遗传 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 490-501.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-105
杨剑( ), 石国娟(
), 石国娟( ), 彭昂惠, 徐清波, 王睿琪, 薛雷, 喻昕阳(
), 彭昂惠, 徐清波, 王睿琪, 薛雷, 喻昕阳( ), 孙艺昊(
), 孙艺昊( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-17
修回日期:2024-05-06
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-05-24
通讯作者:
喻昕阳,博士,助理研究员,研究方向:三维基因组学。E-mail: xyu26@buffalo.edu;孙艺昊,博士,助理研究员,研究方向:果蝇分子遗传学。E-mail: sunyihao@ext.jnu.edu.cn
作者简介:杨剑,博士,主任医师,研究方向:肿瘤生物标记物。E-mail: 58202978@qq.com杨剑和石国娟并列第一作者。
基金资助:
Yang Jian( ), Shi Guojuan(
), Shi Guojuan( ), Peng Anghui, Xu Qingbo, Wang Ruiqi, Xue Lei, Yu Xinyang(
), Peng Anghui, Xu Qingbo, Wang Ruiqi, Xue Lei, Yu Xinyang( ), Sun Yihao(
), Sun Yihao( )
)
Received:2024-04-17
Revised:2024-05-06
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-05-24
Supported by:摘要:
JNK信号通路参与并调控了一系列重要的生理活动,包括细胞增殖、分化、迁移、凋亡及应激反应等,其失调与发育缺陷和肿瘤等多种重大疾病的发生与发展密切相关。筛选鉴定JNK信号通路的新成员,丰富完善该通路网络,对预防和治疗相关癌症具有重要的科学意义和临床价值。本研究利用模式动物果蝇(Drosophila),结合遗传学、发育生物学、生物化学和分子生物学等手段,探究了Tip60与JNK信号通路的互作关系,并揭示了其调控机制。结果表明,Tip60的乙酰基转移酶功能缺失导致JNK信号通路激活,并能诱发JNK依赖的细胞凋亡;遗传上位性分析实验表明,Tip60作用于JNK蛋白的下游,与转录因子FOXO平行;生化结果证明Tip60可以结合FOXO,并将其乙酰化。在果蝇中引入人Tip60,发现其能够很好地挽救果蝇JNK信号激活造成的细胞凋亡表型,证明Tip60对JNK信号的调控从果蝇到人高度保守。本研究进一步完善了JNK信号网络,揭示了Tip60在JNK依赖的细胞凋亡中的作用及机制,为相关癌症的预防和治疗提供了新的思路和潜在的药物靶点。
杨剑, 石国娟, 彭昂惠, 徐清波, 王睿琪, 薛雷, 喻昕阳, 孙艺昊. Tip60-FOXO调节果蝇JNK信号通路介导的细胞凋亡【已撤稿】[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(6): 490-501.
Yang Jian, Shi Guojuan, Peng Anghui, Xu Qingbo, Wang Ruiqi, Xue Lei, Yu Xinyang, Sun Yihao. Tip60-FOXO regulates JNK signaling mediated apoptosis in Drosophila[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(6): 490-501.
