遗传 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 489-498.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-226
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-09-09
修回日期:2024-11-15
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2024-12-30
通讯作者:
梁新乐,博士,教授,研究方向:工业微生物菌种资源及产品开发、微生物-噬菌体机制互作等。E-mail: dbiot@mail.zjgsu.edu.cn作者简介:马佳雯,博士研究生,研究方向:食品生物技术。E-mail: 20020080006@pop.zjgsu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2024-09-09
Revised:2024-11-15
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-12-30
Supported by:摘要:
为了探究浙江传统发酵玫瑰米醋异常发酵的原因,本研究采用Illumina Novaseq高通量测序平台测定分析了其中宏噬菌体组的种群组成、结构及相关功能注释,以期从噬菌体组学角度解析异常发酵机理。实验结果表明,异常发酵醋醪中的优势病毒科与正常发酵醋醪中的明显不同。种群网络分析和主成分分析表明,两种发酵醋醪中的噬菌体种群组成和结构有明显的差异,只有3.29%的病毒簇(viral clusters,VCs)同时存在来自两种发酵醋醪的病毒分类操作单元(viral operational taxonomic units,vOTU);且异常发酵噬菌体组的种群异质性更高,存在属水平上高度优势的噬菌体种群。较低的溶原噬菌体的占比让异常发酵醋醪噬菌体组更倾向于裂解宿主,同时异常发酵醋醪噬菌体组携带更多的细菌细胞壁水解酶也印证了这点。更重要的是,宿主-噬菌体关联性分析表明异常发酵醋醪中预测宿主细菌的群落组成与正常发酵醋醪的差异显著。综上所述,噬菌体组异常结构与功能是导致传统玫瑰醋发酵失败的主要原因之一,噬菌体组学研究为解析传统发酵食品的异常发酵原因及调控改造微生物群落提供了新途径。
马佳雯, 梁新乐. 基于宏病毒组测序技术解析异常发酵醋醪噬菌体群落结构与功能[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(4): 489-498.
Jiawen Ma, Xinle Liang. Analysis of structure and function of phage community occurring in the abnormal fermentation of vinegar mash through virome sequencing[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(4): 489-498.
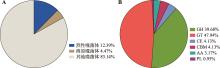
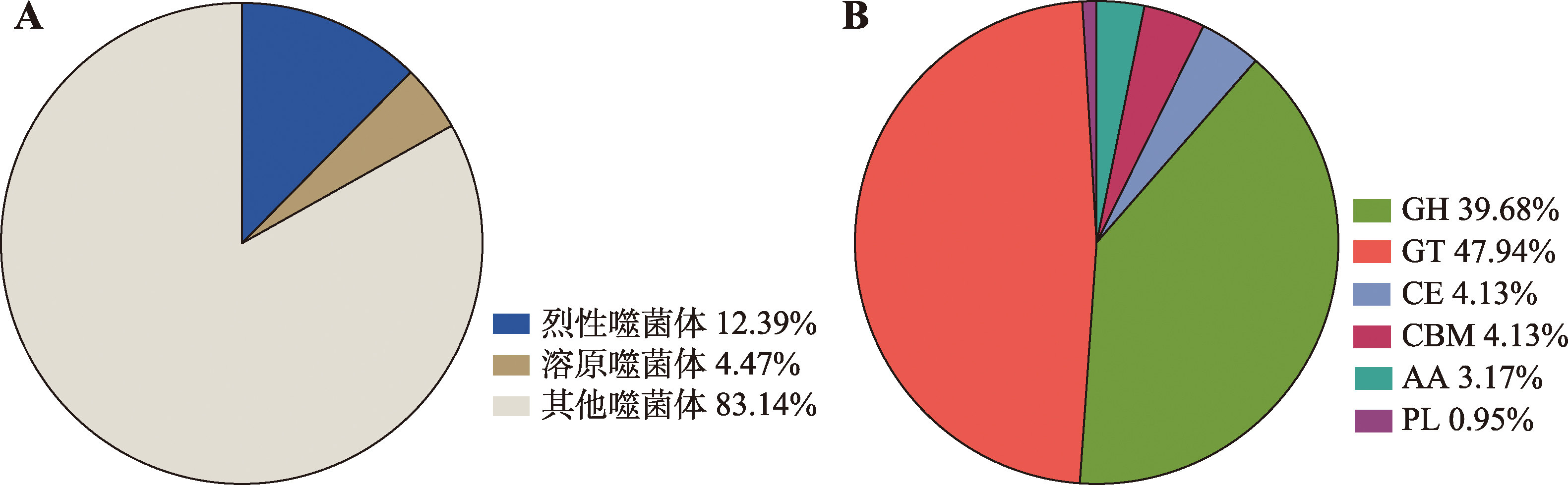
图5
噬菌体种类相对丰度和异常发酵醋醪噬菌体中水解酶种类比例 A:异常发酵中烈性、溶原和其他噬菌体在醋醪中所占的比例图。B:异常发酵醋醪中的噬菌体水解酶的基因功能预测。GH (glycoside hydrolases)、GT (glycosyltransferases)、CE (carbohydrate esterases)、CBM (carbohydrate-binding modules)、AA (auxiliary activities)和PL (polysaccharide lyases)分别为糖苷水解酶、糖基转移酶、碳水化合物酯酶、碳水化合物结合结构域、辅助活动酶和多糖裂解酶。"
| [1] | Zhao DA. Mixed ferment and pure-blood ferment. China Condiment, 2005, (3): 3-8. |
| 赵德安. 混合发酵与纯种发酵. 中国调味品, 2005, (3): 3-8. | |
| [2] |
Camarillo-Guerrero LF, Almeida A, Rangel-Pineros G, Finn RD, Lawley TD. Massive expansion of human gut bacteriophage diversity. Cell, 2021, 184(4): 1098-1109.
