Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (7): 654-664.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-230
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Progress on lncRNA regulated disease resistance traits in domesticated animals
Jinyan Yang1,2( ), Xueqin Liu1,2(
), Xueqin Liu1,2( ), Tianqi Wen1, Yuhong Sun1, Ying Yu1(
), Tianqi Wen1, Yuhong Sun1, Ying Yu1( )
)
- 1. College of Animal Science and Technology, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China
2. College of Animal Science and Technology, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming 650201, China
-
Received:2021-01-10Revised:2021-06-16Online:2021-07-20Published:2021-06-28 -
Contact:Yu Ying E-mail:cauyangjinyan@163.com;cauliuxueqin@163.com;yuying@cau.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(31961143009);Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(31272420);the Beijing Natural Science Foundation No(6182021);the Beijing Dairy Industry Innovation Team No(BAIC06);the National Dairy Industry Technology System Project No(CARS-36)
Cite this article
Jinyan Yang, Xueqin Liu, Tianqi Wen, Yuhong Sun, Ying Yu. Progress on lncRNA regulated disease resistance traits in domesticated animals[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(7): 654-664.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
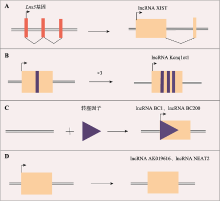
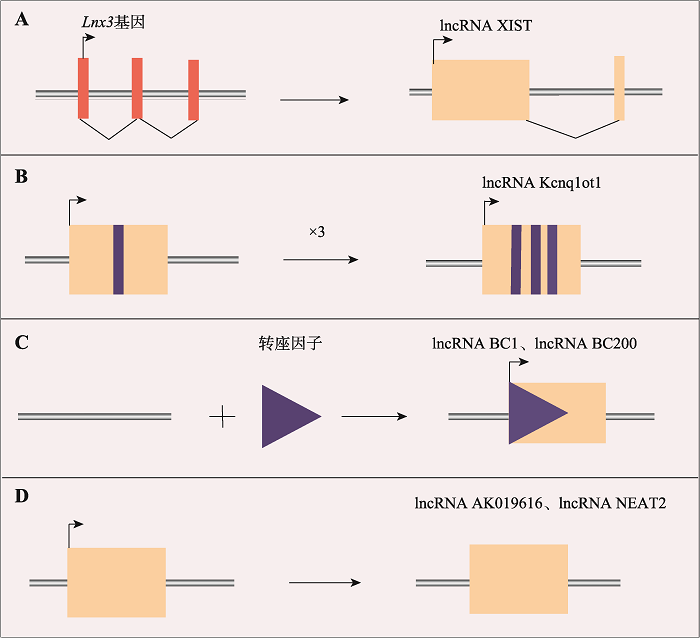
Table 1
The mechanisms of actions and key targets of typical lncRNAs"
| 作用机制 | lncRNA | 主要靶标 | 物种 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因组印记 | H19 | PRC2复合物;let-7 | 人 | [ |
| XIST | PRC2复合物 | 人 | [ | |
| 染色质重塑 | HOTAIR | PRC2复合物 | 小鼠 | [ |
| Kcnq1ot1 | PRC2复合物 | 小鼠 | [ | |
| Air | G9a转移酶 | 小鼠 | [ | |
| 调控细胞凋亡周期 | Gas5 | 糖皮质激素受体的DNA结合域 | 小鼠 | [ |
| 控制mRNA降解 | 1/2-SBSRNA 1 | STUA1;STUA2 | 小鼠 | [ |
| 剪接调控 | MALAT1 | 丝氨酸/精氨酸(SR)剪切因子 | 人 | [ |
| 翻译调控 | Uchl1-as1 | UCHL1蛋白 | 小鼠 | [ |
lncRNAs and target genes related to disease resistance in domesticated animals"
| lncRNA | 畜禽 | 差异表达组织 | 相关疾病 | 靶基因 | 调控方式 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XLOC_672329/ ALDBGALG0000001429 | 鸡 | 鸡原发性巨噬细胞 | 禽白血病 | CH25H/ CISH/IL-1β | cis | [ |
| TCONS_00292296/TCONS_ 00212539/TCONS_00079494 | 鸡 | 鸡脾脏组织 | 禽白血病 | BBX/BCL11B/ ULK3 | cis | [ |
| lncRNA ERL | 鸡 | GaHV-2基因组 TRL/IRL区域 | 禽马立克病 | ADAR1 | / | [ |
| linc-GALMD1 | 鸡 | CD4+ T细胞和 鸡淋巴瘤细胞 | 禽马立克病 | EPYC | trans | [ |
| linc-stab1 | 鸡 | 鸡法式囊 | 禽马立克病 | SATB1 | cis | [ |
