Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 403-421.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-388
• Research Article • Previous Articles
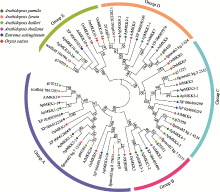
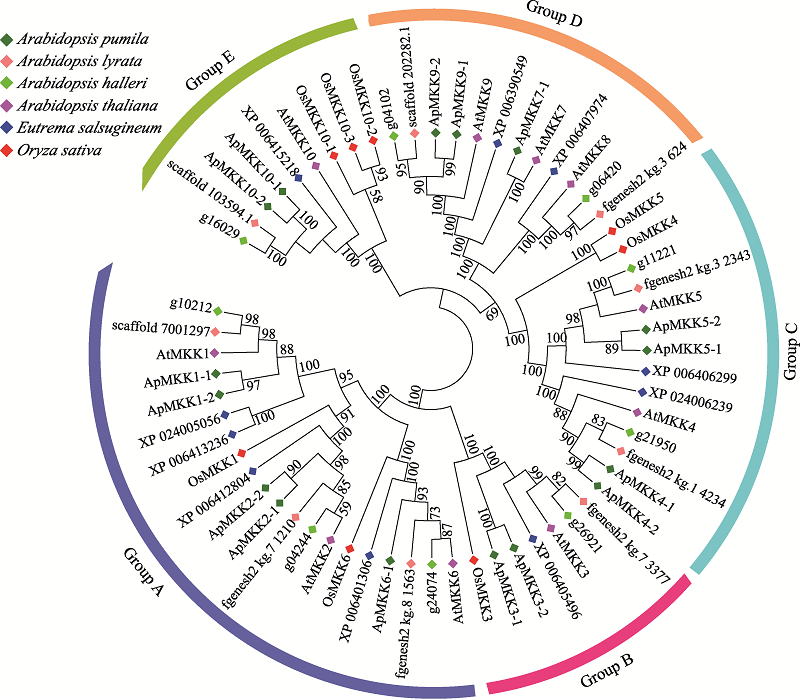
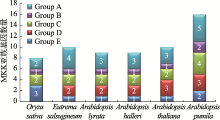
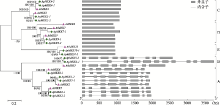
Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic analysis and expression profiling of the MKK gene family in Arabidopsis pumila
Xiaocui Li1, Kaicheng Kang1, Xianzhong Huang2,3( ), Yongbin Fan1, Miaomiao Song1, Yunjie Huang1, Jiajia Ding1
), Yongbin Fan1, Miaomiao Song1, Yunjie Huang1, Jiajia Ding1
- 1. Plant Genomics Laboratory, College of Life Sciences, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832003, China
2. College of Agriculture, Anhui Science and Technology University, Fengyang 233100, China
3. College of Life Sciences, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832003, China
-
Received:2019-12-30Revised:2020-03-15Online:2020-04-20Published:2020-03-27 -
Contact:Huang Xianzhong E-mail:xianzhongh106@163.com -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No(U1303302);International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Shihezi University No(GJHZ201806)
Cite this article
Xiaocui Li, Kaicheng Kang, Xianzhong Huang, Yongbin Fan, Miaomiao Song, Yunjie Huang, Jiajia Ding. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic analysis and expression profiling of the MKK gene family in Arabidopsis pumila[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(4): 403-421.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 2
CDS and protein similarity of ApMKK duplication gene pairs"
| 基因1 | 基因2 | CDS相似性(%) | 蛋白相似性(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApMKK1-1 | ApMKK1-2 | 97.27 | 97.46 |
| ApMKK2-1 | ApMKK2-2 | 97.07 | 98.63 |
| ApMKK3-1 | ApMKK3-2 | 97.95 | 98.66 |
| ApMKK4-1 | ApMKK4-2 | 97.83 | 98.91 |
| ApMKK5-1 | ApMKK5-2 | 97.09 | 98.03 |
| ApMKK9-1 | ApMKK9-2 | 96.59 | 99.04 |
| ApMKK10-1 | ApMKK10-2 | 96.07 | 94.90 |
Table 3
The Ka/Ks ratios of duplicated MKK genes in Arabidopsis pumila"
| 复制基因对 | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | 进化选择模式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ApMKK4-2/ApMKK4-1 | 0.0036 | 0.0755 | 0.0478 | 纯化选择 |
| ApMKK5-1/ApMKK5-2 | 0.0075 | 0.0787 | 0.0955 | 纯化选择 |
| ApMKK3-2/ApMKK3-1 | 0.0058 | 0.0735 | 0.0795 | 纯化选择 |
| ApMKK1-2/ApMKK1-1 | 0.0123 | 0.0828 | 0.1485 | 纯化选择 |
| ApMKK2-1/ApMKK2-2 | 0.0084 | 0.1060 | 0.0794 | 纯化选择 |
| ApMKK10-1/ApMKK10-2 | 0.0228 | 0.0992 | 0.2298 | 纯化选择 |
| ApMKK9-1/ApMKK9-2 | 0.0042 | 0.1434 | 0.0294 | 纯化选择 |
Table 4
Tajima relative rate tests of MKK gene pairs in Arabidopsis pumila"
| 测试组 | Mt | M1 | M2 | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ApMKK4-1/ApMKK4-2-AtMKK4 | 347 | 1 | 2 | 0.33 | 0.56370 |
| ApMKK5-1/ApMKK5-2-AtMKK5 | 335 | 3 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.31731 |
| ApMKK3-1/ApMKK3-2-AtMKK3 | 493 | 5 | 2 | 1.29 | 0.25684 |
| ApMKK1-1/ApMKK1-2-AtMKK1 | 325 | 7 | 1 | 4.50 | 0.03389 |
| ApMKK2-1/ApMKK2-1-AtMKK2 | 352 | 3 | 2 | 0.20 | 0.65472 |
| ApMKK9-1/ApMKK9-2-AtMKK9 | 295 | 2 | 1 | 0.33 | 0.56370 |
| ApMKK10-1/ApMKK10-1-AtMKK10 | 253 | 9 | 4 | 1.92 | 0.16552 |
| [1] | Xiong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK . Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell, 2002,14(Suppl):S165-183. |
| [2] | Kieber JJ, Rothenberg M, Roman G, Feldmann KA, Ecker JR . CTR1, a negative regulator of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis, encodes a member of the raf family of protein kinases. Cell, 1993,72(3):427-441. |
