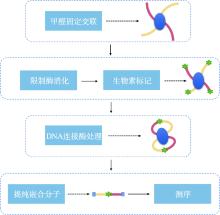
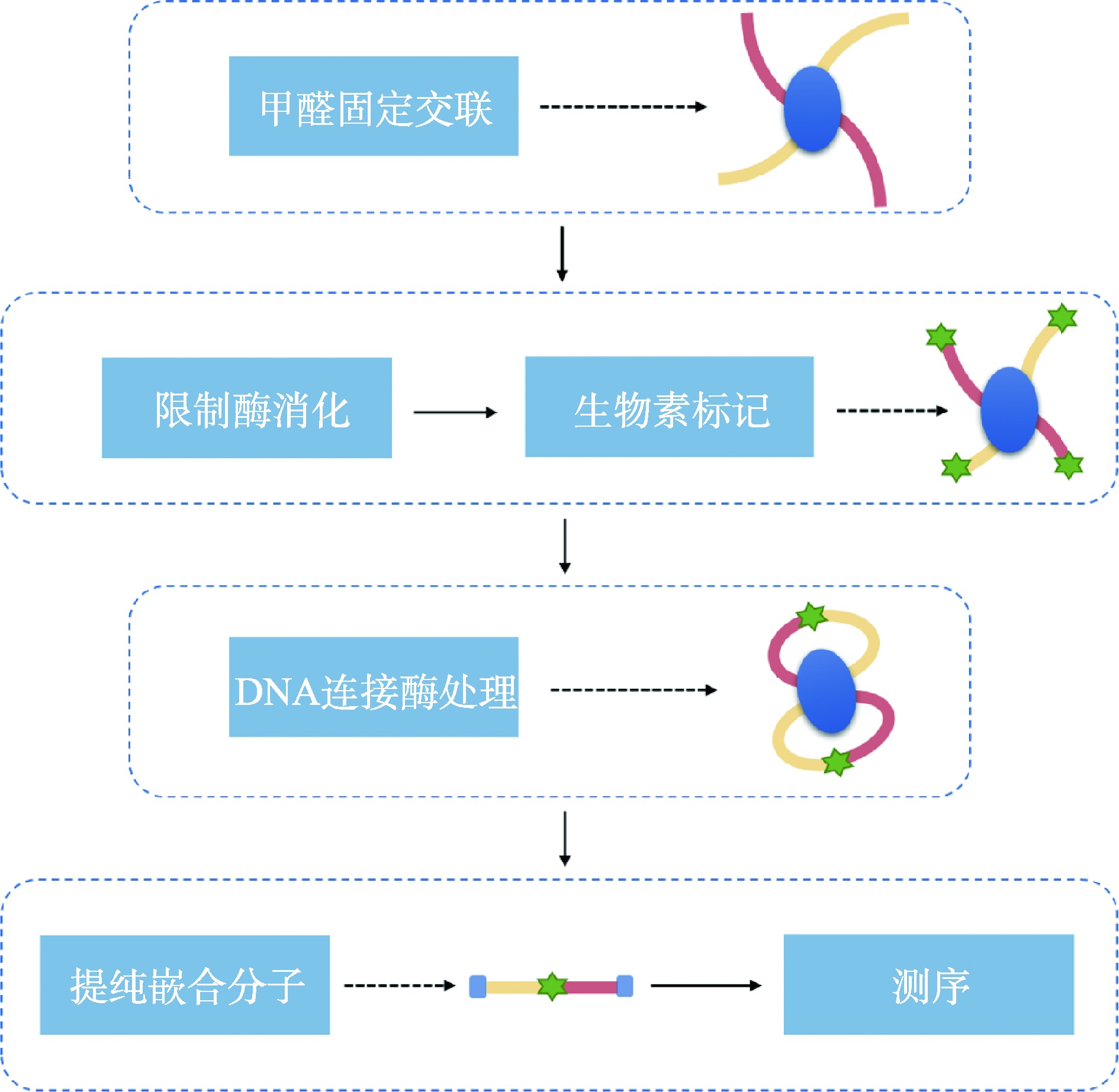
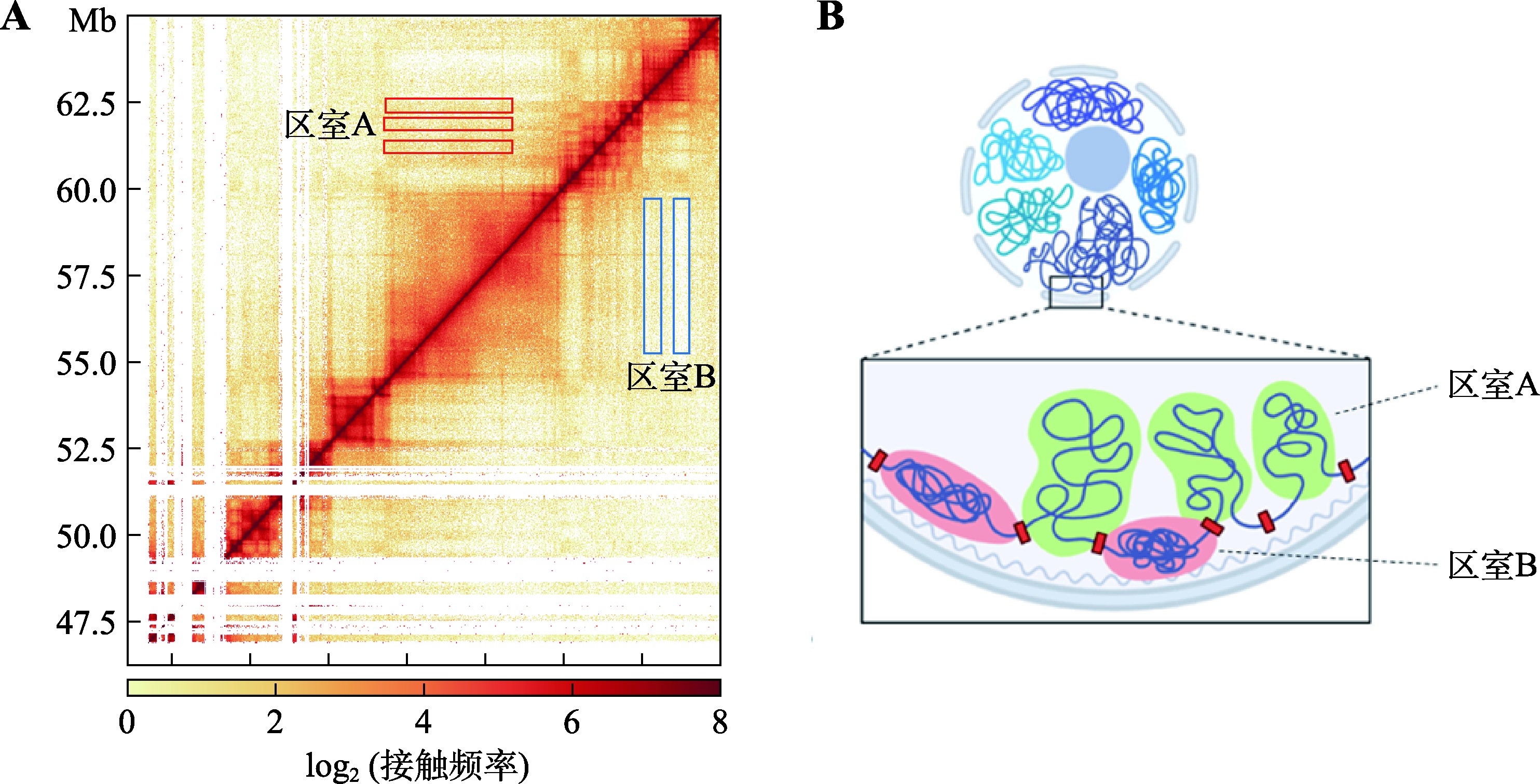
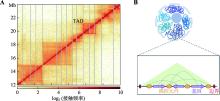
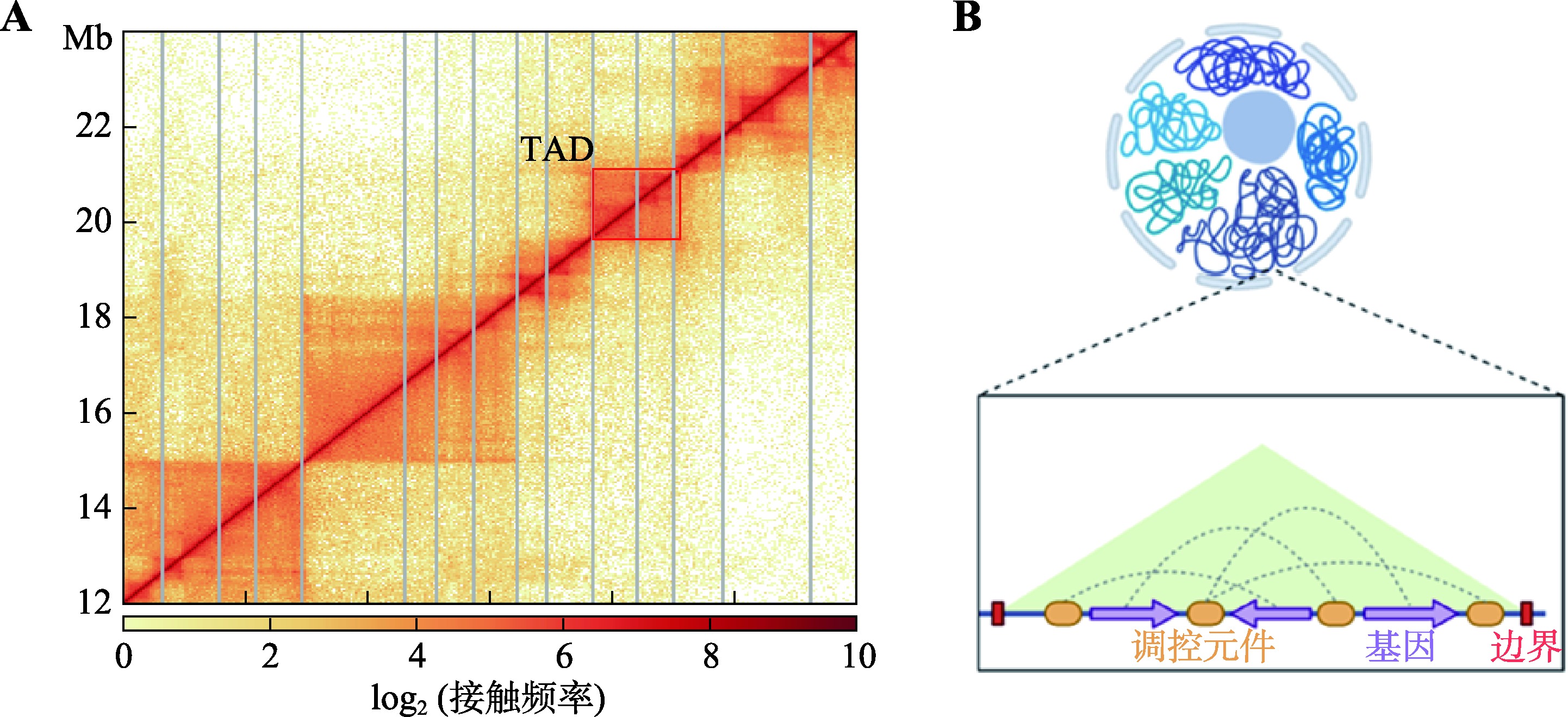
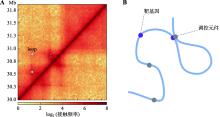
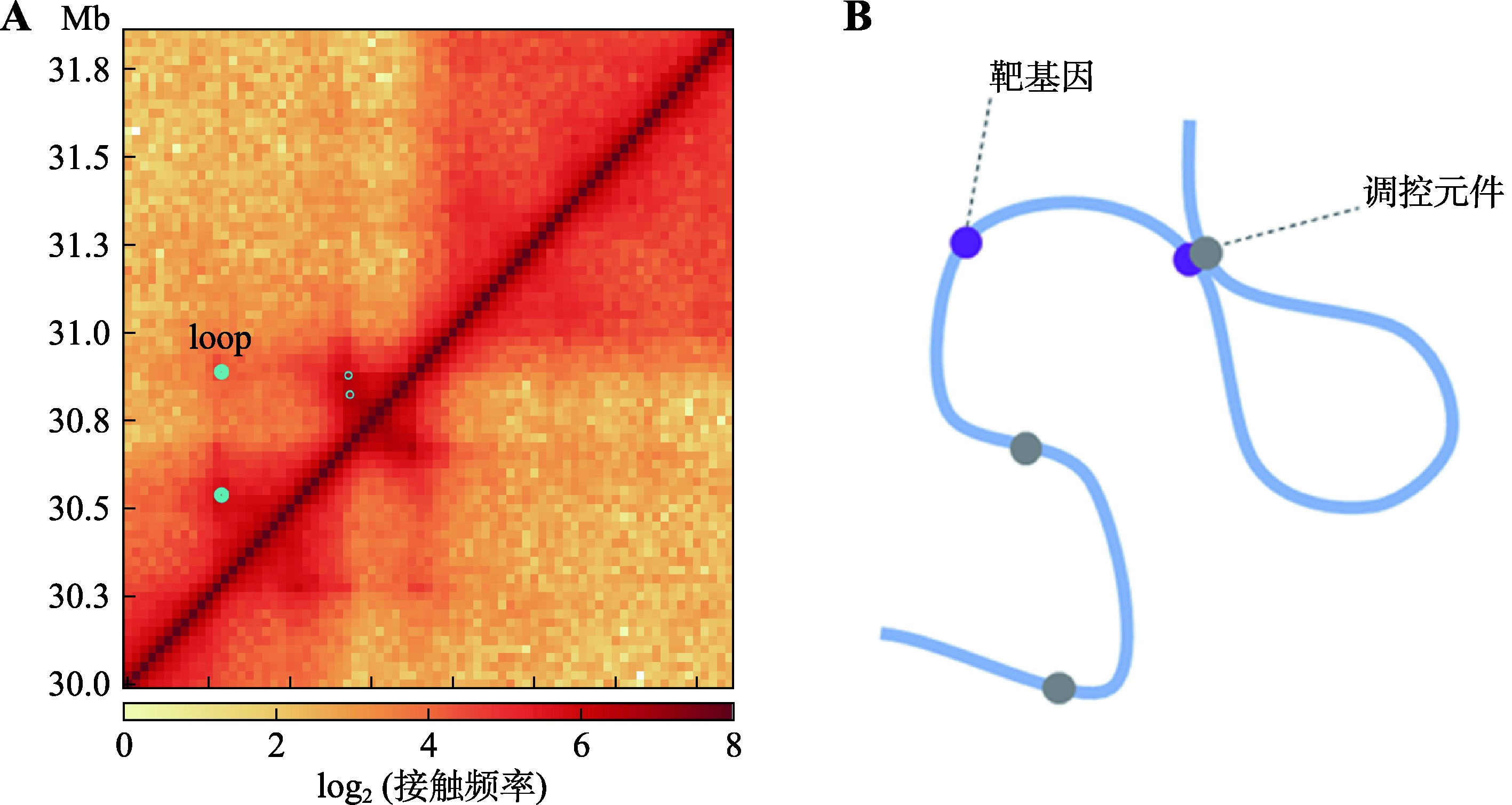
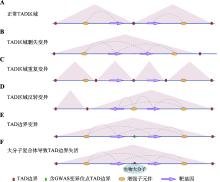
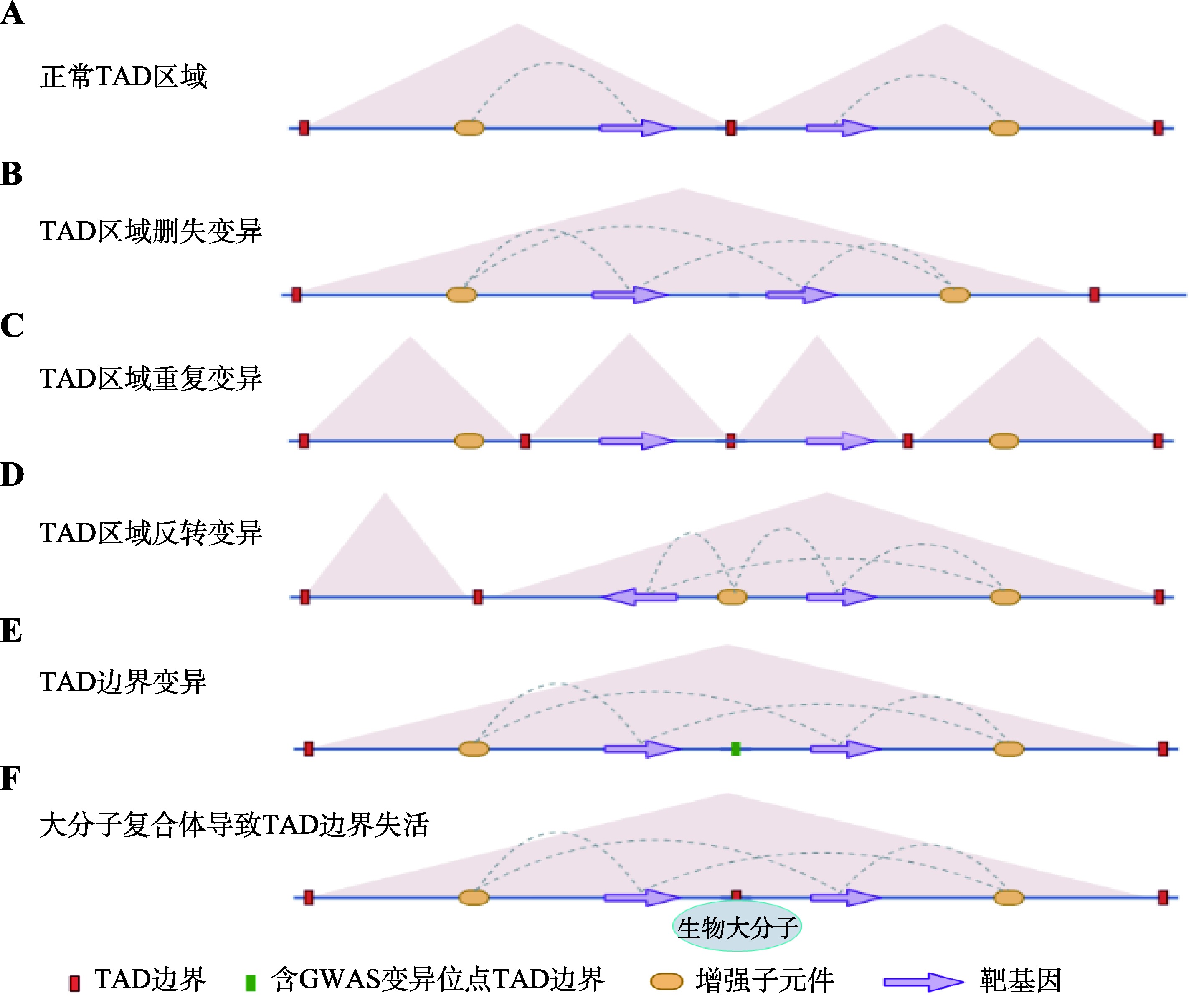
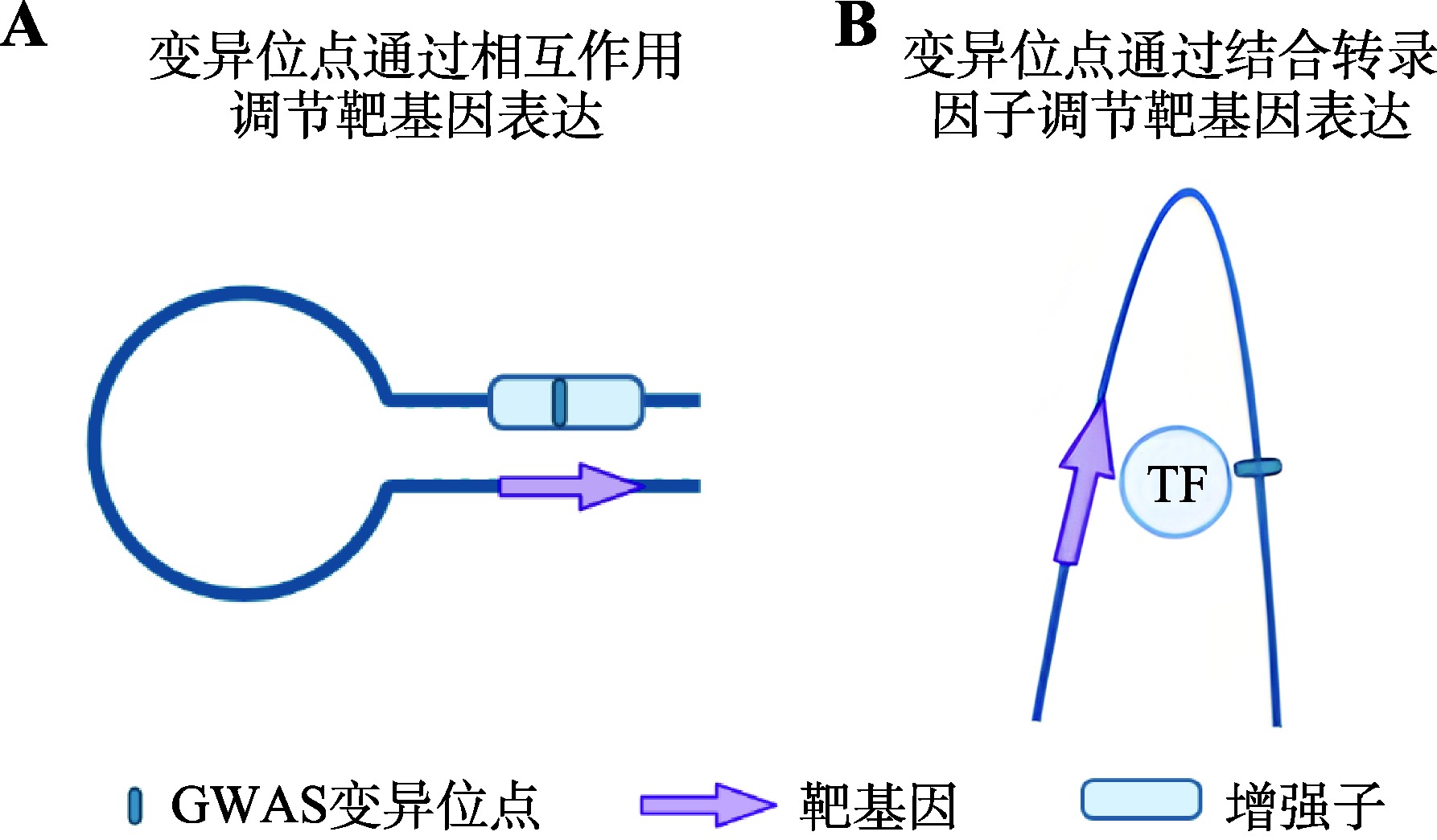
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 279-294.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-390
