY, Chowdhury M, Huang YD, Yu XQ. Insect antimicrobial peptides and their applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2014, 98(13): 5807-5822.
pmid: 24811407 |
| [10] |
Funk CD. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science, 2001, 294(5548): 1871-1875.
pmid: 11729303 |
| [11] | Corey EJ, Albright JO, Barton AE, Hashimoto S. Chemical and enzymic syntheses of 5-HPETE, a key biological precursor of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS), and 5-HETE. J Am Chem Soc, 1980, 102, 1435-1436. |
| [12] |
Stanley DW, Howard RW. Eicosanoids in insect immune signal transduction. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2001, 484: 265-273.
pmid: 11418992 |
| [13] |
Destephano DB, Brady UE, Lovins RE. Synthesis of prostaglandin by reproductive tissue of the male house cricket, Acheta domesticus. Prostaglandins, 1974, 6(1): 71-79.
pmid: 4822206 |
| [14] | Stanley D, Kim Y. Eicosanoid signaling in insects: from discovery to plant protection. Crit Rev Plant Sci, 2014, 33(1): 20-63. |
| [15] |
Stanley-Samuelson DW, Jensen E, Nickerson KW, Tiebel K, Ogg CL, Howard RW. Insect immune response to bacterial infection is mediated by eicosanoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1991, 88(3): 1064-1068.
pmid: 1899480 |
| [16] |
Stanley D, Haas E, Miller J. Eicosanoids: exploiting insect immunity to improve biological control programs. Insects, 2012, 3(2): 492-510.
pmid: 26466540 |
| [17] |
Shafeeq T, Ahmed S, Kim Y. Toll immune signal activates cellular immune response via eicosanoids. Dev Comp Immunol, 2018, 84: 408-419.
pmid: 29577956 |
| [18] |
Shrestha S, Kim Y. Activation of immune-associated phospholipase A2 is functionally linked to Toll/Imd signal pathways in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Dev Comp Immunol, 2010, 34(5): 530-537.
pmid: 20043940 |
| [19] |
Hwang J, Park Y, Kim Y, Hwang J, Lee D. An entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, suppresses expression of antimicrobial peptides controlled by Toll and Imd pathways by blocking eicosanoid biosynthesis. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol, 2013, 83(3): 151-169.
pmid: 23740621 |
| [20] |
Stokes BA, Yadav S, Shokal U, Smith LC, Eleftherianos I. Bacterial and fungal pattern recognition receptors in homologous innate signaling pathways of insects and mammals. Front Microbiol, 2015, 6: 19.
pmid: 25674081 |
| [21] | Stanley D, Kim Y. Chapter Eight-Insect prostaglandins and other eicosanoids: from molecular to physiological actions. Adv Insect Physiol, 2019, 56: 283-343. |
| [22] |
Kim Y, Ahmed S, Stanley D, An CJ. Eicosanoid- mediated immunity in insects. Dev Comp Immunol, 2018, 83: 130-143.
pmid: 29225005 |
| [23] |
Ahmed S, Al Baki MA, Lee J, Seo DY, Lee D, Kim Y. The first report of prostacyclin and its physiological roles in insects. Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2021, 301: 113659.
pmid: 33166533 |
| [24] |
Calder PC. Eicosanoids. Essays Biochem, 2020, 64(3): 423-441.
pmid: 32808658 |
| [25] |
Dennis EA, Cao J, Hsu YH, Magrioti V, Kokotos G. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem Rev, 2011, 111(10): 6130-6185.
pmid: 21910409 |
| [26] |
Leslie CC. Cytosolic phospholipase A2: physiological function and role in disease. J Lipid Res, 2015, 56(8): 1386-1402.
pmid: 25838312 |
| [27] |
Lambeau G, Gelb MH. Biochemistry and physiology of mammalian secreted phospholipases A2. Annu Rev Biochem, 2008, 77: 495-520.
pmid: 18405237 |
| [28] |
Murakami M, Taketomi Y, Miki Y, Sato H, Yamamoto K, Lambeau G. Emerging roles of secreted phospholipase A2 enzymes: the 3rd edition. Biochimie, 2014, 107 Pt A: 105-113.
pmid: 25230085 |
| [29] |
Vázquez M, Rodríguez R, Zurita M. A new peroxinectin-like gene preferentially expressed during oogenesis and early embryogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genes Evol, 2002, 212(11): 526-529.
