Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 194-211.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-250
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification and expression analyses of the NAC transcription factor family in Spartina alterniflora
Taotao Wang1,2( ), Yong Yang1,2, Wei Wei2, Chentao Lin2, Liuyin Ma2(
), Yong Yang1,2, Wei Wei2, Chentao Lin2, Liuyin Ma2( )
)
- 1. College of Forestry, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, China
2. Basic Forestry and Proteomics Research Center, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, China
-
Received:2019-08-27Revised:2019-12-26Online:2020-02-21Published:2020-02-08 -
Supported by:Peak Subject Construction Project of Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University(71201800725);Peak Subject Construction Project of Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University(71201800773);Scientific Research Foundation of the Graduate School of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(324-1122yb043)
Cite this article
Taotao Wang, Yong Yang, Wei Wei, Chentao Lin, Liuyin Ma. Identification and expression analyses of the NAC transcription factor family in Spartina alterniflora[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(2): 194-211.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Primer sequences used in this study"
| 基因名称 | 引物序列(5′→3′) | 引物用途 |
|---|---|---|
| SaNAC1 | F: AACACACTATCCTGCCTGCT | qRT-PCR |
| R: AGCTAGGTTCAAAGGACGCT | ||
| SaNAC5 | F: TCCATCCTTCTGACGCTGAA | qRT-PCR |
| R: TGTTGCCCTGTTTGATCTGC | ||
| SaNAC9 | F: CGAGGAGCTCATCACGTACT | qRT-PCR |
| R: TTAGTGGCACGGTTTGTTCG | ||
| SaNAC11 | F: ACTGCCACCACAAAATCGAC | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: TAACATATGCCGTCCTCCCC | ||
| SaNAC15 | F: CAAGAAGGTGGTCAACGAGC | qRT-PCR |
| R: TCGCCTTCCAGTATCCAGTC | ||
| SaNAC17 | F: CCTCTACAAGTTCGACCCGT | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: GACGAGCGCCTTCTTGATG | ||
| SaNAC18 | F: CTTGGTTCCATACAGCAGCC | qRT-PCR |
| R: GCTCTTCGCCTTGACATCTG | ||
| SaNAC19 | F: ATCATGCACGAGTACAGGCT | qRT-PCR |
| R: GCGCGTTCTTGTTGTTCTTG | ||
| SaNAC22 | F: AACTGGGTCATGCACGAGTA | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: TCATCCTCCTCCTCTTCCCA | ||
| SaNAC24 | F: GGCGAGAAGGAGTGGTACTT | qRT-PCR |
| R: CTCGTGCATGATCCAGTTGG | ||
| SaNAC25 | F: TCAAGGTTCGAACGAGACCA | qRT-PCR |
| R: TTCATAGTGCCATCCCGACA | ||
| SaNAC26 | F: ATCCACATACCCCACCCAAG | qRT-PCR |
| R: CCGGAAGAAGACGACGAGTA | ||
| SaNAC28 | F: GGTGAGGAGGAACAGAACGA | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: CCTGCCCTTGTAGTACACCA | ||
