遗传 ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (9): 858-869.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-173
收稿日期:2020-06-12
修回日期:2020-07-14
出版日期:2020-09-20
发布日期:2020-08-31
通讯作者:
刘利静
E-mail:ljliu@sdu.edu.cn
作者简介:谷晓勇,硕士,助理实验师,研究方向:植物免疫。E-mail: 基金资助:
Xiaoyong Gu, Yang Liu, Lijing Liu( )
)
Received:2020-06-12
Revised:2020-07-14
Online:2020-09-20
Published:2020-08-31
Contact:
Liu Lijing
E-mail:ljliu@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
植物激素水杨酸(salicylic acid,SA)是广泛存在于植物体中的小分子酚类物质,参与植物多种生理过程,特别是在植物免疫中发挥重要功能。植物免疫过程中体内SA大量合成,SA信号通路被激活从而诱导抗病相关基因表达。近年来,随着研究的不断深入,SA生物合成和信号转导都取得一系列重要进展:进一步完善了SA生物合成的异分支酸合酶(isochorismate synthase, ICS)和苯丙氨酸解氨酶(phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, PAL)途径;明确了NPR1 (nonexpresser of PR genes 1)和其同源蛋白NPR3、NPR4是植物接收SA的受体;发现II类TGA (TGACG-binding factor)转录因子通过与不同SA受体互作激活或抑制下游基因表达等。本文系统介绍了SA生物合成和信号转导领域的相关进展,以期为深入研究SA调控植物生长发育和环境胁迫响应提供理论参考。
谷晓勇, 刘扬, 刘利静. 植物激素水杨酸生物合成和信号转导研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(9): 858-869.
Xiaoyong Gu, Yang Liu, Lijing Liu. Progress on the biosynthesis and signal transduction of phytohormone salicylic acid[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(9): 858-869.
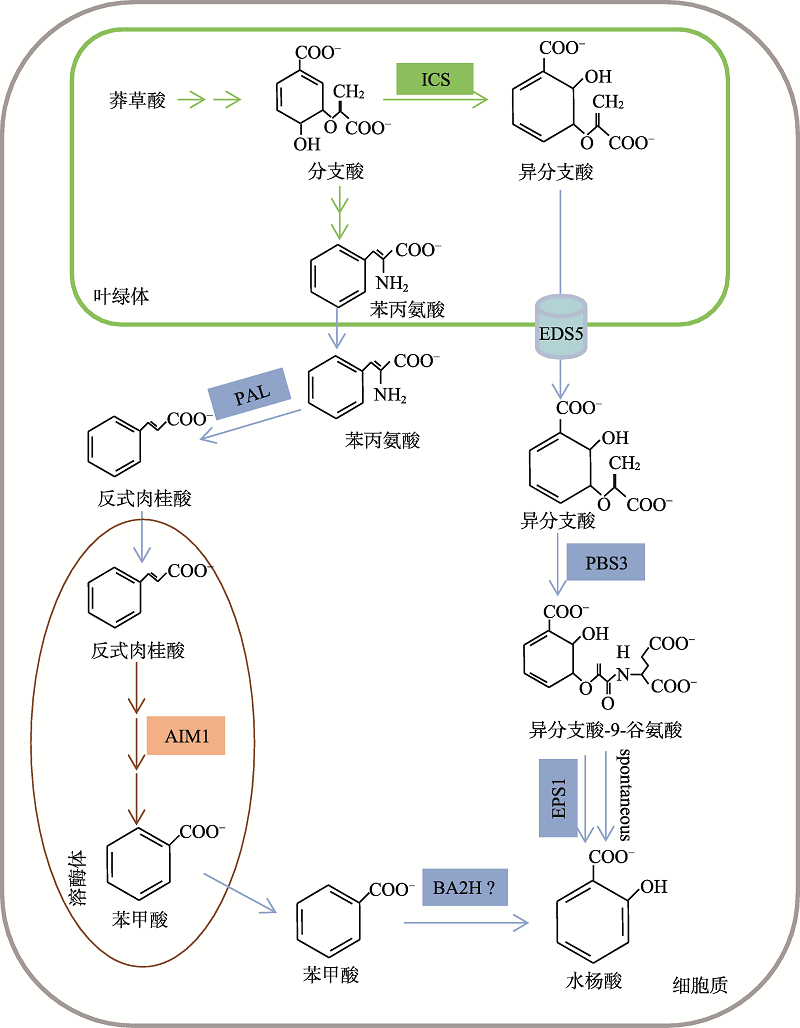
图1
水杨酸合成示意图 植物通过两条途径合成SA。一是ICS途径:ICS催化分支酸产生异分支酸,异分支酸经EDS5转运至细胞质后PBS3催化其与谷氨酸结合生成IC-9-Glu,IC-9-Glu自主分解或经EPS1催化加速分解最终产生水杨酸;二是PAL途径:分支酸经催化产生苯丙氨酸,苯丙氨酸进入细胞质后由PALs催化产生反式肉桂酸,反式肉桂酸进入过氧化物酶体后经β-氧化产生苯甲酸,苯甲酸转运至细胞质后可能由BA2H羟化产生水杨酸。绿色箭头所示为发生在叶绿体中的反应;棕色箭头所示为发生在过氧化物酶体中的反应;蓝色箭头所示为细胞质中的反应过程。ICS:isochorismate synthase;EDS5:enhanced disease susceptibility 5;PBS3:avrPphB susceptible 3;EPS1:enhanced pseudomonas susceptibility 1;PAL:phenylalanine ammonia-lyase;AIM:abnormal inflorescence meristem 1;BA2H:benzoic acid 2-hydroxylase。"
| [1] |
Norn S, Permin H, Kruse PR, Kruse E . From willow bark to acetylsalicylic acid. Dan Medicinhist Arbog, 2009,37:79-98.
pmid: 20509453 |
| [2] |
Sneader W . The discovery of aspirin: a reappraisal. Brit Med J, 2000,321(7276):1591-1594.
pmid: 11124191 |
| [3] |
