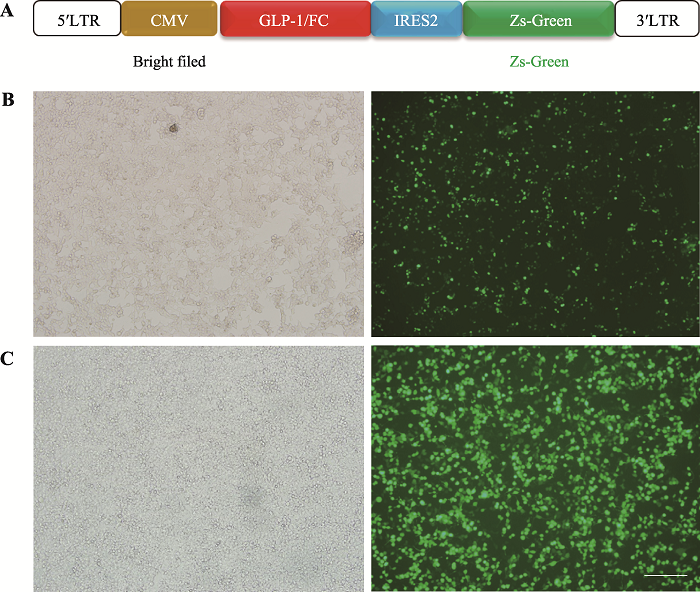
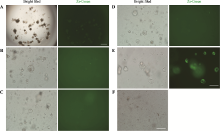
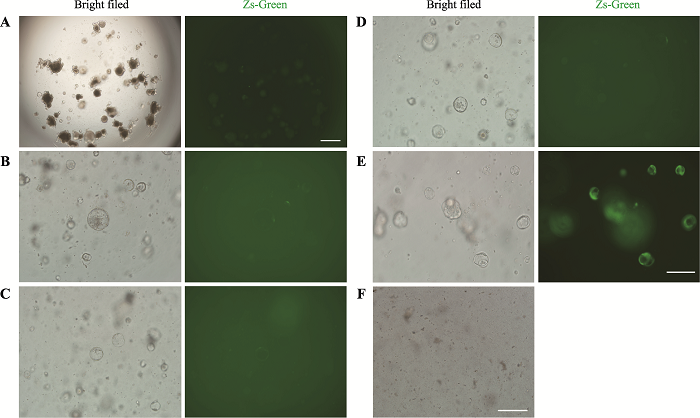
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (7): 694-703.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-423
• Technique and Method • Previous Articles Next Articles
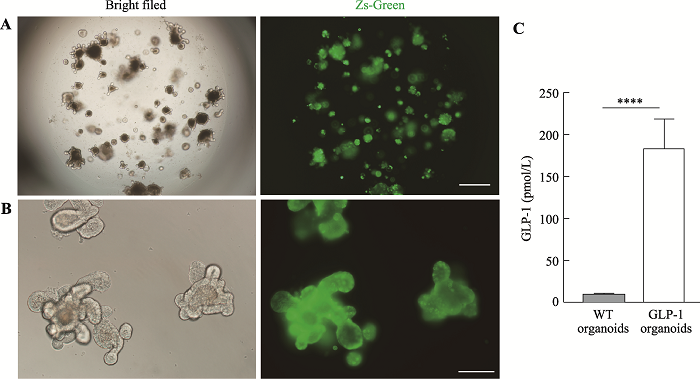
A method for constructing GLP-1 overexpression intestinal organoids
Zhiyang Zeng1( ), Jiawei Lu1, Xiya Cao1, Xinyue Wang2,3, Dali Li1(
), Jiawei Lu1, Xiya Cao1, Xinyue Wang2,3, Dali Li1( )
)
- 1. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, School of Life Sciences, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
2. School of Medicine, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan 232000, China
3. Department of Gastroenterology, South Campus of Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 201499, China
-
Received:2021-03-01Revised:2021-04-14Online:2021-07-20Published:2021-07-20 -
Contact:Li Dali E-mail:52161300029@stu.ecnu.edu.cn;dlli@bio.ecnu.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Key R&D Program of China No(2019YFA0110802)
Cite this article
Zhiyang Zeng, Jiawei Lu, Xiya Cao, Xinyue Wang, Dali Li. A method for constructing GLP-1 overexpression intestinal organoids[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(7): 694-703.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. The glucagon-like peptides. Endocr Rev, 1999, 20(6):876-913.
