遗传 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 476-488.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-341
收稿日期:2024-12-03
修回日期:2025-01-25
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-03-03
通讯作者:
严冬,博士,研究员,研究方向:发育生物学。E-mail: yandong@fudan.edu.cn作者简介:高舒阳,硕士,专业方向:遗传学。E-mail: 24110700016@m.fudan.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shuyang Gao( ), Houguang Lu, Yanhua Wang, Dong Yan(
), Houguang Lu, Yanhua Wang, Dong Yan( )
)
Received:2024-12-03
Revised:2025-01-25
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2025-03-03
Supported by:摘要:
N6-甲基腺嘌呤(N6-methyladenosine,m6A)是mRNA中含量最丰富的化学修饰之一,在动植物发育和各种生理病理过程中发挥关键性的作用。先前的研究已经发现了m6A甲基转移酶复合体、去甲基化酶以及m6A结合蛋白,但作为一条相对较新的RNA修饰通路,可能还存在新的m6A修饰因子。为了探究m6A修饰对组织和器官的影响,本研究在果蝇(Drosophila melanogaster)眼成虫盘中过表达m6A结合蛋白基因Ythdc1。结果显示,过表达Ythdc1导致雄性异位表达Sxl蛋白,雌雄均出现粗糙眼表型,同时也激活了JNK和细胞凋亡通路。为了利用粗糙眼表型进行m6A修饰因子的筛选,本研究进一步构建了过表达Ythdc1的稳定果蝇品系。通过对1,500多个果蝇RNAi品系的筛选,成功鉴定到多个可能参与m6A修饰的抑制子和增强子。这些基因目前在m6A中的研究较少,因此进一步对它们进行了验证和初步的机制探索。总之,本研究发现了m6A修饰通路的多个潜在因子,丰富了对m6A修饰通路调控网络的认知,为探索m6A修饰通路新的调控机制提供了思路和方向。
高舒阳, 陆厚光, 王艳花, 严冬. 果蝇RNA m6A修饰通路因子的筛选[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(4): 476-488.
Shuyang Gao, Houguang Lu, Yanhua Wang, Dong Yan. Screening of Drosophila melanogaster RNA m6A modification pathway factors[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(4): 476-488.
表1
本研究所用的果蝇品系"
| 果蝇品系 | 来源 |
|---|---|
| GMR-Gal4/Cyo | 同济大学薛雷实验室馈赠 |
| UAS-Ythdc1.HA | BDSC77884 |
| UAS-Ythdc1-3A | 本实验室 |
| UAS-Ythdf-Flag | 本实验室 |
| UAS-Ythdf-3A-Flag | 本实验室 |