pmid: 12459925 |
| [30] |
Tootle TL, Spradling AC. Drosophila Pxt: a cyclooxygenase-like facilitator of follicle maturation. Development, 2008, 135(5): 839-847.
pmid: 18216169 |
| [31] |
Shi GQ, Zhou Y, Ren F. Identification and function analysis of BmPxtA in the immune response regulated by PGE2 of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev Comp Immunol, 2022, 130: 104358.
pmid: 35081420 |
| [32] |
Shi GQ, Cheng JQ, Zhou Y, Ren F, Bu YX. BmPxt1 mediated immune response by regulating PGE2 in silkworm, Bombyx mori. Pestic Biochem Physiol, 2023, 197: 105693.
pmid: 38072548 |
| [33] |
Barletta ABF, Trisnadi N, Ramirez JL, Barillas-Mury C. Mosquito midgut prostaglandin release establishes systemic immune priming. iScience, 2019, 19: 54-62.
pmid: 31351392 |
| [34] |
Park J, Stanley D, Kim Y. Roles of peroxinectin in PGE2-mediated cellular immunity in Spodoptera exigua. PLoS One, 2014, 9(9): e105717.
pmid: 25191834 |
| [35] | Zhao YM. Microsporidia influence eicosanoids contents and POX gene expression in Antheraea pernyi[Dissertation]. Shenyang Agricultural University, 2024. |
| 赵益敏. 微孢子虫影响柞蚕类花生酸含量及POX基因表达的研究[学位论文]. 沈阳农业大学, 2024. | |
| [36] |
Laidlaw TM, Buchheit KM, Cahill KN, Hacker J, Cho L, Cui J, Feng CL, Chen CC, Le M, Israel E, Boyce JA. Trial of thromboxane receptor inhibition with ifetroban: TP receptors regulate eicosanoid homeostasis in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2023, 152(3): 700-710.e3.
pmid: 37068712 |
| [37] |
de Luján Alvarez M, Lorenzetti F. Role of eicosanoids in liver repair, regeneration and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol, 2021, 192: 114732.
pmid: 34411565 |
| [38] |
Kulmacz RJ. Prostaglandin G2 levels during reaction of prostaglandin H synthase with arachidonic acid. Prostaglandins, 1987, 34(2): 225-240.
pmid: 3118417 |
| [39] |
Saito M, Tanabe Y, Kudo I, Nakayama K. Endothelium- derived prostaglandin H2 evokes the stretch-induced contraction of rabbit pulmonary artery. Eur J Pharmacol, 2003, 467(1-3): 151-161.
pmid: 12706469 |
| [40] |
Wallace CH, Oliveros G, Serrano PA, Rockwell P, Xie L, Figueiredo-Pereira M. Timapiprant, a prostaglandin D2 receptor antagonist, ameliorates pathology in a rat Alzheimer’s model. Life Sci Alliance, 2022, 5(12): e202201555.
pmid: 36167438 |
| [41] |
Ning YP, Wang WF, Jordan PM, Barth SA, Hofstetter RK, Xu JJ, Zhang XM, Cai Y, Menge C, Chen XC, Werz O. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced prostaglandin J2 and 15-Deoxy-Prostaglandin J2 inhibit inflammatory signals in human M1 macrophages via a negative feedback loop. J Immunol, 2023, 210(10): 1564-1575.
pmid: 37042680 |
| [42] |
Kwon H, Hall DR, Smith RC. Prostaglandin E2 signaling mediates oenocytoid immune cell function and lysis, limiting bacteria and plasmodium oocyst survival in Anopheles gambiae. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 680020.
pmid: 34484178 |
| [43] |
Miao YG, Nair KS. Exogenous prostaglandin F2α as a mediator in the regulation of silkworm growth and silk gland genome. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 2003, 72(3-4): 147-154.
pmid: 14674626 |
| [44] |
Rajan S, Toh HT, Ye H, Wang ZY, Basil AH, Parnaik T, Yoo JY, Lim KL, Yoon HS. Prostaglandin A2 interacts with Nurr1 and ameliorates behavioral deficits in Parkinson's disease fly model. Neuromolecular Med, 2022, 24(4): 469-478.