pmid: 10605628 |
| [2] |
Nauck MA, Homberger E, Siegel EG, Allen RC, Eaton RP, Ebert R, Creutzfeldt W. Incretin effects of increasing glucose loads in man calculated from venous insulin and C-peptide responses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1986, 63(2):492-498.
doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-2-492 |
| [3] |
Perley MJ, Kipnis DM. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest, 1967, 46(12):1954-1962.
pmid: 6074000 |
| [4] |
Meier JJ, Nauck MA, Kranz D, Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Gaeckler D, Schmidt WE, Gallwitz B. Secretion, degradation, and elimination of glucagon-like peptide 1 and gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with chronic renal insufficiency and healthy control subjects. Diabetes, 2004, 53(3):654-662.
doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.3.654 |
| [5] | Hui HX, Farilla L, Merkel P, Perfetti R. The short half-life of glucagon-like peptide-1 in plasma does not reflect its long-lasting beneficial effects. Eur J Endocrinol, 2002, 146(6):863-869. |
| [6] |
Kumar M, Hunag Y, Glinka Y, Prud'homme GJ, Wang Q. Gene therapy of diabetes using a novel GLP-1/IgG1-Fc fusion construct normalizes glucose levels in db/db mice. Gene Ther, 2007, 14(2):162-172.
pmid: 16943856 |
| [7] |
Soltani N, Kumar M, Glinka Y, Prud'homme GJ, Wang Q,. In vivo expression of GLP-1/IgG-Fc fusion protein enhances beta-cell mass and protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Gene Ther, 2007, 14(12):981-988.
pmid: 17410180 |
| [8] |
Shao JW, Xue S, Yu GL, Yu YH, Yang XP, Bai Y, Zhu SC, Yang LF, Yin JL, Wang YD, Liao SY, Guo SW, Xie MQ, Fussenegger M, Ye HF. Smartphone-controlled optogenetically engineered cells enable semiautomatic glucose homeostasis in diabetic mice. Sci Transl Med , 2017, 9(387): eaal2298.
doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal2298 |
| [9] |
Ye HF, Daoud-El Baba M, Peng RW, Fussenegger M. A synthetic optogenetic transcription device enhances blood- glucose homeostasis in mice. Science, 2011, 332(6037):1565-1568.
doi: 10.1126/science.1203535 |
| [10] |
Clevers H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell, 2016, 165(7):1586-1597.
doi: S0092-8674(16)30729-2 pmid: 27315476 |
| [11] |
Sato T, Stange DE, Ferrante M, Vries RG, Van Es JH, Van den Brink S, Van Houdt WJ, Pronk A, Van Gorp J, Siersema PD, Clevers H. Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett's epithelium. Gastroenterology, 2011, 141(5):1762-1772.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.050 |
| [12] |
Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, van de Wetering M, Barker N, Stange DE, van Es JH, Abo A, Kujala P, Peters PJ, Clevers H. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature , 2009, 459(7244):262-265.
doi: 10.1038/nature07935 |
| [13] |
Petersen N, Reimann F, Bartfeld S, Farin HF, Ringnalda FC, Vries RGJ, van den Brink S, Clevers H, Gribble FM, de Koning EJP. Generation of L cells in mouse and human small intestine organoids. Diabetes, 2014, 63(2):410-420.
doi: 10.2337/db13-0991 pmid: 24130334 |
| [14] |
Goldspink DA, Lu VB, Miedzybrodzka EL, Smith CA, Foreman RE, Billing LJ, Kay RG, Reimann F, Gribble FM. Labeling and characterization of human GLP-1-secreting L-cells in primary ileal organoid culture. Cell Rep, 2020, 31(13):107833.
doi: S2211-1247(20)30814-7 pmid: 32610134 |
| [15] |
Lund ML, Sorrentino G, Egerod KL, Kroone C, Mortensen B, Knop FK, Reimann F, Gribble FM, Drucker DJ, de Koning EJP, Schoonjans K, Bäckhed F, Schwartz TW, Petersen N. L-Cell differentiation is induced by bile acids through GPBAR1 and paracrine GLP-1 and serotonin signaling. Diabetes, 2020, 69(4):614-623.
doi: 10.2337/db19-0764 |
| [16] |
Goldspink DA, Lu VB, Billing LJ, Larraufie P, Tolhurst G, Gribble FM, Reimann F. Mechanistic insights into the detection of free fatty and bile acids by ileal glucagon-like peptide-1 secreting cells. Mol Metab, 2018, 7:90-101.