| Sco/Cyo | 本实验室 |
| UAS-Ythdc1-RNAi-1 | VDRC330558 |
| UAS-Ythdc1-RNAi-2 | 本实验室 |
| UAS-Ythdc1-RNAi-3 | 本实验室 |
| UAS-Ythdc1-RNAi-4 | 本实验室 |
| UAS-egr-RNAi | VDRC45253 |
| UAS-Tak1-RNAi | BDSC53377 |
| UAS-hep-RNAi | VDRC109277 |
| UAS-wgn-RNAi | VDRC330339 |
| UAS-bsk-RNAi | BDSC53310 |
| UAS-wts-RNAi | THU2748 |
| UAS-ex-RNAi | THU1263 |
| UAS-ft-RNAi | BDSC34970 |
| UAS-hpo-RNAi | VDRC104169 |
| UAS-yki-RNAi | TH201501131.S |
| UAS-ds-RNAi | THU1156 |
| UAS-dachs-RNAi | TH201501163.S |
| UAS-Mettl25B-RNAi | VDRC25449 |
| UAS-Mettl22-RNAi | VDRC28681 |
| UAS-Mettl17-RNAi | VDRC108021 |
| UAS-Mettl5-RNAi | VDRC45658 |
| UAS-Mettl18-RNAi | VDRC103484 |
| UAS-Mettl23-RNAi | VDRC48108 |
| UAS-Mettl15-RNAi | VDRC52664 |
| UAS-fzy-RNAi-1 | TH2015100428.S |
| UAS-fzy-RNAi-2 | BDSC40933 |
| UAS-Atg2-RNAi | THU3698 |
| UAS-CG9451-RNAi | THU3608 |
| UAS-Pabp2-RNAi-1 | VDRC106466 |
| UAS-Pabp2-RNAi-2 | VDRC33499 |
| UAS-Atx2-RNAi-1 | BDSC36114 |
| UAS-Atx2-RNAi-2 | BDSC44012 |
| 用于筛选的其他UAS-RNAi果蝇 | THU/TH、VDRC、BDSC |
表2
构建RNAi质粒所需的引物"
| 引物名称 | 引物序列(5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| Ythdc1-shRNA-2-F | CTAGCAGTCCGCAAGGAATTGTCTTTCAATAGTTATATTCAAGCATATTGAAAGACAATTCCTTGCGGGCG |
| Ythdc1-shRNA-2-R | AATTCGCCCGCAAGGAATTGTCTTTCAATATGCTTGAATATAACTATTGAAAGACAATTCCTTGCGGACTG |
| Ythdc1-shRNA-3-F | CTAGCAGTCACACGGTTCTTCCTCATCAATAGTTATATTCAAGCATATTGATGAGGAAGAACCGTGTGGCG |
| Ythdc1-shRNA-3-R | AATTCGCCACACGGTTCTTCCTCATCAATATGCTTGAATATAACTATTGATGAGGAAGAACCGTGTGACTG |
