Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (11): 1062-1072.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-112
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
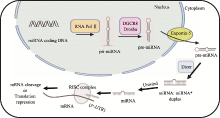
The role of miRNA in kidney development
Xiaoqi Zhao, Ying Ao( ), Haiyun Chen, Hui Wang
), Haiyun Chen, Hui Wang
- Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Developmentally Originated Diseases, Department of Pharmacology, Basic Medical School of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China
-
Received:2020-07-16Revised:2020-09-30Online:2020-11-20Published:2020-10-15 -
Contact:Ao Ying E-mail:yingao@whu.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(81872943);Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(81220108026);Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(81430089);Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(81001466);Hubei Province health and Family Planning Scientific Research Project No(WJ2017M002);the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province No(2017CFB649)
Cite this article
Xiaoqi Zhao, Ying Ao, Haiyun Chen, Hui Wang. The role of miRNA in kidney development[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(11): 1062-1072.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
"
| 种属 | 组织/细胞特异性 | 敲除靶标 | 现象 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非洲爪蟾 (Xenopus laevis) | 非肾脏特异性 | Dicer、 Dgcr8 | 肾脏水肿,前肾导管中肾上皮细胞分化延迟,肾形态异常 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 产生肾素的细胞 | Dicer | 成年肾脏中近球细胞数量严重减少,出现肾血管疾病和条纹状纤维化 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 肾单位祖细胞 | Dicer | 肾单位祖细胞过早耗竭 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 肾单位和UB来源的集合管系统 | Dicer | 肾单位祖细胞过早凋亡,UB分支缺陷 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 肾小管和输尿管芽 | Dicer | 肾小管分支减少,肾单位减少,双侧肾积水 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 前肾间充质 | Dicer | 输尿管芽分支和肾单位祖细胞分化失败 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 肾祖细胞及其衍生物 | miR-17~ 92 | 肾单位数量减少,出生后发展为肾小球功能障碍和蛋白尿性肾脏疾病。 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 泌尿生殖道和肾小管系统 | Dgcr8 | 出生后两个月内出现严重肾积水,肾囊肿,进行性肾衰竭 | [ |
| 小鼠 | 肾脏基质细胞 | Dicer1 | 肾脏发育不良,肾小管和脉管系统异常分化 | [ |
| [1] |
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH . An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol, 2019,234(5):5451-5465.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.27486 pmid: 30471116 |
| [2] |
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME . MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018,141(4):1202-1207.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034 pmid: 29074454 |
| [3] |
Ho J, Kreidberg JA . The long and short of microRNAs in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2012,23(3):400-404.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011080797 |
| [4] | Ma SY, Bai Y, Han N, Wang JH, Weng XY, Bian HW, Zhu MY . Recent research progress of biogenesis and functions of miRNA*. Hereditas(Beijing), 2012,34(4):383-388. |
| 马圣运, 白玉, 韩凝, 王君晖, 翁晓燕, 边红武, 朱睦元 . miRNA*生物合成及其功能研究的新发现. 遗传, 2012,34(4):383-388. | |
| [5] |
Valadkhan S, Gunawardane LS . Role of small nuclear RNAs in eukaryotic gene expression. Essays Biochemistry, 2013,54:79-90.
doi: 10.1042/bse0540079 |
| [6] |
Vasudevan S, Steitz JA . AU-rich-element-mediated upregulation of translation by FXR1 and Argonaute 2. Cell, 2007,128(6):1105-1118.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.038 pmid: 17382880 |
| [7] |
Kawahara Y, Zinshteyn B, Chendrimada TP, Shiekhattar R, Nishikura K . RNA editing of the microRNA-151 precursor blocks cleavage by the Dicer-TRBP complex. EMBO Rep, 2007,8(8):763-769.
doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401011 pmid: 17599088 |
| [8] |
Fuchs Wightman F, Giono LE, Fededa JP, de la Mata M,. Target RNAs strike back on microRNAs. Front Genet, 2018,9:435.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00435 pmid: 30333855 |
| [9] |
Zhang WT, Duan N, Zhang Q, Song T, Li Z, Zhang CG, Chen X, Wang KZ . DNA methylation mediated down- regulation of miR-370 regulates cell growth through activation of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Int J Biol Sci, 2017,13(5):561-573.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.19032 pmid: 28539830 |
| [10] |
Schedl A. Hastie ND . Cross-talk in kidney development. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2000,10:543-549.
doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(00)00125-8 pmid: 10980433 |
| [11] |
Aguilar ALG, Piskol R, Beitzinger M, Zhu JY, Kruspe D, Aszodi A, Moser M, Englert C, Meister G . The small RNA expression profile of the developing murine urinary and reproductive systems. FEBS Lett, 2010,584(21):4426-4434.
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.09.050 pmid: 20933514 |
| [12] |
Nagalakshmi VK, Lindner V, Wessels A, u J. microRNA- dependent temporal gene expression in the ureteric bud epithelium during mammalian kidney development. Dev Dyn, 2015,244(3):444-456.
doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24221 pmid: 25369991 |
| [13] |
Ambros V . MicroRNAs and developmental timing. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2011,21(4):511-517.
doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.04.003 |
| [14] |
Schulman BRM, Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . Reciprocal expression of lin-41 and the microRNAs let-7 and mir-125 during mouse embryogenesis. Dev Dyn, 2005,234(4):1046-1054.
doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20599 pmid: 16247770 |
| [15] |
Yermalovich AV, Osborne JK, Sousa P, Han A, Kinney MA, Chen MJ, Robinton DA, Montie H, Pearson DS, Wilson SB, Combes AN, Little MH, Daley GQ . Lin28 and let-7 regulate the timing of cessation of murine nephrogenesis. Nat Commun, 2019,10(1):168.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08127-4 pmid: 30635573 |
| [16] |
Agrawal R, Tran U, Wessely O . The miR-30 miRNA family regulates Xenopus pronephros development and targets the transcription factor Xlim1/Lhx1. Development, 2009,136(23):3927-3936.
doi: 10.1242/dev.037432 pmid: 19906860 |
| [17] |
Cerqueira DM, Bodnar AJ, Phua YL, Freer R, Hemker SL, Walensky LD, Hukriede NA, Ho J . Bim gene dosage is critical in modulating nephron progenitor survival in the absence of microRNAs during kidney development. FASEB J, 2017,31(8):3540-3554.
pmid: 28446592 |
| [18] |
Sequeira-Lopez MLS, Weatherford ET, Borges GR, Monteagudo MC, Pentz ES, Harfe BD, Carretero O, Sigmund CD, Gomez RA . The microRNA-processing enzyme dicer maintains juxtaglomerular cells. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010,21(3):460-467.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009090964 pmid: 20056748 |
| [19] |
Ho J, Pandey P, Schatton T, Sims-Lucas S, Khalid M, Frank MH, Hartwig S, Kreidberg JA . The pro-apoptotic protein bim is a microRNA target in kidney progenitors. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011,22(6):1053-1063.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010080841 |
| [20] |
Nagalakshmi VK, Ren Q, Pugh MM, Valerius MT, McMahon AP, Yu J. Dicer regulates the development of nephrogenic and ureteric compartments in the mammalian kidney. Kidney Int, 2011,79(3):317-330.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.385 |
| [21] |
Bartram MP, Höhne M, Dafinger C, Völker LA, Albersmeyer M, Heiss J, Göbel H, Brönneke H, Burst V, Liebau MC, Benzing T, Schermer B, Müller RU . Conditional loss of kidney microRNAs results in congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT). J Mol Med (Berl), 2013,91(6):739-748.
doi: 10.1007/s00109-013-1000-x |
| [22] |
Chu JYS, Sims-Lucas S, Bushnell DS, Bodnar AJ, Kreidberg JA, Ho J . Dicer function is required in the metanephric mesenchyme for early kidney development. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2014,306(7):F764-F772.
doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00426.2013 pmid: 24500693 |
| [23] |
Marrone AK, Stolz DB, Bastacky SI, Kostka D, Bodnar AJ, Ho J . MicroRNA-17~92 is required for nephrogenesis and renal function. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014,25(7):1440-1452.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013040390 |
| [24] |
Bartram MP, Dafinger C, Habbig S, Benzing T, Schermer B, Müller RU . Loss of Dgcr8-mediated microRNA expression in the kidney results in hydronephrosis and renal malformation. BMC Nephrol, 2015,16:55.
doi: 10.1186/s12882-015-0053-1 pmid: 25881298 |
| [25] |
Nakagawa N, Xin CY, Roach AM, Naiman N, Shankland SJ, Ligresti G, Ren SY, Szak S, Gomez IG, Duffield JS . Dicer1 activity in the stromal compartment regulates nephron differentiation and vascular patterning during mammalian kidney organogenesis. Kidney Int, 2015,87(6):1125-1140.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.406 pmid: 25651362 |
| [26] |
Kreidberg JA, Sariola H, Loring JM, Maeda M, Pelletier J, Housman D, Jaenisch R . WT-1 is required for early kidney development. Cell, 1993,74(4):679-691.
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90515-r pmid: 8395349 |
| [27] |
Rothenpieler UW, Dressler GR . Pax-2 is required for mesenchyme-to-epithelium conversion during kidney development. Development, 1993,119(3):711-720.
pmid: 8187639 |
| [28] |
Dressler GR, Patel SR . Epigenetics in kidney development and renal disease. Transl Res, 2015,165(1):166-176.
doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.04.007 pmid: 24958601 |
| [29] |
Viñas JL, Ventayol M, Brüne B, Jung M, Sola A, Pi F, Mastora C, Hotter G. miRNA let-7e modulates the Wnt pathway and early nephrogenic markers in mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. PLoS One, 2013,8(4):e60937.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060937 pmid: 23593353 |
| [30] |
Xue MM, Zhou YR, Liu XY, Ni DS, Hu YX, Long YS, Ju P, Zhou Q . Proliferation of metanephric mesenchymal cells is inhibited by miR-743a-mediated WT1 suppression in vitro. Mol Med Rep, 2016,14(5):4315-4320.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5762 pmid: 27667021 |
| [31] |
Dressler GR . The cellular basis of kidney development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 2006,22:509-529.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104340 pmid: 16822174 |
| [32] |
Espiritu EB, Crunk AE, Bais A, Hochbaum D, Cervino AS, Phua YL, Butterworth MB, Goto T, Ho J, Hukriede NA, Cirio MC . The Lhx1-Ldb1 complex interacts with Furry to regulate microRNA expression during pronephric kidney development. Sci Rep, 2018,8(1):16029.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34038-x pmid: 30375416 |
| [33] |
Majumdar A, Vainio S, Kispert A, McMahon J, McMahon AP. Wnt11 and Ret/Gdnf pathways cooperate in regulating ureteric branching during metanephric kidney development. Development, 2003,130(14):3175-3185.
doi: 10.1242/dev.00520 pmid: 12783789 |
| [34] |
Maheu M, Lopez JP, Crapper L, Davoli MA, Turecki G, Mechawar N . MicroRNA regulation of central glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) signalling in depression. Transl Psychiatry, 2015,5(2):e511.
doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.11 |
| [35] |
Kumar A, Kopra J, Varendi K, Porokuokka LL, Panhelainen A, Kuure S, Marshall P, Karalija N, Härma MA, Vilenius C, Lilleväli K, Tekko T, Mijatovic J, Pulkkinen N, Jakobson M, Jakobson M, Ola R, Palm E, Lindahl M, Strömberg I, Võikar V, Piepponen TP, Saarma M, Andressoo JO . GDNF overexpression from the native locus reveals its role in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system function. PLoS Genet, 2015,11(12):e1005710.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005710 pmid: 26681446 |
| [36] |
Li H, Jakobson M, Ola R, Gui YJ, Kumar A, Sipilä P, Sariola H, Kuure S, Andressoo JO . Development of the urogenital system is regulated via the 3'UTR of GDNF. Sci Rep, 2019,9(1):5302.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40457-1 pmid: 30923332 |
| [37] |
Davis BN, Hilyard AC, Lagna G, Hata A . SMAD proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature, 2008,454(7200):56-61.
