Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 52-66.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-293
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of transcriptome in time analysis and donor characterization in blood samples
Jin Zhang1,2( ), Kaihui Liu2, Ying Zhang2, Jinping Hao2, Guangfeng Zhang2, Xiaoyu Xu2, Jingjing Chang2, Xingpeng Liu3, Xueying Yang2(
), Kaihui Liu2, Ying Zhang2, Jinping Hao2, Guangfeng Zhang2, Xiaoyu Xu2, Jingjing Chang2, Xingpeng Liu3, Xueying Yang2( ), Jian Ye1,2(
), Jian Ye1,2( )
)
- 1. People's Public Security University of China, Beijing 100038, China
2. Institute of Forensic Science Ministry of Public Security, Beijing 100038, China
3. Ruijin Public Security Bureau, Ruijin 342500, China
-
Received:2022-10-31Revised:2022-11-29Online:2023-01-20Published:2022-12-09 -
Contact:Yang Xueying,Ye Jian E-mail:zhangjin1101@126.com;yxystyhhp@163.com;yejian77@126.com -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Development Programs of Ministry of Public Security P.R.C(2017JSYJC22);the Public Security Scientific and Technological Achievements Promotion and Guidance Programs of Ministry of Public Security P.R.C(2020TGYDBGAES25);the Basic research Funds for Public Welfare Research Institutes of the Central Government(2020JB008)
Cite this article
Jin Zhang, Kaihui Liu, Ying Zhang, Jinping Hao, Guangfeng Zhang, Xiaoyu Xu, Jingjing Chang, Xingpeng Liu, Xueying Yang, Jian Ye. Application of transcriptome in time analysis and donor characterization in blood samples[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(1): 52-66.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Grouping of experimental samples"
| 物证特征 | 分组 | 样本数量 | 离体时间D (天) | 取样时间点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吸烟 | 吸烟组(smoker) | 56 | 0≤D≤168 | D0、D0.5、D1、D2、D4、D7、D14、D21、D28、D56、D84、D112、D140、D168 |
| 对照组(control) | 70 | 0≤D≤168 | D0、D0.5、D1、D2、D4、D7、D14、D21、D28、D56、D84、D112、D140、D168 | |
| 性别 | 男性组(male) | 140 | 0≤D≤168 | D0、D0.5、D1、D2、D4、D7、D14、D21、D28、D56、D84、D112、D140、D168 |
| 女性组(female) | 138 | 0≤D≤168 | D0、D0.5、D1、D2、D4、D7、D14、D21、D28、D56、D84、D112、D140、D168 | |
| 离体时间 | D0~2组 | 80 | 0≤D≤2 | D0、D0.5、D1、D2 |
| D4~14组 | 58 | 2<D≤14 | D4、D7、D14 | |
| D21~56组 | 60 | 14<D≤56 | D21、D28、D56 | |
| D84~168组 | 80 | 56<D≤168 | D84、D112、D140、D168 |
Table 2
Details of the transcriptome assembly results"
| 分组 | Raw reads (Mean ± SD) | Clean reads (Mean ± SD) | 错误率 (%) (Mean ± SD) | Q20 (%) (Mean ± SD) | Q30 (%) (Mean ± SD) | GC含量 (%) (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吸烟组 (n = 56) | 57928613.071±11306086.212 | 56796377.250±11069341.242 | 0.022 ± 0.004 | 98.226 ± 0.254 | 94.867 ± 0.574 | 56.115 ± 1.985 |
| 对照组 (n = 70) | 59559976.829±12657910.627 | 58188050.543±12252512.979 | 0.021 ± 0.003 | 98.272 ± 0.229 | 94.965 ± 0.508 | 57.314 ± 2.118 |