Raskin I . Salicylate, a new plant hormone. Plant Physiology, 1992,99(3):799-803.
pmid: 16669002 |
| [4] |
Koo YM, Heo AY, Choi HW . Salicylic acid as a safe plant protector and growth regulator. Plant Pathol J, 2020,36(1):1-10.
pmid: 32089657 |
| [5] | Zou LP, Pan C, Wang MX, Cui L, Han BY . Progress on the mechanism of hormones regulating plant flower formation. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020,42(8):739-751. |
| 邹礼平, 潘铖, 王梦馨, 崔林, 韩宝瑜 . 激素调控植物成花机理研究进展. 遗传, 2020,42(8):739-751. | |
| [6] | Huang PX, Dong Z, Guo PR, Zhang X, Qiu YP, Li BS, Wang YC, Guo HW . Salicylic acid suppresses apical hook formation via NPR1-mediated repression of EIN3 and EIL1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2020,32(3):612-629. |
| [7] |
White RF . Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) induces resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in tobacco. Virology, 1979,99(2):410-412.
doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90019-9 |
| [8] |
Zhang YL, Li X . Salicylic acid: Biosynthesis, perception, and contributions to plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2019,50:29-36.
pmid: 30901692 |
| [9] | Jones JDG, Dangl JL . The plant immune system. Nature, 2006,444(7117):323-329. |
| [10] |
Tsuda K, Sato M, Stoddard T, Glazebrook J, Katagiri F . Network properties of robust immunity in plants. PLoS Genet, 2009,5(12):e1000772.
pmid: 20011122 |
| [11] |
Cao H, Glazebrook J, Clarke JD, Volko S, Dong X . The Arabidopsis NPR1 gene that controls systemic acquired resistance encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin repeats. Cell, 1997,88(1):57-63.
pmid: 9019406 |
| [12] |
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye G, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J . Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science, 1993,261(5122):754-756.
pmid: 17757215 |
| [13] |
Seyfferth C, Tsuda K . Salicylic acid signal transduction: The initiation of biosynthesis, perception and transcriptional reprogramming. Front Plant Sci, 2014,5:697.