doi: 10.1038/nature07086 pmid: 18548003 |
| [38] |
Hoppe B, Pietsch S, Franke M, Engel S, Groth M, Platzer M, Englert C . MiR-21 is required for efficient kidney regeneration in fish. BMC Dev Biol, 2015,15:43.
doi: 10.1186/s12861-015-0089-2 pmid: 26577279 |
| [39] |
Faherty N, Curran SP, O'Donovan H, Martin F, Godson C, Brazil DP, Crean JK. CCN2/CTGF increases expression of miR-302 microRNAs, which target the TGFβ type II receptor with implications for nephropathic cell phenotypes. J Cell Sci, 2012,125(pt 23):5621-5629.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.105528 pmid: 22976296 |
| [40] |
Liu TM, Nie F, Yang XG, Wang XY, Yuan Y, Lv ZS, Zhou L, Peng R, Ni DS, Gu YP, Zhou Q, Weng YG . MicroRNA- 590 is an EMT-suppressive microRNA involved in the TGFβ signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep, 2015,12(5):7403-7411.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4374 pmid: 26459119 |
| [41] |
Gong Y, Qin ZX, Zhou BS, Chen H, Shi ZM, Zhang J . MicroRNA-200a inhibits transforming growth factor β1-induced proximal tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting β-catenin. Nephron, 2017,137(3):237-249.
doi: 10.1159/000479168 pmid: 28817830 |
| [42] |
Wang JY, Gao YB, Zhang N, Zou DW, Wang P, Zhu ZY, Li JY, Zhou SN, Wang SC, Wang YY, Yang JK. miR-21 overexpression enhances TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition by target smad7 and aggravates renal damage in diabetic nephropathy. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2014,392(1-2):163-172.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.05.018 pmid: 24887517 |
| [43] |
Choi HI, Park JS, Kim DH, Kim CS, Bae EH, Ma SK, Kim SW . PGC-1α suppresses the activation of TGF-β/Smad signaling via targeting TGFβRI downregulation by let-7b/c upregulation. Int J Mol Sci, 2019,20(20):5084.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20205084 |
| [44] |
Long JY, Badal SS, Wang Y, Chang BHJ, Rodriguez A, Danesh FR . MicroRNA-22 is a master regulator of bone morphogenetic protein-7/6 homeostasis in the kidney. J Biol Chem, 2013,288(51):36202-36214.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.498634 pmid: 24163368 |
| [45] |
Yosypiv IV . Renin-angiotensin system in mammalian kidney development. Pediatr Nephrol, 2020.
doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04795-x pmid: 33151403 |
| [46] |
Butterworth MB . Role of microRNAs in aldosterone signaling. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, 2018,27(5):390-394.
doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000440 pmid: 30074910 |
| [47] |
Stankovic A, Kolaković A, Živković M, Djurić T, Bundalo M, Končar I, Davidović L, Alavantić D . Angiotensin receptor type 1 polymorphism A1166C is associated with altered AT1R and miR-155 expression in carotid plaque tissue and development of hypoechoic carotid plaques. Atherosclerosis, 2016,248:132-139.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.02.032 pmid: 27016615 |
| [48] |
Zheng L, Xu CC, Chen WD, Shen WL, Ruan CC, Zhu LM, Zhu DL, Gao PJ . MicroRNA-155 regulates angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression and phenotypic differentiation in vascular adventitial fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2010,400(4):483-488.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.067 pmid: 20735984 |
| [49] |
Seto E, Yoshida M . Erasers of histone acetylation: the histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2014,6(4):a018713.
