Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 306-323.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-323
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress of visual detection in rapid on-site detection of pathogen nucleic acid
Danni Liu1,2( ), Haiping Wu2,3, Guohua Zhou1,2,3,4(
), Haiping Wu2,3, Guohua Zhou1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. School of Life Science and Technology, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
2. Department of Clinical Pharmacy, General Hospital of Eastern Military Command, Nanjing 210002, China
3. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China
4. School of Pharmacy, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, China
-
Received:2022-12-28Revised:2023-02-05Online:2023-04-20Published:2023-02-16 -
Contact:Zhou Guohua E-mail:1370503352@qq.com;ghzhou@nju.edu.cn -
Supported by:Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(2022300326);National Natural Science Foundation of China(61871403)
Cite this article
Danni Liu, Haiping Wu, Guohua Zhou. Research progress of visual detection in rapid on-site detection of pathogen nucleic acid[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(4): 306-323.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Color change and detection principle of colorimetric LAMP method"
| 检测指示剂 | 指示剂类型 | 检测结果 | 检测原理 |
|---|---|---|---|
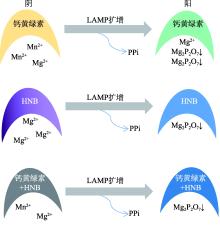
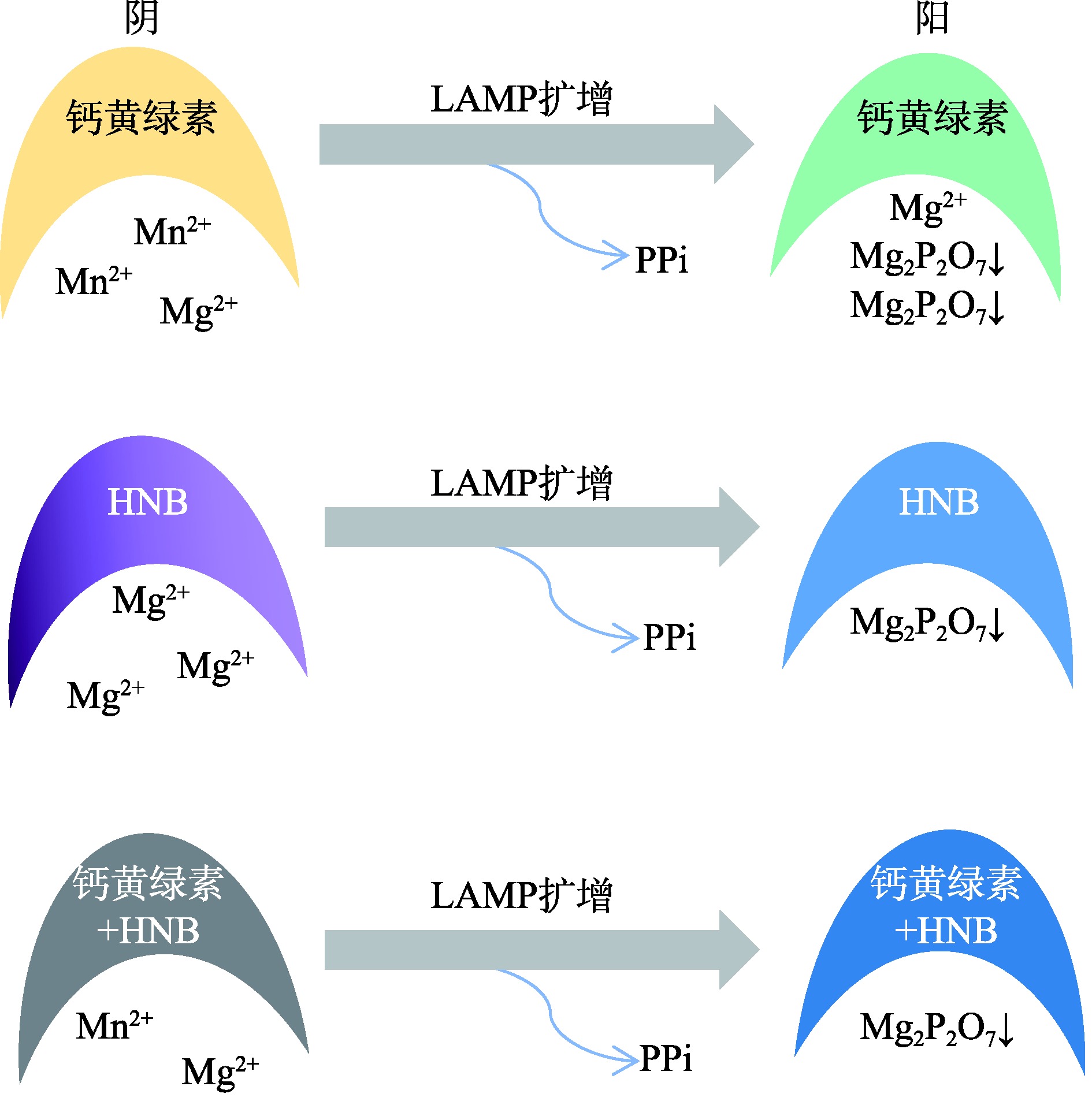
| 钙黄绿素 | 金属指示剂 | 橙色-绿色 | 钙黄绿素与Mn2+结合时反应体系为浅橙色,随着LAMP扩增的进行,扩增副产物PPi会与钙黄绿素竞争性结合Mn2+,使钙黄绿素游离,在紫外照射下会发出强烈荧光,自然光下呈现为绿色。 |
| HNB | 金属指示剂 | 紫色-天蓝色 | HNB与Mg2+结合时反应体系为紫色,随着LAMP扩增的进行,副产物PPi会Mg2+结合形成稳定的络合物,导致HNB游离,反应体系由紫色转变为蓝色。 |
| 酚红 | 酸碱指示剂 | 红色-黄色 | 酚红变色范围:6.8~8.2,体系小于6.8时呈现为黄色,大于8.2时为红色。LAMP扩增时,氢离子不断积累,反应体系由碱性变为酸性,酚红由红色转为黄色。 |
| 中性红 | 酸碱指示剂 | 黄色-红色 | 中性红变色范围:6.4~8.0,体系小于6.4时呈现为红色,大于8.0时为黄色。LAMP扩增时,氢离子不断积累,使反应体系由碱性变为酸性,中性红由黄色转为红色。 |