| SaNAC30 | F: AGTGGTACTTCTTCTCGCCG | qRT-PCR |
| R: CTCGTGCATGATCCAGTTGG | ||
| SaNAC31 | F: GATCGTCTCGCACTACCTCA | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: TTGTCCTTTCCGGTAGCCTT | ||
| SaNAC37 | F: AAGAACGAGTGGGAGAAGGC | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: TAGCTGAGGTCGACGAACAG | ||
| SaNAC38 | F: AGTCTCTCCGTGCTTCAACA | qRT-PCR |
| R: CTCTAGAAGCTCCTGGTCCG | ||
| SaNAC43 | F: CTCCTCCTGGCTAACTCGAC | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: TCCCCACGTTAGGATGATGG | ||
| SaNAC45 | F: GAGGAGCTCATCACGCACTA | qRT-PCR |
| R: AAGATCTCCCTGTCCTTGCC |
Table 1 (Continued)
Primer sequences used in this study"
| 基因名称 | 引物序列(5′→3′) | 引物用途 |
|---|---|---|
| SaNAC46 | F: GGCGAGAAGGAGTGGTACTT | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: CTCGTGCATGATCCAGTTGG | ||
| SaNAC51 | F: GCTCGTCAAATCCTACCTGC | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: TTGGATTTGGCCTCGTTGTG | ||
| SaNAC56 | F: TCGACATGACCACCTCCTAC | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: ATGCTCTGGATGTCGTCGAA | ||
| SaNAC57 | F: GAAGAGCTGGTGGTGCAGTA | qRT-PCR |
| R: CCGGATCGCGAAGAAGTACT | ||
| SaNAC59 | F: CATGATGTTGGACTGGGTGC | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: ATGGAACTGGTGGTGATCGT | ||
| SaNAC60 | F: AGGGCGAGTGGTACTTCTTC | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: CTTCTTGACGCCGATCATGG | ||
| SaACTIN | F: AGGGCAGTTTTCCCTAGCAT | qRT-PCR/RT-PCR |
| R: CTCTCTTGGACTGTGCCTCA | ||
| SaNAC9 | F: TGACCTCGAGACTAGTATGAGTACGGAAGGGTCAGG | 亚细胞定位载体构建 |
| R: AGGTGGAGGTCCCCCGGGCACCTGGTAACCAGCAGCA | ||
| SaNAC49 | F: TGACCTCGAGACTAGTATGGAGATGGAGCAGGATCTC | 亚细胞定位载体构建 |
| R: AGGTGGAGGTCCCCCGGGGTAGAGCAGATTGGCCAGGGT |
Table 2
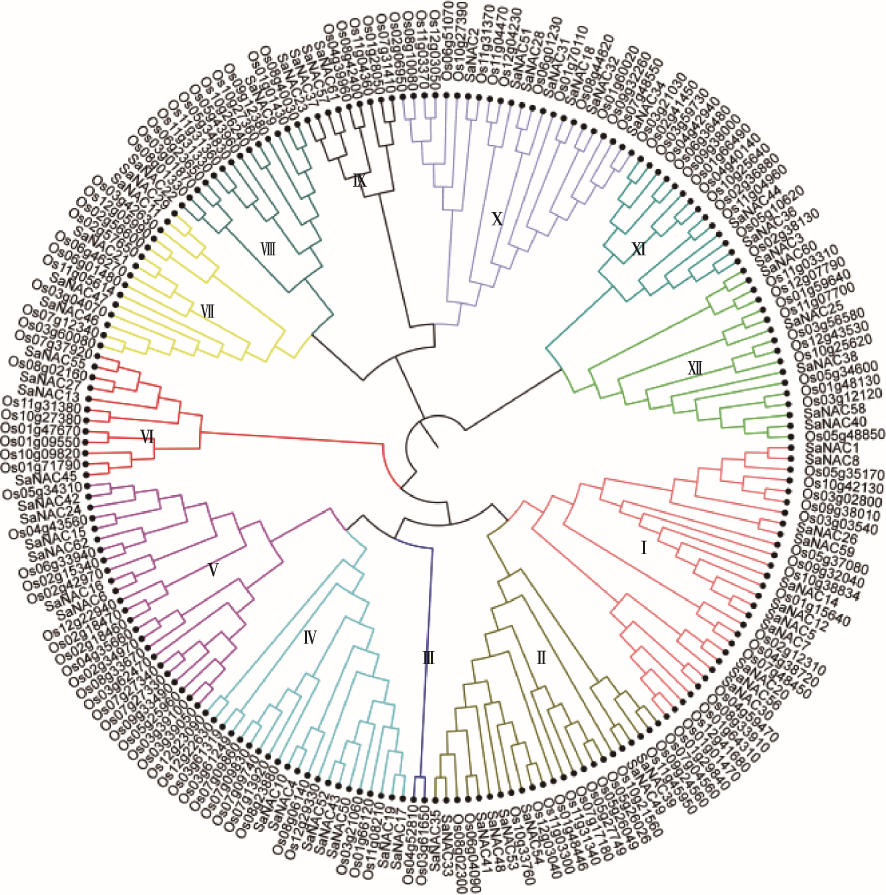
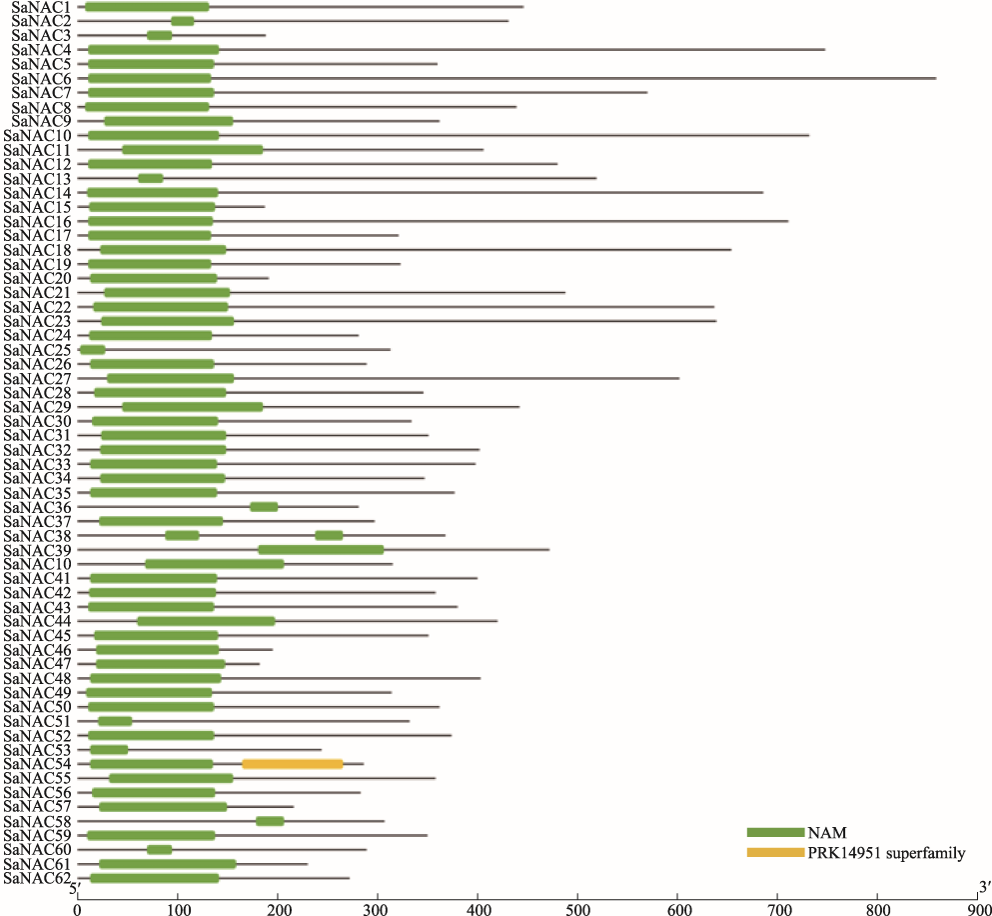
Basic information of Spartina alterniflora NAC proteins"
| 转录本序列号 | 蛋白名称 | 氨基酸数量(aa) | 分子量(kDa) | 等电点 | 预测的蛋白定位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster275-001 | SaNAC1 | 445 | 49.6 | 4.56 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster1229-001 | SaNAC2 | 430 | 61.2 | 4.3 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster1867-001 | SaNAC3 | 187 | 21.4 | 9.91 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster2112-001 | SaNAC4 | 747 | 82.7 | 4.71 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster4261-001 | SaNAC5 | 359 | 39.3 | 5.31 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster4343-001 | SaNAC6 | 858 | 93.2 | 4.47 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster5577-001 | SaNAC7 | 569 | 62.1 | 5.62 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster6349-001 | SaNAC8 | 438 | 48.9 | 4.59 | 细胞核 |