pmid: 33606979 |
| [3] |
Wu R, Davison MR, Nelson WC, Graham EB, Fansler SJ, Farris Y, Bell SL, Godinez I, McDermott JE, Hofmockel KS, Jansson JK. DNA viral diversity, abundance, and functional potential vary across grassland soils with a range of historical moisture regimes. mBio, 2021, 12(6): e0259521.
pmid: 34724822 |
| [4] |
Labbé M, Girard C, Vincent WF, Culley AI. Extreme viral partitioning in a marine-derived high Arctic Lake. mSphere, 2020, 5(3): e00334-20.
pmid: 32404515 |
| [5] | Yao YH, Kang JM, Chen XX, Xue YS, Han BZ. Research progress on function and role of bacteriophage during food fermentation. China Brewing, 2024, 43(2): 7-14. |
| 姚雨桦, 康佳木, 陈小雪, 薛岩松, 韩北忠. 噬菌体在食品发酵中的功能和作用研究进展. 中国酿造, 2024, 43(2): 7-14. | |
| [6] |
Cordero-Bueso G, Moraga J, Ríos-Carrasco M, Ruiz- Muñoz M, Cantoral JM. Bacteriophages as an up-and- coming alternative to the use of sulfur dioxide in winemaking. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10: 2931.
pmid: 32038510 |
| [7] |
Queiroz LL, Lacorte GA, Isidorio WR, Landgraf M, Franco BDGdM, Pinto UM, Hoffmann C. High level of interaction between phages and bacteria in an artisanal raw milk cheese microbial community. mSystems, 2023, 8(1): e0056422.
pmid: 36475872 |
| [8] |
Han YY, Du JH. A comparative study of the effect of bacteria and yeasts communities on inoculated and spontaneously fermented apple cider. Food Microbiol, 2023, 111: 104195.
pmid: 36681399 |
| [9] | 赵友新. 谷氨酸发酵中防止噬菌体污染的措施. 中国酿造, 1991, (3): 46-47. |
| [10] | 黄和照. 浅谈减少谷氨酸发酵噬菌体污染的几个措施. 中国酿造. 1990, (2): 46-47. |
| [11] |
Jolicoeur AP, Lemay ML, Beaubien E, Bélanger J, Bergeron C, Bourque-Leblanc F, Doré L, Dupuis MÈ, Fleury A, Garneau JE, Labrie SJ, Labrie S, Lacasse G, Lamontagne-Drolet M, Lessard-Hurtubise R, Martel B, Menasria R, Morin-Pelchat R, Pageau G, Samson JE, Rousseau GM, Tremblay DM, Duquenne M, Lamoureux M, Moineau S. Longitudinal study of Lactococcus phages in a Canadian cheese factory. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2023, 89(5): e0042123.
pmid: 37074184 |
| [12] |
Ávila M, Sánchez C, Calzada J, Mayer MJ, Berruga MI, López-Díaz TM, Narbad A, Garde S. Isolation and characterization of new bacteriophages active against Clostridium tyrobutyricum and their role in preventing the late blowing defect of cheese. Food Res Int, 2023, 163: 112222.
pmid: 36596151 |
| [13] |
Somerville V, Berthoud H, Schmidt RS, Bachmann HP, Meng YH, Fuchsmann P, von Ah U, Engel P. Functional strain redundancy and persistent phage infection in Swiss hard cheese starter cultures. ISME J, 2022, 16(2): 388-399.