doi: S2212-8778(17)30750-0 pmid: 29167062 |
| [17] |
Yui S, Nakamura T, Sato T, Nemoto Y, Mizutani T, Zheng X, Ichinose S, Nagaishi T, Okamoto R, Tsuchiya K, Clevers H, Watanabe M. Functional engraftment of colon epithelium expanded in vitro from a single adult Lgr5 + stem cell. Nat Med, 2012, 18(4):618-623.
doi: 10.1038/nm.2695 |
| [18] |
Fukuda M, Mizutani T, Mochizuki W, Matsumoto T, Nozaki K, Sakamaki Y, Ichinose S, Okada Y, Tanaka T, Watanabe M, Nakamura T. Small intestinal stem cell identity is maintained with functional Paneth cells in heterotopically grafted epithelium onto the colon. Genes Dev, 2014, 28(16):1752-1757.
doi: 10.1101/gad.245233.114 |
| [19] |
O'Rourke KP, Loizou E, Livshits G, Schatoff EM, Baslan T, Manchado E, Simon J, Romesser PB, Leach B, Han T, Pauli C, Beltran H, Rubin MA, Dow LE, Lowe SW. Transplantation of engineered organoids enables rapid generation of metastatic mouse models of colorectal cancer. Nat Biotechnol, 2017, 35(6):577-582.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3837 pmid: 28459450 |
| [20] | Koo BK, Stange DE, Sato T, Karthaus W, Farin HF, Huch M, van Es JH, Clevers H. Controlled gene expression in primary Lgr5 organoid cultures. Nat Methods, 2011, 9(1):81-83. |
| [21] | Andersson-Rolf A, Fink J, Mustata RC, Koo BK. A video protocol of retroviral infection in primary intestinal organoid culture. J Vis Exp, 2014, (90):e51765. |
| [22] |
Jang HJ, Kokrashvili Z, Theodorakis MJ, Carlson OD, Kim BJ, Zhou J, Kim HH, Xu XR, Chan SL, Juhaszova M, Bernier M, Mosinger B, Margolskee RF, Egan JM. Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(38):15069-15074.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706890104 |
| [23] |
Gorboulev V, Schürmann A, Vallon V, Kipp H, Jaschke A, Klessen D, Friedrich A, Scherneck S, Rieg T, Cunard R, Veyhl-Wichmann M, Srinivasan A, Balen D, Breljak D, Rexhepaj R, Parker HE, Gribble FM, Reimann F, Lang F, Wiese S, Sabolic I, Sendtner M, Koepsell H. Na(+)-D- glucose cotransporter SGLT1 is pivotal for intestinal glucose absorption and glucose-dependent incretin secretion. Diabetes, 2012, 61(1):187-196.
doi: 10.2337/db11-1029 pmid: 22124465 |
| [24] |
Reimann F, Gribble FM. Glucose-sensing in glucagon-like peptide-1-secreting cells. Diabetes, 2002, 51(9):2757-2763.
pmid: 12196469 |
| [25] |
Parker HE, Adriaenssens A, Rogers G, Richards P, Koepsell H, Reimann F, Gribble FM. Predominant role of active versus facilitative glucose transport for glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. Diabetologia, 2012, 55(9):2445-2455.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2585-2 pmid: 22638549 |
| [26] |
Sonne DP, Rehfeld JF, Holst JJ, Vilsboll T, Knop FK. Postprandial gallbladder emptying in patients with type 2 diabetes: potential implications for bile-induced secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1. Eur J Endocrinol, 2014, 171(4):407-419.
doi: 10.1530/EJE-14-0309 |
| [27] |
Baggio LL, Drucker DJ. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology, 2007, 132(6):2131-2157.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.054 |
| [28] |
Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, Thompson VP, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, Chan JC, Choi J, Gustavson SM, Iqbal N, Maggioni AP, Marso SP, Öhman P, Pagidipati NJ, Poulter N, Ramachandran A, Zinman B, Hernandez AF, Group ES. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(13):1228-1239.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1612917 |
| [29] |
Wadden TA, Hollander P, Klein S, Niswender K, Woo V, Hale PM, Aronne L, Investigators NN. weight maintenance and additional weight loss with liraglutide after low-calorie- diet-induced weight loss: the scale maintenance randomized study. Int J Obes (Lond), 2013, 37(11):1443-1451.
doi: 10.1038/ijo.2013.120 |
| [30] | Nauck MA, Niedereichholz U, Ettler R, Holst JJ, Orskov C, Ritzel R, Schmiegel WH. Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibition of gastric emptying outweighs its insulinotropic effects in healthy humans. Am J Physiol, 1997, 273(5):E981-E988. |
| [31] |
Müller TD, Finan B, Bloom SR, D'Alessio D, Drucker DJ, Flatt PR, Fritsche A, Gribble F, Grill HJ, Habener JF, Holst JJ, Langhans W, Meier JJ, Nauck MA, Perez-Tilve D, Pocai A, Reimann F, Sandoval DA, Schwartz TW, Seeley RJ, Stemmer K, Tang-Christensen M, Woods SC, DiMarchi RD, Tschöp MH. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol Metab, 2019, 30:72-130.