| [3] | Jonak C, Okrész L, Bögre L, Hirt H . Complexity, cross talk and integration of plant MAP kinase signalling. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2002,5(5):415-424. |
| [4] | Yu YJ, Liang Y, Lv ML, Wu J, Lu G, Cao JS . Genome- wide identification and characterization of polygalacturonase genes in Cucumis sativus and Citrullus lanatus. Plant Physiol Biochem, 2014,74:263-275. |
| [5] | Xu J, Zhang SQ . Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci, 2015,20(1):56-64. |
| [6] | Caunt CJ, Keyse SM . Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs): shaping the outcome of MAP kinase signalling. FEBS J, 2013,280(2):489-504. |
| [7] | Zhang XY, Xu XY, Yu YJ, Chen C, Wang J, Cai CP, Guo WZ . Integration analysis of MKK and MAPK family members highlights potential MAPK signaling modules in cotton. Sci Rep, 2016,6:29781. |
| [8] | Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ . Structural organization of MAP-kinase signaling modules by scaffold proteins in yeast and mammals. Trends Biochem Sci, 1998,23(12):481-485. |
| [9] | Bardwell AJ, Flatauer LJ, Matsukuma K, Thorner J, Bardwell L . A conserved docking site in MEKs mediates high-affinity binding to MAP kinases and cooperates with a scaffold protein to enhance signal transmission. J Biol Chem, 2001,276(13):10374-10386. |
| [10] | Takekawa M, Tatebayashi K, Saito H . Conserved docking site is essential for activation of mammalian MAP kinase kinases by specific MAP kinase kinase kinases. Mol Cell, 2005,18(3):295-306. |
| [11] | Cardinale F, Meskiene I, Ouaked F, Hirt H . Convergence and divergence of stress-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways at the level of two distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases. Plant Cell, 2002,14(3):703-711. |
| [12] | Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Tena G, Sheen J, Henry Y, Champion A, Kreisc M, Zhang SQ, Hirte H, Wilsone C, Heberle-Borse E, Ellisf BE, Morris PC, Innesh RW, Eckeri JR, Scheelj D, Klessigk DF, Machidal Y, Mundym J, Ohashin Y, Walkero JC . Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci, 2002,7(7):301-308. |
| [13] | Jiang M, Chu ZQ . Comparative analysis of plant MKK gene family reveals novel expansion mechanism of the members and sheds new light on functional conservation. BMC Genomics, 2018,19(1):407. |
| [14] | Zhang MM, Su JB, Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhang SQ . Conveying endogenous and exogenous signals: MAPK cascades in plant growth and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2018,45(Pt A):1-10. |
| [15] | Gao MH, Liu JM, Bi DL, Zhang ZB, Cheng F, Chen SF, Zhang YL . MEKK1, MKK1/MKK2 and MPK4 function together in a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to regulate innate immunity in plants. Cell Res, 2008,18(12):1190-1198. |
| [16] | Qiu JL, Zhou L, Yun BW, Nielsen HB, Fiil BK, Petersen K, Mackinlay J, Loake GJ, Mundy J, Morris PC . Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases MKK1 and MKK2 have overlapping functions in defense signaling mediated by MEKK1, MPK4, and MKS1. Plant Physiol, 2008,148(1):212-222. |
| [17] | Kong Q, Qu N, Gao MH, Zhang ZB, Ding XJ, Yang F, Li YZ, Dong OX, Chen S, Li X, Zhang YL . The MEKK1-MKK1/MKK2-MPK4 kinase cascade negatively regulates immunity mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2012,24(5):2225-2236. |
| [18] | Zhao CZ, Wang PC, Si T, Hsu CC, Wang L, Zayed O, Yu ZP, Zhu YF, Dong J, Tao WA, Zhu JK. MAP kinase cascades regulate the cold response by modulating ICE1 protein stability. Dev Cell, 2017,43(5): 618-629.e5. |