pmid: 34363005 |
| [14] | Zhang R, Yan R. Application of anti-phage starter in dairy industry and control of fermentation process. China Food Saf Mag, 2024, (5): 16-18. |
| 张荣, 岩蓉. 抗噬菌体发酵剂在乳品工业中的应用及对发酵过程的控制. 食品安全导刊, 2024, (5): 16-18. | |
| [15] | Chai SY, Guo J, Battur M, Ma RR, Chen X. Screening and adsorption characteristics of phage-resistant Lactobacillus plantarum strain. Food Res Dev, 2019, 40(24): 198-204. |
| 柴诗语, 郭静, 孟根其其格, 马瑞瑞, 陈霞. 抗噬菌体P2的植物乳杆菌突变菌株的筛选及其吸附特性研究. 食品研究与开发, 2019, 40(24): 198-204. | |
| [16] |
Xia K, Li YD, Sun J, Liang XL. Comparative genomics of Acetobacter pasteurianus Ab3, an acetic acid producing strain isolated from Chinese traditional rice vinegar Meiguichu. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0162172.
pmid: 27611790 |
| [17] |
Ma JW, Qian CG, Hu QJ, Zhang JP, Gu GZ, Liang XL, Zhang L. The bacteriome-coupled phage communities continuously contract and shift to orchestrate the traditional rice vinegar fermentation. Food Res Int, 2024, 184: 114244.
pmid: 38609223 |
| [18] | Nie WX, Zheng X, Feng W, Liu Y, Li YD, Liang XL. Characterization of bacterial cellulose produced by Acetobacter pasteurianus MGC-N8819 utilizing lotus rhizome. LWT, 2022, 165: 113763. |
| [19] |
Yu Z, Ma Y, Guan YF, Zhu YY, Wang K, Wang YQ, Liu P, Chen J, Yu YJ. Metagenomics of virus diversities in solid-state brewing process of traditional Chinese vinegar. Foods, 2022, 11(20): 3296.
pmid: 37431044 |
| [20] |
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(14): 1754-1760.
pmid: 19451168 |
| [21] |
von Meijenfeldt FAB, Arkhipova K, Cambuy DD, Coutinho FH, Dutilh BE. Robust taxonomic classification of uncharted microbial sequences and bins with CAT and BAT. Genome Biol, 2019, 20(1): 217.
pmid: 31640809 |
| [22] |
Ren J, Ahlgren NA, Lu YY, Fuhrman JA, Sun FZ. VirFinder: a novel k-mer based tool for identifying viral sequences from assembled metagenomic data. Microbiome, 2017, 5(1): 69.
pmid: 28683828 |
| [23] |
Guo JR, Bolduc B, Zayed AA, Varsani A, Dominguez- Huerta G, Delmont TO, Pratama AA, Gazitúa MC, Vik D, Sullivan MB, Roux S. VirSorter2: a multi-classifier, expert-guided approach to detect diverse DNA and RNA viruses. Microbiome, 2021, 9(1): 37.
pmid: 33522966 |
| [24] |
Camargo AP, Nayfach S, Chen IA, Palaniappan K, Ratner A, Chu K, Ritter SJ, Reddy TBK, Mukherjee S, Schulz F, Call L, Neches RY, Woyke T, Ivanova NN, Eloe-Fadrosh EA, Kyrpides NC, Roux S. IMG/VR v4:an expanded database of uncultivated virus genomes within a framework of extensive functional, taxonomic, and ecological metadata. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(D1): D733-D743.
pmid: 36399502 |
| [25] |
Roux S, Adriaenssens EM, Dutilh BE, Koonin EV, Kropinski AM, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Lavigne R, Brister JR, Varsani A, Amid C, Aziz RK, Bordenstein SR, Bork P, Breitbart M, Cochrane GR, Daly RA, Desnues C, Duhaime MB, Emerson JB, Enault F, Fuhrman JA, Hingamp P, Hugenholtz P, Hurwitz BL, Ivanova NN, Labonté JM, Lee KB, Malmstrom RR, Martinez-Garcia M, Mizrachi IK, Ogata H, Páez-Espino D, Petit MA, Putonti C, Rattei T, Reyes A, Rodriguez-Valera F, Rosario K, Schriml L, Schulz F, Steward GF, Sullivan MB, Sunagawa S, Suttle CA, Temperton B, Tringe SG, Thurber RV, Webster NS, Whiteson KL, Wilhelm SW, Wommack KE, Woyke T, Wrighton KC, Yilmaz P, Yoshida T, Young MJ, Yutin N, Allen LZ, Kyrpides NC, Eloe-Fadrosh EA. Minimum information about an uncultivated virus genome (MIUViG). Nat Biotechnol, 2019, 37(1): 29-37.
