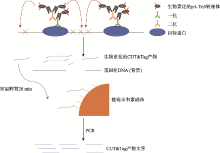
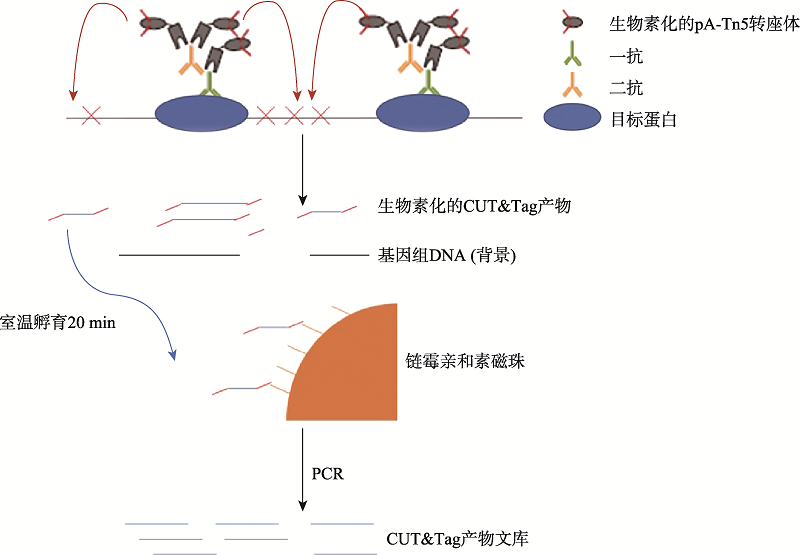
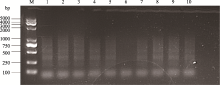
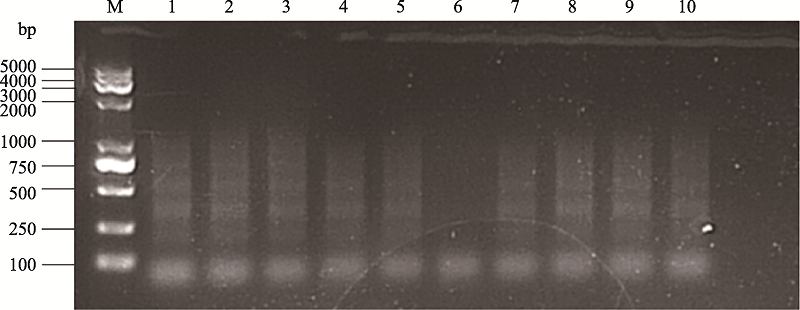
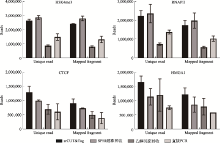
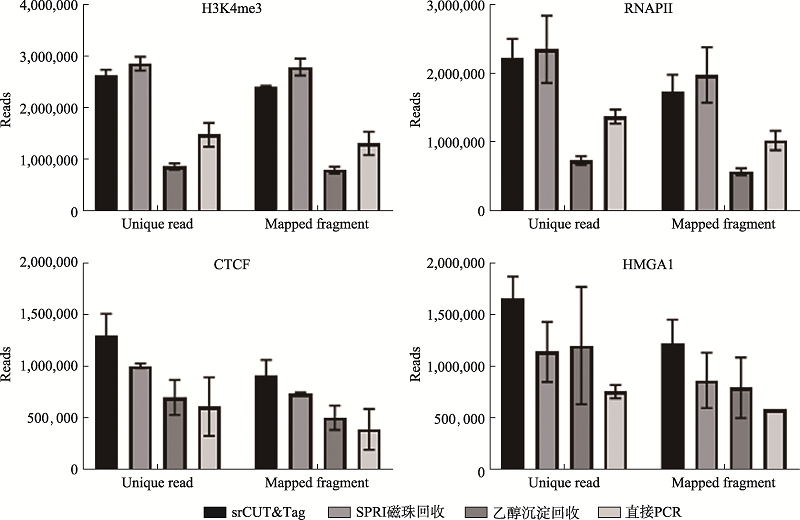
