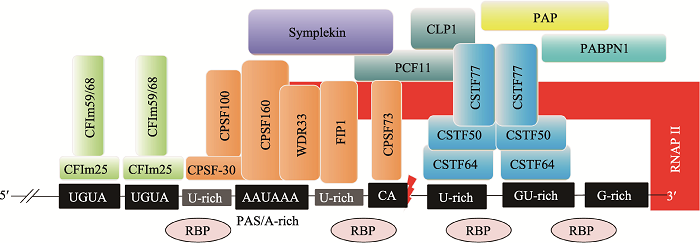
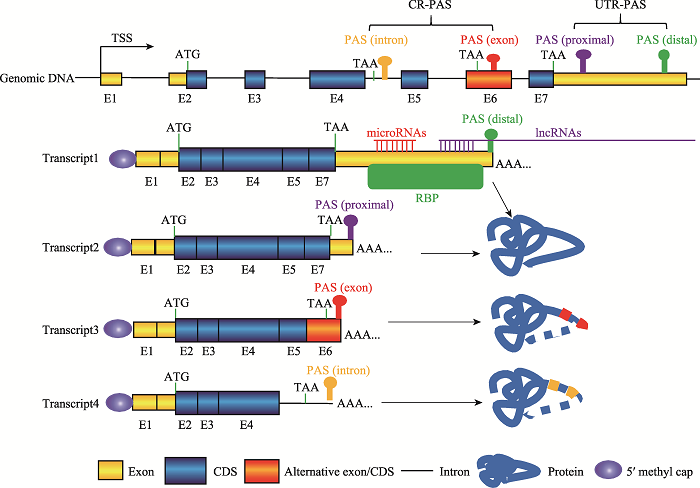
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 4-15.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-200
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances of functional consequences and regulation mechanisms of alternative cleavage and polyadenylation
Haidong Xu1,2,3, Bolin Ning1,2,3, Fang Mu1,2,3, Hui Li1,2,3, Ning Wang1,2,3( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Chicken Genetics and Breeding, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Harbin 150030, China
2. Key Laboratory of Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction, Education Department of Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150030, China
3. College of Animal Science and Technology, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
-
Received:2020-07-07Revised:2020-10-19Online:2021-01-20Published:2020-12-11 -
Contact:Wang Ning E-mail:wangning@neau.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(31572392);Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(3187131154);the China Agriculture Research System No(CARS-41)
Cite this article
Haidong Xu, Bolin Ning, Fang Mu, Hui Li, Ning Wang. Advances of functional consequences and regulation mechanisms of alternative cleavage and polyadenylation[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(1): 4-15.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Tian B, Manley JL . Alternative polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017,18(1):18-30.
doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.116 pmid: 27677860 |
| [2] |
Derti A, Garrett-Engele P, Macisaac KD, Stevens RC, Sriram S, Chen RH, Rohl CA, Johnson JM, Babak T . A quantitative atlas of polyadenylation in five mammals. Genome Res, 2012,22(6):1173-1183.
doi: 10.1101/gr.132563.111 |
| [3] |
Brutman JN, Zhou X, Zhang YZ, Michal J, Stark B, Jiang ZH, Davis JF . Mapping diet-induced alternative polyadenylation of hypothalamic transcripts in the obese rat. Physiol Behav, 2018,188:173-180.
doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.01.026 pmid: 29391168 |
| [4] |
Curinha A, Oliveira Braz S, Pereira-Castro I, Cruz A, Moreira A . Implications of polyadenylation in health and disease. Nucleus, 2014,5(6):508-519.
doi: 10.4161/nucl.36360 pmid: 25484187 |
| [5] |
Gruber AJ, Zavolan M . Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation in health and disease. Nat Rev Genet, 2019,20(10):599-614.
doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0145-z pmid: 31267064 |
| [6] |
Patel R, Brophy C, Hickling M, Neve J, Furger A . Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation of genes associated with protein turnover and mitochondrial function are deregulated in Parkinson's, Alzheimer's and ALS disease. BMC Med Genomics, 2019,12(1):60.
doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0509-4 pmid: 31072331 |
| [7] |
Nourse J, Spada S, Danckwardt S . Emerging roles of RNA 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation in pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of human disorders. Biomolecules, 2020,10(6):915.
