Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 859-873.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-180
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Massively parallel reporter assay: a novel technique for analyzing the regulation of gene expression
Meng Yuan1,2,3( ), Hui Li1,2,3, Shouzhi Wang1,2,3(
), Hui Li1,2,3, Shouzhi Wang1,2,3( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Chicken Genetics and Breeding, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Harbin 150030, China
2. Key Laboratory of Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction, Education Department of Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150030, China
3. College of Animal Science and Technology, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
-
Received:2023-07-03Revised:2023-09-30Online:2023-10-20Published:2023-10-07 -
Contact:Shouzhi Wang E-mail:yuanmeng1501@163.com;shouzhiwang@neau.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFF1000201);National Natural Science Foundation of China(31572394);China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA(CARS-41);Joint Guidance Project of Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation(LH2021C036)
Cite this article
Meng Yuan, Hui Li, Shouzhi Wang. Massively parallel reporter assay: a novel technique for analyzing the regulation of gene expression[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(10): 859-873.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
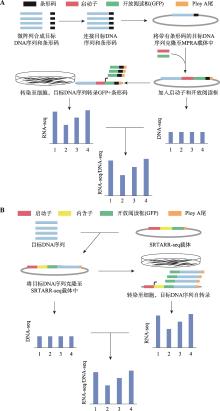
Table 1
Comparison between different MPRA"
| 方法 | 有无条 形码 | 目标序列 来源 | 载体 | 转染方式 | 应用 | 优缺点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规MPRA | 有 | 合成、基因剪切或DNA捕获 | MPRA载体 | 电或化学转染 | 鉴定基因组顺式调控元件、分析转录后调控对表型的影响 | 需要条形码,不会造成测序结果的偏差;实验操作繁琐 | [ |