Table 2
Application of visualization analysis in pathogen nucleic acid detection"
| 可视化检测方法 | 检测原理 | 检测病原体 | LOD | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
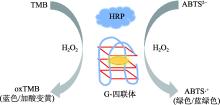
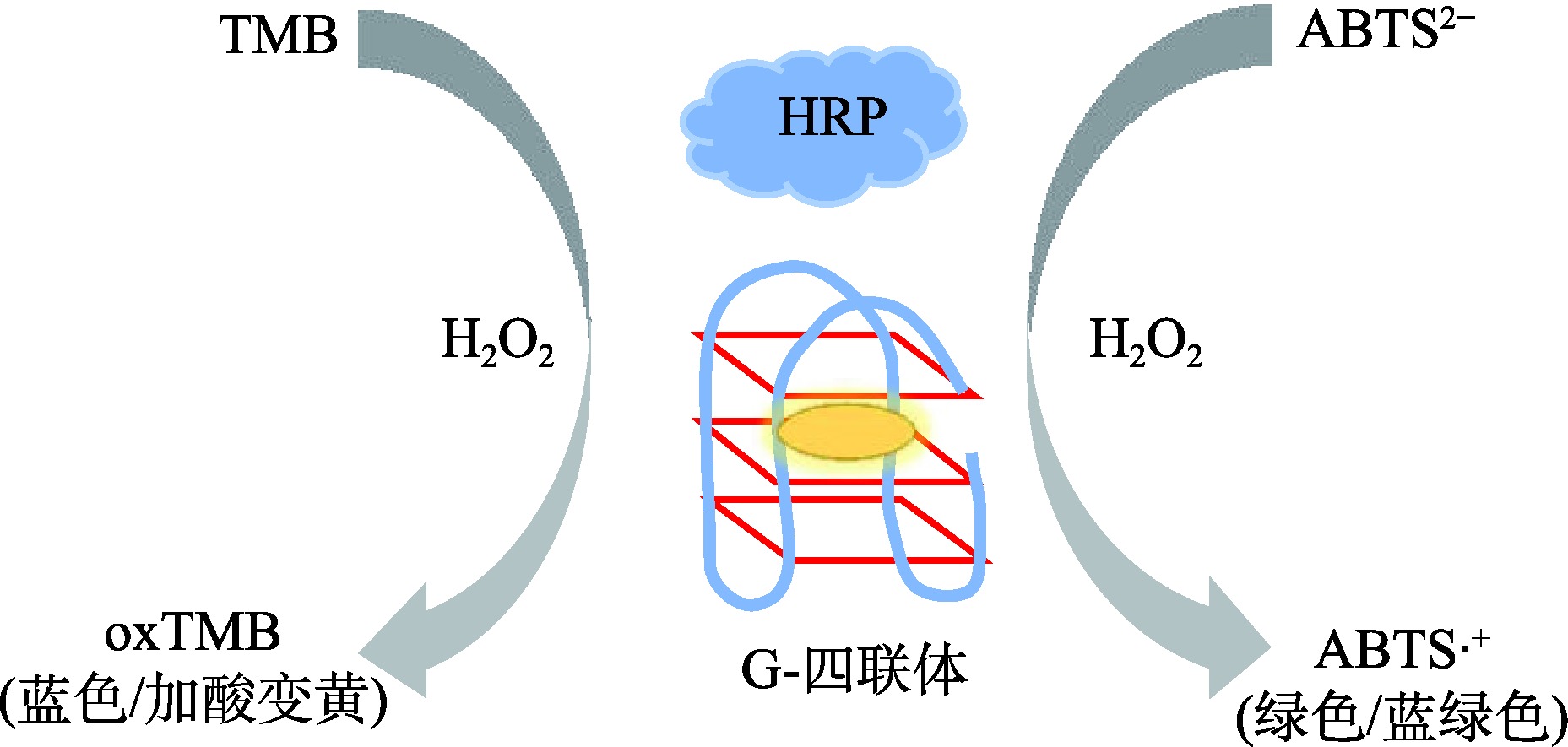
| 酶促底物 显色 | 在H2O2作用下,HRP催化ABTS2-显色 | SARS-CoV-2 | 0.28 pmol/L | [ |
| G-四链体/血红素具有类过氧化酶活性,可催化TMB显色 | 副溶血弧菌 | 100 CFU/mL | [ | |
| 纳米颗粒 显色 | 利用可以与靶标序列互补的寡核苷酸修饰的AuNPs作为比色报告物,对扩增产物进行特异性识别,促使AuNPs聚集 | SARS-CoV-2 N基因 | 10拷贝/反应 | [ |
| 通过核酸侵入反应识别多重PCR扩增产物,通过AuNPs杂交反应指示检测结果 | HPV分型检测 | 0.5拷贝/μL | [ | |
| 通过核酸侵入反应识别多重RT-LAMP扩增产物,通过AuNPs杂交反应指示检测结果 | 副流感A/H1N1、 副流感A/H3、 副流感B | 10拷贝/反应、 10拷贝/反应、 100拷贝/反应 | [ | |
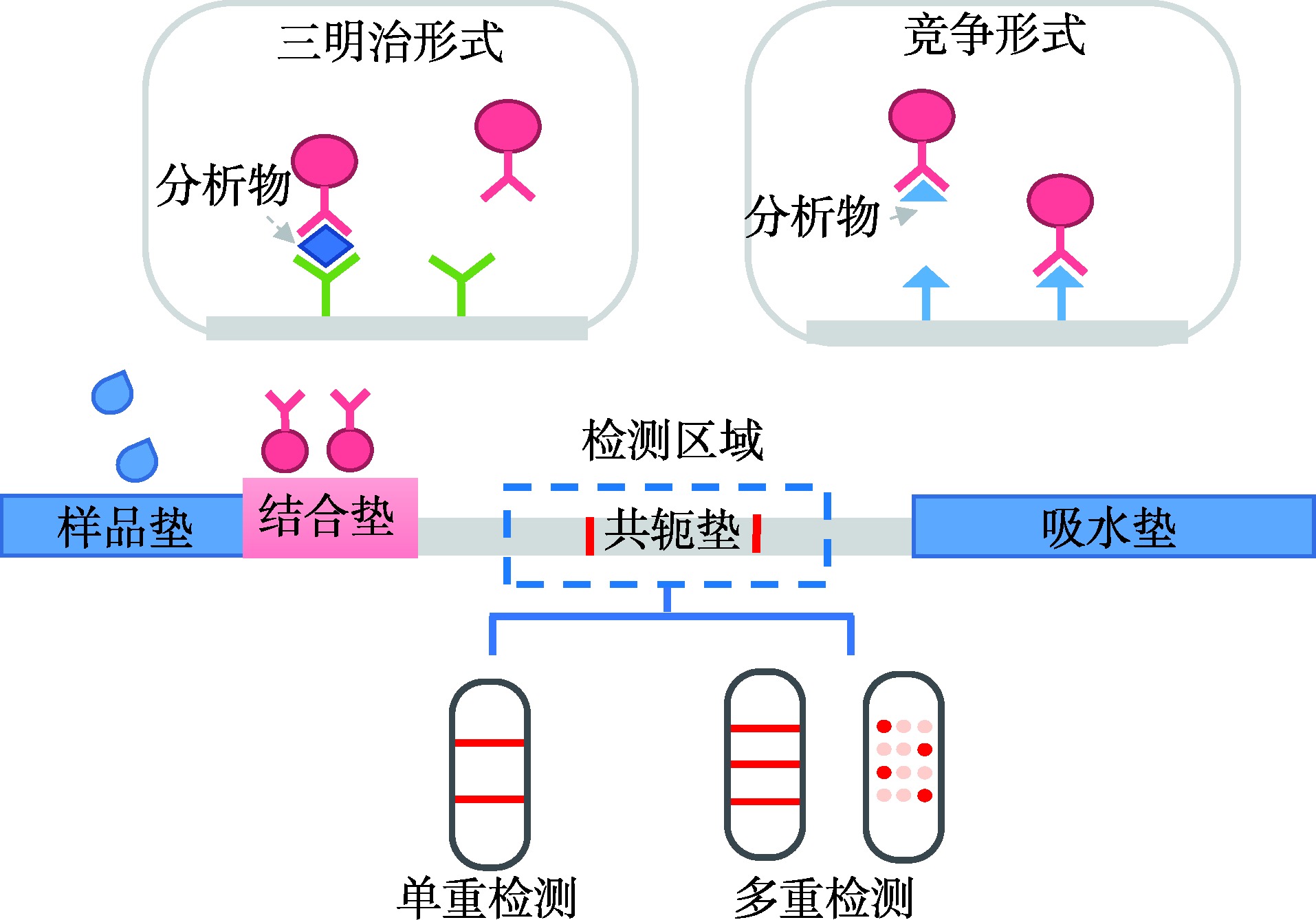
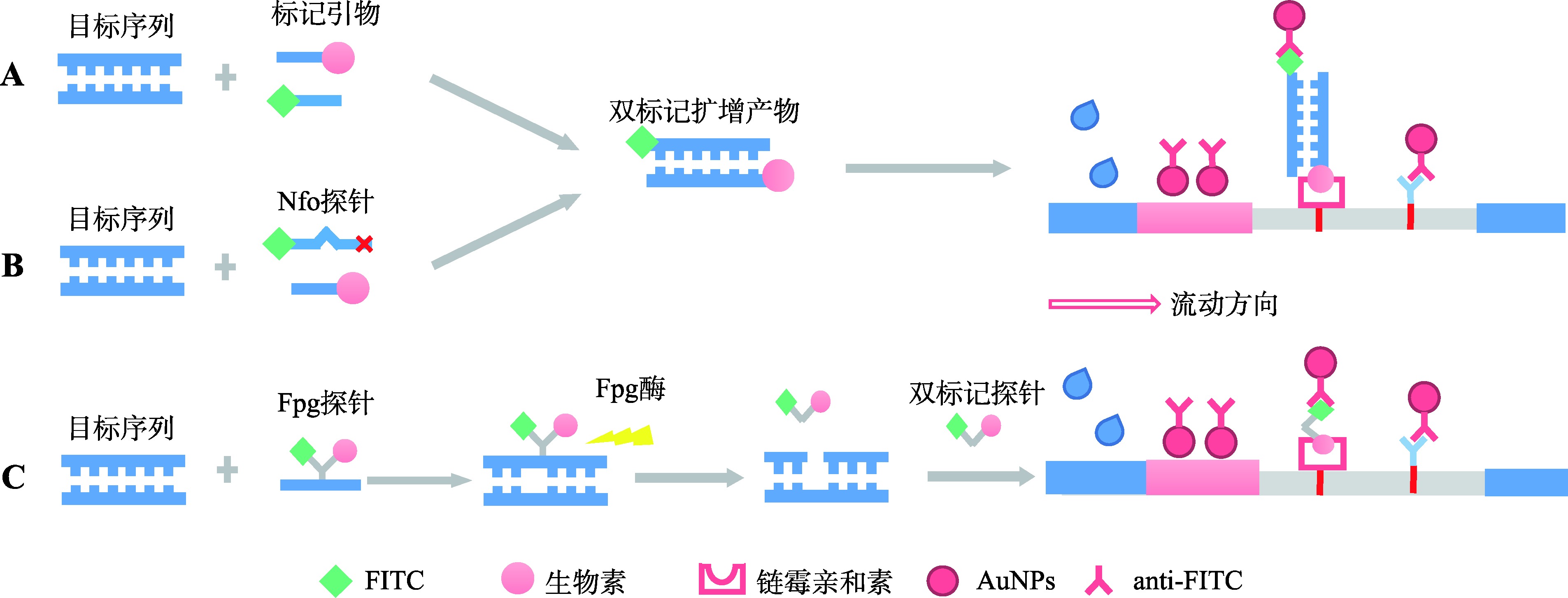
| 横向流动 分析 | LAMP-LFA方法 通过双引物标记、单引物标记、无标签标记的策略构建双标记扩增产物,并将其加载到横向流动试纸条上,通过抗原抗体杂交使信号标签在T线上不断积累 | SARS-CoV-2、 肺炎链球菌 | 2拷贝/μL 25 fg/反应 | [ |
| RPA-Nfo-LFA 通过引入生物素标记RPA引物及Nfo探针构建双标记扩增产物,通过抗原抗体杂交实现信号标签在T线上的累积 | 肠道病毒、 SARS-CoV-2 寨卡病毒 | 5拷贝/反应 7.59拷贝/μL 10拷贝/μL | [ | |
| mRT-LAMP +三线横向流动试纸条 通过对mRT-LAMP的扩增引物进行不同标记,实现扩增产物的双标记且产物间的标记不同,再加载到三线横向流动试纸条上 | SARS-CoV-2的ORF1ab和N基因 | 12拷贝/反应 | [ |
Table 3
Application of CRISPR / Cas technology in visual nucleic acid detection of pathogens"
| 可视化检 测方法 | CRISPR/ Cas系统 | 扩增方法 | 检测原理 | 检测病原体 | 检测时长 | LOD | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNAzyme | Cas9 | RT-LAMP | Cas9切割DNAzyme结构,关闭比色信号 | SARS-CoV-2 ORF1ab、N、 S基因 | 50 min | 10、9、13拷贝/反应 | [ |
| Cas12a | LAMP | 被激活的Cas12a切割DNAzyme结构,使显色底物无法显色 | 副溶血弧菌 | 150 min | 9.8 CFU/反应 | [ | |
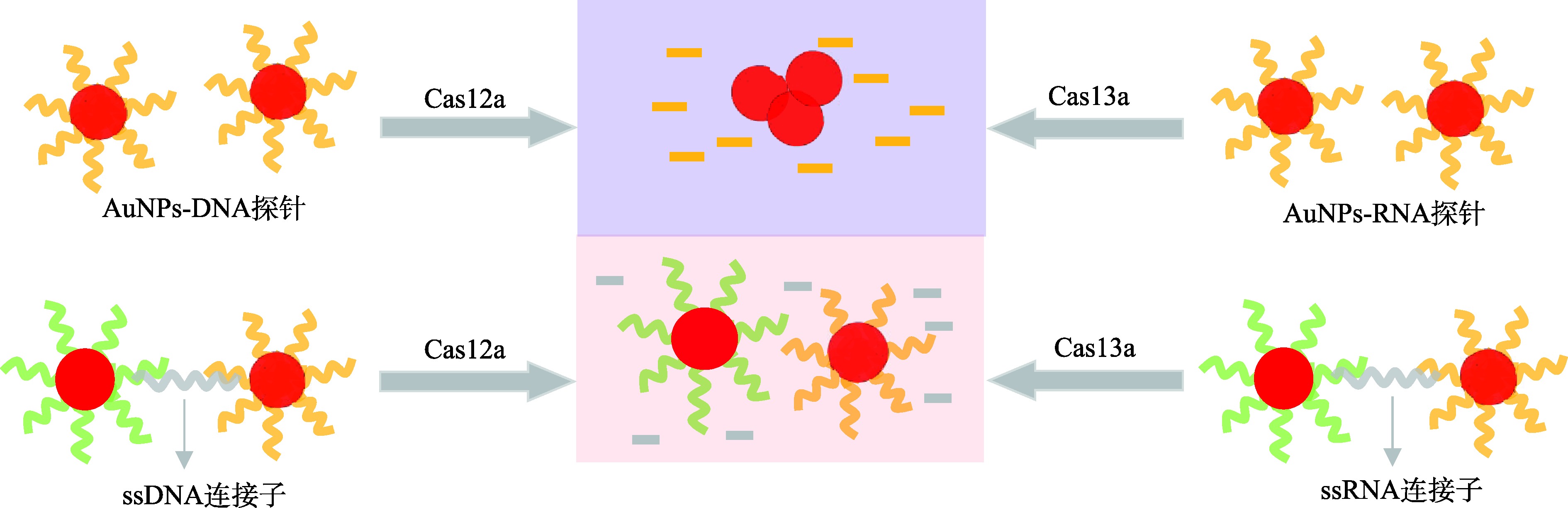
| AuNPs | Cas12a | RT-RPA | 被激活的Cas12a切割AuNPs上起稳定作用的ssDNA,使AuNPs聚集 | SARS-CoV-2 | 60 min | 单拷贝/反应 | [ |
| Cas13a | RT-RPA/ T7转录 | 被激活的Cas12a切割AuNPs上起稳定作用的ssRNA,AuNPs聚集 | SARS-CoV-2 | 120 min | 3 fmol/L | [ | |