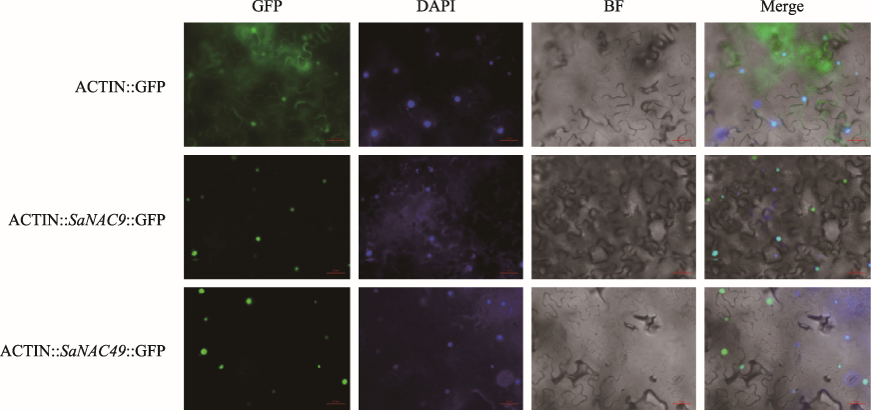
| Cluster7422-001 | SaNAC9 | 361 | 39.1 | 8.93 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster9525-001 | SaNAC10 | 731 | 80.7 | 4.86 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster10144-001 | SaNAC11 | 405 | 45.6 | 8.48 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster12101-001 | SaNAC12 | 479 | 52.8 | 5.8 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster13102-001 | SaNAC13 | 518 | 56 | 5.55 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster14225-001 | SaNAC14 | 685 | 75.8 | 4.85 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster15400-004 | SaNAC15 | 186 | 21.2 | 9.57 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster15711-001 | SaNAC16 | 710 | 77.7 | 4.61 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster16418-001 | SaNAC17 | 320 | 34.8 | 5.92 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster17526-001 | SaNAC18 | 653 | 71.4 | 4.73 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster17869-001 | SaNAC19 | 322 | 35.2 | 6.01 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster18322-001 | SaNAC20 | 190 | 21.5 | 9.94 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster18506-001 | SaNAC21 | 487 | 53.4 | 4.46 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster18550-001 | SaNAC22 | 636 | 69.1 | 4.53 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster18579-001 | SaNAC23 | 638 | 69.4 | 4.5 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster19615-001 | SaNAC24 | 280 | 31.2 | 8.74 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster20092-001 | SaNAC25 | 312 | 34.2 | 4 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster20280-001 | SaNAC26 | 288 | 31.9 | 6.92 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster21221-001 | SaNAC27 | 601 | 67 | 5.76 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster23463-001 | SaNAC28 | 345 | 39.8 | 6.25 | 细胞核 |
Table 2 (Continued)
Basic information of Spartina alterniflora NAC proteins"
| 转录本序列号 | 蛋白名称 | 氨基酸数量(aa) | 分子量(kDa) | 等电点 | 预测的蛋白定位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster24200-001 | SaNAC29 | 441 | 49.8 | 7.43 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster24596-001 | SaNAC30 | 333 | 36.5 | 5.75 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster24844-001 | SaNAC31 | 350 | 38.6 | 5.97 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster24971-001 | SaNAC32 | 401 | 43.7 | 6.2 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster25024-001 | SaNAC33 | 397 | 42.6 | 6.39 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster25479-001 | SaNAC34 | 346 | 38.2 | 6.03 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster25519-001 | SaNAC35 | 376 | 40.4 | 6.27 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster25968-001 | SaNAC36 | 280 | 31.7 | 7.62 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster26335-001 | SaNAC37 | 296 | 33.3 | 5.84 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster26479-001 | SaNAC38 | 367 | 40.3 | 8.97 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster26810-001 | SaNAC39 | 471 | 53 | 8.25 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster26901-001 | SaNAC40 | 314 | 34.7 | 8.68 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster27315-001 | SaNAC41 | 399 | 43.3 | 6.59 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster27759-001 | SaNAC42 | 357 | 40 | 5.59 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster27876-001 | SaNAC43 | 379 | 41 | 8.26 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster27938-001 | SaNAC44 | 419 | 46.8 | 5.18 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster28031-001 | SaNAC45 | 350 | 37.8 | 6.4 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster28253-001 | SaNAC46 | 194 | 21.7 | 9.97 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster28923-001 | SaNAC47 | 181 | 20.1 | 10.4 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster28941-001 | SaNAC48 | 402 | 44.1 | 6.12 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster28982-001 | SaNAC49 | 313 | 35.2 | 6.72 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster29067-001 | SaNAC50 | 361 | 40.2 | 6.79 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster29514-001 | SaNAC51 | 331 | 35.6 | 6.12 | 细胞外 |
| Cluster29630-001 | SaNAC52 | 373 | 40.5 | 8.26 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster29846-001 | SaNAC53 | 243 | 26.8 | 9.78 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster30123-001 | SaNAC54 | 285 | 31.3 | 8.43 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster30128-001 | SaNAC55 | 357 | 39.5 | 9.36 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster30156-001 | SaNAC56 | 282 | 31.5 | 8.69 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster30326-001 | SaNAC57 | 215 | 23.2 | 9.96 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster30465-001 | SaNAC58 | 306 | 33.9 | 8.63 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster30667-001 | SaNAC59 | 349 | 38.8 | 6.35 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster30676-001 | SaNAC60 | 288 | 31.7 | 8.92 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster31570-001 | SaNAC61 | 229 | 24.4 | 10.15 | 细胞核 |