| AAV MPRA | 有 | DNA捕获 | 腺病毒载体 | 电转染 | 体内分析顺式调控元件活性 | 可将DNA文库转导至体内,开展体内MPRA研究 | [ |
| lentiMPRA | 有 | ChIP-seq | 慢病毒载体 | 化学转染 | 分析调控元件活性 | 用于任何能被慢病毒感染的细胞,扩展MPRA应用范围 | [ |
| patchMPRA | 有 | 公司合成 | pGL4.23载体 | 电转染 | 检测区域染色质和顺式调控元件对基因表达的影响 | 在全基因组范围内研究区域染色质与顺式调控元件对基因表达的影响 | [ |
| scMPRA | 有 | 公司合成 | MPRA载体 | 电或化学转染 | 分析细胞类型和状态对顺式调控元件活性的影响 | 检测具有细胞类型或细胞状态特异性的顺式调控元件;mRNA回收率低 | [ |
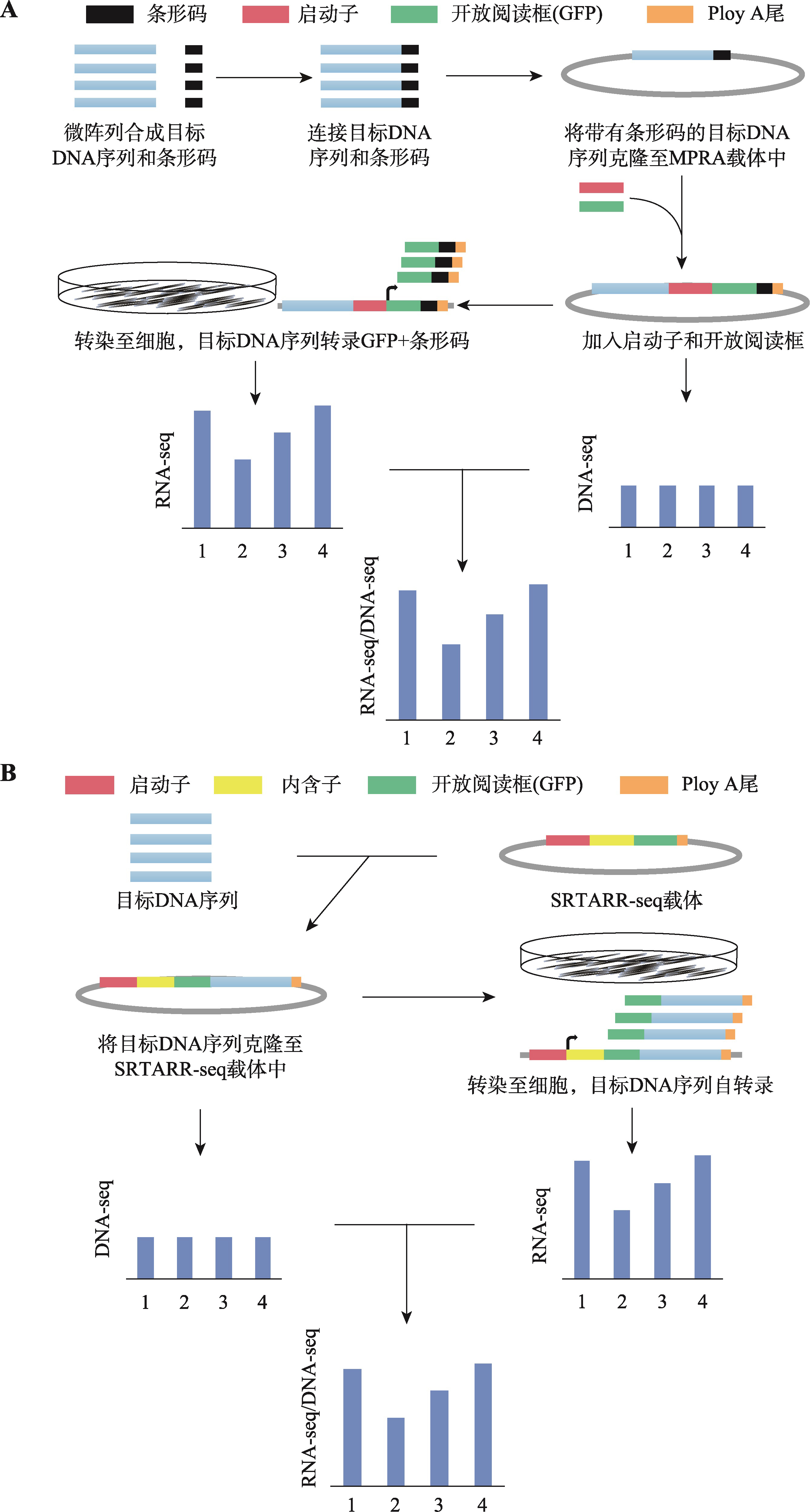
| 常规STARR-seq | 无 | 基因剪切 | STARR-seq载体 | 电或化学转染 | 鉴定增强子和沉默子 | 无条形码序列,可能会造成测序结果的偏差;操作简单 | [ |
| CapSTARR-seq | 无 | 基因剪切 | STARR-seq载体 | 电转染 | 鉴定哺乳动物增强子和沉默子 | 解决了哺乳动物因基因组过于复杂而使文库制备困难和测序深度过深的问题 | [ |
| BiT-STARR-seq | 无 | 公司合成 | pGL4.23载体 | 电转染 | 检测不同等位基因特异性表达 | 反转录引入UMI解决了因文库复杂性而导致的误差 | [ |
| ATAC-STARR-seq | 无 | ATAC-seq | STARR-seq载体 | 电转染 | 检测基因组染色质开放区对转录调控活性 | 可检测来自开放染色质片段的活性;文库比基因剪切的文库具有更高的覆盖率 | [ |
| mSTARR-seq | 无 | 基因剪切 | mSTARR-seq载体 | 化学转染 | 研究DNA甲基化对基因表达的影响 | 在全基因组内高通量检测调控元件甲基化对基因表达的影响 | [ |
Table 2
Comparison of MPRA data analysis techniques"
| 方法 | 原理 | 优缺点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| QuASAR-MPRA | 用β-二项式分布对RNA和DNA读数进行建模 | 考虑了质粒比例的不平衡和测序误差等问题对测序结果的影响,简化了重复试验的统计分析;对等位基因特异性表达以外差异分析具有局限性 | [ |
| mpralm | 基于voom使用线性模型来分析活性差异 | 通用于MPRA活性差异分析,优于目前存在的分析方法 | [ |
| MPRAnalyze | 用图形模型将DNA和RNA读数联系起来,将数据直接建模为结构化数据 | 对DNA和RNA读数中的噪声进行建模,并使用嵌套广义线性模型控制条形码的特异性噪声,并利用条形码的多重性提高统计功效 | [ |
| MPRAflow | 一种基于Nextflow的MPRA数据分析方法,用DNA和mRNA测序结果拟合广义线性模型来分析每个CRE的转录效率 | 操作简单,扩展一些数据分析方法的应用范围 | [ |
| STARRPeaker | 通过负二项回归法精确模拟基础转录率 | 考虑了潜在的干扰因素,如:RNA二级结构、热力学稳定性和文库复杂性等对STARR-seq测序结果的影响 | [ |
| Fast-NR | 通过整合测序读数和图形特征,利用STARR-seq实验产生的数据检测负调控元件 | 用于负调控元件的识别和功能性变异的鉴定 | [ |
| FORECAST | 通过基于最大似然法的推断方法和Flow-seq实验概率模型对实验和分析参数进行系统的探索 | 优化实验设计和数据分析方法 | [ |
| [1] |
Venters BJ, Pugh BF. How eukaryotic genes are transcribed. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol, 2009, 44(2-3): 117-141.