pmid: 25538725 |
| [14] |
Garcion C, Lohmann A, Lamodiere E, Catinot J, Buchala A, Doermann P, Metraux JP . Characterization and biological function of the isochorismate synthase2 gene of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2008,147(3):1279-1287.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.119420 pmid: 18451262 |
| [15] |
Wildermuth MC, Dewdney J, Wu G, Ausubel FM . Isochorismate synthase is required to synthesize salicylic acid for plant defence. Nature, 2001,414(6863):562-565.
pmid: 11734859 |
| [16] |
Macaulay KM, Heath GA, Ciulli A, Murphy AM, Abell C, Carr JP, Smith AG . The biochemical properties of the two Arabidopsis thaliana isochorismate synthases. Biochem J, 2017,474(10):1579-1590.
pmid: 28356402 |
| [17] |
Serino L, Reimmann C, Baur H, Beyeler M, Visca P, Haas D . Structural genes for salicylate biosynthesis from chorismate in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet, 1995,249(2):217-228.
pmid: 7500944 |
| [18] |
Jagadeeswaran G, Raina S, Acharya BR, Maqbool SB, Mosher SL, Appel HM, Schultz JC, Klessig DF, Raina R . Arabidopsis GH3-LIKE DEFENSE GENE 1 is required for accumulation of salicylic acid, activation of defense responses and resistance to pseudomonas syringae. Plant J, 2007,51(2):234-246.
pmid: 17521413 |
| [19] |
Zheng ZY, Qualley A, Fan BF, Dudareva N, Chen ZX . An important role of a BAHD acyl transferase-like protein in plant innate immunity. Plant J, 2009,57(6):1040-1053.
pmid: 19036031 |
| [20] |
Rekhter D, Lüdke D, Ding YL, Feussner K, Zienkiewicz K, Lipka V, Wiermer M, Zhang YL, Feussner I . Isochorismate- derived biosynthesis of the plant stress hormone salicylic acid. Science, 2019,365(6452):498-502.
pmid: 31371615 |
| [21] |
Torrens-Spence MP, Bobokalonova A, Carballo V, Glinkerman CM, Pluskal T, Shen A, Weng JK . PBS3 and EPS1 complete salicylic acid biosynthesis from isochorismate in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant, 2019,12(12):1577-1586.
pmid: 31760159 |
| [22] |
Okrent RA, Brooks MD, Wildermuth MC . Arabidopsis GH3.12 (PBS3) conjugates amino acids to 4-substituted benzoates and is inhibited by salicylate. J Biol Chem, 2009,284(15):9742-9754.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806662200 pmid: 19189963 |
| [23] | Okrent RA, Wildermuth MC . Evolutionary history of the GH3 family of acyl adenylases in rosids. Plant Mol Biol, 2011,76(6):489-505. |
| [24] | Nawrath C, Heck S, Parinthawong N, Metraux JP . EDS5, an essential component of salicylic acid-dependent signaling for disease resistance in Arabidopsis, is a member of the mate transporter family. Plant Cell, 2002,14(1):275-286. |
| [25] | Serrano M, Wang BJ, Aryal B, Garcion C, Abou-Mansour E, Heck S, Geisler M, Mauch F, Nawrath C, Metraux JP . Export of salicylic acid from the chloroplast requires the multidrug and toxin extrusion-like transporter EDS5. Plant Physiol, 2013,162(4):1815-1821. |
| [26] | Ribnicky DM, Shulaev V, Raskin II . Intermediates of salicylic acid biosynthesis in tobacco. Plant Physiol, 1998,118(2):565-572. |
| [27] | Leon J, Yalpani N, Raskin I, Lawton MA . Induction of benzoic acid 2-hydroxylase in virus-inoculated tobacco. Plant Physiol, 1993,103(2):323-328. |
| [28] | Koukol J, Conn EE . The metabolism of aromatic compounds in higher plans. IV. Purification and properties of the phenylalanine deaminase of hordeum vulgare. J Biol Chem, 1961,236(10):2692-2698. |
| [29] | Huang JL, Gu M, Lai ZB, Fan BF, Shi K, Zhou YH, Yu JQ, Chen ZX . Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis PAL gene family in plant growth, development, and response to environmental stress. Plant Physiol, 2010,153(4):1526-1538. |