doi: 10.3390/biom10060915 |
| [8] |
Jafari Najaf Abadi MH, Shafabakhsh R, Asemi Z, Mirzaei HR, Sahebnasagh R, Mirzaei H, Hamblin MR . CFIm25 and alternative polyadenylation: conflicting roles in cancer. Cancer Lett, 2019,459:112-121.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.114430 pmid: 31181319 |
| [9] | Neve J, Patel R, Wang ZQ, Louey A, Furger AM . Cleavage and polyadenylation: ending the message expands gene regulation. RNA Biololgy, 2017,14(7):865-890. |
| [10] |
Zheng DH, Tian B . RNA-binding proteins in regulation of alternative cleavage and polyadenylation. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2014,825:97-127.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1221-6_3 |
| [11] | Knipe DM, Howley PM. Fields virology. 6th ed. 2013: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Publishing. |
| [12] |
Chan SL, Huppertz I, Yao CG, Weng LJ, Moresco JJ, Yates JR 3rd, Ule J, Manley JL, Shi YS,. CPSF30 and Wdr33 directly bind to AAUAAA in mammalian mRNA 3' processing. Genes Dev, 2014,28(21):2370-2380.
doi: 10.1101/gad.250993.114 pmid: 25301780 |
| [13] |
Hamilton K, Sun YD, Tong L . Biophysical characterizations of the recognition of the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal. RNA, 2019,25(12):1673-1680.
doi: 10.1261/rna.070870.119 pmid: 31462423 |
| [14] |
Sha QQ, Zhang J, Fan HY . A story of birth and death: mRNA translation and clearance at the onset of maternal- to-zygotic transition in mammals. Biol Reprod, 2019,101(3):579-590.
doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioz012 pmid: 30715134 |
| [15] |
Winata CL, Łapiński M, Pryszcz L, Vaz C, Bin Ismail MH, Nama S, Hajan HS, Lee SGP, Korzh V, Sampath P, Tanavde V, Mathavan S. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation- mediated translational control of maternal mRNAs directs maternal-to-zygotic transition. Development, 2018,145(1): dev159566.
doi: 10.1242/dev.160051 pmid: 29217751 |
| [16] |
Shao M, Lu T, Zhang C, Zhang YZ, Kong SH, Shi DL . Rbm24 controls poly(A) tail length and translation efficiency of crystallin mRNAs in the lens via cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020,117(13):7245-7254.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1917922117 pmid: 32170011 |
| [17] |
Villalba A, Coll O, Gebauer F . Cytoplasmic polyadenylation and translational control. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2011,21(4):452-457.
doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.04.006 |
| [18] |
Dai XX, Jiang JC, Sha QQ, Jiang Y, Ou XH, Fan HY . A combinatorial code for mRNA 3'-UTR-mediated translational control in the mouse oocyte. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019,47(1):328-340.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gky971 pmid: 30335155 |
| [19] |
Charlesworth A, Meijer HA, de Moor CH,. Specificity factors in cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2013,4(4):437-461.
doi: 10.1002/wrna.1171 pmid: 23776146 |
| [20] |
Chen W, Jia Q, Song YF, Fu HH, Wei G, Ni T . Alternative polyadenylation: methods, findings, and impacts. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2017,15(5):287-300.
doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2017.06.001 pmid: 29031844 |
| [21] | Lau SL . Molecular characterization of the chicken growth hormone receptor gene. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University, 2005. |
| [22] |
Lau JS, Yip CW, Law KM, Leung FC . Cloning and characterization of chicken growth hormone binding protein (cGHBP). Domest Anim Endocrinol, 2007,33(1):107-121.
doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2006.04.012 pmid: 16814975 |
| [23] |
Dehkhoda F, Lee CMM, Medina J, Brooks AJ . The growth hormone receptor: mechanism of receptor activation, cell signaling, and physiological aspects. Front Endocrinol, 2018,9:35.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00035 |
| [24] |
Cheng LC, Zheng DH, Baljinnyam E, Sun FZ, Ogami K, Yeung PL, Hoque M, Lu CW, Manley JL, Tian B . Widespread transcript shortening through alternative polyadenylation in secretory cell differentiation. Nat Commun, 2020,11(1):3182.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16959-2 pmid: 32576858 |
| [25] |
Di Giammartino DC, Li WC, Ogami K, Yashinskie JJ, Hoque M, Tian B, Manley JL . RBBP6 isoforms regulate the human polyadenylation machinery and modulate expression of mRNAs with AU-rich 3' UTRs. Genes Dev, 2014,28(20):2248-2260.
