Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 1117-1127.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-171
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances in epigenetic modification affecting anthocyanin synthesis
Yangjinghui Zhang( ), Peiyao Chang, Zishu Yang, Yuhang Xue, Xueqi Li, Yang Zhang(
), Peiyao Chang, Zishu Yang, Yuhang Xue, Xueqi Li, Yang Zhang( )
)
- College of Life Sciences, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040, China
-
Received:2022-05-24Revised:2022-08-24Online:2022-12-20Published:2022-09-26 -
Contact:Zhang Yang E-mail:2019213077@nefu.edu.cn;summerzhang@126.com -
Supported by:the National Key R&D Program of China(2018YFD1000400);the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province(LH2021C006)
Cite this article
Yangjinghui Zhang, Peiyao Chang, Zishu Yang, Yuhang Xue, Xueqi Li, Yang Zhang. Advances in epigenetic modification affecting anthocyanin synthesis[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1117-1127.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Ballaré CL. Stress under the sun: spotlight on ultraviolet-B responses. Plant Physiol, 2003, 132(4): 1725-1727.
pmid: 12913130 |
| [2] |
Petroni K, Tonelli C. Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Sci, 2011, 181(3): 219-229.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.05.009 pmid: 21763532 |
| [3] |
Hou JN, Lu DD, Mason AS, Li BQ, Xiao ML, An SF, Fu DH. Non-coding RNAs and transposable elements in plant genomes: emergence, regulatory mechanisms and roles in plant development and stress responses. Planta, 2019, 250(1): 23-40.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03166-7 pmid: 30993403 |
| [4] |
Zhao T, Zhan ZP, Jiang DH. Histone modifications and their regulatory roles in plant development and environmental memory. J Genet Genomics, 2019, 46(10): 467-476.
doi: S1673-8527(19)30154-7 pmid: 31813758 |
| [5] |
Jarillo JA, Piñeiro M, Cubas P, Martínez-Zapater JM. Chromatin remodeling in plant development. Int J Dev Biol, 2009, 53(8-10): 1581-1596.
doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072460jj pmid: 19247973 |
| [6] |
Iyer VR. Nucleosome positioning: bringing order to the eukaryotic genome. Trends Cell Biol, 2012, 22(5): 250-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.02.004 pmid: 22421062 |
| [7] | Thapa B, Shrestha A. Epigenetic mechanisms and its role in plant growth and development. J Plant Biochem Physiol, 2020, 8(6): 255. |
| [8] |
Holton TA, Cornish EC. Genetics and biochemistry of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell, 1995, 7(7): 1071-1083.
doi: 10.2307/3870058 |
| [9] |
Mol J, Jenkins G, Schäfer E, Weiss D, Walbot V. Signal perception, transduction, and gene expression involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis. Crit Rev Plant Sci, 1996, 15(5-6): 525-557.
doi: 10.1080/07352689609382369 |
| [10] |
Gonzalez A, Zhao MZ, Leavitt JM, Lloyd AM. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J, 2008, 53(5): 814-827.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03373.x |
| [11] |
Shi MZ, Xie DY. Biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of anthocyanins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Recent Pat Biotechnol, 2014, 8(1): 47-60.
doi: 10.2174/1872208307666131218123538 |
| [12] |
Xu WJ, Dubos C, Lepiniec L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci, 2015, 20(3): 176-185.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.12.001 pmid: 25577424 |
| [13] |
Wang QB, Wang YP, Sun HH, Sun L, Zhang L. Transposon- induced methylation of the RsMYB1 promoter disturbs anthocyanin accumulation in red- fleshed radish. J Exp Bot, 2020, 71(9): 2537-2550.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa010 |
| [14] |
Jia HR, Jia HF, Lu SW, Zhang ZB, Su ZW, Sadeghnezhad E, Li T, Xiao X, Wang MT, Pervaiz T, Dong TY, Fang JG. DNA and histone methylation regulates different types of fruit ripening by transcriptome and proteome analyses. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(11): 3541-3556.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06391 |
| [15] |
Maier A, Schrader A, Kokkelink L, Falke C, Welter B, Iniesto E, Rubio V, Uhrig JF, Hülskamp M, Hoecker U. Light and the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1/SPA control the protein stability of the MYB transcription factors PAP1 and PAP2 involved in anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2013, 74(4): 638-651.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12153 |
| [16] | Liu BD, Wang HL. Sensitive analysis of DNA methylation and demethylation intermediates for eukaryotes. Chin Bull Life Sci, 2018, 30(4): 374-382. |
| [17] |
Zhang HM, Lang ZB, Zhu JK. Dynamics and function of DNA methylation in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19(8): 489-506.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0016-z |
| [18] |
Vanyushin BF, Ashapkin VV. DNA methylation in higher plants: Past, present and future. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2011, 1809(8): 360-368.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.04.006 pmid: 21549230 |
| [19] |
Jullien PE, Susaki D, Yelagandula R, Higashiyama T, Berger F. DNA methylation dynamics during sexual reproduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol, 2012, 22(19): 1825-1830.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.061 pmid: 22940470 |
| [20] |
Matzke MA, Mosher RA. RNA-directed DNA methylation: an epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity. Nat Rev Genet, 2014, 15(6): 394-408.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3683 pmid: 24805120 |
| [21] |
Tirnaz S, Batley J. DNA Methylation: toward crop disease resistance improvement. Trends Plant Sci, 2019, 24(12): 1137-1150.
