Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (9): 1042-1056.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-340
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction and analysis of molecular genetic map of perennial Chinese rice
Tingshen Peng1( ), Jiuyan Lu1, Yuxin Yan1, Lin Tan1, Wenbin Nan1, Xiaojian Qin1, Ming Li1, Junyi Gong2, Yongshu Liang1(
), Jiuyan Lu1, Yuxin Yan1, Lin Tan1, Wenbin Nan1, Xiaojian Qin1, Ming Li1, Junyi Gong2, Yongshu Liang1( )
)
- 1. Chongqing Key Laboratory of Plant Environmental Adaptation Biology, Chongqing Normal University, Chongqing 401331, China
2. National Rice Research Institute, Hangzhou 310006, China
-
Received:2024-12-03Revised:2025-01-11Online:2025-04-08Published:2025-04-08 -
Contact:Yongshu Liang E-mail:pengtingshen@163.com;Yongshuliang@yeah.net -
Supported by:State Key Laboratory of Crop Gene Exploration and Utilization in Southwest China(SKL-KF202226);Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing City(Cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0007);Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology(20190202)
Cite this article
Tingshen Peng, Jiuyan Lu, Yuxin Yan, Lin Tan, Wenbin Nan, Xiaojian Qin, Ming Li, Junyi Gong, Yongshu Liang. Construction and analysis of molecular genetic map of perennial Chinese rice[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(9): 1042-1056.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
SSR marker with good polymorphism in chromosomesof both HN2#/XQZB and CB7#/XQZB hybrid cross"
| 染色体 | 标记数 | “黄糯2号/协青早B”组合 | “长白7号/协青早B”组合 | 公共多态性标记 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多态性标记 | 多态性频率 (%) | 多态性标记 | 多态性频率 (%) | 多态性标记 | 多态性频率 (%) | ||
| 1 | 57 | 13 | 22.81 | 14 | 24.56 | 8 | 14.04 |
| 2 | 47 | 9 | 19.15 | 9 | 19.15 | 5 | 10.64 |
| 3 | 67 | 17 | 25.37 | 14 | 20.90 | 9 | 13.43 |
| 4 | 41 | 9 | 21.95 | 8 | 19.51 | 7 | 17.07 |
| 5 | 47 | 9 | 19.15 | 9 | 19.15 | 6 | 12.77 |
| 6 | 56 | 9 | 16.07 | 13 | 23.21 | 7 | 12.50 |
| 7 | 36 | 12 | 33.33 | 13 | 36.11 | 9 | 25.00 |
| 8 | 29 | 11 | 37.93 | 9 | 31.03 | 9 | 31.03 |
| 9 | 30 | 5 | 16.67 | 5 | 16.67 | 5 | 16.67 |
| 10 | 36 | 6 | 16.67 | 7 | 19.44 | 4 | 11.11 |
| 11 | 35 | 3 | 8.57 | 2 | 5.71 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 12 | 26 | 5 | 19.23 | 6 | 23.08 | 5 | 19.23 |
| 总数 | 507 | 108 | 21.30 | 109 | 21.50 | 74 | 14.60 |
Table 2
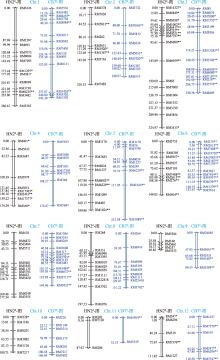
Molecular linkage map of the F2 populations derived from both “HN2#/XQZB” and “CB7#/XQZB” hybrid cross"
| 染色体 | “黄糯2号/协青早B”F2群体分子连锁图谱 (cM) | “长白7号/协青早B”F2群体分子连锁图谱 (cM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 遗传距离 | 标记间平均图距 | 变幅 | 遗传距离 | 标记间平均图距 | 变幅 | |
| 1 | 266.61 | 20.51 | 6.32~87.69 | 243.30 | 17.38 | 17.38 ~84.22 |
| 2 | 210.33 | 23.37 | 5.48~68.29 | 188.97 | 21.00 | 21.00~48.00 |
| 3 | 324.97 | 19.12 | 3.18~55.20 | 230.36 | 16.45 | 16.45~49.17 |
| 4 | 179.39 | 19.93 | 6.19~58.06 | 176.87 | 22.11 | 22.11~68.60 |
| 5 | 189.86 | 21.10 | 10.48~41.47 | 211.58 | 23.51 | 23.51~94.63 |
| 6 | 149.03 | 16.56 | 2.38~40.67 | 133.67 | 10.28 | 10.28~21.65 |
| 7 | 177.54 | 14.80 | 3.06~42.77 | 144.96 | 11.15 | 11.15~21.91 |
| 8 | 197.73 | 17.98 | 1.16~60.12 | 151.22 | 16.80 | 16.80~40.37 |
| 9 | 40.84 | 8.17 | 2.47~25.58 | 99.53 | 19.91 | 19.91~47.93 |
| 10 | 100.71 | 16.79 | 15.01~24.99 | 106.64 | 15.23 | 15.23~26.38 |
| 11 | 87.67 | 29.22 | 8.16~79.51 | 72.57 | 36.29 | 36.29~72.57 |
| 12 | 111.42 | 22.28 | 1.26~44.98 | 118.56 | 19.76 | 19.76~47.58 |
