遗传 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 556-566.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-153
罗熹晨1( ), 刘慧2, 刘学英2, 李欣欣1, 廖红1, 傅向东1,2,3(
), 刘慧2, 刘学英2, 李欣欣1, 廖红1, 傅向东1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-10
修回日期:2022-06-08
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-07-01
通讯作者:
傅向东
E-mail:luoxichen1984@163.com;xdfu@genetics.ac.cn
作者简介:罗熹晨,硕士,专业方向:植物营养分子生物学。E-mail: 基金资助:
Xichen Luo1( ), Hui Liu2, Xueying Liu2, Xinxin Li1, Hong Liao1, Xiangdong Fu1,2,3(
), Hui Liu2, Xueying Liu2, Xinxin Li1, Hong Liao1, Xiangdong Fu1,2,3( )
)
Received:2022-05-10
Revised:2022-06-08
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-07-01
Contact:
Fu Xiangdong
E-mail:luoxichen1984@163.com;xdfu@genetics.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
高等植物在应对复杂环境变化时,需要整合和协调不同器官与组织感知的信息,并通过一套精细且复杂的机制经维管系统向受体组织或器官传递,进而系统性协调植物整体的生长发育和环境响应。在维管系统中移动的信号物质称为长距离信号。近年来研究发现,能够长距离移动的信号分子主要有小RNA、mRNA、小肽、激素、第二信使以及蛋白质等几类,这些信号分子能够将细胞外刺激从感知组织传递到靶器官,从而系统性地调控植物发育进程和环境响应。本文重点总结了植物体内长距离移动的RNA、小肽和蛋白质这3类长距离信号分子在调控植物器官发育、养分吸收以及环境响应等方面的研究进展,并对该领域在作物育种方面的应用潜力进行了探讨和展望,以期为作物遗传育种应用提供理论基础。
罗熹晨, 刘慧, 刘学英, 李欣欣, 廖红, 傅向东. 植物响应环境变化的长距离信号传导[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(7): 556-566.
Xichen Luo, Hui Liu, Xueying Liu, Xinxin Li, Hong Liao, Xiangdong Fu. Long distance signal transduction in response to environmental changes in plants[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(7): 556-566.
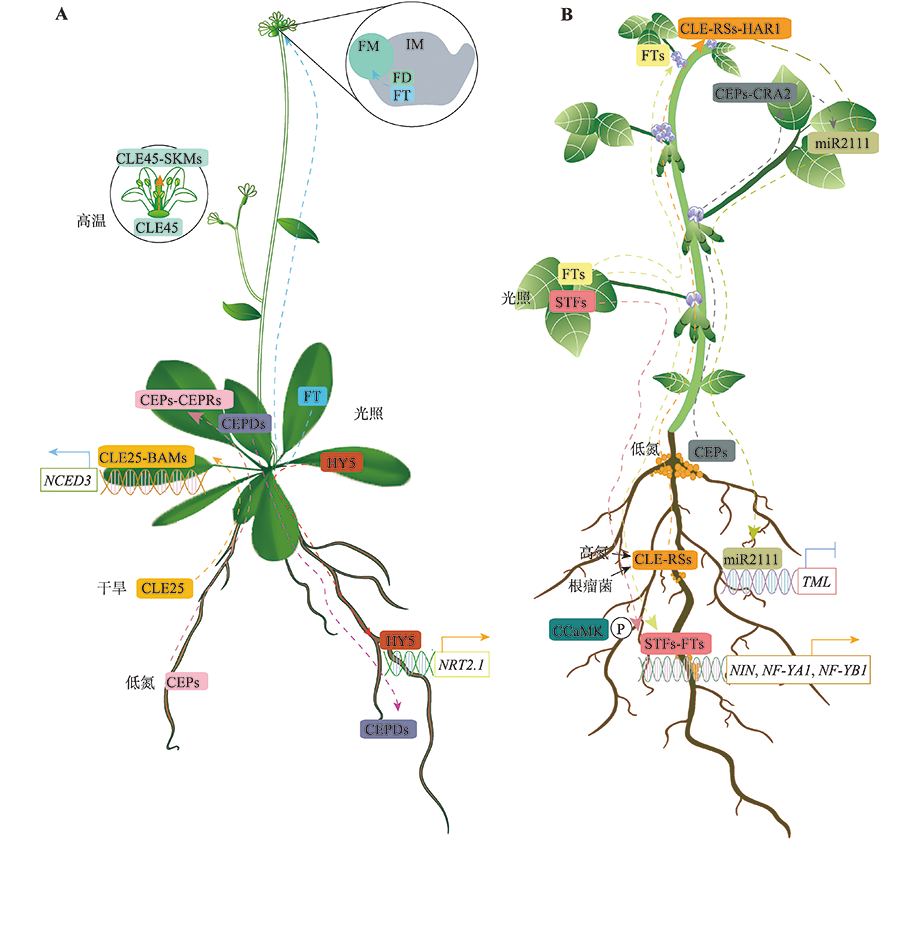
图2