| Cas12a | RT-PCR | 被激活的Cas12a切割AuNPs之间的连接子,AuNPs游离,体系呈红色 | SARS-CoV-2 | 90 min | 1拷贝/μL | [ | |
| Cas12a | RT-RPA | 被激活的Cas12a切割AuNPs与磁珠的连接子,AuNPs游离,体系呈红色 | SARS-CoV-2 | 90 min | 50拷贝/反应 | [ | |
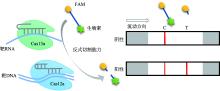
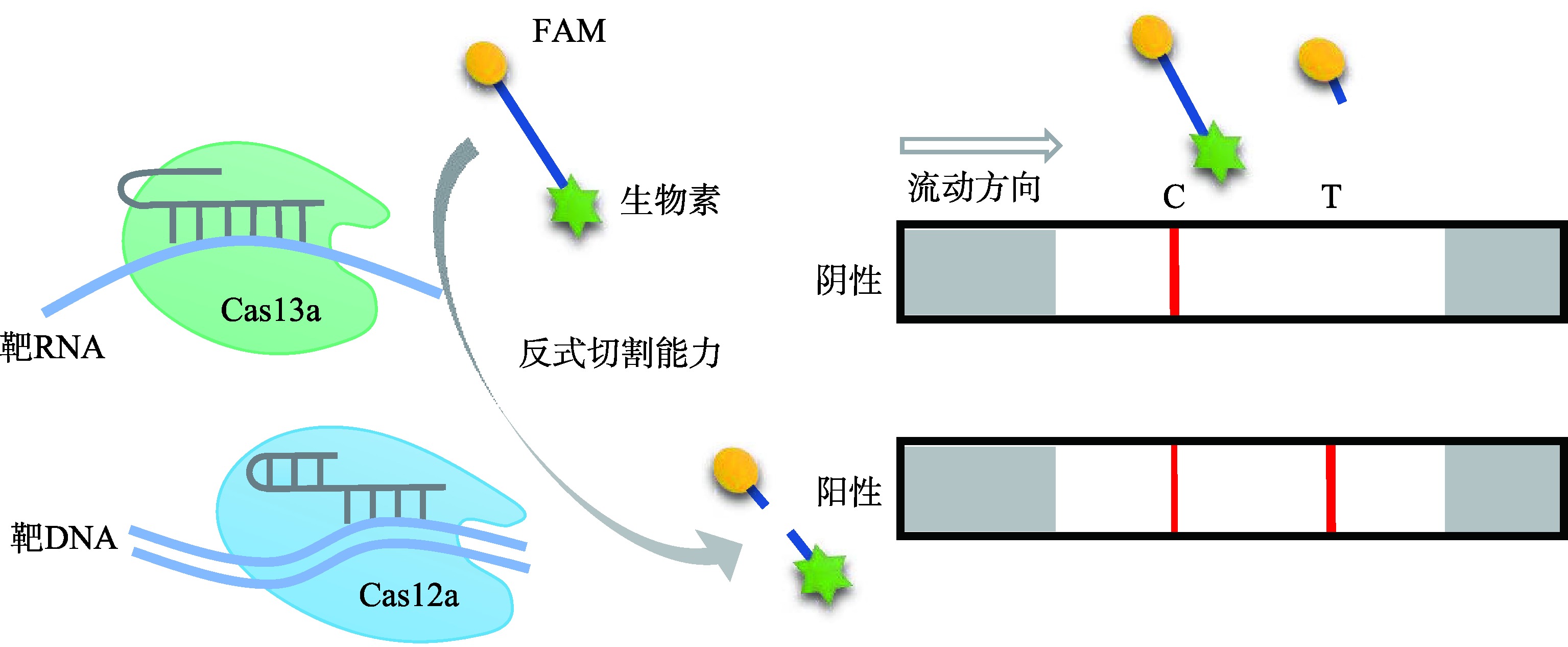
| 横向流动 分析法 | Cas13a | RT-RPA/ T7转录 | 被激活的Cas13a切割ssRNA报告分子,再进行LFA | SARS-CoV-2、猪流行性腹泻 病毒 | 50 min、 45 min | 100拷贝/μL、10拷贝/反应 | [ |
| Cas12a | RT-LAMP | 被激活的Cas12a切割ssDNA报告分子,再进行LFA | SARS-CoV-2 | 60 min | 1拷贝/μL | [ | |
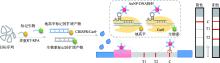
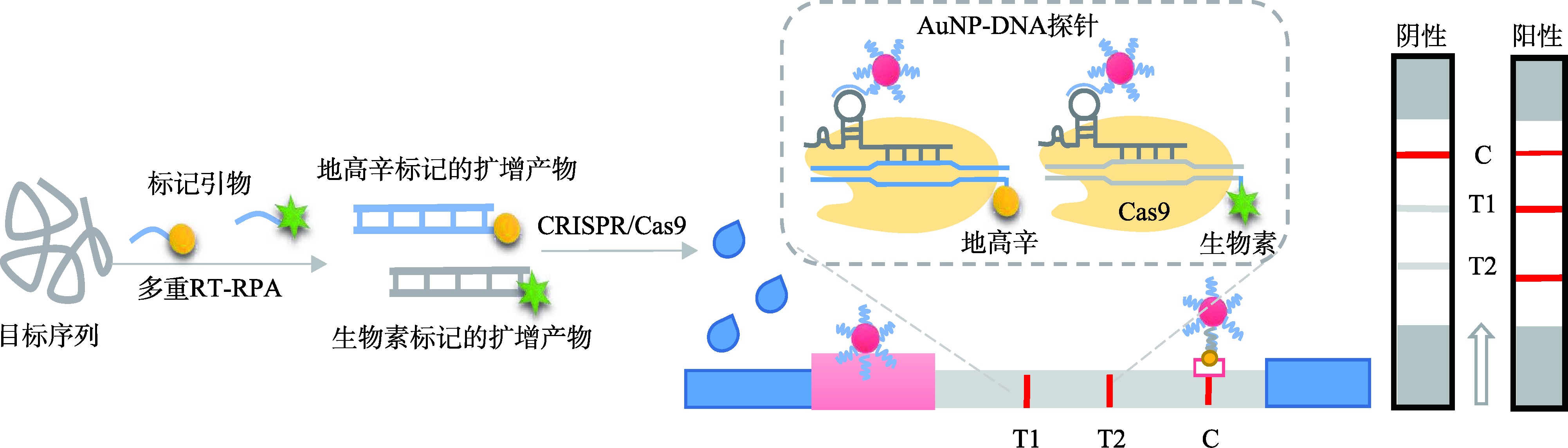
| 多重横向 流动分析 | Cas9 | mRT-RPA | 通过在Cas9系统的gRNA序列中保留AuNPs-DNA探针识别区域,实现AuNPs-DNA探针T线上的不断聚集 | SARS-CoV-2 E 和ORF1ab基因 | 60 min | 100拷贝/反应 | [ |
| Cas12a+ Cas13a | RT-RPA+ RT-RPA/ T7转录 | 利用Cas12a和Cas13a的不同的切割偏好切割相应的报告分子后加载到三线横向流动试纸条 | SARS-CoV-2 | 60 min | 10拷贝/反应 | [ |
Table 4
Summary and comparison of different visual nucleic acid detection methods"
| 可视化检测方法 | 检测原理 | 检测结果 | 优点 | 缺点 |
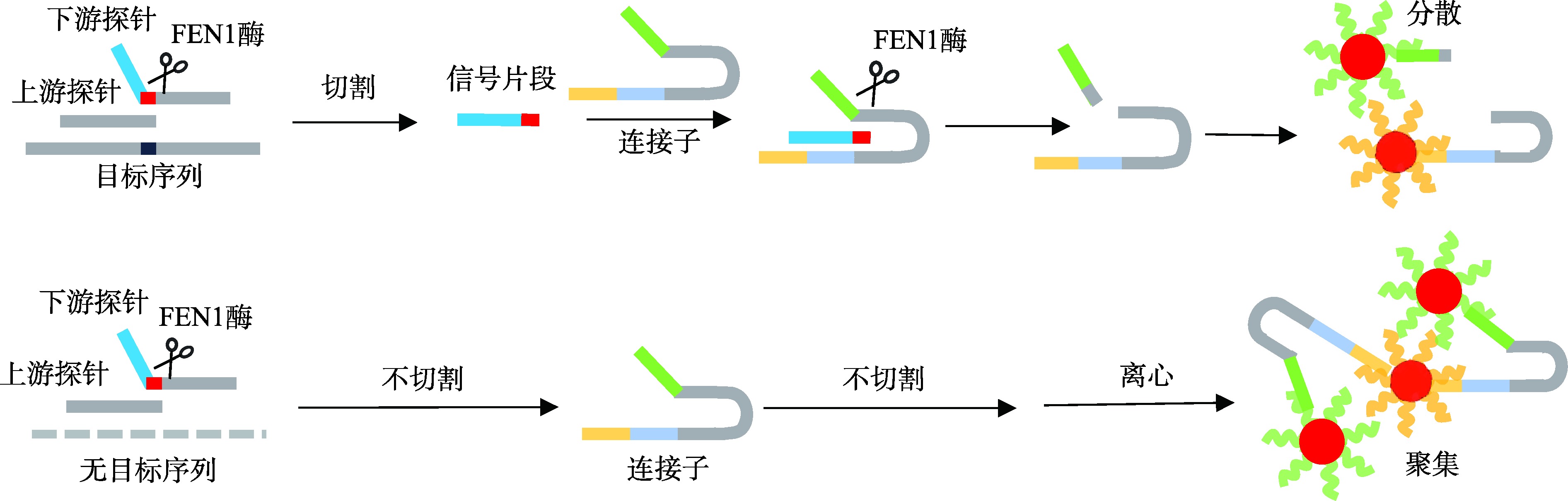
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非特异性的可视化检测方法 | ||||
| 比浊法 | LAMP副产物焦磷酸根离子与体系中的Mg2+结合,生成不溶于水的白色沉淀。 | 阴:体系澄清 阳:体系浑浊/离心后有白色沉淀 | 成本低廉、操作简单、可实时监测 | 白色沉淀不易观察、灵敏度低;非特异性检测 |
| 指示剂显色法 | 金属指示剂: 因LAMP扩增导致游离的Mg2+浓度下降使指示剂呈现不同颜色。 | 以HNB为例: 阴:紫 阳:蓝 | 操作简单、成本低廉 | 对比效应不明显,易出现结果误读;非特异性检测 |
| 酸碱指示剂: 因LAMP扩增导致的H+浓度上升而指示剂结构发生改变从而呈现不同颜色。 | 以酚红为例: 阴:红 阳:黄 | 直观、快速、简便 | 易受到样品干扰;非特异性检测 | |
| 序列特异性的可视化检测方法 | ||||
| 酶促底物显色法 | HRP或G-四链体/血红素在H2O2的作用下催化显色底物显色 | 以ABTS2-为例 阴:无色 阳:绿色 | 酶催化具有高效性、G-四链体DNAzyme成本低、 | 天然酶对环境要求高,DNAzyme催化活性会出现下降 |
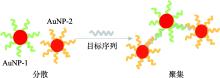
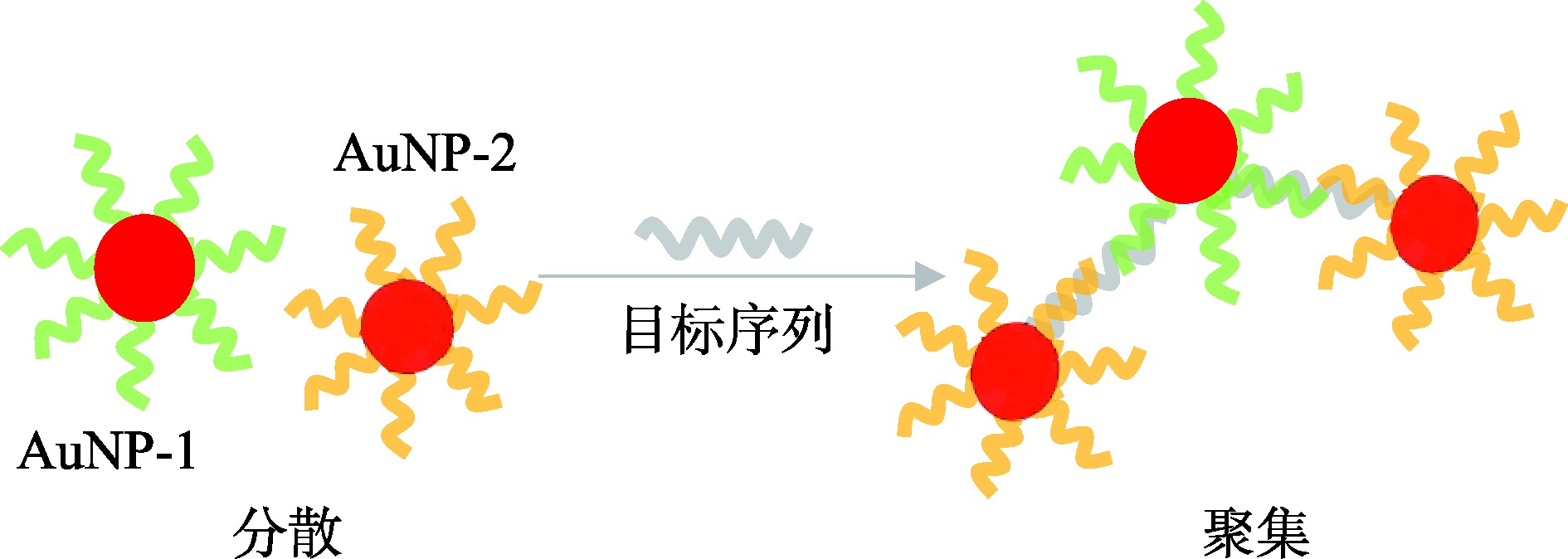
| 纳米颗粒显色法 | 通过诱导AuNPs呈现不同状态(聚集/分散),从而观察到颜色的转变 | 分散:红色 聚集:紫色/离心后沉淀 | 直观、快速、低成本 | 难以实现单管多重检测、AuNPs状态易受体系影响 |
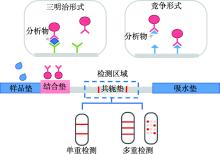
| 横向流动分析法 | 抗原抗体结合 | 阴:C线 阳:T线&C线 | 直观、快速、可多重检测 | 脱靶现象;检测的灵活度受限 |