doi: 10.1101/gad.245787.114 pmid: 25319826 |
| [26] |
Turner RE, Pattison AD, Beilharz TH . Alternative polyadenylation in the regulation and dysregulation of gene expression. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2018,75:61-69.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.08.056 pmid: 28867199 |
| [27] |
Graham RR, Kyogoku C, Sigurdsson S, Vlasova IA, Davies LRL, Baechler EC, Plenge RM, Koeuth T, Ortmann WA, Hom G, Bauer JW, Gillett C, Burtt N, Cunninghame Graham DS, Onofrio R, Petri M, Gunnarsson I, Svenungsson E, Rönnblom L, Nordmark G, Gregersen PK, Moser K, Gaffney PM, Criswell LA, Vyse TJ, Syvänen AC, Bohjanen PR, Daly MJ, Behrens TW, Altshuler D . Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007,104(16):6758-6763.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701266104 pmid: 17412832 |
| [28] |
Boutet SC, Cheung TH, Quach NL, Liu L, Prescott SL, Edalati A, Iori K, Rando TA . Alternative polyadenylation mediates microRNA regulation of muscle stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell, 2012,10(3):327-336.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.01.017 |
| [29] |
de Morree A, Klein JDD, Gan Q, Farup J, Urtasun A, Kanugovi A, Bilen B, van Velthoven CTJ, Quarta M, Rando TA . Alternative polyadenylation of Pax3 controls muscle stem cell fate and muscle function. Science, 2019,366(6466):734-738.
doi: 10.1126/science.aax1694 pmid: 31699935 |
| [30] |
Gruber AR, Martin G, Müller P, Schmidt A, Gruber AJ, Gumienny R, Mittal N, Jayachandran R, Pieters J, Keller W, van Nimwegen E, Zavolan M,. Global 3' UTR shortening has a limited effect on protein abundance in proliferating T cells. Nat Commun, 2014,5:5465.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6465 pmid: 25413384 |
| [31] |
Spies N, Burge CB, Bartel DP . 3' UTR-isoform choice has limited influence on the stability and translational efficiency of most mRNAs in mouse fibroblasts. Genome Res, 2013,23(12):2078-2090.
doi: 10.1101/gr.156919.113 |
| [32] |
Spangenberg L, Shigunov P, Abud APR, Cofré AR, Stimamiglio MA, Kuligovski C, Zych J, Schittini AV, Costa ADT, Rebelatto CK, Brofman PRS, Goldenberg S, Correa A, Naya H, Dallagiovanna B . Polysome profiling shows extensive posttranscriptional regulation during human adipocyte stem cell differentiation into adipocytes. Stem Cell Res, 2013,11(2):902-912.
doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2013.06.002 pmid: 23845413 |
| [33] |
Jambhekar A, Derisi JL . Cis-acting determinants of asymmetric, cytoplasmic RNA transport. RNA, 2007,13(5):625-642.
doi: 10.1261/rna.262607 pmid: 17449729 |
| [34] |
Shi M, Zhang H, Wu XD, He ZS, Wang LT, Yin SY, Tian B, Li GH, Cheng H . ALYREF mainly binds to the 5' and the 3' regions of the mRNA in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017,45(16):9640-9653.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx597 pmid: 28934468 |
| [35] |
Ruepp MD, Aringhieri C, Vivarelli S, Cardinale S, Paro S, Schümperli D, Barabino SML . Mammalian pre-mRNA 3' end processing factor CF I m 68 functions in mRNA export. Mol Biol Cell, 2009,20(24):5211-5223.
doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-05-0389 pmid: 19864460 |
| [36] |
Chen SL, Wang RJ, Zheng DH, Zhang H, Chang XY, Wang K, Li WC, Fan J, Tian B, Cheng H. The mRNA export receptor NXF1 coordinates transcriptional dynamics, alternative polyadenylation, mRNA export. Mol Cell, 2019, 74(1): 118- 131.e7.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.026 pmid: 30819645 |
| [37] |
An JJ, Gharami K, Liao GY, Woo NH, Lau AG, Vanevski F, Torre ER, Jones KR, Feng Y, Lu B, Xu BJ . Distinct role of long 3' UTR BDNF mRNA in spine morphology and synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Cell, 2008,134(1):175-187.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.045 pmid: 18614020 |
| [38] |
Andreassi C, Riccio A . To localize or not to localize: mRNA fate is in 3'UTR ends. Trends Cell Biol, 2009,19(9):465-474.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.06.001 |
| [39] |
Berkovits BD, Mayr C . Alternative 3' UTRs act as scaffolds to regulate membrane protein localization. Nature, 2015,522(7556):363-367.
doi: 10.1038/nature14321 pmid: 25896326 |
| [40] |
Davis R, Shi YS . The polyadenylation code: a unified model for the regulation of mRNA alternative polyadenylation. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2014,15(5):429-437.
doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1400076 pmid: 24793760 |
| [41] |
Marsollier AC, Joubert R, Mariot V, Dumonceaux J . Targeting the polyadenylation signal of pre-mRNA: a new gene silencing approach for facioscapulohumeral dystrophy. Int J Mol Sci, 2018,19(5):1347.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19051347 |
| [42] |
Nanavaty V, Abrash EW, Hong CJ, Park S, Fink EE, Li ZY, Sweet TJ, Bhasin JM, Singuri S, Lee BH, Hwang TH, Ting AH. DNA methylation regulates alternative polyadenylation via CTCF and the cohesin complex. Mol Cell, 2020, 78(4): 752-764. e6.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.024 pmid: 32333838 |
| [43] |
Michaels KK, Mohd Mostafa S, Ruiz Capella J, Moore CL . Regulation of alternative polyadenylation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by histone H3K4 and H3K36 methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020,48(10):5407-5425.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa292 pmid: 32356874 |
| [44] |
Yue YN, Liu J, Cui XL, Cao J, Luo GZ, Zhang ZZ, Cheng T, Gao MS, Shu X, Ma HH, Wang FQ, Wang XX, Shen B, Wang YZ, Feng XH, He C, Liu JZ . VIRMA mediates preferential m 6A mRNA methylation in 3'UTR and near stop codon and associates with alternative polyadenylation . Cell Discov, 2018,4:10.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-018-0019-0 pmid: 29507755 |
| [45] |
Patraquim P, Warnefors M, Alonso CR . Evolution of Hox post-transcriptional regulation by alternative polyadenylation and microRNA modulation within 12 Drosophila genomes. Mol Biol Evol, 2011,28(9):2453-2460.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr073 |
| [46] |
Pinto PAB, Henriques T, Freitas MO, Martins T, Domingues RG, Wyrzykowska PS, Coelho PA, Carmo AM, Sunkel CE, Proudfoot NJ, Moreira A . RNA polymerase II kinetics in polo polyadenylation signal selection. EMBO J, 2011,30(12):2431-2444.
doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.156 |
| [47] |
Maita H, Nakagawa S . What is the switch for coupling transcription and splicing? RNA Polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation, phase separation and beyond. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2020,11(1):e1574.
doi: 10.1002/wrna.1574 pmid: 31680436 |
| [48] |
Yu LJ, Volkert MR . UV damage regulates alternative polyadenylation of the RPB2 gene in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013,41(5):3104-3114.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt020 pmid: 23355614 |
| [49] |
Nazim M, Masuda A, Rahman MA, Nasrin F, Takeda JI, Ohe K, Ohkawara B, Ito M, Ohno K . Competitive regulation of alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation by hnRNP H and CstF64 determines acetylcholinesterase isoforms. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017,45(3):1455-1468.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw823 pmid: 28180311 |
| [50] |
Lackford B, Yao CG, Charles GM, Weng LJ, Zheng XF, Choi EA, Xie XH, Wan J, Xing Y, Freudenberg JM, Yang PY, Jothi R, Hu G, Shi YS . Fip1 regulates mRNA alternative polyadenylation to promote stem cell self- renewal. EMBO J, 2014,33(8):878-889.
doi: 10.1002/embj.201386537 |
| [51] |
Hwang HW, Park CY, Goodarzi H, Fak JJ, Mele A, Moore MJ, Saito Y, Darnell RB . PAPERCLIP identifies microRNA targets and a role of CstF64/64tau in promoting non- canonical poly(A) site usage. Cell Rep, 2016,15(2):423-435.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.023 pmid: 27050522 |
| [52] |
Zhou ZJ, Qu J, He L, Zhu Y, Yang SZ, Zhang F, Guo T, Peng H, Chen P, Zhou Y . Stiff matrix instigates type I collagen biogenesis by mammalian cleavage factor I complex-mediated alternative polyadenylation. JCI Insight, 2020,5(3):e133972.
doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.133972 |
| [53] |
Fontana GA, Rigamonti A, Lenzken SC, Filosa G, Alvarez R, Calogero R, Bianchi ME, Barabino SML . Oxidative stress controls the choice of alternative last exons via a Brahma-BRCA1-CstF pathway. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017,45(2):902-914.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw780 pmid: 27591253 |
| [54] |
Brumbaugh J, Di Stefano B, Wang XY, Borkent M, Forouzmand E, Clowers KJ, Ji F, Schwarz BA, Kalocsay M, Elledge SJ, Chen Y, Sadreyev RI, Gygi SP, Hu G, Shi YS, Hochedlinger K. Nudt21 controls cell fate by connecting alternative polyadenylation to chromatin signaling. Cell, 2018,172(1-2): 106-120. e21.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.023 pmid: 29249356 |
| [55] |
Roy D, Bhanja Chowdhury J, Ghosh S . Polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) associates with intronic and exonic domains to squelch nuclear export of unspliced RNA. FEBS Lett, 2013,587(23):3802-3807.
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.10.005 |
| [56] |
Gawande B, Robida MD, Rahn A, Singh R . Drosophila Sex-lethal protein mediates polyadenylation switching in the female germline. EMBO J, 2006,25(6):1263-1272.
doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601022 pmid: 16511567 |
| [57] |
Jenal M, Elkon R, Loayza-Puch F, van Haaften G, Kühn U, Menzies FM, Oude Vrielink JAF, Bos AJ, Drost J, Rooijers K, Rubinsztein DC, Agami R,. The poly(A)- binding protein nuclear 1 suppresses alternative cleavage and polyadenylation sites. Cell, 2012,149(3):538-553.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.022 pmid: 22502866 |
| [58] | Mohibi S, Zhang J, Chen XB . PABPN1, a target of p63, modulates keratinocyte differentiation through regulation of p63α mRNA translation. J Invest Dermatol, 2020,11(140):2166-2177. |
| [59] |
Naganuma T, Nakagawa S, Tanigawa A, Sasaki YF, Goshima N, Hirose T . Alternative 3'-end processing of long noncoding RNA initiates construction of nuclear paraspeckles. EMBO J, 2012,31(20):4020-4034.
doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.251 |
| [60] |
Naganuma T, Hirose T . Paraspeckle formation during the biogenesis of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol, 2013,10(3):456-461.
doi: 10.4161/rna.23547 |
| [61] |
Ji XJ, Wan J, Vishnu M, Xing Y, Liebhaber SA. αCP Poly(C) binding proteins act as global regulators of alternative polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol, 2013,33(13):2560-2573.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.01380-12 |
| [62] |
Juge F, Audibert A, Benoit B, Simonelig M . Tissue- specific autoregulation of Drosophila suppressor of forked by alternative poly(A) site utilization leads to accumulation of the suppressor of forked protein in mitotically active cells. RNA, 2000,6(11):1529-1538.
doi: 10.1017/s1355838200001266 pmid: 11105753 |
| [63] |
Luo WT, Ji Z, Pan ZH, You B, Hoque M, Li WC, Gunderson SI, Tian B . The conserved intronic cleavage and polyadenylation site of CstF-77 gene imparts control of 3' end processing activity through feedback autoregulation and by U1 snRNP. Plos Genet, 2013,9(7):e1003613.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003613 pmid: 23874216 |
| [64] |
Yao CG, Biesinger J, Wan J, Weng LJ, Xing Y, Xie XH, Shi YS . Transcriptome-wide analyses of CstF64-RNA interactions in global regulation of mRNA alternative polyadenylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012,109(46):18773-18778.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211101109 pmid: 23112178 |
| [65] |
Yao CG, Choi EA, Weng LJ, Xie XH, Wan J, Xing Y, Moresco JJ, Tu PG, Yates JR, Shi YS . Overlapping and distinct functions of CstF64 and CstF64τ in mammalian mRNA 3' processing. RNA, 2013,19(12):1781-1790.