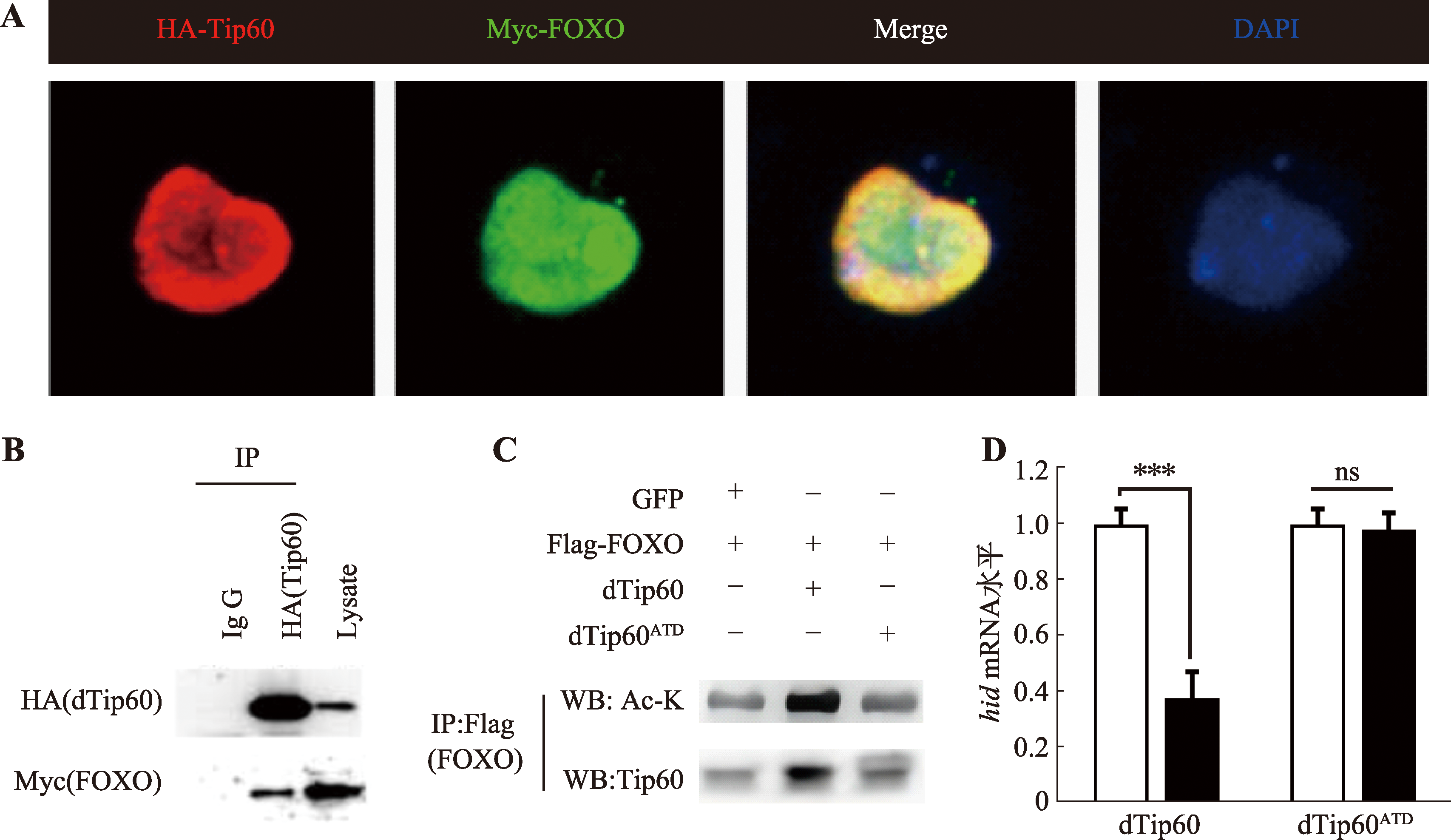
图6
Tip60通过乙酰化FOXO抑制JNK信号通路 A:果蝇S2细胞共同转染HA-Tip60和Myc-FOXO。红色荧光标记Tip60,绿色荧光标记FOXO;B:Tip60-FOXO免疫共沉淀实验结果。IgG为对照,Lysate为S2细胞总蛋白提取物中所含Tip60,IP采用HA标签抗体,Western blot采用HA及Myc标签抗体。C:免疫共沉淀实验结果。IP使用Flag标签抗体,Western blot采用乙酰化赖氨酸抗体及Tip60抗体。D:果蝇S2细胞分别转染Tip60和Tip60ATD后RT-PCR检测细胞中hid mRNA水平的统计图。ns:P>0.05;***:P<0.001。"
| [1] | Chen WQ, Xia CF, Zheng RS, Zhou MG, Lin CQ, Zeng HM, Zhang SW, Wang LJ, Yang ZX, Sun KX, Li H, Brown MD, Islami F, Bray F, Jemal A, He J. Disparities by province, age, and sex in site-specific cancer burden attributable to 23 potentially modifiable risk factors in China: a comparative risk assessment. Lancet Glob Health, 2019, 7(2): e257-e269. |
| [2] | Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Baade PD, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132. |
| [3] | Labi V, Erlacher M. How cell death shapes cancer. Cell Death Dis, 2015, 6(3): e1675. |
| [4] |
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell, 2011, 147(2): 275-292.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024 pmid: 22000009 |
| [5] | Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP. JNK-signaling: a multiplexing hub in programmed cell death. Genes Cancer, 2017, 8(9-10): 682-694. |
| [6] | Hu YM, Leo C, Yu S, Huang BCB, Wang H, Shen M, Luo Y, Daniel-Issakani S, Payan DG, Xu X. Identification and functional characterization of a novel human Misshapen/ Nck interacting kinase-related kinase, hMINKβ. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(52): 54387-54397. |
| [7] |
Kamine J, Elangovan B, Subramanian T, Coleman D, Chinnadurai G. Identification of a cellular protein that specifically interacts with the essential cysteine region of the HIV-1 Tat transactivator. Virology, 1996, 216(2): 357-366.