| [1] | Reusken CBEM, Broberg EK, Haagmans B, Meijer A, Corman VM, Papa A, Charrel R, Drosten C, Koopmans M, Leitmeyer K,EVD-LabNet and ERLI-Net. Laboratory readiness and response for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in expert laboratories in 30 EU/EEA countries, January 2020. Euro Surveill, 2020, 25(6): 2000082. |
| [2] | Patel R, Babady E, Theel ES, Storch GA, Pinsky BA, St. George K, Smith TC, Bertuzzi S. Report from the American society for microbiology COVID-19 international summit, 23 March 2020: value of diagnostic testing for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19. mBio, 2020, 11(2): e00722-20. |
| [3] | Zhou J, Tian FY, Jiao BN, He Y. Applications of visual colorimetric detection methods based on nanomaterials in detecting foodborne pathogens. Food Ferment Ind, 2019: 259-267. |
| 周静, 田风玉, 焦必宁, 何悦. 基于纳米材料的可视化比色检测技术在食源性致病菌检测中的应用研究进展. 食品与发酵工业, 2019: 259-267. | |
| [4] | Chen D, Liu MH, Zhang W, Lian ML. Progress in colorimetric analysis of nanomaterials with peroxidase- like activity. Mater Rep, 2022, 36(13): 36-49. |
| 陈达, 刘美含, 张伟, 练美玲. 具有类过氧化物酶活性的纳米材料在比色分析中的研究进展. 材料导报, 2022; 36(13): 36-49. | |
| [5] |
Garrido-Maestu A, Prado M. Naked-eye detection strategies coupled with isothermal nucleic acid amplification techniques for the detection of human pathogens. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf, 2022, 21(2): 1913-1939.
doi: 10.1111/crf3.v21.2 |
| [6] |
Pumford EA, Lu JK, Spaczai I, Prasetyo ME, Zheng EM, Zhang HX, Kamei DT. Developments in integrating nucleic acid isothermal amplification and detection systems for point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron, 2020, 170: 112674.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112674 |
| [7] |
Xu N, Jin S, Wang L. Metal nanoparticles-based nanoplatforms for colorimetric sensing: a review. Rev Anal Chem, 2020, 40(1): 1-11.
doi: 10.1515/revac-2021-0122 |
| [8] |