| [30] | Tonnessen BW, Manosalva P, Lang JM, Baraoidan M, Bordeos A, Mauleon R, Oard J, Hulbert S, Leung H, Leach JE . Rice phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene osPAL4 is associated with broad spectrum disease resistance. Plant Mol Biol, 2015,87(3):273-286. |
| [31] | Zhou XG, Liao HC, Chern M, Yin JJ, Chen YF, Wang JP, Zhu XB, Chen ZX, Yuan C, Zhao W, Wang J, Li WT, He M, Ma B, Wang JC, Qin P, Chen WL, Wang YP, Liu JL, Qian YW, Wang WM, Wu XJ, Li P, Zhu LH, Li SG, Ronald PC, Chen XW . Loss of function of a rice TPR- domain RNA-binding protein confers broad-spectrum disease resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018,115(12):3174-3179. |
| [32] | Ning Y, Wang GL . Breeding plant broad-spectrum resistance without yield penalties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018,115(12):2859-2861. |
| [33] | He J, Liu YQ, Yuan DY, Duan MJ, Liu YL, Shen ZJ, Yang CY, Qiu ZY, Liu DM, Wen PZ, Huang J, Fan DJ, Xiao SZ, Xin YY, Chen XN, Jiang L, Wang HY, Yuan LP, Wan JM . An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020,117(1):271-277. |
| [34] | Colquhoun TA, Marciniak DM, Wedde AE, Kim JY, Schwieterman ML, Levin LA, Moerkercke AV, Schuurink RC, Clark DG . A peroxisomally localized acyl-activating enzyme is required for volatile benzenoid formation in a petuniaxhybrida cv. 'Mitchell diploid' flower. J Exp Bot, 2012,63(13):4821-4833. |
| [35] | Moerkercke AV, Schauvinhold I, Pichersky E, Haring MA, Schuurink RC . A plant thiolase involved in benzoic acid biosynthesis and volatile benzenoid production. Plant J, 2009,60(2):292-302. |
| [36] | Klempien A, Kaminaga Y, Qualley A, Nagegowda DA, Widhalm JR, Orlova I, Shasany AK, Taguchi G, Kish CM, Cooper BR, D'Auria JC, Rhodes D, Pichersky E, Dudareva N,. Contribution of CoA ligases to benzenoid biosynthesis in petunia flowers. Plant Cell, 2012,24(5):2015-2030. |
| [37] | Bussell JD, Reichelt M, Wiszniewski AAG, Gershenzon J, Smith SM . Peroxisomal ATP-binding cassette transporter comatose and the multifunctional protein abnormal inflorescence meristem are required for the production of benzoylated metabolites in Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol, 2014,164(1):48-54. |
| [38] | Xu L, Zhao HY, Ruan WY, Deng MJ, Wang F, Peng JR, Luo J, Chen ZX, Yi KK . Abnormal inflorescence meristem1 functions in salicylic acid biosynthesis to maintain proper reactive oxygen species levels for root meristem activity in rice. Plant Cell, 2017,29(3):560-574. |
| [39] | Sadeghi M, Dehghan S, Fischer R, Wenzel U, Vilcinskas A, Kavousi HR, Rahnamaeian M . Isolation and characterization of isochorismate synthase and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase during salinity stress, wounding, and salicylic acid treatment in carthamus tinctorius. Plant Signal Behav, 2013,8(11):e27335. |
| [40] | Uppalapati SR, Ishiga Y, Wangdi T, Kunkel BN, Anand A, Mysore KS, Bender CL . The phytotoxin coronatine contributes to pathogen fitness and is required for suppression of salicylic acid accumulation in tomato inoculated with pseudomonas syringae pv. Tomato DC3000. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 2007,20(8):955-965. |
| [41] | Meuwly P, Molders W, Buchala A, Metraux JP . Local and systemic biosynthesis of salicylic acid in infected cucumber plants. Plant Physiol, 1995,109(3):1107-1114. |
| [42] | Yuan YN, Chung JD, Fu XY, Johnson VE, Ranjan P, Booth SL, Harding SA, Tsai CJ . Alternative splicing and gene duplication differentially shaped the regulation of isochorismate synthase in populus and Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009,106(51):22020-22025. |