| MSTRG.360.1/MSTRG.6754.1/ MSTRG.15539.1 | 鸡 | 鸡脾脏组织 | 禽马立克病 | CTLA4/CXCL12 | cis | [ |
| LNC_001066/LNC_000231 | 猪 | 猪回肠组织 | C型产气荚膜 梭菌型腹泻 | TLR8/IRAK3/ TNFRSF11A | trans | [ |
| ALDBSSCG0000006854/ XLOC_078370 | 猪 | 猪回肠上皮细胞 | C型产气荚膜 梭菌型腹泻 | ABCB1 | cis/trans | [ |
| ALDBSSCT0000006510/ ALDBSSCT0000004760 | 猪 | 猪回肠上皮细胞 | C型产气荚膜 梭菌型腹泻 | TRAF2/MAPK8 | trans | [ |
| LOC102157546/XLOC_025930 | 猪 | 仔猪小肠上皮细胞 | 仔猪腹泻 | KCNMB1/GRB2 | trans | [ |
| TCONS_00058367 | 猪 | 猪小肠上皮细胞 | 猪传染性胃肠炎 | PML | cis | [ |
| lncRNA 9606 | 猪 | 猪小肠上皮细胞 | 猪流行性腹泻 | TCR | cis | [ |
| lncRNA XR_297549.1 | 猪 | 猪肺泡巨噬细胞 | 猪繁殖与呼吸综合征 | PTGS2 | cis/trans | [ |
| TCONS_00054158 | 猪 | 猪子宫内膜上皮细胞 | 猪繁殖与呼吸综合征 | TNFSF10 | cis | [ |
| LTCONS_00010766/ LTCONS_00045988 | 猪 | 猪子宫内膜上皮细胞 | 猪繁殖与呼吸综合征 | MUM1X7/GAMT | cis | [ |
| lncRNA H19 | 牛 | 牛乳腺上皮细胞 | 奶牛乳房炎 | CCL5/CXCL2 | / | [ |
| lncRNA XIST | 牛 | 牛乳腺上皮细胞 | 奶牛乳房炎 | NF-κB p65 | cis | [ |
| ALDBBTAT0000007617/ ALDBBTAT0000006520 | 牛 | 牛乳腺组织 | 奶牛乳房炎 | TLR2/MyD88 | trans | [ |
| ALDBBTAG0000003135/ XLOC_018926 | 牛 | 牛肾细胞 | 牛病毒性腹泻 | CHD2/ZMAT3 | cis | [ |
| LOC112443855/LOC112448807/ LOC100847453 | 牛 | 牛肾细胞 | 牛病毒性腹泻 | ATG4D/ATG16L1 | cis | [ |
| XLOC_033995 | 牛 | 牛巨噬细胞 | 牛副结核病 | TNFAIP3 | trans | [ |
| MSTRG.12.1 | 牛 | 牛瘤胃组织 | 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒 | / | trans | [ |
| XLOC_000016/XLOC_002851 | 牛 | 角粘膜层组织 | 牛角鳞状细胞癌 | CNFN/CDSN | cis | [ |
| TOCNS_00059692/ TCONS_00053949 | 羊 | 绵羊脾脏 | 腹泻 | TIMM29/CARM1/ MYO1G | cis | [ |
| IFNG-AS1 | 人、猪、 牛、羊 | 布氏杆菌病患者血清 | 布氏杆菌病 | IFNG | / | [ |
| PSMB8-AS1 | 人、鸡、 猪 | 人肺上皮细胞 | H1N1 | PSMB8/TAP1 | cis | [ |
| [1] | Qian JH, Lian LS. Research progress of breeding for disease resistance in livestock. Anim Sci & Vet Med, 2004, 21(1):53-55. |
| 钱锦花, 连林生. 畜禽抗病育种研究进展. 动物科学与动物医学, 2004, 21(1):53-55. | |
| [2] |
Best A, White A, Boots M. Maintenance of host variation in tolerance to pathogens and parasites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(52):20786-20791.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809558105 |
| [3] |
Wang XP, Xu SZ, Gao X, Ren HY, Chen JB. Genetic polymorphism of TLR4 gene and correlation with mastitis in cattle. J Genet Genomics , 2007, 34(5):406-412.
doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(07)60044-7 |
| [4] |
Gong CG, Maquat LE. LncRNAs transactivate STAU1- mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3' UTRs via Alu elements. Nature, 2011, 470(7333):284-288.