| Cluster32036-001 | SaNAC62 | 271 | 30.6 | 7.03 | 细胞核 |
| [1] |
Zhu JK . Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell, 2016,167(2):313-324.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.029 pmid: 27716505 |
| [2] | Anumalla M, Roychowdhury R, Geda CK, Bharathkumar S, Goutam KD, Dev TSSM . Mechanism of stress signal transduction and involvement of stress inducible transcription factors and genes in response to abiotic stresses in plants. Int J Sci Res, 2016,7(8):12754-12771. |
| [3] |
Khan SA, Li MZ, Wang SM, Yin HJ . Revisiting the role of plant transcription factors in the battle against abiotic stress. Int J Mol Sci, 2018,19(6):E1634.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19061634 pmid: 29857524 |
| [4] |
Aida M, Ishida T, Fukaki H, Fujisawa H, Tasaka M . Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: an analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant. Plant Cell, 1997,9(6):841-857.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.6.841 pmid: 9212461 |
| [5] |
Ooka H, Satoh K , Doi K, Nagata T, Otomo Y, Murakami K, Matsubara K, Osato N, Kawai J, Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y, Suzuki K, Kojima K, Takahara Y, Yamamoto K, Kikuchi S. Comprehensive analysis of NAC family genes in Oryza sativa# and Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res, 2003,10(6):239-247.
doi: 10.1093/dnares/10.6.239 pmid: 15029955 |
| [6] |
Sablowski RW, Meyerowitz EM . A homolog of NO APICAL MERISTEM is an immediate target of the floral homeotic genes APETALA3/PISTILLATA. Cell, 1998,92(1):93-103.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80902-2 pmid: 9489703 |
| [7] |
Wang TZ, Liu M, Zhao MG, Chen R, Zhang WH . Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs involved in osmotic and salt stress in Medicago Truncatula using genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol, 2015,15:131.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0530-5 pmid: 26048392 |
| [8] |
Kim HJ, Nam HG, Lim PO . Regulatory network of NAC transcription factors in leaf senescence. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2016,33:48-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2016.06.002 pmid: 27314623 |
| [9] |
Park J, Kim YS, Kim SG, Jung JH, Woo JC, Park CM . Integration of auxin and salt signals by the NAC transcription factor NTM2 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2011,156(2):537-549.