| 总计 | 2,036.10 | 18.85 | 5.43~52.44 | 1,878.23 | 17.23 | 17.23~51.92 |
Table 3
Genotypes for the F2 populations derived from both “HN2#/XQZB” and “CB7#/XQZB” hybrid cross"
| “黄糯2号/协青早B”F2群体 | “长白7号/协青早B”F2群体 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因型 | 总数 | 缺失 | 偏离方向 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 基因型 | 总数 | 缺失 | 偏离方向 | 卡方值 (χ2) | |||||
| 黄糯 2号 | 杂合 | 协青 早B | 长白 7号 | 杂合 | 协青 早B | |||||||||
| 扩增条带数 | 1,844 | 4,497 | 2,621 | 8,962 | 542 | 协青早B | 134.85>χ20.05= 5.99 | 1,744 | 4,116 | 2,822 | 8,682 | 910 | 协青早B | 291.02>χ20.05= 5.99 |
| 百分比(%) | 20.57 | 50.18 | 29.25 | 100 | 20.09 | 47.41 | 32.50 | 100 | ||||||
Table 4
Genotypes for chromosomes of the F2 populations derived from both HN2#/XQZB and CB7#/XQZB hybrid cross"
| 染色体 | “黄糯2号/协青早B”F2群体 | “长白7号/协青早B”F2群体 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多态性 标记数 | 基因型 | 总数 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | 多态性 标记数 | 基因型 | 总数 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | |||||
| 黄糯2号 | 杂合 | 协青早B | 长白7号 | 杂合 | 协青早B | |||||||||
| 1 | 13 | 214 | 587 | 239 | 1,040 | 18.47** | 杂合 | 14 | 255 | 527 | 340 | 1,122 | 17.00** | 协青早B |
| 2 | 9 | 141 | 359 | 231 | 731 | 22.39** | 协青早B | 9 | 203 | 325 | 184 | 712 | 6.41* | 长白7号 |
| 3 | 17 | 237 | 609 | 562 | 1,408 | 175.67** | 协青早B | 14 | 207 | 475 | 410 | 1,092 | 93.94** | 协青早B |
| 4 | 9 | 132 | 381 | 226 | 739 | 24.63** | 协青早B | 8 | 136 | 324 | 175 | 635 | 5.06 | 无 |
| 5 | 9 | 204 | 393 | 163 | 760 | 5.31 | 无 | 9 | 213 | 355 | 170 | 738 | 6.07* | 长白7号 |
| 6 | 9 | 123 | 362 | 263 | 748 | 53.18** | 协青早B | 13 | 120 | 502 | 436 | 1,058 | 191.52** | 协青早B |
| 7 | 12 | 262 | 519 | 233 | 1,014 | 2.23 | 无 | 13 | 179 | 547 | 366 | 1,092 | 64.05** | 协青早B |
| 8 | 11 | 196 | 498 | 234 | 928 | 8.09* | 杂合 | 9 | 158 | 335 | 199 | 692 | 5.56 | 无 |
| 9 | 5 | 91 | 206 | 130 | 427 | 7.65* | 协青早B | 5 | 79 | 180 | 144 | 403 | 25.56** | 协青早B |
| 10 | 6 | 100 | 262 | 144 | 506 | 8.29* | 协青早B | 7 | 105 | 267 | 130 | 502 | 4.53 | 无 |
| 11 | 3 | 62 | 106 | 72 | 240 | 4.10 | 无 | 2 | 24 | 43 | 72 | 139 | 53.36** | 协青早B |
| 12 | 5 | 82 | 215 | 124 | 421 | 8.57* | 协青早B | 6 | 65 | 236 | 196 | 497 | 70.32** | 协青早B |
Table 5
Genotypes for the F2 individuals derived from the “HN2#/XQZB” hybrid cross"
| 单株号 | 基因型 | 卡方值(χ2) | 偏离方向 | 单株号 | 基因型 | 卡方值(χ2) | 偏离方向 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄糯2号 | 杂合 | 协青早B | 黄糯2号 | 杂合 | 协青早B | ||||||
| 1 | 21 | 68 | 18 | 8.03* | 杂合 | 20 | 3 | 58 | 46 | 35.32** | 协青早B |
| 2 | 23 | 67 | 14 | 10.21** | 杂合 | 21 | 21 | 44 | 42 | 11.62** | 协青早B |
| 3 | 8 | 42 | 48 | 34.65** | 协青早B | 22 | 17 | 66 | 21 | 7.85* | 杂合 |
| 4 | 16 | 42 | 32 | 6.09* | 协青早B | 23 | 32 | 60 | 14 | 7.96* | 杂合 |
| 5 | 9 | 59 | 35 | 15.31** | 协青早B | 24 | 9 | 54 | 39 | 18.00** | 协青早B |
| 6 | 10 | 71 | 24 | 16.77** | 杂合 | 25 | 11 | 59 | 27 | 9.82** | 杂合 |
| 7 | 5 | 44 | 54 | 48.81** | 协青早B | 26 | 26 | 33 | 40 | 14.96** | 协青早B |
| 8 | 11 | 49 | 41 | 17.91** | 协青早B | 27 | 14 | 49 | 34 | 8.26 | 协青早B |
| 9 | 12 | 58 | 37 | 12.44** | 协青早B | 28 | 20 | 40 | 43 | 15.41** | 协青早B |
| 10 | 34 | 38 | 32 | 7.62* | 黄糯2号 | 29 | 16 | 65 | 24 | 7.17* | 杂合 |
| 11 | 9 | 66 | 29 | 15.23** | 杂合 | 30 | 23 | 44 | 37 | 6.23* | 协青早B |
| 12 | 21 | 40 | 42 | 13.70** | 协青早B | 31 | 15 | 60 | 30 | 6.43* | 杂合 |
| 13 | 21 | 63 | 17 | 6.50* | 杂合 | 32 | 14 | 56 | 31 | 6.92* | 协青早B |
| 14 | 8 | 56 | 29 | 13.37** | 杂合 | 33 | 13 | 60 | 31 | 8.69* | 协青早B |
| 15 | 16 | 50 | 38 | 9.46** | 协青早B | 34 | 40 | 39 | 27 | 10.58** | 黄糯2号 |