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of Hi-C technology in three-dimensional genomics research and disease pathogenesis analysis
Shunze Wang( ), Feng Jiang, Dongli Zhu, Tie-Lin Yang, Yan Guo(
), Feng Jiang, Dongli Zhu, Tie-Lin Yang, Yan Guo( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Biomedical Information Engineering of Ministry of Education, Biomedical Informatics & Genomics Center, School of Life Science and Technology, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
-
Received:2022-12-25Revised:2023-02-11Online:2023-04-20Published:2023-02-22 -
Contact:Guo Yan E-mail:nexus169@stu.xjtu.edu.cn;guoyan253@xjtu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(82170896);Innovative Science and Technology Team of Shannxi Province(2022TD-44)
Cite this article
Shunze Wang, Feng Jiang, Dongli Zhu, Tie-Lin Yang, Yan Guo. Application of Hi-C technology in three-dimensional genomics research and disease pathogenesis analysis[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(4): 279-294.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
de Wit E, de Laat W. A decade of 3C technologies: insights into nuclear organization. Gene Dev, 2012, 26(1): 11-24.
doi: 10.1101/gad.179804.111 pmid: 22215806 |
| [2] |
Lieberman-Aiden E, van Berkum NL, Williams L, Imakaev M, Ragoczy T, Telling A, Amit I, Lajoie BR, Sabo PJ, Dorschner MO, Sandstrom R, Bernstein B, Bender MA, Groudine M, Gnirke A, Stamatoyannopoulos J, Mirny LA, Lander ES, Dekker J. Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science, 2009, 326(5950): 289-293.
doi: 10.1126/science.1181369 pmid: 19815776 |
| [3] |
Dekker J, Rippe K, Dekker M, Kleckner N. Capturing chromosome conformation. Science, 2002, 295(5558): 1306-1311.