Watson JD, Crick FH. Molecular structure of nucleic acids: a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature, 1953, 171(4356): 737-738.
doi: 10.1038/171737a0 |
| [9] |
Mullis K, Faloona F, Scharf S, Saiki R, Horn G, Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol, 1986, 51: 263-273.
doi: 10.1101/SQB.1986.051.01.032 |
| [10] |
Wellinghausen N, Wirths B, Essig A, Wassill L. Evaluation of the hyplex bloodscreen multiplex PCR-enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay system for direct Identification of gram-positive cocci and gram-negative bacilli from positive blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol, 2004, 42(7): 3147-3152.
pmid: 15243074 |
| [11] |
Laitinen R, Malinen E, Palva A. PCR-ELISA I: application to simultaneous analysis of mixed bacterial samples composed of intestinal species. Syst Appl Microbiol, 2002, 25(2): 241-248.
pmid: 12353879 |
| [12] |
Higuchi R, Dollinger G, Walsh PS, Griffith R. Simultaneous amplification and detection of specific DNA sequences. Biotechnology (N Y), 1992, 10(4): 413-417.
doi: 10.1038/nbt0492-413 |
| [13] | Feng XJ, Yi HM, Ren XX, Ren JL, Ge JR, Wang FG. Digital PCR and its application in biological detection. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(4): 363-373. |
| 冯秀晶, 易红梅, 任星旭, 任佳丽, 葛建镕, 王凤格. 数字PCR技术及其在检测领域的应用. 遗传, 2020, 42(4): 363-73. | |
| [14] |
Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL, Mucic RC, Storhoff JJ. A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials. Nature, 1996, 382(6592): 607-609.
doi: 10.1038/382607a0 |
| [15] |
Li HX, Rothberg LJ. Label-free colorimetric detection of specific sequences in genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(35): 10958-10961.
pmid: 15339181 |
| [16] |
Li HX, Rothberg L. Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004, 101(39): 14036-14039.