doi: S2212-8778(19)30913-5 pmid: 31767182 |
| [32] |
Parsons GB, Souza DW, Wu H, Yu D, Wadsworth SG, Gregory RJ, Armentano D. Ectopic expression of glucagon- like peptide 1 for gene therapy of type II diabetes. Gene Ther, 2007, 14(1):38-48.
pmid: 16929351 |
| [1] | Chengan Lv, Ruoran Wang, Zhuo-Xian Meng. Molecular mechanism of islet β-cell functional alternations during type 2 diabetes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 840-852. |
| [2] | Lan Cao, Zhiqiang Li, Yongyong Shi, Yun Liu. Telomere length and type 2 diabetes: Mendelian randomization study and polygenic risk score analysis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(9): 882-888. |
| [3] | Yuzhuo Wang, Yiming Zhang, Xiaolian Dong, Xuecai Wang, Jianfu Zhu, Na Wang, Feng Jiang, Yue Chen, Qingwu Jiang, Chaowei Fu. Modification effects of T2DM-susceptible SNPs on the reduction of blood glucose in response to lifestyle interventions [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(5): 483-492. |
| [4] | Xian Gong, Chao Zhang, Aisa Yiliyasi, Ying Shi, Xuewei Yang, Aosiman Nuersimanguli, Yaqun Guan, Shuhua Xu. A comparative analysis of genetic diversity of candidate genes associated with type 2 diabetes in worldwide populations [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016, 38(6): 543-559. |
| [5] | Ri Wu,Chao Ma,Xiaodan Li,Huikun Duan,Yanli Ji,Yu Wang,Pingzhe Jiang,Haisong Wang,Peipei Tu,Miao Li,Ganggang Ni,Baicheng Ma,Minggang Li. Construction of yeast strains expressing long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and their therapeutic effects on type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse model [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(2): 183-191. |
| [6] | TANG Lin-Lin LIU Qiong BU Shi-Zhong XU Lei-Ting WANG Qin-Wen MAI Yi-Feng DUAN Shi-Wei. The effect of environmental factors and DNA methylation on type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(10): 1143-1152. |
| [7] | PU Lian-Mei, NAN Nan, YANG Ze, JIN Ze-Ning. Association between SUMO4 polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(3): 315-325. |
| [8] | TANG Xiao-Li, DENG Li-Bin, LI Gui-Lin, LIU Shuang-Mei, LIN Jia-Ri, XIE Jin-Yan, LIU Jun, KONG Fan-Jun, LIANG Shang-Dong. Analysis of gene expression profile of peripheral ganglia in early stage type Ⅱ diabetic rats [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(2): 198-207. |
| [9] | WANG Min, BANG Chan, JUE E-Chi, HUANG Jing-Yang. Association and meta-analysis of ENPP1 K121Q with type 2 diabetes in Han Chinese [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(8): 808-816. |
| [10] | CHEN Fang-Jian, YU Hong, FAN Fan, LU Jian-Xin. Mitochondrial D-Loop gene polymorphisms in the patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. HEREDITAS, 2009, 31(3): 265-272. |
| [11] | SU Yan, PENG Shu-Bin, LI Zhi-Qiong, HUANG Qing-Yang. Association study between PPARGC1A Thr394Thr/ Gly482Ser polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes [J]. HEREDITAS, 2008, 30(3): 304-308. |
| [12] | DU Ji-Kun, HUANG Qing-Yang, LI Shou-Hua, XIONG Guo-Mei. Association of HindⅢ RFLP in lipoprotein lipase gene with type 2 diabetes [J]. HEREDITAS, 2007, 29(8): 929-929―933. |
| [13] | . Study on a new point mutation of nt7444 G→A of mitochondrial DNA in a type 2 diabetes mellitus family [J]. HEREDITAS, 2007, 29(4): 433-437. |
| [14] | DU Ji-Kun, HUANG Qing-Yang. Research progress of lipoprotein lipase gene [J]. HEREDITAS, 2007, 29(1): 8-16. |
| [15] | JI Sen-Lin, HUANG Qing-Yang. PPARγ Variant and Complex Diseases [J]. HEREDITAS, 2006, 28(8): 993-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||