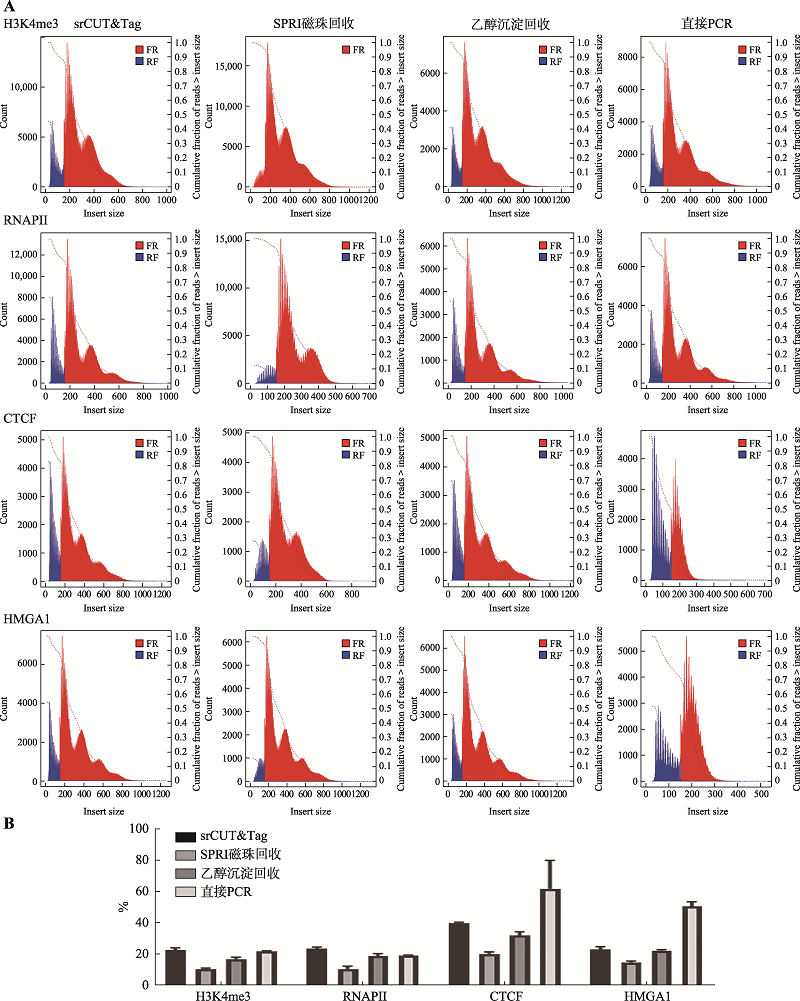
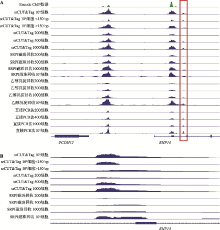
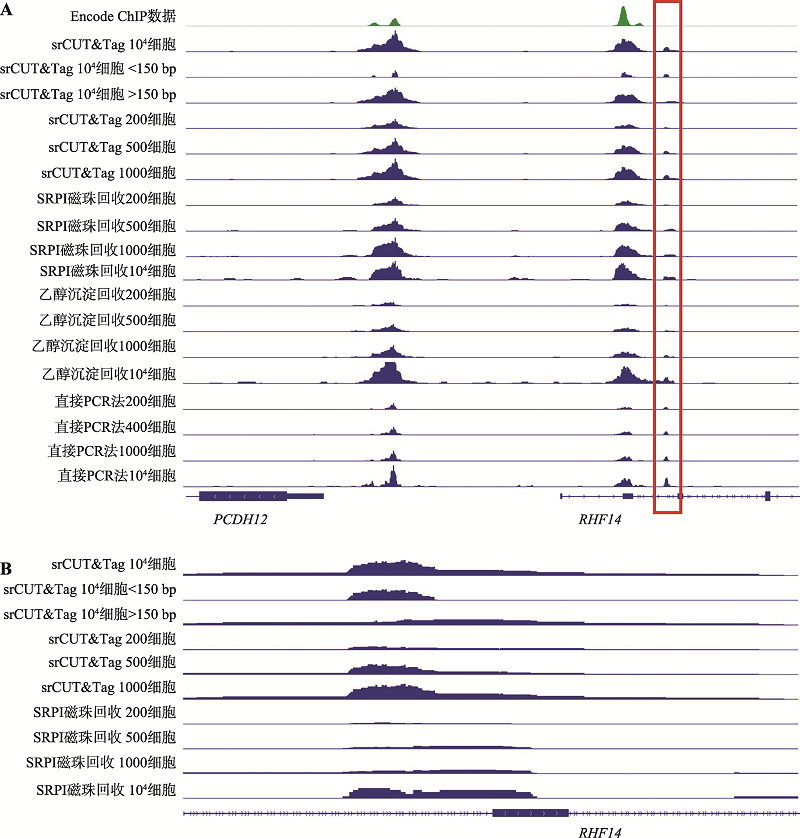
| [1] |
Kidder BL, Hu GQ, Zhao KJ. ChIP-Seq: technical considerations for obtaining high-quality data. Nat Immunol, 2011,12(10):918-922.