长距离信号调控植物环境响应和豆科植物结瘤 A:长距离信号调控拟南芥响应外界光照、水分、温度以及氮素变化。植物通过长距离和细胞间通信,整合远端器官之间的环境信息,以适应变化的环境条件。在缺水条件下,拟南芥CLE25小肽长距离传递水分胁迫信号至叶片,诱导叶片中ABA的积累,从而调节气孔关闭,防止水分从植物体内流失;在氮浓度分布不均的土壤中,分泌的小信号肽CEP1受到根的局部氮缺乏上调,并通过木质部转移到地上部,当CEP1被叶片韧皮部中的CEPR1和CEPR2感知时,诱导非分泌的小信号肽CEPD1和CEPD2表达,并进一步通过韧皮部转移至高氮区域的根系中,促进根系发育;高温环境下,CLE45在雌蕊中移动可以改善高温下花粉管的伸长缺陷;开花转变过程中,FT编码的成花素蛋白长距离转运至花序分生组织中调控植物的开花时间;光照条件下,HY5蛋白能够从植物地上部长距离移动至根系,自激活根系HY5表达,同时激活高亲和性硝酸根转运蛋白基因NRT2.1的表达,进而促进根系生长和氮吸收。B:长距离信号调控豆科植物开花以及结瘤过程。在施肥较多时,诱导信号肽CLE-RS在豆科植物根中的表达,CLE-RS肽通过木质部向外移动至地上部,被受体激酶HAR1识别,调节细胞分裂,抑制根瘤的形成。另一方面,CLE-RS-HAR1复合体可导致地上部miR2111下调。miR2111能够通过韧皮组织从叶片移动至根部,抑制参与结瘤的TML基因表达,促进结瘤。在低氮条件下,CEP1能够长距离运输到地上部分,与CRA2受体结合,并促进miR2111前体的表达,从而抑制TML靶基因在根部表达,促进结瘤;在光照诱导条件下,GmFT2a与GmSTF3/4能够长距离移动至根中并发生相互作用,且在GmCCaMK激酶的磷酸化作用下,GmCCaMK-STF-FT三者共同激活结瘤起始关键基因的转录,调控根瘤形成。"
| [1] |
Hohmann-Marriott MF, Blankenship RE. Evolution of photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2011, 62:515-548.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103811 pmid: 21438681 |
| [2] |
Jia ZT, Giehl RFH, von Wirén N. Nutrient-hormone relations: driving root plasticity in plants. Mol Plant, 2022, 15(1):86-103.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.12.004 |
| [3] |
Yang Y, Liu HT. Coordinated shoot and root responses to light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Commun, 2020, 1(2):100026.
doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100026 |
| [4] | Chi XF, Han L. Study on plant stress. Seed Sci Technol, 2019, 37(13):122-124. |
| 迟晓峰, 韩琳. 对植物逆境胁迫的研究. 种子科技, 2019, 37(13):122-124. | |
| [5] |
Yang YQ, Guo Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol, 2018, 217(2):523-539.