doi: 10.1126/science.1067799 pmid: 11847345 |
| [4] |
Lyu HQ, Hao LL, Liu EH, Wu ZF, Han JQ, Liu Y. Current status and future perspectives in bioinformatical analysis of Hi-C data. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(1): 87-99.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-163 pmid: 31956099 |
|
吕红强, 郝乐乐, 刘二虎, 吴志芳, 韩九强, 刘源. 基于生物信息学的Hi-C研究现状与发展趋势. 遗传, 2020, 42(1): 87-99.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-163 pmid: 31956099 |
|
| [5] | Zhang XY, He C, Ye BY, Xie DJ, Shi ML, Zhang Y, Shen WL, Li P, Zhao ZH. Optimization and quality control of genome-wide Hi-C library preparation. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(9): 847-855. |
| 张香媛, 何超, 叶丙雨, 谢德健, 师明磊, 张彦, 沈文龙, 李平, 赵志虎. 全基因组染色质相互作用Hi-C文库制备的优化及其质量控制. 遗传, 2017, 39(9): 847-855. | |
| [6] | van Berkum NL, Lieberman-Aiden E, Williams L, Imakaev M, Gnirke A, Mirny LA, Dekker J, Lander ES. Hi-C: a method to study the three-dimensional architecture of genomes. J Vis Exp, 2010, (39): 1869. |
| [7] |
Rao SSP, Huntley MH, Durand NC, Stamenova EK, Bochkov ID, Robinson JT, Sanborn AL, Machol I, Omer AD, Lander ES, Aiden EL. A 3D Map of the Human Genome at Kilobase Resolution Reveals Principles of Chromatin Looping. Cell, 2014, 159(7): 1665-1680.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.021 pmid: 25497547 |
| [8] |
Hong P, Jiang H, Xu W, Lin D, Xu Q, Cao G, Li GL. The DLO Hi-C tool for digestion-ligation-only Hi-C chromosome conformation capture data analysis. Genes (Basel), 2020, 11(3): 289.
doi: 10.3390/genes11030289 |
| [9] |
Kempfer R, Pombo A. Methods for mapping 3D chromosome architecture. Nat Rev Genet, 2020, 21(4): 207-226.
doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0195-2 pmid: 31848476 |
| [10] | Zhang XL, Fang H, Wang XW. The advancement of analysis methods of chromosome conformation capture data. Prog Biochem Biophys, 2018, 45(11): 1093-1105. |
| 张祥林, 方欢, 汪小我. 三维基因组数据分析方法进展. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2018, 45(11): 1093-1105. | |
| [11] |
Jin FL, Li Y, Dixon JR, Selvaraj S, Ye Z, Lee AY, Yen CA, Schmitt AD, Espinoza CA, Ren B. A high-resolution map of the three-dimensional chromatin interactome in human cells. Nature, 2013, 503(7475): 290-294.
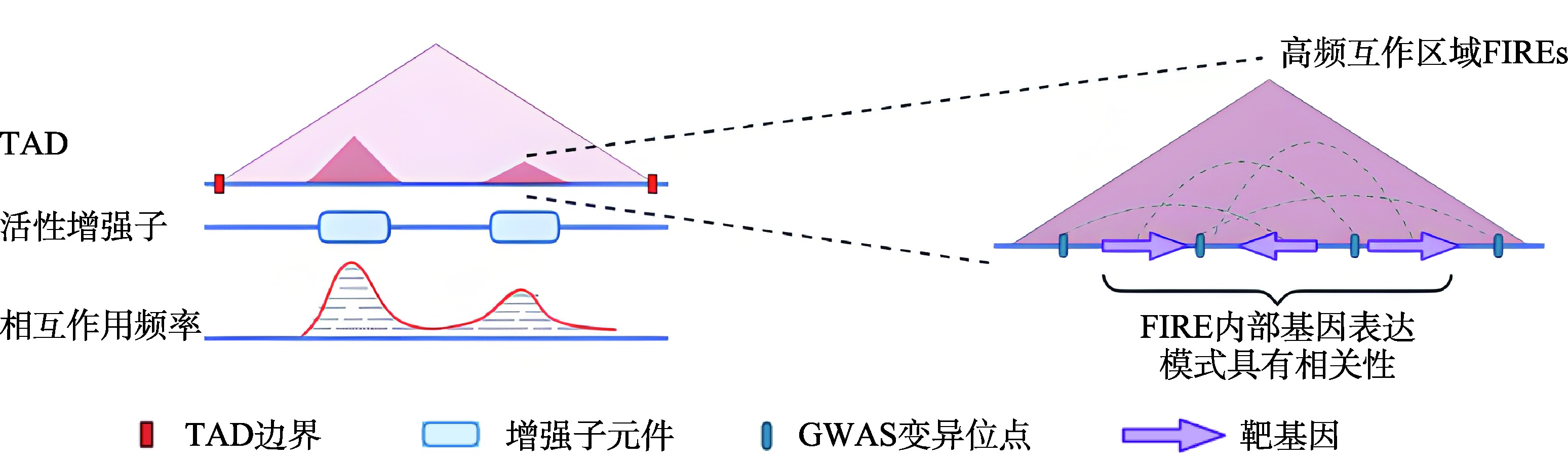
doi: 10.1038/nature12644 |
| [12] |
Dixon JR, Jung I, Selvaraj S, Shen Y, Antosiewicz- Bourget JE, Lee AY, Ye Z, Kim A, Rajagopal N, Xie W, Diao YR, Liang J, Zhao HM, Lobanenkov VV, Ecker JR, Thomson JA, Ren B. Chromatin architecture reorganization during stem cell differentiation. Nature, 2015, 518(7539): 331-336.
doi: 10.1038/nature14222 |
| [13] |
van Steensel B, Belmont AS. Lamina-associated domains: links with chromosome architecture, heterochromatin, and gene repression. Cell, 2017, 169(5): 780-791.
doi: S0092-8674(17)30473-7 pmid: 28525751 |
| [14] |
Bouchard JJ, Otero JH, Scott DC, Szulc E, Martin EW, Sabri N, Granata D, Marzahn MR, Lindorff-Larsen K, Salvatella X, Schulman BA, Mittag T. Cancer mutations of the tumor suppressor SPOP disrupt the formation of active, phase-separated compartments. Mol Cell, 2018, 72(1): 19-36.e8.