| 16 | 12 | 48 | 47 | 24.03** | 协青早B | 35 | 17 | 69 | 17 | 11.89** | 杂合 |
| 17 | 21 | 29 | 43 | 23.58** | 协青早B | 36 | 20 | 25 | 36 | 18.19** | 协青早B |
| 18 | 27 | 38 | 38 | 9.43** | 协青早B | 37 | 24 | 40 | 41 | 11.46** | 协青早B |
| 19 | 17 | 44 | 34 | 6.60 | 协青早B | 38 | 15 | 37 | 35 | 11.14** | 协青早B |
Table 6
Genotypes for the F2 individuals derived from the “CB7# / XQZB” hybrid cross"
| 单株号 | 基因型 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | 单株号 | 基因型 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长白7号 | 杂合 | 协青早B | 长白7号 | 杂合 | 协青早B | ||||||
| 1 | 16 | 46 | 38 | 10.32** | 协青早B | 25 | 41 | 42 | 23 | 10.68** | 长白7号 |
| 2 | 8 | 44 | 55 | 44.66** | 协青早B | 26 | 20 | 46 | 41 | 10.35** | 协青早B |
| 3 | 21 | 43 | 41 | 11.06** | 协青早B | 27 | 16 | 49 | 41 | 12.40** | 协青早B |
| 4 | 17 | 48 | 42 | 12.81** | 协青早B | 28 | 16 | 51 | 39 | 10.13** | 协青早B |
| 5 | 12 | 38 | 32 | 10.20** | 协青早B | 29 | 15 | 54 | 33 | 6.71* | 协青早B |
| 6 | 16 | 64 | 25 | 6.58* | 杂合 | 30 | 22 | 42 | 41 | 11.08** | 协青早B |
| 7 | 20 | 40 | 41 | 13.10** | 协青早B | 31 | 13 | 50 | 42 | 16.26** | 协青早B |
| 8 | 13 | 48 | 38 | 12.72** | 协青早B | 32 | 9 | 48 | 42 | 22.09** | 协青早B |
| 9 | 12 | 65 | 29 | 10.89** | 杂合 | 33 | 11 | 39 | 52 | 38.61** | 协青早B |
| 10 | 29 | 31 | 31 | 9.33** | 协青早B | 34 | 6 | 44 | 57 | 51.99** | 协青早B |
| 11 | 15 | 55 | 35 | 7.86* | 协青早B | 35 | 12 | 54 | 39 | 13.97** | 协青早B |
| 12 | 11 | 55 | 40 | 16.02** | 协青早B | 36 | 21 | 47 | 37 | 6.03* | 协青早B |
| 13 | 19 | 39 | 47 | 21.88** | 协青早B | 37 | 26 | 65 | 15 | 7.72* | 杂合 |
| 14 | 6 | 37 | 50 | 45.52** | 协青早B | 38 | 20 | 28 | 49 | 34.67** | 协青早B |
| 15 | 29 | 31 | 32 | 9.98** | 协青早B | 39 | 9 | 57 | 16 | 13.68** | 杂合 |
| 16 | 13 | 41 | 49 | 29.45** | 协青早B | 40 | 23 | 66 | 18 | 6.31* | 杂合 |
| 17 | 12 | 29 | 53 | 49.55** | 协青早B | 41 | 24 | 69 | 11 | 14.37** | 杂合 |
| 18 | 4 | 52 | 47 | 35.91** | 协青早B | 42 | 44 | 43 | 20 | 14.89** | 长白7号 |
| 19 | 37 | 43 | 29 | 6.03* | 长白7号 | 43 | 10 | 32 | 39 | 24.33** | 协青早B |
| 20 | 11 | 35 | 60 | 57.53** | 协青早B | 44 | 11 | 42 | 47 | 28.48** | 协青早B |
| 21 | 7 | 37 | 59 | 60.67** | 协青早B | 45 | 15 | 62 | 23 | 7.04* | 杂合 |
| 22 | 18 | 50 | 39 | 8.70* | 协青早B | 46 | 38 | 51 | 10 | 15.93** | 长白7号 |
| 23 | 5 | 29 | 62 | 82.73** | 协青早B | 47 | 8 | 41 | 43 | 27.72** | 协青早B |
| 24 | 15 | 50 | 32 | 6.05* | 协青早B | ||||||
Table 7
Segregation distorted markers in the F2 population derived from “HN2#/XQZB” hybrid cross"
| 染色体 | 标记 | 基因型 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | 染色体 | 标记 | 基因型 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄糯2号 | 杂合 | 协早青B | 黄糯2号 | 杂合 | 协早青B | ||||||||
| 1 | RM1297 | 12 | 48 | 14 | 6.65* | 杂合 | 4 | RM401 | 11 | 54 | 21 | 7.95* | 杂合 |
| 1 | RM8235 | 20 | 56 | 10 | 10.19** | 杂合 | 4 | RM17303 | 12 | 46 | 29 | 6.93* | 杂合 |
| 2 | RM5812 | 19 | 24 | 35 | 18.10** | 协青早B | 4 | RM2441 | 11 | 36 | 36 | 16.52** | 协青早B |
| 2 | RM1920 | 9 | 41 | 27 | 8.74* | 协青早B | 4 | RM17377 | 12 | 42 | 29 | 6.98* | 协青早B |
| 2 | RM1367 | 11 | 33 | 29 | 9.55** | 协青早B | 4 | RM348 | 11 | 50 | 25 | 6.84* | 杂合 |
| 3 | RM14327 | 18 | 34 | 33 | 8.69* | 协青早B | 5 | RM1024 | 23 | 29 | 36 | 14.07** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM6038 | 17 | 37 | 34 | 8.80* | 协青早B | 5 | RM6082 | 24 | 52 | 6 | 13.80** | 杂合 |
| 3 | RM6849 | 16 | 30 | 29 | 7.51* | 协青早B | 5 | RM6229 | 29 | 50 | 0 | 26.87** | 黄糯2号 |