doi: 10.1111/nph.14920 |
| [6] |
Takahashi F, Shinozaki K. Long-distance signaling in plant stress response. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2019, 47:106-111.
doi: S1369-5266(18)30075-X pmid: 30445314 |
| [7] |
De Rybel B, Mähönen AP, Helariutta Y, Weijers D. Plant vascular development: from early specification to differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016, 17(1):30-40.
doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.6 |
| [8] |
Heo JO, Roszak P, Furuta KM, Helariutta Y. Phloem development: current knowledge and future perspectives. Am J Bot, 2014, 101(9):1393-1402.
doi: 10.3732/ajb.1400197 |
| [9] |
Stadler R, Wright KM, Lauterbach C, Amon G, Gahrtz M, Feuerstein A, Oparka KJ, Sauer N. Expression of GFP-fusions in Arabidopsis companion cells reveals non-specific protein trafficking into sieve elements and identifies a novel post-phloem domain in roots. Plant J, 2005, 41(2):319-331.
pmid: 15634207 |
| [10] |
Yang YZ, Mao LY, Jittayasothorn Y, Kang YM, Jiao C, Fei ZJ, Zhong GY. Messenger RNA exchange between scions and rootstocks in grafted grapevines. BMC Plant Biol, 2015, 15:251.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0626-y |
| [11] |
Kehr J, Buhtz A. Long distance transport and movement of RNA through the phloem. J Exp Bot, 2008, 59(1):85-92.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm176 |
| [12] |
Santa Cruz S. Perspective: phloem transport of viruses and macromolecules-what goes in must come out. Trends Microbiol, 1999, 7(6):237-241.
pmid: 10366860 |
| [13] |
Wang Y, Ding B. Viroids: small probes for exploring the vast universe of RNA trafficking in plants. J Integr Plant Biol, 2010, 52(1):28-39.
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00900.x |
| [14] |
Carrington JC, Kasschau KD, Mahajan SK, Schaad MC. Cell-to-cell and long-distance transport of viruses in plants. Plant Cell, 1996, 8(10):1669-1681.
doi: 10.2307/3870221 |
| [15] |
Seo JK, Vo Phan MS, Kang SH, Choi HS, Kim KH. The charged residues in the surface-exposed C-terminus of the Soybean mosaic virus coat protein are critical for cell-to-cell movement. Virology, 2013, 446(1-2):95-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.07.033 |
| [16] | Mathioudakis MM, Maliogka VI, Katsiani AT, Katis NI. Incidence and molecular variability of Apple stem pitting and Apple chlorotic leaf spot viruses in apple and pear orchards in greece. J Plant Pathol, 2010, 92(1):139-147. |
| [17] | Koshkina TE, Baranova EN, Usacheva EA, Zavriev SK. A point mutation in the coat protein gene affects long distance transport of the tobacco mosaic virus. Mol Biol, 2003, 37(4):742-748. |
| [18] |
Gera A, Deom CM, Donson J, Shaw JJ, Lewandowski DJ, Dawson WO. Tobacco mosaic tobamovirus does not require concomitant synthesis of movement protein during vascular transport. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 1995, 8(5):784-787.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-8-0784 |
| [19] |
Gopinath K, Kao CC. Replication-independent long-distance trafficking by viral RNAs in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(4):1179-1191.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.050088 |
| [20] |
Wang JJ, Meng XW, Dobrovolskaya OB, Orlov YL, Chen M. Non-coding RNAs and their roles in stress response in plants. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2017, 15(5):301-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2017.01.007 |
| [21] |
Waterhouse PM, Wang MB, Lough T. Gene silencing as an adaptive defence against viruses. Nature, 2001, 411(6839):834-842.