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018713 pmid: 24691964 |
| [50] |
de Groh ED, Swanhart LM, Cosentino CC, Jackson RL, Dai WX, Kitchens CA, Day BW, Smithgall TE, Hukriede NA . Inhibition of histone deacetylase expands the renal progenitor cell population. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010,21(5):794-802.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009080851 pmid: 20378823 |
| [51] |
Chen SW, Bellew C, Yao X, Stefkova J, Dipp S, Saifudeen Z, Bachvarov D, El-Dahr SS . Histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity is critical for embryonic kidney gene expression, growth, and differentiation. J Biol Chem, 2011,286(37):32775-32789.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.248278 pmid: 21778236 |
| [52] |
Lin CL, Lee PH, Hsu YC, Lei CC, Ko JY, Chuang PC, Huang YT, Wang SY, Wu SL, Chen YS, Chiang WC, Reiser J, Wang FS . MicroRNA-29a promotion of nephrin acetylation ameliorates hyperglycemia-induced podocyte dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014,25(8):1698-1709.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013050527 |
| [53] |
Gong YF, Himmerkus N, Plain A, Bleich M, Hou JH . Epigenetic regulation of microRNAs controlling CLDN14 expression as a mechanism for renal calcium handling. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2015,26(3):663-676.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014020129 pmid: 25071082 |
| [54] |
Nicolaou N, Renkema KY, Bongers EMHF, Giles RH, Knoers NVAM . Genetic, environmental, and epigenetic factors involved in CAKUT. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2015,11(12):720-731.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.140 pmid: 26281895 |
| [55] |
Bertram JF, Goldstein SL, Pape L, Schaefer F, Shroff RC, Warady BA . Kidney disease in children: latest advances and remaining challenges. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2016,12(3):182-191.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.219 pmid: 26831913 |
| [56] |
Avni FE, Lahoche A, Langlois C, Garel C, Hall M, Vivier PH . Renal involvement in children with HNF1β mutation: early sonographic appearances and long-term follow-up. Eur Radiol, 2015,25(5):1479-1486.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3550-x pmid: 25638216 |
| [57] |
Skinner MA, Safford SD, Reeves JG, Jackson ME, Freemerman AJ . Renal aplasia in humans is associated with RET mutations. Am J Hum Genet, 2008,82(2):344-351.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.10.008 |
| [58] |
Weber S, Moriniere V, Knüppel T, Charbit M, Dusek J, Ghiggeri GM, Jankauskiené A, Mir S, Montini G, Peco-Antic A, Wühl E, Zurowska AM, Mehls O, Antignac C, Schaefer F, Salomon R . Prevalence of mutations in renal developmental genes in children with renal hypodysplasia: results of the ESCAPE study. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2006,17(10):2864-2870.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006030277 pmid: 16971658 |
| [59] |
Juvet C, Simeoni U, Yzydorczyk C, Siddeek B, Armengaud JB, Nardou K, Juvet P, Benahmed M, Cachat F, Chehade H . Effect of early postnatal nutrition on chronic kidney disease and arterial hypertension in adulthood: a narrative review. J Dev Orig Health Dis, 2018,9(6):598-614.
doi: 10.1017/S2040174418000454 pmid: 30078383 |
| [60] |
Brophy P . Maternal determinants of renal mass and function in the fetus and neonate. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med, 2017,22(2):67-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2017.01.004 pmid: 28347404 |
| [61] |
Dötsch J, Alejandre-Alcazar M, Janoschek R, Nüsken E, Weber LT, Nüsken KD . Perinatal programming of renal function. Curr Opin Pediatr, 2016,28(2):188-194.
doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000312 pmid: 26963856 |
| [62] |
Ergaz Z, Avgil M, Ornoy A . Intrauterine growth restriction- etiology and consequences: what do we know about the human situation and experimental animal models? Reprod Toxicol, 2005,20(3):301-322.
doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2005.04.007 pmid: 15982850 |
| [63] |
Corrêa RRM, Pucci KRM, Rocha LP, Júnior CDP, Helmo FR, Machado JR, Rocha LB, Rodrigues ARA, Glória MA, Guimarães CSO, Câmara NOS, Reis MA . Acute kidney injury and progression of renal failure after fetal programming in the offspring of diabetic rats. Pediatr Res, 2014,77(3):440-446.