| [43] | Yalpani N, Leon J, Lawton MA, Raskin I . Pathway of salicylic acid biosynthesis in healthy and virus-inoculated tobacco. Plant Physiol, 1993,103(2):315-321. |
| [44] | Wang L, Tsuda K, Sato M, Cohen JD, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J . Arabidopsis CaM binding protein CBP60g contributes to MAMP-induced SA accumulation and is involved in disease resistance against pseudomonas syringae. PLoS Pathog, 2009,5(2):e1000301. |
| [45] | van Verk MC, Bol JF, Linthorst HJM . WRKY transcription factors involved in activation of SA biosynthesis genes. BMC Plant Biol, 2011,11:89. |
| [46] | Wang XY, Gao J, Zhu Z, Dong X, Wang XX, Ren GD, Zhou X, Kuai BK . TCP transcription factors are critical for the coordinated regulation of isochorismate synthase 1 expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J, 2015,82(1):151-162. |
| [47] | Zhang YX, Xu SH, Ding PT, Wang DM, Cheng YT, He J, Gao MH, Xu F, Li Y, Zhu ZH, Li X, Zhang YL . Control of salicylic acid synthesis and systemic acquired resistance by two members of a plant-specific family of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010,107(42):18220-18225. |
| [48] | Sun TJ, Busta L, Zhang Q, Ding PT, Jetter R, Zhang YL . TGACG-binding factor 1 (TGA1) and TGA4 regulate salicylic acid and pipecolic acid biosynthesis by modulating the expression of systemic acquired resistance deficient 1 (SARD1) and calmodulin-binding protein 60g (CBP60g). New Phytol, 2018,217(1):344-354. |
| [49] | Sun TJ, Zhang YX, Li Y, Zhang Q, Ding YL, Zhang YL . ChIP-seq reveals broad roles of SARD1 and CBP60g in regulating plant immunity. Nat Commun, 2015,6:10159. |
| [50] | Wang L, Tsuda K, Truman W, Sato M, Nguyen LV, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J . CBP60g and SARD1 play partially redundant critical roles in salicylic acid signaling. Plant J, 2011,67(6):1029-1041. |
| [51] | Zheng XY, Spivey NW, Zeng WQ, Liu PP, Fu ZQ, Klessig DF, He SY, Dong XN . Coronatine promotes pseudomonas syringae virulence in plants by activating a signaling cascade that inhibits salicylic acid accumulation. Cell Host Microbe, 2012,11(6):587-596. |
| [52] | Wang D, Amornsiripanitch N, Dong XN . A genomic approach to identify regulatory nodes in the transcriptional network of systemic acquired resistance in plants. PLoS Pathog, 2006,2(11):e123. |
| [53] | Truman W, Sreekanta S, Lu Y, Bethke G, Tsuda K, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J . The calmodulin-binding protein60 family includes both negative and positive regulators of plant immunity. Plant Physiol, 2013,163(4):1741-1751. |
| [54] | Chen HM, Xue L, Chintamanani S, Germain H, Lin HQ, Cui HT, Cai R, Zuo JR, Tang XY, Li X, Guo HW, Zhou JM . Ethylene insensitive3 and ethylene insensitive3-like1 repress salicylic acid induction deficient2 expression to negatively regulate plant innate immunity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2009,21(8):2527-2540. |
| [55] | Cao H, Bowling SA, Gordon AS, Dong X . Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell, 1994,6(11):1583-1592. |
| [56] | Delaney TP, Friedrich L, Ryals JA . Arabidopsis signal transduction mutant defective in chemically and biologically induced disease resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1995,92(14):6602-6606. |
| [57] | Shah J, Tsui F, Klessig DF . Characterization of a salicylic acid-insensitive mutant ( sai1) of Arabidopsis thaliana, identified in a selective screen utilizing the SA-inducible expression of the tms2 gene. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 1997,10(1):69-78. |
| [58] | Withers J, Dong XN . Posttranslational modifications of NPR1: A single protein playing multiple roles in plant immunity and physiology. PLoS Pathog, 2016,12(8):e1005707. |
| [59] | Saleh A, Withers J, Mohan R, Marqueés J, Gu YN, Yan SP, Zavaliev R, Nomoto M, Tada Y, Dong XN . Posttranslational modifications of the master transcriptional regulator NPR1 enable dynamic but tight control of plant immune responses. Cell Host Microbe, 2015,18(2):169-182. |
| [60] | Wu Y, Zhang D, Chu JY, Boyle P, Wang Y, Brindle ID, De Luca V, Després C . The Arabidopsis NPR1 protein is a receptor for the plant defense hormone salicylic acid. Cell Rep, 2012,1(6):639-647. |
| [61] | Ding YL, Sun TJ, Ao K, Peng YJ, Zhang YX, Li X, Zhang YL,. Opposite roles of salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in transcriptional regulation of plant immunity. Cell, 2018, 173(6): 1454-1467. e15. |
| [62] | Zhang YL, Cheng YT, Qu N, Zhao QG, Bi DL, Li X . Negative regulation of defense responses in Arabidopsis by two NPR1 paralogs. Plant J, 2006,48(5):647-656. |
| [63] | Fu ZQ, Yan SP, Saleh A, Wang W, Ruble J, Oka N, Mohan R, Spoel SH, Tada Y, Zheng N, Dong XN . NPR3 and NPR4 are receptors for the immune signal salicylic acid in plants. Nature, 2012,486(7402):228-232. |
| [64] | Yan S, Dong X . Perception of the plant immune signal salicylic acid. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2014,20:64-68. |
| [65] | Ding PT, Ding YL . Stories of salicylic acid: A plant defense hormone. Trends Plant Sci, 2020,25(6):549-565. |
| [66] | Liu LJ, Sonbol FM, Huot B, Gu YN, Withers J, Mwimba M, Yao J, He SY, Dong XN . Salicylic acid receptors activate jasmonic acid signalling through a non-canonical pathway to promote effector-triggered immunity. Nat Commun, 2016,7:13099. |
| [67] | Chang M, Zhao JP, Chen H, Li GY, Chen J, Li M, Palmer IA, Song JQ, Alfano JR, Liu FQ, Fu ZQ . PBS3 protects EDS1 from proteasome-mediated degradation in plant immunity. Mol Plant, 2019,12(5):678-688. |
| [68] | Manohar M, Tian MY, Moreau M, Park SW, Choi HW, Fei ZJ, Friso G, Asif M, Manosalva P, von Dahl CC, Shi K, Ma SS, Dinesh-Kumar SP, O'Doherty I, Schroeder FC, van Wijk KJ, Klessig DF. Identification of multiple salicylic acid-binding proteins using two high throughput screens. Front Plant Sci, 2015,5:777. |
| [69] | Castelló MJ, Medina-Puche L, Lamilla J, Tornero P . NPR1 paralogs of Arabidopsis and their role in salicylic acid perception. PLoS One, 2018,13(12):e0209835. |
| [70] | Pokotylo I, Kravets V, Ruelland E . Salicylic acid binding proteins (SABPs): The hidden forefront of salicylic acid signalling. Int J Mol Sci, 2019,20(18):4377. |
| [71] | Forouhar F, Yang Y, Kumar D, Chen Y, Fridman E, Park SW, Chiang YW, Acton TB, Montelione GT, Pichersky E, Klessig DF, Tong L . Structural and biochemical studies identify tobacco SABP2 as a methyl salicylate esterase and implicate it in plant innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005,102(5):1773-1778. |
| [72] | Yuan HM, Liu WC, Lu YT . Catalase2 coordinates SA-mediated repression of both auxin accumulation and JA biosynthesis in plant defenses. Cell Host Microbe, 2017,21(2):143-155. |
| [73] | Chen Z, Klessig DF . Identification of a soluble salicylic acid-binding protein that may function in signal transduction in the plant disease-resistance response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1991,88(18):8179-8183. |
| [74] | Chen Z, Ricigliano JW, Klessig DF . Purification and characterization of a soluble salicylic acid-binding protein from tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1993,90(20):9533-9537. |
