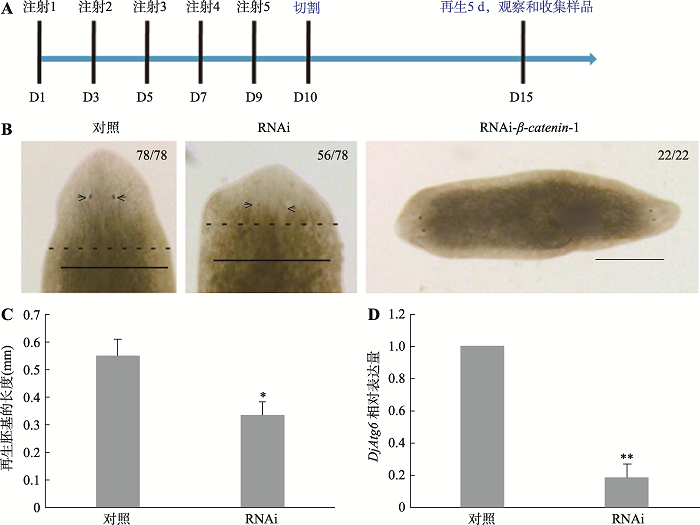
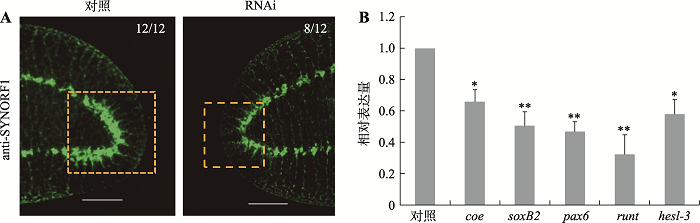
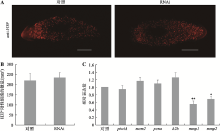
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (8): 792-801.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-118
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Functional analysis of autophagy-related gene Atg6 in planarian central nervous system regeneration
Kexue Ma( ), Rui Li, Fangying Guo, Gege Song, Meng Wu, Guangwen Chen(
), Rui Li, Fangying Guo, Gege Song, Meng Wu, Guangwen Chen( ), Dezeng Liu
), Dezeng Liu
- College of Life Sciences, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang 453007, China
-
Received:2021-03-30Revised:2021-06-21Online:2021-08-20Published:2021-07-21 -
Contact:Chen Guangwen E-mail:makexue@sina.com;Chengw0183@sina.com -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(31572267);Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(31471965)
Cite this article
Kexue Ma, Rui Li, Fangying Guo, Gege Song, Meng Wu, Guangwen Chen, Dezeng Liu. Functional analysis of autophagy-related gene Atg6 in planarian central nervous system regeneration[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(8): 792-801.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
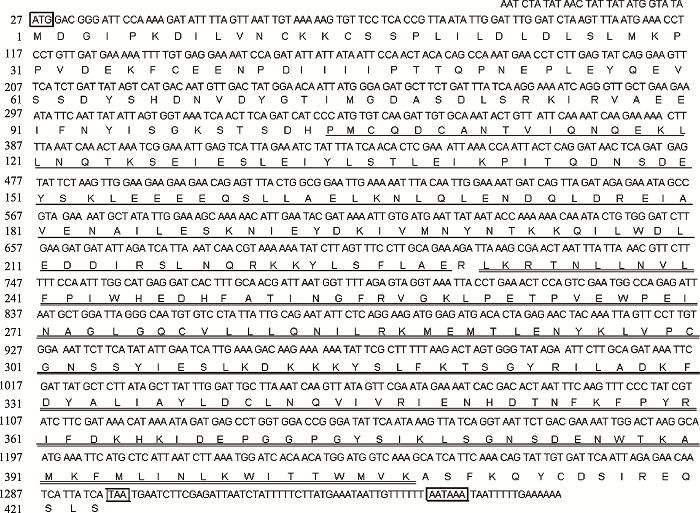
Supplementary Table 1
Primers used in this study"
| 引物名称 | 用途 | 序列 | 长度(bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5GSP1 | 5ʹ-RACE | 5ʹ-GCTATTTCTCTATCTAACTGATC-3ʹ | 565 |
| 5GSP2 | 5ʹ-RACE | 5ʹ-CAGTAAACTCTGTTCTTCTTCTTCC-3ʹ | 512 |
| 3GSP1 | 3ʹ-RACE | 5ʹ-TACCTGAAACTCCAGTCGAATGGC-3ʹ | 562 |
| 3GSP2 | 3ʹ-RACE | 5ʹ-TTGCAGAATATTCTCAGGAAGATGG-3ʹ | 500 |
| qAtg6F | qPCR | 5ʹ-GGAACAATTATGGGAGATGC-3ʹ | 281 |
| qAtg6R | qPCR | 5ʹ-AATTCCGCCAGTAAACTCTG -3ʹ | |
| Atg6F1 | WISH | 5ʹ-GTTAATTGTAAAAAGTGTTCCTCACCGTT-3ʹ | 1212 |
| Atg6R1 | WISH | 5ʹ-ATACTGTTTGAATGATGCTTTGACC-3ʹ | |