doi: S1097-2765(18)30687-7 pmid: 30244836 |
| [15] |
Dekker J, Marti-Renom MA, Mirny LA. Exploring the three-dimensional organization of genomes: interpreting chromatin interaction data. Nat Rev Genet, 2013, 14(6): 390-403.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3454 pmid: 23657480 |
| [16] |
Dixon JR, Selvaraj S, Yue F, Kim A, Li Y, Shen Y, Hu M, Liu JS, Ren B. Topological domains in mammalian genomes identified by analysis of chromatin interactions. Nature, 2012, 485(7398): 376-380.
doi: 10.1038/nature11082 |
| [17] |
Servant N, Varoquaux N, Lajoie BR, Viara E, Chen CJ, Vert JP, Heard E, Dekker J, Barillot E. HiC-Pro: an optimized and flexible pipeline for Hi-C data processing. Genome Biol, 2015, 16: 259.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0831-x pmid: 26619908 |
| [18] |
Durand NC, Shamim MS, Machol I, Rao SS, Huntley MH, Lander ES, Aiden EL. Juicer provides a one-click system for analyzing loop-resolution Hi-C experiments. Cell Syst, 2016, 3(1): 95-98.
doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2016.07.002 pmid: 27467249 |
| [19] | Nora EP, Lajoie BR, Schulz EG, Giorgetti L, Okamoto I, Servant N, Piolot T, van Berkum NL, Meisig J, Sedat J, Gribnau J, Barillot E, Blüthgen N, Dekker J, Heard E. Spatial partitioning of the regulatory landscape of the X-inactivation centre. Nature, 2012, 485(7398): 381-385. |
| [20] |
de Wit E. TADs as the Caller Calls Them. J Mol Biol, 2020, 432(3): 638-642.
doi: S0022-2836(19)30592-3 pmid: 31654669 |
| [21] |
Fudenberg G, Imakaev M, Lu C, Goloborodko A, Abdennur N, Mirny LA. Formation of chromosomal domains by loop extrusion. Cell Rep, 2016, 15(9): 2038-2049.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.085 pmid: 27210764 |
| [22] |
Zhou C, Zhou QW, Cheng S, Li GL. Research progress of CTCF in mediating 3D genome formation and regulating gene expression. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 816-821.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-326 pmid: 34702695 |
|
周聪, 周强伟, 成盛, 李国亮. CTCF在介导三维基因组形成及调控基因表达中的研究进展. 遗传, 2021, 43(9): 816-821.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-326 pmid: 34702695 |
|
| [23] |
Xi W, Beer MA. Loop competition and extrusion model predicts CTCF interaction specificity. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1046.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21368-0 pmid: 33594051 |
| [24] |
Guo Y, Xu Q, Canzio D, Shou J, Li JH, Gorkin DU, Jung I, Wu HY, Zhai YN, Tang YN, Lu YC, Wu YH, Jia ZL, Li W, Zhang MQ, Ren B, Krainer AR, Maniatis T, Wu Q. CRISPR inversion of CTCF sites alters genome topology and enhancer/promoter function. Cell, 2015, 162(4): 900-910.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.038 pmid: 26276636 |
| [25] |
Henderson J, Ly V, Olichwier S, Chainani P, Liu Y, Soibam B. Accurate prediction of boundaries of high resolution topologically associated domains (TADs) in fruit flies using deep learning. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(13): e78.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz315 |
| [26] |
Li MF, Gan JB, Sun Y, Xu ZH, Yang JS, Sun YH, Li C. Architectural proteins for the formation and maintenance of the 3D genome. Sci China Life Sci, 2020, 63(6): 795-810.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-019-1613-3 pmid: 32249389 |
| [27] |
Tang ZH, Luo OJ, Li XW, Zheng MZ, Zhu JJ, Szalaj P, Trzaskoma P, Magalska A, Wlodarczyk J, Ruszczycki B, Michalski P, Piecuch E, Wang P, Wang DJ, Tian SZ, Penrad-Mobayed MM, Sachs LM, Ruan XA, Wei CL, Liu ET, Wilczynski GM, Plewczynski D, Li GL, Ruan YJ. CTCF-mediated human 3D genome architecture reveals chromatin topology for transcription. Cell, 2015, 163(7): 1611-1627.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.024 pmid: 26686651 |
| [28] |
Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E, Lin YC, Laslo P, Cheng JX, Murre C, Singh H, Glass CK. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell, 2010, 38(4): 576-589.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.004 pmid: 20513432 |
| [29] |
Krijger PH, de Laat W. Regulation of disease-associated gene expression in the 3D genome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016, 17(12): 771-782.
doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.138 |
| [30] |
Dixon JR, Xu J, Dileep V, Zhan Y, Song F, Le VT, Yardımcı GG, Chakraborty A, Bann DV, Wang YL, Clark R, Zhang LJ, Yang HB, Liu TT, Iyyanki S, An L, Pool C, Sasaki T, Rivera-Mulia JC, Ozadam H, Lajoie BR, Kaul R, Buckley M, Lee K, Diegel M, Pezic D, Ernst C, Hadjur S, Odom DT, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Hardison RC, Ay F, Noble WS, Dekker J, Gilbert DM, Yue F. Integrative detection and analysis of structural variation in cancer genomes. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(10): 1388-1398.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0195-8 pmid: 30202056 |
| [31] | Du YX, Gu ZT, Li ZZ, Yuan Z, Zhao Y, Zheng XH, Bo XC, Chen HB, Wang CF. Dynamic interplay between structural variations and 3D genome organization in pancreatic cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2022, 9(18): e2200818. |
| [32] |
Northcott PA, Lee C, Zichner T, Stütz AM, Erkek S, Kawauchi D, Shih DJ, Hovestadt V, Zapatka M, Sturm D, Jones DT, Kool M, Remke M, Cavalli FM, Zuyderduyn S, Bader GD, VandenBerg S, Esparza LA, Ryzhova M, Wang W, Wittmann A, Stark S, Sieber L, Seker-Cin H, Linke L, Kratochwil F, Jäger N, Buchhalter I, Imbusch CD, Zipprich G, Raeder B, Schmidt S, Diessl N, Wolf S, Wiemann S, Brors B, Lawerenz C, Eils J, Warnatz HJ, Risch T, Yaspo ML, Weber UD, Bartholomae CC, von Kalle C, Turányi E, Hauser P, Sanden E, Darabi A, Siesjö P, Sterba J, Zitterbart K, Sumerauer D, van Sluis P, Versteeg R, Volckmann R, Koster J, Schuhmann MU, Ebinger M, Grimes HL, Robinson GW, Gajjar A, Mynarek M, von Hoff K, Rutkowski S, Pietsch T, Scheurlen W, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Kulozik AE, von Deimling A, Witt O, Eils R, Gilbertson RJ, Korshunov A, Taylor MD, Lichter P, Korbel JO, Wechsler-Reya RJ, Pfister SM. Enhancer hijacking activates GFI1 family oncogenes in medulloblastoma. Nature, 2014, 511(7510): 428-434.