| 3 | RM1002 | 5 | 37 | 43 | 35.40** | 协青早B | 6 | RM2615 | 13 | 38 | 35 | 12.42** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM6417 | 5 | 31 | 39 | 33.08** | 协青早B | 6 | RM276 | 13 | 38 | 36 | 13.55** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM7197 | 4 | 34 | 42 | 37.90** | 协青早B | 6 | RM7488 | 13 | 37 | 34 | 11.69** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM4321 | 4 | 37 | 47 | 44.25** | 协青早B | 6 | RM564 | 0 | 53 | 23 | 25.76** | 杂合 |
| 3 | RM232 | 4 | 38 | 36 | 26.31** | 协青早B | 6 | RM5957 | 11 | 43 | 28 | 7.24* | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM6080 | 1 | 42 | 41 | 38.10** | 协青早B | 10 | RM228 | 13 | 51 | 16 | 6.28* | 杂合 |
| 3 | RM6959 | 9 | 21 | 48 | 55.62** | 协青早B | 12 | RM247 | 17 | 33 | 30 | 6.68* | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM3513 | 22 | 34 | 31 | 6.01* | 协青早B | 12 | RM7376 | 11 | 56 | 18 | 9.73** | 杂合 |
Table 8
Segregation distorted markers in the F2 population derived from “CB7#/XQZB” hybrid cross"
| 染色体 | 标记 | 基因型 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | 染色体 | 标记 | 基因型 | 卡方值 (χ2) | 偏离方向 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长白7号 | 杂合 | 协早青B | 长白7号 | 杂合 | 协早青B | ||||||||
| 1 | RM3426 | 15 | 26 | 30 | 11.42** | 协青早B | 6 | RM3183 | 12 | 32 | 43 | 28.17** | 协青早B |
| 1 | RM8084 | 13 | 33 | 31 | 9.99** | 协青早B | 6 | RM7193 | 12 | 32 | 41 | 24.98** | 协青早B |
| 1 | RM8235 | 16 | 36 | 33 | 8.79* | 协青早B | 6 | RM7434 | 12 | 33 | 38 | 19.77** | 协青早B |
| 2 | RM7636 | 18 | 64 | 5 | 23.21** | 杂合 | 6 | RM5957 | 10 | 39 | 37 | 17.70** | 杂合 |
| 2 | RM5651 | 29 | 27 | 16 | 9.19* | 长白7号 | 6 | RM6395 | 11 | 44 | 33 | 11.00** | 杂合 |
| 2 | RM1920 | 34 | 32 | 20 | 10.19** | 长白7号 | 6 | RM1370 | 9 | 51 | 25 | 9.42** | 杂合 |
| 3 | RM7576 | 3 | 27 | 27 | 20.37** | 协青早B | 7 | RM3831 | 16 | 26 | 36 | 18.92** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM218 | 3 | 27 | 50 | 63.68** | 协青早B | 7 | RM5711 | 14 | 38 | 35 | 11.53** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM6080 | 0 | 44 | 41 | 39.66** | 协青早B | 7 | RM3484 | 13 | 39 | 32 | 9.02* | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM6959 | 0 | 36 | 33 | 31.70** | 协青早B | 7 | RM6872 | 11 | 41 | 33 | 11.49** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM7197 | 2 | 31 | 52 | 65.05** | 协青早B | 7 | RM5793 | 11 | 46 | 26 | 6.40* | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM15283 | 33 | 20 | 23 | 19.68** | 长白7号 | 7 | RM432 | 9 | 46 | 32 | 12.45** | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM1352 | 30 | 23 | 23 | 13.13** | 长白7号 | 7 | RM11 | 11 | 47 | 28 | 7.47* | 协青早B |
| 3 | RM7000 | 29 | 27 | 24 | 9.08* | 长白7号 | 8 | RM3702 | 20 | 25 | 26 | 7.23* | 协青早B |
| 5 | RM1024 | 19 | 53 | 9 | 10.19** | 杂合 | 9 | RM5661 | 29 | 26 | 29 | 12.19** | 协青早B |
| 5 | RM1089 | 29 | 25 | 24 | 10.69** | 长白7号 | 9 | RM160 | 12 | 38 | 33 | 11.22** | 协青早B |
| 5 | RM6229 | 26 | 44 | 8 | 9.59** | 长白7号 | 9 | RM5384 | 9 | 35 | 38 | 22.27** | 协青早B |
| 6 | RM2615 | 4 | 35 | 36 | 27.64** | 协青早B | 11 | RM4504 | 7 | 11 | 50 | 85.50** | 协青早B |
| 6 | RM276 | 5 | 30 | 40 | 35.67** | 协青早B | 12 | RM3747 | 2 | 36 | 45 | 46.01** | 协青早B |
| 6 | RM7488 | 8 | 38 | 31 | 13.75** | 协青早B | 12 | RM247 | 8 | 38 | 35 | 18.31** | 协青早B |
| 6 | RM19720 | 5 | 44 | 39 | 26.27** | 协青早B | 12 | RM6296 | 10 | 36 | 38 | 20.38** | 协青早B |
| 6 | RM19835 | 7 | 37 | 25 | 9.75** | 协青早B | 12 | RM7376 | 9 | 46 | 28 | 9.67** | 协青早B |
| [1] |
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang RL, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong JP, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang SP, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen LL, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S. A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science, 2002, 296(5565): 92-100.