| Ythdc1-shRNA-4-F | CTAGCAGTCGGGCACTCAGCACAAGAGAATAGTTATATTCAAGCATATTCTCTTGTGCTGAGTGCCCGGCG |
| Ythdc1-shRNA-4-R | AATTCGCCGGGCACTCAGCACAAGAGAATATGCTTGAATATAACTATTCTCTTGTGCTGAGTGCCCGACTG |
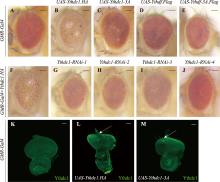
图2
过表达Ythdc1.HA造成果蝇成虫粗糙眼 A~J:果蝇成虫眼图片。与GMR-Gal4对照(A)相比,过表达Ythdc1.HA会引起粗糙眼表型(B),而过表达功能域突变的Ythdc1-3A不会产生粗糙眼表型(C);过表达Ythdf.Flag(D)或功能域突变的Ythdf-3A.Flag(E)均无明显表型变化。GMR-Gal4>Ythdc1.HA产生的粗糙眼表型(F)可被4个靶向Ythdc1基因不同区域的RNAi所挽救(G~J)。K~M:果蝇幼虫眼成虫盘Ythdc1抗体染色。与对照组(K)相比,Ythdc1.HA(L)与Ythdc1-3A(M)过表达蛋白量相似(箭头所示)。A~J图比例尺为100 μm;K~M图比例尺为50 μm。"

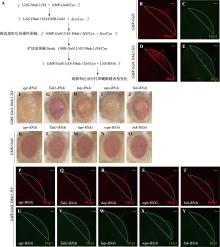
图3
JNK信号通路筛选 A:构建稳定的粗糙眼表型品系并进行RNAi筛选;B~E:果蝇幼虫眼成虫盘Dcp-1和Mmp1抗体染色。图中虚线为GMR-Gal4的表达部位。与对照(B)和(C)相比,过表达Ythdc1.HA能够激活cleaved Dcp-1和Mmp1的表达;比例尺为30 μm。F~O:果蝇成虫眼睛图片。敲低JNK信号通路中的成员egr、Tak1、hep、wgn和bsk不能够挽救粗糙眼表型。使用GMR-Gal4仅敲低JNK信号通路中的成员也未产生眼睛表型;比例尺为100 μm。P~Y:果蝇幼虫眼成虫盘Dcp-1和Mmp1抗体染色。与对照(D)和(E)相比,敲低JNK信号通路中的成员可明显减少Dcp1和Mmp1的表达。"

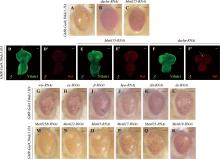
图4
挽救粗糙眼表型的候选基因 A~C:果蝇成虫眼睛图片。与对照组相比,敲低dachs或Mettl15可以明显挽救粗糙眼表型。比例尺为100 μm。D~F′:雄性幼虫眼睛成虫盘Ythdc1和Sxl抗体染色。敲低dachs可明显抑制雄性果蝇异位表达的Sxl蛋白(箭头),而敲低Mettl15对Sxl异位表达无影响;图中雄性果蝇根据Sxl抗体染色用♂标出,比例尺为50 μm。G~L:果蝇成虫眼睛图片。与对照组(A)相比,敲低Hippo信号通路中的成员wts、ex、ft、hpo、yki或ds不能够挽救粗糙眼表型;比例尺为100 μm。M~R:与对照组(A)相比,敲低不同的甲基化转移酶不能够挽救粗糙眼表型。比例尺为100 μm。"
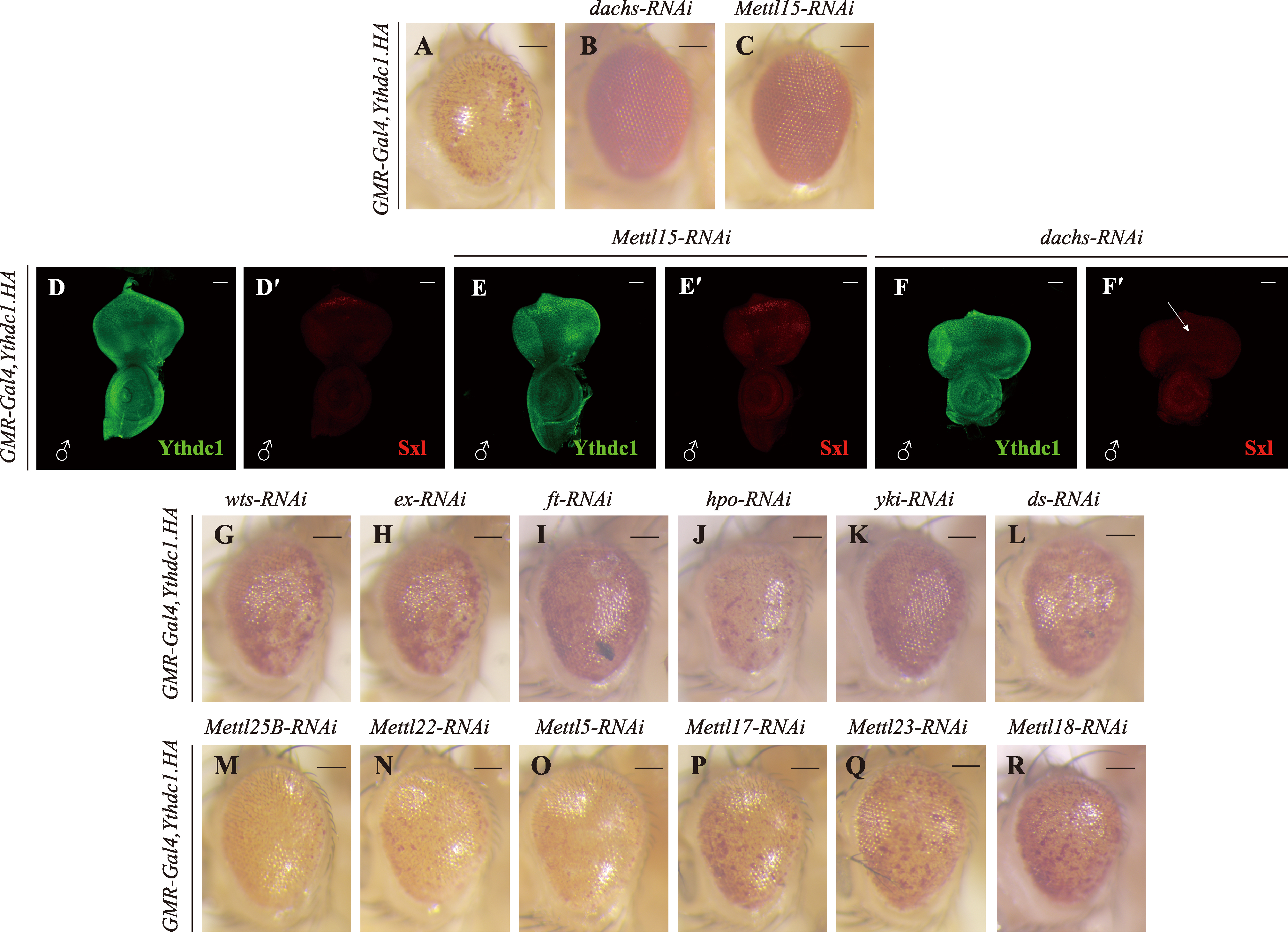
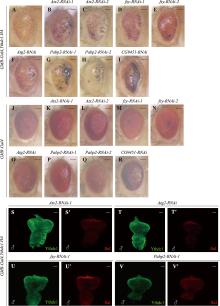
图5
加重粗糙眼表型的候选基因 A~R:果蝇成虫眼睛图片。与对照组GMR-Gal4,Ythdc1.HA(A)相比,使用RNAi敲低Atx2、fzy、Atg2、Pabp2和CG9451时使眼睛表型发生更加严重的变化(B~I)。与对照组GMR-Gal4(J)相比,使用RNAi敲低Atx2、fzy、Atg2、Pabp2和CG9451时眼睛发生轻微甚者无明显变化(K~R)。比例尺为100 μm。S~V′:雄性幼虫眼成虫盘Ythdc1和Sxl抗体染色。敲低Atx2、fzy、Atg2和Pabp2时,Ythdc1和Sxl的表达量并没有发生明显的改变。图中雄性根据Sxl抗体染色用♂标出,比例尺为50 μm。"