pmid: 8607265 |
| [8] |
Squatrito M, Gorrini C, Amati B. Tip60 in DNA damage response and growth control: many tricks in one HAT. Trends Cell Biol, 2006, 16(9): 433-442.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.07.007 pmid: 16904321 |
| [9] |
Ikura T, Ogryzko VV, Grigoriev M, Groisman R, Wang J, Horikoshi M, Scully R, Qin J, Nakatani Y. Involvement of the TIP60 histone acetylase complex in DNA repair and apoptosis. Cell, 2000, 102(4): 463-473.
pmid: 10966108 |
| [10] |
Doyon Y, Selleck W, Lane WS, Tan S, Côté J. Structural and functional conservation of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex from yeast to humans. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(5): 1884-1896.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.1884-1896.2004 pmid: 14966270 |
| [11] |
Kusch T, Florens L, Macdonald WH, Swanson SK, Yates JR 3rd, Abmayr SM, Washburn MP, Workman JL. Acetylation by Tip60 is required for selective histone variant exchange at DNA lesions. Science, 2004, 306(5704): 2084-2087.
pmid: 15528408 |
| [12] |
Yamamoto T, Horikoshi M. Novel substrate specificity of the histone acetyltransferase activity of HIV-1-Tat interactive protein Tip60. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(49): 30595-30598.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.49.30595 pmid: 9388189 |
| [13] |
Patel JH, Du YP, Ard PG, Phillips C, Carella B, Chen CJ, Rakowski C, Chatterjee C, Lieberman PM, Lane WS, Blobel GA, Mcmahon SB. The c-MYC oncoprotein is a substrate of the acetyltransferases hGCN5/PCAF and TIP60. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(24): 10826-10834.
pmid: 15572685 |
| [14] |
Legube G, Linares LK, Tyteca S, Caron C, Scheffner M, Chevillard-Briet M, Trouche D. Role of the histone acetyl transferase Tip60 in the p53 pathway. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(43): 44825-44833.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407478200 pmid: 15310756 |
| [15] | Sapountzi V, Logan IR, Robson CN. Cellular functions of TIP60. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2006, 38(9): 1496-1509. |
| [16] |
Adamowicz M, Vermezovic J, D’Adda Di Fagagna F. NOTCH1 inhibits activation of ATM by impairing the formation of an ATM-FOXO3a-KAT5/Tip60 complex. Cell Rep, 2016, 16(8): 2068-2076.
doi: S2211-1247(16)30956-1 pmid: 27524627 |
| [17] | Khan C, Rusan NM. Using Drosophila to uncover the role of organismal physiology and the tumor microenvironment in cancer. Trends Cancer, 2024, 10(4): 289-311. |
| [18] | Tsintzas E, Niccoli T. Using Drosophila amyloid toxicity models to study Alzheimer's disease. Ann Hum Genet, 2024. |
| [19] |
Banerjee U, Girard JR, Goins LM, Spratford CM. Drosophila as a genetic model for hematopoiesis. Genetics, 2019, 211(2): 367-417.
doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300223 pmid: 30733377 |
| [20] | Kahney EW, Snedeker JC, Chen X. Regulation of Drosophila germline stem cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2019, 60: 27-35. |
| [21] |
Enomoto M, Siow C, Igaki T. Drosophila as a cancer model. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1076: 173-194.
doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0529-0_10 pmid: 29951820 |
| [22] |
Weston CR, Davis RJ. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2007, 19(2): 142-149.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.02.001 pmid: 17303404 |
| [23] | Gan T, Fan LX, Zhao L, Misra M, Liu M, Zhang M, Su Y. JNK signaling in Drosophila aging and longevity. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9649. |
| [24] | Semba T, Sammons R, Wang XP, Xie XM, Dalby KN, Ueno NT. JNK signaling in stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(7): 2613. |
| [25] |
Rana A, Rana B, Mishra R, Sondarva G, Rangasamy V, Das S, Viswakarma N, Kanthasamy A. Mixed lineage kinase-c-Jun N-terminal kinase axis: a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Genes Cancer, 2013, 4(9-10): 334-341.
doi: 10.1177/1947601913485415 pmid: 24349631 |
| [26] |
Solinas G, Becattini B. JNK at the crossroad of obesity, insulin resistance, and cell stress response. Mol Metab, 2017, 6(2): 174-184.
doi: S2212-8778(16)30244-7 pmid: 28180059 |
| [27] |
Weston CR, Davis RJ. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2002, 12(1): 14-21.
pmid: 11790549 |
| [28] |
Cavigelli M, Li WW, Lin A, Su B, Yoshioka K, Karin M. The tumor promoter arsenite stimulates AP-1 activity by inhibiting a JNK phosphatase. EMBO J, 1996, 15(22): 6269-6279.
pmid: 8947050 |
| [29] |
Kockel L, Homsy JG, Bohmann D. Drosophila AP-1: lessons from an invertebrate. Oncogene, 2001, 20(19): 2347-2364.
pmid: 11402332 |
| [30] |
Luo X, Puig O, Hyun J, Bohmann D, Jasper H. Foxo and Fos regulate the decision between cell death and survival in response to UV irradiation. EMBO J, 2007, 26(2): 380-390.
pmid: 17183370 |
| [31] |
Uhlirova M, Bohmann D. JNK- and Fos-regulated Mmp1 expression cooperates with Ras to induce invasive tumors in Drosophila. EMBO J, 2006, 25(22): 5294-5304.
doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601401 pmid: 17082773 |
| [32] |
Essers MAG, Weijzen S, Saarloos I, de Ruiter ND, Bos JL, Burgering BMT. FOXO transcription factor activation by oxidative stress mediated by the small GTPase Ral and JNK. EMBO J, 2004, 23(24): 4802-4812.
doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600476 pmid: 15538382 |
| [33] |
Lei K, Davis RJ. JNK phosphorylation of Bim-related members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(5): 2432-2437.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0438011100 pmid: 12591950 |
| [34] |
Brown AK, Webb AE. Regulation of FOXO factors in mammalian cells. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2018, 127: 165-192.
doi: S0070-2153(17)30055-8 pmid: 29433737 |
| [35] |
Snigdha K, Singh A, Kango-Singh M. Yorkie-Cactus (IkappaBalpha)-JNK axis promotes tumor growth and progression in Drosophila. Oncogene, 2021, 40(24): 4124-4136.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01831-4 pmid: 34017079 |
| [36] | Lam D, Shah S, de Castro IP, Loh SHY, Martins LM. Drosophila happyhour modulates JNK-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Dis, 2010, 1(8): e66. |
| [37] | Camilleri-Robles C, Serras F, Corominas M. Role of D-GADD45 in JNK-dependent apoptosis and regeneration in Drosophila. Genes(Basel), 2019, 10(5): 378. |
| [38] | Igaki T. Correcting developmental errors by apoptosis: lessons from Drosophila JNK signaling. Apoptosis, 2009, 14(8): 1021-1028. |
| [39] | Sun YL, Jiang XF, Price BD. Tip60: connecting chromatin to DNA damage signaling. Cell Cycle, 2014, 9(5): 930-936. |
| [40] |
Tafesh-Edwards G, Eleftherianos I. JNK signaling in Drosophila immunity and homeostasis. Immunol Lett, 2020, 226: 7-11.