| 男性组 (n = 140) | 58822285.871±12184267.688 | 57535769.014±11852506.630 | 0.021 ± 0.003 | 98.258 ± 0.239 | 94.933 ± 0.534 | 56.736 ± 2.117 |
| 女性组 (n = 138) | 56861638.043±13407561.979 | 55739764.043±13003300.979 | 0.022 ± 0.004 | 98.168 ± 0.272 | 94.716 ± 0.581 | 55.667 ± 2.543 |
| D0~2组 (n = 80) | 69324109.250±9861979.513 | 67804445.700±9697013.881 | 0.021 ± 0.003 | 98.220 ± 0.190 | 94.877 ± 0.437 | 53.855 ± 1.214 |
| D4~14组 (n = 58) | 64783625.207±10637521.112 | 63346337.621±10173427.925 | 0.022 ± 0.004 | 98.204 ± 0.291 | 94.837 ± 0.672 | 56.134 ± 1.580 |
| D21~56组 (n = 60) | 50664396.800±7061084.292 | 49725835.000±6685845.152 | 0.021 ± 0.002 | 98.321 ± 0.193 | 95.032 ± 0.447 | 59.043 ± 1.099 |
| D84~168组 (n = 80) | 46734790.775±5268303.017 | 45813772.025±5235594.729 | 0.023 ± 0.005 | 98.132 ± 0.307 | 94.610 ± 0.612 | 56.480 ± 2.041 |
Table 3
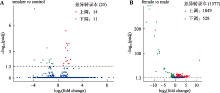
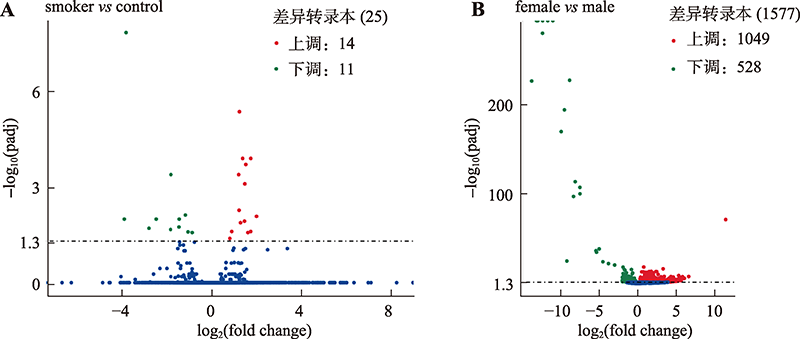
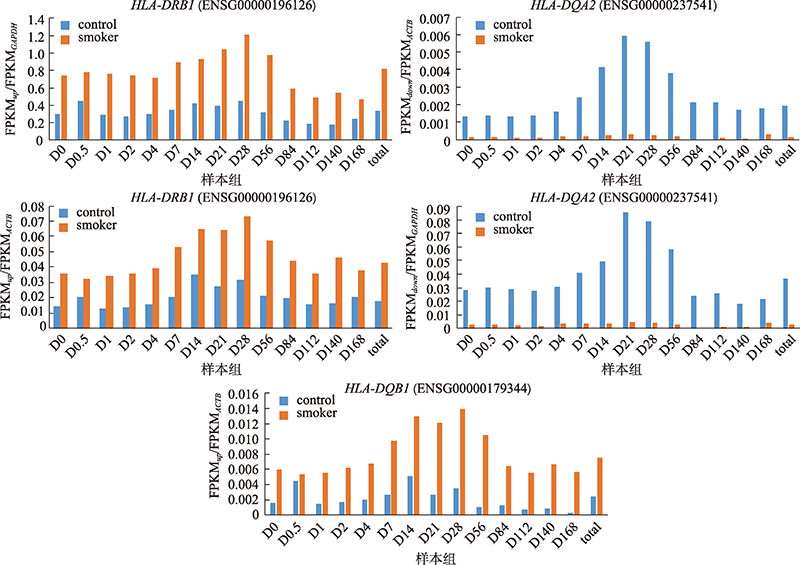
Smoking habit related differential expressed transcripts"
| 上调转录本 | 下调转录本 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 序号 | 基因 ID | 基因名称 | 序号 | 基因 ID | 基因名称 |
| 1 | ENSG00000196126 | HLA-DRB1 | 1 | ENSG00000237541 | HLA-DQA2 |
| 2 | ENSG00000019169 | MARCO | 2 | ENSG00000276345 | AC004556.1 |
| 3 | ENSG00000196735 | HLA-DQA1 | 3 | ENSG00000284690 | CD300H |
| 4 | ENSG00000103355 | PRSS33 | 4 | ENSG00000060709 | RIMBP2 |
| 5 | ENSG00000105205 | CLC | 5 | ENSG00000174171 | - |
| 6 | ENSG00000276085 | CCL3L1 | 6 | ENSG00000229391 | - |
| 7 | ENSG00000214026 | MRPL23 | 7 | ENSG00000211821 | TRDV2 |
| 8 | ENSG00000179344 | HLA-DQB1 | 8 | ENSG00000204345 | CD300LD |
| 9 | ENSG00000189068 | VSTM1 | 9 | ENSG00000211638 | IGLV8-61 |
| 10 | ENSG00000105366 | SIGLEC8 | 10 | ENSG00000022556 | NLRP2 |
| 11 | ENSG00000172322 | CLEC12A | 11 | ENSG00000211666 | IGLV2-14 |
| 12 | ENSG00000205927 | OLIG2 | |||
| 13 | ENSG00000277632 | CCL3 | |||
| 14 | ENSG00000092067 | CEBPE | |||
Table 5
11 important transcripts in the Random Forest classifier"
| 序号 | 基因 ID | 基因名称 | MDA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ENSG00000078747 | ITCH | 2.1454 |
| 2 | ENSG00000128585 | MKLN1 | 2.1290 |
| 3 | ENSG00000215421 | ZNF407 | 2.1264 |
| 4 | ENSG00000126945 | HNRNPH2 | 2.0812 |
| 5 | ENSG00000143751 | SDE2 | 2.0780 |
| 6 | ENSG00000127954 | STEAP4 | 2.0617 |
| 7 | ENSG00000113580 | NR3C1 | 1.9407 |
| 8 | ENSG00000112096 | SOD2 | 1.9382 |
| 9 | ENSG00000198105 | ZNF248 | 1.9331 |
| 10 | ENSG00000125304 | TM9SF2 | 1.9190 |
| 11 | ENSG00000103994 | ZNF106 | 1.9133 |
Table 6
Biomarkers and threshold values"
| 性别特征刻画 | 吸烟特征刻画 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 判别标志 | 男性 | 女性 | 判别标志 | 吸烟 | 不吸烟 |
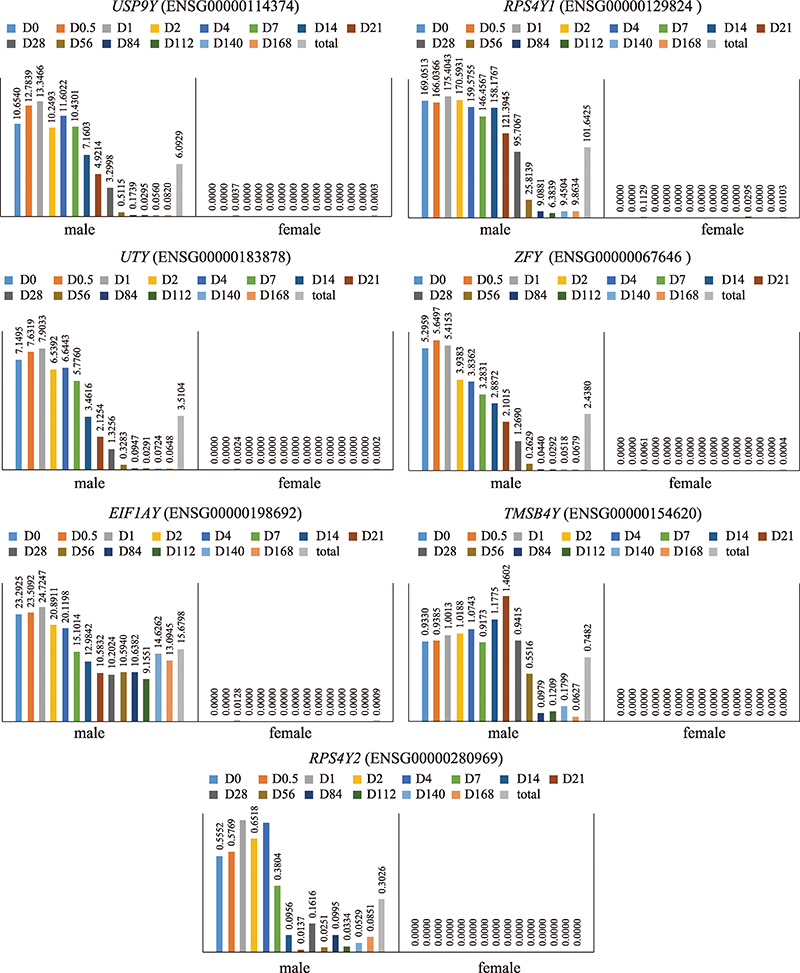
| RPS4Y1 | FPKM≥1 | FPKM<1 | HLA-DRB1/ACTB | RER HLA-DRB1/ACTB≥0.04099 | RER HLA-DRB1/ACTB≤0.02322 |
| EIF1AY | FPKM≥1 | FPKM<1 | HLA-DRB1/GAPDH | RER HLA-DRB1/GAPDH≥0.67420 | RER HLA-DRB1/GAPDH≤0.3564 |
| HLA-DQB1/ACTB | RER HLA-DQB1/ACTB≥0.00651 | RER HLA-DQB1/ACTB≤0.00269 | |||
| HLA-DQA2/ACTB | RER HLA-DQA2/ACTB≤0.00026 | RER HLA-DQA2/ACTB≥0.00193 | |||
| HLA-DQA2/GAPDH | RER HLA-DQA2/GAPDH≤0.00397 | RER HLA-DQA2/GAPDH≥0.02989 | |||
Table 7
Results of cross-validation for time analysis and donor characterization"
| 时间信息/供体特征 | 判别标志 | 交叉验证组别 | 随机抽取样本数 | 样本判断正确率 | 平均正确率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
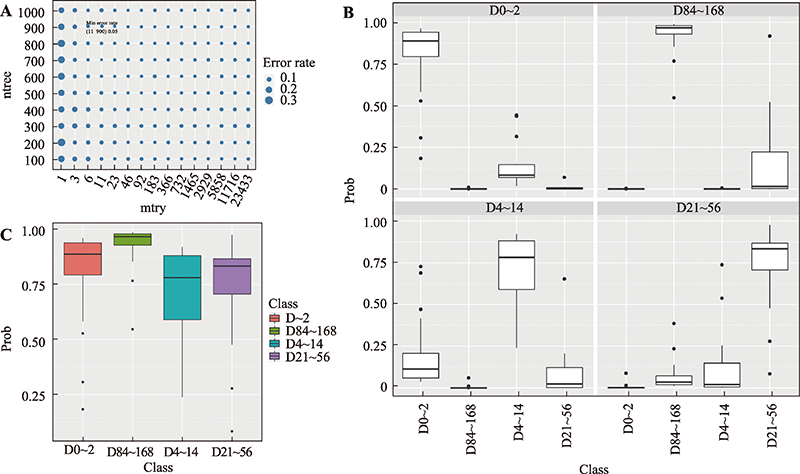
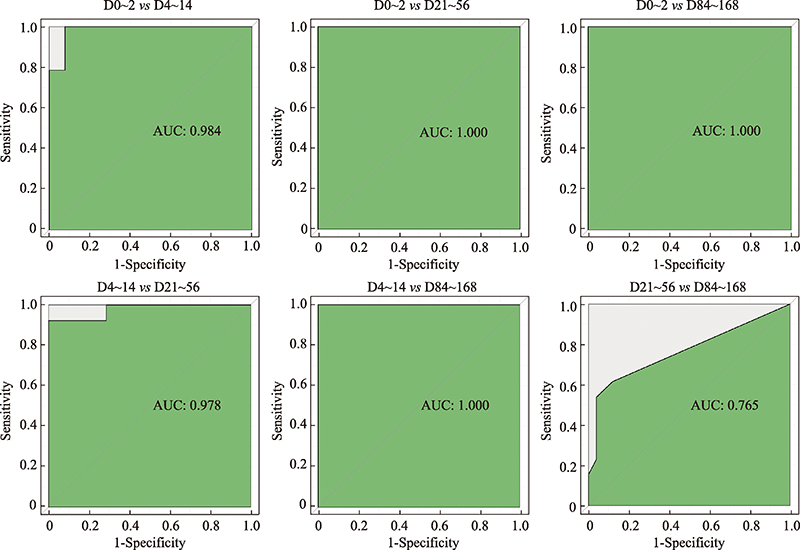
| 离体时间 | - | D0~2 | 26 | 92.31% | 91.03% |
| D4~14 | 14 | 85.71% | |||
| D21~56 | 13 | 76.92% | |||
| D84~168 | 25 | 100% | |||
| 吸烟习惯 | HLA-DRB1/ACTB | 1 | 13 | 92.31% | 76.92% |
| 2 | 13 | 76.92% | |||
| 3 | 13 | 46.15% | |||
| 4 | 13 | 84.62% | |||
| 5 | 13 | 84.62% | |||
| HLA-DRB1/GAPDH | 1 | 13 | 69.23% | 73.85% | |
| 2 | 13 | 76.92% | |||
| 3 | 13 | 53.85% | |||
| 4 | 13 | 84.62% | |||
| 5 | 13 | 84.62% | |||
| HLA-DQB1/ACTB | 1 | 13 | 92.31% | 72.31% | |
| 2 | 13 | 61.54% | |||
| 3 | 13 | 61.54% | |||
| 4 | 13 | 76.92% | |||
| 5 | 13 | 69.23% | |||
| HLA-DQA2/ACTB | 1 | 13 | 69.23% | 55.39% | |
| 2 | 13 | 53.85% | |||
| 3 | 13 | 46.15% | |||
| 4 | 13 | 53.85% | |||
| 5 | 13 | 53.85% | |||
| HLA-DQA2/GAPDH | 1 | 13 | 69.23% | 58.46% | |
| 2 | 13 | 61.54% | |||
| 3 | 13 | 46.15% | |||
| 4 | 13 | 69.23% | |||
| 5 | 13 | 46.15% | |||
| 性别 | RPS4Y1 | 1 | 28 | 100% | 100% |
| 2 | 28 | 100% | |||
| 3 | 28 | 100% | |||
| 4 | 28 | 100% | |||
| 5 | 28 | 100% | |||
| EIF1AY | 1 | 28 | 100% | 100% | |
| 2 | 28 | 100% | |||
| 3 | 28 | 100% | |||
| 4 | 28 | 100% | |||
| 5 | 28 | 100% |
| [1] | 侯一平.法医物证学: 第4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016, 1-5. |
| [2] | 布尔特尔, 侯一平译. 法医DNA分型专论: 方法学(第3版). 科学出版社, 2013, 83-90. |
| [3] | Li M, Li Y, Yang YF, Yan YW, Liu F, Li CX, Zeng FM, Zhao WT. Human facial shape related SNP analysis in Han Chinese populations. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(7): 680-690. |
| 刘明, 李祎, 杨亚芳, 晏于文, 刘凡, 李彩霞, 曾发明, 赵雯婷. 中国汉族人群脸部特征相关SNP位点研究. 遗传, 2020, 42(7): 680-690. | |
| [4] | Zhang T, Yang RQ. Review of the application of spectral imaging and mass spectrometry imaging infingerprint analysis. Forensic Pract, 2015, (1): 71-75. |
| 张婷, 杨瑞琴. 指印中化学物质光谱质谱成像分析技术研究进展. 中国司法鉴定, 2015, (1): 71-75. | |
| [5] | Mei HC, Zhu J, Quan YK, Wang GQ. Inferring the donor’s living spatial-temporal information by stable isotope analysis of the biological evidence. Forensic Sci Technol, 2016, 41(2): 87-92. |
| 梅宏成, 朱军, 权养科, 王桂强. 稳定同位素检验推断生物物证供体的生活时空信息. 刑事技术, 2016, 41(2): 87-92. | |
| [6] | Zhang J, Gao S, Chang JJ, Zhang Y, Yang XY, Liu KH. Advances in the research of predicting the time since deposition of evidentiary stains. Chin J Forensic Med, 2018, 33(1): 39-42. |
| 张瑾, 高珊, 畅晶晶, 张颖, 杨雪莹, 刘开会. 现场生物斑迹遗留时间推断研究进展. 中国法医学杂志, 2018, 33(1): 39-42. | |
| [7] | Rajamannar K. Determination of the age of bloodstains using immunoelectrophoresis. J Forensic Sci, 1977, 22(1): 159-164. |
| [8] | Li B, Beveridge P, O'Hare WT, Islam M. The estimation of the age of a blood stain using reflectance spectroscopy with a microspectrophotometer, spectral pre-processing and linear discriminant analysis. Forensic Sci Int, 2011, 212(1-3): 198-204. |
| [9] | Bremmer RH, Nadort A, van Leeuwen TG, Aalders MCG. Age estimation of blood stains by hemoglobin derivative determination using reflectance spectroscopy. Forensic Sci Int, 2011, 206(1-3): 166-171. |
| [10] | Hanson EK, Ballantyne J. A blue spectral shift of the hemoglobin soret band correlates with the age (time since deposition) of dried bloodstains. PLoS One, 2010, 5(9): e12830. |
| [11] | Gao QY, Gao SM. Authentication of age of blooding using UV visible reflection spectrum. Spectrosc Spectral Anal, 2015, 35(8): 2221-2224. |
| 高茜钰, 高士明. 利用紫外可见反射光谱鉴定血迹陈旧度. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(8): 2221-2224. | |
| [12] | Edelman G, van Leeuwen TG, Aalders MCG. Hyperspectral imaging for the age estimation of blood stains at the crime scene. Forensic Sci Int, 2012, 223(1-3): 72-77. |
| [13] | Edelman G, Manti V, van Ruth SM, van Leeuwen T, Aalders M. Identification and age estimation of blood stains on colored backgrounds by near infrared spectroscopy. Forensic Sci Int, 2012, 220(1-3): 239-244. |
| [14] | Doty KC, McLaughlin G, Lednev IK. A Raman “spectroscopic clock” for bloodstain age determination: the first week after deposition. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2016, 408(15): 3993-4001. |
| [15] | Thanakiatkrai P, Yaodam A, Kitpipit T. Age estimation of bloodstains using smartphones and digital image analysis. Forensic Sci Int, 2013, 233(1-3): 288-297. |
| [16] | Alshehhi S, McCallum NA, Haddrill PR. Quantification of RNA degradation of blood-specific markers to indicate the age of bloodstains. Forensic Sci Int Genet Suppl Ser, 2017, 6: e453-e455. |
| [17] | Anderson S, Howard B, Hobbs GR, Bishop CP. A method for determining the age of a bloodstain. Forensic Sci Int, 2005, 148(1): 37-45. |
| [18] | Bauer M, Polzin S, Patzelt D. Quantification of RNA degradation by semi-quantitative duplex and competitive RT-PCR: a possible indicator of the age of bloodstains? Forensic Sci Int, 2003, 138(1-3): 94-103. |
| [19] | Anderson SE, Hobbs GR, Bishop CP. Multivariate analysis for estimating the age of a bloodstain. J Forensic Sci, 2011, 56(1): 186-193. |
| [20] | Mohammed AT, Khalil SR, Ali HA, Awad A. Validation of mRNA and microRNA profiling as tools in qPCR for estimation of the age of bloodstains. Life Sci J, 2018, 15(6): 1-7. |
| [21] | Glynn CL. Potential applications of microRNA profiling to forensic investigations. RNA, 2020, 26(1): 1-9. |
| [22] | Hampson C, Louhelainen J, McColl S. An RNA expression method for aging forensic hair samples. J Forensic Sci, 2011, 56(2): 359-365. |
| [23] | Alshehhi S, Haddrill PR. Estimating time since deposition using quantification of RNA degradation in body fluid specific markers. Forensic Sci Int, 2019, 298: 58-63. |
| [24] | Fu J, Allen RW. A method to estimate the age of bloodstains using quantitative PCR. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2019, 39: 103-108. |
| [25] | Wang Y.Measurement of DNA degradation kinetics in serum, urine and saliva based on automatic STR analysis system [Dissertation]. Dalian Medical University, 2014. |
| 王瑶.基于STR自动检测系统对DNA在血清、尿液和唾液中降解动力学的测定[学位论文]. 大连医科大学, 2014. | |
| [26] | Johnson LA, Ferris JAJ. Analysis of postmortem DNA degradation by single-cell gel electrophoresis. Forensic Sci Int, 2002, 126(1): 43-47. |
| [27] | Cossette ML, Stotesbury T, Shafer ABA. Quantifying visible absorbance changes and DNA degradation in aging bloodstains under extreme temperatures. Forensic Sci Int, 2021, 318: 110627. |
| [28] | Díez López C, Kayser M, Vidaki A. Estimating the time since deposition of saliva stains with a targeted bacterial DNA approach: a proof-of-principle study. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 647933. |
| [29] | Weinbrecht KD, Fu J, Payton ME, Allen RW. Time- dependent loss of mRNA transcripts from forensic stains. Res Rep Forensic Med Sci, 2017, 7: 1-12. |
| [30] | Ramaprasad A, Subudhi AK, Culleton R, Pain A. A fast and cost-effective microsampling protocol incorporating reduced animal usage for time-series transcriptomics in rodent malaria parasites. Malar J, 2019, 18(1): 26. |
| [31] | Jang JS, Berg B, Holicky E, Eckloff B, Mutawe M, Carrasquillo MM, Ertekin-Taner N, Cuninngham JM. Comparative evaluation for the globin gene depletion methods for mRNA sequencing using the whole blood- derived total RNAs. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21(1): 890. |
| [32] | Lopez JP, Diallo A, Cruceanu C, Fiori LM, Laboissiere S, Guillet I, Fontaine J, Ragoussis J, Benes V, Turecki G, Ernst C. Biomarker discovery: quantification of microRNAs and other small non-coding RNAs using next generation sequencing. BMC Med Genomics, 2015, 8: 35. |
| [33] | Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods, 2015, 12(4): 357-360. |
| [34] | Raplee ID, Evsikov AV, de Evsikova CM. Aligning the aligners: comparison of RNA sequencing data alignment and gene expression quantification tools for clinical breast cancer research. J Pers Med, 2019, 9(2): 18. |