pmid: 30556814 |
| [26] |
Yang KM, Wang XF, Hou RJ, Lu CX, Fan Z, Li JX, Wang S, Xu YC, Shen QR, Friman VP, Wei Z. Rhizosphere phage communities drive soil suppressiveness to bacterial wilt disease. Microbiome, 2023, 11(1): 16.
pmid: 36721270 |
| [27] |
Camargo AP, Roux S, Schulz F, Babinski M, Xu Y, Hu B, Chain PSG, Nayfach S, Kyrpides NC. Identification of mobile genetic elements with geNomad. Nat Biotechnol, 2023, 42(8): 1303-1312.
pmid: 37735266 |
| [28] |
Shang JY, Peng C, Liao HR, Tang XB, Sun YN. PhaBOX: a web server for identifying and characterizing phage contigs in metagenomic data. Bioinform Adv, 2023, 3(1): vbad101.
pmid: 37641717 |
| [29] |
Bin Jang H, Bolduc B, Zablocki O, Kuhn JH, Roux S, Adriaenssens EM, Brister JR, Kropinski AM, Krupovic M, Lavigne R, Turner D, Sullivan MB. Taxonomic assignment of uncultivated prokaryotic virus genomes is enabled by gene-sharing networks. Nat Biotechnol, 2019, 37(6): 632-639.
pmid: 31061483 |
| [30] |
Hyatt D, LoCascio PF, Hauser LJ, Uberbacher EC. Gene and translation initiation site prediction in metagenomic sequences. Bioinformatics. 2012, 28(17): 2223-2230.
pmid: 22796954 |
| [31] |
Zheng JF, Ge QW, Yan YC, Zhang XP, Huang L, Yin YB. dbCAN3: automated carbohydrate-active enzyme and substrate annotation. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(W1): W115-W121.
pmid: 37125649 |
| [32] | Peng MY, Huang T, Zhang XJ, Chai LJ, Lu ZM, Shi JS, Xu ZH. Comparative genomics reveals the functional differences between Acetobacter pasteurianus and Komagataeibacter europaeus in vinegar pei of Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar. Acta Microbiol Sin, 2023, 63(2): 638-655. |
| 彭铭烨, 黄婷, 张晓娟, 柴丽娟, 陆震鸣, 史劲松, 许正宏. 比较基因组学解析谷物醋醋醅中巴氏醋杆菌和欧洲驹形杆菌的功能差异. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(2): 638-655. | |
| [33] | Athiappan M, Dinesh Kumar S, Umamaheswari S, Rajaprabu M. Chapter 13—Rhizosphere engineering through pesticides-degrading beneficial bacteria. Rhizosphere Eng, 2022, 239-257. |
| [34] |
Yabe S, Sakai Y, Abe K, Yokota A, Také A, Matsumoto A, Sugiharto A, Susilowati D, Hamada M, Nara K, Made Sudiana I, Otsuka S. Dictyobacter aurantiacus gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Ktedonobacteraceae, isolated from soil, and emended description of the genus Thermosporothrix. Int J Sys Evol Microbiol, 2017, 67(8): 2615-2621.
pmid: 28758628 |
| [35] |
Zhang J, Luo D, Lin ZM, Zhou WY, Rao JL, Li YQ, Wu JH, Peng H, Lou TQ. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota in adult idiopathic membranous nephropathy with nephrotic syndrome. Microb Pathog, 2020, 147: 104359.
pmid: 32599137 |
| [36] |
Qian CG, Ma JW, Liang JL, Zhang L, Liang XL. Comprehensive deciphering prophages in genus Acetobacter on the ecology, genomic features, toxin-antitoxin system, and linkage with CRISPR-Cas system. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13: 951030.
pmid: 35983328 |
| [37] | Li TM, Du B. CRISPR-Cas system and coevolution of bacteria and phages. Hereditas (Beijing), 2011, 33(3): 213-218. |
| 李铁民, 杜波. CRISPR-Cas系统与细菌和噬菌体的共进化. 遗传, 2011, 33(3): 213-218. | |
| [38] | Xia K, Liang XL, Li YD. Comparative genomics and evolutionary analysis of CRISPR loci in acetic acid bacteria. Hereditas (Beijing), 2015, 37(12): 1242-1250. |
| 夏凯, 梁新乐, 李余动. 醋酸菌中CRISPR位点的比较基因组学与进化分析. 遗传, 2015, 37(12): 1242-1250. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:

