Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 176-183.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-332
• Genetics Teaching • Previous Articles
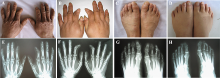
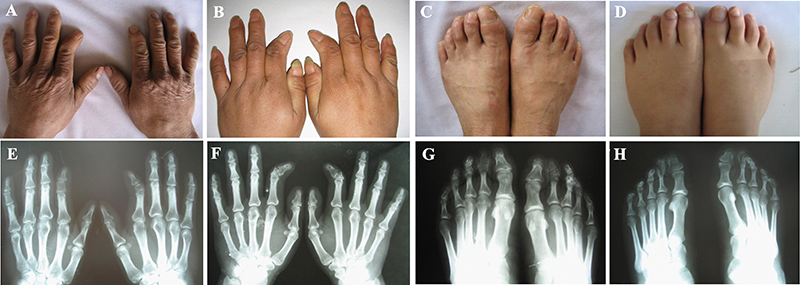
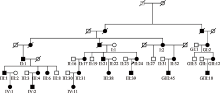
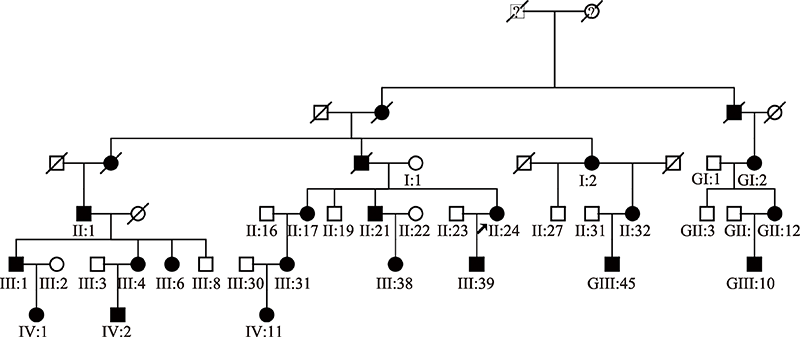
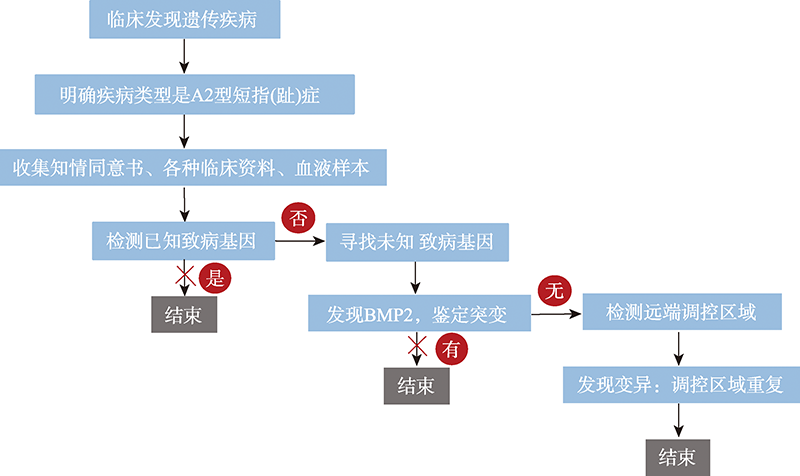
PBL teaching design of medical genetics with the case of brachydactyly type A2
Jie Ma1( ), Lujie Huang1,2, Qiaoxia Zhang1, Yan Zhu2, Lu Qian2(
), Lujie Huang1,2, Qiaoxia Zhang1, Yan Zhu2, Lu Qian2( )
)
- 1. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xi’an Jiaotong University Health Science Center, Xi’an 710061, China
2. Department of Teaching, Xi’an No.3 Hospital, Xi’an 710018, China
-
Received:2022-10-18Revised:2022-12-05Online:2023-02-20Published:2023-01-06 -
Contact:Ma Jie,Qian Lu E-mail:2640933799@qq.com;majie@xjtu.edu.cn -
Supported by:Projects of Medical Education Research in 2018 of the Society of Medical Education of Chinese Medical Association and the Committee of Medical Education of Chinese Higher Education Association(2018B-N02199);Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China(2022JM-440);Project of Xi'an Health Commission(2022ZP10);the National Natural Science Foundation of China(31371298)
Cite this article
Jie Ma, Lujie Huang, Qiaoxia Zhang, Yan Zhu, Lu Qian. PBL teaching design of medical genetics with the case of brachydactyly type A2[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(2): 176-183.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | Yang YL, Luo L, Qian Y, Yang F. Cultivation of undergraduates’ self-regulated learning ability in medical genetics based on PAD class. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(11): 1133-1139. |
| 杨榆玲, 罗兰, 钱源, 杨芳. 对分课堂下本科生医学遗传学自主学习能力的培养. 遗传, 2020, 42(11): 1133-1139. | |
| [2] |
Wang T, Liang L, Zheng MH. Application of formative evaluation and teaching feedback in PBL teaching of medical genetics. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(8): 810-816.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-068 pmid: 32952116 |
|
王涛, 梁亮, 郑敏化. 形成性评价与教学反馈在医学遗传学PBL教学中的应用. 遗传, 2020, 42(8): 810-816.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-068 pmid: 32952116 |
|
| [3] | Chen HM, Dou H, Shen SN, Wang YP. Experimental training of medical genetics based on typical diseases. Chin J Med Edu Res, 2011, 10(2): 236-238. |
| 陈慧梅, 窦环, 沈苏南, 王亚平. 以疾病为主线的医学遗传学实验技能培养. 中华医学教育探索杂志, 2011, 10(2): 236-238. | |
| [4] | Zhou WJ, Yang HY, Xu XM. Creative teaching model of medical genetics. Chin J Med Edu, 2010, 30(3): 366-367. |
| 周万军, 杨海英, 徐湘民. 医学遗传学创新性教学模式的探索. 中华医学教育杂志, 2010, 30(3): 366-367. | |
| [5] |
Zimmerman BJ. A social cognitive view of self-regulated academic learning. J Educ Psychol, 1989, 81(3): 329-339.
doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.81.3.329 |
| [6] |
Temtamy SA, Aglan MS. Brachydactyly. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2008, 3: 15.
doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-3-15 pmid: 18554391 |
| [7] | Temtamy SA, Mckusick VA. The genetics of hand malformations. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser, 1978, 14(3): i-xviii, 1-619. |
| [8] |
Lehmann K, Seemann P, Boergermann J, Morin G, Reif S, Knaus P, Mundlos S.A novel R486Q mutation in BMPR1B resulting in either a brachydactyly type C/symphalangism- like phenotype or brachydactyly type A2. Eur J Hum Genet, 2006, 14(12): 1248-1254.
doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201708 |
| [9] | Mohr OL, Wriedt C.A new type of hereditary brachyphalangy in man. Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington, 1919, 5-64. |
| [10] |
Lehmann K, Seemann P, Stricker S, Sammar M, Meyer B, Süring K, Majewski F, Tinschert S, Grzeschik KH, Müller D, Knaus P, Nürnberg P, Mundlos S.Mutations in bone morphogenetic protein receptor 1b cause brachydactyly type A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(21): 12277-12282.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2133476100 pmid: 14523231 |
| [11] |
Seemann P, Schwappacher R, Kjaer KW, Krakow D, Lehmann K, Dawson K, Stricker S, Pohl J, Plöger F, Staub E, Nickel J, Sebald W, Knaus P, Mundlos S. Activating and deactivating mutations in the receptor interaction site of GDF 5 cause symphalangism or brachydactyly type A2. J Clin Invest, 2005, 115(9): 2373-2381.
pmid: 16127465 |
| [12] |
Kjaer KW, Eiberg H, Hansen L, van der Hagen CB, Rosendahl K, Tommerup N, Mundlos S. A mutation in the receptor binding site of GDF 5 causes Mohr-Wriedt brachydactyly type A2. J Med Genet, 2006, 43(3): 225-231.
pmid: 16014698 |
| [13] |
Plöger F, Seemann P, Schmidt-von Kegler M, Lehmann K, Seidel J, Kjaer KW, Pohl J, Mundlos S. Brachydactyly type A2 associated with a defect in proGDF5 processing. Hum Mol Genet, 2008, 17(9): 1222-1233.
doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn012 pmid: 18203755 |
| [14] |
Dathe K, Kjaer KW, Brehm A, Meinecke P, Nürnberg P, Neto JC, Brunoni D, Tommerup N, Ott CE, Klopocki E, Seemann P, Mundlos S. Duplications involving a conserved regulatory element downstream of BMP 2 are associated with brachydactyly type A2. Am J Hum Genet, 2009, 84(4): 483-492.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.03.001 |
| [15] |
Su PQ, Ding HK, Huang DS, Zhou Y, Huang WJ, Zhong LY, Vyse TJ, Wang YM. A 4.6 kb genomic duplication on 20p12. 2-12.3 is associated with brachydactyly type A 2 in a Chinese family. J Med Genet, 2011, 48(5): 312-316.
doi: 10.1136/jmg.2010.084814 |
| [16] |
Liu XD, Gao LH, Zhao AM, Zhang R, Ji BH, Wang L, Zheng YL, Zeng BF, Valenzuela RK, He L, Ma J. Identification of duplication downstream of BMP2 in a Chinese family with brachydactyly type A2 (BDA2). PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e94201.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094201 |
| [17] |
Wang WB, Jia YC, Zhang Z, Xu J, Zou RT, Kang QL. A novel duplication downstream of BMP2 in a Chinese family with brachydactyly type A2 (BDA2). Gene, 2018, 642: 110-115.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.11.024 |
| [18] |
Chandler RL, Chandler KJ, Mcfarland KA, Mortlock DP. BMP2 transcription in osteoblast progenitors is regulated by a distant 3′ enhancer located 156.3 kilobases from the promoter. Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 27(8): 2934-2951.
