Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 513-532.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-252
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Progress on the regulation of muscle regeneration by microRNA
Taizeng Zhou1,2,3( ), Qiuyang Chen1,2,3, Yiting Yang1,2,3, Mailin Gan1,2,3, Li Zhu1,2,3, Linyuan Shen1,2,3(
), Qiuyang Chen1,2,3, Yiting Yang1,2,3, Mailin Gan1,2,3, Li Zhu1,2,3, Linyuan Shen1,2,3( )
)
- 1. National Key Laboratory of Pig and Poultry Seed Industry, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu 611130, China
2. Sichuan Provincial Key Laboratory of Exploration and Innovative Utilization of Livestock and Poultry Genetic Resources, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu 611130, China
3. Key Laboratory of Livestock and Poultry Biomics, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, College of Animal Science and Technology, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu 611130, China
-
Received:2024-09-02Revised:2024-12-08Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-01-10 -
Contact:Linyuan Shen E-mail:zhoutaizeng666666@163.com;shenlinyuan@sicau.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program(2021YFD1200801);Sichuan Science and Technology Program(2021YFYZ0030);Sichuan Science and Technology Program(2021ZDZX0008);Program for Pig Industry Technology System Innovation Team of Sichuan Province(SCCXTD-2024-8);China Agriculture Research System(CARS-35);Central Government Guides the Local Science and Technology Development Fund Program(2023ZYDF056)
Cite this article
Taizeng Zhou, Qiuyang Chen, Yiting Yang, Mailin Gan, Li Zhu, Linyuan Shen. Progress on the regulation of muscle regeneration by microRNA[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(5): 513-532.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
miRNA regulating the quiescent state of satellite cells"
| miRNA | miRNA表达趋势 | 靶基因或调控对象 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-708 | 上调 | TNS3 | 拮抗细胞迁移来调节卫星静止和自我更新 | [ |
| miR-31 | 下调 | IL-34 | 促进了增殖细胞的不对称细胞命运分离,导致卫星细胞重新进入静止状态 | [ |
| miR-489 | 上调 | DEK | 作为卫星细胞静止的调节剂 | [ |
| miR-31 | 上调 | Myf5 | 抑制Myf5在静止卫星细胞中积累 | [ |
| miR-140 | 上调 | Hey1、Notch1 | 抑制肌生成并维持肌肉卫星细胞静止 | [ |
| miR-378 | 上调 | IGF1R | 延迟卫星细胞活化 | [ |
Table 2
miRNA regulating myoblast proliferation"
| miRNA | miRNA表达趋势 | 靶基因或调控对象 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1、miR-29、miR-206、miR-27b、miR-128a | 上调 | Pax3 | 降低骨骼肌卫星细胞的增殖能力 | [ |
| miR-1、miR-106b、miR-133、miR-204、miR-206、miR-499 | 下调 | Pax7 | 促进成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-208b | 上调 | CDKN1A | 促进原代成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-33a | 上调 | CCND1 | 抑制成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-27b-3p | 上调 | MSTN | 促进成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-22 | 上调 | TGFBR1 | 抑制C2C12成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-452 | 上调 | ANGPT1 | 促进C2C12成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-127-3p | 上调 | SEPT7 | 促进成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-365 | 上调 | IGF-I | 抑制成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-664-5p | 上调 | SRF | 促进成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-499 | 上调 | TGFβ-R1 | 抑制小鼠成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-543 | 上调 | KLF6 | 抑制小鼠成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-16-5p | 上调 | SESN1 | 通过p53信号通路,抑制成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-130b | 上调 | Sp1 | 抑制成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-146b-3p | 上调 | AKT1、MDFIC | 抑制PI3K/AKT通路,抑制鸡成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-92b-3p | 上调 | SGK3 | 抑制C2C12细胞增殖、迁移 | [ |
| miR-152 | 下调 | E2F3 | 抑制成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-325-3p、miR-429-3p、miR-141-3p、miR-320-3p | 上调 | CFL2 | 增强细胞增殖和细胞周期进程 | [ |
| miR-103-3p、miR-302a、miR-665-3p | 上调 | TWF1 | 增强细胞增殖和细胞周期进程 | [ |
| miR-495-3p | 下调 | CDH2 | 抑制C2C12增殖 | [ |
| miR-100-5p | 上调 | TRIB2 | 促进成肌细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-193b-3p | 上调 | IGF2BP1 | 促进山羊骨骼肌卫星细胞增殖 | [ |
| miR-222-3p、miR-487b-3p | 下调 | IRS1 | 抑制PI3K/AKT通路来抑制成肌细胞的增殖 | [ |
| miR-24-3p | 上调 | CAMK2B | 促进牛肌肉原代细胞和C2C12细胞增殖 | [ |
Table 3
miRNA regulating the differentiation of myoblasts"
| miRNA | miRNA表达趋势 | 靶基因或调控对象 | 功能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1、miR-206、miR-106b | 上调 | Pax7 | 促进肌源性分化 | [ |
| miR-16-5p | 下调 | SESN1 | 促进成肌细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-152 | 上调 | E2F3 | 促进成肌细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-495-3p | 上调 | CDH2 | 促进C2C12成肌分化 | [ |
| miR-100-5p | 下调 | TRIB2 | 失活mTOR/S6K通路来抑制成肌细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-487b-3p | 上调 | IRS1 | 通过PI3K/AKT通路抑制C2C12的分化 | [ |
| miR-10b-5p | 上调 | NFAT5 | 抑制C2C12细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-424-5p | 下调 | HSP90AA1、Ezh1 | 抑制骨骼肌发育中的细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-9-5p | 上调 | IGF2BP3 | 抑制肌肉卫星细胞的分化 | [ |
| miR-148a-3p | 上调 | Meox2 | 激活PI3K/AKT通路来促进鸡成肌细胞的分化 | [ |
| miR-483 | 下调 | IGF1 | 下调PI3/AKT信号通路关键蛋白的表达,抑制成肌细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-128 | 下调 | SYNDECAN-4 | 抑制卫星细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-24 | 下调 | GLYPICAN-1 | 抑制卫星细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-885 | 下调 | MyoD1 | 抑制成肌细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-92a、miR-130b | 下调 | Sp1 | 诱导MyoD的表达,抑制成肌细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-22-3p、miR-29c、 miR-378a-3p、miR-206 | 上调 | HDAC4 | 调节骨骼肌生长并促进成肌细胞的分化 | [ |
| miR-214 | 上调 | TRMT61A | 促进鸡成肌细胞分化 | [ |
| miR-24-3p | 上调 | Hmga1 | 促进骨骼肌分化 | [ |
| miR-29c | 下调 | IGF1 | 促进山羊原代成肌细胞的分化 | [ |
| miR-103-3p | 下调 | TWF1、BTG2、MAP4 | 抑制C2C12成肌分化 | [ |
| [1] |
Liu J, Saul D, Böker KO, Ernst J, Lehman W, Schilling AF. Current methods for skeletal muscle tissue repair and regeneration. Biomed Res Int, 2018, 2018: 1984879.
pmid: 29850487 |
| [2] |
Greising SM, Corona BT, Call JA. Musculoskeletal regeneration, rehabilitation, and plasticity following traumatic injury. Int J Sports Med, 2020, 41(8): 495-504.
pmid: 32242332 |
| [3] |
Gilbreath HR, Castro D, Iannaccone ST. Congenital myopathies and muscular dystrophies. Neurol Clin, 2014, 32(3): 689-703.
pmid: 25037085 |
| [4] |
Galli F, Mouly V, Butler-Browne G, Cossu G. Challenges in cell transplantation for muscular dystrophy. Exp Cell Res, 2021, 409(1): 112908.
pmid: 34736920 |
| [5] |
Dowling P, Swandulla D, Ohlendieck K. Cellular pathogenesis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: progressive myofibre degeneration, chronic inflammation, reactive myofibrosis and satellite cell dysfunction. Eur J Transl Myol, 2023, 33(4): 11856.
pmid: 37846661 |
| [6] |
Rodriguez-Outeiriño L, Hernandez-Torres F, Ramírez-de Acuña F, Matías-Valiente L, Sanchez-Fernandez C, Franco D, Aranega AE. Muscle satellite cell heterogeneity: does embryonic origin matter? Frontiers Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 750534.
pmid: 34722534 |
| [7] |
Cutler AA, Pawlikowski B, Wheeler JR, Dalla Betta N, Elston T, O'rourke R, Jones K, Olwin BB. The regenerating skeletal muscle niche drives satellite cell return to quiescence. iScience, 2022, 25(6): 104444.
