遗传 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 237-249.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-336
吕娇1( ), 龚一富1(
), 龚一富1( ), 章丽1, 胡媛1, 王何瑜2(
), 章丽1, 胡媛1, 王何瑜2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-24
修回日期:2023-01-10
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2023-02-10
通讯作者:
龚一富,王何瑜
E-mail:1459336048@qq.com;gongyifu@163.com;wangheyu@nbu.edu.cn
作者简介:吕娇,在读硕士研究生,专业方向:生物学。E-mail: 基金资助:
Jiao Lv1( ), Yifu Gong1(
), Yifu Gong1( ), Li Zhang1, Yuan Hu1, Heyu Wang2(
), Li Zhang1, Yuan Hu1, Heyu Wang2( )
)
Received:2022-10-24
Revised:2023-01-10
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-02-10
Contact:
Gong Yifu,Wang Heyu
E-mail:1459336048@qq.com;gongyifu@163.com;wangheyu@nbu.edu.cn
摘要:
加权基因共表达网络分析(weighted gene co-expression network analysis,WGCNA)是一种分析多个样本间基因表达模式的方法,可将表达模式相近的基因聚类并发掘与特定的性状或表型相关的关键基因。本研究采用转录组测序和WGCNA方法,分析了三角褐指藻(Phaeodactylum tricornutum)在缺磷、红光和黄光等非生物胁迫下对岩藻黄素积累的影响。结果表明,与对照组相比,岩藻黄素含量在缺磷和红光处理后显著提高(P<0.05),但是在黄光处理后显著降低(P<0.05)。利用转录组测序得到的10,392个基因构建加权基因共表达网络,为了确保无标度网络,选择β=18(R2>0.8)作为软阈值。通过对岩藻黄素含量进行关联分析,共鉴定了10个共表达模块,其中purple模块与岩藻黄素含量呈正相关(r=0.9,P=1E-200),并确定了9个关键基因,包括5个岩藻黄素合成通路上的基因(DXR、PSY、PDS1、ZEP2、VDL2)和4个转录因子基因(bHLH5、HOX2、CCHH13、HSF1b)。进一步利用qRT-PCR证实,关键基因在缺磷处理时表达量更高,线性回归分析结果表明基因相对表达量均与转录组数据高度相关。本研究结果为进一步研究三角褐指藻中岩藻黄素的复杂调控机制奠定了基础。
吕娇, 龚一富, 章丽, 胡媛, 王何瑜. 基于WGCNA发掘缺磷、红光和黄光处理下三角褐指藻岩藻黄素合成关键基因[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(3): 237-249.
Jiao Lv, Yifu Gong, Li Zhang, Yuan Hu, Heyu Wang. Exploring the key genes of fucoxanthin biosynthesis in Phaeodactylum tricornutum under phosphorus deficiency, red light and yellow light using WGCNA[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(3): 237-249.
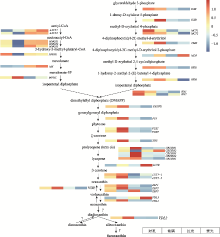
图4