doi: 10.1038/nature13379 |
| [33] |
Helmsauer K, Valieva ME, Ali S, Chamorro González R, Schöpflin R, Röefzaad C, Bei Y, Dorado Garcia H, Rodriguez-Fos E, Puiggròs M, Kasack K, Haase K, Keskeny C, Chen CY, Kuschel LP, Euskirchen P, Heinrich V, Robson MI, Rosswog C, Toedling J, Szymansky A, Hertwig F, Fischer M, Torrents D, Eggert A, Schulte JH, Mundlos S, Henssen AG, Koche RP. Enhancer hijacking determines extrachromosomal circular MYCN amplicon architecture in neuroblastoma. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5823.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19452-y pmid: 33199677 |
| [34] |
Ooi WF, Nargund AM, Lim KJ, Zhang SL, Xing MJ, Mandoli A, Mandoli A, Lim JQ, Ho SWT, Guo Y, Yao XS, Lin SJ, Nandi T, Xu C, Ong XW, Lee MH, Tan ALK, Lam YN, Teo JX, Kaneda A, White KP, Lim WK, Rozen SG, Teh BT, Li S, Skanderup AJ, Tan P. Integrated paired-end enhancer profiling and whole-genome sequencing reveals recurrent CCNE1 and IGF2 enhancer hijacking in primary gastric adenocarcinoma. Gut, 2020, 69(6): 1039-1052.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317612 |
| [35] |
Barutcu AR, Lajoie BR, McCord RP, Tye CE, Hong D, Messier TL, Browne G, van Wijnen AJ, Lian JB, Stein JL, Dekker J, Imbalzano AN, Stein GS. Chromatin interaction analysis reveals changes in small chromosome and telomere clustering between epithelial and breast cancer cells. Genome Biol, 2015, 16: 214.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0768-0 pmid: 26415882 |
| [36] |
Rosa-Garrido M, Chapski DJ, Schmitt AD, Kimball TH, Karbassi E, Monte E, Balderas E, Pellegrini M, Shih TT, Soehalim E, Liem D, Ping P, Galjart NJ, Ren S, Wang Y, Ren B, Vondriska TM. High-resolution mapping of chromatin conformation in cardiac myocytes reveals structural remodeling of the epigenome in heart failure. Circulation, 2017, 136(17): 1613-1625.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029430 pmid: 28802249 |
| [37] |
Siegenfeld AP, Roseman SA, Roh H, Lue NZ, Wagen CC, Zhou E, Johnstone SE, Aryee MJ, Liau BB. Polycomb-lamina antagonism partitions heterochromatin at the nuclear periphery. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 4199.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31857-5 pmid: 35859152 |
| [38] |
Lupianez DG, Kraft K, Heinrich V, Krawitz P, Brancati F, Klopocki E, Horn D, Kayserili H, Opitz JM, Laxova R, Santos-Simarro F, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Wittler L, Borschiwer M, Haas SA, Osterwalder M, Franke M, Timmermann B, Hecht J, Spielmann M, Visel A, Mundlos S. Disruptions of topological chromatin domains cause pathogenic rewiring of gene-enhancer interactions. Cell, 2015, 161(5): 1012-1025.
doi: S0092-8674(15)00377-3 pmid: 25959774 |
| [39] |
Flavahan WA, Drier Y, Liau BB, Gillespie SM, Venteicher AS, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Suvà ML, Bernstein BE. Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant gliomas. Nature, 2016, 529(7584): 110-114.
doi: 10.1038/nature16490 |
| [40] |
Flavahan WA, Drier Y, Johnstone SE, Hemming ML, Tarjan DR, Hegazi E, Shareef SJ, Javed NM, Raut CP, Eschle BK, Gokhale PC, Hornick JL, Sicinska ET, Demetri GD, Bernstein BE. Altered chromosomal topology drives oncogenic programs in SDH-deficient GISTs. Nature, 2019, 575(7781): 229-233.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1668-3 |
| [41] |
Luo HC, Zhu GQ, Eshelman MA, Fung TK, Lai Q, Wang F, Zeisig BB, Lesperance J, Ma XY, Chen S, Cesari N, Cogle C, Chen BA, Xu B, Yang FC, So CWE, Qiu Y, Xu MJ, Huang SM. HOTTIP-dependent R-loop formation regulates CTCF boundary activity and TAD integrity in leukemia. Mol Cell, 2022, 82(4): 833-851.e11.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.01.014 pmid: 35180428 |
| [42] |
Smemo S, Tena JJ, Kim KH, Gamazon ER, Sakabe NJ, Gómez-Marín C, Aneas I, Credidio FL, Sobreira DR, Wasserman NF, Lee JH, Puviindran V, Tam D, Shen M, Son JE, Vakili NA, Sung HK, Naranjo S, Acemel RD, Manzanares M, Nagy A, Cox NJ, Hui CC, Gomez- Skarmeta JL, Nóbrega MA.Obesity-associated variants within FTO form long-range functional connections with IRX3. Nature, 2014, 507(7492): 371-375.
doi: 10.1038/nature13138 |
| [43] |
Huang JL, Li KL, Cai WQ, Liu X, Zhang YY, Orkin SH, Xu J, Yuan GC. Dissecting super-enhancer hierarchy based on chromatin interactions. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 943.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03279-9 pmid: 29507293 |
| [44] |
Schuijers J, Manteiga JC, Weintraub AS, Day DS, Zamudio AV, Hnisz D, Lee TI, Young RA. Transcriptional dysregulation of MYC reveals common enhancer-docking mechanism. Cell Rep, 2018, 23(2): 349-360.