pmid: 35733848 |
| [8] |
Punch VG, Jones AE, Rudnicki MA. Transcriptional networks that regulate muscle stem cell function. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med, 2009, 1(1): 128-140.
pmid: 20835986 |
| [9] |
Higgs PG, Lehman N. The RNA world: molecular cooperation at the origins of life. Nat Rev Genet, 2015, 16(1): 7-17.
pmid: 25385129 |
| [10] |
Buonaiuto G, Desideri F, Taliani V, Ballarino M. Muscle regeneration and RNA: new perspectives for ancient molecules. Cells, 2021, 10(10): 2512.
pmid: 34685492 |
| [11] |
Zhang PJ, Wu WY, Chen Q, Chen M. Non-coding RNAs and their integrated networks. J Integr Bioinform, 2019, 16(3): 20190027.
pmid: 31301674 |
| [12] |
Hemberg M, Gray JM, Cloonan N, Kuersten S, Grimmond S, Greenberg ME, Kreiman G. Integrated genome analysis suggests that most conserved non-coding sequences are regulatory factor binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012, 40(16): 7858-7869.
pmid: 22684627 |
| [13] |
Carninci P. Non-coding RNA transcription: turning on neighbours. Nat Cell Biol, 2008, 10(9): 1023-1024.
pmid: 18758492 |
| [14] |
Hombach S, Kretz M. Non-coding RNAs: classification, biology and functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2016, 937: 3-17.
pmid: 27573892 |
| [15] |
Cech TR, Steitz JA. The noncoding RNA revolution- trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell, 2014, 157(1): 77-94.
pmid: 24679528 |
| [16] |
Liu M, Zhang SB, Zhou H, Hu XY, Li JN, Fu BS, Wei MJ, Huang HL, Wu HZ. The interplay between non-coding RNAs and alternative splicing: from regulatory mechanism to therapeutic implications in cancer. Theranostics, 2023, 13(8): 2616-2631.
pmid: 37215575 |
| [17] |
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH. An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(5): 5451-5465.
pmid: 30471116 |
| [18] |
Diao LT, Xie SJ, Lei H, Qiu XS, Huang MC, Tao S, Hou YR, Hu YX, Sun YJ, Zhang Q, Xiao ZD. METTL3 regulates skeletal muscle specific miRNAs at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 552: 52-58.
pmid: 33740664 |
| [19] |
Zhao Y, Chen MM, Lian D, Li Y, Li Y, Wang JH, Deng SL, Yu K, Lian ZX. Non-coding RNA regulates the myogenesis of skeletal muscle satellite cells, injury repair and diseases. Cells, 2019, 8(9): 988.
pmid: 31461973 |
| [20] |
Koopmans PJ, Ismaeel A, Goljanek-Whysall K, Murach KA. The roles of miRNAs in adult skeletal muscle satellite cells. Free Radic Biol Med, 2023, 209(Pt 2): 228-238.
pmid: 37879420 |
| [21] |
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell, 1993, 75(5): 843-854.
pmid: 8252621 |
| [22] |
Lou RH, Chen JL, Zhou F, Zhang T, Chen XP, Wang CM, Guo B, Lin LG. Exosomal miRNA-155-5p from M1-polarized macrophages suppresses angiogenesis by targeting GDF6 to interrupt diabetic wound healing. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2023, 34: 102074.
pmid: 38074896 |
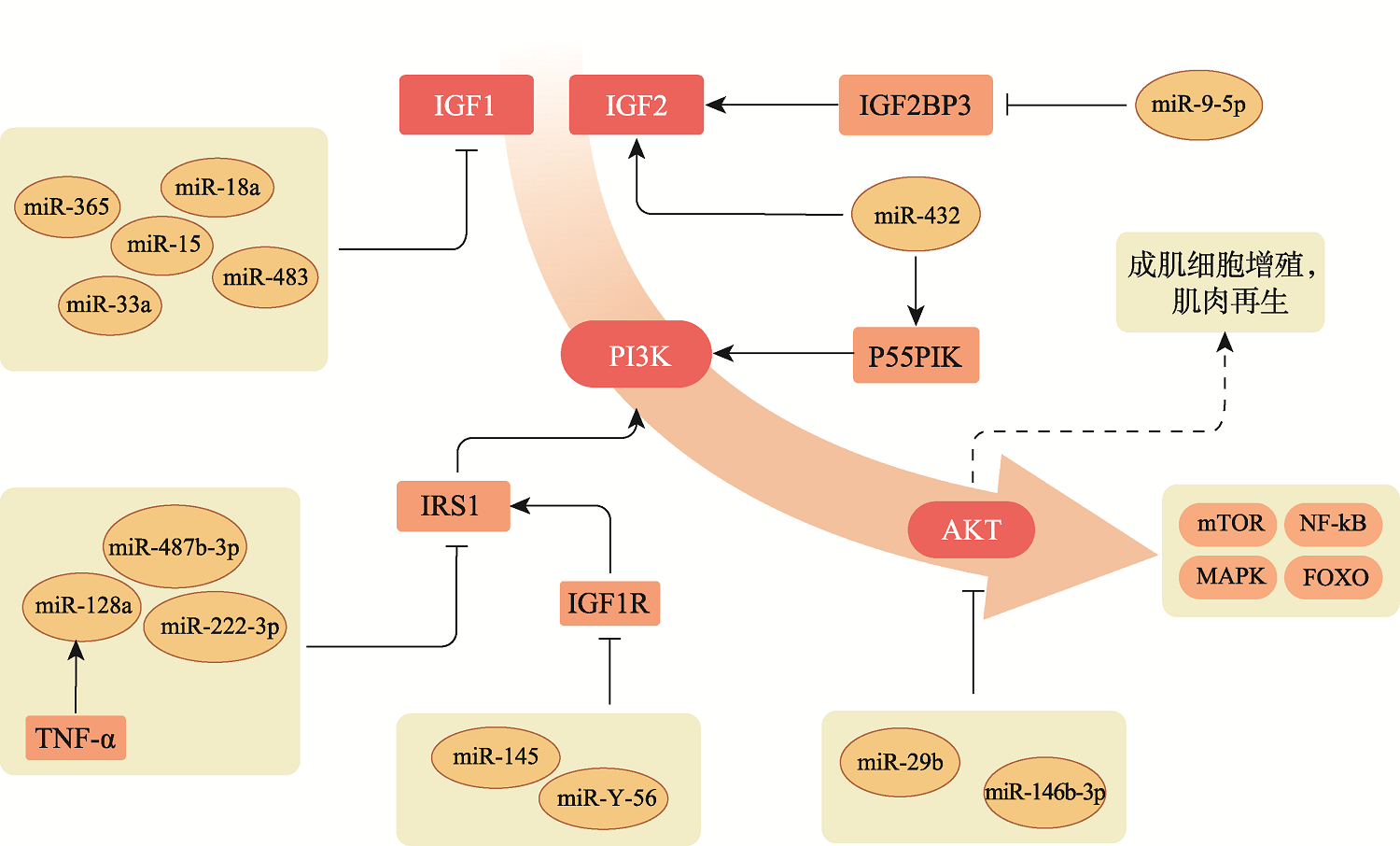
| [23] |
Zhao KY, Liu JH, Sun T, Zeng L, Cai ZD, Li ZR, Liu R. The miR-25802/KLF4/NF-κB signaling axis regulates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Behav Immun, 2024, 118: 31-48.
pmid: 38360375 |
| [24] |
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(Database issue): D68-D73.
pmid: 24275495 |
| [25] |
Medley JC, Panzade G, Zinovyeva AY. microRNA strand selection: unwinding the rules. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2021, 12(3): e1627.
pmid: 32954644 |
| [26] |
Komatsu S, Kitai H, Suzuki HI. Network regulation of microRNA biogenesis and target interaction. Cells, 2023, 12(2): 306.
pmid: 36672241 |
| [27] |
Lee Y-Y, Kim H, Kim VN. Sequence determinant of small RNA production by DICER. Nature, 2023, 615(7951): 323-330.