doi: 10.1038/pr.2014.205 pmid: 25521920 |
| [64] |
Li B, Zhu YN, Chen HY, Gao H, He HY, Zuo N, Pei LG, Xie W, Chen LB, Ao Y, Wang H . Decreased H3K9ac level of AT2R mediates the developmental origin of glomerulosclerosis induced by prenatal dexamethasone exposure in male offspring rats. Toxicology, 2019,411:32-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2018.10.013 pmid: 30359671 |
| [65] |
Stangenberg S, Nguyen LT, Chen H, Al-Odat I, Killingsworth MC, Gosnell ME, Anwer AG, Goldys EM, Pollock CA, Saad S . Oxidative stress, mitochondrial perturbations and fetal programming of renal disease induced by maternal smoking. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2015,64:81-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.03.017 pmid: 25849459 |
| [66] |
Gray SP, Denton KM, Cullen-McEwen L, Bertram JF, Moritz KM. Prenatal exposure to alcohol reduces nephron number and raises blood pressure in progeny. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010,21(11):1891-1902.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010040368 pmid: 20829403 |
| [67] |
Goodyer P, Kurpad A, Rekha S, Muthayya S, Dwarkanath P, Iyengar A, Philip B, Mhaskar A, Benjamin A, Maharaj S, Laforte D, Raju C, Phadke K . Effects of maternal vitamin A status on kidney development: a pilot study. Pediatr Nephrol, 2007,22(2):209-214.
doi: 10.1007/s00467-006-0213-4 pmid: 17093988 |
| [68] |
Rosenblum S, Pal A, Reidy K . Renal development in the fetus and premature infant. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med, 2017,22(2):58-66.
doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2017.01.001 pmid: 28161315 |
| [69] |
Luyckx VA, Brenner BM . Birth weight, malnutrition and kidney-associated outcomes--a global concern. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2015,11(3):135-149.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.251 pmid: 25599618 |
| [70] |
Chen HY, Zhu YN, Zhao XQ, He HY, Luo JS, Ao Y, Wang H . Prenatal ethanol exposure increased the susceptibility of adult offspring rats to glomerulosclerosis. Toxicol Lett, 2020,321:44-53.
doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.11.026 pmid: 31811911 |
| [71] |
Ao Y, Sun ZX, Hu SS, Zuo N, Li B, Yang SL, Xia LP, Wu Y, Wang LL, He Z, Wang H . Low functional programming of renal AT2R mediates the developmental origin of glomerulosclerosis in adult offspring induced by prenatal caffeine exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2015,287(2):128-138.
doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.05.007 pmid: 25986755 |
| [72] |
Sun ZX, Hu SS, Zuo N, Yang SL, He Z, Ao Y, Wang H . Prenatal nicotine exposure induced GDNF/c-Ret pathway repression-related fetal renal dysplasia and adult glomerulosclerosis in male offspring. Toxicology Research, 2015,4(4):1045-1058.
doi: 10.1039/C5TX00040H |
| [73] |
Zhu YN, Chen HY, Zhao XQ, Li B, He HY, Cheng H, Wang H, Ao Y . Decreased H3K9ac level of KLF4 mediates podocyte developmental toxicity induced by prenatal caffeine exposure in male offspring rats. Toxicol Lett, 2019,314:63-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.07.011 pmid: 31306741 |
| [74] |
Sheen JM, Yu HR, Tiao MM, Chen CC, Huang LT, Chang HY, Tain YL . Prenatal dexamethasone-induced programmed hypertension and renal programming. Life Sci, 2015,132:41-48.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.04.005 pmid: 25921765 |
| [75] |
Jovanovic I, Zivkovic M, Kostic M, Krstic Z, Djuric T, Kolic I, Alavantic D, Stankovic A . Transcriptome-wide based identification of miRs in congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT) in children: the significant upregulation of tissue miR-144 expression. J Transl Med, 2016,14(1):193.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0955-0 pmid: 27364533 |
| [76] |
de Pontual L, Yao E, Callier P, Faivre L, Drouin V, Cariou S, Van Haeringen A, Geneviève D, Goldenberg A, Oufadem M, Manouvrier S, Munnich A, Vidigal JA, Vekemans M, Lyonnet S, Henrion-Caude A, Ventura A, Amiel J . Germline deletion of the miR-17∼92 cluster causes skeletal and growth defects in humans. Nat Genet, 2011,43(10):1026-1030.