doi: 10.1080/10409230902858785 |
| [2] |
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS. Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet, 2009, 10(3): 155-159.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2521 pmid: 19188922 |
| [3] |
Di Iulio J, Bartha I, Wong EHM, Yu HC, Lavrenko V, Yang DC, Jung I, Hicks MA, Shah N, Kirkness EF, Fabani MM, Biggs WH, Ren B, Venter JC, Telenti A. The human noncoding genome defined by genetic diversity. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(3): 333-337.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0062-7 pmid: 29483654 |
| [4] |
Nord AS, West AE. Neurobiological functions of transcriptional enhancers. Nat Neurosci, 2020, 23(1): 5-14.
doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0538-5 pmid: 31740812 |
| [5] |
Newman A. RNA splicing. Curr Biol, 1998, 8(25): R903-R905.
doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)00005-0 pmid: 9889110 |
| [6] |
Nimmich ML, Heidelberg LS, Fisher JL. RNA editing of the GABA(A) receptor alpha3 subunit alters the functional properties of recombinant receptors. Neurosci Res, 2009, 63(4): 288-293.
doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2009.01.003 pmid: 19367790 |
| [7] |
Shi YG. Mechanistic insights into precursor messenger RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18(11): 655-670.
doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.86 |
| [8] |
Corbett AH. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression and human disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2018, 52: 96-104.
doi: S0955-0674(17)30153-9 pmid: 29518673 |
| [9] |
Rosenberg AB, Patwardhan RP, Shendure J, Seelig G. Learning the sequence determinants of alternative splicing from millions of random sequences. Cell, 2015, 163(3): 698-711.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.054 pmid: 26496609 |
| [10] |
Choudhury M, Fu T, Amoah K, Jun HI, Chan TW, Park S, Walker DW, Bahn JH, Xiao XS. Widespread RNA hypoediting in schizophrenia and its relevance to mitochondrial function. Sci Adv, 2023, 9(14): eade9997.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade9997 |
| [11] |
Rabani M, Pieper L, Chew GL, Schier AF. A massively parallel reporter assay of 3′UTR sequences identifies in vivo rules for mRNA degradation. Mol Cell, 2017, 68(6): 1083-1094.e5.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.11.014 |
| [12] |
Lu XM, Chen XT, Forney C, Donmez O, Miller D, Parameswaran S, Hong T, Huang YB, Pujato M, Cazares T, Miraldi ER, Ray JP, de Boer CG, Harley JB, Weirauch MT, Kottyan LC. Global discovery of lupus genetic risk variant allelic enhancer activity. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1611.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21854-5 pmid: 33712590 |
| [13] |
Abell NS, DeGorter MK, Gloudemans MJ, Greenwald E, Smith KS, He ZH, Montgomery SB. Multiple causal variants underlie genetic associations in humans. Science, 2022, 375(6586): 1247-1254.
doi: 10.1126/science.abj5117 pmid: 35298243 |
| [14] |
Wang WJ, Li YD, Li ZW, Wang N, Xiao F, Gao HH, Guo HS, Li H, Wang SZ. Polymorphisms of KLF3 gene coding region and identification of their functionality for abdominal fat in chickens. Vet Med Sci, 2021, 7(3): 792-799.
doi: 10.1002/vms3.422 pmid: 33369233 |
| [15] |
Li Z, Liu X, Li Y, Wang W, Wang N, Xiao F, Gao H, Guo H, Li H, Wang S. Chicken C/EBPζ gene: expression profiles, association analysis, and identification of functional variants for abdominal fat. Domest Anim Endocrinol, 2021, 76: 106631.
doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2021.106631 |
| [16] |
Chatterjee S, Ahituv N. Gene regulatory elements, major drivers of human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet, 2017, 18: 45-63.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091416-035537 pmid: 28399667 |
| [17] |
Cheng BH, Zhang H, Liu C, Chen X, Chen YF, Sun YH, Leng L, Li YM, Luan P, Li H. Functional intronic variant in the retinoblastoma 1 gene underlies broiler chicken adiposity by altering nuclear factor-kB and SRY-related HMG box protein 2 binding sites. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(35): 9727-9737.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01719 |
| [18] |
Araujo AC, Carneiro PLS, Alvarenga AB, Oliveira HR, Miller SP, Retallick K, Brito LF. Haplotype-based single-step GWAS for yearling temperament in American Angus cattle. Genes (Basel), 2021, 13(1): 17.
doi: 10.3390/genes13010017 |
| [19] |
Welter D, MacArthur J, Morales J, Burdett T, Hall P, Junkins H, Klemm A, Flicek P, Manolio T, Hindorff L, Parkinson H. The NHGRI GWAS Catalog, a curated resource of SNP-trait associations. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(Database issue): D1001-D1006.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1229 |
| [20] |
Barrett LW, Fletcher S, Wilton SD. Regulation of eukaryotic gene expression by the untranslated gene regions and other non-coding elements. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2012, 69(21): 3613-3634.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0990-9 pmid: 22538991 |
| [21] |
Tewhey R, Kotliar D, Park DS, Liu B, Winnicki S, Reilly SK, Andersen KG, Mikkelsen TS, Lander ES, Schaffner SF, Sabeti PC. Direct identification of hundreds of expression-modulating variants using a multiplexed reporter assay. Cell, 2016, 165(6): 1519-1529.