pmid: 36813957 |
| [28] | Zhao XQ, Ao Y, Chen HY, Wang H. The role of miRNA in kidney development. Hereditas (Beijing), 2020, 42(11): 1062-1072. |
| 赵晓琪, 敖英, 陈海云, 汪晖. miRNA与肾脏发育. 遗传, 2020, 42(11): 1062-1072. | |
| [29] | Liang WQ, Hou Y, Zhao CY. Schizophrenia-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms affecting microRNA function. Hereditas (Beijing), 2019, 41(8): 677-685. |
| 梁文权, 侯豫, 赵存友. 精神分裂症相关单核苷酸多态性调控microRNA功能研究进展. 遗传, 2019, 41(8): 677-685. | |
| [30] |
Stavast CJ, Erkeland SJ. The non-canonical aspects of microRNAs: many roads to gene regulation. Cells, 2019, 8(11): 1465.
pmid: 31752361 |
| [31] |
Santovito D, Weber C. Non-canonical features of microRNAs: paradigms emerging from cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2022, 19(9): 620-638.
pmid: 35304600 |
| [32] |
Salim U, Kumar A, Kulshreshtha R, Vivekanandan P. Biogenesis, characterization, and functions of mirtrons. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2022, 13(1): e1680.
pmid: 34155810 |
| [33] |
Ruby JG, Jan CH, Bartel DP. Intronic microRNA precursors that bypass Drosha processing. Nature, 2007, 448(7149): 83-86.
pmid: 17589500 |
| [34] |
Cheloufi S, Dos Santos CO, Chong MMW, Hannon GJ. A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis. Nature, 2010, 465(7298): 584-589.
pmid: 20424607 |
| [35] |
Kakumani PK, Ko Y, Ramakrishna S, Christopher G, Dodgson M, Shrinet J, Harvey LM, Shin C, Simard MJ. CSDE1 promotes miR-451 biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(17): 9385-9396.
pmid: 37493604 |
| [36] |
Xu YF, Hannafon BN, Khatri U, Gin A, Ding WQ. The origin of exosomal miR-1246 in human cancer cells. RNA Biol, 2019, 16(6): 770-784.
pmid: 30806147 |
| [37] |
Meerson A. Leptin-responsive MiR-4443 is a small regulatory RNA independent of the canonic microRNA biogenesis pathway. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(2): 293.
pmid: 32069948 |
| [38] |
Conley J, Genenger B, Ashford B, Ranson M. MicroRNA dysregulation in keratinocyte carcinomas: clinical evidence, functional impact, and future directions. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(15): 8493.
pmid: 39126067 |
| [39] |
Paul D, Ansari AH, Lal M, Mukhopadhyay A. Human brain shows recurrent non-canonical microRNA editing events enriched for seed sequence with possible functional consequence. Noncoding RNA, 2020, 6(2): 21.
pmid: 32498345 |
| [40] |
Zheng ZS, Zeng XB, Zhu YC, Leng MX, Zhang ZY, Wang Q, Liu XC, Zeng SY, Xiao YY, Hu CX, Pang SY, Wang T, Xu BH, Peng PD, Li F, Tan WL. CircPPAP2B controls metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via HNRNPC-dependent alternative splicing and targeting the miR-182-5p/CYP1B1 axis. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 4.
pmid: 38184608 |
| [41] |
Scuderi SA, Calabrese G, Paterniti I, Campolo M, Lanza M, Capra AP, Pantaleo L, Munaò S, Colarossi L, Forte S, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E. The biological function of microRNAs in bone tumors. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(4): 2348.
pmid: 35216464 |
| [42] |
Bhasuran B, Manoharan S, Iyyappan OR, Murugesan G, Prabahar A, Raja K. Large language models and genomics for summarizing the role of microRNA in regulating mRNA expression. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(7): 1535.
pmid: 39062108 |
| [43] |
Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y. Life of RISC: formation, action, and degradation of RNA-induced silencing complex. Mol Cell, 2022, 82(1): 30-43.
pmid: 34942118 |
| [44] |
Lytle JR, Yario TA, Steitz JA. Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5′ UTR as in the 3′ UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(23): 9667-9672.
pmid: 17535905 |
| [45] |
Lauressergues D, Ormancey M, Guillotin B, San Clemente H, Camborde L, Duboé C, Tourneur S, Charpentier P, Barozet A, Jauneau A, Le Ru A, Thuleau P, Gervais V, Plaza S, Combier JP. Characterization of plant microRNA-encoded peptides (miPEPs) reveals molecular mechanisms from the translation to activity and specificity. Cell Rep, 2022, 38(6): 110339.
pmid: 35139385 |
| [46] |
Erokhina TN, Ryazantsev DY, Zavriev SK, Morozov SY. Regulatory miPEP open reading frames contained in the primary transcripts of microRNAs. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2114.
pmid: 36768436 |
| [47] |
Cătană CS, Marta MM, Văleanu M, Dican L, Crișan CA. Human leukocyte antigen and microRNAs as key orchestrators of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(15): 8544.
pmid: 39126112 |
| [48] |
Saleh RO, Al-Ouqaili MTS, Ali E, Alhajlah S, Kareem AH, Shakir MN, Alasheqi MQ, Mustafa YF, Alawadi A, Alsaalamy A. lncRNA-microRNA axis in cancer drug resistance: particular focus on signaling pathways. Med Oncol, 2024, 41(2): 52.
pmid: 38195957 |
| [49] |
Kim WR, Park EG, Lee DH, Lee YJ, Bae WH, Kim HS. The tumorigenic role of circular RNA-microRNA axis in cancer. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 3050.
pmid: 36769372 |
| [50] |
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ, Dahiya R. MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(5): 1608-1613.
pmid: 18227514 |
| [51] |
Li NN, Zhou GP. MicroRNA-548k upregulates a spliced variant of human CD2-associated protein by targeting its promoter. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2020, 29(6): 677-682.
pmid: 32608582 |
| [52] |
Kim TK, Hemberg M, Gray JM, Costa AM, Bear DM, Wu J, Harmin DA, Laptewicz M, Barbara-Haley K, Kuersten S, Markenscoff-Papadimitriou E, Kuhl D, Bito H, Worley PF, Kreiman G, Greenberg ME. Widespread transcription at neuronal activity-regulated enhancers. Nature, 2010, 465(7295): 182-187.
pmid: 20393465 |
| [53] |
Jin WW, Jiang GH, Yang YB, Yang JY, Yang WQ, Wang DY, Niu XH, Zhong R, Zhang Z, Gong J. Animal- eRNAdb: a comprehensive animal enhancer RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(D1): D46-D53.
pmid: 34551433 |
| [54] |
Xiao M, Li J, Li W, Wang Y, Wu FZ, Xi YP, Zhang L, Ding C, Luo HB, Li Y, Peng LN, Zhao LP, Peng SL, Xiao Y, Dong SH, Cao J, Yu WQ. MicroRNAs activate gene transcription epigenetically as an enhancer trigger. RNA Biol, 2017, 14(10): 1326-1334.
pmid: 26853707 |
| [55] |
Yang X, Liu LJ, Shen XM, Shi LJ, Liu W. Dysregulation and implications of lncRNAs and miRNAs in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: in reply with emphasis on the role of ceRNAs. Oral Oncol, 2023, 136: 106277.
pmid: 36508884 |
| [56] |
Jia SN, Yu L, Wang LH, Peng LP. The functional significance of circRNA/miRNA/mRNA interactions as a regulatory network in lung cancer biology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2024, 169: 106548.
pmid: 38360264 |
| [57] |
Majchrzak K, Hentschel E, Hönzke K, Geithe C, Von Maltzahn J. We need to talk-how muscle stem cells communicate. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2024, 12: 1378548.
pmid: 39050890 |
| [58] |
Schmidt M, Schüler SC, Hüttner SS, Von Eyss B, Von Maltzahn J. Adult stem cells at work: regenerating skeletal muscle. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(13): 2559-2570.
pmid: 30976839 |
| [59] |
Collins CA, Olsen I, Zammit PS, Heslop L, Petrie A, Partridge TA, Morgan JE. Stem cell function, self- renewal, and behavioral heterogeneity of cells from the adult muscle satellite cell niche. Cell, 2005, 122(2): 289-301.
pmid: 16051152 |
| [60] |
Gugliuzza MV, Crist C. Muscle stem cell adaptations to cellular and environmental stress. Skelet Muscle, 2022, 12(1): 5.
pmid: 35151369 |
| [61] |
Mauro A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol, 1961, 9(2): 493-495.