pmid: 35482177 |
| [45] |
van den Berk LCJ, Jansen BJH, Snowden S, Siebers-Vermeulen KGC, Gilissen C, Kögler G, Figdor CG, Wheelock CE, Torensma R. Cord blood mesenchymal stem cells suppress DC-T Cell proliferation via prostaglandin B2. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23(14): 1582-1593.
pmid: 24649980 |
| [46] | Ahmed S, Kim Y. PGE2 mediates hemocyte-spreading behavior by activating aquaporin via cAMP and rearranging actin cytoskeleton via Ca2+. Dev Comp Immunol, 2021, 125: 104230. |
| [47] | Schröder O, Sjöström M, Qiu H, Stein J, Jakobsson PJ, Haeggström JZ. Molecular and catalytic properties of three rat leukotriene C4 synthase homologs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2003, 312(2): 271-276. |
| [48] |
Lämmermann T, Afonso PV, Angermann BR, Wang JM, Kastenmüller W, Parent CA, Germain RN. Neutrophil swarms require LTB4 and integrins at sites of cell death in vivo. Nature, 2013, 498(7454): 371-375.
pmid: 23708969 |
| [49] |
Jiang SF, Wan Q, Wang XJ, Di LC, Li XZ, Kang RT, Li S, Huang LN. LXA4 attenuates perioperative neurocognitive disorders by suppressing neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 123: 110788.
pmid: 37591120 |
| [50] |
Dakin SG, Colas RA, Wheway K, Watkins B, Appleton L, Rees J, Gwilym S, Little C, Dalli J, Carr AJ. Proresolving mediators LXB4 and RvE1 regulate inflammation in stromal cells from patients with shoulder tendon tears. Am J Pathol, 2019, 189(11): 2258-2268.
pmid: 31437425 |
| [51] |
Smyrniotis CJ, Barbour SR, Xia ZX, Hixon MS, Holman TR. ATP allosterically activates the human 5-lipoxygenase molecular mechanism of arachidonic acid and 5(S)- hydroperoxy-6(E),8(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-eicosatetraenoic acid. Biochemistry, 2014, 53(27): 4407-4419.
pmid: 24893149 |
| [52] |
Pickens CA, Sordillo LM, Zhang C, Fenton JI. Obesity is positively associated with arachidonic acid-derived 5- and 11-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE). Metabolism, 2017, 70: 177-191.
pmid: 28403941 |
| [53] |
Cazade M, Bidaud I, Hansen PB, Lory P, Chemin J. 5,6-EET potently inhibits T-type calcium channels: implication in the regulation of the vascular tone. Pflugers Arch, 2014, 466(9): 1759-1768.
pmid: 24327205 |
| [54] |
Pozzi A, Macias-Perez I, Abair T, Wei SZ, Su Y, Zent R, Falck JR, Capdevila JH. Characterization of 5,6- and 8,9-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (5,6- and 8,9-EET) as potent in vivo angiogenic lipids. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(29): 27138-27146.
pmid: 15917237 |
| [55] |
Tamang DL, Pirzai W, Priebe GP, Traficante DC, Pier GB, Falck JR, Morisseau C, Hammock BD, McCormick BA, Gronert K, Hurley BP. Hepoxilin A3 facilitates neutrophilic breach of lipoxygenase-expressing airway epithelial barriers. J Immunol, 2012, 189(10): 4960-4969.
pmid: 23045615 |
| [56] |
Antón R, Camacho M, Puig L, Vila L. Hepoxilin B3 and its enzymatically formed derivative trioxilin B3 are incorporated into phospholipids in psoriatic lesions. J Invest Dermatol, 2002, 118(1): 139-146.
pmid: 11851887 |
| [57] |
Roy MC, Nam K, Kim J, Stanley D, Kim Y. Thromboxane mobilizes insect blood cells to infection foci. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 791319.
pmid: 34987515 |
| [58] |
Downer RGH, Moore SJ, Diehl-Jones WL, Mandato CA. The effects of eicosanoid biosynthesis inhibitors on prophenoloxidase activation, phagocytosis and cell spreading in Galleria mellonella. J Insect Physiol, 1997, 43(1): 1-8.
pmid: 12769924 |
| [59] |
Dean P, Gadsden JC, Richards EH, Edwards JP, Charnley AK, Reynolds SE. Modulation by eicosanoid biosynthesis inhibitors of immune responses by the insect Manduca sexta to the pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. J Invertebr Pathol, 2002, 79(2): 93-101.