doi: S0092-8674(16)30421-4 pmid: 27259153 |
| [22] |
Ulirsch JC, Nandakumar SK, Wang L, Giani FC, Zhang XL, Rogov P, Melnikov A, McDonel P, Do R, Mikkelsen TS, Sankaran VG. Systematic functional dissection of common genetic variation affecting red blood cell traits. Cell, 2016, 165(6): 1530-1545.
doi: S0092-8674(16)30493-7 pmid: 27259154 |
| [23] |
Cooper YA, Teyssier N, Dräger NM, Guo QY, Davis JE, Sattler SM, Yang ZA, Patel A, Wu S, Kosuri S, Coppola G, Kampmann M, Geschwind DH. Functional regulatory variants implicate distinct transcriptional networks in dementia. Science, 2022, 377(6608): eabi8654.
doi: 10.1126/science.abi8654 |
| [24] |
Choi J, Zhang TW, Vu A, Ablain J, Makowski MM, Colli LM, Xu M, Hennessey RC, Yin JH, Rothschild H, Gräwe C, Kovacs MA, Funderburk KM, Brossard M, Taylor J, Pasaniuc B, Chari R, Chanock SJ, Hoggart CJ, Demenais F, Barrett JH, Law MH, Iles MM, Yu K, Vermeulen M, Zon LI, Brown KM. Massively parallel reporter assays of melanoma risk variants identify MX2 as a gene promoting melanoma. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 2718.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16590-1 pmid: 32483191 |
| [25] |
Sample PJ, Wang B, Reid DW, Presnyak V, McFadyen IJ, Morris DR, Seelig G. Human 5′UTR design and variant effect prediction from a massively parallel translation assay. Nat Biotechnol, 2019, 37(7): 803-809.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0164-5 pmid: 31267113 |
| [26] |
Mulvey B, Dougherty JD. Transcriptional-regulatory convergence across functional MDD risk variants identified by massively parallel reporter assays. Transl Psychiatry, 2021, 11(1): 403.
doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01493-6 |
| [27] |
Safra M, Nir R, Farouq D, Slutskin IV, Schwartz S. TRUB1 is the predominant pseudouridine synthase acting on mammalian mRNA via a predictable and conserved code. Genome Res, 2017, 27(3): 393-406.
doi: 10.1101/gr.207613.116 pmid: 28073919 |
| [28] |
Rhine CL, Neil C, Wang J, Maguire S, Buerer L, Salomon M, Meremikwu IC, Kim J, Strande NT, Fairbrother WG. Massively parallel reporter assays discover de novo exonic splicing mutants in paralogs of Autism genes. PLoS Genet, 2022, 18(1): e1009884.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009884 |
| [29] |
Patwardhan RP, Lee C, Litvin O, Young DL, Pe’er D, Shendure J. High-resolution analysis of DNA regulatory elements by synthetic saturation mutagenesis. Nat Biotechnol, 2009, 27(12): 1173-1175.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1589 pmid: 19915551 |
| [30] |
Melnikov A, Murugan A, Zhang XL, Tesileanu T, Wang L, Rogov P, Feizi S, Gnirke A, Callan CG, Kinney JB, Kellis M, Lander ES, Mikkelsen TS. Systematic dissection and optimization of inducible enhancers in human cells using a massively parallel reporter assay. Nat Biotechnol, 2012, 30(3): 271-277.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2137 pmid: 22371084 |
| [31] |
Arnold CD, Gerlach D, Stelzer C, Boryń ŁM, Rath M, Stark A. Genome-wide quantitative enhancer activity maps identified by STARR-seq. Science, 2013, 339(6123): 1074-1077.
doi: 10.1126/science.1232542 pmid: 23328393 |
| [32] |
Vanhille L, Griffon A, Maqbool MA, Zacarias-Cabeza J, Dao LTM, Fernandez N, Ballester B, Andrau JC, Spicuglia S. High-throughput and quantitative assessment of enhancer activity in mammals by CapStarr-seq. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 6905.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7905 pmid: 25872643 |
| [33] |
Shen SQ, Myers CA, Hughes AEO, Byrne LC, Flannery JG, Corbo JC. Massively parallel cis-regulatory analysis in the mammalian central nervous system. Genome Res, 2016, 26(2): 238-255.
doi: 10.1101/gr.193789.115 pmid: 26576614 |
| [34] |
Inoue F, Kircher M, Martin B, Cooper GM, Witten DM, McManus MT, Ahituv N, Shendure J. A systematic comparison reveals substantial differences in chromosomal versus episomal encoding of enhancer activity. Genome Res, 2017, 27(1): 38-52.