pmid: 13768451 |
| [62] |
Zammit PS, Partridge TA, Yablonka-Reuveni Z. The skeletal muscle satellite cell: the stem cell that came in from the cold. J Histochem Cytochem, 2006, 54(11): 1177-1191.
pmid: 16899758 |
| [63] |
Dumont NA, Wang YX, Rudnicki MA. Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell function. Development, 2015, 142(9): 1572-1581.
pmid: 25922523 |
| [64] |
Zhang SY, Yang F, Huang YL, He LQ, Li YY, Wan YCE, Ding YZ, Chan KM, Xie T, Sun H, Wang HT. ATF3 induction prevents precocious activation of skeletal muscle stem cell by regulating H2B expression. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 4978.
pmid: 37591871 |
| [65] |
Kuang S, Kuroda K, Le Grand F, Rudnicki MA. Asymmetric self-renewal and commitment of satellite stem cells in muscle. Cell, 2007, 129(5): 999-1010.
pmid: 17540178 |
| [66] |
Shea KL, Xiang WY, Laporta VS, Licht JD, Keller C, Basson MA, Brack AS. Sprouty1 regulates reversible quiescence of a self-renewing adult muscle stem cell pool during regeneration. Cell Stem Cell, 2010, 6(2): 117-129.
pmid: 20144785 |
| [67] |
Song T, Sadayappan S. Featured characteristics and pivotal roles of satellite cells in skeletal muscle regeneration. J Muscle Res Cell Motil, 2020, 41(4): 341-353.
pmid: 31494813 |
| [68] |
Nalbandian M, Radak Z, Takeda M. Lactate metabolism and satellite cell fate. Front Physiol, 2020, 11: 610983.
pmid: 33362583 |
| [69] |
Sousa-Victor P, García-Prat L, Muñoz-Cánoves P. Control of satellite cell function in muscle regeneration and its disruption in ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(3): 204-226.
pmid: 34663964 |
| [70] |
Luo LF, Chua YJB, Liu TY, Liang K, Chua MWJ, Ma WW, Goh JW, Wang YF, Su JL, Ho YS, Li CW, Liu KH, Teh BT, Yu K, Shyh-Chang N. Muscle injuries induce a Prostacyclin-PPARγ/PGC1a-FAO spike that boosts regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(21): e2301519.
pmid: 37140179 |
| [71] |
Ciuffoli V, Feng XS, Jiang K, Acevedo-Luna N, Ko KD, Wang AHJ, Riparini G, Khateb M, Glancy B, Dell'orso S, Sartorelli V. Psat1-generated α-ketoglutarate and glutamine promote muscle stem cell activation and regeneration. Genes Dev, 2024, 38(3-4): 151-167.
pmid: 38453480 |
| [72] |
Wang XY, Zhou L. The multifaceted role of macrophages in homeostatic and injured skeletal muscle. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1274816.
pmid: 37954602 |
| [73] |
Dewi L, Lin YC, Nicholls A, Condello G, Huang CY, Kuo CH. Pax7+ satellite cells in human skeletal muscle after exercise: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med, 2023, 53(2): 457-480.
pmid: 36266373 |
| [74] |
Chrysostomou E, Mourikis P. The extracellular matrix niche of muscle stem cells. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2024, 158: 123-150.
pmid: 38670702 |
| [75] |
Chen X, Zhu Y, Song CC, Chen YQ, Wang YH, Lai M, Zhang CL, Fang XT. MiR-424-5p targets HSP90AA1 to facilitate proliferation and restrain differentiation in skeletal muscle development. Anim Biotechnol, 2023, 34(7): 2514-2526.
pmid: 35875894 |
| [76] |
Liu YW, Yao YL, Zhang YS, Yan C, Yang MS, Wang ZS, Li WZ, Li FQY, Wang W, Yang YL, Li XY, Tang ZL. MicroRNA-200c-5p regulates migration and differentiation of myoblasts via targeting Adamts5 in skeletal muscle regeneration and myogenesis. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(5): 4995.
pmid: 36902425 |
| [77] |
Shintani-Ishida K, Tsurumi R, Ikegaya H. Decrease in the expression of muscle-specific miRNAs, miR-133a and miR-1, in myoblasts with replicative senescence. PLoS One, 2023, 18(1): e0280527.
pmid: 36649291 |
| [78] |
Yang YL, Wu J, Liu WJ, Zhao YM, Chen H. The function and regulation mechanism of non-coding RNAs in muscle development. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 14534.
pmid: 37833983 |
| [79] |
Baghdadi MB, Firmino J, Soni K, Evano B, Di Girolamo D, Mourikis P, Castel D, Tajbakhsh S. Notch-induced miR-708 antagonizes satellite cell migration and maintains quiescence. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23(6): 859-868.e5.
pmid: 30416072 |
| [80] |
Su Y, Yu YY, Liu CC, Zhang YY, Liu C, Ge MX, Li L, Lan MM, Wang TT, Li M, Liu F, Xiong L, Wang K, He T, Shi JY, Song YL, Zhao YF, Li N, Yu ZQ, Meng QY. Fate decision of satellite cell differentiation and self-renewal by miR-31-IL34 axis. Cell Death Differ, 2020, 27(3): 949-965.
pmid: 31332295 |
| [81] |
Cheung TH, Quach NL, Charville GW, Liu L, Park L, Edalati A, Yoo B, Hoang P, Rando TA. Maintenance of muscle stem-cell quiescence by microRNA-489. Nature, 2012, 482(7386): 524-528.
pmid: 22358842 |
| [82] |
Crist CG, Montarras D, Buckingham M. Muscle satellite cells are primed for myogenesis but maintain quiescence with sequestration of Myf5 mRNA targeted by microRNA-31 in mRNP granules. Cell Stem Cell, 2012, 11(1): 118-126.
pmid: 22770245 |
| [83] |
Khayrullin A, Smith L, Mistry D, Dukes A, Pan YA, Hamrick MW. Chronic alcohol exposure induces muscle atrophy (myopathy) in zebrafish and alters the expression of microRNAs targeting the Notch pathway in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 479(3): 590-595.
pmid: 27671199 |
| [84] |
Zeng P, Han WH, Li CY, Li H, Zhu DH, Zhang Y, Liu XH. miR-378 attenuates muscle regeneration by delaying satellite cell activation and differentiation in mice. Acta Biochim Biophys Sinica (Shanghai), 2016, 48(9): 833-839.
pmid: 27563005 |
| [85] |
Koning M, Werker PMN, Van Luyn MJA, Krenning G, Harmsen MC. A global downregulation of microRNAs occurs in human quiescent satellite cells during myogenesis. Differentiation, 2012, 84(4): 314-321.
pmid: 23023067 |
| [86] |
Castel D, Baghdadi MB, Mella S, Gayraud-Morel B, Marty V, Cavaillé J, Antoniewski C, Tajbakhsh S. Small-RNA sequencing identifies dynamic microRNA deregulation during skeletal muscle lineage progression. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 4208.
pmid: 29523801 |
| [87] |
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Croce CM. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(24): 15524-15529.
pmid: 12434020 |
| [88] |
Lim S, Lee DE, Morena da Silva F, Koopmans PJ, Vechetti IJ Jr, Von Walden F, Greene NP, Murach KA. MicroRNA control of the myogenic cell transcriptome and proteome: the role of miR-16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2023, 324(5): C1101-C1109.
pmid: 36971422 |
| [89] |
Langdon CG, Gadek KE, Garcia MR, Evans MK, Reed KB, Bush M, Hanna JA, Drummond CJ, Maguire MC, Leavey PJ, Finkelstein D, Jin HJ, Schreiner PA, Rehg JE, Hatley ME. Synthetic essentiality between PTEN and core dependency factor PAX7 dictates rhabdomyosarcoma identity. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 5520.
pmid: 34535684 |
| [90] |
Baker N, Wade S, Triolo M, Girgis J, Chwastek D, Larrigan S, Feige P, Fujita R, Crist C, Rudnicki MA, Burelle Y, Khacho M. The mitochondrial protein OPA1 regulates the quiescent state of adult muscle stem cells. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(9): 1315-1332.e9.
pmid: 35998642 |
| [91] |
Li Y, Ma RS, Hao X. Therapeutic role of PTEN in tissue regeneration for management of neurological disorders: stem cell behaviors to an in-depth review. Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15(4): 268.
pmid: 38627382 |
| [92] |
Sato T, Yamamoto T, Sehara-Fujisawa A. miR-195/497 induce postnatal quiescence of skeletal muscle stem cells. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 4597.