doi: 10.1038/nature09701 |
| [5] |
Yap KL, Li SD, Munoz-Cabello AM, Raguz S, Zeng L, Mujtaba S, Gil J, Walsh MJ, Zhou MM. Molecular interplay of the noncoding RNA ANRIL and methylated histone H3 lysine 27 by polycomb CBX7 in transcriptional silencing of INK4a. Mol Cell, 2010, 38(5):662-674.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.021 |
| [6] |
Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Khalil AM, Wood DE, Sahagan BG, Morgan TE, Finch CE, Laurent GS, Kenny PJ, Wahlestedt C. Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer's disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of beta-secretase. Nat Med, 2008, 14(7):723-730.
doi: 10.1038/nm1784 |
| [7] |
Brannan CI, Dees EC, Ingram RS, Tilghman SM. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol, 1990, 10(1):28-36.
pmid: 1688465 |
| [8] |
Heard E, Mongelard F, Arnaud D, Chureau C, Vourc'h C, Avner P. Human XIST yeast artificial chromosome transgenes show partial X inactivation center function in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96(12):6841-6846.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6841 |
| [9] |
Okazaki Y, Furuno M, Kasukawa T, Adachi J, Bono H, Kondo S, Nikaido I, Osato N, Saito R, Suzuki H, Yamanaka I, Kiyosawa H, Yagi K, Tomaru Y, Hasegawa Y, Nogami A, Schönbach C, Gojobori T, Baldarelli R, Hill DP, Bult C, Hume DA, Quackenbush J, Schriml LM, Kanapin A, Matsuda H, Batalov S, Beisel KW, Blake JA, Bradt D, Brusic V, Chothia C, Corbani LE, Cousins S, Dalla E, Dragani TA, Fletcher CF, Forrest A, Frazer KS, Gaasterland T, Gariboldi M, Gissi C, Godzik A, Gough J, Grimmond S, Gustincich S, Hirokawa N, Jackson IJ, Jarvis ED, Kanai A, Kawaji H, Kawasawa Y, Kedzierski RM, King BL, Konagaya A, Kurochkin IV, Lee Y, Lenhard B, Lyons PA, Maglott DR, Maltais L, Marchionni L, Mckenzie L, Miki H, Nagashima T, Numata K, Okido T, Pavan WJ, Pertea G, Pesole G, Petrovsky N, Pillai R, Pontius JU, Qi D, Ramachandran S, Ravasi T, Reed JC, Reed DJ, Reid J, Ring BZ, Ringwald M, Sandelin A, Schneider C, Semple CAM, Setou M, Shimada K, Sultana R, Takenaka Y, Taylor MS, Teasdale RD, Tomita M, Verardo R, Wagner L, Wahlestedt C, Wang Y, Watanabe Y, Wells C, Wilming LG, Wynshaw-Boris A, Yanagisawa M, Yang I, Yang L, Yuan Z, Zavolan M, Zhu Y, Zimmer A, Carninci P, Hayatsu N, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Konno H, Nakamura M, Sakazume N, Sato K, Shiraki T, Waki K, Kawai J, Aizawa K, Arakawa T, Fukuda S, Hara A, Hashizume W, Imotani K, Ishii Y, Itoh M, Kagawa I, Miyazaki A, Sakai K, Sasaki D, Shibata K, Shinagawa A, Yasunishi A, Yoshino M, Waterston R, Lander ES, Rogers J, Birney E, Hayashizaki Y, FANTOM Consortium; RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group Phase I & II Team. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature, 2002, 420(6915):563-573.
doi: 10.1038/nature01266 |
| [10] |
Spizzo R, Almeida MI, Colombatti A, Calin GA. Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: A new frontier of translational research? Oncogene, 2012, 31(43):4577-4587.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.621 pmid: 22266873 |
| [11] |
Kurihara Y, Matsui A, Hanada K, Kawashima M, Ishida J, Morosawa T, Tanaka M, Kaminuma E, Mochizuki Y, Matsushima A, Toyoda T, Shinozaki K, Seki M. Genome- wide suppression of aberrant mRNA-like noncoding RNAs by NMD in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(7):2453-2458.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808902106 |
| [12] |
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell, 2009, 136(4):629-641.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006 pmid: 19239885 |
| [13] |
Schoenherr CJ, Levorse JM, Tilghman SM. CTCF maintains differential methylation at theIgf2/H19 locus. Nat Genet , 2003, 33(1):66-69.