| Atg6F2 | dsRNA | 5ʹ-ATCAACTTCAGATCATCCCATGTG-3ʹ | 946 |
| Atg6R2 | dsRNA | 5ʹ-ATACTGTTTGAATGATGCTTTGACC-3ʹ | |
| β-cateninF | dsRNA | 5ʹ-ACAACCATCGAATCTTATCCGCCAG-3ʹ | 1325 |
| β-cateninR | dsRNA | 5ʹ-CATTGTGTAACCGAATTATGTCTGT-3ʹ | |
| GFPF | dsRNA | 5ʹ-CGTGCAGTGCTTCAGCCGCTACCCC-3ʹ | 507 |
| GFPR | dsRNA | 5ʹ-AGCTCGTCCATGCCGTGAGTGATCC-3ʹ | |
| coeF | qPCR | 5ʹ-GCACCAGGAAGATTCGCATACAT-3ʹ | 284 |
| coeR | qPCR | 5ʹ-GTTAGGATTATTGGAGGCAGTAGAT-3ʹ | |
| soxB2F | qPCR | 5ʹ-AGTAAGTCCTCATTCAGCCAGT-3ʹ | 218 |
| soxB2R | qPCR | 5ʹ-CACCTGTTAGCATTCCACTCAT-3ʹ | |
| pax6F | qPCR | 5ʹ-ACGAGGTCATTCTGGAATCAATC-3ʹ | 246 |
| pax6R | qPCR | 5ʹ-ACAACTGAACTGGTAGCAACTC-3ʹ | |
| runtF | qPCR | 5ʹ-CCAATGCGAGGTGACTGACTTGAA-3ʹ | 291 |
| runtR | qPCR | 5ʹ-TGATTCTCCAATGTGAAGGTAACTG-3ʹ | |
| hesl-3F | qPCR | 5ʹ-CATCGTGAAGGAATTACCAGTC-3ʹ | 283 |
| hesl-3R | qPCR | 5ʹ-TACTCGTCTGTGCAGGATAATG-3ʹ | |
| pcnaF | qPCR | 5ʹ-AGCTACCGGAGATATTGGTAATGG-3ʹ | 168 |
| pcnaR | qPCR | 5ʹ-GAGACACGATAGGTGAAAGAGGC-3ʹ | |
| piwiAF | qPCR | 5ʹ-GGTTATTCCACAACTATTACAAGAG-3ʹ | 220 |
| piwiAR | qPCR | 5ʹ-AATCTACTTCGTCATTGATATCC-3ʹ | |
| mcm2F | qPCR | 5ʹ-GAGGAGGAGAAGAAGGATGT-3ʹ | 161 |
| mcm2R | qPCR | 5ʹ-GCTGTGCTCAAACTGGGACT-3ʹ | |
| mmp1F1 | qPCR | 5ʹ-ATGGCTGGAATAGAACAAGATGG-3ʹ | 202 |
| mmp1R1 | qPCR | 5ʹ-GACGAACTTCTCCTTCAGACATAG-3ʹ | |
| mmp2F1 | qPCR | 5ʹ-GAGCCTTAATAGTCGGTCTTCAAT-3ʹ | 259 |
| mmp2R2 | qPCR | 5ʹ-TCCTTCGGTCCATTCTTCAGCTG-3ʹ | |
| mmp1F2 | dsRNA | 5ʹ-TATGTCTGAAGGAGAAGTTCGTCG-3ʹ | 850 |
| mmp1R2 | dsRNA | 5ʹ-ATCGTGATACGAACTTTGTCTTGC-3ʹ | |
| mmp2F2 | dsRNA | 5ʹ-TGAGTTTTGCCGATGCTGAACACG-3ʹ | 746 |
| mmp2R2 | dsRNA | 5ʹ-GTCTTATCTCTCACGATTGCTGCG-3ʹ | |
| DjEF2F | qPCR | 5ʹ-TTAATGATGGGAAGATATGTTG-3ʹ | 250 |
| DjEF2R | qPCR | 5ʹ-GTACCATAGGATCTGACTTTGC-3ʹ |
| [1] |
Kenific CM, Wittmann T, Debnath J. Autophagy in adhesion and migration. J Cell Sci, 2016, 129(20):3685-3693.