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.177071 |
| [10] |
Sun LJ, Li DY, Zhang HJ, Song FM . Functions of NAC transcription factors in biotic and abiotic stress responses in plants. Hereditas(Beijing), 2012,34(8):993-1002.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2012.00993 |
|
孙利军, 李大勇, 张慧娟, 宋凤鸣 . NAC转录因子在植物抗病和抗非生物胁迫反应中的作用. 遗传, 2012,34(8):993-1002.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2012.00993 |
|
| [11] |
Mao XG, Chen SS, Li A, Zhai CC, Jing RL . Novel NAC transcription factor TaNAC67 confers enhanced multi-abiotic stress tolerances in Arabidopsis. PLoS One, 2014,9(1):e84359.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084359 pmid: 24427285 |
| [12] |
Mao XG, Zhang HY, Qian XY, Li A, Zhao GY, Jing RL . TaNAC2, a NAC-type wheat transcription factor conferring enhanced multiple abiotic stress tolerances in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot, 2012,63(8):2933-2946.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/err462 |
| [13] |
Zhang LN, Zhang LC, Xia C, Zhao GY, Jia JZ, Kong XY . The novel wheat transcription factor TaNAC47 enhances multiple abiotic stress tolerances in transgenic plants. Front Plant Sci, 2015,6:1174.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01174 pmid: 26834757 |
| [14] |
Wang LQ, Li Z, Lu MZ, Wang YC . ThNAC13, a NAC transcription factor from Tamarix hispida, confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance to transgenic Tamarix and Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci, 2017,8:635.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00635 pmid: 28491072 |
| [15] |
Nuruzzaman M, Manimekalai R, Sharoni AM, Satoh K, Kondoh H, Ooka H, Kikuchi S . Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Gene, 2010,465(1-2):30-44.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.06.008 pmid: 20600702 |
| [16] |
Sun H, Hu ML, Li JY, Chen L, Li M, Zhang SQ, Zhang XL, Yang XY . Comprehensive analysis of NAC transcription factors uncovers their roles during fiber development and stress response in cotton. BMC Plant Biol, 2018,18(1):150.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1367-5 pmid: 30041622 |
| [17] | Ma JH, Tong DD, Zhang WL, Zhang DJ, Shao Y, Yang Y, Jiang L . Identification and analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in Triticum urartu. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016,38(3):243-253. |
| 马建辉, 仝豆豆, 张文利, 张黛静, 邵云, 杨云, 姜丽娜 . 乌拉尔图小麦NAC转录因子的筛选与分析. 遗传, 2016,38(3):243-253. | |
| [18] |
Gong X, Zhao LY, Song XF, Lin ZK, Gu BJ, Yan JX, Zhang SL, Tao ST, Huang XS . Genome-wide analyses and expression patterns under abiotic stress of NAC transcription factors in white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). BMC Plant Biol, 2019,19(1):161.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1760-8 pmid: 31023218 |
| [19] |
Pascual MB, Cánovas FM, Ávila C . The NAC transcription factor family in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster): molecular regulation of two genes involved in stress responses. BMC Plant Biol, 2015,15:254.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0640-0 pmid: 26500018 |
| [20] |
Zhuo XK, Zheng TC, Zhang ZY, Zhang YC, Jiang LB, Ahmad S, Sun DL, Wang J, Cheng TR, Zhang QX . Genome-wide analysis of the NAC transcription factor gene family reveals differential expression patterns and cold-stress responses in the woody plant Prunus mume. Genes, 2018,9(10):494.