三角褐指藻岩藻黄素生物合成相关基因的表达热图 红色表示高表达,蓝色表示低表达。DXS:1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase;DXR:1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase;MCT:2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidyltransferase;CMK:4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase;MDS:2C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase;HDS:1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate synthase;HDR:1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate reductase;IDI:isopentenyl diphosphate:dimethylallyl diphosphate isomerase;GGDS:geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase;PSY:phytoene synthase;PDS:phytoene desaturase;ZDS:ζ-carotene desaturase;CRTISO:carotenoid isomerase;LCYB:lycopene β-cyclase;LUT-like:lutein deficient-like;ZEP:zeaxanthin epoxidase;VDE:violaxanthin de-epoxidase;VDL:violaxanthin de-epoxidase-like;?代表催化该过程的酶未知。"
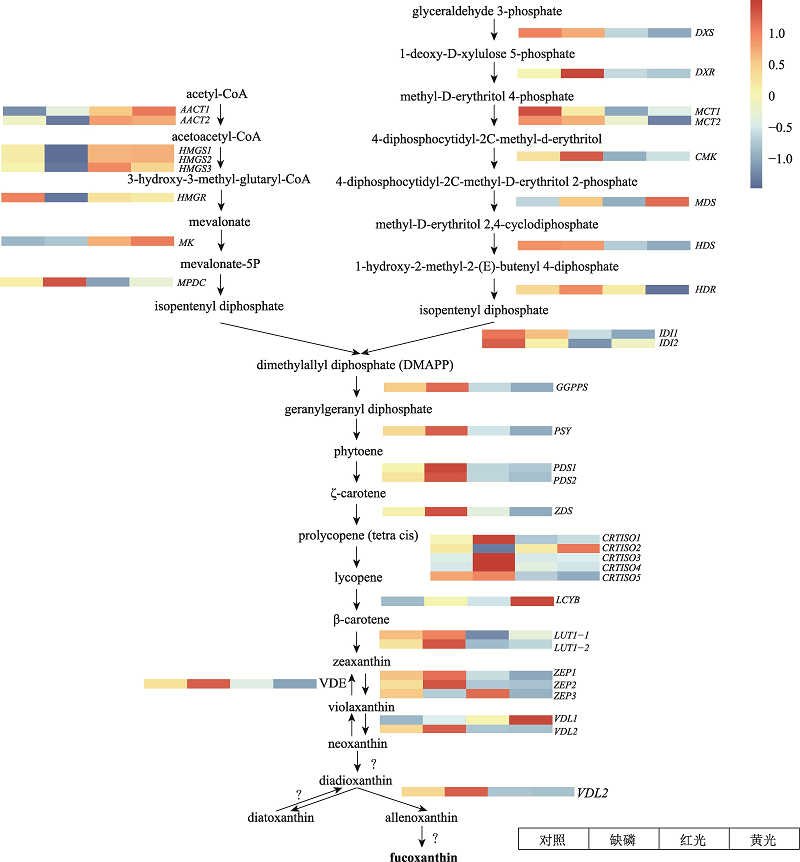
表1
Purple模块中所有转录因子与基因ID对应表"
| 基因_ID | 基因名称 | 转录因子_ID | 所属基因家族 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7195238 | Pt_CXC4 | PHATRDRAFT_48955 | CXC/tesmin |
| 7195642 | Pt_HSF4.5d | PHATRDRAFT_39786 | HSF |
| 7195857 | Pt_Myb1R_SHAQKYF1b | PHATRDRAFT_49526 | MYB |
| 7196438 | Pt_CCCH6 | PHATRDRAFT_42841 | ZF |
| 7197059 | Pt_CXC1 | PHATRDRAFT_32462 | CXC/tesmin |
| 7197406 | Pt_bHLH5 | PHATRDRAFT_43365 | bHLH |
| 7198282 | Pt_HSF4.6c | PHATRDRAFT_49620 | HSF |
| 7198402 | Pt_Myb2R8 | PHATRDRAFT_49720 | MYB |
| 7198927 | Pt_Hox2 | PHATRDRAFT_ex44808 | CCAAT-binding |
| 7198996 | Pt_CCCH11 | PHATRDRAFT_50345 | ZF |
| 7199537 | Pt_CCHH8 | PHATRDRAFT_45032 | ZF |
| 7199623 | Pt_CCHH3 | PHATRDRAFT_54326 | ZF |
| 7199692 | Pt_Myb1R5 | PHATRDRAFT_45029 | MYB |
| 7200785 | Pt_TAZ4_PHD2_ZZ2 | PHATRDRAFT_45764 | ZF |
| 7201568 | Pt_CCHH18 | PHATRDRAFT_46478 | ZF |
| 7201958 | Pt_HSF1b | PHATRDRAFT_47181 | HSF |
| 7202412 | Pt_CCHH13 | PHATRDRAFT_37547 | ZF |
| 7203253 | Pt_MybR+R | PHATRDRAFT_48038 | MYB |
| 7204890 | Pt_bZIP9 | PHATRDRAFT_1724 | bZIP |
| [1] | Liaaen JS, Scheuer PJ,eds. Chapter 1—Marine carotenoids. Marine Natural Products Academic Press, 1978, 1: 1-73. |
| [2] |
Peng J, Yuan JP, Wu CF, Wang JH. Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid present in brown seaweeds and diatoms: metabolism and bioactivities relevant to human health. Mar Drugs, 2011, 9(10): 1806-1828.
