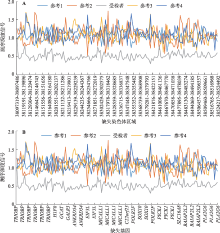
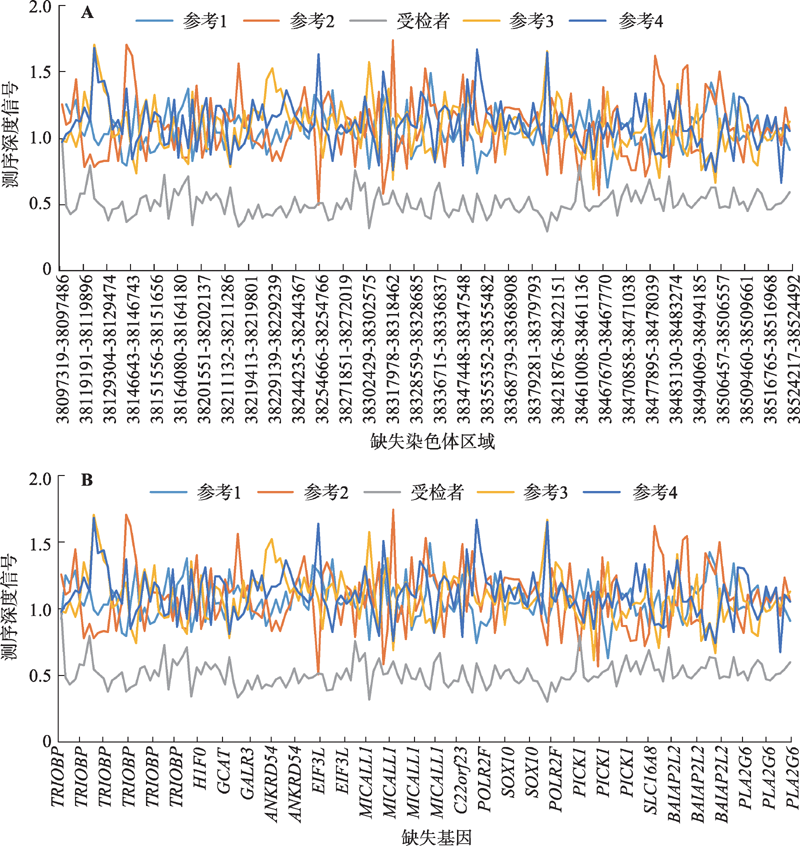
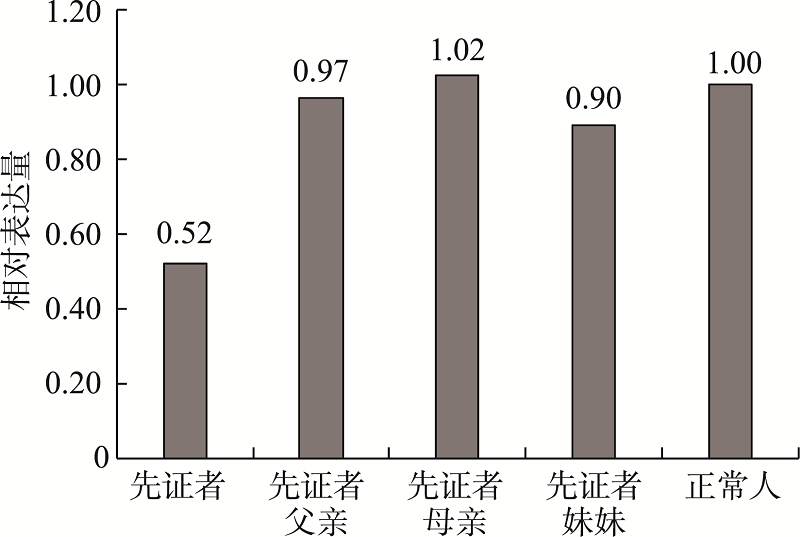
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 1158-1166.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-161
• Genetic Resource • Previous Articles Next Articles
Diagnosis and genetic analysis of a case of Waardenburg syndrome type 2 with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism caused by SOX10 gene deletion
Siqi Wang( ), Yang Chen, Kuanhong Luo, Ningjie Shi, Kangli Xiao, Zhenhai Cui, Tianshu Zeng, Huiqing Li(
), Yang Chen, Kuanhong Luo, Ningjie Shi, Kangli Xiao, Zhenhai Cui, Tianshu Zeng, Huiqing Li( )
)
- Department of Endocrinology, Union Hospital, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, China
-
Received:2022-07-31Revised:2022-09-21Online:2022-12-20Published:2022-10-09 -
Contact:Li Huiqing E-mail:wangsiqi8958@163.com;lhqing5@126.com
Cite this article
Siqi Wang, Yang Chen, Kuanhong Luo, Ningjie Shi, Kangli Xiao, Zhenhai Cui, Tianshu Zeng, Huiqing Li. Diagnosis and genetic analysis of a case of Waardenburg syndrome type 2 with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism caused by SOX10 gene deletion[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1158-1166.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Results of the patient’s laboratory tests"
| 基本特征与实验室检查 | 结果 | 参考范围 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 男 | — | |||
| 年龄 | 18 | — | |||
| 身高/cm | 171 | — | |||
| 体重/kg | 44 | — | |||
| 性激素 | |||||
| 促黄体生成素(IU/L) | 2.6 | 1.7~8.6 | |||
| 促卵泡生成素(IU/L) | 2.45 | 1.5~12.4 | |||
| 泌乳素(ng/mL) | 11.61 | 2.7~15.2 | |||
| 孕酮(ng/mL) | 0.11 | <0.149 | |||
| 雌二醇(pg/mL) | <5.00 | 11.3~43.2 | |||
| 睾酮(nmol/L) | 0.81 | Tanner 5期:6.5~30.6 | |||
| 戈那瑞林兴奋实验 | 基础值 | 峰值 | |||
| 促卵泡生成素(IU/L) | 1.63 | 5.01 | FSH增加0.5~2倍 | ||
| 促黄体生成素(IU/L) | 1.40 | 12.67 | LH峰值升高>5倍 | ||
| 睾酮(ng/mL) | 0.62 | ||||
| 人绒毛膜促性腺激素兴奋实验 | 实验前 | 注射HCG 3天后 | |||
| 睾酮(ng/mL) | 0.51 | 8.26 | 注射HCG后,睾酮平均增加0.5~2倍 | ||
| 甲状腺激素 | |||||
| FT3(pmol/L) | 4.5 | 3.47~10.43 | |||
| FT4(pmol/L) | 12.9 | 11.2~20.1 | |||
| TSH(μIU/mL) | 3.11 | 0.34~5.06 | |||
| 8 am | 4 pm | 12 pm | |||
| 皮质醇(μg/L) | 57.35 | 41.0 | 9.65 | — | |