| [19] | Xing Y, Jia WS, Zhang JH . AtMKK1 mediates ABA- induced CAT1 expression and H2O2 production via AtMPK6-coupled signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2008,54(3):440-451. |
| [20] | Melikant B, Giuliani C, Halbmayer-Watzina S, Limmongkon A, Heberle-Bors E, Wilson C . The Arabidopsis thaliana MEK AtMKK6 activates the MAP kinase AtMPK13. FEBS Lett, 2004,576(1-2):5-8. |
| [21] | Li YY, Cai HX, Liu P, Wang CY, Gao HY, Wu CA, Yan K, Zhang SZ, Huang JG, Zheng CC . Arabidopsis MAPKKK18 positively regulates drought stress resistance via downstream MAPKK3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017,484(2):292-297. |
| [22] | Takahashi F, Yoshida R, Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Seo S, Yonezawa M, Maruyama K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K . The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade MKK3-MPK6 is an important part of the jasmonate signal transduction pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2007,19(3):805-818. |
| [23] | Sethi V, Raghuram B, Sinha AK, Chattopadhyay S . A mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade module, MKK3- MPK6 and MYC2, is involved in blue light-mediated seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2014,26(8):3343-3357. |
| [24] | Dai Y, Wang HZ, Li BH, Huang J, Liu XF, Zhou YH, Mou ZL, Li JY . Increased expression of MAP KINASE KINASE7 causes deficiency in polar auxin transport and leads to plant architectural abnormality in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2006,18(2):308-320. |
| [25] | Lei L, Li Y, Wang Q, Xu J, Chen YF, Yang HL, Ren DT . Activation of MKK9-MPK3/MPK6 enhances phosphate acquisition in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol, 2014,203(4):1146-1160. |
| [26] | Xu J, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu HX, Lei L, Yang HL, Liu GQ, Ren DT . Activation of MAPK kinase 9 induces ethylene and camalexin biosynthesis and enhances sensitivity to salt stress in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem, 2008,283(40):26996-27006. |
| [27] | Yoo SD, Cho YH, Tena G, Xiong Y, Sheen J . Dual control of nuclear EIN3 by bifurcate MAPK cascades in C2H4 signalling. Nature, 2008,451(7180):789-795. |
| [28] | Soyano T, Nishihama R, Morikiyo K, Ishikawa M, Machida Y . NQK1/NtMEK1 is a MAPKK that acts in the NPK1 MAPKKK-mediated MAPK cascade and is required for plant cytokinesis. Genes Dev, 2003,17(8):1055-1067. |
| [29] | Kong XP, Pan JW, Zhang MY, Xing X, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Li DP, Li DQ . ZmMKK4, a novel group C mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in maize ( Zea mays), confers salt and cold tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ, 2011,34(8):1291-1303. |
| [30] | Cai GH, Wang GD, Wang L, Liu Y, Pan JW, Li DQ . A maize mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, ZmMKK1, positively regulated the salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol, 2014,171(12):1003-1016. |
| [31] | Lu WJ, Chu XQ, Li YZ, Wang C, Guo XQ . Cotton GhMKK1 induces the tolerance of salt and drought stress, and mediates defence responses to pathogen infection in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS One, 2013,8(7):e68503. |
| [32] | Wang C, Lu W, He X, Wang F, Zhou Y, Guo X, Guo X . The cotton mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 functions in drought tolerance by regulating stomatal responses and root growth. Plant Cell Physiol, 2016,57(8):1629-1642. |