pmid: 12095238 |
| [60] |
Sanda NB, Hou BF, Hou YM. The entomopathogenic nematodes H. bacteriophora and S. carpocapsae inhibit the activation of proPO system of the nipa palm hispid Octodonta nipae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Life (Basel), 2022, 12(7): 1019.
pmid: 35888107 |
| [61] |
Stanley D, Shapiro M. Eicosanoid biosynthesis inhibitors increase the susceptibility of Lymantria dispar to nucleopolyhedrovirus LdMNPV. J Invertebr Pathol, 2007, 95(2): 119-124.
pmid: 17386933 |
| [62] |
Yi YH, Wu GQ, Lv JL, Li M. Eicosanoids mediate Galleria mellonella immune response to hemocoel injection of entomopathogenic nematode cuticles. Parasitol Res, 2016, 115(2): 597-608.
pmid: 26472713 |
| [63] |
Vatanparast M, Lee DH, Kim Y. Biosynthesis and immunity of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in a lepidopteran insect, Spodoptera exigua. Dev Comp Immunol, 2020, 107: 103643.
pmid: 32067998 |
| [64] |
Vatanparast M, Ahmed S, Lee DH, Hwang SH, Hammock B, Kim Y. EpOMEs act as immune suppressors in a lepidopteran insect, Spodoptera exigua. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 20183.
pmid: 33214688 |
| [65] |
Ji JY, Yin ZH, Zhang SS, Shen DX, An CJ. PLA2 mediates the innate immune response in Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis. Insect Sci, 2022, 29(1): 245-258.
pmid: 34080301 |
| [66] |
Miller JS, Howard RW, Rana RL, Tunaz H, Stanley DW. Eicosanoids mediate nodulation reactions to bacterial infections in adults of the cricket, Gryllus assimilis. J Insect Physiol, 1999, 45(1): 75-83.
pmid: 12770398 |
| [67] | Park Y, Stanley D. The entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, impairs hemocytic immunity by inhibition of eicosanoid biosynthesis in adult crickets, Gryllus firmus. Biol Control, 2006, 38(2): 247-253. |
| [68] |
Tunaz H, Bedick JC, Miller JS, Hoback WW, Rana RL, Stanley DW. Eicosanoids mediate nodulation reactions to bacterial infections in adults of two 17-year periodical cicadas, Magicicada septendecim and M. cassini. J Insect Physiol, 1999, 45(10): 923-931.
pmid: 12770285 |
| [69] | Miller JS, Howard RW, Nguyen T, Nguyen A, Rosario RMT, Stanley-Samuelson DW. Eicosanoids mediate nodulation responses to bacterial infections in larvae of the tenebrionid beetle, Zophobas atratus. J Insect Physiol, 1996, 42(1): 3-12. |
| [70] |
Bedick JC, Tunaz H, Nor Aliza AR, Putnam SM, Ellis MD, Stanley DW. Eicosanoids act in nodulation reactions to bacterial infections in newly emerged adult honey bees, Apis mellifera, but not in older foragers. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol, 2001, 130(1): 107-117.
pmid: 11544147 |
| [71] |
Baker MD, Wolanin PM, Stock JB. Systems biology of bacterial chemotaxis. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2006, 9(2): 187-192.
pmid: 16529985 |
| [72] |
Jin T, Hereld D. Moving toward understanding eukaryotic chemotaxis. Eur J Cell Biol, 2006, 85(9-10): 905-913.
pmid: 16735076 |
| [73] |
Marasco WA, Phan SH, Krutzsch H, Showell HJ, Feltner DE, Nairn R, Becker EL, Ward PA. Purification and identification of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine as the major peptide neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem, 1984, 259(9): 5430-5439.
pmid: 6371005 |
| [74] |
Merchant D, Ertl RL, Rennard SI, Stanley DW, Miller JS. Eicosanoids mediate insect hemocyte migration. J Insect Physiol, 2008, 54(1): 215-221.
pmid: 17996890 |
| [75] |
Trepat X, Chen ZZ, Jacobson K. Cell migration. Compr Physiol, 2012, 2(4): 2369-2392.
pmid: 23720251 |
| [76] |
Miller JS, Nguyen T, Stanley-Samuelson DW. Eicosanoids mediate insect nodulation responses to bacterial infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1994, 91(26): 12418-12422.