doi: S1360-1385(19)30220-1 pmid: 31604599 |
| [22] |
Liu RE, Lang ZB. The mechanism and function of active DNA demethylation in plants. J Integr Plant Biol, 2020, 62(1): 148-159.
doi: 10.1111/jipb.12879 |
| [23] |
Lang ZB, Lei MG, Wang XG, Tang K, Miki D, Zhang HM, Mangrauthia SK, Liu WS, Nie WF, Ma GJ, Yan J, Duan CG, Hsu CC, Wang CL, Tao WA. Gong ZZ, Zhu JK. The Methyl-CpG-binding protein MBD7 facilitates active DNA demethylation to limit DNA hyper-methylation and transcriptional gene silencing. Mol Cell, 2015, 57(6): 971- 983.
doi: S1097-2765(15)00010-6 pmid: 25684209 |
| [24] |
Korotko U, Chwiałkowska K, Sańko-Sawczenko I, Kwasniewski M. DNA demethylation in response to heat stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4): 1555.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22041555 |
| [25] |
Deng J, Fu ZY, Chen S, Damaris RN, Wang K, Li TT, Yang PF. Proteomic and epigenetic analyses of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) petals between red and white cultivars. Plant Cell Physiol, 2015, 56(8): 1546-1555.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv077 pmid: 26019267 |
| [26] |
Wang ZG, Meng D, Wang AD, Li TL, Jiang SL, Cong PH, Li TZ. The methylation of the PcMYB10 promoter is associated with green-skinned sport in max red bartlett pear. Plant Physiol, 2013, 162(2): 885-896.
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.214700 |
| [27] | Li WF.Molecular mechanism of fruit skin coloration in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) cv. ‘Red Delicious’ Bud Sport Mutants [Dissertation]. Gansu Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 李文芳.‘元帅’系苹果芽变品种着色分子机理研究[学位论文]. 甘肃农业大学, 2020. | |
| [28] |
Bai SL, Tuan PA, Saito T, Honda C, Hatsuyama Y, Ito A, Moriguchi T. Epigenetic regulation of MdMYB1 is associated with paper bagging-induced red pigmentation of apples. Planta, 2016, 244(3): 573-586.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2524-4 pmid: 27105885 |
| [29] |
Over RS, Michaels SD. Open and closed: the roles of linker histones in plants and animals. Mol Plant, 2014, 7(3): 481-491.
doi: 10.1093/mp/sst164 pmid: 24270504 |
| [30] |
Jenuwein T. Re-SET-ting heterochromatin by histone methyltransferases. Trends Cell Biol, 2001, 11(6): 266-273.