| [35] | Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(2): 166-169. |
| [36] | Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol, 2010, 28(5): 511-515. |
| [37] | Tiedt S, Prestel M, Malik R, Schieferdecker N, Duering M, Kautzky V, Stoycheva I, Böck J, Northoff BH, Klein M, Dorn F, Krohn K, Teupser D, Liesz A, Plesnila N, Holdt LM, Dichgans M. RNA-seq identifies circulating miR-125a-5p, miR-125b-5p, and miR-143-3p as potential biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Circ Res, 2017, 121(8): 970-980. |
| [38] | Li J, Zhao FQ, Wang YD, Chen JR, Tao J, Tian G, Wu SL, Liu WB, Cui QH, Geng B, Zhang WL, Weldon R, Auguste K, Yang L, Liu XY, Chen L, Yang XC, Zhu BL, Cai J. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome, 2017, 5(1): 14. |
| [39] | Kong YQ, Liu JK, Gu JQ, Xu JY, Zheng YN, Wei YL, Wu SY. Optimization scheme of machine learning model for genetic division between northern Han, southern Han, Korean and Japanese. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(11): 1028-1043. |
| 孔永强, 刘金凯, 顾佳琪, 徐景怡, 郑雨诺, 魏以梁, 伍少远. 南-北方汉族人、韩国人和日本人遗传划分机器学习模型优化方案. 遗传, 2022, 44(11): 1028-1043. | |
| [40] | Lin HJ.The prediction and functional analysis of IncRNA in embryonic development process [Dissertation]. Nanchang University, 2016. |
| 林海军.胚胎中lncRNA的预测及其在胚胎发育过程中的功能分析[学位论文]. 南昌大学, 2016. | |
| [41] | Ming TY, Jiang LR, Liu J, Chang JJ, Hou YP, Zhang GF, Wang Z. Y-Chromosomal genetic markers: forensic application and prospect. Forensic Sci Technol, 2022, 47(4): 411-418. |
| [42] | 明天悦, 蒋礼蓉, 刘京, 畅晶晶, 侯一平, 张广峰, 王正. Y染色体遗传标记的法医学应用及展望. 刑事技术, 2022, 47(4): 411-418. |
| Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature, 2012, 486(7402): 207-214. | |
| [43] | Zhao YX, Hu S, Ye J, Sun QF, Ji AQ. Researches of mRNA profiling for forensic body fluid identification. Forensic Sci Technol, 2019, 44(5): 388-394. |
| 赵一霞, 胡胜, 叶健, 孙启凡, 季安全. mRNA分析在体液斑迹组织来源推断中的应用研究进展. 刑事技术, 2019, 44(5): 388-394. | |
| [44] | Zhang Q, Zhao HM, Li YJ, Chen J, Chang JJ, Yang RQ, Wang C. Application of non-coding RNA in body fluid stain identification. Chin J Forensic Med, 2020, 35(5): 514-517. |
| 张琦, 赵禾苗, 李永久, 陈静, 畅晶晶, 杨瑞琴, 王冲. 非编码RNA在体液斑迹鉴定中的应用. 中国法医学杂志, 2020, 35(5): 514-517. | |
| [45] | Lehman DC. Forensic microbiology. Clin Lab Sci, 2012, 25(2): 114-119. |
| [46] | García MG, Pérez-Cárceles MD, Osuna E, Legaz I. Impact of the human microbiome in forensic sciences: a systematic review. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2020, 86(22): e01451-20. |
| [47] | Ventura Spagnolo E, Stassi C, Mondello C, Zerbo S, Milone L, Argo A. Forensic microbiology applications: a systematic review. Leg Med (Tokyo), 2019, 36: 73-80. |
| [48] | Jia F, Sun XK, Yu SB, Yu J, Lin CM, Kan XS, ShaoW. An age estimation method based on DNA methylation detection in the field of forensic science. Chin J Forensic Med, 2021, 3(4): 373-378. |