pmid: 11935018 |
| [2] |
Yu J, Hu SN, Wang J, Wong GKS, Li SG, Liu B, Deng YJ, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang XQ, Cao ML, Liu J, Sun JD, Tang JB, Chen YJ, Huang XB, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong LJ, Geng JN, Han YJ, Li L, Li W, Hu GQ, Huang XG, Li WJ, Li J, Liu ZW, Li L, Liu JP, Qi QH, Liu JS, Li L, Li T, Wang XG, Lu H, Wu TT, Zhu M, Ni PX, Han H, Dong W, Ren XY, Feng XL, Cui P, Li XR, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai WX, Xu Z, Zhang JS, He SJ, Zhang JG, Xu JC, Zhang KL, Zheng XW, Dong JH, Zeng WY, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren XD, Chen XW, He J, Liu DF, Tian W, Tian CG, Xia HG, Bao QY, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao WM, Li P, Chen W, Wang XD, Zhang Y, Hu JF, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang GY, Xiong YQ, Li ZJ, Mao L, Zhou CS, Zhu Z, Chen RS, Hao BL, Zheng WM, Chen SY, Guo W, Li GJ, Liu SQ, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu LH, Yuan LP, Yang HM. A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science, 2002, 296(5565): 79-92.
pmid: 11935017 |
| [3] |
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu YB, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu BY, Maghirang R, Li ZK, Xiong YZ, Zhang QF, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, Declerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L). DNA Res, 2002, 9(6): 199-207.
pmid: 12597276 |
| [4] |
International rice genome sequencing project. The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature, 2005, 436(7052): 793-800.
pmid: 16100779 |
| [5] |
McCouch SR, Chen X, Panaud O, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, Huang N, Ishii T, Blair M. Microsatellite marker development, mapping and applications in rice genetics and breeding. Plant Mol Biol, 1997, 35(1-2): 89-99.
pmid: 9291963 |
| [6] |
Miyao A, Zhong HS, Monna L, Yano M, Yamamoto K, Havukkala I, Minobe Y, Sasaki T. Characterization and genetic mapping of simple sequence repeats in the rice genome. DNA Res, 1996, 3(4): 233-238.
pmid: 8946163 |
| [7] |
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S. Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res, 2001, 11(8): 1441-1452.
pmid: 11483586 |
| [8] | Shen LS, He P, Xu YB, Tan ZB, Lu CF, Zhu LH. Genetic molecular linkage map construction and genome analysis of rice doubled haploid population. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1998, 40(12): 1115-1122. |
| 沈利爽, 何平, 徐云碧, 谭震波, 陆朝福, 朱立煌. 水稻DH群体的分子连锁图谱及基因组分析. 植物学报, 1998, 40(12): 1115-1122. | |
| [9] | Zhang QJ, Ye SP, Yu DR, Li P, Lu CG, Zou JS. Comparison of six rice genetic linkage maps. Southwest China Journal Agriculture Science, 2005, 18(5): 584-592. |
| 张启军, 叶少平, 虞德容, 李平, 吕川根, 邹江石. 六张水稻遗传连锁图谱的比较分析. 西南农业学报, 2005, 18(5): 584-592. | |
| [10] | Akagi H, Yolozeki Y, Inagaki A, Fujimura T. Highly polymorphic microsatellites of rice consist of AT repeats, and a classification of closely related cultivars with these microsatellite loci. Theor Appl Genet, 1997, 94(1): 61-67. |
| [11] | Zhuang JY, Shi YF, Ying JZ, E ZG, Zeng RZ, Chen J, Zhu ZW. Construction and testing of primary microsatellite database of major rice varieties in China. China Journal Rice Science, 2006, 20(5): 460-468. |
|
庄杰云, 施勇烽, 应杰政, 鄂志国, 曾瑞珍, 陈洁, 朱智伟. 中国主栽水稻品种微卫星标记数据库的初步构建. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(5): 460-468.
pmid: 19352746 |
|
| [12] | Blair MW, McCouch SR. Microsatellite and sequence- tagged site markers diagnostic for the rice bacterial leaf blight resistance gene Xa-5. Theor Appl Genet, 1997, 95(1): 174-184. |
| [13] | Wang YC, Ban YJ, Jiang YD, Wang YX, Liu JJ, Liu XQ, Cheng YL, Wang N, Feng P. Phenotypic identification and fine mapping of male sterile mutant tpa1 in rice. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 1104-1114. |
| 万应春, 班义结, 蒋钰东, 王亚欣, 刘晶晶, 刘晓晴, 程育林, 王楠, 冯萍. 水稻雄性不育突变体tpa1的表型鉴定与精细定位. 作物学报, 2024, 50(5): 1104-1114. | |
| [14] |
Liang YS, Zheng J, Yan C, Li XX, Liu SF, Zhou JJ, Qin XJ, Nan WB, Yang YQ, Zhang HM. Locating QTLs controlling overwintering trait in Chinese perennial Dongxiang wild rice. Mol Genet Genomics, 2018, 293(1): 81-93.
pmid: 28879498 |
| [15] | Zhang YD, Liang WH, He L, Zhao CF, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao QY, Zhao L, Yao S, Zhou LH, Lu K, Wang CL. Construction of high-density genetic map and QTL analysis of grain shape in rice RIL population. Scientia Agricultural Sinica, 2021, 54(24): 5163-5176. |
| 张亚东, 梁文化, 赫磊, 赵春芳, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 路凯, 王才林. 水稻RIL群体高密度遗传图谱构建及粒型QTL定位. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(24): 5163-5176. | |
| [16] |
Li XY, Qian Q, Fu ZM, Wang YH, Xiong GS, Zeng DL, Wang XQ, Liu XF, Teng S, Hiroshi F, Yuan M, Luo D, Han B, Li JY. Control of tillering in rice. Nature, 2003, 422(6932): 618-621.
pmid: 12687001 |
| [17] |
Xue WY, Xing YZ, Weng XY, Zhao Y, Tang WJ, Wang L, Zhou HJ, Yu SB, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF. Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genetic, 2008, 40(6): 761-767.
pmid: 18454147 |
| [18] | Deng QY, Yuan LP, Liang FS, Li JM, Li XQ, Wang LG, Wang B. Studies on yield-enhancing genes from wild rice and their marker-assisted selection in hybrid rice. Hybrid Rice, 2004, 19(1): 6-10. |
| 邓启云, 袁隆平, 梁凤山, 李继明, 李新奇, 王乐光, 王斌. 野生稻高产基因及其分子标记辅助育种研究. 杂交水稻, 2004, 19(1): 6-10. | |
| [19] | Chen ZW, Zheng Y, Wu WR, Zhao CJ. Screening and application of an SSR marker closely linked to Pi-2(t), a gene resistant to rice blast. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2004, 2(3): 321-325. |
| 陈志伟, 郑燕, 吴为人, 赵长江. 抗稻瘟病基因Pi2(t)紧密连锁的SSR标记的筛选与应用. 分子植物育种, 2004, 2(3): 321-325. | |
| [20] | Guo XJ, Zhang T, Jiang KF, Yang L, Cao YJ, Yang QH, You SM, Wan XQ, Luo J, Li ZX, Gao L, Zheng JK. Comparison of panicle length QTL based on F2 and F8 populations derived from rice subspecies cross. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(23): 4849-4857. |
| 郭小蛟, 张涛, 蒋开锋, 杨莉, 曹应江, 杨乾华, 游书梅, 万先齐, 罗婧, 李昭祥, 高磊, 郑家奎. 水稻籼粳交F8、F2群体穗长QTL比较分析. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(23): 4849-4857. | |
| [21] |
Liang YS, Yan C, Qin XJ, Nan WB, Zhang HM. Construction of three half-sib SSR linkage maps derived from overwintering cultivated rice and segregation distortion loci mapping. Genome, 2020, 63(4): 239-251.
pmid: 32053407 |
| [22] |
Liang YS, Zhang QJ, Wang SQ, Cao LY, Gao ZQ, Li P, Cheng SH. Microsatellite analysis of homozygosity progression of heterozygous genotypes segregating in the rice subspecies cross Pei’ai64s/Nipponbare. Biochem Genet, 2011, 49(9-10): 611-624.