doi: 10.3390/genes9100494 pmid: 30322087 |
| [21] |
Rhoads A, Au KF . PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2015,13(5):278-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.08.002 pmid: 26542840 |
| [22] |
Karan R, Subudhi PK . Overexpression of an adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation factor gene from the halophytic grass Spartina alterniflora confers salinity and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep, 2014,33(2):373-384.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-013-1537-8 pmid: 24247851 |
| [23] |
Ye WB, Wang TT, Wei W, Lou ST, Lan FX, Zhu S, Li QZ, Ji GL, Lin CT, Wu XH, Ma LY . The full-length transcriptome of Spartina alterniflora reveals the complexity of high salt tolerance in monocotyledonous halophyte. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2020,DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcaa013.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcaa013 pmid: 32044993 |
| [24] |
Langmead B, Salzberg SL . Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods, 2012,9(4):357-359.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923 pmid: 22388286 |
| [25] |
Li B, Dewey CN . RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics, 2011,12:323.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-323 pmid: 21816040 |
| [26] |
Finkelstein R . Abscisic acid synthesis and response. Arabidopsis Book, 2013,11:e0166.
doi: 10.1199/tab.0166 pmid: 24273463 |
| [27] |
Todaka D, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K . Recent advances in the dissection of drought-stress regulatory networks and strategies for development of drought- tolerant transgenic rice plants. Front Plant Sci, 2015,6:84.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00084 pmid: 25741357 |
| [28] |
Yuan X, Wang H, Cai JT, Bi Y, Li DY, Song FM . Rice NAC transcription factor ONAC066 functions as a positive regulator of drought and oxidative stress response. BMC Plant Biol, 2019,19(1):278.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1883-y pmid: 31238869 |
| [29] |
Huang L, Hong YB, Zhang HJ, Li DY, Song FM . Rice NAC transcription factor ONAC095 plays opposite roles in drought and cold stress tolerance. BMC Plant Biol, 2016,16(1):203.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0897-y pmid: 27646344 |
| [30] |
Hussain RM, Ali M, Feng X, Li X . The essence of NAC gene family to the cultivation of drought-resistant soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) cultivars. BMC Plant Biol, 2017,17(1):55.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1001-y pmid: 28241800 |
| [31] |
Duval M, Hsieh TF, Kim SY, Thomas TL . Molecular characterization of AtNAM: a member of the Arabidopsis NAC domain superfamily. Plant Mol Biol, 2002,50(2):237-248.
doi: 10.1023/a:1016028530943 pmid: 12175016 |
| [32] |
Bedre R, Mangu VR, Srivastava S, Sanchez LE, Baisakh N . Transcriptome analysis of smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora Loisel), a monocot halophyte, reveals candidate genes involved in its adaptation to salinity. BMC Genomics, 2016,17(1):657.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3017-3 pmid: 27542721 |
| [33] |
Lee S, Seo PJ, Lee HJ, Park CM . A NAC transcription factor NTL4 promotes reactive oxygen species production during drought-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2012,70(5):831-844.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04932.x |
| [34] |
Wu YZ, Hou JX, Yu F, Nguyen STT, Mccurdy DW . Transcript profiling Identifies NAC-domain genes involved in regulating wall ingrowth deposition in phloem parenchyma transfer cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci, 2018,9:341.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00341 pmid: 29599795 |
| [35] |
Hussey SG, Mizrachi E, Spokevicius AV, Bossinger G, Berger DK, Myburg AA . SND2, a NAC transcription factor gene, regulates genes involved in secondary cell wall development in Arabidopsis fibres and increases fibre cell area in Eucalyptus. BMC Plant Biol, 2011,11:173.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-173 pmid: 22133261 |
| [36] | Skelding AD, Winterbotham J . The structure and development of the hydathodes of Spartina townsendii Groves. New Phytologist, 1939,38(1):69-79. |
| [37] |
Jyothi-Prakash PA, Mohanty B, Wijaya E, Lim TM, Lin Q, Loh CS, Kumar PP . Identification of salt gland-associated genes and characterization of a dehydrin from the salt secretor mangrove Avicennia officinalis. BMC Plant Biol, 2014,14:291.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0291-6 pmid: 25404140 |
| [38] |
Haak DC, Fukao T, Grene R, Hua Z, Ivanov R, Perrella G, Li S . Multilevel regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. Front Plant Sci, 2017,8:1564.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01564 pmid: 29033955 |
| [39] |
Takasaki H, Maruyama K, Takahashi F, Fujita M, Yoshida T, Nakashima K, Myouga F, Toyooka K, Yamaguchi- Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K . SNAC-As, stress-responsive NAC transcription factors, mediate ABA-inducible leaf senescence. Plant J, 2015,84(6):1114-1123.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13067 pmid: 26518251 |
| [40] |
Liu YC, Sun J, Wu YR . Arabidopsis ATAF1 enhances the tolerance to salt stress and ABA in transgenic rice. J Plant Res, 2016,129(5):955-962.
doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0833-0 pmid: 27216423 |
| [1] | Kai Chen, Hao Wang, Yiting Chen, Ke Fu, Zhigang Han, Cong Li, Jinping Si, Donghong Chen. Functional analysis of WOX family genes in Dendrobium catenatum during growth and development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(8): 700-714. |
| [2] | Feifei Li, Yun Wang, Jihai Gu, Yuming Zhang, Fengsong Liu, Zhihua Ni. E2F family play important roles in tumorigenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(7): 580-592. |
| [3] | Shunze Wang, Feng Jiang, Dongli Zhu, Tie-Lin Yang, Yan Guo. Application of Hi-C technology in three-dimensional genomics research and disease pathogenesis analysis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(4): 279-294. |
| [4] | Fengyu Sun, Qianghua Xu. Research progress of microRNAs involved in hematopoiesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 756-771. |
| [5] | Rongrong Mu, Qingqing Niu, Yuqiang Sun, Jun Mei, Meng Miao. Cloning and characterization of the MYB transcription factor gene GhTT2 in Gossypium hirsutum [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(8): 720-728. |
| [6] | Siyuan Xu, Jia Shou, Qiang Wu. Additional evidence of HS5-1 enhancer eRNA PEARL for protocadherin alpha gene regulation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(8): 695-764. |
| [7] | Shuang Zhang, Shanshan Guo, Ruwen Wang, Renyan Ma, Xianmin Wu, Peijie Chen, Ru Wang. The roles of PARK gene family in myopathy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(7): 545-555. |
| [8] | Yan Zhao, Chenxin Wang, Tianming Yang, Chunshuang Li, Lihong Zhang, Dongni Du, Ruoxi Wang, Jing Wang, Min Wei, Xueqing Ba. Linking oxidative DNA lesion 8-OxoG to tumor development and progression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 466-477. |
| [9] | Qianbin Zhu, Zhicheng Gan, Xiaocui Li, Yingjie Zhang, Heming Zhao, Xianzhong Huang. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic and expression of MAPKKK gene family in Arabidopsis pumila [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(11): 1044-1055. |
| [10] | Cong Zhou, Qiangwei Zhou, Sheng Cheng, Guoliang Li. Research progress of CTCF in mediating 3D genome formation and regulating gene expression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 816-821. |
| [11] | Menggang Lv, Aijia Liu, Qingwei Li, Peng Su. Progress on the origin, function and evolutionary mechanism of RHR transcription factor family [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(3): 215-225. |
| [12] | Haidong Xu, Bolin Ning, Fang Mu, Hui Li, Ning Wang. Advances of functional consequences and regulation mechanisms of alternative cleavage and polyadenylation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(1): 4-15. |
| [13] | Xiaofen Qiu, Dong’e Tang, Haiyan Yu, Qiuyan Liao, Zhiyang Hu, Jun Zhou, Xin Zhao, Huiyan He, Zhuojian Liang, Chengming Xu, Ming Yang, Yong Dai. Analysis of transcription factors in accessible open chromatin in the 18-trisomy syndrome based on single cell ATAC sequencing technique [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(1): 74-83. |
| [14] | Xiaomei Tuo, Dongli Zhu, Xiaofeng Chen, Yu Rong, Yan Guo, Tielin Yang. The osteoporosis susceptible SNP rs4325274 remotely regulates the SOX6 gene through enhancers [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(9): 889-897. |
| [15] | Jie Wu, Jianping Quan, Yong Ye, ZhenFang Wu, Jie Yang, Ming Yang, Enqin Zheng. Advances in assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(4): 333-346. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||