doi: 10.1101/gr.212092.116 pmid: 27831498 |
| [35] |
Romero IG, Lea AJ. Leveraging massively parallel reporter assays for evolutionary questions. Genome Biol, 2023, 24(1): 26.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02856-6 pmid: 36788564 |
| [36] |
Kalita CA, Brown CD, Freiman A, Isherwood J, Wen XQ, Pique-Regi R, Luca F. High-throughput characterization of genetic effects on DNA-protein binding and gene transcription. Genome Res, 2018, 28(11): 1701-1708.aa
doi: 10.1101/gr.237354.118 pmid: 30254052 |
| [37] |
Wang XC, He L, Goggin SM, Saadat A, Wang L, Sinnott-Armstrong N, Claussnitzer M, Kellis M. High-resolution genome-wide functional dissection of transcriptional regulatory regions and nucleotides in human. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 5380.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07746-1 pmid: 30568279 |
| [38] |
Lea AJ, Vockley CM, Johnston RA, Del Carpio CA, Barreiro LB, Reddy TE, Tung J. Genome-wide quantification of the effects of DNA methylation on human gene regulation. eLife, 2018, 7: e37513.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.37513 |
| [39] |
Maricque BB, Chaudhari HG, Cohen BA. A massively parallel reporter assay dissects the influence of chromatin structure on cis-regulatory activity. Nat Biotechnol, 2019, 37: 90-95.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.4285 |
| [40] |
Zhao SQ, Hong CKY, Myers CA, Granas DM, White MA, Corbo JC, Cohen BA. A single-cell massively parallel reporter assay detects cell-type-specific gene regulation. Nat Genet, 2023, 55(2): 346-354.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01278-7 pmid: 36635387 |
| [41] |
Liu S, Liu YW, Zhang Q, Wu JY, Liang JB, Yu S, Wei GH, White KP, Wang XY. Systematic identification of regulatory variants associated with cancer risk. Genome Biol, 2017, 18(1): 194.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1322-z pmid: 29061142 |
| [42] |
McAfee JC, Bell JL, Krupa O, Matoba N, Stein JL, Won H. Focus on your locus with a massively parallel reporter assay. J Neurodev Disord, 2022, 14(1): 50.
doi: 10.1186/s11689-022-09461-x pmid: 36085003 |
| [43] |
Jiwaji M, Daly R, Pansare K, McLean P, Yang JL, Kolch W, Pitt AR. The Renilla luciferase gene as a reference gene for normalization of gene expression in transiently transfected cells. BMC Mol Biol, 2010, 11: 103.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-103 pmid: 21194418 |
| [44] | Zheng YJ, VanDusen NJ. Massively parallel reporter assays for high-throughput in vivo analysis of cis-regulatory elements. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis, 2023, 10(4): 144. |
| [45] |
Lee D, Shi MM, Moran J, Wall M, Zhang J, Liu J, Fitzgerald D, Kyono Y, Ma LJ, White KP, Gerstein M. STARRPeaker: uniform processing and accurate identification of STARR-seq active regions. Genome Biol, 2020, 21(1): 298.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02194-x pmid: 33292397 |
| [46] |
Muerdter F, Boryń ŁM, Woodfin AR, Neumayr C, Rath M, Zabidi MA, Pagani M, Haberle V, Kazmar T, Catarino RR, Schernhuber K, Arnold CD, Stark A. Resolving systematic errors in widely used enhancer activity assays in human cells. Nat Methods, 2018, 15(2): 141-149.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4534 pmid: 29256496 |
| [47] |
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S.Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(12): 550.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 |
| [48] |
Law CW, Chen YS, Shi W, Smyth GK. Voom: precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(2): R29.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r29 |
| [49] |
Kalita CA, Moyerbrailean GA, Brown C, Wen XQ, Luca F, Pique-Regi R. QuASAR-MPRA: accurate allele-specific analysis for massively parallel reporter assays. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(5): 787-794.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx598 pmid: 29028988 |
| [50] |
Harvey CT, Moyerbrailean GA, Davis GO, Wen XQ, Luca F, Pique-Regi R. QuASAR: quantitative allele-specific analysis of reads. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(8): 1235-1242.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu802 pmid: 25480375 |
| [51] |
Myint L, Avramopoulos DG, Goff LA, Hansen KD. Linear models enable powerful differential activity analysis in massively parallel reporter assays. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1): 209.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5556-x pmid: 30866806 |
| [52] |
Ashuach T, Fischer DS, Kreimer A, Ahituv N, Theis FJ, Yosef N. MPRAnalyze: statistical framework for massively parallel reporter assays. Genome Biol, 2019, 20(1): 183.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1787-z pmid: 31477158 |
| [53] |
Gordon MG, Inoue F, Martin B, Schubach M, Agarwal V, Whalen S, Feng SY, Zhao JJ, Ashuach T, Ziffra R, Kreimer A, Georgakopoulos-Soares I, Yosef N, Ye CJ, Pollard KS, Shendure J, Kircher M, Ahituv N. lentiMPRA and MPRAflow for high-throughput functional characterization of gene regulatory elements. Nat Protoc, 2020, 15(8): 2387-2412.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-0333-5 pmid: 32641802 |
| [54] |
Di Tommaso P, Chatzou M, Floden EW, Barja PP, Palumbo E, Notredame C.Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nat Biotechnol, 2017, 35(4): 316-319.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3820 pmid: 28398311 |
| [55] |
He N, Wang WJ, Fang C, Tan YJ, Li L, Hou CH. Integration of count difference and curve similarity in negative regulatory element detection. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 818344.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.818344 |
| [56] |
Gilliot PA, Gorochowski TE. Effective design and inference for cell sorting and sequencing based massively parallel reporter assays. Bioinformatics, 2023, 39(5): btad277.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad277 |
| [57] |
Slobodin B, Agami R. Transcription initiation determines its end. Mol Cell, 2015, 57(2): 205-206.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.006 pmid: 25616066 |
| [58] |
Haberle V, Lenhard B. Promoter architectures and developmental gene regulation. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2016, 57: 11-23.