pmid: 27672021 |
| [2] |
Phadwal K, Watson AS, Simon AK. Tightrope act: autophagy in stem cell renewal, differentiation, proliferation, and aging. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2013, 70(1):89-103.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1032-3 |
| [3] |
Fleming A, Rubinsztein DC. Autophagy in neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci, 2020, 43(10):767-779.
doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.07.003 |
| [4] |
He M, Ding YT, Chu C, Tang J, Xiao Q, Luo ZG. Autophagy induction stabilizes microtubules and promotes axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(40):11324-11329.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611282113 |
| [5] |
Yazdankhah M, Farioli-Vecchioli S, Tonchev AB, Stoykova A, Cecconi F. The autophagy regulators Ambra1 and Beclin 1 are required for adult neurogenesis in the brain subventricular zone. Cell Death Dis, 2014, 5(9):e1403.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.358 |
| [6] |
Pickford F, Masliah E, Britschgi M, Lucin K, Narasimhan R, Jaeger PA, Small S, Spencer B, Rockenstein E, Levine B, Wyss-Coray T. The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid beta accumulation in mice. J Clin Invest, 2008, 118(6):2190-2199.
doi: 10.1172/JCI33585 pmid: 18497889 |
| [7] |
Cebrià F, Nakazawa M, Mineta K, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Agata K. Dissecting planarian central nervous system regeneration by the expression of neural-specific genes. Dev Growth Differ, 2002, 44(2):135-146.
doi: 10.1046/j.1440-169x.2002.00629.x |
| [8] |
Petersen CP, Reddien PW. Polarized notum activation at wounds inhibits Wnt function to promote planarian head regeneration. Science, 2011, 332(6031):852-855.
doi: 10.1126/science.1202143 |
| [9] |
Cowles MW, Brown DDR, Nisperos SV, Stanley BN, Pearson BJ, Zayas RM. Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH gene family in planarians identifies factors required for adult neurogenesis and neuronal regeneration. Development, 2013, 140(23):4691-4702.
doi: 10.1242/dev.098616 |
| [10] |
Roberts-Galbraith RH, Brubacher JL, Newmark PA. A functional genomics screen in planarians reveals regulators of whole-brain regeneration. eLife, 2016, 5:e17002.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.17002 |
| [11] |
González-Estévez C. Autophagy meets planarians. Autophagy, 2009, 5(3):290-297.
pmid: 19164934 |
| [12] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods, 2001, 25(4):402-408
pmid: 11846609 |
| [13] | Ma KX, Zhang YM, Song GG, Wu M, Chen GW. Identification of autophagy-related gene 7 and autophagic cell death in the planarian Dugesia japonica. Front Physiol, 2018, 9:1223 |
| [14] |
Sánchez Alvarado A, Newmark PA. Double-stranded RNA specifically disrupts gene expression during planarian regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96(9):5049-5054.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.9.5049 |
| [15] |
Vásquez-Doorman C, Petersen CP. Zic-1 expression in planarian neoblasts after injury controls anterior pole regeneration. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10(7):e1004452
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004452 |
| [16] |
Isolani ME, Abril JF, Saló E, Deri P, Bianucci AM, Batistoni R. Planarians as a model to assessin vivo the role of matrix metalloproteinase genes during homeostasis and regeneration. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2):e55649.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055649 |
| [17] |
Rouhana L, Weiss JA, Forsthoefel DJ, Lee H, King RS, Inoue T, Shibata N, Agata K, Newmark PA. RNA interference by feedingin vitro-synthesized double-stranded RNA to planarians: methodology and dynamics. Dev Dyn, 2013, 242(6):718-730.
doi: 10.1002/dvdy.v242.6 |
| [18] |
Cebrià F, Newmark PA. Planarian homologs of netrin and netrin receptor are required for proper regeneration of the central nervous system and the maintenance of nervous system architecture. Development, 2005, 132(16):3691-3703.
doi: 10.1242/dev.01941 |
| [19] |
Cowles MW, Omuro KC, Stanley BN, Quintanilla CG, Zayas RM. COE loss-of-function analysis reveals a genetic program underlying maintenance and regeneration of the nervous system in planarians. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10(10):e1004746.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004746 |
| [20] |
Li YQ, Zeng A, Han XS, Wang C, Li G, Zhang ZC, Wang JY, Qin YW, Jing Q. Argonaute-2 regulates the proliferation of adult stem cells in planarian. Cell Res, 2011, 21(12):1750-1754.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.151 |
| [21] |
Mei Y, Glover K, Su MF, Sinha SC. Conformational flexibility of BECN1: Essential to its key role in autophagy and beyond. Protein Sci, 2016, 25(10):1767-1785.