| [33] | Xu HY, Zhang C, Li ZC, Wang ZR, Jiang XX, Shi YF, Tian SN, Braun E, Mei Y, Qiu WL, Li S, Wang B, Xu J, Navarre D, Ren D, Cheng N, Nakata PA, Graham MA, Whitham SA, Liu JZ . The MAPK kinase kinase GmMEKK1 regulates cell death and defense responses. Plant Physiol, 2018,178(2):907-922. |
| [34] | Kiegerl S, Cardinale F, Siligan C, Gross A, Baudouin E, Liwosz A, Eklöf S, Till S, Bögre L, Hirt H, Meskiene I . SIMKK, a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase, is a specific activator of the salt stress-induced MAPK, SIMK. Plant Cell, 2000,12(11):2247-2258. |
| [35] | Wang XJ, Zhu SY, Lu YF, Zhao R, Xin Q, Wang XF, Zhang DP . Two coupled components of the mitogen- activated protein kinase cascade MdMPK1 and MdMKK1 from apple function in ABA signal transduction. Plant Cell Physiol, 2010,51(5):754-766. |
| [36] | Xie G, Kato H, Imai R . Biochemical identification of the OsMKK6-OsMPK3 signalling pathway for chilling stress tolerance in rice. Biochem J, 2012,443(1):95-102. |
| [37] | Xu R, Duan PG, Yu HY, Zhou ZK, Zhang BL, Wang RC, Li J, Zhang GZ, Zhuang SS, Lyu J, Li N, Chai T, Tian ZX, Yao SG, Li YH . Control of grain size and weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK6 signaling pathway in rice. Mol Plant, 2018,11(6):860-873. |
| [38] | Huang XZ, Yang LF, Jin YH, Lin J, Liu F . Generation, annotation, and analysis of a large-scale expressed sequence tag library from Arabidopsis pumila to explore salt-responsive genes. Front Plant Sci, 2017,8:955. |
| [39] | Zhang HB, Liu P, Liu LH, Lan HY, Zhang FC . Preliminary study on salt tolerance of ephemeral plant Arabidopsis pumila in Xinjiang. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin, 2007,27(2):286-290. |
| 张海波, 刘彭, 刘立鸿, 兰海燕, 张富春 . 新疆短命植物小拟南芥耐盐性的初步研究. 西北植物学报, 2007,27(2):286-290. | |
| [40] | Yang LF, Jin YH, Huang W, Sun Q, Liu F, Huang XZ . Full-length transcriptome sequences of ephemeral plant Arabidopsis pumila provides insight into gene expression dynamics during continuous salt stress. BMC Genomics, 2018,19(1):717. |
| [41] | Chang JZ, Yan FX, Qiao LY, Zheng J, Zhang FY, Liu QS . Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SBP-box gene family in Sorghum bicolor L. Hereditas (Beijing), 2016,38(6):569-580. |
| 常建忠, 闫凤霞, 乔麟轶, 郑军, 张福耀, 柳青山 . 高粱SBP-box基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 遗传, 2016,38(6):569-580. | |
| [42] | Schilling S, Kennedy A, Pan S, Jermiin LS, Melzer R . Genome-wide analysis of MIKC-type MADS-box genes in wheat: pervasive duplications, functional conservation and putative neofunctionalization. New Phytol, 2020,225(1):511-529. |
| [43] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S . MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol, 2013,30(12):2725-2729. |
| [44] | Xu L, Chen W, Si GY, Huang YY, Lin Y, Cai YP, Gao JS . Genome-wide analysis of the GST gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. Hereditas (Beijing), 2017,39(8):737-752. |
| 许磊, 陈文, 司国阳, 黄艺园, 林毅, 蔡永萍, 高俊山 . 陆地棉GST基因家族全基因组分析. 遗传, 2017,39(8):737-752. | |
| [45] | Xue HY, Xu GX, Guo CC, Shan HY, Kong HZ . Comparative evolutionary analysis of MADS-box genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and A. lyrata. Biodiv Sci, 2010,18(2):109-124. |
| 薛皓月, 徐桂霞, 国春策, 山红艳, 孔宏智 . 拟南芥和琴叶拟南芥中MADS-box基因的比较进化分析. 生物多样性, 2010,18(2):109-124. | |
| [46] | Tang K, Dong CJ, Liu JY . Genome-wide comparative analysis of the phospholipase D gene families among allotetraploid cotton and its diploid progenitors. PLoS One, 2016,11(5):e0156281. |