| 促肾上腺皮质激素(pg/mL) | 57.35 | 9.65 | 28.16 | — | |
| 胰岛素样生长因子-1(ng/mL) | 1210.52 | 12岁:143~693;成人:141~483 | |||
| 左手骨龄片 | 13 | — | |||
Table 2
Clinical features of patients with KS with SOX10 mutations"
| 病例 | 年龄 | 性别 | 自发性青春期 | 嗅觉 | 听力损失 | 其他临床症状 | 核苷酸变异 | 氨基酸改变 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 | 男 | 无 | 缺失 | 单侧 | 白发,隐睾症 | c.2T>G | p.? | [ |
| 2 | 18 | 女 | 无 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 上睑下垂 | c.331T>G | p.Phe111Val | [ |
| 3 | 39 | 女 | 无 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 肥胖 | c.424T>C | p.Trp142Arg | [ |
| 4 | 25 | 女 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 双侧 | — | c.698-1G>C | p.spl? | [ |
| 5 | 20 | 男 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 隐睾症 | c.1290del | p.Ser431Argfs*71 | [ |
| 6 | 20 | 男 | 未描述 | 缺失 | 正常 | 智力障碍,先天畸形 | c.1298G>A | p.Arg433Gln | [ |
| 7 | 33 | 男 | 无 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 上睑下垂 | c.323T>C | p.Met108Trh | [ |
| 8 | 19 | 女 | 无 | 缺失 | 正常 | 巨腿畸形 | c.451C>T | p.Arg151Cys | [ |
| 9 | 25 | 男 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 上睑下垂,隐睾症 | c.122G>T | p.Gly41Val | [ |
| 10 | 20 | 男 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 正常 | — | c.131C>G | p.Ala44Gly | [ |
| 11 | 38 | 男 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 单侧 | — | c.238C>G | p.Leu80Val | [ |
| 12 | 17 | 男 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 灰白发,鼻根宽大 | c.184G>T | p.Glu62X | [ |
| 13 | 13 | 女 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 额前白发,虹膜色素缺失 | c.506delC | p.Pro169fsX117 | [ |
| 14 | 15 | 男 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 蓝色虹膜 | c.434T>C | p.Leu145Pro | [ |
| 15 | 30 | 男 | 延迟 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 虹膜色素缺失,甲亢 | c.565G>T | p.Phe189X | [ |
| 16 | 17 | 男 | 无 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 虹膜色素缺失 | c.373C>T | p.Glu125X | [ |
| 17 | 15 | 女 | 无 | 缺失 | 双侧 | 虹膜色素缺失,先天性巨结肠 | c.124delC | p.Leu42Cysfs*67 | [ |
| 18 | 25 | 男 | 无 | 缺失 | 双侧 | — | c.475C>T | p.Arg159Trp | [ |
| 19 | 18 | 男 | 无 | 减退 | 双侧 | 额前白发,虹膜色素缺失 | 22q13.1微缺失 | — |
| [1] |
Millar AC, Faghfoury H, Bieniek JM. Genetics of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Transl Androl Urol, 2021, 10(3): 1401-1409.