pmid: 7809052 |
| [77] |
Clark KD, Pech LL, Strand MR. Isolation and identification of a plasmatocyte-spreading peptide from the hemolymph of the lepidopteran insect Pseudoplusia includens. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(37): 23440-23447.
pmid: 9287360 |
| [78] |
Miller JS. Eicosanoids influence in vitro elongation of plasmatocytes from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol, 2005, 59(1): 42-51.
pmid: 15822094 |
| [79] | Park J, Kim Y. Change in hemocyte populations of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua, in response to bacterial infection and eicosanoid mediation. Korean J Appl Entomol, 2012, 51(4): 349-356. [DOI |
| [80] |
Kim Y, Jung S, Madanagopal N. Antagonistic effect of juvenile hormone on hemocyte-spreading behavior of Spodoptera exigua in response to an insect cytokine and its putative membrane action. J Insect Physiol, 2008, 54(6): 909-915.
pmid: 18485359 |
| [81] |
Park J, Stanley D, Kim Y. Rac1 mediates cytokine- stimulated hemocyte spreading via prostaglandin biosynthesis in the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. J Insect Physiol, 2013, 59(7): 682-689.
pmid: 23660478 |
| [82] |
Ishii K, Adachi T, Hamamoto H, Oonishi T, Kamimura M, Imamura K, Sekimizu K. Insect cytokine paralytic peptide activates innate immunity via nitric oxide production in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Dev Comp Immunol, 2013, 39(3): 147-153.
pmid: 23178406 |
| [83] |
Sadekuzzaman M, Stanley D, Kim Y. Nitric oxide mediates insect cellular immunity via phospholipase A2 activation. J Innate Immun, 2018, 10(1): 70-81.
pmid: 29035888 |
| [84] |
Liu W, Wang Y, Leng ZM, Wang Q, Duan XX, Luo YT, Jiang YR, Qin L. Nitric oxide plays a crucial role in midgut immunity under microsporidian infection in Antheraea pernyi. Mol Immunol, 2020, 126: 65-72.
pmid: 32768860 |
| [85] |
Ohnishi A, Hull JJ, Matsumoto S. Targeted disruption of genes in the Bombyx mori sex pheromone biosynthetic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(12): 4398-4403.
pmid: 16537410 |
| [86] |
Zhuo XR, Chen L, Wang GJ, Liu XS, Wang YF, Liu K, Yu XQ, Wang JL. 20-Hydroxyecdysone promotes release of GBP-binding protein from oenocytoids to suppress hemocytic encapsulation. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2018, 92: 53-64.
pmid: 29175381 |
| [87] |
Srikanth K, Park J, Stanley DW, Kim Y. Plasmatocyte- spreading peptide influences hemocyte behavior via eicosanoids. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol, 2011, 78(3): 145-160.
pmid: 22006534 |
| [88] |
Groen CM, Spracklen AJ, Fagan TN, Tootle TL. Drosophila fascin is a novel downstream target of prostaglandin signaling during actin remodeling. Mol Biol Cell, 2012, 23(23): 4567-4578.
pmid: 23051736 |
| [89] |
Otuka H, Sato R. Serotonin- and eicosanoid-dependent rapid hemocyte aggregation in the hemolymph is the first step in nodule formation in Bombyx mori larvae. J Insect Physiol, 2023, 145: 104486.
pmid: 36669557 |
| [90] |
Sato R. Mechanisms and roles of the first stage of nodule formation in lepidopteran insects. J Insect Sci, 2023, 23(4): 3.
pmid: 37405874 |
| [91] |
Stanley-Samuelson D, Rana RL, Pedibhotla VK, Miller JS, Jurenka RA. Eicosanoids mediate microaggregation and nodulation responses to bacterial infections in black cutworms, Agrotis ipsilon, and true armyworms, Pseudaletia unipuncta. J Insect Physiol, 1997, 43(2): 125-133.
pmid: 12769916 |
| [92] |
Shrestha S, Kim Y. Various eicosanoids modulate the cellular and humoral immune responses of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2009, 73(9): 2077-2084.
pmid: 19734670 |
| [93] |
Miller JS, Stanley DW. Eicosanoids mediate microaggregation reactions to bacterial challenge in isolated insect hemocyte preparations. J Insect Physiol, 2001, 47(12): 1409-1417.