doi: S1084-9521(16)30014-3 pmid: 26783721 |
| [59] |
Lai HY, Zhang ZY, Su ZD, Su W, Ding H, Chen W, Lin H. iProEP: a computational predictor for predicting promoter. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2019, 17: 337-346.
doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.028 |
| [60] |
Kircher M, Xiong CL, Martin B, Schubach M, Inoue F, Bell RJA, Costello JF, Shendure J, Ahituv N. Saturation mutagenesis of twenty disease-associated regulatory elements at single base-pair resolution. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 3583.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11526-w pmid: 31395865 |
| [61] |
Koesterich J, An JY, Inoue F, Sohota A, Ahituv N, Sanders SJ, Kreimer A. Characterization of de novo promoter variants in autism spectrum disorder with massively parallel reporter assays. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(4): 3509.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24043509 |
| [62] |
Jores T, Tonnies J, Wrightsman T, Buckler ES, Cuperus JT, Fields S, Queitsch C. Synthetic promoter designs enabled by a comprehensive analysis of plant core promoters. Nat Plants, 2021, 7(6): 842-855.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00932-y pmid: 34083762 |
| [63] |
Arrowsmith CH, Bountra C, Fish PV, Lee K, Schapira M. Epigenetic protein families: a new frontier for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2012, 11(5): 384-400.
doi: 10.1038/nrd3674 pmid: 22498752 |
| [64] |
Wu YQ, Zhang YD, Liu H, Gao Y, Liu YY, Chen L, Liu L, Irwin DM, Hou CH, Zhou ZY, Zhang YP. Genome-wide identification of functional enhancers and their potential roles in pig breeding. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2022, 13(1): 75.
doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00726-y |
| [65] |
Sun JL, He N, Niu LJ, Huang YZ, Shen W, Zhang YD, Li L, Hou CH. Global quantitative mapping of enhancers in rice by STARR-seq. Genom Proteom Bioinf, 2019, 17(2): 140-153.
doi: S1672-0229(19)30094-4 pmid: 31201999 |
| [66] |
Gilbert W, Müller-Hill B. Isolation of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1966, 56(6): 1891-1898.
pmid: 16591435 |
| [67] |
Ogbourne S, Antalis TM. Transcriptional control and the role of silencers in transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes. Biochem J, 1998, 331(Pt 1): 1-14.
doi: 10.1042/bj3310001 |
| [68] |
Doni Jayavelu N, Jajodia A, Mishra A, Hawkins RD. Candidate silencer elements for the human and mouse genomes. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 1061.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14853-5 pmid: 32103011 |
| [69] | Mouri K, Dewey HB, Castro R, Berenzy D, Kales S, Tewhey R. Whole-genome functional characterization of RE1 silencers using a modified massively parallel reporter assay. Cell Genom, 2022, 3(1): 100234. |
| [70] |
Hussain S, Sadouni N, van Essen D, Dao LTM, Ferré Q, Charbonnier G, Torres M, Gallardo F, Lecellier CH, Sexton T, Saccani S, Spicuglia S. Short tandem repeats are important contributors to silencer elements in T cells. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(10): 4845-4866.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad187 |
| [71] |
Maniatis T, Reed R. An extensive network of coupling among gene expression machines. Nature, 2002, 416(6880): 499-506.