doi: 10.1038/35081168 |
| [22] |
Himber C, Dunoyer P, Moissiard G, Ritzenthaler C, Voinnet O. Transitivity-dependent and -independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing. EMBO J, 2003, 22(17):4523-4533.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg431 |
| [23] |
Yoo BC, Kragler F, Varkonyi-Gasic E, Haywood V, Archer-Evans S, Lee YM, Lough TJ, Lucas WJ. A systemic small RNA signaling system in plants. Plant Cell, 2004, 16(8):1979-2000.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.023614 |
| [24] |
Hamilton A, Voinnet O, Chappell L, Baulcombe D. Two classes of short interfering RNA in RNA silencing. EMBO J, 2002, 21(17):4671-4679.
pmid: 12198169 |
| [25] |
Carlsbecker A, Lee JY, Roberts CJ, Dettmer J, Lehesranta S, Zhou J, Lindgren O, Moreno-Risueno MA, Vatén A, Thitamadee S, Campilho A, Sebastian J, Bowman JL, Helariutta Y, Benfey PN. Cell signalling by microRNA165/6 directs gene dose-dependent root cell fate. Nature, 2010, 465(7296):316-321.
doi: 10.1038/nature08977 |
| [26] |
Marin E, Jouannet V, Herz A, Lokerse AS, Weijers D, Vaucheret H, Nussaume L, Crespi MD, Maizel A,. miR390, Arabidopsis TAS3 tasiRNAs, and their AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR targets define an autoregulatory network quantitatively regulating lateral root growth. Plant Cell, 2010, 22(4):1104-1117.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.072553 |
| [27] |
Bhogale S, Mahajan AS, Natarajan B, Rajabhoj M, Thulasiram HV, Banerjee AK. MicroRNA156: a potential graft-transmissible microRNA that modulates plant architecture and tuberization in Solanum tuberosum ssp. andigena. Plant Physiol, 2014, 164(2):1011-1027.
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.230714 pmid: 24351688 |
| [28] |
Martin A, Adam H, Díaz-Mendoza M, Zurczak M, González-Schain ND, Suárez-López P. Graft-transmissible induction of potato tuberization by the microRNA miR172. Development, 2009, 136(17):2873-2881.
doi: 10.1242/dev.031658 |
| [29] |
Lin SI, Chiang SF, Lin WY, Chen JW, Tseng CY, Wu PC, Chiou TJ. Regulatory network of microRNA399 and PHO2 by systemic signaling. Plant Physiol, 2008, 147(2):732-746.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.116269 |
| [30] |
Kawashima CG, Matthewman CA, Huang SQ, Lee BR, Yoshimoto N, Koprivova A, Rubio-Somoza I, Todesco M, Rathjen T, Saito K, Takahashi H, Dalmay T, Kopriva S. Interplay of SLIM1 and miR395 in the regulation of sulfate assimilation in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2011, 66(5):863-876.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04547.x |
| [31] |
Chen L, Zhu QH, Kaufmann K. Long non-coding RNAs in plants: emerging modulators of gene activity in development and stress responses. Planta, 2020, 252(5):92
doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03480-5 pmid: 33099688 |
| [32] |
Zhang ZL, Zheng Y, Ham BK, Zhang SP, Fei ZJ, Lucas WJ. Plant lncRNAs are enriched in and move systemically through the phloem in response to phosphate deficiency. J Integr Plant Biol, 2019, 61(4):492-508.
doi: 10.1111/jipb.12715 |
| [33] |
Wu YG, Luo D, Fang LF, Zhou Q, Liu WX, Liu ZP. Bidirectional lncRNA transfer between Cuscuta Parasites and their host plant. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(1):561.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23010561 |
| [34] |
Ueki S, Citovsky V. RNA commutes to work: regulation of plant gene expression by systemically transported RNA molecules. Bioessays, 2001, 23(12):1087-1090.
pmid: 11746226 |
| [35] |
Ruiz-Medrano R, Xoconostle-Cázares B, Lucas WJ. Phloem long-distance transport of CmNACP mRNA: implications for supracellular regulation in plants. Development, 1999, 126(20):4405-4419.