pmid: 15381774 |
| [17] | Aveyard J, Mehrabi M, Cossins A, Braven H, Wilson R. One step visual detection of PCR products with gold nanoparticles and a nucleic acid lateral flow (NALF) device. Chem Commun (Camb), 2007, (41): 4251-4253. |
| [18] |
Mao X, Ma YQ, Zhang AG, Zhang LR, Zeng LW, Liu GD. Disposable nucleic acid biosensors based on gold nanoparticle probes and lateral flow strip. Anal Chem, 2009, 81(4): 1660-1668.
doi: 10.1021/ac8024653 pmid: 19159221 |
| [19] |
Kim YT, Chen YC, Choi JY, Kim WJ, Dae HM, Jung J, Seo TS. Integrated microdevice of reverse transcription- polymerase chain reaction with colorimetric immunochromatographic detection for rapid gene expression analysis of influenza A H1N1 virus. Biosens Bioelectron, 2012, 33(1): 88-94.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.12.024 |
| [20] |
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res, 2000, 28(12): E63.
doi: 10.1093/nar/28.12.e63 pmid: 10871386 |
| [21] |
Piepenburg O, Williams CH, Stemple DL, Armes NA. DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLOS Biol, 2006, 4(7): e204.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040204 |
| [22] | Xie CM, Wu HP, Ma XP, Zhou GH.New molecular diagnostic technologies for clinical detection of SARS- CoV-2. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 42(9): 870-881. |
| 谢春梅, 武海萍, 马雪萍, 周国华. 用于临床新型冠状病毒核酸检测的分子诊断新技术. 遗传, 2020, 42(9): 870-881. | |
| [23] | He XP, Zou BJ, Qi XM, Chen S, Lu Y, Huang Q, Zhou GH. Methods of isothermal nucleic acid amplification-based microfluidic chips for pathogen microorganism detection. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(7): 611-624. |
| 何祥鹏, 邹秉杰, 齐谢敏, 陈杉, 陆妍, 黄青, 周国华. 基于核酸等温扩增的病原微生物微流控检测技术. 遗传, 2019, 41(7): 611-624. | |
| [24] | Niu XR, Yin SM, Chen X, Shao TT, Li DL. Gene editing technology and its recent progress in disease therapy. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(7): 582-598 |
| 牛煦然, 尹树明, 陈曦, 邵婷婷, 李大力. 基因编辑技术及其在疾病治疗中的研究进展. 遗传, 2019, 41(7): 582-598. | |
| [25] |
Chen YO, Bao Y, Ma HZ, Yi ZY, Zhou Z, Wei WS. Gene editing technology and its research progress in China. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(10): 900-915.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-195 pmid: 30369472 |
|
陈一欧, 宝颖, 马华峥, 伊宗裔, 周卓, 魏文胜. 基因编辑技术及其在中国的研究发展. 遗传, 2018, 40(10): 900-915.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-195 pmid: 30369472 |
|
| [26] |
East-Seletsky A, O’Connell MR, Knight SC, Burstein D, Cate JHD, Tjian R, Doudna JA. Two distinct RNase activities of CRISPR-C2c2 enable guide-RNA processing and RNA detection. Nature, 2016, 538(7624): 270-273.
doi: 10.1038/nature19802 |
| [27] |
Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, Lee JW, Essletzbichler P, Dy AJ, Joung J, Verdine V, Donghia N, Daringer NM, Freije CA, Myhrvold C, Bhattacharyya RP, Livny J, Regev A, Koonin EV, Hung DT, Sabeti PC, Collins JJ, Zhang F. Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2. Science, 2017, 356(6336): 438-442.
doi: 10.1126/science.aam9321 pmid: 28408723 |
| [28] |
Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, Kellner MJ, Joung J, Collins JJ, Zhang F.Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Science, 2018, 360(6387): 439-444.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaq0179 pmid: 29449508 |
| [29] |
Chen JS, Ma E, Harrington LB, Da Costa M, Tian XR, Palefsky JM, Doudna JA. CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity. Science, 2018, 360(6387): 436-439.
doi: 10.1126/science.aar6245 pmid: 29449511 |
| [30] |
Li SY, Cheng QX, Wang JM, Li XY, Zhang ZL, Gao S, Cao RB, Zhao GP, Wang J. CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted nucleic acid detection. Cell Discov, 2018, 4(1): 20.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-018-0028-z |
| [31] |
Mori Y, Nagamine K, Tomita N, Notomi T. Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2001, 289(1): 150-154.
doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5921 |
| [32] |
Wong YP, Othman S, Lau YL, Radu S, Chee HY. Loop- mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): a versatile technique for detection of micro-organisms. J Appl Microbiol, 2018, 124(3): 626-643.
doi: 10.1111/jam.13647 pmid: 29165905 |
| [33] |
Mori Y, Kitao M, Tomita N, Notomi T. Real-time turbidimetry of LAMP reaction for quantifying template DNA. J Biochem Biophys Methods, 2004, 59(2): 145-157.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbbm.2003.12.005 pmid: 15163526 |
| [34] |
Fang XE, Liu YY, Kong JL, Jiang XY. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification integrated on microfluidic chips for point-of-care quantitative detection of pathogens. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(7): 3002-3006.
doi: 10.1021/ac1000652 pmid: 20218572 |
| [35] |
Tomita N, Mori Y, Kanda H, Notomi T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of gene sequences and simple visual detection of products. Nat Protoc, 2008, 3(5): 877-882.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.57 pmid: 18451795 |
| [36] |
Yan C, Cui J, Huang L, Du B, Chen L, Xue G, Li S, Zhang W, Zhao L, Sun Y, Yao H, Li N, Zhao H, Feng Y, Liu S, Zhang Q, Liu D, Yuan J. Rapid and visual detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) by a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2020, 26(6): 773-779.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.001 |
| [37] |
Goto M, Honda E, Ogura A, Nomoto A, Hanaki KI. Colorimetric detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. Biotechniques, 2009, 46(3): 167-172.
doi: 10.2144/000113072 pmid: 19317660 |
| [38] |
Zhong Q, Li K, Chen D, Wang H, Lin Q, Liu W. Rapid detection and subtyping of human papillomaviruses in condyloma acuminatum using loop-mediated isothermal amplification with hydroxynaphthol blue dye. Br J Biomed Sci, 2018, 75(3): 110-115.
doi: 10.1080/09674845.2017.1411864 |
| [39] |
Pang B, Yao S, Xu K, Wang J, Song XL, Mu Y, Zhao C, Li J. A novel visual-mixed-dye for LAMP and its application in the detection of foodborne pathogens. Anal Biochem, 2019, 574: 1-6.
doi: S0003-2697(19)30107-1 pmid: 30862446 |
| [40] |
Tanner NA, Zhang YH, Evans Jr TC. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. BioTechniques, 2015, 58(2): 59-68.
doi: 10.2144/000114253 pmid: 25652028 |
| [41] |
Nawattanapaiboon K, Pasomsub E, Prombun P, Wongbunmak A, Jenjitwanich A, Mahasupachai P, Vetcho P, Chayrach C, Manatjaroenlap N, Samphaongern C, Watthanachockchai T, Leedorkmai P, Manopwisedjaroen S, Akkarawongsapat R, Thitithanyanont A, Phanchana M, Panbangred W, Chauvatcharin S, Srikhirin T.Colorimetric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) as a visual diagnostic platform for the detection of the emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Analyst, 2021, 146(2): 471-477.
doi: 10.1039/d0an01775b pmid: 33165486 |
| [42] |
He YH, Xie T, Tong YG. Rapid and highly sensitive one-tube colorimetric RT-LAMP assay for visual detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Biosens Bioelectron, 2021, 187: 113330.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113330 |
| [43] |
Wang Y, Dai JF, Liu YS, Yang JF, Hou Q, Ou YW, Ding YZ, Ma B, Chen HT, Li MM, Sun YF, Zheng HX, Zhang KS, Wubshet AK, Zaberezhny AD, Aliper TI, Tarasiuk K, Pejsak Z, Liu ZJ, Zhang YG, Zhang J. Development of a potential penside colorimetric LAMP assay using neutral red for detection of african swine fever virus. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 609821.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.609821 |
| [44] |
Alhamid G, Tombuloglu H, Motabagani D, Motabagani D, Rabaan AA, Unver K, Dorado G, Al-Suhaimi E, Unver T. Colorimetric and fluorometric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. Funct Integr Genomics, 2022, 22(6): 1391-1401.
doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00900-5 |
| [45] |
Bokelmann L, Nickel O, Maricic T, Pääbo S, Meyer M, Borte S, Riesenberg S. Point-of-care bulk testing for SARS-CoV-2 by combining hybridization capture with improved colorimetric LAMP. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1467.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21627-0 pmid: 33674580 |
| [46] |
Dao Thi VL, Herbst K, Boerner K, Meurer M, Kremer LP, Kirrmaier D, Freistaedter A, Papagiannidis D, Galmozzi C, Stanifer ML, Boulant S, Klein S, Chlanda P, Khalid D, Barreto Miranda I, Schnitzler P, Kräusslich HG, Knop M, Anders S. A colorimetric RT-LAMP assay and LAMP- sequencing for detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in clinical samples. Sci Transl Med, 2020, 12(556): eabc7075.
doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abc7075 |
| [47] |
Meagher RJ, Priye A, Light YK, Huang C, Wang E. Impact of primer dimers and self-amplifying hairpins on reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection of viral RNA. Analyst, 2018, 143(8): 1924-1933.
doi: 10.1039/c7an01897e pmid: 29620773 |
| [48] |
Luo GC, Yi TT, Wang Q, Guo B, Fang L, Zhang GY, Guo XL. Stem-loop-primer assisted isothermal amplification enabling high-specific and ultrasensitive nucleic acid detection. Biosens Bioelectron, 2021, 184: 113239.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113239 |
| [49] |
Ye X, Zhou H, Guo X, Liu D, Li Z, Sun J, Huang J, Liu T, Zhao P, Xu H, Li K, Wang H, Wang J, Wang L, Zhao W, Liu Q, Xu S, Feng Y. Argonaute-integrated isothermal amplification for rapid, portable, multiplex detection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses. Biosens Bioelectron, 2022, 207: 114169.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114169 |
| [50] |
Xu GL, Zhao H, Cooper JM, Reboud J. A capillary-based multiplexed isothermal nucleic acid-based test for sexually transmitted diseases in patients. Chem Commun (Camb), 2016, 52(82): 12187-12190.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC05679B |
| [51] |
Song JZ, Liu CC, Mauk MG, Rankin SC, Lok JB, Greenberg RM, Bau HH. Two-stage isothermal enzymatic amplification for concurrent multiplex molecular detection. Clin Chem, 2017, 63(3): 714-722.
doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.263665 pmid: 28073898 |
| [52] |
Wang MH, Lin YX, Lu JY, Sun ZW, Deng Y, Wang L, Yi YX, Li JL, Yang J, Li GX. Visual naked-eye detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA based on covalent organic framework capsules. Chem Eng J, 2022, 429: 132332.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132332 |
| [53] |
Sen D, Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature, 1988, 334(6180): 364- 366.
doi: 10.1038/334364a0 |
| [54] |
Lee JE, Mun H, Kim SR, Kim MG, Chang JY, Shim WB. A colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay based on HRP-mimicking molecular beacon for the rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biosens Bioelectron, 2020, 151: 111968.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111968 |
| [55] |
He HF, Zhou Y, Chen B, Zhang Y, Zhong XW, Xu L, Guo B, Yin C, Zhou X, Li QR, Huang Z, Luo GC, Guo XL. Nucleic acid amplification with specific signal filtration and magnification for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection. Talanta, 2023, 253: 123978.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123978 |
| [56] |
Baetsen-Young AM, Vasher M, Matta LL, Colgan P, Alocilja EC, Day B. Direct colorimetric detection of unamplified pathogen DNA by dextrin-capped gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron, 2018, 101: 29-36.
doi: S0956-5663(17)30670-X pmid: 29031887 |
| [57] |
Moitra P, Alafeef M, Dighe K, Frieman MB, Pan D. Selective naked-eye detection of SARS-CoV-2 mediated by N gene targeted antisense oligonucleotide capped plasmonic nanoparticles. Acs Nano, 2020, 14(6): 7617-7627.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c03822 pmid: 32437124 |
| [58] |
Alafeef M, Moitra P, Dighe K, Pan D.RNA-extraction-free nano-amplified colorimetric test for point-of-care clinical diagnosis of COVID-19. Nat Protoc, 2021, 16(6): 3141-3162.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00546-w pmid: 33931780 |
| [59] |
Kong C, Wang Y, Fodjo EK, Yang GX, Han F, Shen XS. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for visual detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus using gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta, 2018, 185(1): 35.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-017-2594-4 |
| [60] |
Ma Y, Gong CY, Qi XM, Zou BJ, Song QX, Zhou GH. Multiplex Detection of viral DNAs in blood by colorimetrically identifying polymerase chain reaction amplicons with serial invasive reaction assisted gold nanoparticle probes assembling. J Nanosci Nanotechnol, 2020, 20(10): 6140-6147.
doi: 10.1166/jnn.2020.18122 pmid: 32384963 |
| [61] |
Weng JX, Sheng N, Wang RY, Liang S, Wang C, Bai X, Zhou GH, Zou BJ, Song QX. Multiplex visualized closed- tube PCR with hamming distance 2 code for 15 HPV subtype typing. Anal Chem, 2021, 93(13): 5529-5536.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00035 |
| [62] |
Ge YY, Zhou Q, Zhao KC, Chi Y, Liu B, Min XY, Shi ZY, Zou BJ, Cui LB. Detection of influenza viruses by coupling multiplex reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification with cascade invasive reaction using nanoparticles as a sensor. Int J Nanomedicine, 2017, 12: 2645-2656.
doi: 10.2147/IJN |
| [63] | Sun M, Gao J, Qin XY, Guo YR, Jia R, Hou LG, Luo SY, Zhang YD, Zhang XW, Zhang WC. Progress of nucleic acid detection strip detection approaches. Chin J Biotechnol, 2022, 42(12): 69-78. |
| 孙萌, 郜晶, 秦雪怡, 郭颖然, 贾蕊, 侯立功, 罗淑颖, 张耀东, 张现伟, 张万存. 核酸试纸条检测方法研究进展. 中国生物工程杂志, 2022, 42(12): 69-78. | |
| [64] |
Landaverde L, Wong W, Hernandez G, Fan A, Klapperich C.Method for the elucidation of LAMP products captured on lateral flow strips in a point of care test for HPV 16. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2020, 412(24): 6199-6209.
doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02702-9 pmid: 32488390 |
| [65] |
Zhang C, Zheng TT, Wang H, Chen W, Huang XY, Liang JQ, Qiu LP, Han D, Tan WH. Rapid one-pot detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on a lateral flow assay in clinical samples. Anal Chem, 2021, 93(7): 3325-3330.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05059 pmid: 33570399 |
| [66] |
Wang Y, Wang Y, Li DX, Xu JG, Ye CY. Detection of nucleic acids and elimination of carryover contamination by using loop-mediated isothermal amplification and antarctic thermal sensitive uracil-DNA-glycosylase in a lateral flow biosensor: application to the detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microchim Acta, 2018, 185(4): 212.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-2723-8 |
| [67] |
Cherkaoui D, Huang D, Miller BS, Turbé V, McKendry RA. Harnessing recombinase polymerase amplification for rapid multi-gene detection of SARS-CoV-2 in resource- limited settings. Biosens Bioelectron, 2021, 189: 113328.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113328 |
| [68] |
Li ZY, Ding X, Yin K, Avery L, Ballesteros E, Liu C. Instrument-free, CRISPR-based diagnostics of SARS- CoV-2 using self-contained microfluidic system. Biosens Bioelectron, 2022, 199: 113865.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113865 |
| [69] |
Yang XH, Xie J, Hu SQ, Zhan WL, Duan L, Chen KY, Zhang CB, Yin AH, Luo MY. Rapid and visual detection of enterovirus using recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strips. Sens Actuators B Chem, 2020, 311: 127903.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.127903 |
| [70] |
Wang YL, Zhang X, Wang Q, Liu PX, Tang W, Guo R, Zhang HY, Chen ZG, Han XG, Jiang W. Rapid and visual detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk using a recombinase polymerase amplification‐lateral flow assay combined with immunomagnetic separation. J Appl Microbiol, 2022, 133(6): 3741-3754.
doi: 10.1111/jam.15811 |
| [71] |
Lau YL, Ismail I binti, Mustapa NI binti, Lai MY, Tuan Soh TS, Haji Hassan A, Peariasamy KM, Lee YL, Abdul Kahar MKB, Chong J, Goh PP. Development of a reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid and direct visual detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). PLoS One, 2021, 16(1): e0245164.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245164 |
| [72] |
Yang B, Kong Jl, Fang XE. Bandage-like wearable flexible microfluidic recombinase polymerase amplification sensor for the rapid visual detection of nucleic acids. Talanta, 2019, 204: 685-692.
doi: S0039-9140(19)30656-3 pmid: 31357353 |
| [73] |
Powell ML, Bowler FR, Martinez AJ, Greenwood CJ, Armes N, Piepenburg O. New fpg probe chemistry for direct detection of recombinase polymerase amplification on lateral flow strips. Anal Biochem, 2018, 543: 108-115.
doi: S0003-2697(17)30496-7 pmid: 29233680 |
| [74] |
Zhu X, Wang XX, Han LM, Chen T, Wang LC, Li H, Li S, He LF, Fu XY, Chen SJ, Xing M, Chen H, Wang Y. Multiplex reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Biosens Bioelectron, 2020, 166: 112437.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112437 |
| [75] |
Jin B, Ma B, Li JL, Hong Y, Zhang MZ. Simultaneous detection of five foodborne pathogens using a mini automatic nucleic acid extractor combined with recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow immunoassay. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(7): 1352.