pmid: 17283059 |
| [1] | Libin Mei, Yiyuan Zhang, Xianjing Huang, Hong Ji, Pingping Qiu, Lu Ding, Xuemei He, Ping Li. Identification of a pathogenic variant and pre-implantation genetic testing for a Chinese family affected with split-hand/foot malformation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(9): 750-756. |
| [2] | Panhui Tian, Yue Xu, Yongqing Zhang, Tianyun Wang. Genetic diseases are not necessarily inherited: suggestion on its Chinese translation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(9): 673-676. |
| [3] | Hui Li, Ruyi Zhang, Changye Li, Xiaolin Zhang, Qingyin Zheng, Xiuzhen Liu. A case study of Duchenne muscular dystrophy caused by Alu element insertion in DMD gene and analysis of its gray-hair symptoms [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(7): 570-580. |
| [4] | Shujie Liang, Yihua Peng, Jiahong Lei, Aimin Jia, Hong Jiang, Yan Cai. Effect of mutation at c.493T>C locus of transcription factor HNF1α gene on its protein level [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(3): 256-262. |
| [5] | Yang Luan, Xinyue You, Jin Yang. Application of next-generation sequencing in the detection of low-abundance mutations [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(2): 126-139. |
| [6] | Deyang Zhang, Wenchuan Zhou, Jiale Li, Zhepeng Wang. A non-synonymous variant of C21R in the ABCG2 gene is significantly associated with brown eggshell color of Lueyang black-boned chicken [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(12): 1066-1075. |
| [7] | Mao Zhang, Yanyan Wang, Yun Bai, Xuedan Chen, Hong Guo. Investigation on the construction of teaching case base in medical genetics [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(1): 78-87. |
| [8] | Juan Huang, Wenhua Miao, Xiaofeng Guo, Wei Ji. Diagnosis and genetic testing analysis of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2U caused by a compound heterozygous mutation in the ISPD gene [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(6): 536-542. |
| [9] | Yiming Gong, Xiangyu Wang, Xiaoyun He, Yufang Liu, Ping Yu, Mingxing Chu, Ran Di. Progress on the effect of FecB mutation on BMPR1B activity and BMP/SMAD pathway in sheep [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(4): 295-305. |
| [10] | Kai Xia, Fangmei Liu, Yuqing Chen, Shanshan Chen, Chunying Huang, Xuequn Zhao, Ruyi Sha, Jun Huang. Mechanism and evolutionary analysis of Yarrowia lipolytica CA20 capable of producing erythritol with a high yield based on comparative genomics [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(10): 904-921. |
| [11] | Luyang Li, Sunqiang Liu, Yun Shi, Chengcheng Zhao, Hongwen Zhou, Xuqin Zheng. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of a case of hypoglycemia caused by glucokinase gene mutation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 810-818. |
| [12] | Shaozheng Song, Zhengyi He, Yong Cheng, Baoli Yu, Ting Zhang, Dan Li. MSTN modification in goat mediated by TALENs and performance analysis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 531-542. |
| [13] | Qingqing Song, Susu Zhang, Zhen Zhang, Jia Sun, Rui Yang, Jitong Li , Hong Chen. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of 11β -hydroxylase deficiency caused by CYP11B gene mutation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1175-1182. |
| [14] | Siqi Wang, Yang Chen, Kuanhong Luo, Ningjie Shi, Kangli Xiao, Zhenhai Cui, Tianshu Zeng, Huiqing Li. Diagnosis and genetic analysis of a case of Waardenburg syndrome type 2 with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism caused by SOX10 gene deletion [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1158-1166. |
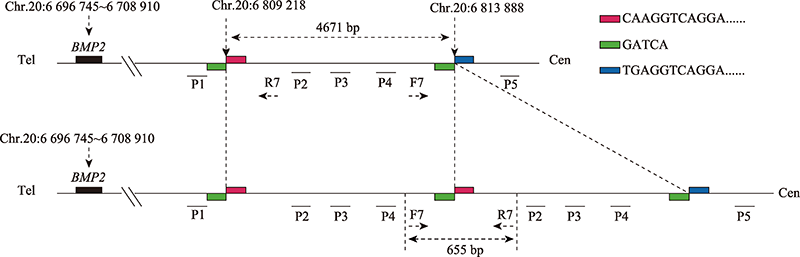
| [15] | Xingqi Wan, Wanzhen Wei, Shengliang Guo, Yixiao Cui, Xueying Jing, Lujie Huang, Jie Ma. Functional analysis of the long-range regulatory element of BMP2 gene [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1141-1147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||