| [1] |
Zaccara S, Ries RJ, Jaffrey SR. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 20(10): 608-624.
pmid: 31520073 |
| [2] |
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18(1): 31-42.
pmid: 27808276 |
| [3] |
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS, Yang YG. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res, 2018, 28(6): 616-624.
pmid: 29789545 |
| [4] |
Bokar JA, Rath-Shambaugh ME, Ludwiczak R, Narayan P, Rottman F. Characterization and partial purification of mRNA N6-adenosine methyltransferase from HeLa cell nuclei. Internal mRNA methylation requires a multisubunit complex. J Biol Chem, 1994, 269(26): 17697-17704.
pmid: 8021282 |
| [5] |
Bokar JA, Shambaugh ME, Polayes D, Matera AG, Rottman FM. Purification and cDNA cloning of the AdoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA (N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase. RNA, 1997, 3(11): 1233-1247.
pmid: 9409616 |
| [6] |
Ortega A, Niksic M, Bachi A, Wilm M, Sánchez L, Hastie N, Valcárcel J. Biochemical function of female-lethal (2)D/Wilms' tumor suppressor-1-associated proteins in alternative pre-mRNA splicing. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(5): 3040-3047.
pmid: 12444081 |
| [7] |
Schöller E, Weichmann F, Treiber T, Ringle S, Treiber N, Flatley A, Feederle R, Bruckmann A, Meister G. Interactions, localization, and phosphorylation of the m6A generating Mettl3-Mettl14-Wtap complex. RNA, 2018, 24(4): 499-512.
pmid: 29348140 |
| [8] |
Yue YN, Liu J, Cui XL, Cao J, Luo GZ, Zhang ZZ, Cheng T, Gao MS, Shu X, Ma HH, Wang FQ, Wang XX, Shen B, Wang YZ, Feng XH, He C, Liu JZ. Vrima mediates preferential m6A mRNA methylation in 3′UTR and near stop codon and associates with alternative polyadenylation. Cell Discov, 2018, 4: 10.
pmid: 29507755 |
| [9] |
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A, Jackson C, Guttman M, Jaffrey SR. m6A RNA methylation promotes Xist-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature, 2016, 537(7620): 369-373.
pmid: 27602518 |
| [10] |
Knuckles P, Lence T, Haussmann IU, Jacob D, Kreim N, Carl SH, Masiello I, Hares T, Villaseñor R, Hess D, Andrade-Navarro MA, Biggiogera M, Helm M, Soller M, Bühler M, Roignant JY. Zc3h13/Flacc is required for adenosine methylation by bridging the mRNA-binding factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m6A machinery component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes Dev, 2018, 32(5-6): 415-429.
pmid: 29535189 |
| [11] |
Wen J, Lv RT, Ma HH, Shen HJ, He CX, Wang JH, Jiao FF, Liu H, Yang PY, Tan L, Lan F, Shi YG, He C, Shi Y, Diao JB. Zc3h13 regulates nuclear RNA m6A methylation and mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Mol Cell, 2018, 69(6): 1028-1038.e6.
pmid: 29547716 |
| [12] |
Růžička K, Zhang M, Campilho A, Bodi Z, Kashif M, Saleh M, Eeckhout D, El-Showk S, Li HY, Zhong SL, De Jaeger G, Mongan NP, Hejátko J, Helariutta Y, Fray RG. Identification of factors required for m6A mRNA methylation in Arabidopsis reveals a role for the conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase HAKAI. New Phytol, 2017, 215(1): 157-172.
pmid: 28503769 |
| [13] |
Wang YH, Zhang LF, Ren H, Ma LJ, Guo J, Mao DC, Lu ZW, Lu LJ, Yan D. Role of Hakai in m6A modification pathway in Drosophila. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2159.
pmid: 33846330 |
| [14] |
Jia GF, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng GQ, Yang Y, Yi CQ, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG, He C. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol, 2011, 7(12): 885-887.
pmid: 22002720 |
| [15] |
Zhao X, Yang Y, Sun BF, Shi Y, Yang X, Xiao W, Hao YJ, Ping XL, Chen YS, Wang WJ, Jin KX, Wang X, Huang CM, Fu Y, Ge XM, Song SH, Jeong HS, Yanagisawa H, Niu YM, Jia GF, Wu W, Tong WM, Okamoto A, He C, Rendtlew Danielsen JM, Wang XJ, Yang YG. FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res, 2014, 24(12): 1403-1419.
pmid: 25412662 |
| [16] |
Zheng GQ, Dahl JA, Niu YM, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li CJ, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, Lu ZK, Bosmans RPG, Dai Q, Hao YJ, Yang X, Zhao WM, Tong WM, Wang XJ, Bogdan F, Furu K, Fu Y, Jia GF, Zhao X, Liu J, Krokan HE, Klungland A, Yang YG, He C. Alkb5h is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell, 2013, 49(1): 18-29.
pmid: 23177736 |
| [17] |
Tang C, Klukovich R, Peng HY, Wang ZQ, Yu T, Zhang Y, Zheng HL, Klungland A, Yan W. Alkb5h-dependent m6A demethylation controls splicing and stability of long 3′-UTR mRNAs in male germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(2): E325-E333.
pmid: 29279410 |
| [18] |
Dai ZK, Asgari S. Alkbh8 as a potential N(6)- methyladenosine (m6A) eraser in insects. Insect Mol Biol, 2023, 32(5): 461-468.
pmid: 37119026 |
| [19] |
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY, Wang X, Ma HL, Huang CM, Yang Y, Huang N, Jiang GB, Wang HL, Zhou Q, Wang XJ, Zhao YL, Yang YG. Nuclear m6A reader Ythdc1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell, 2016, 61(4): 507-519.