doi: 10.1038/ng1057 |
| [14] |
Kallen AN, Zhou XB, Xu J, Qiao C, Ma J, Yan L, Lu LG, Liu CC, Yi JS, Zhang HF, Min W, Bennett AM, Gregory RI, Ding Y, Huang YQ. The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol Cell, 2013, 52(1):101-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.027 |
| [15] |
Zhao J, Sun BK, Erwin JA, Song JJ, Lee JT. Polycomb proteins targeted by a short repeat RNA to the mouse X chromosome. Science, 2008, 322(5902):750-756.
doi: 10.1126/science.1163045 |
| [16] |
Wutz A, Rasmussen TP, Jaenisch R. Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA. Nat Genet, 2002, 30(2):167-174.
doi: 10.1038/ng820 |
| [17] |
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, Wang YL, Brzoska P, Kong B, Li R, West RB, van de Vijver MJ, Sukumar S, Chang HY. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature, 2010, 464(7291):1071-1076.
doi: 10.1038/nature08975 |
| [18] |
Pandey RR, Mondal T, Mohammad F, Enroth S, Redrup L, Komorowski J, Nagano T, Mancini-Dinardo D, Kanduri C. Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage- specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol Cell, 2008, 32(2):232-246.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.022 pmid: 18951091 |
| [19] |
Nagano T, Mitchell JA, Sanz LA, Pauler FM, Ferguson- Smith AC, Feil R, Fraser P. The Air noncoding RNA epigenetically silences transcription by targeting G9a to chromatin. Science, 2008, 322(5908):1717-1720.
doi: 10.1126/science.1163802 |
| [20] | Kino T, Hurt DE, Ichijo T, Nader N, Chrousos GP. Noncoding RNA gas5 is a growth arrest-and starvation- associated repressor of the glucocorticoid receptor. Sci Signal , 2010, 3(107): ra8. |
| [21] |
Gong CG, Maquat LE. lncRNAs transactivate STAU1- mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3' UTRs via Alu elements. Nature, 2011, 470(7333):284-288.
doi: 10.1038/nature09701 |
| [22] |
Tripathi V, Ellis JD, Shen Z, Song DY, Pan Q, Watt AT, Freier SM, Bennett CF, Sharma A, Bubulya PA, Blencowe BJ, Prasanth SG, Prasanth KV. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol Cell, 2010, 39(6):925-938.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.011 pmid: 20797886 |
| [23] |
Carrieri C, Cimatti L, Biagioli M, Beugnet A, Zucchelli S, Fedele S, Pesce E, Ferrer I, Collavin L, Santoro C, Forrest ARR, Carninci P, Biffo S, Stupka E, Gustincich S. Long non-coding antisense RNA controlsUchl1 translation through an embedded SINEB2 repeat. Nature , 2012, 491(7424):454-457.
doi: 10.1038/nature11508 |
| [24] |
Dai MM, Feng M, Xie TT, Zhang XQ. Long non-coding RNA and microRNA profiling provides comprehensive insight into non-coding RNA involved host immune responses in ALV-J-infected chicken primary macrophage. Dev Comp Immunol, 2019, 100:103414.
doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.103414 |
| [25] |
Qiu LL, Chang GB, Li ZT, Bi YL, Liu XP, Chen GH. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis reveals competing endogenous RNA networks during avian leukosis virus, subgroup J-induced tumorigenesis in chickens. Front Physiol, 2018, 9:996.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00996 |
| [26] |
Figueroa T, Boumart I, Coupeau D, Rasschaert D. Hyperediting byADAR1 of a new herpesvirus lncRNA during the lytic phase of the oncogenic Marek's disease virus. J Gen Virol , 2016, 97(11):2973-2988.
doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000606 |
| [27] |
Han B, He YH, Zhang L, Ding Y, Lian L, Zhao CF, Song JZ, Yang N. Long intergenic non-coding RNA GALMD3 in chicken Marek's disease. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):10294.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10900-2 pmid: 28860661 |
| [28] |
He YH, Ding Y, Zhan F, Zhang HM, Han B, Hu GQ, Zhao KJ, Yang N, Yu Y, Mao L, Song JZ. The conservation and signatures of lincRNAs in Marek's disease of chicken. Sci Rep, 2015, 5:15184.