pmid: 21509472 |
| [23] |
Liang YS, Nan WB, Qin XJ, Zhang HM. Field performance on grain yield and quality and genetic diversity of overwintering cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) in southwest China. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 1846.
pmid: 33469098 |
| [24] | Zhang SL, Huang GF, Zhang YJ, Lv XT, Wan KJ, Liang J, Feng YP, Dao JR, Wu SK, Zhang L, Yang X, Lian XP, Huang LY, Shao L, Zhang J, Qin SW, Tao DY, Crews TE, Sacks EJ, Lyu J, Wade LJ, Hu FY. Sustained productivity and agronomic potential of perennial rice. Nat Sustain, 2023, 6(1): 28-38. |
| [25] | Liang YS, Gong JY, Yan YX, Wang BB, Gong WA, Wen H, Wu Q, Nan WB, Qin XJ, Zhang HM. Survey of overwintering trait in Chinese rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L). Euphytica, 2022, 218: 94. |
| [26] | Zhao HX, Xie P, Huang ZJ, Ju CM, Zhou Y. An improved method of extracting rice genomic DNA. Journal of Hubei University (Natural Science), 2006, 28(4): 389-392. |
| 赵红霞, 谢攀, 黄志坚, 居超明, 周勇. 一种改良的水稻总DNA提取方法. 湖北大学学报 (自然科学版), 2006, 28(4): 389-392. | |
| [27] |
Bassam BJ, Gresshoff PM. Silver staining DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Nature Protoc, 2007, 2(11): 2649-2654.
pmid: 1716076 |
| [28] | Meng L, Li HH, Zhang LY, Wang JK. QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J, 2015, 3(3): 269-283. |
| [29] | Pearson K. On the criterion that a given system of deviations from the probable in the case of a correlated system of variables is such that it can be reasonably supposed to have arisen from random sampling. Philos Mag, 1900, 5(2): 157-172. |
| [30] |
Orjuela J, Garavito A, Bouniol M, Arbelaez JD, Moreno L, Kimball J, Wilson G, Rami JF, Tohme J, McCouch SR, Lorieux M. A universal core genetic map for rice. Theor Appl Genet, 2010, 120(3): 563-572.
pmid: 19847389 |
| [31] | Zhang RJ, Chang ZY, Ye SH, Ye J, Zhai RR, Zhang XM. Analysis of genetic diversity and construction of DNA fingerprint for conventional japonica rice. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(17): 5765-5775. |
| 张锐剑, 常志远, 叶胜海, 叶靖, 翟荣荣, 张小明. 常规粳稻品种遗传多样性分析及DNA指纹图谱构建. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(17): 5765-5775. | |
| [32] |
Harushima Y, Kurata N, Yano M, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T, Minobe Y, Nakagahra M. Detection of segregation distortions in an indica-japonica rice cross using a high- resolution molecular map. Theor Appl Genet, 1996, 92(2): 145-150.
pmid: 24166160 |
| [33] |
Lu H, Romero-Severson J, Bernardo R. Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distortion in maize. Theor Appl Genet, 2002, 105(4): 622-628.
pmid: 12582513 |
| [34] |
Harushima Y, Nakagahra M, Yano M, Sasaki T, Kurata N. Diverse variation of reproductive barriers in three intraspecific rice crosses. Genetics, 2002, 160(1): 313-322.
pmid: 11805066 |
| [35] |
Lin SY, Ikehashi H, Yanagihara S, Kawashima A. Segregation distortion via male gametes in hybrids between Indica and Japonica or wide-compatibility varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 1992, 84(7-8): 812-818.
pmid: 24201479 |
| [36] |
Xu Y, Zhu L, Xiao J, Huang N, McCouch SR. Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred populations in rice (Oryza sativa L). Mol Gen Genet, 1997, 253(5): 535-545.