pmid: 26876937 |
| [20] |
Kretschmer J, Rao H, Hackert P, Sloan KE, Höbartner C, Bohnsack MT. The m6A reader protein Ythdc2 interacts with the small ribosomal subunit and the 5′-3′ exoribonuclease XRN1. RNA, 2018, 24(10): 1339-1350.
pmid: 29970596 |
| [21] |
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu ZK, Han DL, Ma HH, Weng XC, Chen K, Shi HL, He C. N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell, 2015, 161(6): 1388-1399.
pmid: 26046440 |
| [22] |
Wang X, Lu ZK, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue YN, Han DL, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia GF, Ren B, Pan T, He C. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature, 2014, 505(7481): 117-120.
pmid: 24284625 |
| [23] |
Du H, Zhao Y, He JQ, Zhang Y, Xi HR, Liu MF, Ma JB, Wu LG. Ythdf2 destabilizes m6A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 12626.
pmid: 27558897 |
| [24] |
Li A, Chen YS, Ping XL, Yang X, Xiao W, Yang Y, Sun HY, Zhu Q, Baidya P, Wang X, Bhattarai DP, Zhao YL, Sun BF, Yang YG. Cytoplasmic m6A reader Ythdf3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res, 2017, 27(3): 444-447.
pmid: 28106076 |
| [25] |
Shi HL, Wang X, Lu ZK, Zhao BS, Ma HH, Hsu PJ, Liu C, He C. Ythdf3 facilitates translation and decay of N(6)- methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res, 2017, 27(3): 315-328.
pmid: 28106072 |
| [26] |
Tian M, Maniatis T. A splicing enhancer complex controls alternative splicing of doublesex pre-mRNA. Cell, 1993, 74(1): 105-114.
pmid: 8334698 |
| [27] |
Billeter JC, Rideout EJ, Dornan AJ, Goodwin SF. Control of male sexual behavior in Drosophila by the sex determination pathway. Curr Biol, 2006, 16(17): R766-R776.
pmid: 16950103 |
| [28] |
Guo J, Tang HW, Li J, Perrimon N, Yan D. Xio is a component of the Drosophila sex determination pathway and RNA N(6)-methyladenosine methyltransferase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(14): 3674-3679.
pmid: 29555755 |
| [29] |
Lence T, Akhtar J, Bayer M, Schmid K, Spindler L, Ho CH, Kreim N, Andrade-Navarro MA, Poeck B, Helm M, Roignant JY. m6A modulates neuronal functions and sex determination in Drosophila. Nature, 2016, 540(7632): 242-247.
pmid: 27919077 |
| [30] |
He PC, He C. m6A RNA methylation: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential. EMBO J, 2021, 40(3): e105977.
pmid: 33470439 |
| [31] |
Zhao BS, Wang X, Beadell AV, Lu ZK, Shi HL, Kuuspalu A, Ho RK, He C. m6A-dependent maternal mRNA clearance facilitates zebrafish maternal-to-zygotic transition. Nature, 2017, 542(7642): 475-478.
pmid: 28192787 |
| [32] |
Zhang CX, Chen YS, Sun BF, Wang L, Yang Y, Ma DY, Lv JH, Heng J, Ding YY, Xue YY, Lu XY, Xiao W, Yang YG, Liu F. m6A modulates haematopoietic stem and progenitor cell specification. Nature, 2017, 549(7671): 273-276.
pmid: 28869969 |
| [33] |
Arribas-Hernández L, Bressendorff S, Hansen MH, Poulsen C, Erdmann S, Brodersen P. An m(6)A-YTH module controls developmental timing and morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2018, 30(5): 952-967.
pmid: 29643069 |
| [34] |
Yu Q, Liu S, Yu L, Xiao Y, Zhang SS, Wang XP, Xu YY, Yu H, Li YL, Yang JB, Tang J, Duan HC, Wei LH, Zhang HY, Wei JB, Tang Q, Wang CL, Zhang WT, Wang Y, Song PZ, Lu Q, Zhang W, Dong SQ, Song BA, He C, Jia GF. RNA demethylation increases the yield and biomass of rice and potato plants in field trials. Nat Biotechnol, 2021, 39(12): 1581-1588.