doi: 10.1038/srep15184 |
| [29] |
You Z, Zhang QH, Liu CJ, Song JZ, Yang N, Lian L. Integrated analysis of lncRNA and mRNA repertoires in Marek's disease infected spleens identifies genes relevant to resistance. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1):245.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5625-1 |
| [30] |
Huang XY, Sun WY, Yan ZQ, Shi HR, Yang QL, Wang PF, Li SG, Liu LX, Zhao SG, Gun SB. Novel insights reveal anti-microbial gene regulation of piglet intestine immune in response toClostridium perfringens infection. Sci Rep , 2019, 9(1):1963.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37898-5 pmid: 30760749 |
| [31] |
Huang XY, Sun WY, Yan ZQ, Shi HR, Yang QL, Wang PF, Li SG, Liu LX, Zhao SG, Gun SB. Integrative analyses of long non-coding RNA and mRNA involved in piglet ileum immune response toClostridium perfringens type C infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol , 2019, 9:130.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00130 |
| [32] | Luo RR, Huang XY, Yan ZQ, Gao XL, Wang PF, Yang QL, Wang W, Xie KH, Gun SB. Identification and characterization of MAPK signaling pathway genes and associated lncRNAs in the ileum of piglets infected by Clostridium perfringens type C. Biomed Res Int , 2020, 2020:8496872. |
| [33] |
Augustino SMA, Xu QL, Liu XQ, Mi SY, Shi LY, Liu YB, Wen H, Wang D, Liu L, Zhang Q, Yu Y. Integrated analysis of lncRNAs and mRNAs reveals keytrans-target genes associated with ETEC-F4ac adhesion phenotype in porcine small intestine epithelial cells. BMC Genomics , 2020, 21(1):780.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07192-8 |
| [34] |
Ma XL, Zhao XM, Wang KL, Tang XY, Guo JX, Mi M, Qi YP, Chang LL, Huang Y, Tong DW. Identification and analysis of long non-coding RNAs that are involved in inflammatory process in response to transmissible gastroenteritis virus infection. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1):806.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6156-5 |
| [35] |
Chen JN, Zhang CY, Zhang N, Liu GL. Porcine endemic diarrhea virus infection regulates long noncoding RNA expression. Virology, 2019, 527:89-97.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.11.007 |
| [36] | Zeng NF, Wang C, Liu SY, Miao Q, Zhou L, Ge XN, Han J, Guo X, Yang HC. Transcriptome analysis reveals dynamic gene expression profiles in porcine alveolar macrophages in response to the Chinese highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Biomed Res Int, 2018, 2018:1538127. |
| [37] |
Zhang J, Sun P, Gan LP, Bai WJ, Wang ZJ, Li D, Cao YM, Fu YF, Li PH, Bai XW, Ma XQ, Bao HF, Chen YL, Liu ZX, Lu ZJ. Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA profiling in PRRSV-infected PAM cells by RNA sequencing. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):4952.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05279-z pmid: 28694521 |
| [38] |
Zhang K, Ge LJ, Dong SS, Liu Y, Wang D, Zhou CY, Ma C, Wang YC, Su F, Jiang YL. Global miRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA transcriptome profiling of endometrial epithelial cells reveals genes related to porcine reproductive failure caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Front Immunol, 2019, 10:1221.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01221 pmid: 31231376 |
| [39] |
Li XZ, Wang H, Zhang YF, Zhang JJ, Qi SP, Zhang Y, Gao MQ. Overexpression of lncRNA H19 changes basic characteristics and affects immune response of bovine mammary epithelial cells. Peer J, 2019, 7:e6715.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.6715 |
| [40] |
Ma MR, Pei YF, Wang XX, Feng JX, Zhang Y, Gao MQ. LncRNA XIST mediates bovine mammary epithelial cell inflammatory response via NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Cell Prolif, 2019, 52(1):e12525.
doi: 10.1111/cpr.2019.52.issue-1 |
| [41] |
Özdemir S, Altun S. Genome-wide analysis of mRNAs and lncRNAs inMycoplasma bovis infected and non-infected bovine mammary gland tissues. Mol Cell Probes , 2020, 50:101512.
doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101512 |
| [42] |
Ma QM, Li LY, Tang Y, Fu Q, Liu S, Hu SW, Qiao J, Chen CF, Ni W. Analyses of long non-coding RNAs and mRNA profiling through RNA sequencing of MDBK cells at different stages of bovine viral diarrhea virus infection. Res Vet Sci, 2017, 115:508-516.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2017.09.020 |
| [43] |
Gao XW, Niu C, Wang Z, Jia S, Han MJ, Ma YY, Guan XT, Wang L, Qiao XY, Xu YG. Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA expression profiles in cytopathic biotype BVDV-infected MDBK cells provides an insight into biological contexts of host-BVDV interactions. Virulence, 2021, 12(1):20-34.
doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1857572 |
| [44] |
Gupta P, Peter S, Jung M, Lewin A, Hemmrich-Stanisak G, Franke A, von Kleist M, Schütte C, Einspanier R, Sharbati S, Bruegge JZ. Analysis of long non-coding RNA and mRNA expression in bovine macrophages brings up novel aspects ofMycobacterium avium subspeciesparatuberculosis infections. Sci Rep , 2019, 9(1):1571.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38141-x |
| [45] |
Mahmoudi B, Fayazi J, Roshanfekr H, Sari M, Bakhtiarizadeh MR. Genome-wide identification and characterization of novel long non-coding RNA in Ruminal tissue affected with sub-acute Ruminal acidosis from Holstein cattle. Vet Res Commun, 2020, 44(1):19-27.
doi: 10.1007/s11259-020-09769-w pmid: 32043213 |
| [46] |
Sabara PH, Jakhesara SJ, Panchal KJ, Joshi CG, Koringa PG. Transcriptomic analysis to affirm the regulatory role of long non-coding RNA in horn cancer of Indian zebu cattle breed Kankrej (Bos indicus). Funct Integr Genomics , 2020, 20(1):75-87.
doi: 10.1007/s10142-019-00700-4 |
| [47] |
Jin CY, Bao JJ, Wang Y, Chen WH, Wu TY, Wang LH, Lv XY, Gao W, Wang BZ, Zhu GQ, Dai GJ, Sun W. Changes in long non-coding RNA expression profiles related to the antagonistic effects ofEscherichia coliF17 on lamb spleens. Sci Rep , 2018, 8(1):16514.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34291-0 |
| [48] |
Gheitasi R, Jourghasemi S, Pakzad I, Sarmadi VH, Samieipour Y, Sekawi Z, Jalilian FA. A potential marker in brucellosis, long non coding RNA IFNG-AS1. Mol Biol Rep, 2019, 46(6):6495-6500.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05095-w pmid: 31595441 |
| [49] |
More S, Zhu ZY, Lin K, Huang CQ, Pushparaj S, Liang YR, Sathiaseelan R, Yang XY, Liu L. Long non-coding RNA PSMB8-AS1 regulates influenza virus replication. RNA Biol, 2019, 16(3):340-353.
doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1572448 |
| [50] | Zhang HH, Liu Q, Qiu B, Liu GZ, Cheng ZQ. Mixed infection of ALV-J and MDV in a flock of Shandong free range chickens. Acta Vet Et Zootech Sin, 2009, 40(8):1215-1221. |
| 张洪海, 刘青, 邱波, 刘功振, 成子强. 地方柴鸡中J亚群禽白血病与马立克氏病的混合感染. 畜牧兽医学报, 2009, 40(8):1215-1221. | |
| [51] | Qin LT, Gao YL, Pan W, Deng XY, Sun FF, Li K, Qi XL, Gao HL, Liu CN, Wang XM. Investigation of co-infection of ALV-J with REV, MDV, CAV in layer chicken flocks in some regions of China. Chin J Prev Vet Med, 2010, 32(2):90-93. |
| 秦立廷, 高玉龙, 潘伟, 邓小芸, 孙芬芬, 李凯, 祁小乐, 高宏雷, 刘超男, 王笑梅. 我国部分地区蛋鸡群ALV-J及与REV、MDV、CAV混合感染检测. 中国预防兽医学报, 2010, 32(2):90-93. | |
| [52] | Wang GJ, Wei P, He XM, Li KR, Xiong LW, Yang L, Mo ML, Tao JH. A survey of the epizootiology of three neoplastic diseases in Guangxi province. China Poultry, 2002, 24(10):13-15. |
| 王桂军, 韦平, 何秀苗, 李康然, 熊丽文, 杨乐, 磨美兰, 陶锦华. 鸡三种肿瘤病在广西的流行病学研究. 中国家禽, 2002, 24(10):13-15. | |
| [53] |
Wakabayashi Y, Watanabe H, Inoue J, Takeda N, Sakata J, Mishima Y, Hitomi J, Yamamoto T, Utsuyama M, Niwa O, Aizawa S, Kominami R. Bcl11b is required for differentiation and survival of alphabeta T lymphocytes. Nat Immunol , 2003, 4(6):533-539.
pmid: 12717433 |
| [54] |
Zhao CF, Li X, Han B, You Z, Qu LJ, Liu CJ, Song JZ, Lian L, Yang N. Gga-miR-219b targetingBCL11B suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of Marek's disease tumor cell MSB1. Sci Rep , 2017, 7(1):4247.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04434-w |
| [55] |
Ulitsky I, Bartel DP. LincRNAs: genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell, 2013, 154(1):26-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.020 pmid: 23827673 |
| [56] |
Kim MJ, Frausto RF, Rosenwasser GOD, Bui T, Le DJ, Stone EM, Aldave AJ. Posterior amorphous corneal dystrophy is associated with a deletion of small leucine- rich proteoglycans on chromosome 12. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4):e95037.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095037 |
| [57] |
Han HJ, Russo J, Kohwi Y, Kohwi-Shigematsu T. SATB1 reprogrammes gene expression to promote breast tumour growth and metastasis. Nature , 2008, 452(7184):187-193.