| 贾菲, 孙学科, 喻少波, 于蛟, 林春美, 阚旭升, 邵武. DNA甲基化水平的法医学个体年龄推断. 中国法医学杂志, 2021, 36(4): 373-378. | |
| [49] | Mameli A, Scudiero CM, Delogu G, Ghiani ME. Successful analysis of a 100 years old semen stain generating a complete DNA STR profile. J Forensic Leg Med, 2019, 61: 78-81. |
| [50] | Xu TS, Li XG, Jiao DJ, Xie ZH, Dai ZM. Mechanism of 5′-to-3′ degradation of eukaryotic and prokaryotic mRNA. Hereditas(Beijing), 2015, 37(3): 250-258. |
| 许禔森, 李学贵, 焦德杰, 谢兆辉, 戴忠民. 真核生物和原核生物mRNA 5′至3′方向的降解机制. 遗传, 2015, 37(3): 250-258. | |
| [51] | Althaf MM, El Kossi M, Jin JK, Sharma A, Halawa AM. Human leukocyte antigen typing and crossmatch: a comprehensive review. World J Transplant, 2017, 7(6): 339-348. |
| [52] | Gao H, Han Y, Zhai XX, Gao FS. The research progress of antigen presentation by MHC molecules. Chin Bull Life Sci, 2017, 29(5): 450-461. |
| 高花, 韩勇, 翟晓鑫, 高凤山. MHC分子抗原递呈机制的研究进展. 生命科学, 2017, 29(5): 450-461. | |
| [53] | Lu BH.Effects of smoking on autoantibodies and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [Dissertation]. Hubei Minzu University, 2020. |
| 鲁邦华.吸烟对类风湿关节炎自身抗体及疾病活动的影响[学位论文]. 湖北民族大学, 2020. | |
| [54] | Jiang WQ, Chen ZY, Zhou LL, Lian SY, Zhang XM. Investigation on disease cognition status and influencing factors of control level in patients with bronchial asthma. Prog Mod Biomed, 2022, 22(2): 342-346. |
| 蒋文青, 陈宗喻, 周垒垒, 练思雨, 张先明. 支气管哮喘患者疾病认知状况调查及控制水平的影响因素分析. 现代生物医学进展, 2022, 22(2): 342-346. | |
| [55] | Heneghan N, Fu J, Pritchard J, Payton M, Allen RW. The effect of environmental conditions on the rate of RNA degradation in dried blood stains. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2021, 51: 102456. |
| [56] | Zhao CC, Zhao MZ, Zhu Y, Zhang L, Zheng Z, Wang Q, Li YG, Zhang P, Zhu SS, Ding SJ, Li JB. The persistence and stability of miRNA in bloodstained samples under different environmental conditions. Forensic Sci Int, 2021, 318: 110594. |
| [57] | Salzmann AP, Arora N, Russo G, Kreutzer S, Snipen L, Haas C. Assessing time dependent changes in microbial composition of biological crime scene traces using microbial RNA markers. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2021, 53: 102537. |
| [1] | Hongyu Dai, Dong Ji, Cheng Tan, Jie Sun, Hao Yao. Research progress on the role and regulatory mechanism of pathogenic Th17 cells in neuroinflammation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(4): 289-299. |
| [2] | Jiani Guo, Fan Liu, Lu Wang. Zebrafish blood disease models and applications [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(8): 725-738. |
| [3] | Liwen Bao, Yiye Zhou, Fanyi Zeng. Advances in gene therapy for β-thalassemia and hemophilia based on the CRISPR/Cas9 technology [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(10): 949-964. |