doi: 10.1242/dev.126.20.4405 pmid: 10498677 |
| [36] |
Kim M, Canio W, Kessler S, Sinha N. Developmental changes due to long-distance movement of a homeobox fusion transcript in tomato. Science, 2001, 293(5528):287-289.
pmid: 11452121 |
| [37] |
Banerjee AK, Chatterjee M, Yu YY, Suh SG, Miller WA, Hannapel DJ. Dynamics of a mobile RNA of potato involved in a long-distance signaling pathway. Plant Cell, 2006, 18(12):3443-3457.
pmid: 17189340 |
| [38] |
Notaguchi M, Wolf S, Lucas WJ. Phloem-mobile Aux/IAA transcripts target to the root tip and modify root architecture. J Integr Plant Biol, 2012, 54(10):760-772.
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2012.01155.x |
| [39] |
Haywood V, Yu TS, Huang NC, Lucas WJ. Phloem long-distance trafficking of GIBBERELLIC ACID- INSENSITIVE RNA regulates leaf development. Plant J, 2005, 42(1):49-68.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02351.x |
| [40] |
Zhang ZL, Zheng Y, Ham BK, Chen JY, Yoshida A, Kochian LV, Fei ZJ, Lucas WJ. Vascular-mediated signalling involved in early phosphate stress response in plants. Nat Plants, 2016, 2:16033.
doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.33 |
| [41] | Hao PB, Lv XM, Fu MM, Xu Z, Tian J, Wang Y, Zhang XZ, Xu XF, Wu T, Han ZH. Long-distance mobile mRNA CAX3 modulates iron uptake and zinc compartmentalization. EMBO Rep, 2022, 23(5):e53698. |
| [42] |
Yang L, Perrera V, Saplaoura E, Apelt F, Bahin M, Kramdi A, Olas J, Mueller-Roeber B, Sokolowska E, Zhang WN, Li RS, Pitzalis N, Heinlein M, Zhang SD, Genovesio A, Colot V, Kragler F,. m5C methylation guides systemic transport of messenger RNA over graft junctions in plants. Curr Biol, 2019, 29(15): 2465-2476.e5.
doi: S0960-9822(19)30769-9 pmid: 31327714 |
| [43] |
Murphy E, Smith S, De Smet I. Small signaling peptides in Arabidopsis development: how cells communicate over a short distance. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(8):3198-3217.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.099010 |
| [44] |
Olsson V, Joos L, Zhu SS, Gevaert K, Butenko MA, De Smet I. Look closely, the beautiful may be small: precursor-derived peptides in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2019, 70:153-186.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040413 pmid: 30525926 |
| [45] |
Munemasa S, Hauser F, Park J, Waadt R, Brandt B, Schroeder JI. Mechanisms of abscisic acid-mediated control of stomatal aperture. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2015, 28:154-162.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.10.010 |
| [46] |
Takahashi F, Suzuki T, Osakabe Y, Betsuyaku S, Kondo Y, Dohmae N, Fukuda H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. A small peptide modulates stomatal control via abscisic acid in long-distance signalling. Nature, 2018, 556(7700):235-238.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0009-2 |
| [47] |
Gruber BD, Giehl RFH, Friedel S, von Wirén N. Plasticity of the Arabidopsis root system under nutrient deficiencies. Plant Physiol, 2013, 163(1):161-179.
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.218453 |
| [48] |
Ota R, Ohkubo Y, Yamashita Y, Ogawa-Ohnishi M, Matsubayashi Y. Shoot-to-root mobile CEPD-like 2 integrates shoot nitrogen status to systemically regulate nitrate uptake in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1):641.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14440-8 |
| [49] |
Endo S, Shinohara H, Matsubayashi Y, Fukuda H. A novel pollen-pistil interaction conferring high-temperature tolerance during reproduction via CLE45 signaling. Curr Biol, 2013, 23(17):1670-1676.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.06.060 |
| [50] |
Golecki B, Schulz A, Carstens-Behrens U, Kollmann CB. Evidence for graft transmission of structural phloem proteins or their precursors in heterografts of Cucurbitaceae. Planta, 1998, 206(4):630-640.