pmid: 25119651 |
| [93] |
Campion DR. The muscle satellite cell: a review. Int Rev Cytol, 1984, 87: 225-251.
pmid: 6370890 |
| [94] |
Machida S, Booth FW. Insulin-like growth factor 1 and muscle growth: implication for satellite cell proliferation. Proc Nutr Soc, 2004, 63(2): 337-340.
pmid: 15294052 |
| [95] |
Tidball JG. Regulation of muscle growth and regeneration by the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol, 2017, 17(3): 165-178.
pmid: 28163303 |
| [96] |
Núñez-Álvarez Y, Hurtado E, Muñoz M, García-Tuñon I, Rech GE, Pluvinet R, Sumoy L, Pendás AM, Peinado MA, Suelves M. Loss of HDAC11 accelerates skeletal muscle regeneration in mice. FEBS J, 2021, 288(4): 1201-123.
pmid: 32602219 |
| [97] |
Ahmad SS, Ahmad K, Lee EJ, Lee YH, Choi I. Implications of insulin-like growth factor-1 in skeletal muscle and various diseases. Cells, 2020, 9(8): 1773.
pmid: 32722232 |
| [98] |
Guo Y, Luo F, Yi YH, Xu DY. Fibroblast growth factor 21 potentially inhibits microRNA-33 expression to affect macrophage actions. Lipids Health Dis, 2016, 15(1): 208.
pmid: 27905947 |
| [99] |
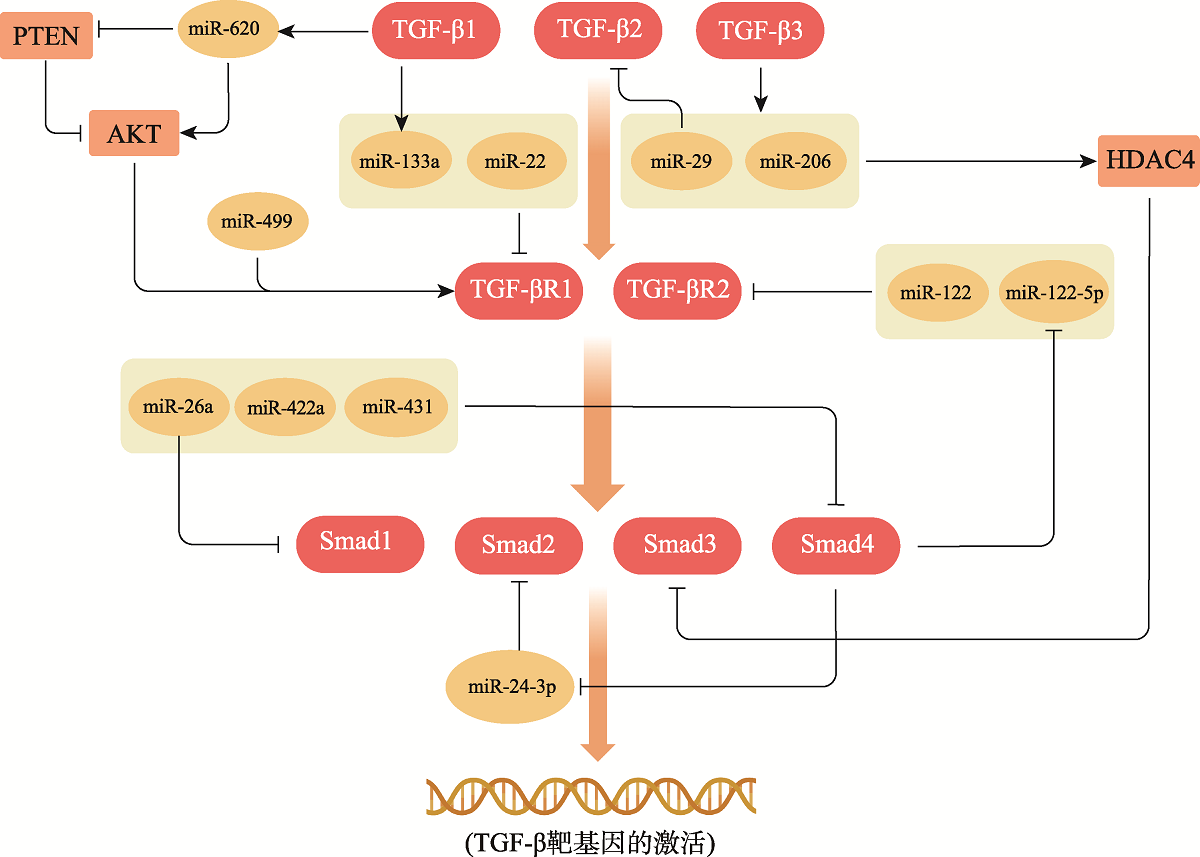
Chen H, Guo SX, Zhang S, Li XD, Wang H, Li XW. MiRNA-620 promotes TGF-β1-induced proliferation of airway smooth muscle cell through controlling PTEN/ AKT signaling pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2020, 36(11): 869-877.
pmid: 32583575 |
| [100] |
Motohashi N, Alexander MS, Casar JC, Kunkel LM. Identification of a novel microRNA that regulates the proliferation and differentiation in muscle side population cells. Stem Cells Dev, 2012, 21(16): 3031-3043.
pmid: 22541023 |
| [101] |
Li LH, Sarver AL, Alamgir S, Subramanian S. Downregulation of microRNAs miR-1, -206 and -29 stabilizes PAX3 and CCND2 expression in rhabdomyosarcoma. Lab Invest, 2012, 92(4): 571-583.
pmid: 22330340 |
| [102] |
Ling YH, Sui MH, Zheng Q, Wang KY, Wu H, Li WY, Liu Y, Chu MX, Fang FG, Xu LN. miR-27b regulates myogenic proliferation and differentiation by targeting Pax3 in goat. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 3909.
pmid: 29500394 |
| [103] |
Rodriguez-Outeiriño L, Hernandez-Torres F, Ramirez de Acuña F, Rastrojo A, Creus C, Carvajal A, Salmeron L, Montolio M, Soblechero-Martin P, Arechavala-Gomeza V, Franco D, Aranega AE. miR-106b is a novel target to promote muscle regeneration and restore satellite stem cell function in injured Duchenne dystrophic muscle. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2022, 29: 769-786.
pmid: 36159592 |
| [104] |
Duran BO, Fernandez GJ, Mareco EA, Moraes LN, Salomão RA, Gutierrez De Paula T, Santos VB, Carvalho RF, Dal-Pai-Silva M. Differential microRNA expression in fast- and slow-twitch skeletal muscle of Piaractus mesopotamicus during growth. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0141967.
pmid: 26529415 |
| [105] |
Lai XY, Bi ZJ, Yang XL, Hu RG, Wang L, Jin MM, Li LX, Bu BT. Upregulation of circ-FBL promotes myogenic proliferation in myasthenia gravis by regulation of miR-133/PAX7. Cell Biol Int, 2021, 45(11): 2287-2293.
pmid: 34363272 |
| [106] |
Tan Y, Shen LY, Gan ML, Fan Y, Cheng X, Zheng T, Niu LL, Chen L, Jiang DM, Li XW, Zhang SH, Zhu L. Downregulated miR-204 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 3183296.
pmid: 33282943 |
| [107] |
Chen JF, Tao YZ, Li J, Deng ZL, Yan Z, Xiao X, Wang DZ. microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing Pax7. J Cell Biol, 2010, 190(5): 867-879.
pmid: 20819939 |
| [108] |
Wang J, Song CC, Cao XK, Li H, Cai HF, Ma YL, Huang YZ, Lan XY, Lei CZ, Ma Y, Bai YY, Lin FP, Chen H. MiR-208b regulates cell cycle and promotes skeletal muscle cell proliferation by targeting CDKN1A. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(4): 3720-3729.
pmid: 30317561 |
| [109] |
Li XX, Qiu JM, Liu HH, Deng Y, Hu SQ, Hu JW, Wang YS, Wang JW. MicroRNA-33a negatively regulates myoblast proliferation by targeting IGF1, follistatin and cyclin D1. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(6): BSR20191327.
pmid: 32436962 |
| [110] |
Zhang GX, He ML, Wu PF, Zhang XC, Zhou KZ, Li TT, Zhang T, Xie KZ, Dai GJ, Wang JY. MicroRNA-27b-3p targets the myostatin gene to regulate myoblast proliferation and is involved in myoblast differentiation. Cells, 2021, 10(2): 423.
pmid: 33671389 |
| [111] |
Wang H, Zhang Q, Wang BB, Wu WJ, Wei JL, Li PH, Huang RH. miR-22 regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation by targeting TGFBR1. Eur J Cell Biol, 2018, 97(4): 257-268.
pmid: 29588073 |
| [112] |
Yang LZ, Qi Q, Wang J, Song CC, Wang YH, Chen X, Chen H, Zhang CL, Hu LY, Fang XT. MiR-452 regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation via targeting ANGPT1. Front Genet, 2021, 12: 640807.
pmid: 33777108 |
| [113] |
Li J, Wang GF, Jiang J, Zhang L, Zhou P, Ren HX. MicroRNA-127-3p regulates myoblast proliferation by targeting Sept7. Biotechnol Lett, 2020, 42(9): 1633-1644.
pmid: 32382971 |
| [114] |
Sun WQ, Hu SQ, Hu JW, Yang S, Hu B, Qiu JM, Gan X, Liu HH, Li L, Wang JW. miR-365 inhibits duck myoblast proliferation by targeting IGF-I via PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep, 2019, 39(11): BSR20190295.
pmid: 31658358 |
| [115] |
Cai R, Qimuge N, Ma ML, Wang YQ, Tang GR, Zhang Q, Sun YM, Chen XC, Yu TY, Dong WZ, Yang GS, Pang WJ. MicroRNA-664-5p promotes myoblast proliferation and inhibits myoblast differentiation by targeting serum response factor and Wnt1. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293(50): 19177-19190.
pmid: 30323063 |
| [116] |
Wu JY, Yue BL, Lan XY, Wang YH, Fang XT, Ma Y, Bai YY, Qi XS, Zhang CL, Chen H. MiR-499 regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation by targeting transforming growth factor β receptor 1. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(3): 2523-2536.
pmid: 30230540 |
| [117] |
Kang TT, Xing WK, Xi Y, Chen K, Zhan MS, Tang XY, Wang YY, Zhang RR, Lei MG. MiR-543 regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 cells by targeting KLF6. J Cell Biochem, 2020, 121(12): 4827-4837.
pmid: 32348593 |
| [118] |
Cai BL, Ma MT, Chen B, Li ZH, Abdalla BA, Nie QH, Zhang XQ. MiR-16-5p targets SESN1 to regulate the p53 signaling pathway, affecting myoblast proliferation and apoptosis, and is involved in myoblast differentiation. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(3): 367.
pmid: 29511169 |
| [119] |
Wang YC, Yao XH, Ma M, Zhang HH, Wang H, Zhao L, Liu SN, Sun C, Li P, Wu YT, Li XH, Jiang JJ, Li YY, Li Y, Ying H. miR-130b inhibits proliferation and promotes differentiation in myocytes via targeting Sp1. J Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 13(6): 422-432.
pmid: 33751053 |
| [120] |
Huang WL, Guo LJ, Zhao MX, Zhang DX, Xu HP, Nie QH. The inhibition on MDFIC and PI3K/AKT pathway caused by miR-146b-3p triggers suppression of myoblast proliferation and differentiation and promotion of apoptosis. Cells, 2019, 8(7): 656.
pmid: 31261950 |
| [121] |
Ye ZJ, Shi J, Ning ZC, Hou LJ, Hu CY, Wang C. MiR-92b-3p inhibits proliferation and migration of C2C12 cells. Cell Cycle, 2020, 19(21): 2906-2917.
pmid: 33043788 |
| [122] |
Gan ML, Du JJ, Shen LY, Yang DL, Jiang AA, Li Q, Jiang YZ, Tang GQ, Li MZ, Wang JY, Li XW, Zhang SH, Zhu L. miR-152 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by targeting E2F3. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 2018, 54(4): 304-310.
pmid: 29508126 |
| [123] |
Nguyen MT, Lee W. MiR-141-3p regulates myogenic differentiation in C2C12 myoblasts via CFL2-YAP- mediated mechanotransduction. BMB Rep, 2022, 55(2): 104-109.
pmid: 35000671 |
| [124] |
Nguyen MT, Lee W. Role of miR-325-3p in the regulation of CFL2 and myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. Cells, 2021, 10(10): 2725.
pmid: 34685705 |
| [125] |
Nguyen MT, Lee W. MiR-320-3p regulates the proliferation and differentiation of myogenic progenitor cells by modulating actin remodeling. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(2): 801.
pmid: 35054986 |
| [126] |
Nguyen MT, Min KH, Lee W. Palmitic acid-induced miR-429-3p impairs myoblast differentiation by downregulating CFL2. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(20): 10972.
pmid: 34681631 |
| [127] |
Nguyen MT, Lee W. Saturated fatty acid-inducible miR-103-3p impairs the myogenic differentiation of progenitor cells by enhancing cell proliferation through Twinfilin-1/F-actin/YAP1 axis. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol, 2023, 27(3): 277-287.
pmid: 37078301 |
| [128] |
Nguyen MT, Lee W. Mir-302a/TWF1 axis impairs the myogenic differentiation of progenitor cells through F-actin-mediated YAP1 activation. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(7): 6341.
pmid: 37047312 |
| [129] |
Nguyen MT, Lee W. Induction of miR-665-3p impairs the differentiation of myogenic progenitor cells by regulating the TWF1-YAP1 axis. Cells, 2023, 12(8): 1114.
pmid: 37190023 |
| [130] |
Song CC, Wang Q, Qi Q, Chen X, Wang YH, Zhang CL, Fang XT. MiR-495-3p regulates myoblasts proliferation and differentiation through targeting cadherin 2. Anim Biotechnol, 2023, 34(7): 2617-2625.
pmid: 35951546 |
| [131] |
Wang KM, Liufu S, Yu ZG, Xu XL, Ai NN, Li XT, Liu XL, Chen BH, Zhang YB, Ma HM, Yin YL. miR-100-5p regulates skeletal muscle myogenesis through the Trib2/mTOR/S6K signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(10): 8906.
pmid: 37240251 |
| [132] |
Li L, Zhang X, Yang HL, Xu XL, Chen Y, Dai DH, Zhan SY, Guo JZ, Zhong T, Wang LJ, Cao JX, Zhang HP. miR-193b-3p promotes proliferation of goat skeletal muscle satellite cells through activating IGF2BP1. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(24): 15760.
pmid: 36555418 |
| [133] |
Lyu M, Wang X, Meng XY, Qian HR, Li Q, Ma BX, Zhang ZY, Xu K. chi-miR-487b-3p inhibits goat myoblast proliferation and differentiation by targeting IRS1 through the IRS1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 23(1): 115.
pmid: 35008541 |
| [134] |
Wei XF, Wang J, Sun YQ, Zhao T, Luo XM, Lu JY, Hou W, Yu XJ, Xue LL, Yan Y, Wang HD. MiR-222-3p suppresses C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation via the inhibition of IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Biochem, 2023, 124(9): 1379-1390.
pmid: 37565526 |
| [135] |
Yang G, Wu ML, Liu XQ, Wang FW, Li M, An XY, Bai FX, Lei CZ, Dang RH. MiR-24-3p conservatively regulates muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting common gene CAMK2B in rat and cattle. Animals (Basel), 2022, 12(4): 505.
pmid: 35203213 |
| [136] |
Crist CG, Montarras D, Pallafacchina G, Rocancourt D, Cumano A, Conway SJ, Buckingham M. Muscle stem cell behavior is modified by microRNA-27 regulation of Pax3 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(32): 13383-13387.
pmid: 19666532 |
| [137] |
Ge GH, Yang DL, Tan Y, Chen Y, Jiang DM, Jiang AA, Li Q, Liu YH, Zhong ZJ, Li XW, Zhang SH, Zhu L. miR-10b-5p regulates C2C12 myoblasts proliferation and differentiation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2019, 83(2): 291-299.
pmid: 30336746 |
| [138] |
Huang ZQ, Chen XL, Yu B, He J, Chen DW. MicroRNA-27a promotes myoblast proliferation by targeting myostatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 423(2): 265-269.
pmid: 22640741 |
| [139] |
Zhang W, Wang SY, Deng SY, Gao L, Yang LW, Liu XN, Shi GQ. MiR-27b promotes sheep skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation by targeting myostatin gene. J Genet, 2018, 97(5): 1107-1117.
pmid: 30555060 |
| [140] |
Shi L, Zhou B, Li PH, Schinckel AP, Liang TT, Wang H, Li HZ, Fu LL, Chu QP, Huang RH. MicroRNA-128 targets myostatin at coding domain sequence to regulate myoblasts in skeletal muscle development. Cell Signal, 2015, 27(9): 1895-1904.
pmid: 25958325 |
| [141] | Yuan J, Han H, Dong W, Wang RC, Hao HL. Effect of miR-424-5p on the drug resistance of diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma cells by regulating PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway. Journal of Experimental Hematology, 2023, 31(1): 96-103. |
| 袁军, 韩虎, 董巍, 王瑞仓, 郝洪岭. MiR-424-5p调控PD-1/PD-L1信号通路对弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤细胞耐药性的影响. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2023, 31(1): 96-103. | |
| [142] |
Fei KL, Zhang HH, Zhang WS, Liao C. MiR-424-5p inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis of the HTR-8/SVneo cells through targeting LRP6 mediated β-catenin. Reprod Sci, 2024, 31(11): 3428-3439.
pmid: 38997540 |
| [143] |
Yue YQ, Feng XX, Jia YG, Luo SJ, Jiang ML, Luo JD, Hua YL, Zhang JY, Lin YQ, Li J, Xiong Y. miR-424(322)-5p targets Ezh1 to inhibit the proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2023, 55(3): 472-483.
pmid: 36988349 |
| [144] |
Zhong R, Miao RL, Meng J, Wu RM, Zhang Y, Zhu DH. Acetoacetate promotes muscle cell proliferation via the miR-133b/SRF axis through the Mek-Erk-MEF2 pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2021, 53(8): 1009-1016.
pmid: 34184741 |
| [145] |
Yin HD, He HR, Shen XX, Zhao J, Cao XN, Han SS, Cui C, Chen YQ, Wei YH, Xia L, Wang Y, Li DY, Zhu Q. miR-9-5p inhibits skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting IGF2BP3 through the IGF2-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(5): 1655.
pmid: 32121275 |
| [146] |
Yin HD, He HR, Shen XX, Tang SY, Zhao J, Cao XN, Han SS, Cui C, Chen YQ, Wei YH, Wang Y, Li DY, Zhu Q. MicroRNA profiling reveals an abundant miR-200a-3p promotes skeletal muscle satellite cell development by targeting TGF-β2 and regulating the TGF‑β2/SMAD signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(9): 3274.
pmid: 32380777 |
| [147] |
Yin HD, He HR, Cao XN, Shen XX, Han SS, Cui C, Zhao J, Wei YH, Chen YQ, Xia L, Wang Y, Li DY, Zhu Q. MiR-148a-3p regulates skeletal muscle satellite cell differentiation and apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by targeting Meox2. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 512.
pmid: 32582277 |
| [148] |
Jafari M, Ghadami E, Dadkhah T, Akhavan-Niaki H. PI3k/AKT signaling pathway: erythropoiesis and beyond. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(3): 2373-2385.
pmid: 30192008 |
| [149] |
Song CC, Yang ZX, Dong D, Xu JW, Wang J, Li H, Huang YZ, Lan XY, Lei CZ, Ma Y, Chen H. miR-483 inhibits bovine myoblast cell proliferation and differentiation via IGF1/PI3K/AKT signal pathway. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(6): 9839-9848.
pmid: 30422322 |
| [150] |
Li ZH, Cai BL, Abdalla BA, Zhu XN, Zheng M, Han PG, Nie QH, Zhang XQ. LncIRS1 controls muscle atrophy via sponging miR-15 family to activate IGF1-PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2019, 10(2): 391-410.
pmid: 30701698 |
| [151] |
Liu CC, Wang M, Chen M, Zhang K, Gu LJ, Li QY, Yu ZQ, Li N, Meng QY. miR-18a induces myotubes atrophy by down-regulating IgfI. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2017, 90: 145-154.
pmid: 28782600 |
| [152] |
Shen XM, Tang J, Jiang R, Wang XG, Yang ZX, Huang YZ, Lan XY, Lei CZ, Chen H. CircRILPL1 promotes muscle proliferation and differentiation via binding miR-145 to activate IGF1R/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(2): 142.
pmid: 33542215 |
| [153] |
Motohashi N, Alexander MS, Shimizu-Motohashi Y, Myers JA, Kawahara G, Kunkel LM. Regulation of IRS1/Akt insulin signaling by microRNA-128a during myogenesis. J Cell Sci, 2013, 126(Pt 12): 2678-2691.
pmid: 23606743 |
| [154] |
Yue BL, Wang J, Ru WX, Wu JY, Cao XK, Yang HY, Huang YZ, Lan XY, Lei CZ, Huang BZ, Chen H. The circular RNA circHUWE1 sponges the miR-29b- AKT3 axis to regulate myoblast development. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2020, 19: 1086-1097.
pmid: 32045877 |
| [155] |
Harding RL, Velleman SG. MicroRNA regulation of myogenic satellite cell proliferation and differentiation. Mol Cell Biochem, 2016, 412(1-2): 181-195.
pmid: 26715133 |
| [156] |
Elsaeid Elnour I, Dong D, Wang XG, Zhansaya T, Khan R, Jian W, Jie C, Chen H. Bta-miR-885 promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of myoblasts by targeting MyoD1. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(10): 6625-6636.
pmid: 31985035 |
| [157] |
Lee SY, Yang JM, Park JH, Shin HK, Kim WJ, Kim SY, Lee EJ, Hwang I, Lee CS, Lee J, Kim HS. The microRNA-92a/Sp1/MyoD axis regulates hypoxic stimulation of myogenic lineage differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Ther, 2020, 28(1): 142-156.
pmid: 31606324 |
| [158] |
Samani A, Hightower RM, Reid AL, English KG, Lopez MA, Doyle JS, Conklin MJ, Schneider DA, Bamman MM, Widrick JJ, Crossman DK, Xie M, Jee D, Lai EC, Alexander MS. miR-486 is essential for muscle function and suppresses a dystrophic transcriptome. Life Sci Alliance, 2022, 5(9): e202101215.
pmid: 35512829 |
| [159] |
Sohi G, Dilworth FJ. Noncoding RNAs as epigenetic mediators of skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS J, 2015, 282(9): 1630-1646.
pmid: 25483175 |
| [160] |
Singh K, Dilworth FJ. Differential modulation of cell cycle progression distinguishes members of the myogenic regulatory factor family of transcription factors. FEBS J, 2013, 280(17): 3991-4003.
pmid: 23419170 |
| [161] |
Duan YJ, Wu YL, Yin XM, Li TT, Chen FX, Wu PF, Zhang SS, Wang JY, Zhang GX. MicroRNA-214 inhibits chicken myoblasts proliferation, promotes their differentiation, and targets the TRMT61A gene. Genes (Basel), 2020, 11(12): 1400.
pmid: 33255823 |
| [162] |
Dey P, Soyer MA, Dey BK. MicroRNA-24-3p promotes skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration by regulating HMGA1. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2022, 79(3): 170.
pmid: 35238991 |
| [163] |
Zhang Z, Fan YX, Deng KP, Liang YX, Zhang GM, Gao XX, El-Samahy MA, Zhang YL, Deng MT, Wang F. Circular RNA circUSP13 sponges miR-29c to promote differentiation and inhibit apoptosis of goat myoblasts by targeting IGF1. FASEB J, 2022, 36(1): e22097.
pmid: 34935184 |
| [164] |
Zhang XX, Huang SH, Niu X, Li S, Wang JF, Ran XQ. miR-103-3p regulates the differentiation and autophagy of myoblasts by targeting MAP4. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(4): 4130.
pmid: 36835542 |
| [165] |
He YL, Yang PY, Yuan TT, Zhang L, Yang GS, Jin JJ, Yu TY. miR-103-3p regulates the proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by targeting BTG2. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(20): 15318.
pmid: 37894995 |
| [166] |
Shirakawa T, Toyono T, Inoue A, Matsubara T, Kawamoto T, Kokabu S. Factors regulating or regulated by myogenic regulatory factors in skeletal muscle stem cells. Cells, 2022, 11(9): 1493.
pmid: 35563799 |
| [167] |
Cao Y, Yao ZZ, Sarkar D, Lawrence M, Sanchez GJ, Parker MH, Macquarrie KL, Davison J, Morgan MT, Ruzzo WL, Gentleman RC, Tapscott SJ. Genome-wide MyoD binding in skeletal muscle cells: a potential for broad cellular reprogramming. Dev Cell, 2010, 18(4): 662-674.
pmid: 20412780 |
| [168] |
Wang RT, Chen FL, Chen Q, Wan X, Shi ML, Chen AK, Ma Z, Li GH, Wang M, Ying YC, Liu QY, Li H, Zhang X, Ma JB, Zhong JY, Chen MH, Zhang MQ, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Zhu DH. MyoD is a 3D genome structure organizer for muscle cell identity. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 205.
pmid: 35017543 |
| [169] |
Wei XF, Li H, Zhang BW, Li CX, Dong D, Lan XY, Huang YZ, Bai YY, Lin FP, Zhao X, Chen H. miR-378a-3p promotes differentiation and inhibits proliferation of myoblasts by targeting HDAC4 in skeletal muscle development. RNA Biol, 2016, 13(12): 1300-1309.
pmid: 27661135 |
| [170] |
Silva WJ, Graça FA, Cruz A, Silvestre JG, Labeit S, Miyabara EH, Yan CYI, Wang DZ, Moriscot AS. miR-29c improves skeletal muscle mass and function throughout myocyte proliferation and differentiation and by repressing atrophy-related genes. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 2019, 226(4): e13278.
pmid: 30943315 |
| [171] |
Pegoraro V, Marozzo R, Angelini C. MicroRNAs and HDAC4 protein expression in the skeletal muscle of ALS patients. Clin Neuropathol, 2020, 39(3): 105-114.
pmid: 32000889 |
| [172] |
Li RY, Li BJ, Cao Y, Li WJ, Dai WL, Zhang LL, Zhang X, Ning CB, Li HQ, Yao YL, Tao JL, Jia C, Wu WJ, Liu HL. Long non-coding RNA Mir22hg-derived miR-22-3p promotes skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration by inhibiting HDAC4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2021, 24: 200-211.
pmid: 33767916 |
| [173] |
Nguyen MT, Min KH, Kim D, Park SY, Lee W. CFL2 is an essential mediator for myogenic differentiation in C2C12 myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 533(4): 710-716.
pmid: 33187645 |
| [174] |
Nguyen MT, Won YH, Kwon TW, Lee W. Twinfilin-1 is an essential regulator of myogenic differentiation through the modulation of YAP in C2C12 myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 599: 17-23.
pmid: 35168059 |
| [175] |
Nguyen MT, Min KH, Lee W. MiR-96-5p induced by palmitic acid suppresses the myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by targeting FHL1. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(24): 9445.
pmid: 33322515 |
| [176] |
Nguyen MT, Min KH, Lee W. MiR-183-5p induced by saturated fatty acids regulates the myogenic differentiation by directly targeting FHL1 in C2C12 myoblasts. BMB Rep, 2020, 53(11): 605-610.
pmid: 33148375 |
| [177] |
Li ZF, Zhu MX, Hu BQ, Liu WX, Wu JL, Wen CG, Jian SQ, Yang G. Effects of suppressing Smads expression on wound healing in Hyriopsis cumingii. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2020, 97: 455-464.
pmid: 31870970 |
| [178] |
Dey BK, Gagan J, Yan Z, Dutta A. miR-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice. Genes Dev, 2012, 26(19): 2180-2191.
pmid: 23028144 |
| [179] |
Cheung KS, Sposito N, Stumpf PS, Wilson DI, Sanchez-Elsner T, Oreffo RO. MicroRNA-146a regulates human foetal femur derived skeletal stem cell differentiation by down-regulating SMAD2 and SMAD3. PLoS One, 2014, 9(6): e98063.
pmid: 24892945 |
| [180] |
Ding ZC, Lin JR, Sun YY, Cong S, Liu SH, Zhang YH, Chen QY, Chen JW. miR-122-5p negatively regulates the transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling pathway in skeletal muscle myogenesis. Cell Biochem Funct, 2020, 38(2): 231-238.
pmid: 31710120 |
| [181] |
Winbanks CE, Wang B, Beyer C, Koh P, White L, Kantharidis P, Gregorevic P. TGF-beta regulates miR-206 and miR-29 to control myogenic differentiation through regulation of HDAC4. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(16): 13805-13814.
pmid: 21324893 |
| [182] |
Biferali B, Mocciaro E, Runfola V, Gabellini D. Long non-coding RNAs and their role in muscle regeneration. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2024, 158: 433-465.
pmid: 38670715 |
| [183] |
Yang ZX, Song CC, Jiang R, Huang YZ, Lan XY, Lei CZ, Qi XL, Zhang CL, Huang BZ, Chen H. CircNDST1 regulates bovine myoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the miR-411a/Smad4 Axis. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(32): 10044-10057.
pmid: 35916743 |
| [184] |
Qi A, Ru WX, Yang HY, Yang Y, Tang J, Yang SL, Lan XY, Lei CZ, Sun XZ, Chen H. Circular RNA ACTA1 acts as a sponge for miR-199a-5p and miR-433 to regulate bovine myoblast development through the MAP3K11/MAP2K7/JNK pathway. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(10): 3357-3373.
pmid: 35234473 |
| [185] |
Zhao JZ, Li QY, Lin JJ, Yang LY, Du MY, Wang Y, Liu KX, Jiang ZA, Li HH, Wang SF, Sun B, Mu SQ, Li B, Liu K, Gong M, Sun SG. Integrated analysis of tRNA-derived small RNAs in proliferative human aortic smooth muscle cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2022, 27(1): 47.
pmid: 35705912 |
| [1] | Lingling Wu, Xiaoyu Zhang, Xiao Li, Jianjun Jin, Gongshe Yang, Xin’e Shi. miR-196b-5p promotes myoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(5): 435-446. |
| [2] | Fengyu Sun, Qianghua Xu. Research progress of microRNAs involved in hematopoiesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 756-771. |
| [3] | Chunxia Zhang, Feng Liu. Regulatory signaling pathways in hematopoietic stem cell development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(4): 295-307. |
| [4] | Enquan Zhang, Weicong Cai, Guiling Li, Jian Li, Jingwen Liu. Analysis of microRNA expression profile in Emiliania huxleyi in response to virus infection [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(11): 1088-1100. |
| [5] | Xiaoqi Zhao, Ying Ao, Haiyun Chen, Hui Wang. The role of miRNA in kidney development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(11): 1062-1072. |
| [6] | Lingqian Yin,Jinshan Ran,Jingjing Li,Peng Ren,Xianxian Zhang,Yiping Liu. Genetic regulation of broodiness in poultry [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(5): 391-403. |
| [7] | Zhaojie Lyu, Zhihao Wang, Shuxian Lu, Peirong Liu, Jing Tian. Brachydactyly and the molecular mechanisms of digit formation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(12): 1073-1083. |
| [8] | Ziying Huang, Long Li, Qianqian Li, Xiangdong Liu, Changchun Li. The effect of lncRNA TCONS_00815878 on differentiation of porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(12): 1119-1128. |
| [9] | Juntao Li,Wei Zhao,Dandan Li,Jing Feng,Gui Ba,Tianzeng Song,Hongping Zhang. miR-101a targeting EZH2 promotes the differentiation of goat skeletal muscle satellite cells [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(9): 828-836. |
| [10] | Shan He, Lingqiang Zhang. Research progress in linear ubiquitin modification [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(9): 911-917. |
| [11] | Xue Zhou, Yilan Du, Ping Jin, Fei Ma. Bioinformatic analysis of cancer-related microRNAs and their target genes [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(9): 855-864. |
| [12] | Jingqiu Li, Jie Yang, Ping Zhou, Yanping Le, Zhaohui Gong. The biological functions and regulations of competing endogenous RNA [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(8): 756-764. |
| [13] | Yuntao Guo, Xiangyang Miao. MicroRNAs in the regulation of brown adipocyte differentiation [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(3): 240-249. |
| [14] | Lu Zhang, Yanjun Zhang, Rui Su, Ruijun Wang, Jinquan Li. The regulatory mechanism of microRNAs in skin and hair follicle development [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(7): 655-660. |
| [15] | Lihua Yang, Xingkai Shen, Jingqiu Li, Jie Yang, Yanping Le, Zhaohui Gong. MicroRNAs affect tumor metastasis through regulating epithelial- mesenchymal transition [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(7): 637-645. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||