| [4] | Jian Hu,Yiren Zhou,Jialin Ding,Zhiyuan Wang,Ling Liu,Yekai Wang,Huiling Lou,Shouyi Qiao,Yanhua Wu. Simplification of genotyping techniques of the ABO blood type experiment and exploration of population genetics [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(5): 423-429. |
| [5] | Jian Zhao, Dongmei Hu, Dade Yu, Mingliang Dong, Yun Li, Yingming Fan, Yanwei Wang, Jinfeng Zhang. Teaching design and practice of human blood type traits in genetics comprehensive laboratory course [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(5): 461-466. |
| [6] | Hongdong Li,Guini Hong,Zheng Guo. Age-related DNA methylation changes in peripheral whole blood [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(2): 165-173. |
| [7] | Yanping Wang, Huaizhong Wang, Jianfeng Guo, Haifei Wang, Jianfeng Liu, Jiying Wang. Gene expression analysis of porcine peripheral blood mononuclear cell in response to immune stimulation of Poly I:C [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(1): 63-69. |
| [8] | PI Yan, LI Xiao-Ying, HUAI Cong, WANG Shi-Ming, QIAO Shou-Yi, LU Da-Ru. Exploration on human blood type case in teaching practice of genetics [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(8): 1040-1044. |
| [9] | BAI Ru-Feng, JIANG Li-Zhe, ZHANG Zhong, SHI Mei-Sen. Genetic polymorphism and forensic application of 30 InDel loci of Han population in Beijing [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(12): 1368-1376. |
| [10] | XU Rui-Wei, YAN Wei-Li. Advances in genome-wide association studies on essential hypertension [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(7): 793-809. |
| [11] | CA Hai-Jiang, LIU Hai-Chao, SHI Bin, LI An, TANG Wen-Ru, LUO Ying. Recent Advance of Whole Genome Amplification and its Application prospect in Forensic Individual Identification [J]. HEREDITAS, 2010, 32(11): 1119-1125. |
| [12] | XU Xian-Guo, LIU Ying, HONG Xiao-Zhen, MA Kai-Rong, ZHU Fa-Ming, LV Hang-Jun, YAN Li-Xing. Molecular genetic analysis of rare cisAB variants in Chinese population [J]. HEREDITAS, 2008, 30(10): 1295-1300. |
| [13] | LIU Wei-Yu, JIN Chun-Lian, Liu Li-Ying, LIN Chang-Kun, WANG Yan, SUN Kai-Lai. Detection of fetal nucleated red blood cells in the maternal circula-tion by Kleihauer test [J]. HEREDITAS, 2007, 29(3): 289-289―292. |
| [14] | JIN Mei, CUI Yi-Hou, FU Zhong-Yang, GAO Wen-Bo, WANG Wei. The Correlation Analysis of Blood Protein Polymorphism with Economic Traits in Liaoning New-breeding Cashmere Goat [J]. HEREDITAS, 2006, 28(5): 529-532. |
| [15] | SUN, Chong, ZHAO, Zhou-Zhou, GAO, Li, SUN, Yan, SHAO, Huan-Jie, LI, Wen-Xin. Cloning and Characterization of Two Novel Transcripts of ZNF268 [J]. HEREDITAS, 2006, 28(5): 513-517. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||