doi: 10.21037/tau.2020.03.33 pmid: 33850776 |
| [2] |
Schwanzel-Fukuda M, Bick D, Pfaff DW. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH)-expressing cells do not migrate normally in an inherited hypogonadal (Kallmann) syndrome. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 1989, 6(4): 311-326.
doi: 10.1016/0169-328X(89)90076-4 |
| [3] | Boehm U, Bouloux PM, Dattani MT, de Roux N, Dodé C, Dunkel L, Dwyer AA, Giacobini P, Hardelin JP, Juul A, Maghnie M, Pitteloud N, Prevot V, Raivio T, Tena-Sempere M, Quinton R, Young J. Expert consensus document: European consensus statement on congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism—pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2015, 11(9): 547-564. |
| [4] |
Pingault V, Bodereau V, Baral V, Marcos S, Watanabe Y, Chaoui A, Fouveaut C, Leroy C, Vérier-Mine O, Francannet C, Dupin-Deguine D, Archambeaud F, Kurtz FJ, Young J, Bertherat J, Marlin S, Goossens M, Hardelin JP, Dodé C, Bondurand N. Loss-of-function mutations in SOX10 cause Kallmann syndrome with deafness. Am J Hum Genet, 2013, 92(5): 707-724.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.03.024 |
| [5] | Chen K, Wang HY, Lai YX. Kallmann syndrome due to heterozygous mutation in SOX10 coexisting with Waardenburg syndrome type II:case report and review of literature. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 11: 592831. |
| [6] |
Hamada J, Ochi F, Sei Y, Takemoto K, Hirai H, Honda M, Shibata H, Hasegawa T, Eguchi M. A novel SOX10 variant in a Japanese girl with Waardenburg syndrome type 4C and Kallmann syndrome. Hum Genome Var, 2020, 7: 30.
doi: 10.1038/s41439-020-00118-6 |
| [7] |
Suzuki E, Izumi Y, Chiba Y, Horikawa R, Matsubara Y, Tanaka M, Ogata T, Fukami M, Naiki Y. Loss-of-function SOX10 mutation in a patient with Kallmann syndrome, hearing loss, and iris hypopigmentation. Horm Res Paediatr, 2015, 84(3): 212-216.
doi: 10.1159/000436965 |
| [8] | Wakabayashi T, Takei A, Okada N, Shinohara M, Takahashi M, Nagashima S, Okada K, Ebihara K, Ishibashi S. A novel SOX10 nonsense mutation in a patient with Kallmann syndrome and Waardenburg syndrome. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep, 2021, 2021: 20-0145. |
| [9] |
Pingault V, Zerad L, Bertani-Torres W, Bondurand N. SOX10: 20 years of phenotypic plurality and current understanding of its developmental function. J Med Genet, 2022, 59(2): 105-114.
doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-108105 |
| [10] |
Huang SD, Song J, He CF, Cai XZ, Yuan K, Mei LY, Feng Y. Genetic insights, disease mechanisms, and biological therapeutics for Waardenburg syndrome. Gene Ther, 2021, 29(9): 479-497.
doi: 10.1038/s41434-021-00240-2 |
| [11] |
Dai WT, Wu JY, Zhao YG, Jiang F, Zheng RZ, Chen DN, Men MC, Li JD. Functional analysis of SOX10 mutations identified in Chinese patients with Kallmann syndrome. Gene, 2019, 702: 99-106.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.03.039 |
| [12] |
Vaaralahti K, Tommiska J, Tillmann V, Liivak N, Känsäkoski J, Laitinen EM, Raivio T. De novo SOX10 nonsense mutation in a patient with Kallmann syndrome and hearing loss. Pediatr Res, 2014, 76(1): 115-116.