| [75] | Backer R , Naidoo S, van den Berg N. The nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes 1 (NPR1) and related family: Mechanistic insights in plant disease resistance. Front Plant Sci, 2019,10:102. |
| [76] | Zhang JY, Wang QJ, Guo ZR . Progresses on plant AP2/ERF transcription factors. Hereditas(Beijing), 2012,34(7):835-847. |
| 张计育, 王庆菊, 郭忠仁 . 植物AP2/ERF类转录因子研究进展. 遗传, 2012,34(7):835-847. | |
| [77] | Zhang Y, Fan W, Kinkema M, Li X, Dong X . Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999,96(11):6523-6528. |
| [78] | Zhou JM, Trifa Y, Silva H, Pontier D, Lam E, Shah J, Klessig DF . NPR1 differentially interacts with members of the TGA/OBF family of transcription factors that bind an element of the PR-1 gene required for induction by salicylic acid. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 2000,13(2):191-202. |
| [79] | Després C, DeLong C, Glaze S, Liu E, Fobert PR,. The Arabidopsis NPR1/NIM1 protein enhances the DNA binding activity of a subgroup of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors. Plant Cell, 2000,12(2):279-290. |
| [80] | Kesarwani M, Yoo J, Dong XN . Genetic interactions of TGA transcription factors in the regulation of pathogenesis-related genes and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2007,144(1):336-346. |
| [81] | Jin HS, Choi SM, Kang MJ, Yun SH, Kwon DJ, Noh YS, Noh B . Salicylic acid-induced transcriptional reprogramming by the HAC-NPR1-TGA histone acetyltransferase complex in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018,46(22):11712-11725. |
| [82] | Weigel RR, Bäuscher C, Pfitzner AJ, Pfitzner UM . NIMIN-1, NIMIN-2 and NIMIN-3, members of a novel family of proteins from Arabidopsis that interact with NPR1/NIM1, a key regulator of systemic acquired resistance in plants. Plant Mol Biol, 2001,46(2):143-160. |
| [83] | Weigel RR, Pfitzner UM, Gatz C . Interaction of NIMIN1 with NPR1 modulates PR gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2005,17(4):1279-1291. |
| [84] | Hermann M, Maier F, Masroor A, Hirth S, Pfitzner AJP, Pfitzner UM . The Arabidopsis NIMIN proteins affect NPR1 differentially. Front Plant Sci, 2013,4:88. |
| [85] | Maleck K, Levine A, Eulgem T, Morgan A, Schmid J, Lawton KA, Dangl JL, Dietrich RA . The transcriptome of Arabidopsis thaliana during systemic acquired resistance. Nat Genet, 2000,26(4):403-410. |
| [86] | Dong JX, Chen CH, Chen ZX . Expression profiles of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Mol Biol, 2003,51(1):21-37. |
| [87] | Ulker B, Somssich IE . WRKY transcription factors: From DNA binding towards biological function. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2004,7(5):491-498. |
| [88] | Pandey SP, Somssich IE . The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity. Plant Physiol, 2009,150(4):1648-1655. |
| [89] | Chen J, Mohan R, Zhang YQ, Li M, Chen H, Palmer IA, Chang M, Qi G, Spoel SH, Mengiste T, Wang DW, Liu FQ, Fu ZQ . NPR1 promotes its own and target gene expression in plant defense by recruiting CDK8. Plant Physiol, 2019,181(1):289-304. |
| [90] | Hussain RMF, Sheikh AH, Haider I, Quareshy M, Linthorst HJM . Arabidopsis WRKY50 and TGA transcription factors synergistically activate expression of PR1. Front Plant Sci, 2018,9:930. |
| [91] | Xu GY, Yuan M, Ai CR, Liu LJ, Zhuang E, Karapetyan S, Wang SP , Dong XN. uORF-mediated translation allows engineered plant disease resistance without fitness costs. Nature, 2017,545(7655):491-494. |
| [1] | 艾尔肯·热合曼,孜比尔尼沙·吾买尔,阿西卡·拉武克,阿吉尼沙·马木提. 新疆蒙古族对糖精和乙酰水杨酸尝味能力的分析[J]. 遗传, 2002, 24(4): 410-160. |
| [2] | 余多慰,朱红阳. 汉族人群中三种物质尝味能力的分析[J]. 遗传, 1991, 13(5): 30-32. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