| [47] | Wang M, Yue H, Feng KW, Deng PC, Song WN, Nie XJ . Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expressional profiles of mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) gene family in bread wheat ( Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genomics, 2016,17(1):668. |
| [48] | Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao- Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A . DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol Biol Evol, 2017,34(12):3299-3302. |
| [49] | Yadav CB, Bonthala VS, Muthamilarasan M, Pandey G, Khan Y, Prasad M . Genome-wide development of transposable elements-based markers in foxtail millet and construction of an integrated database. DNA Res, 2015,22(1):79-90. |
| [50] | Jin X, Zhu L, Yao Q, Meng X, Ding G, Wang D, Xie Q, Tong Z, Tao C, Yu L, Li H, Wang X . Expression profiling of mitogen-activated protein kinase genes reveals their evolutionary and functional diversity in different rubber tree ( Hevea brasiliensis) cultivars. Genes (Basel), 2017,8(10):261. |
| [51] | Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA . Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res, 2009,19(9):1639-1645. |
| [52] | Jiang M, Wen F, Cao JM, Li P, She J, Chu ZQ . Genome-wide exploration of the molecular evolution and regulatory network of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades upon multiple stresses in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genomics, 2015,16(1):228. |
| [53] | Liang W, Yang B, Yu BJ, Zhou Z, Li C, Jia M, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Wu F, Zhang H, Wang B, Deyholos MK, Jiang YQ . Identification and analysis of MKK and MPK gene families in canola( Brassica napus L.). BMC Genomics, 2013,14:392. |
| [54] | Wang J, Pan CT, Wang Y, Ye L, Wu J, Chen LF, Zou T, Lu G . Genome-wide identification of MAPK, MAPKK, and MAPKKK gene families and transcriptional profiling analysis during development and stress response in cucumber. BMC Genomics, 2015,16(1):386. |
| [55] | Shan HX, Fu C . The recent advances on plant MAPK cascade pathway under adverse stress conditions. J Nucl Agric Sci, 2017,31(4):680-688. |
| 单鸿轩, 付畅 . 逆境胁迫下植物MAPK级联反应途径研究新进展. 核农学报, 2017,31(4):680-688. | |
| [56] | Zhu X, Wang M, Li X, Jiu S, Wang C, Fang J . Genome- wide analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in grape ( Vitis vinifera): structure, evolution, and expression profiles. Genes (Basel), 2017,8(4):111. |
| [57] | Cui LC, Yang G, Yan JL, Pan Y, Nie XJ . Genome-wide identification, expression profiles and regulatory network of MAPK cascade gene family in barley. BMC Genomics, 2019,20(1):750. |
| [58] | Wu J, Wang J, Pan CT, Guan XY, Wang Y, Liu SY, He YJ, Chen JL, Chen LF, Lu G . Genome-wide identification of MAPKK and MAPKKK gene families in tomato and transcriptional profiling analysis during development and stress response. PLoS One, 2014,9(7):e103032. |
| [59] | Zhang SZ, Xu RR, Luo XC, Jiang ZS, Shu HR . Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MAPK and MAPKK gene family in Malus domestica. Gene, 2013,531(2):377-387. |
| [60] | Kong XP, Lv W, Zhang D, Jiang SS, Zhang SZ, Li DQ . Genome-wide identification and analysis of expression profiles of maize mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase. PLoS One, 2013,8(2):e57714. |
| [61] | Chen LH, Hu W, Tan SL, Wang M, Ma ZB, Zhou SY, Deng XM, Zhang Y, Huang C, Yang GX, He GY . Genome-wide identification and analysis of MAPK and MAPKK gene families in Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS One, 2012,7(10):e46744. |