doi: 10.1038/nature06781 |
| [58] |
Scharff RL. Economic burden from health losses due to foodborne illness in the United States. J Food Prot, 2012, 75(1):123-131.
doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-058 |
| [59] |
Waters M, Savoie A, Garmory HS, Bueschel D, Popoff MR, Songer JG, Titball RW, Mcclane BA, Sarker MR. Genotyping and phenotyping of beta2-toxigenicClostridium perfringensfecal isolates associated with gastrointestinal diseases in piglets. J Clin Microbiol , 2003, 41(8):3584-3591.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3584-3591.2003 |
| [60] |
Sayeed S, Uzal FA, Fisher DJ, Saputo J, Vidal JE, Chen Y, Gupta P, Rood JI, Mcclane BA. Beta toxin is essential for the intestinal virulence ofClostridium perfringens type C disease isolate CN3685 in a rabbit ileal loop model. Mol Microbiol , 2008, 67(1):15-30.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.2008.67.issue-1 |
| [61] |
Duan X, Nauwynck HJ, Favoreel HW, Pensaert MB. Identification of a putative receptor for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on porcine alveolar macrophages. J Virol, 1998, 72(5):4520-4523.
pmid: 9557752 |
| [62] |
Carpenter S, Aiello D, Atianand MK, Ricci EP, Gandhi P, Hall LL, Byron M, Monks B, Henry-Bezy M, Lawrence JB, O'Neill LAJ, Moore MJ, Caffrey DR, Fitzgerald KA. A long noncoding RNA mediates both activation and repression of immune response genes. Science, 2013, 341(6147):789-792.
doi: 10.1126/science.1240925 pmid: 23907535 |
| [63] | Laine AL, Burdon JJ, Nemri A, Thrall PH. Host ecotype generates evolutionary and epidemiological divergence across a pathogen metapopulation. Proc Biol Sci, 2014, 281(1787):20140522. |
| [64] |
Yan ZQ, Huang XY, Sun WY, Yang QL, Shi HR, Jiang TT, Li SG, Wang PF, Gun SB. Analyses of long non-coding RNA and mRNA profiling in the spleen of diarrheic piglets caused byClostridium perfringens type C. Peer J , 2018, 6:e5997.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.5997 |
| [65] |
Li YH, Qiu XT, Li HJ, Zhang Q. Adhesive patterns of Escherichia coli F4 in piglets of three breeds. J Genet Genomics , 2007, 34(7):591-599.
doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(07)60067-8 |
| [66] |
Lunney JK, Fang Y, Ladinig A, Chen NH, Li YH, Rowland B, Renukaradhya GJ. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV): Pathogenesis and interaction with the immune system. Annu Rev Anim Biosci, 2016, 4:129-154.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-022114-111025 pmid: 26646630 |
| [67] |
Li YF, Wang XL, Bo KT, Wang XW, Tang B, Yang BS, Jiang WM, Jiang P. Emergence of a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in the Mid-Eastern region of China. Vet J, 2007, 174(3):577-584.
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.07.032 |
| [68] |
Duan X, Nauwynck HJ, Pensaert MB. Effects of origin and state of differentiation and activation of monocytes/ macrophages on their susceptibility to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Arch Virol, 1997, 142(12):2483-2497.
pmid: 9672608 |
| [69] |
Badaoui B, Rutigliano T, Anselmo A, Vanhee M, Nauwynck H, Giuffra E, Botti S. RNA-sequence analysis of primary alveolar macrophages afterin vitro infection with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strains of differing virulence. PLoS One , 2014, 9(3):e91918.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091918 |
| [70] |
Bar-Gal GK, Blum SE, Hadas L, Ehricht R, Monecke S, Leitner G. Host-specificity ofStaphylococcus aureus causing intramammary infections in dairy animals assessed by genotyping and virulence genes. Vet Microbiol , 2015, 176(1-2):143-154.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.01.007 pmid: 25631254 |
| [71] | Bayoumi FA, Farver TB, Bushnell B, Oliveria M. Enzootic mycoplasmal mastitis in a large dairy during an eight-year period. J Am Vet Med Assoc, 1988, 192(7):905-909. |
| [72] |
Fox LK, Gay JM. Contagious mastitis. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract, 1993, 9(3):475-487.