doi: 10.1007/s004250050441 |
| [51] |
Golecki B, Schulz A, Thompson GA. Translocation of structural P proteins in the phloem. Plant Cell, 1999, 11(1):127-140.
pmid: 9878637 |
| [52] |
Putterill J, Varkonyi-Gasic E. FT and florigen long- distance flowering control in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2016, 33:77-82.
doi: S1369-5266(16)30091-7 pmid: 27348248 |
| [53] |
Corbesier L, Vincent C, Jang S, Fornara F, Fan QZ, Searle I, Giakountis A, Farrona S, Gissot L, Turnbull C, Coupland G. FT protein movement contributes to long- distance signaling in floral induction of Arabidopsis. Science, 2007, 316(5827):1030-1033.
pmid: 17446353 |
| [54] |
Jaeger KE, Wigge PA. FT protein acts as a long-range signal in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol, 2007, 17(12):1050-1054.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.05.008 pmid: 17540569 |
| [55] |
Tamaki S, Matsuo S, Wong HL, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K. Hd3a protein is a mobile flowering signal in rice. Science, 2007, 316(5827):1033-1036.
doi: 10.1126/science.1141753 |
| [56] |
Navarro C, Abelenda JA, Cruz-Oró E, Cuéllar CA, Tamaki S, Silva J, Shimamoto K, Prat S. Control of flowering and storage organ formation in potato by FLOWERING LOCUS T. Nature, 2011, 478(7367):119-122.
doi: 10.1038/nature10431 |
| [57] |
Liu L, Liu C, Hou XL, Xi WY, Shen LS, Tao Z, Wang Y, Yu H. FTIP1 is an essential regulator required for florigen transport. PLoS Biol, 2012, 10(4):e1001313.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001313 |
| [58] |
Oyama T, Shimura Y, Okada K. The Arabidopsis HY5 gene encodes a bZIP protein that regulates stimulus- induced development of root and hypocotyl. Genes Dev, 1997, 11(22):2983-2995.
doi: 10.1101/gad.11.22.2983 |
| [59] |
Li C, Qi LJ, Zhang SM, Dong XJ, Jing YJ, Cheng JK, Feng ZY, Peng J, Li H, Zhou YY, Wang XJ, Han R, Duan J, Terzaghi W, Lin RC, Li JG. Mutual upregulation of HY5 and TZP in mediating phytochrome a signaling. Plant Cell, 2022, 34(1):633-654.
doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab254 |
| [60] |
Mao ZL, Wei XX, Li L, Xu P, Zhang JY, Wang WX, Guo TT, Kou S, Wang WT, Miao LX, Cao XL, Zhao JC, Yang GQ, Zhang SL, Lian HL, Yang HQ. Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 controls photomorphogenesis through regulation of H2A.Z deposition. Plant Cell, 2021, 33(6):1961-1979.
doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab091 |
| [61] |
Yang Y, Liang T, Zhang LB, Shao K, Gu XX, Shang RX, Shi N, Li X, Zhang P, Liu HT. UVR8 interacts with WRKY36 to regulate HY5 transcription and hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants, 2018, 4(2):98-107.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-017-0099-0 pmid: 29379156 |
| [62] |
Podolec R, Ulm R. Photoreceptor-mediated regulation of the COP1/SPA E3 ubiquitin ligase. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2018, 45(Pt A):18-25.