doi: 10.1038/ni.2117
pmid: 21934668
|
| [2] |
Policastro RA, Zentner GE. Enzymatic methods for genome-wide profiling of protein binding sites. Brief Funct Genomics, 2018,17(2):138-145.
pmid: 29028882
|
| [3] |
Ludwig CH, Bintu L. Mapping chromatin modifications at the single cell level. Development, 2019,146(12): dev170217.
doi: 10.1242/dev.170217
pmid: 31249006
|
| [4] |
Kaya-Okur HS, Wu SJ, Codomo CA, Pledger ES, Bryson TD, Henikoff JG, Ahmad K, Henikoff S. CUT&Tag for efficient epigenomic profiling of small samples and single cells. Nat Commun, 2019,10(1):1930.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09982-5
pmid: 31036827
|
| [5] |
Douse CH, Tchasovnikarova IA, Timms RT, Protasio AV, Seczynska M, Prigozhin DM, Albecka A, Wagstaff J, Williamson JC, Freund SMV, Lehner PJ, Modis Y. TASOR is a pseudo-PARP that directs HUSH complex assembly and epigenetic transposon control. Nat Commun, 2020,11(1):4940.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18761-6
pmid: 33009411
|
| [6] |
Ye BY, Yang GG, Li YM, Zhang CY, Wang QW, Yu GY. ZNF143 in chromatin looping and gene regulation. Front Genet, 2020,11:338.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00338
pmid: 32318100
|
| [7] |
Janssens DH, Meers MP, Wu SJ, Babaeva E, Meshinchi S, Sarthy JF, Ahmad K, Henikoff S. Automated CUT&Tag profiling of chromatin heterogeneity in mixed-lineage leukemia. bioRxiv, 2020.
doi: 10.1101/2021.03.29.437516
pmid: 33821279
|
| [8] |
Henikoff S, Henikoff JG, Kaya-Okur HS, Ahmad K. Efficient chromatin accessibility mapping in situ by nucleosome-tethered tagmentation. eLife, 2020,9:e63274.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.63274
pmid: 33191916
|
| [9] |
Kaya-Okur HS, Janssens DH, Henikoff JG, Ahmad K, Henikoff S. Efficient low-cost chromatin profiling with CUT&Tag. Nat Protoc, 2020,15(10):3264-3283.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-0373-x
pmid: 32913232
|
| [10] |
Skene PJ, Henikoff JG, Henikoff S. Targeted in situ genome-wide profiling with high efficiency for low cell numbers. Nat Protoc, 2018,13(5):1006-1019.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2018.015
pmid: 29651053
|
| [11] |
Yu FL, Sankaran VG, Yuan GC. CUT&RUNTools 2.0: A pipeline for single-cell and bulk-level CUT&RUN and CUT&Tag data analysis. bioRxiv, 2021.
doi: 10.1101/2021.03.29.437516
pmid: 33821279
|
| [12] |
Tao XY, Feng SL, Zhao T, Guan XY. Efficient chromatin profiling of H3K4me3 modification in cotton using CUT&Tag. Plant Methods, 2020,16:120.
doi: 10.1186/s13007-020-00664-8
pmid: 32884577
|
 ), Huaxing Zhu2,*(
), Huaxing Zhu2,*( )
)