pmid: 11356363 |
| [31] |
Biswas S, Rao CM. Epigenetic tools (The Writers, The Readers and The Erasers) and their implications in cancer therapy. Eur J Pharmacol, 2018, 837: 8-24.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.08.021 |
| [32] |
Black JC, Van Rechem C, Whetstine JR. Histone lysine methylation dynamics: establishment, regulation, and biological impact. Mol Cell, 2012, 48(4): 491-507.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.006 pmid: 23200123 |
| [33] |
Hu HM, Du JM. Structure and mechanism of histone methylation dynamics in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2022, 67: 102211.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102211 |
| [34] | Xiao J, Lee US, Wagne D.Tug of war: adding and removing histone lysine methylation in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2016, 34: 41-53. |
| [35] |
Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell, 2007, 128(4): 693-705.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.005 pmid: 17320507 |
| [36] |
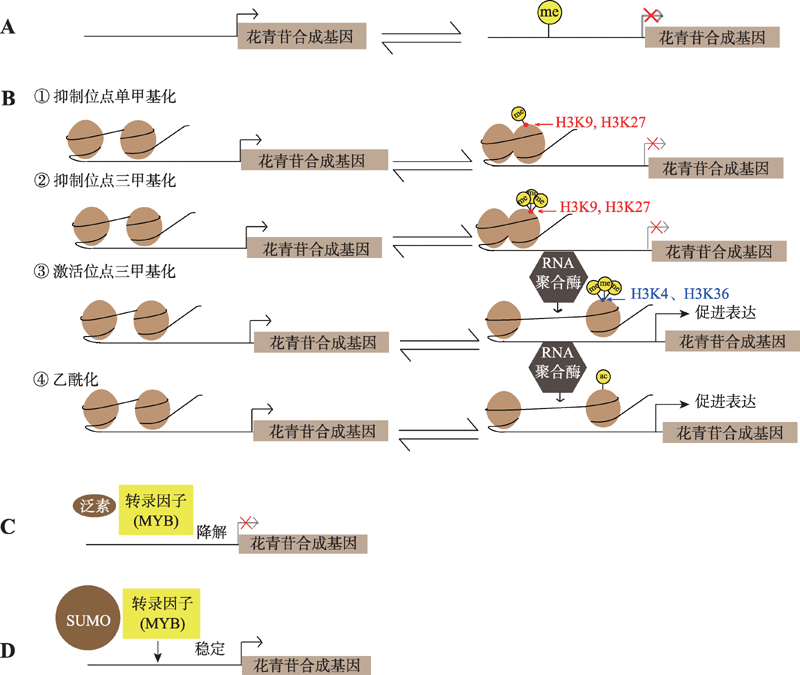
Cai HY, Zhang M, Chai MN, He Q, Huang XY, Zhao LH, Qin Y.Epigenetic regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by an antagonistic interaction between H2A.Z and H3K4me3. New Phytol, 2019, 221(1): 295-308.
doi: 10.1111/nph.15306 pmid: 29959895 |
| [37] |
Fan D, Wang XQ, Tang XF, Ye X, Ren S, Wang DH, Luo KM. Histone H3K9 demethylase JMJ25 epigenetically modulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in poplar. Plant J, 2018, 96(6): 1121-1136.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.14092 |
| [38] |
Nguyen NH, Jeong CY, Kang GH, Yoo SD, Hong SW, Lee H. MYBD employed by HY 5 increases anthocyanin accumulation via repression of MYBL2 in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2015, 84(6): 1192-1205.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13077 |
| [39] |
Zheng T, Tan WR, Yang H, Zhang LE, Li TT, Liu BH, Zhang DW, Lin HH. Regulation of anthocyanin accumulation via MYB75/HAT1/TPL-mediated transcriptional repression. PLoS Genet, 2019, 15(3): e1007993.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007993 |
| [40] |
An JP, Wang XF, Zhang XW, Xu HF, Bi SQ, You CX, Hao YJ. An apple MYB transcription factor regulates cold tolerance and anthocyanin accumulation and undergoes MIEL1- mediated degradation. Plant Biotechnol J, 2019, 18(2): 337-353.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13201 |
| [41] |
Li KT, Zhang J, Kang YH, Chen MC, Song TT, Geng H, Tian J, Yao YC. McMYB10 modulates the expression of a Ubiquitin Ligase, McCOP1 during leaf coloration in crabapple. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9: 704.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00704 |
| [42] |
Zhou LJ, Li YY, Zhang RF, Zhang CL, Xie XB, Zhao C, Hao YJ. The small ubiquitin-like modifier E3 ligase MdSIZ1 promotes anthocyanin accumulation by sumoylating MdMYB1 under low-temperature conditions in apple. Plant Cell Environ, 2017, 40(10): 2068-2080.