pmid: 12770147 |
| [94] |
Durmuş Y, Büyükgüzel E, Terzi B, Tunaz H, Stanley D, Büyükgüzel K. Eicosanoids mediate melanotic nodulation reactions to viral infection in larvae of the parasitic wasp, Pimpla turionellae. J Insect Physiol, 2008, 54(1): 17-24.
pmid: 17904576 |
| [95] |
Kim GS, Nalini M, Kim Y, Lee DW. Octopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine mediate hemocytic phagocytosis and nodule formation via eicosanoids in the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol, 2009, 70(3): 162-176.
pmid: 19140126 |
| [96] |
Wu TY, Zhao Y, Wang ZY, Song QS, Wang ZX, Xu QW, Wang YJ, Wang LB, Zhang YQ, Feng CJ. β-1,3-Glucan recognition protein 3 activates the prophenoloxidase system in response to bacterial infection in Ostrinia furnacalis Guenée. Dev Comp Immunol, 2018, 79: 31-43.
pmid: 29032241 |
| [97] |
Wang Y, Yang F, Cao XL, Zou Z, Lu ZQ, Kanost MR, Jiang HB. Hemolymph protease-5 links the melanization and Toll immune pathways in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(38): 23581-23587.
pmid: 32900946 |
| [98] |
Shrestha S, Kim Y. Eicosanoids mediate prophenoloxidase release from oenocytoids in the beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2008, 38(1): 99-112.
pmid: 18070669 |
| [99] |
Dudzic JP, Hanson MA, Iatsenko I, Kondo S, Lemaitre B. More than black or white: melanization and Toll share regulatory serine proteases in Drosophila. Cell Rep, 2019, 27(4): 1050-1061.e3.
pmid: 31018123 |
| [100] |
Bidla G, Lindgren M, Theopold U, Dushay MS. Hemolymph coagulation and phenoloxidase in Drosophila larvae. Dev Comp Immunol, 2005, 29(8): 669-679.
pmid: 15854679 |
| [101] |
Ahmed S, Kim Y. Prostaglandin catabolism in Spodoptera exigua, a lepidopteran insect. J Exp Biol, 2020, 223(Pt 21): jeb233221.
pmid: 32978320 |
| [102] |
Büyükgüzel E. Eicosanoids mediate cellular immune response and phenoloxidase reaction to viral infection in adult Pimpla turionellae. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol, 2012, 81(1): 20-33.
pmid: 22622947 |
| [103] |
Brivio MF, Pagani M, Restelli S. Immune suppression of Galleria mellonella (Insecta, Lepidoptera) humoral defenses induced by Steinernema feltiae (Nematoda, Rhabditida): involvement of the parasite cuticle. Exp Parasitol, 2002, 101(2-3): 149-156.
pmid: 12427469 |
| [104] |
Shrestha S, Stanley D, Kim Y. PGE2 induces oenocytoid cell lysis via a G protein-coupled receptor in the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. J Insect Physiol, 2011, 57(11): 1568-1576.
pmid: 21867708 |
| [105] |
Stanley D, Kim Y. Prostaglandins and other eicosanoids in insects: biosynthesis and biological actions. Front Physiol, 2019, 9: 1927.
pmid: 30792667 |
| [106] |
Ahn HM, Lee KS, Lee DS, Yu K. JNK/FOXO mediated Peroxiredoxin V expression regulates redox homeostasis during Drosophila melanogaster gut infection. Dev Comp Immunol, 2012, 38(3): 466-473.
pmid: 22858408 |
| [107] |
Sajjadian SM, Kim Y. PGE2 upregulates gene expression of dual oxidase in a lepidopteran insect midgut via cAMP signalling pathway. Open Biol, 2020, 10(10): 200197.
pmid: 33081632 |
| [108] |
Yin HY, Zhou YH, Zhu MJ, Hou S, Li Z, Zhong HQ, Lu JH, Meng T, Wang JH, Xia L, Xu Y, Wu YC. Role of mitochondria in programmed cell death mediated by arachidonic acid-derived eicosanoids. Mitochondrion, 2013, 13(3): 209-224.
pmid: 23063711 |
| [109] |
Wang Y, Goodman CL, Ringbauer J, Li YF, Stanley D. Prostaglandin A2 induces apoptosis in three cell lines derived from the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol, 2021, 108(3): e21844.