| [62] | Rao KP, Richa T, Kumar K, Raghuram B, Sinha AK . In silico analysis reveals 75 members of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase gene family in rice. DNA Res, 2010,17(3):139-153. |
| [63] | Hoffmann MH, Schmuths H, Koch C, Meister A, Fritsch RM. Comparative analysis of growth, genome size, chromosome numbers and phylogeny of Arabidopsis thaliana and three co-occurring species of the Brassicaceae from Uzbekistan. J Bot, 2010. Article ID 504613. DOI: 10.1155/2010/504613. |
| [64] | Van de Peer Y, Maere S, Meyer A . The evolutionary significance of ancient genome duplications. Nat Rev Genet, 2009,10(10):725-732. |
| [65] | Hu TT, Pattyn P, Bakker EG, Cao J, Cheng JF, Clark RM, Fahlgren N, Fawcett JA, Grimwood J, Gundlach H, Haberer G, Hollister JD, Ossowski S, Ottilar RP, Salamov AA, Schneeberger K, Spannagl M, Wang X, Yang L, Nasrallah ME, Bergelson J, Carrington JC, Gaut BS, Schmutz J, Mayer KF, Van de Peer Y, Grigoriev IV, Nordborg M, Weigel D, Guo YL, . The Arabidopsis lyrata genome sequence and the basis of rapid genome size change. Nat Genet, 2011,43(5):476-481. |
| [66] | Gu YB, Ji ZR, Chi FM, Qiao Z, Xu CN, Zhang JX, Zhou ZS, Dong QL . Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in peach. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016,38(3):254-270. |
| 谷彦冰, 冀志蕊, 迟福梅, 乔壮, 徐成楠, 张俊祥, 周宗山, 董庆龙 . 桃WRKY基因家族全基因组鉴定和表达分析. 遗传, 2016,38(3):254-270. | |
| [67] | Zhang T, Qiao Q, Novikova PY, Wang Q, Yue J, Guan Y, Ming S, Liu T, De J, Liu Y, Al-Shehbaz IA, Sun H, Van Montagu M, Huang J, Van de Peer Y, Qiong L . Genome of Crucihimalaya himalaica, a close relative of Arabidopsis, shows ecological adaptation to high altitude. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019,116(14):7137-7146. |
| [68] | Maere S, De Bodt S, Raes J, Casneuf T, Van Montagu M, Kuiper M, Van de Peer Y . Modeling gene and genome duplications in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005,102(15):5454-5459. |
| [69] | Jiao Y, Wickett NJ, Ayyampalayam S, Chanderbali AS, Landherr L, Ralph PE, Tomsho LP, Hu Y, Liang H, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Clifton SW, Schlarbaum SE, Schuster SC, Ma H, Leebens-Mack J, de Pamphilis CW, . Ancestral polyploidy in seed plants and angiosperms. Nature, 2011,473(7345):97-100. |
| [70] | Blanc G, Wolfe KH . Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell, 2004,16(7):1667-1678. |
| [71] | Ueno Y, Yoshida R, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Matsushita A, Jiang CJ, Goto S, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Takatsuji H . Abiotic stresses antagonize the rice defence pathway through the tyrosine-dephosphorylation of OsMPK6. PLoS Pathog, 2015,11(10):e1005231. |
| [72] | Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J . MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature, 2002,415(6875):977-983. |
| [73] | Li H, Ding YL, Shi YT, Zhang XY, Zhang SY, Gong ZZ, Yang SH. MPK3- and MPK6-mediated ICE1 phosphorylation negatively regulates ICE1 stability and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell, 2017, 43(5): 630-642.e4. |
| [74] | Zhu Q, Shao Y, Ge S, Zhang M, Zhang T, Hu X, Liu Y, Walker J, Zhang S, Xu J . A MAPK cascade downstream of IDA-HAE/HSL2 ligand-receptor pair in lateral root emergence. Nat Plants, 2019,5(4):414-423. |
| [75] | Li K, Yang F, Zhang G, Song S, Li Y, Ren D, Miao Y, Song CP . AIK1, A mitogen-activated protein kinase, modulates abscisic acid responses through the MKK5- MPK6 kinase cascade. Plant Physiol, 2017,173(2):1391-1408. |
| [1] | Kai Chen, Hao Wang, Yiting Chen, Ke Fu, Zhigang Han, Cong Li, Jinping Si, Donghong Chen. Functional analysis of WOX family genes in Dendrobium catenatum during growth and development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(8): 700-714. |
| [2] | Feifei Li, Yun Wang, Jihai Gu, Yuming Zhang, Fengsong Liu, Zhihua Ni. E2F family play important roles in tumorigenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(7): 580-592. |
| [3] | Shuang Zhang, Shanshan Guo, Ruwen Wang, Renyan Ma, Xianmin Wu, Peijie Chen, Ru Wang. The roles of PARK gene family in myopathy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(7): 545-555. |
| [4] | Qianbin Zhu, Zhicheng Gan, Xiaocui Li, Yingjie Zhang, Heming Zhao, Xianzhong Huang. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic and expression of MAPKKK gene family in Arabidopsis pumila [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(11): 1044-1055. |
| [5] | Yongguang Li, Yuhuan Jin, Li Guo, Hao Ai, Ruining Li, Xianzhong Huang. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the PEBP genes in Arabidopsis pumila [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(1): 80-91. |
| [6] | Taotao Wang, Yong Yang, Wei Wei, Chentao Lin, Liuyin Ma. Identification and expression analyses of the NAC transcription factor family in Spartina alterniflora [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(2): 194-211. |
| [7] | Yu Meng,Ruolin Yang. Comparative analysis of gene family size provides insight into the adaptive evolution of vertebrates [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(2): 158-174. |
| [8] | Ming Li,Feiyue Cheng,Luyao Gong,Hua Xiang. Systematic discovery of novel prokaryotic defense systems: progress and prospects [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(4): 259-265. |
| [9] | Zongchang Xu,Yingzhen Kong. Genome-wide identification, subcellular localization and gene expression analysis of the members of CESA gene family in common tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(6): 512-524. |
| [10] | Shuaiqi Zhu,Yifu Gong,Li Zhang,Kai Yu,Heyu Wang,Xiaojun Yan. Expression analysis of different β-carotenoid hydroxylase gene families in stress response in Dunaliella viridis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(2): 156-165. |
| [11] | Yimin He, Mingmin Gu. Research progress of myosin heavy chain genes in human genetic diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(10): 877-887. |
| [12] | Xiaohua Xiang, Xinru Wu, Jiangtao Chao, Minglei Yang, Fan Yang, Guo Chen, Guanshan Liu, Yuanying Wang. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in common tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016, 38(9): 840-856. |
| [13] | Jianzhong Chang, Fengxia Yan, Linyi Qiao, Jun Zheng, Fuyao Zhang, Qingshan Liu. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SBP-box gene family in Sorghum bicolor L. [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(6): 569-580. |
| [14] | Minglei Yang, Jiangtao Chao, Dawei Wang, Junhua Hu, Hua Wu, Daping Gong, Guanshan Liu. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the C2H2-type zinc finger protein transcription factor family in tobacco [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(4): 337-349. |
| [15] | Yanbing Gu, Zhirui Ji, Fumei Chi, Zhuang Qiao, Chengnan Xu, Junxiang Zhang, Zongshan Zhou, Qinglong Dong. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in peach [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(3): 254-270. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||