doi: 10.1038/416499a |
| [72] | Kornblihtt AR, Schor IE, Alló M, Dujardin G, Petrillo E, Muñoz MJ. Alternative splicing: a pivotal step between eukaryotic transcription and translation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2013, 14(3): 153-165. |
| [73] |
Irimia M, Blencowe BJ. Alternative splicing: decoding an expansive regulatory layer. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2012, 24(3): 323-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.03.005 pmid: 22465326 |
| [74] | Snyman M, Xu S. The effects of mutations on gene expression and alternative splicing. Proc Biol Sci, 2023, 290(2002): 20230565. |
| [75] |
Qi T, Wu Y, Fang HL, Zhang FT, Liu SY, Zeng J, Yang J. Genetic control of RNA splicing and its distinct role in complex trait variation. Nat Genet, 2022, 54(9): 1355-1363.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01154-4 pmid: 35982161 |
| [76] |
Fabo T, Khavari P. Functional characterization of human genomic variation linked to polygenic diseases. Trends Genet, 2023, 39(6): 462-490.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2023.02.014 |
| [77] |
French JD, Edwards SL. The role of noncoding variants in heritable disease. Trends Genet, 2020, 36(11): 880-891.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2020.07.004 pmid: 32741549 |
| [78] |
Soemedi R, Cygan KJ, Rhine CL, Wang J, Bulacan C, Yang J, Bayrak-Toydemir P, McDonald J, Fairbrother WG. Pathogenic variants that alter protein code often disrupt splicing. Nat Genet, 2017, 49(6): 848-855.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3837 pmid: 28416821 |
| [79] |
Iwanami Y, Brown GM. Methylated bases of ribosomal ribonucleic acid from HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys, 1968, 126(1): 8-15.
pmid: 5671075 |
| [80] | Cantara WA, Crain PF, Rozenski J, McCloskey JA, Harris KA, Zhang XN, Vendeix FAP, Fabris D, Agris PF. The RNA modification database, RNAMDB: 2011 update. Nucleic Acids Res, 2011, 39(Database issue): D195-D201. |
| [81] |
Christofi T, Zaravinos A. RNA editing in the forefront of epitranscriptomics and human health. J Transl Med, 2019, 17(1): 319.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2071-4 pmid: 31547885 |
| [82] |
Walkley CR, Li JB. Rewriting the transcriptome: adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing by ADARs. Genome Biol, 2017, 18(1): 205.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1347-3 pmid: 29084589 |
| [83] |
Hsiao YHE, Bahn JH, Yang Y, Lin XZ, Tran S, Yang EW, Quinones-Valdez G, Xiao XS. RNA editing in nascent RNA affects pre-mRNA splicing. Genome Res, 2018, 28(6): 812-823.
doi: 10.1101/gr.231209.117 |
| [84] |
Brümmer A, Yang Y, Chan TW, Xiao XS. Structure- mediated modulation of mRNA abundance by A-to-I editing. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 1255.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01459-7 pmid: 29093448 |
| [85] |
Bazak L, Haviv A, Barak M, Jacob-Hirsch J, Deng P, Zhang R, Isaacs FJ, Rechavi G, Li JB, Eisenberg E, Levanon EY. A-to-I RNA editing occurs at over a hundred million genomic sites, located in a majority of human genes. Genome Res, 2014, 24(3): 365-376.
doi: 10.1101/gr.164749.113 pmid: 24347612 |
| [86] |
Krestel H, Meier JC. RNA editing and retrotransposons in neurology. Front Mol Neurosci, 2018, 11: 163.
doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00163 pmid: 29875629 |
| [87] |
CRICK FH. On protein synthesis. Symp Soc Exp Biol, 1958, 12: 138-163.
pmid: 13580867 |
| [88] | Araujo PR, Yoon K, Ko D, Smith AD, Qiao M, Suresh U, Burns SC, Penalva LOF. Before it gets started: regulating translation at the 5′UTR. Comp Funct Genomics, 2012, 2012: 475731. |
| [89] |
Mayr C. What are 3′UTRs doing? Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2019, 11(10): a034728.
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034728 |
| [90] |
Zhao WX, Pollack JL, Blagev DP, Zaitlen N, McManus MT, Erle DJ. Massively parallel functional annotation of 3′ untranslated regions. Nat Biotechnol, 2014, 32(4): 387-391.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2851 |
| [91] |
Jia LF, Mao YH, Ji QQ, Dersh D, Yewdell JW, Qian SB. Decoding mRNA translatability and stability from the 5′UTR. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2020, 27(9): 814-821.
doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-0465-x |
| [92] |
Siegel DA, Le Tonqueze O, Biton A, Zaitlen N, Erle DJ.Massively parallel analysis of human 3′UTRs reveals that AU-rich element length and registration predict mRNA destabilization. G3 (Bethesda), 2022, 12(1): jkab404.
doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab404 |
| [93] |
Pratt BM, Won H. Advances in profiling chromatin architecture shed light on the regulatory dynamics underlying brain disorders. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 121: 153-160.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.08.013 |
| [94] |
Dixit A, Parnas O, Li BY, Chen J, Fulco CP, Jerby-Arnon L, Marjanovic ND, Dionne D, Burks T, Raychowdhury R, Adamson B, Norman TM, Lander ES, Weissman JS, Friedman N, Regev A. Perturb-Seq: dissecting molecular circuits with scalable single-cell RNA profiling of pooled genetic screens. Cell, 2016, 167(7): 1853-1866.e17.