doi: 10.3390/md9101806 pmid: 22072997 |
| [3] |
Veith T, Brauns J, Weisheit W, Mittag M, Büchel C. Identification of a specific fucoxanthin-chlorophyll protein in the light harvesting complex of photosystem I in the diatom Cyclotella meneghiniana. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2009, 1787(7): 905-912.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.04.006 pmid: 19397889 |
| [4] |
Gundermann K, Wagner V, Mittag M, Büchel C. Fucoxanthin-chlorophyll protein complexes of the centric diatom Cyclotella Meneghiniana differ in Lhcx1 and Lhcx6_1 content. Plant Physiol, 2019, 179(4): 1779-1795.
doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01363 pmid: 30733257 |
| [5] |
Bailleul B, Rogato A, De Martino A, Coesel S, Cardol P, Bowler C, Falciatore A, Finazzi G. An atypical member of the light-harvesting complex stress-related protein family modulates diatom responses to light. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(42): 18214-18219.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007703107 pmid: 20921421 |
| [6] |
Sachindra NM, Sato E, Maeda H, Hosokawa M, Niwano Y, Kohno M, Miyashita K. Radical scavenging and singlet oxygen quenching activity of marine carotenoid fucoxanthin and its metabolites. J Agric Food Chem, 2007, 55(21): 8516-8522.
doi: 10.1021/jf071848a |
| [7] |
Xiang SY, Liu FF, Lin JJ, Chen HX, Huang CH, Chen LP, Zhou YY, Ye LY, Zhang K, Jin JK, Zhen JC, Wang C, He S, Wang QW, Cui W, Zhang JR. Fucoxanthin inhibits β-amyloid assembly and attenuates β-amyloid oligomer- induced cognitive impairments. J Agric Food Chem, 2017, 65(20): 4092-4102.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00805 |
| [8] |
Vílchez C, Forján E, Cuaresma M, Bédmar F, Garbayo I, Vega JM. Marine carotenoids: biological functions and commercial applications. Mar Drugs, 2011, 9(3): 319-333.
doi: 10.3390/md9030319 pmid: 21556162 |
| [9] |
Yang RQ, Wei D, Xie J. Diatoms as cell factories for high-value products: chrysolaminarin, eicosapentaenoic acid, and fucoxanthin. Crit Rev Biotechnol, 2020, 40(7): 993-1009.
doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1805402 pmid: 32777952 |
| [10] |
Méresse S, Fodil M, Fleury F, Chénais B. Fucoxanthin, a marine-derived carotenoid from brown seaweeds and microalgae: a promising bioactive compound for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(23): 9273.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21239273 |
| [11] |
Afonso C, Bragança AR, Rebelo BA, Serra TS, Abranches R. Optimal nitrate supplementation in Phaeodactylum tricornutum culture medium increases biomass and fucoxanthin production. Foods, 2022, 11(4): 568.
doi: 10.3390/foods11040568 |
| [12] |
Bai Y, Cao TJ, Dautermann O, Buschbeck P, Cantrell MB, Chen YJ, Lein CD, Shi XH, Ware MA, Yang FH, Zhang H, Zhang LH, Peers G, Li XB, Lohr M. Green diatom mutants reveal an intricate biosynthetic pathway of fucoxanthin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(38): e2203708119.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2203708119 |
| [13] |
Cen SY, Li DW, Huang XL, Huang D, Balamurugan S, Liu WJ, Zheng JW, Yang WD, Li HY. Crucial carotenogenic genes elevate hyperaccumulation of both fucoxanthin and β-carotene in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Algal Res, 2022, 64: 102691.
doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2022.102691 |
| [14] |
Zhang L, Gong YF, Zhu SQ, Liu H, Li SR, Xie ZH, Wang HY. Effects of acetylsalicylic acid on fucoxanthin content in Phaeodactylum tricornutum and its’ molecular mechanism. J Nucl Agric Sci, 2020, 34(7): 1432-1439.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.07.1432 |
|
章丽, 龚一富, 朱帅旗, 刘浩, 李申睿, 谢志浩, 王何瑜. 乙酰水杨酸对三角褐指藻岩藻黄质含量的影响及其分子机理研究. 核农学报, 2020, 34(7): 1432-1439.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.07.1432 |
|
| [15] |
Zhao D, Yu D, Kim M, Gu MY, Kim SM, Pan CH, Kim GH, Chung D. Effects of temperature, light, and pH on the stability of fucoxanthin in an oil-in-water emulsion. Food Chem, 2019, 291: 87-93.