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071352 |
| [76] |
Kasahara K, Ishikawa H, Sato S, Shimakawa Y, Watanabe K. Development of multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays to detect medically important yeasts in dairy products. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2014, 357(2): 208-216.
doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12512 pmid: 24965944 |
| [77] |
Zhai JJ, Wang LM, Qiao XL, Zhao JP, Wang XX, He XH. Correction: detection of neisseria gonorrhoeae and chlamydia trachomatis infections in pregnant women by multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e0271836.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271836 |
| [78] | Lin WH, Zou BJ, Song QX, Zhou GH. Progress in multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. Hereditas (Beijing), 2015, 37(9): 899-910. |
| 林文慧, 邹秉杰, 宋沁馨, 周国华. 多重环介导等温扩增技术研究进展. 遗传, 2015, 37(9): 899-910. | |
| [79] |
Song J, Cha B, Moon J, Jang H, Kim S, Jang J, Yong D, Kwon H-J, Lee IC, Lim EK, Jung J, Park HG, Kang T. Smartphone-based SARS-CoV-2 and variants detection system using colorimetric DNAzyme reaction triggered by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) with clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR). ACS Nano, 2022, 16(7): 11300-11314.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c04840 |
| [80] |
Chen XY, Wang L, He F, Chen GH, Bai LL, He KY, Zhang F, Xu XH. Label-free colorimetric method for detection of vibrio parahaemolyticus by trimming the G-quadruplex DNAzyme with CRISPR/Cas12a. Anal Chem, 2021, 93(42): 14300-14306.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03468 |
| [81] |
Zhang WS, Pan JB, Li F, Zhu M, Xu MT, Zhu HY, Yu YY, Su GX. Reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification coupled with CRISPR-Cas12a for facile and highly sensitive colorimetric SARS-CoV-2 detection. Anal Chem, 2021, 93(8): 4126-4133.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00013 pmid: 33570401 |
| [82] |
López-Valls M, Escalona-Noguero C, Rodríguez-Díaz C, Pardo D, Castellanos M, Milán-Rois P, Martínez-Garay C, Coloma R, Abreu M, Cantón R, Carlos Galán J, Miranda R, Somoza Á, Sot B. CASCADE: naked eye-detection of SARS-CoV-2 using Cas13a and gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta, 2022, 1205: 339749.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339749 |
| [83] |
Ma L, Yin LJ, Li XY, Chen S, Peng L, Liu GZ, Ye SY, Zhang WL, Man SL. A smartphone-based visual biosensor for CRISPR-Cas powered SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron, 2022, 195: 113646.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113646 |
| [84] |
Jiang YZ, Hu ML, Liu AA, Lin Y, Liu LL, Yu B, Zhou XM, Pang DW. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by CRISPR/Cas12a- enhanced colorimetry. ACS Sens, 2021, 6(3): 1086-1093.
doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c02365 |
| [85] |
Arizti-Sanz J, Freije CA, Stanton AC, Petros BA, Boehm CK, Siddiqui S, Shaw BM, Adams G, Kosoko-Thoroddsen TF, Kemball ME, Uwanibe JN, Ajogbasile FV, Eromon PE, Gross R, Wronka L, Caviness K, Hensley LE, Bergman NH, MacInnis BL, Happi CT, Lemieux JE, Sabeti PC, Myhrvold C. Streamlined inactivation, amplification, and Cas13-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5921.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19097-x pmid: 33219225 |
| [86] |
Yin DD, Yin L, Guo H, Wang JR, Shen XH, Zhao RH, Pan XC, Dai Y. Visual detection and differentiation of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus wild-type strains and attenuated vaccine strains using CRISPR/Cas13a-based lateral flow strip. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 976137.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.976137 |
| [87] |
Broughton JP, Deng XD, Yu GX, Fasching CL, Servellita V, Singh J, Miao X, Streithorst JA, Granados A, Sotomayor-Gonzalez A, Zorn K, Gopez A, Hsu E, Gu W, Miller S, Pan CY, Guevara H, Wadford DA, Chen JS, Chiu CY.CRISPR-Cas12-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Biotechnol, 2020, 38(7): 870-874.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0513-4 pmid: 32300245 |
| [88] |
Nguyen PQ, Soenksen LR, Donghia NM, Angenent-Mari NM, de Puig H, Huang A, Lee R, Slomovic S, Galbersanini T, Lansberry G, Sallum HM, Zhao EM, Niemi JB, Collins JJ. Wearable materials with embedded synthetic biology sensors for biomolecule detection. Nat Biotechnol, 2021, 39(11): 1366-1374.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-00950-3 pmid: 34183860 |
| [89] | Tang YD, Qi LJ, Liu YC, Guo LL, Zhao RJ, Yang MT, Du Y, Li BL. CLIPON: a CRISPR‐enabled strategy that turns commercial pregnancy test strips into general point-of-need test devices. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2022, 61(12): e202115907 |
| [90] |
Huang D, Shi ZW, Qian JJ, Bi K, Fang MJ, Xu ZN.A CRISPR-Cas12a-derived biosensor enabling portable personal glucose meter readout for quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2. Biotechnol Bioeng, 2021, 118(4): 1587-1596.
doi: 10.1002/bit.27673 pmid: 33410130 |
| [91] | Xiong E, Jiang L, Tian T, Hu ML, Yue HH, Huang MQ, Lin W, Jiang YZ, Zhu DB, Zhou XM. Simultaneous dual- gene diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 based on CRISPR/Cas9- mediated lateral flow assay. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2021, 60(10): 5307-5315. |
| [92] |
Su GX, Zhu M, Li DY, Xu MT, Zhu YD, Zhang Y, Zhu HY, Li F, Yu YY. Multiplexed lateral flow assay integrated with orthogonal CRISPR-Cas system for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Sens Actuators B Chem, 2022, 371: 132537.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.132537 |
| [1] | Yu Chen, Xiaoyun Chen, Cheng Peng, Junfeng Xu, Jie Shen, Yueying Li, Xiaofu Wang. Establishment of a field visual detection method for genetically modified maize ‘Shuangkang’12-5 by fluorescence RPA [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(8): 802-812. |
| [2] | Xiangpeng He,Bingjie Zou,Xiemin Qi,Shan Chen,Yan Lu,Qing Huang,Guohua Zhou. Methods of isothermal nucleic acid amplification-based microfluidic chips for pathogen microorganism detection [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(7): 611-624. |
| [3] | Caijiao Liang, Fanmei Meng, Yuncan Ai. CRISPR/Cas systems in genome engineering of bacteriophages [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(5): 378-389. |
| [4] | Wenhui Lin, Bingjie Zou, Qinxin Song, Guohua Zhou. Progress in multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(9): 899-910. |
| [5] | Qihan Wang,Cong Huai,Ruilin Sun,Hua Zhuang,Hongyan Chen,Jian Fei,Daru Lu. A quick and efficient method to generate hemophilia B mouse models by the CRISPR/Cas system [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(11): 1143-1148. |
| [6] | LI Jun, ZHANG Yi, CHEN Kun-Ling, SHAN Qi-Wei, WANG Yan-Peng, LIANG Zhen, GAO Cai-Xia. CRISPR/Cas: a novel way of RNA-guided genome editing [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(11): 1265-1273. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||