pmid: 34519097 |
| [110] |
Wrońska AK, Kaczmarek A, Kazek M, Boguś MI. Infection of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera) larvae with the entomopathogenic fungus Conidiobolus coronatus (Entomophthorales) induces apoptosis of hemocytes and affects the concentration of eicosanoids in the hemolymph. Front Physiol, 2022, 12: 774086.
pmid: 35069239 |
| [111] |
De Gregorio E, Spellman PT, Tzou P, Rubin GM, Lemaitre B. The Toll and Imd pathways are the major regulators of the immune response in Drosophila. EMBO J, 2002, 21(11): 2568-2579.
pmid: 12032070 |
| [112] |
Aggarwal K, Rus F, Vriesema-Magnuson C, Ertürk- Hasdemir D, Paquette N, Silverman N. Rudra interrupts receptor signaling complexes to negatively regulate the IMD pathway. PLoS Pathog, 2008, 4(8): e1000120.
pmid: 18688280 |
| [113] |
Huan YC, Kong Q, Mou HJ, Yi HX. Antimicrobial peptides: classification, design, application and research progress in multiple fields. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11: 582779.
pmid: 33178164 |
| [114] |
Yajima M, Takada M, Takahashi N, Kikuchi H, Natori S, Oshima Y, Kurata S. A newly established in vitro culture using transgenic Drosophila reveals functional coupling between the phospholipase A2-generated fatty acid cascade and lipopolysaccharide-dependent activation of the immune deficiency (imd) pathway in insect immunity. Biochem J, 2003, 371(Pt 1): 205-210.
pmid: 12513692 |
| [115] |
Park JA, Kim Y. Eicosanoid biosynthesis is activated via Toll, but not Imd signal pathway in response to fungal infection. J Invertebr Pathol, 2012, 110(3): 382-388.
pmid: 22569137 |
| [116] |
Park JA, Kim Y. Toll recognition signal activates oenocytoid cell lysis via a crosstalk between plasmatocyte-spreading peptide and eicosanoids in response to a fungal infection. Cell Immunol, 2012, 279(2): 117-123.
pmid: 23220607 |
| [117] |
Shrestha S, Park Y, Stanley D, Kim Y. Genes encoding phospholipases A2 mediate insect nodulation reactions to bacterial challenge. J Insect Physiol, 2010, 56(3): 324-332.
pmid: 19931277 |
| [118] |
Morishima I, Yamano Y, Inoue K, Matsuo N. Eicosanoids mediate induction of immune genes in the fat body of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. FEBS Lett, 1997, 419(1): 83-86.
pmid: 9426224 |
| [119] |
Stanley-Samuelson DW, Ogg CL. Prostaglandin biosynthesis by fat body from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 1994, 24(5): 481-491.
pmid: 8205144 |
| [120] |
Barletta ABF, Alves E Silva TL, Talyuli OAC, Luna- Gomes T, Sim S, Angleró-Rodríguez Y, Dimopoulos G, Bandeira-Melo C, Sorgine MHF. Prostaglandins regulate humoral immune responses in Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2020, 14(10): e0008706.
pmid: 32464135 |
| [121] |
Kim Y, Stanley D. Eicosanoid signaling in insect immunology: new genes and unresolved issues. Genes (Basel), 2021, 12(2): 211.
pmid: 33535438 |
| [122] |
Kim Y, Ahmed S, Al Baki MA, Kumar S, Kim K, Park Y, Stanley D. Deletion mutant of PGE2 receptor using CRISPR-Cas9 exhibits larval immunosuppression and adult infertility in a lepidopteran insect, Spodoptera exigua. Dev Comp Immunol, 2020, 111: 103743.
pmid: 33095767 |
| [123] | Zhao Y, Zhao F, Zhu F. Research advance in role of eicosanoids in insect cellular immunity. Chin J Appl Entomol, 2010, 47(3): 446-450. |
| 赵耀, 赵福, 朱芬. 类花生酸在昆虫细胞免疫中的作用研究进展. 昆虫知识, 2010, 47 (3): 446-450. |
| [1] | Xiangyi Wei, Dongchun Hu, Zupeng Gao, Congjing Feng. JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its regulation on insect immunity [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(3): 229-236. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||