doi: 10.1016/S0749-0720(15)30615-0 |
| [73] |
He XX, Liu WJ, Shi MY, Yang ZT, Zhang XC, Gong PT. Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates LPS-stimulated inflammatory response by regulating the PPARγ/NF-κB pathways in primary bovine mammary epithelial cells. Res Vet Sci, 2017, 112:7-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2016.12.011 |
| [74] |
Wang JJ, Guo CM, Wei ZK, He XX, Kou JH, Zhou ES, Yang ZT, Fu YH. Morin suppresses inflammatory cytokine expression by downregulation of nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated primary bovine mammary epithelial cells. J Dairy Sci, 2016, 99(4):3016-3022.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-10330 |
| [75] |
De Schepper S, De Ketelaere A, Bannerman DD, Paape MJ, Peelman L, Burvenich C. The toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4) pathway and its possible role in the pathogenesis ofEscherichia colimastitis in dairy cattle. Vet Res , 2008, 39(1):5.
doi: 10.1051/vetres:2007044 |
| [76] |
Usman T, Yu Y, Liu C, Wang X, Zhang Q, Wang YC. Genetic effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms inJAK2 and STAT5A genes on susceptibility of Chinese Holsteins to mastitis. Mol Biol Rep , 2014, 41(12):8293-8301.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3730-4 |
| [77] |
Kobayashi K, Oyama S, Numata A, Rahman MM, Kumura H. Lipopolysaccharide disrupts the milk-blood barrier by modulating claudins in mammary alveolar tight junctions. PLoS One, 2013, 8(4):e62187.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062187 |
| [78] |
Wang Y, Liu SL, Li Y, Wang Q, Shao JR, Chen Y, Xin JQ. Mycoplasma bovis-derived lipid-associated membrane proteins activate IL-1β production through the NF-κB pathway viatoll-like receptor 2 and MyD88. Dev Comp Immunol , 2016, 55:111-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2015.10.017 |
| [79] |
Perdrizet JA, Rebhun WC, Dubovi EJ, Donis RO. Bovine virus diarrhea—clinical syndromes in dairy herds. Cornell Vet, 1987, 77(1):46-74.
pmid: 3802830 |
| [80] |
Sweeney RW. Pathogenesis of paratuberculosis. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract, 2011, 27(3):537-546.
doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2011.07.001 |
| [81] |
López-Ortega O, Ovalle-García E, Ortega-Blake I, Antillón A, Chávez-Munguía B, Patiño-López G, Fragoso-Soriano R, Santos-Argumedo L. Myo1g is an active player in maintaining cell stiffness in B-lymphocytes. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken), 2016, 73(5):258-268.
doi: 10.1002/cm.21299 pmid: 27106882 |
| [1] | Wandi Xiong, Kaiyu Xu, Lin Lu, Jiali Li. Research progress on lncRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(3): 189-197. |
| [2] | Zilong Wen, Yiqiang Zhao. Progress on animal domestication under population genetics [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(3): 226-239. |
| [3] | Ziying Huang, Long Li, Qianqian Li, Xiangdong Liu, Changchun Li. The effect of lncRNA TCONS_00815878 on differentiation of porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(12): 1119-1128. |
| [4] | Jian Shi,Yanming Li,Xiangdong Fang. The mechanism and clinical significance of long noncoding RNA-mediated gene expression via nuclear architecture [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(3): 189-199. |
| [5] | Chenyu Qin, He Cai, Hanrui Qing, Li, Hongping Zhang. Recent advances on the role of long non-coding RNA H19 in regulating mammalian muscle growth and development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(12): 1150-1157. |
| [6] | Zhangyuan Pan, Xiaoyun He, Xiangyu Wang, Xiaofei Guo, Xiaohan Cao, Wenping Hu, Ran Di, Qiuyue Liu, Mingxing Chu. Selection signature in domesticated animals [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016, 38(12): 1069-1080. |
| [7] | Lingyun Sun, Xingyu Li, Zhiwei Sun. Progress of epigenetics and its therapeutic application in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(6): 517-527. |
| [8] | Xiaoqing Huang,Dandan Li,Juan Wu. Long non-coding RNAs in plants [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(4): 344-359. |
| [9] | Wanli Hu,Ai Gao. The role of long non-coding RNAs in hematologic malignancies [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(11): 1095-1104. |
| [10] | XIA Tian, XIAO Bing-Xiu, GUO Jun-Ming. Acting mechanisms and research methods of long noncoding RNAs [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(3): 269-280. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||