doi: S0092-8674(16)31610-5 pmid: 27984732 |
| [95] |
Klein JC, Agarwal V, Inoue F, Keith A, Martin B, Kircher M, Ahituv N, Shendure J. A systematic evaluation of the design and context dependencies of massively parallel reporter assays. Nat Methods, 2020, 17(11): 1083-1091.
doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-0965-y pmid: 33046894 |
| [96] |
Johnson GD, Barrera A, McDowell IC, D’Ippolito AM, Majoros WH, Vockley CM, Wang XY, Allen AS, Reddy TE. Human genome-wide measurement of drug-responsive regulatory activity. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 5317.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07607-x pmid: 30575722 |
| [97] |
Penaud-Budloo M, Le Guiner C, Nowrouzi A, Toromanoff A, Chérel Y, Chenuaud P, Schmidt M, von Kalle C, Rolling F, Moullier P, Snyder RO. Adeno-associated virus vector genomes persist as episomal chromatin in primate muscle. J Virol, 2008, 82(16): 7875-7885.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00649-08 pmid: 18524821 |
| [98] |
Duan D, Sharma P, Yang J, Yue Y, Dudus L, Zhang Y, Fisher KJ, Engelhardt JF. Circular intermediates of recombinant adeno-associated virus have defined structural characteristics responsible for long-term episomal persistence in muscle tissue. J Virol, 1998, 72(11): 8568-8577.
pmid: 9765395 |
| [99] |
Kvon EZ, Zhu YW, Kelman G, Novak CS, Plajzer-Frick I, Kato M, Garvin TH, Pham Q, Harrington AN, Hunter RD, Godoy J, Meky EM, Akiyama JA, Afzal V, Tran S, Escande F, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Jean-Marçais N, Hudaiberdiev S, Ovcharenko I, Dobbs MB, Gurnett CA, Manouvrier-Hanu S, Petit F, Visel A, Dickel DE, Pennacchio LA. Comprehensive in vivo interrogation reveals phenotypic impact of human enhancer variants. Cell, 2020, 180(6): 1262-1271.e15.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.031 |
| [100] |
Hanson-Smith V, Kolaczkowski B, Thornton JW. Robustness of ancestral sequence reconstruction to phylogenetic uncertainty. Mol Biol Evol, 2010, 27(9): 1988-1999.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq081 pmid: 20368266 |
| [1] | Yuanyuan Hao, Xiangqian Zhao, Fudeng Huang, Chunshou Li. The role of PPR proteins in posttranscriptional regulation of organelle components in plants [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(11): 1050-1065. |
| [2] | Haidong Xu, Bolin Ning, Fang Mu, Hui Li, Ning Wang. Advances of functional consequences and regulation mechanisms of alternative cleavage and polyadenylation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(1): 4-15. |
| [3] | Jian Shi,Yanming Li,Xiangdong Fang. The mechanism and clinical significance of long noncoding RNA-mediated gene expression via nuclear architecture [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(3): 189-199. |
| [4] | Chang Lu, Yinhua Huang. Progress in long non-coding RNAs in animals [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(11): 1054-1065. |
| [5] | Xiaoqing Huang,Dandan Li,Juan Wu. Long non-coding RNAs in plants [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(4): 344-359. |
| [6] | Deling Lin, Ying Luo, Yi Song. The post-transcriptional regulation of the DNA damage response [J]. HEREDITAS, 2014, 36(4): 309-318. |
| [7] | XIA Tian, XIAO Bing-Xiu, GUO Jun-Ming. Acting mechanisms and research methods of long noncoding RNAs [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(3): 269-280. |
| [8] | QIN Dan, XU Cun-Shuan. Characterization and identification of functional elements in non-coding DNA sequences [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(11): 1253-1264. |
| [9] | ZHANG Gao-Hua, WANG He, WANG Xu-Da, FENG Ming, LI Huai-Mei, LI Shu-Ying. Isolation of the promoter region of HAK gene from Aeluropus littoralis and functional analysis in rice [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(6): 742-748. |
| [10] | LUO Mao, ZHANG Zhi-Ming, GAO Jian, ZENG Xing, PAN Guang-Tang. The role of miR319 in plant development regulation [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(11): 1203-1211. |
| [11] | . Molecular mechanisms of regulation of estrogen receptor a expression level in breast cancer [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(3): 191-197. |
| [12] | DING Yan-Fei, WANG Guang-Yue, FU E-Ping, SHU Cheng. The role of miR398 in plant stress responses [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(2): 129-134. |
| [13] | YANG Dong, JIANG Ying, HE Fu-Chu. KAP-1, a scaffold protein in transcription regulation [J]. HEREDITAS, 2007, 29(2): 131-131―136. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||