doi: 10.1038/pr.2014.60 pmid: 24769923 |
| [13] |
Izumi Y, Musha I, Suzuki E, Iso M, Jinno T, Horikawa R, Amemiya S, Ogata T, Fukami M, Ohtake A. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in a female patient previously diagnosed as having Waardenburg syndrome due to a sox10 mutation. Endocrine, 2015, 49(2): 553-556.
doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0434-4 pmid: 25273316 |
| [14] | Wang F, Zhao SL, Xie YH, Yang WJ, Mo ZH. De novo SOX10 nonsense mutation in a patient with Kallmann syndrome, deafness, iris hypopigmentation, and hyperthyroidism. Ann Clin Lab Sci, 2018, 48(2): 248-252. |
| [15] | Zhang Q, He HH, Janjua MU, Wang F, Yang YB, Mo ZH, Liu J, Jin P. Identification of two novel mutations in three Chinese families with Kallmann syndrome using whole exome sequencing. Andrologia, 2020, 52(7): e13594. |
| [16] |
Ritter KE, Martin DM. Neural crest contributions to the ear: implications for congenital hearing disorders. Hear Res, 2019, 376: 22-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.11.005 |
| [17] |
Hou L, Pavan WJ.? Transcriptional and signaling regulation in neural crest stem cell-derived melanocyte development: do all roads lead to Mitf? Cell Res, 2008, 18(12): 1163-1176.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.303 pmid: 19002157 |
| [18] |
Bondurand N, Pingault V, Goerich DE, Lemort N, Sock E, Le Caignec C, Wegner M, Goossens M. Interaction among SOX10, PAX3 and MITF, three genes altered in Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Mol Genet, 2000, 9(13): 1907-1917.
pmid: 10942418 |
| [19] |
Harris ML, Baxter LL, Loftus SK, Pavan WJ. Sox proteins in melanocyte development and melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res, 2010, 23(4): 496-513.
doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2010.00711.x |
| [20] |
Marathe HG, Watkins-Chow DE, Weider M, Hoffmann A, Mehta G, Trivedi A, Aras S, Basuroy T, Mehrotra A, Bennett DC, Wegner M, Pavan WJ, de la Serna IL. BRG1 interacts with SOX10 to establish the melanocyte lineage and to promote differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(11): 6442-6458.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx259 pmid: 28431046 |
| [21] |
Bondurand N, Sham MH. The role of SOX10 during enteric nervous system development. Dev Biol, 2013, 382(1): 330-343.
doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.04.024 pmid: 23644063 |
| [22] |
Wray S. From nose to brain: development of gonadotrophin- releasing hormone-1 neurones. J Neuroendocrinol, 2010, 22(7): 743-753.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02034.x pmid: 20646175 |
| [23] |
Zhu YL, Cao L, Su ZD, Mu LF, Yuan YM, Gao L, Qiu Y, He C. Olfactory ensheathing cells: attractant of neural progenitor migration to olfactory bulb. Glia, 2010, 58(6): 716-729.
doi: 10.1002/glia.20957 pmid: 20091794 |
| [24] |
Chaoui A, Watanabe Y, Touraine R, Baral V, Goossens M, Pingault V, Bondurand N. Identification and functional analysis of SOX10 missense mutations in different subtypes of Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Mutat, 2011, 32(12): 1436-1449.
doi: 10.1002/humu.21583 pmid: 21898658 |
| [25] | Oshimo T, Fukai K, Abe Y, Hozumi Y, Yokoi T, Tanaka A, Yamanishi K, Ishii M, Suzuki T. Pediatric case report: clinical profile of a patient with PCWH with p. Q377X nonsense mutation in the SOX10 gene. J Dermatol, 2012, 39(12): 1022-1025. |
| [26] | LeBel DP 2nd, Wolff DJ, Batalis NI, Ellingham T, Matics N, Patwardhan SC, Znoyko IY, Schandl CA. First report of prenatal ascertainment of a fetus with homozygous loss of the SOX10 gene and phenotypic correlation by autopsy examination. Pediatr Dev Pathol, 2018, 21(6): 561-567. |
| [27] |
Stevenson RE, Vincent V, Spellicy CJ, Friez MJ, Chaubey A. Biallelic deletions of the Waardenburg II syndrome gene, SOX10, cause a recognizable arthrogryposis syndrome. Am J Med Genet A, 2018, 176(9): 1968-1971.
doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.40362 pmid: 30113773 |
| [28] |
Liu YJ, Zhi X. Advances in genetic diagnosis of Kallmann syndrome and genetic interruption. Reprod Sci, 2022, 29(6): 1697-1709.
doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00638-8 |
| [29] |
Meczekalski B, Podfigurna-Stopa A, Smolarczyk R, Katulski K, Genazzani AR. Kallmann syndrome in women: from genes to diagnosis and treatment. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2013, 29(4): 296-300.
doi: 10.3109/09513590.2012.752459 pmid: 23368665 |
| [30] |
Palmert MR, Dunkel L. Clinical practice. Delayed puberty. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366(5): 443-453.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1109290 |
| [1] | Juan Huang, Wenhua Miao, Xiaofeng Guo, Wei Ji. Diagnosis and genetic testing analysis of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2U caused by a compound heterozygous mutation in the ISPD gene [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(6): 536-542. |
| [2] | Yiming Gong, Xiangyu Wang, Xiaoyun He, Yufang Liu, Ping Yu, Mingxing Chu, Ran Di. Progress on the effect of FecB mutation on BMPR1B activity and BMP/SMAD pathway in sheep [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(4): 295-305. |
| [3] | Jie Ma, Lujie Huang, Qiaoxia Zhang, Yan Zhu, Lu Qian. PBL teaching design of medical genetics with the case of brachydactyly type A2 [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(2): 176-183. |
| [4] | Luyang Li, Sunqiang Liu, Yun Shi, Chengcheng Zhao, Hongwen Zhou, Xuqin Zheng. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of a case of hypoglycemia caused by glucokinase gene mutation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 810-818. |
| [5] | Shaozheng Song, Zhengyi He, Yong Cheng, Baoli Yu, Ting Zhang, Dan Li. MSTN modification in goat mediated by TALENs and performance analysis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 531-542. |
| [6] | Qingqing Song, Susu Zhang, Zhen Zhang, Jia Sun, Rui Yang, Jitong Li , Hong Chen. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of 11β -hydroxylase deficiency caused by CYP11B gene mutation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1175-1182. |
| [7] | Ruizhi Jiajue, Cheng Xiao, Yiwen Liu, Ran Li, Huabing Zhang, Miao Yu. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of two cases of congenital hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia caused by GCK gene mutation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(11): 1056-1062. |
| [8] | Cheng Xiao, Jieying Liu, Chunru Yang, Miao Yu. Advances in lipodystrophy syndrome caused by LMNA gene mutation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 913-925. |
| [9] | Zhiyong Liu, He Ren, Chong Chen, Jingjing Zhang, Xiaomeng Zhang, Yan Shi, Linyu Shi, Ying Chen, Feng Cheng, Li Jia, Man Chen, Qingwei Fan, Jiarong Zhang, Wanting Li, Mengchun Wang, Zilin Ren, Yacheng Liu, Ming Ni, Hongyu Sun, Jiangwei Yan. Actual mutational research of 19 autosomal STRs based on restricted mutation model and big data [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(10): 949-961. |
| [10] | Linan Zhao, Na Wang, Guoliang Yang, Xianbin Su, Zeguang Han. A method for reliable detection of genomic point mutations based on single-cell target-sequencing [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(7): 703-712. |
| [11] | Miaomiao Cheng, Yanyan Cao. The NMD escape mechanism and its application in disease therapy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(4): 354-362. |
| [12] | Qianqian Zhang,Li Zhang,Yaohua Tang,Xiarong Li,Xiaopeng Xu,Ming Qi,Xiangmin Xu. A comprehensive repository of mutation data and a clinical assistant decision system for hemoglobinopathy in the Chinese population [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(8): 746-753. |
| [13] | Zhaoqing Sun, Bo Yan. The roles and regulation mechanism of transcription factor GATA6 in cardiovascular diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(5): 375-383. |
| [14] | Nan Li, Yajuan Li, Haibin Guo, Xiangqian Zhang. Design and exploration of genetic comprehensive experiments based on Ds insertion mutants [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(12): 1148-1155. |
| [15] | Furu Xu, Wenjun Jiang, Tao Zhang, Qian Jiang, Ruixue Zhang, Hongsheng Bi. Fibrillin-2 gene mutations associated with hereditary connective tissue diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(10): 919-927. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||