pmid: 34294912 |
| [35] |
Ma XJ, Huang JH, Yang LX, Yang Y, Li WZ, Xue L. Nopo modulates egr-induced JNK-independent cell death in Drosophila. Cell Res, 2012, 22(2): 425-431.
pmid: 21844890 |
| [36] |
Li Y, Liu DY, Wang HC, Zhang XJ, Lu BW, Li SX. The Ire1/Xbp1 axis restores ER and tissue homeostasis perturbed by excess notch in Drosophila. Dev Biol, 2024, 507: 11-19.
pmid: 38142805 |
| [37] |
Kan LJ, Ott S, Joseph B, Park ES, Dai W, Kleiner RE, Claridge-Chang A, Lai EC. A neural m6A/Ythdf pathway is required for learning and memory in Drosophila. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1458.
pmid: 33674589 |
| [38] |
Mao YP, Rauskolb C, Cho E, Hu WL, Hayter H, Minihan G, Katz FN, Irvine KD. Dachs: an unconventional myosin that functions downstream of Fat to regulate growth, affinity and gene expression in Drosophila. Development, 2006, 133(13): 2539-2551.
pmid: 16735478 |
| [39] |
Vrabioiu AM, Struhl G. Fat/Dachsous signaling promotes Drosophila wing growth by regulating the conformational state of the NDR kinase warts. Dev Cell, 2015, 35(6): 737-749.
pmid: 26702832 |
| [40] |
Misra JR, Irvine KD. Vamana couples fat signaling to the Hippo pathway. Dev Cell, 2016, 39(2): 254-266.
pmid: 27746048 |
| [41] |
Kwon Y, Vinayagam A, Sun XY, Dephoure N, Gygi SP, Hong PY, Perrimon N. The Hippo signaling pathway interactome. Science, 2013, 342(6159): 737-740.
pmid: 24114784 |
| [42] |
Imbert G, Saudou F, Yvert G, Devys D, Trottier Y, Garnier JM, Weber C, Mandel JL, Cancel G, Abbas N, Dürr A, Didierjean O, Stevanin G, Agid Y, Brice A. Cloning of the gene for spinocerebellar ataxia 2 reveals a locus with high sensitivity to expanded CAG/glutamine repeats. Nat Genet, 1996, 14(3): 285-291.
pmid: 8896557 |
| [43] |
Pulst SM, Nechiporuk A, Nechiporuk T, Gispert S, Chen XN, Lopes-Cendes I, Pearlman S, Starkman S, Orozco- Diaz G, Lunkes A, DeJong P, Rouleau GA, Auburger G, Korenberg JR, Figueroa C, Sahba S. Moderate expansion of a normally biallelic trinucleotide repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Nat Genet, 1996, 14(3): 269-276.
pmid: 8896555 |
| [44] |
Elden AC, Kim HJ, Hart MP, Chen-Plotkin AS, Johnson BS, Fang XD, Armakola M, Geser F, Greene R, Lu MM, Padmanabhan A, Clay-Falcone D, McCluskey L, Elman L, Juhr D, Gruber PJ, Rüb U, Auburger G, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY, Van Deerlin VM, Bonini NM, Gitler AD. Ataxin-2 intermediate-length polyglutamine expansions are associated with increased risk for ALS. Nature, 2010, 466(7310): 1069-1075.
pmid: 20740007 |
| [45] |
Lim C, Allada R. Ataxin-2 activates period translation to sustain circadian rhythms in Drosophila. Science, 2013, 340(6134): 875-879.
pmid: 23687047 |
| [46] |
Zhang Y, Ling JL, Yuan CY, Dubruille R, Emery P. A role for Drosophila Atx2 in activation of per translation and circadian behavior. Science, 2013, 340(6134): 879-882.