doi: S0308-8146(19)30652-1 pmid: 31006475 |
| [16] | Xu RJ, Gong YF, Chen WT, Li SR, Chen RY, Zheng XY, Chen XMZ, Wang HY. Effects of LED monochromatic light quality of different colors on fucoxanthin content and expression levels of related genes in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Acta Opt Sin, 2019, 39(9): 299-307. |
| 徐润洁, 龚一富, 陈文婷, 李申睿, 陈若莹, 郑小恽, 陈璇木子, 王何瑜. 不同发光二极管单色光质对三角褐指藻中岩藻黄素含量及相关基因表达的影响. 光学学报, 2019, 39(9): 299-307. | |
| [17] |
Eilers U, Bikoulis A, Breitenbach J, Büchel C, Sandmann G. Limitations in the biosynthesis of fucoxanthin as targets for genetic engineering in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Appl Phycol, 2016, 28(1): 123-129.
doi: 10.1007/s10811-015-0583-8 |
| [18] |
Kadono T, Kira N, Suzuki K, Iwata O, Ohama T, Okada S, Nishimura T, Akakabe M, Tsuda M, Adachi M. Effect of an introduced phytoene synthase gene expression on carotenoid biosynthesis in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Marine Drugs, 2015, 13(8): 5334-5357.
doi: 10.3390/md13085334 pmid: 26308005 |
| [19] |
Mcclure DD, Luiz A, Gerber B, Barton GW, Kavanagh JM. An investigation into the effect of culture conditions on fucoxanthin production using the marine microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Algal Res, 2018, 29: 41-48.
doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2017.11.015 |
| [20] | Xu RJ, Gong YF, Wei FJ, Li SR, Chen RY, Zheng XY, Fang QS, Chen WT, Wang HY. Correlation analysis of photosynthetic physiological indexes and content of fucoxanthin in Phaeodactylum tricornutum under different light quality conditions. Chin J Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 471-479. |
| 徐润洁, 龚一富, 韦凤娟, 李申睿, 陈若莹, 郑小恽, 方清姝, 陈文婷, 王何瑜. 不同光质条件下三角褐指藻光合生理指标与岩藻黄素含量的相关性分析. 中国激光, 2020, 47(5): 471-479. | |
| [21] | Shu MY, Gong YF, Lv XM, Jia ZM, Wang B, Liu XX, Wang HY. Cloning, bioinformatics and induced expression analysis of dxs gene in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Acta Hydrobiol Sin, 2022, 46(9): 1310-1318. |
| 舒明雨, 龚一富, 吕欣梦, 贾泽茗, 王博, 刘瑄瑄, 王何瑜. 三角褐指藻dxs基因克隆与诱导表达. 水生生物学报, 2022, 46(9): 1310-1318. | |
| [22] |
Li YL, Sun H, Wu T, Fu YL, He YJ, Mao XM, Chen F. Storage carbon metabolism of Isochrysis zhangjiangensis under different light intensities and its application for co-production of fucoxanthin and stearidonic acid. Bioresour Technol, 2019, 282: 94-102.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.127 |
| [23] | Zhang WY, Gao BY, Li AF, Zhang CW. Effects of different culture conditions on growth and accumulation of bioactive components by Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Mar Sci, 2016, 40(5): 57-65. |
| 张文源, 高保燕, 李爱芬, 张成武. 不同培养条件对三角褐指藻生长及其生物活性成分积累的影响. 海洋科学, 2016, 40(05): 57-65. | |
| [24] |
Benitez-Nelson CR. The biogeochemical cycling of phosphorus in marine systems. Earth-Sci Rev, 2000, 51(1): 109-135.
doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(00)00018-0 |
| [25] | Zhu WN, Gong YF, Guo RD, Yang Y, Cai JS, Wang HY, Wang R. Effects of phosphorus restriction lipid content and expression of related genes of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc, 2021, 36(7): 93-99. |
| 朱文娜, 龚一富, 郭芮栋, 杨雨, 蔡嘉硕, 王何瑜, 汪如. 磷限制对三角褐指藻脂质含量及相关基因表达的影响. 中国粮油学报, 2021, 36(7): 93-99. | |
| [26] |
Brembu T, Mühlroth A, Alipanah L, Bones AM. The effects of phosphorus limitation on carbon metabolism in diatoms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 2017, 372(1728): 20160406.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0406 |
| [27] |
Cruz De Carvalho MH, Sun HX, Bowler C, Chua NH. Noncoding and coding transcriptome responses of a marine diatom to phosphate fluctuations. New Phytol, 2016, 210(2): 497-510.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13787 pmid: 26680538 |
| [28] |
Yang ZK, Zheng JW, Niu YF, Yang WD, Liu JS, Li HY. Systems-level analysis of the metabolic responses of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum to phosphorus stress. Environ Microbiol, 2014, 16(6): 1793-1807.
doi: 10.1111/emi.2014.16.issue-6 |
| [29] |
Yang RQ, Wei D. Improving fucoxanthin production in mixotrophic culture of marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum by LED light shift and nitrogen supplementation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2020, 8: 820.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00820 |
| [30] |
Yi ZQ, Su YX, Cherek P, Nelson DR, Lin JP, Rolfsson O, Wu H, Salehi-Ashtiani K, Brynjolfsson S, Fu WQ. Combined artificial high-silicate medium and LED illumination promote carotenoid accumulation in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Microb Cell Fact, 2019, 18(1): 209.
doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1263-1 pmid: 31791335 |
| [31] |
Yang PH, Chang YJ, Wang LF, Wang SM, Wu J. Regulatory mechanisms of the resistance to common bacterial blight revealed by transcriptomic analysis in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Front Plant Sci, 2021, 12: 800535.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.800535 |
| [32] |
Langfelder P, Horvath S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 2008, 9: 559.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-559 pmid: 19114008 |
| [33] |
Panahi B, Hejazi MA. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis of the salt-responsive transcriptomes reveals novel hub genes in green halophytic microalgae Dunaliella salina. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 1607.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80945-3 pmid: 33452393 |
| [34] |
Zhu MD, Xie HJ, Wei XJ, Dossa K, Yu YY, Hui SZ, Tang GH, Zeng XS, Yu YH, Hu PS, Wang JL. WGCNA analysis of salt-responsive core transcriptome identifies novel hub genes in rice. Genes (Basel), 2019, 10(9): 719.
doi: 10.3390/genes10090719 |
| [35] |
Dileo MV, Strahan GD, Den Bakker M, Hoekenga OA. Weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) applied to the tomato fruit metabolome. PLoS One, 2011, 6(10): e26683.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026683 |
| [36] |
Li H, Han SL, Huo YQ, Ma GF, Sun ZX, Li HY, Hou SY, Han YH. Comparative metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals a coexpression network of the carotenoid metabolism pathway in the panicle of Setaria italica. BMC Plant Biol, 2022, 22(1): 105.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03467-2 pmid: 35260077 |
| [37] |
Guillard RR, Ryther JH. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) Gran. Can J Microbiol, 1962, 8: 229-239.
doi: 10.1139/m62-029 |
| [38] | Yan XY, Liu YX, Wu YP, Lu ZH, Guo CH. Optimizing the processes of extracting and purifying fucoxanthin from Laminaria japonica. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol, 2014, 14(3): 115-121. |
| 闫相勇, 刘翼翔, 吴永沛, 卢珍华, 郭彩华. 海带岩藻黄素的提取及纯化工艺研究. 中国食品学报, 2014, 14(3): 115-121. | |
| [39] |
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods, 2015, 12(4): 357-360.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317 pmid: 25751142 |
| [40] |
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, Mccue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods, 2008, 5(7): 621-628.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1226 pmid: 18516045 |
| [41] | Li B, Dewey CN. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics, 2011, 12: 323. |
| [42] |
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S.Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(12): 550.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 |
| [43] | Husson F, Josse J, Lê S. FactoMineR: an R package for multivariate analysis. J Stat Softw, 2008, 25(1): 1-18. |
| [44] | Valero-Mora P. Ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Journal of Statistical Software, Book Reviews, 2010, 35(1): 1-3. |
| [45] |
Bergkvist A, Rusnakova V, Sindelka R, Garda JMA, Sjögreen B, Lindh D, Forootan A, Kubista M. Gene expression profiling—Clusters of possibilities. Methods, 2010, 50(4): 323-335.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.009 pmid: 20079843 |
| [46] |
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res, 2003, 13(11): 2498-2504.
doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303 pmid: 14597658 |
| [47] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [48] |
Athanasakoglou A, Kampranis SC. Diatom isoprenoids: advances and biotechnological potential. Biotechnol Adv, 2019, 37(8): 107417.
doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107417 |
| [49] |
Carretero-Paulet L, Cairó A, Botella-Pavía P, Besumbes O, Campos N, Boronat A, Rodríguez-Concepción M. Enhanced flux through the methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway in Arabidopsis plants overexpressing deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase. Plant Mol Biol, 2006, 62: 683-695.
pmid: 16941216 |
| [50] |
Mcquinn RP, Wong B, Giovannoni JJ. AtPDS overexpression in tomato: exposing unique patterns of carotenoid self-regulation and an alternative strategy for the enhancement of fruit carotenoid content. Plant Biotechnol J, 2018, 16(2): 482-494.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2018.16.issue-2 |
| [51] |
Cazzonelli CI, Pogson BJ. Source to sink: regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(5): 266-274.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.02.003 pmid: 20303820 |
| [52] | Manfellotto F, Stella GR, Falciatore A, Brunet C, Ferrante MI. Engineering the unicellular alga Phaeodactylum tricornutum for enhancing carotenoid production. Antioxidants (Basel), 2020, 9(8): 757. |
| [53] |
Rayko E, Maumus F, Maheswari U, Jabbari K, Bowler C. Transcription factor families inferred from genome sequences of photosynthetic stramenopiles. New Phytol, 2010, 188(1): 52-66.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03371.x pmid: 20646219 |
| [54] | Ohno N, Inoue T, Yamashiki R, Nakajima K, Kitahara Y, Ishibashi M, Matsuda Y. CO(2)-cAMP-responsive cis- elements targeted by a transcription factor with CREB/ ATF-like basic zipper domain in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Plant Physiol, 2012, 158(1): 499-513. |
| [55] |
Huysman MJJ, Fortunato AE, Matthijs M, Costa BS, Vanderhaeghen R, Van Den Daele H, Sachse M, Inzé D, Bowler C, Kroth PG, Wilhelm C, Falciatore A, Vyverman W, De Veylder L. AUREOCHROME1a-mediated induction of the diatom-specific cyclin dsCYC2 controls the onset of cell division in diatoms (Phaeodactylum tricornutum). Plant Cell, 2013, 25(1): 215-228.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.106377 |
| [56] |
Matthijs M, Fabris M, Obata T, Foubert I, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Solano R, Fernie AR, Vyverman W, Goossens A.The transcription factor bZIP14 regulates the TCA cycle in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. EMBO J, 2017, 36(11): 1559-1576.
doi: 10.15252/embj.201696392 pmid: 28420744 |
| [57] |
Sharma A, Mühlroth A, Jouhet J, Marechal E, Alipanah L, Kissen R, Brembu T, Bones A, Winge P. The Myb—like transcription factor Phosphorus Starvation Response (PtPSR) controls conditional P acquisition and remodelling in marine microalgae. New Phytol, 2019, 225(6): 2380-2395.
doi: 10.1111/nph.v225.6 |
| [58] |
Shen H, Zhu L, Castillon A, Majee M, Downie B, Huq E. Light-induced phosphorylation and degradation of the negative regulator PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR1 from Arabidopsis depend upon its direct physical interactions with photoactivated phytochromes. Plant Cell, 2008, 20(6): 1586-1602.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.060020 pmid: 18539749 |
| [59] |
Xing C, Li JY, Yuan HL, Yang JS. Physiological and transcription level responses of microalgae Auxenochlorella protothecoides to cold and heat induced oxidative stress. Environ Res, 2022, 211: 113023.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113023 |
| [60] |
Toledo-Ortiz G, Huq E, Rodríguez-Concepción M. Direct regulation of phytoene synthase gene expression and carotenoid biosynthesis by phytochrome-interacting factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(25): 11626-11631.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914428107 pmid: 20534526 |
| [1] | 李萌, 贺竹梅. 遗传学教学中性别决定关键基因的阐述[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(6): 611-617. |
| [2] | 唐建新,陈卓,胡晗华 . 利用抑制差减杂交技术分离三角褐指藻在缺氮条件下上调表达的基因[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(8): 865-870. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