pmid: 9065686 |
| [37] | Wang SH. Effect of segregation distortion causing by male gametic selection. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2009, 7(5): 990-995. |
| 王石华. 雄配子体选择在遗传偏分离中的效应分析. 分子植物育种, 2009, 7(5): 990-995. | |
| [38] | Zhang XY, Zhang HY, Xu PZ, Chen XQ, Jiang B, Han MP, Chen YT, Wang Z, Huang TY, Wu XJ. Analysis of segregation distortion of SSR and Indel markers in F2 population derived from the cross of indica and japonica rice. China Rice, 2014, 20(5): 13-17. |
| 张向阳, 张红宇, 徐培洲, 陈晓琼, 蒋彬, 韩弥鹏, 陈钰堂, 王志, 黄廷友, 吴先军. 水稻SSR及Indel分子标记在籼粳交F2群体的偏分离分析. 中国稻米, 2014, 20(5): 13-17. | |
| [39] | Kinoshita T. Report of committee on gene symbolization, nomenclature, and linkage groups. Rice Genet Newl, 1995, 12: 5-153. |
| [40] | Peng Y, Liang YS, Wang SQ, Wu FQ, Li SC, Deng QM, Li P. Analysis of segregation distortion of SSR markers in the RI population of rice. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2006, 4(6): 786-790. |
| 彭勇, 梁永书, 王世全, 吴发强, 李双成, 邓其明, 李平. 水稻SSR标记在RI群体的偏分离分析. 分子植物育种, 2006, 4(6): 786-790. | |
| [41] | Zhao B, Deng QM, Zhang QJ, Li JQ, Ye SP, Liang YS, Peng Y, Li P. Analysis of segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2 population of rice. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2006, 33(5): 449-457. |
| 赵兵, 邓其明, 张启军, 李杰勤, 叶少平, 梁永书, 彭勇, 李平. 水稻日本晴与广陆矮4号杂交F2群体SSR标记偏分离原因探析. 遗传学报, 2006, 33(5): 449-457. | |
| [42] | Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR. Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 2000, 100: 697-712. |
| [43] | Lan T, Zheng J, Wu WR, Wang B. Construction of a microsatellite linkage map in a DH population. Heredtias (Beijing), 2003, 25(5): 557-562. |
| 兰涛, 郑军, 吴为人, 汪斌. 用微卫星标记构建两系稻培矮64s/E32的分子遗传连锁图. 遗传, 2003, 25(5): 557-562. | |
| [44] | Zhang QJ, Ye SP, Li JQ, Zhao B, Liang YS, Peng Y, Li P. Construction of a microsatellite linkage map with two sequenced rice varieties. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2006, 33(2): 152-160. |
| 张启军, 叶少平, 李杰勤, 赵兵, 梁永书, 彭勇, 李平. 利用两个测序水稻品种构建微卫星连锁图谱. 遗传学报, 2006, 33(2): 152-160. | |
| [45] | Shen XH, Chen SG, Cao LY, Zhan XD, Chen DB, Wu WM, Cheng SH. Construction of genetic linkage map based on a RIL population derived from super hybrid rice, XY9308. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2008, 6(5): 861-866. |
| 沈希宏, 陈沈广, 曹立勇, 占小登, 陈代波, 吴伟明, 程式华. 超级杂交稻协优9308重组自交系的分子遗传图谱构建. 分子植物育种, 2008, 6(5): 861-866. |
| [1] |
Yanyan Cao, Miaomiao Cheng, Fang Song, Yujin Qu, Jinli Bai, Hong Wang.
|
| [2] |
Xining Geng, Te Lu, Kang Du, Jun Yang, Xiangyang Kang.
|
| [3] | Xiaoling Zhang,Yun Long,Fei Ge,Zhongrong Guan,Xiaoxiang Zhang,Yanli Wang,Yaou Shen,Guangtang Pan. A genetic study of the regeneration capacity of embryonic callus from the maize immature embryo culture [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(2): 143-155. |
| [4] | Wenchao Zou, Linlin Shen, Jianguo Shen, Wei Cai, Jiasui Zhan, Fangluan Gao. A multigene phylogentic analysis of Potato virus Y and its application in strain identification [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(10): 918-929. |
| [5] | Xuli Qian, Xin Cao. Phenotype predictions of the pathogenic nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in deafness-causing gene COCH [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(7): 664-672. |
| [6] | ZHANG Wei, SHEN Min, LI Huan, GAO Lei, LIANG Yao-Wei, YANG Jing-Quan, LIU Shou-Ren, WANG Xin-Hua, GAN Shang-Quan. Detection and analysis of polymorphisms of 59571364 and 59912586 loci on X chromosome in fat-tail and thin-tail sheep flocks [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(12): 1384-1390. |
| [7] | GAN Shang-Quan ZHANG Wei SHEN Min LI Huan YANG Jing-Quan LIANG Yao-Wei GAO Lei LIU Shou-Ren WANG Xin-Hua. Correlation analysis between polymorphism of the 59383635th locus on X chromosome and fat-tail trait in sheep [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(10): 1209-1216. |
| [8] | ZHAO Lu, FENG Yue, XIA Xue-Shan. The different epidemic and evolution of HCV genotypes [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(6): 666-672. |
| [9] | ZHANG Li, WANG Peng, WEI Sha-Chi, LIU Chun-Jie. Advances in relationship between gastric disease and polymorphisms in both helicobacter pylori virulence factors and host genetics [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(6): 558-566. |
| [10] | CHEN Jun, LUO Wei-Xiong, LI Meng, LUO Qiong. Chromosome recombination in rice meiosis [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(6): 648-653. |
| [11] | WEI Jin-Pu, BO Hua-Feng, LI Gong-Quan, DUAN Fei. Distribution and evolution of simple repeats in the mtDNA D-loop in mammalian [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(1): 67-74. |
| [12] | . SSR linkage map construction and QTL mapping for leaf area in maize [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(6): 625-631. |
| [13] | LIU Han, JIANG Ba-Yang-Zong, WANG Jiang, LING Yao, GU Xue-Dong, TUN Ke-Liang, ZHANG Gao. Effects of multi-genes for reproductive traits in Tibet pig [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(5): 480-485. |
| [14] | LI Mo-Chang, WANG Yong-Fei, MA San-Mei, GUO Shi-Wei. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a high-tillering mutant (ht1) in rice [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(10): 1065-1070. |
| [15] | WANG Xiu-Ye, LI Mu-Wang, DIAO Yun-Po, XU An-Yang, GUO Qiu-Gong, HUANG Yong-Beng, GUO Ti-Jie. Mapping of non-lepis wing gene nlw in silkworm (Bombyx mori) using SSR and STS markers [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(1): 54-58. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||