doi: 10.1111/pce.12978 |
| [43] |
Zheng T, Li YL, Lei W, Qiao K, Liu BH, Zhang DW, Lin HH.SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 stabilizes MYB75 to regulate anthocyanin accumulation under high light conditions in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci, 2020, 292: 110355.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110355 |
| [44] |
Jiang FG, Doudna JA. CRISPR-Cas9 structures and mechanisms. Annu Rev Biophys, 2017, 46: 505-529.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-062215-010822 pmid: 28375731 |
| [45] |
Qi LS, Larson MH, Gilbert LA, Doudna JA, Weissman JS, Arkin AP, Lim WA. Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA- guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Cell, 2013, 152(5): 1173-1183.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.022 |
| [46] |
Gilbert LA, Larson MH, Morsut L, Liu ZR, Brar GA, Torres SE, Stern-Ginossar N, Brandman O, Whitehead EH, Doudna JA, Lim WA, Weissman JS, Qi LS. CRISPR- mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. Cell, 2013, 154(2): 442-451.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.044 pmid: 23849981 |
| [47] |
Maeder ML, Linder SJ, Cascio VM, Fu YF, Ho QH, Joung JK. CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes. Nat Methods, 2013, 10(10): 977-979.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2598 pmid: 23892898 |
| [48] | Gallego-Bartolomé J, Gardiner J, Liu WL, Papikian A, Ghoshal B, Kuo HY, Zhao JMC, Segal DJ, Jacobsen SE. Targeted DNA demethylation of the Arabidopsis genome using the human TET1 catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(9): E2125-E2134. |
| [49] |
Li JW, Yang DL, Huang H, Zhang GP, He L, Pang J, Lozano-Durán R, Lang ZB, Zhu JK. Epigenetic memory marks determine epiallele stability at loci targeted by de novo DNA methylation. Nat Plants, 2020, 6(6): 661-674.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0671-x pmid: 32514141 |
| [50] |
Lu AR, Wang JM, Sun WH, Huang WR, Cai ZM, Zhao GP, Wang J. Reprogrammable CRISPR/dCas9-based recruitment of DNMT1 for site-specific DNA demethylation and gene regulation. Cell Discov, 2019, 5: 22.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-019-0090-1 pmid: 31016028 |
| [51] | Ghoshal B, Gardiner J. CRISPR-dCas9-based targeted manipulation of DNA methylation in plants. CRISPR- Cas Methods, 2021, 57-71. |
| [52] |
Paixão JFR, Gillet FX, Ribeiro TP, Bournaud C, Lourenço- Tessutti IT, Noriega DD, de Melo BP, de Almeida-Engler J, Grossi-de-Sa MF. Improved drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis by CRISPR/dCas9 fusion with a Histone AcetylTransferase. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 8080.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44571-y |
| [53] |
Chen XT, Wei MY, Liu XW, Song S, Wang L, Yang XK, Song YL. Construction and validation of the CRISPR/ dCas9-EZH2 system for targeted H3K27Me3 modification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 511(2): 246-252.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.011 |
| [54] |
Zhao WY, Xu Y, Wang YF, Gao D, King J, Xu YJ, Liang FS. Investigating crosstalk between H3K27 acetylation and H3K4 trimethylation in CRISPR/dCas-based epigenome editing and gene activation. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 15912.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95398-5 pmid: 34354157 |
| [55] |
Selma S, Sanmartín N, Espinosa-Ruiz A, Gianoglio S, Lopez-Gresa MP, Vázquez-Vilar M, Flors V, Granell A, Orzaez D. Custom-made design of metabolite composition in N. benthamiana leaves using CRISPR activators. Plant Biotechnol J, 2022, 20(8): 1578-1590.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13834 pmid: 35514036 |
| [56] |
Lowder LG, Paul JW, Qi YP. Multiplexed transcriptional activation or repression in plants using CRISPR- dCas9-based systems. Methods Mol Biol, 2017, 1629: 167-184.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7125-1_12 pmid: 28623586 |
| [57] |
Park JJ, Dempewolf E, Zhang WZ, Wang ZY. RNA-guided transcriptional activation via CRISPR/dCas9 mimics overexpression phenotypes in Arabidopsis. PLoS One, 2017, 12(6): e0179410.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179410 |
| [58] |
Ren C, Li HY, Liu YF, Li SH, Liang ZC. Highly efficient activation of endogenous gene in grape using CRISPR/ dCas9-based transcriptional activators. Hortic Res, 2022, 9: uhab037.
doi: 10.1093/hr/uhab037 |
| [59] |
Kribelbauer JF, Lu XJ, Rohs R, Mann RS, Bussemaker HJ. Toward a mechanistic understanding of DNA methylation readout by transcription factors. J Mol Biol, 2019, 432(6): 1801-1815.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.10.021 |
| [60] |
O'Malley RC, Huang SSC, Song L, Lewsey MG, Bartlett A, Nery JR, Galli M, Gallavotti A, Ecker JR. Cistrome and epicistrome features shape the regulatory DNA landscape. Cell, 2016, 165(5): 1280-1292.
doi: S0092-8674(16)30481-0 pmid: 27203113 |
| [61] | Karlson CKS, Mohd-Noor SN, Nolte N, Tan BC. CRISPR/dCas9-based systems: mechanisms and applications in plant sciences. Plants (Basel), 2021, 10(10): 2055. |
| [62] | Cui CJ, Li JM, Chen YY, Zhang RZ, Zhu QL.Isolation and expression analysis of an anthocyanin transportrelated NtAN9 gene from Nicotiana tabacum. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin, 2016, 36(7): 1337-1342. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||