doi: S2211-1247(18)30401-7 pmid: 29641996 |
| [45] |
Schmitt AD, Hu M, Jung I, Xu Z, Qiu YJ, Tan CL, Tan CL, Li Y, Lin S, Lin Y, Barr CL, Ren B. A compendium of chromatin contact maps reveals spatially active regions in the human genome. Cell Rep, 2016, 17(8): 2042-2059.
doi: S2211-1247(16)31481-4 pmid: 27851967 |
| [46] |
Gorkin DU, Qiu YJ, Hu M, Fletez-Brant K, Liu T, Schmitt AD, Noor A, Chiou J, Gaulton KJ, Sebat J, Li Y, Hansen KD, Ren B. Common DNA sequence variation influences 3-dimensional conformation of the human genome. Genome Biol, 2019, 20(1): 255.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1855-4 pmid: 31779666 |
| [47] | Crowley C, Yang Y, Qiu Y, Hu B, Abnousi A, Lipiński J, Plewczyński D, Wu D, Won H, Ren B, Hu M, Li Y. FIREcaller: detecting frequently interacting regions from Hi-C data. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2021, 19: 355-362. |
| [48] |
Hu B, Won H, Mah W, Park RB, Kassim B, Spiess K, Kozlenkov A, Crowley CA, Pochareddy S, PsychENCODE Consortium, Li Y, Dracheva S, Sestan N, Akbarian S, Geschwind DH. Neuronal and glial 3D chromatin architecture informs the cellular etiology of brain disorders. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 3968.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24243-0 pmid: 34172755 |
| [49] |
Deng W, Shi XH, Tjian R, Lionnet T, Singer RH. CASFISH: CRISPR/Cas9-mediated in situ labeling of genomic loci in fixed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(38): 11870-11875.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515692112 pmid: 26324940 |
| [50] |
Wang HF, Nakamura M, Abbott TR, Zhao DH, Luo KW, Yu C, Nguyen CM, Lo A, Daley TP, La Russa M, Liu YX, Qi LS. CRISPR-mediated live imaging of genome editing and transcription. Science, 2019, 365(6459): 1301-1305.
doi: 10.1126/science.aax7852 pmid: 31488703 |
| [51] |
Guo Y, Perez AA, Hazelett DJ, Coetzee GA, Rhie SK, Farnham PJ. CRISPR-mediated deletion of prostate cancer risk-associated CTCF loop anchors identifies repressive chromatin loops. Genome Biol, 2018, 19(1): 160.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1531-0 pmid: 30296942 |
| [52] |
Ahmed M, Soares F, Xia JH, Yang Y, Li J, Guo HY, Su PR, Tian YJ, Lee HJ, Wang M, Akhtar N, Houlahan KE, Bosch A, Zhou S, Mazrooei P, Hua JT, Chen SJ, Petricca J, Zeng Y, Davies A, Fraser M, Quigley DA, Feng FY, Boutros PC, Lupien M, Zoubeidi A, Wang L, Walsh MJ, Wang T, Ren SC, Wei GH, He HH. CRISPRi screens reveal a DNA methylation-mediated 3D genome dependent causal mechanism in prostate cancer. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1781.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21867-0 pmid: 33741908 |
| [53] |
Fulco CP, Munschauer M, Anyoha R, Munson G, Grossman SR, Perez EM, Kane M, Cleary B, Lander ES, Engreitz JM. Systematic mapping of functional enhancer- promoter connections with CRISPR interference. Science, 2016, 354(6313): 769-773.
doi: 10.1126/science.aag2445 |
| [54] |
Wang HF, Xu XS, Nguyen CM, Liu YX, Gao YC, Lin XQ, Daley T, Kipniss NH, La Russa M, Qi LS. CRISPR- mediated programmable 3D genome positioning and nuclear organization. Cell, 2018, 175(5): 1405-1417.e14.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.013 |
| [1] | Cong Zhou, Qiangwei Zhou, Sheng Cheng, Guoliang Li. Research progress of CTCF in mediating 3D genome formation and regulating gene expression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 816-821. |
| [2] | Weihang Deng, Xinhui Li. Resolving nucleosomal positioning and occupancy with MNase-seq [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(12): 1143-1155. |
| [3] | Hongqiang Lyu, Lele Hao, Erhu Liu, Zhifang Wu, Jiuqiang Han, Yuan Liu. Current status and future perspectives in bioinformatical analysis of Hi-C data [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(1): 87-99. |
| [4] | Qianli Dong, Jinbin Wang, Xiaochong Li, Lei Gong. Progresses in the plant 3D chromatin architecture [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(1): 73-86. |
| [5] | Chunyou Ning,Mengnan He,Qianzi Tang,Qing Zhu,Mingzhou Li,Diyan Li. Advances in mammalian three-dimensional genome by using Hi-C technology approach [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(3): 215-233. |
| [6] | Xiangyuan Zhang,Chao He,Bingyu Ye,Dejian Xie,Minglei Shi,Yan Zhang,Wenlong Shen,Ping Li,Zhihu Zhao. Optimization and quality control of genome-wide Hi-C library preparation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(9): 847-855. |
| [7] | Yajun Liu,Feng Zhang,Hongde Liu,Xiao Sun. The application of next-generation sequencing techniques in studying transcriptional regulation in embryonic stem cells [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(8): 717-725. |
| [8] | Yanan Zhai, Quan Xu, Ya Guo, Qiang Wu. Characterization of a cluster of CTCF-binding sites in a protocadherin regulatory region [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(4): 323-336. |
| [9] | Jinxuan Zhao, Fang Wang, Zhengrong Xu, Yimei Fan. The epigenetic effect on pre-mRNA alternative splicing [J]. HEREDITAS, 2014, 36(3): 248-255. |
| [10] | MENG Ya-Nan, MENG Li-Jun, SONG E-Juan, LIU Mei-Ling, ZHANG Xiu-Jun. Small RNA molecules and regulation of spermatogenesis [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(1): 9-16. |
| [11] | SUN Ye-Ying, DENG Xiao-Jian, LV Yan, DONG Chun-Ling, WANG Ping-Rong, HUANG Xiao-Qun. Progress in Regulation of Rice Wx Gene Expression [J]. HEREDITAS, 2005, 27(6): 1013-1019. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||