doi: 10.1261/rna.042317.113 |
| [66] |
Ceelie H, Spaargaren-van Riel CC, Bertina RM, Vos HL. G20210A is a functional mutation in the prothrombin gene; effect on protein levels and 3'-end formation. J Thromb Haemost, 2004,2(1):119-127.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2003.00493.x pmid: 14717975 |
| [67] | Shima T, Davis AG, Miyauchi S, Kochi Y, Johnson DT, Stoner SA, Junichiro Y, Miyamoto T, Zhou JH, Ball ED, Akashi K, Zhang DE . CPSF1 regulates AML1-ETO fusion gene polyadenylation and stability in t(8; 21) acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood, 2017,130(Suppl.1):2498. |
| [68] |
Haneklaus M, O'neil JD, Clark AR, Masters SL, O'neill LAJ. The RNA-binding protein Tristetraprolin (TTP) is a critical negative regulator of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Biol Chem, 2017,292(17):6869-6881.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.772947 pmid: 28302726 |
| [69] |
Masamha CP, Xia Z, Yang JX, Albrecht TR, Li M, Shyu AB, Li W, Wagner EJ . CFIm25 links alternative polyadenylation to glioblastoma tumour suppression. Nature, 2014,510(7505):412-416.
doi: 10.1038/nature13261 |
| [70] |
Melamed Z, López-Erauskin J, Baughn MW, Zhang OY, Drenner K, Sun Y, Freyermuth F, Mcmahon MA, Beccari MS, Artates JW, Ohkubo T, Rodriguez M, Lin NW, Wu DM, Bennett CF, Rigo F, Da Cruz S, Ravits J, Lagier- Tourenne C, Cleveland DW . Premature polyadenylation- mediated loss of stathmin-2 is a hallmark of TDP-43- dependent neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci, 2019,22(2):180-190.
doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0293-z pmid: 30643298 |
| [71] |
Dickson JR, Kruse C, Montagna DR, Finsen B, Wolfe MS . Alternative polyadenylation and miR-34 family members regulate tau expression. J Neurochem, 2013,127(6):739-749.
doi: 10.1111/jnc.12437 pmid: 24032460 |
| [72] |
Rhinn H, Qiang L, Yamashita T, Rhee D, Zolin A, Vanti W, Abeliovich A . Alternative α-synuclein transcript usage as a convergent mechanism in Parkinson's disease pathology. Nat Commun, 2012,3:1084.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2032 pmid: 23011138 |
| [73] |
Lee SH, Singh I, Tisdale S, Abdel-Wahab O, Leslie CS, Mayr C . Widespread intronic polyadenylation inactivates tumour suppressor genes in leukaemia. Nature, 2018,561(7721):127-131.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0465-8 pmid: 30150773 |
| [74] |
Singh I, Lee SH, Sperling AS, Samur MK, Tai YT, Fulciniti M, Munshi NC, Mayr C, Leslie CS . Widespread intronic polyadenylation diversifies immune cell transcriptomes. Nat Commun, 2018,9(1):1716.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04112-z pmid: 29712909 |
| [1] | Jian Shi,Yanming Li,Xiangdong Fang. The mechanism and clinical significance of long noncoding RNA-mediated gene expression via nuclear architecture [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(3): 189-199. |
| [2] | Chang Lu, Yinhua Huang. Progress in long non-coding RNAs in animals [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(11): 1054-1065. |
| [3] | Xiaoqing Huang,Dandan Li,Juan Wu. Long non-coding RNAs in plants [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(4): 344-359. |
| [4] | XIA Tian, XIAO Bing-Xiu, GUO Jun-Ming. Acting mechanisms and research methods of long noncoding RNAs [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(3): 269-280. |
| [5] | QIN Dan, XU Cun-Shuan. Characterization and identification of functional elements in non-coding DNA sequences [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(11): 1253-1264. |
| [6] | LUO Mao, ZHANG Zhi-Ming, GAO Jian, ZENG Xing, PAN Guang-Tang. The role of miR319 in plant development regulation [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(11): 1203-1211. |
| [7] | . Molecular mechanisms of regulation of estrogen receptor a expression level in breast cancer [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(3): 191-197. |
| [8] | DING Yan-Fei, WANG Guang-Yue, FU E-Ping, SHU Cheng. The role of miR398 in plant stress responses [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(2): 129-134. |
| [9] | YANG Dong, JIANG Ying, HE Fu-Chu. KAP-1, a scaffold protein in transcription regulation [J]. HEREDITAS, 2007, 29(2): 131-131―136. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||