doi: S1369-5266(17)30208-X pmid: 29775763 |
| [63] |
van Gelderen K, Kang C, Paalman R, Keuskamp D, Hayes S, Pierik R. Far-red light detection in the shoot regulates lateral root development through the HY5 transcription factor. Plant Cell, 2018, 30(1):101-116.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00771 |
| [64] |
Yang PY, Wen QM, Yu RB, Han X, Deng XW, Chen HD. Light modulates the gravitropic responses through organ-specific PIFs and HY5 regulation of LAZY4 expression in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(31):18840-18848.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005871117 |
| [65] |
Chen XB, Yao QF, Gao XH, Jiang CF, Harberd NP, Fu XD. Shoot-to-Root mobile transcription factor HY5 coordinates plant carbon and nitrogen acquisition. Curr Biol, 2016, 26(5):640-646.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.066 |
| [66] |
Sakuraba Y, Kanno S, Mabuchi A, Monda K, Iba K, Yanagisawa S. A phytochrome-B-mediated regulatory mechanism of phosphorus acquisition. Nat Plants, 2018, 4(12):1089-1101.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0294-7 |
| [67] | Guo ZX, Xu J, Wang Y, Hu CY, Shi K, Zhou J, Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Foyer CH, Yu JQ. The phyB-dependent induction of HY5 promotes iron uptake by systemically activating FER expression. EMBO Rep, 2021, 22(7):e51944. |
| [68] |
Kouchi H, Imaizumi-Anraku H, Hayashi M, Hakoyama T, Nakagawa T, Umehara Y, Suganuma N, Kawaguchi M. How many peas in a pod? Legume genes responsible for mutualistic symbioses underground. Plant Cell Physiol, 2010, 51(9):1381-1397.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq107 |
| [69] |
Tjepkema JD, Winship LJ. Energy requirement for nitrogen fixation in actinorhizal and legume root nodules. Science, 1980, 209(4453):279-281.
pmid: 7384801 |
| [70] |
Oka-Kira E, Kawaguchi M. Long-distance signaling to control root nodule number. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2006, 9(5):496-502.
pmid: 16877028 |
| [71] |
Ferguson BJ, Mens C, Hastwell AH, Zhang MB, Su HN, Jones CH, Chu XT, Gresshoff PM. Legume nodulation: the host controls the party. Plant Cell Environ, 2019, 42(1):41-51.
doi: 10.1111/pce.13348 |
| [72] |
Nishida H, Tanaka S, Handa Y, Ito M, Sakamoto Y, Matsunaga S, Betsuyaku S, Miura K, Soyano T, Kawaguchi M, Suzaki T. A NIN-like protein mediates nitrate-induced control of root nodule symbiosis in Lotus japonicus. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1):499.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02831-x pmid: 29403008 |
| [73] |
Okamoto S, Tabata R, Matsubayashi Y. Long-distance peptide signaling essential for nutrient homeostasis in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2016, 34:35-40.
doi: S1369-5266(16)30114-5 pmid: 27552346 |
| [74] |
Tsikou D, Yan Z, Holt DB, Abel NB, Reid DE, Madsen LH, Bhasin H, Sexauer M, Stougaard J, Markmann K. Systemic control of legume susceptibility to rhizobial infection by a mobile microRNA. Science, 2018, 362(6411):233-236.
doi: 10.1126/science.aat6907 |
| [75] |
Gautrat P, Laffont C, Frugier F. Compact root architecture 2 promotes root competence for nodulation through the miR2111 systemic effector. Curr Biol, 2020, 30(7): 1339-1345.e3.
doi: S0960-9822(20)30164-0 pmid: 32109394 |
| [76] |
Cai YP, Wang LW, Chen L, Wu TT, Liu LP, Sun S, Wu CX, Yao WW, Jiang BJ, Yuan S, Han TF, Hou WS. Mutagenesis of GmFT2a and GmFT5a mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 contributes for expanding the regional adaptability of soybean. Plant Biotechnol J, 2020, 18(1):298-309.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13199 |
| [77] |
Wang T, Guo J, Peng YQ, Lyu XG, Liu B, Sun SY, Wang XL. Light-induced mobile factors from shoots regulate rhizobium-triggered soybean root nodulation. Science, 2021, 374(6563):65-71.
doi: 10.1126/science.abh2890 pmid: 34591638 |
| [78] |
Zimmermann MR, Hafke JB, van Bel AJE, Furch ACU., Interaction of xylem and phloem during exudation and wound occlusion in Cucurbita maxima. Plant Cell Environ, 2013, 36(1):237-247.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02571.x |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