pmid: 23687048 |
| [47] |
McCann C, Holohan EE, Das S, Dervan A, Larkin A, Lee JA, Rodrigues V, Parker R, Ramaswami M. The Ataxin-2 protein is required for microRNA function and synapse- specific long-term olfactory habituation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(36): E655-E662.
pmid: 21795609 |
| [48] |
Ciosk R, DePalma M, Priess JR. Atx-2, the C. elegans ortholog of ataxin-2, functions in translational regulation in the germline. Development, 2004, 131(19): 4831-4841.
pmid: 15342467 |
| [49] |
Xiong XS, Hou L, Park YP, Molinie B, GTEx Consortium, Gregory RI, Kellis M. Genetic drivers of m6A methylation in human brain, lung, heart and muscle. Nat Genet, 2021, 53(8): 1156-1165.
pmid: 34211177 |
| [50] |
Layalle S, They L, Ourghani S, Raoul C, Soustelle L. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(2): 904.
pmid: 33477509 |
| [1] | 杨剑, 石国娟, 彭昂惠, 徐清波, 王睿琪, 薛雷, 喻昕阳, 孙艺昊. Tip60-FOXO调节果蝇JNK信号通路介导的细胞凋亡【已撤稿】[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(6): 490-501. |
| [2] | 安钧浩, 赵雪莹, 乔守怡, 卢大儒, 皮妍. 现代计算机技术在遗传学实验教学中的应用——移动端轻量级高精度果蝇遗传性状批量识别系统的开发[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(4): 354-363. |
| [3] | 王孟晓, 何淑君. 神经胶质细胞调控黑腹果蝇生理行为研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(4): 300-312. |
| [4] | 韩玉婷, 许博文, 李羽童, 卢心怡, 董习之, 邱雨浩, 车沁耘, 朱芮葆, 郑丽, 李孝宸, 司绪, 倪建泉. 模式动物果蝇的基因调控前沿技术[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(1): 3-14. |
| [5] | 刘学文, 吴红梅, 白瑛, 曾群, 曹泽民, 吴秀山, 唐旻. 钾离子通道蛋白Shaker对果蝇心脏衰老的保护作用[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(1): 94-99. |
| [6] | 杜倍倍, 刘磊, 朱洋洋. RNA结合蛋白Roquin负调控STING依赖的果蝇天然免疫反应[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(12): 1201-1210. |
| [7] | 陈万银, 颜一丹, 栾晓瑾, 王敏, 方杰. CG8005基因在果蝇睾丸生殖细胞中的功能分析[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(11): 1122-1132. |
| [8] | 王珏, 黄娟, 许蕊. 利用CRISPR/Cas9和piggyBac实现果蝇基因组无缝编辑[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(5): 422-429. |
| [9] | 唐浚博, 曹浩伟, 许蕊, 张丹丹, 黄娟. 果蝇睾丸基因敲除突变体的构建及表型分析[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(6): 478-487. |
| [10] | 李恩惠,赵欣,张策,刘威. 脆性X智力低下蛋白参与非编码RNA通路的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(2): 87-94. |
| [11] | 孙书国, 吴世安, 张雷. Hippo信号通路在果蝇遗传学研究中的发现与扩展[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(7): 537-545. |
| [12] | 张笑, 贾桂芳. RNA表观遗传修饰:N6-甲基腺嘌呤[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(4): 275-288. |
| [13] | 苏方, 黄宗靓, 郭雅文, 焦仁杰, 李孜, 陈建明, 刘继勇. 从随机突变到精确编辑:果蝇基因组编辑技术的发展及演化[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(1): 17-27. |
| [14] | 李刚, 陈凡国. 果蝇唾腺多线染色体研究进展及其在遗传学教学中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(6): 605-612. |
| [15] | 霍桂桃, 吕建军, 屈哲, 林志, 张頔, 杨艳伟, 李波. 果蝇在肿瘤学研究中的优势及应用前景[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(1): 30-40. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