pmid: 21892160 |
| [77] |
Patel V, Williams D, Hajarnis S, Hunter R, Pontoglio M, Somlo S , Igarashi P. miR-17~92 miRNA cluster promotes kidney cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013,110(26):10765-10770.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301693110 pmid: 23759744 |
| [78] |
Lakhia R, Hajarnis S, Williams D, Aboudehen K, Yheskel M, Xing C, Hatley ME, Torres VE, Wallace DP, Patel V . MicroRNA-21 aggravates cyst growth in a model of polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016,27(8):2319-2330.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015060634 pmid: 26677864 |
| [79] |
Hönig J, Mižíková I, Nardiello C, Solaligue DES, Daume MJ, Vadász I, Mayer K, Herold S, Günther S, Seeger W, Morty RE . Transmission of microRNA antimiRs to mouse offspring via the maternal-placental-fetal unit. RNA, 2020,24(6):865-879.
doi: 10.1261/rna.063206.117 pmid: 29540511 |
| [80] |
de Barros Sene L, Mesquita FF, de Moraes LN, Santos DC, Carvalho R, Gontijo JAR, Boer PA . Involvement of renal corpuscle microRNA expression on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in maternal low protein diet in adult programmed rats. PLoS One, 2013,8(8):e71310.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071310 pmid: 23977013 |
| [1] | Qianwen Lv, Yongfang Yang. The biological functions of peptide signaling in plant and the advances on its utilization for crop improvement [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(9): 813-828. |
| [2] | Yang Yang, Mingxing Chu, Qiuyue Liu. The mechanism of circadian clock and its influence on animal circannual rhythm [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(5): 409-424. |
| [3] | Beiping Zeng, Hongen Xu, Lu Mao, Wenxue Tang. Molecular diagnosis of hereditary deafness and application of stepwise testing strategy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(1): 29-41. |
| [4] | Fengyu Sun, Qianghua Xu. Research progress of microRNAs involved in hematopoiesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 756-771. |
| [5] | Sihan Qi, Qilin Wang, Junyou Zhang, Qian Liu, Chunyan Li. The regulatory mechanisms by enhancers during cancer initiation and progression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(4): 275-288. |
| [6] | Hui Qu, Yi Liu, Yawen Chen, Hui Wang. Alteration of imprinted genes and offspring organ development caused by environmental factors [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(2): 107-116. |
| [7] | Min Shen, Yong Gu, Changjiang Ying, Mei Zhang, Tao Yang, Yang Chen. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of a case with fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(11): 1079-1086. |
| [8] | Jiaqi Liang, Chang Liu, Wenxiang Zhang, Siyu Chen. Interaction between hepatokines and metabolic diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 853-866. |
| [9] | Cheng Xiao, Jieying Liu, Chunru Yang, Miao Yu. Advances in lipodystrophy syndrome caused by LMNA gene mutation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 913-925. |
| [10] | Chengan Lv, Ruoran Wang, Zhuo-Xian Meng. Molecular mechanism of islet β-cell functional alternations during type 2 diabetes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 840-852. |
| [11] | Xinyuan Wang, Rui Sun, Yuanqing Gao. Advances in genetic mechanisms of hypothalamic dysfunction in Prader-Willi syndrome [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 899-912. |
| [12] | Shanshan Gao, Jinliang Li, Jiani Yang, Tong Zhou, Rui Liu, Xiaoping Wang, Li Yu. Progresses on adaptive evolution of gliding and flying ability in mammals [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(1): 46-58. |
| [13] | Heng Yang, Yue Pang, Qingwei Li. Research progress of bile acids tolerance mechanism in lamprey biliary atresia [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(1): 59-67. |
| [14] | Ling Wang, Jinhuan Li, Haiyan Huang, Qiang Wu. Serial deletions of tandem reverse CTCF sites reveal balanced HOXD regulatory landscape of enhancers [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(8): 775-791. |
| [15] | Yanni Kou, Shan Cen, Xiaoyu Li. Research and application on LINE-1 in diagnosis and treatment of tumorigenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(6): 571-579. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||