doi: 10.1002/pro.v25.10 |
| [22] |
Chan ZCK, Oentaryo MJ, Lee CW. MMP-mediated modulation of ECM environment during axonal growth and NMJ development. Neurosci Lett, 2020, 724:134822.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134822 |
| [23] |
Sîrbulescu RF, Ilieş I, Zupanc GKH. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in the cerebellum of teleost fish: Functional implications for adult neurogenesis. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2015, 68:9-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.03.015 pmid: 25827096 |
| [24] |
Kenific CM, Debnath J. NBR1-dependent selective autophagy is required for efficient cell-matrix adhesion site disassembly. Autophagy, 2016, 12(10):1958-1959.
pmid: 27484104 |
| [25] |
Petri R, Pircs K, Jönsson ME, Åkerblom M, Brattås PL, Klussendorf T, Jakobsson J. let-7 regulates radial migration of new-born neurons through positive regulation of autophagy. EMBO J, 2017, 36(10):1379-1391.
doi: 10.15252/embj.201695235 |
| [1] | Huan Zhao, Bin Zhou. Pancreatic beta cells regeneration [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(5): 370-382. |
| [2] | Jing Liu, Cong Yi, Shiming Xu. The regulatory effect of protein acetylation modification on autophagy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(1): 15-24. |
| [3] | Yakun Song,Min Zhang,Qiaochu Wang,Yuli Peng,Fangxing Jia,Chunhong Yu. Laboratory design and practice for undergraduates: Using RNAi to modulate gene expression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(7): 653-661. |
| [4] | Quan Rong, Li Guoling, Mo Jianxin, Zhong Cuili, Li Zicong, Gu Ting, Zheng Enqin, Liu Dewu, Cai Gengyuan, Wu Zhenfang, Zhang Xianwei. Effects of RNA interference on the porcine NHEJ pathway repair factors on HR efficiency [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(9): 749-757. |
| [5] | Zhi Yang, Jun Yao, Xin Cao. Roles of the FGF signaling pathway in regulating inner ear development and hair cell regeneration [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(7): 515-524. |
| [6] | Yongyu Wang,Wei Yu,Bin Zhou. Hippo signaling pathway in cardiovascular development and diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(7): 576-587. |
| [7] | Yuan Gu, Lei Zhang, Faxing Yu. Functions and regulations of the Hippo signaling pathway in intestinal homeostasis, regeneration and tumorigenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(7): 588-596. |
| [8] | Siling Fu,Wanying Zhao,Wenjing Zhang,Hai Song,Hongbin Ji,Nan Tang. Hippo signaling pathway in lung development, regeneration, and diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(7): 597-606. |
| [9] | Yuxi Li, Junhong Li, Dawang Zhou, . Hippo signaling pathway in liver tissue homeostasis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(7): 607-616. |
| [10] | Wang Shiming, Song Xiao, Zhao Xueying, Chen Hongyan, Wang Jiucun, Wu Junjie, Gao Zhiqiang, Qian Ji, Bai Chunxue, Li Qiang, Han Baohui, Lu Daru. Association between polymorphisms of autophagy pathway and responses in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(3): 250-262. |
| [11] | Xiaoling Zhang,Yun Long,Fei Ge,Zhongrong Guan,Xiaoxiang Zhang,Yanli Wang,Yaou Shen,Guangtang Pan. A genetic study of the regeneration capacity of embryonic callus from the maize immature embryo culture [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(2): 143-155. |
| [12] | Qingqing Fan, Feilong Meng, Ran Fang, Gaopeng Li, Xiaoli Zhao. Functions of Wnt signaling pathway in hair cell differentiation and regeneration [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(10): 897-907. |
| [13] | Xiaowei Zeng, Cuicui Liu, Ning Han, Hongwu Bian, Muyuan Zhu. Progress on the autophagic regulators and receptors in plants [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(7): 644-650. |
| [14] | Qiwen Wang, Wei Jin, Cuifang Chang, Cunshuan Xu. Regulation of autophagy on dendritic cells during rat liver regeneration by IPA [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(3): 276-282. |
| [15] | Qiwen Wang,Cuifang Chang,Ningning Gu,Cuiyun Pan,Cunshuan Xu. Effect of autophagy on liver regeneration [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(11): 1116-1124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||