doi: S0165-2478(20)30348-5 pmid: 32598968 |
| [41] | Garg R, Kumariya S, Katekar R, Verma S, Goand UK, Gayen JR. JNK signaling pathway in metabolic disorders: an emerging therapeutic target. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 901: 174079. |
| [42] |
Saline M, Badertscher L, Wolter M, Lau R, Gunnarsson A, Jacso T, Norris T, Ottmann C, Snijder A. AMPK and AKT protein kinases hierarchically phosphorylate the N-terminus of the FOXO1 transcription factor, modulating interactions with 14-3-3 proteins. J Biol Chem, 2019, 294(35): 13106-13116.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008649 pmid: 31308176 |
| [43] |
Drazic A, Myklebust LM, Ree R, Arnesen T. The world of protein acetylation. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016, 1864(10): 1372-1401.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.06.007 pmid: 27296530 |
| [44] | Shen L, Lee S, Joo JC, Hong E, Cui ZY, Jo E, Park SJ, Jang HJ. Chelidonium majus induces apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cells via ATF3-mediated regulation of Foxo3a by Tip60. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2022, 32(4): 493-503. |
| [45] | Tan KN, Avery VM, Carrasco-Pozo C. Metabolic roles of androgen receptor and Tip60 in androgen-dependent prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(18): 6622. |
| [1] | 王翠玲, 刘信燚, 王亚会, 张争, 王治东, 周钢桥. MCM2通过抑制p53信号通路促进胆管癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(3): 230-244. |
| [2] | 秦中勇, 石晓, 曹平平, 褚鹰, 管蔚, 杨楠, 程禾, 孙玉洁. 细胞凋亡反应中NOXA基因启动子发挥增强子功能调节BCL2基因表达[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(11): 1110-1121. |
| [3] | 余同露,蔡栋梁,朱根凤,叶晓娟,闵太善,陈红岩,卢大儒,陈浩明. CSN4基因干扰对乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(4): 318-326. |
| [4] | 赵建元,丁寄葳,米泽云,周金明,魏涛,岑山. HIV-1初始传播病毒Vpr基因遗传变异对诱导G2期阻滞及细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(5): 480-486. |
| [5] | 毕丹,徐扬,逄越,李庆伟. 质膜组分磷脂酰丝氨酸外翻的分子调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(2): 140-147. |
| [6] | 张蕾, 隋御, 王婷, 李利坚, 李元杰, 金彩霞, 徐方. hMMS2基因对结肠癌细胞耐药逆转的影响[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(4): 346-353. |
| [7] | 张柿平,薛雷. 黑腹果蝇细胞谱系分析方法进展[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(7): 819-828. |
| [8] | 王师尧,金巍娜,吴丹. 青少年型神经元蜡样脂褐质沉积病(JNCL)的发病机制[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(8): 779-784. |
| [9] | 马向东,马兴,吴小明,陈必良,王德堂 . 胚胎神经管缺陷大鼠模型差异基因的表达[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(3): 280-284. |
| [10] | 郭芬,刘兆宇,李月琴,李弘剑,周天鸿. Prosaposin对细胞增殖和凋亡的调控及其分子机制[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(12): 1226-1232. |
| [11] | 付浩,赵丹懿,孙秀菊,滑君,阎杨,邱广蓉,尚超,富伟能,孙开来. B-RAF基因特异的siRNA干扰对胃癌BGC823细胞的影响[J]. 遗传, 2007, 29(5): 537-537―540. |
| [12] | 王琳,梁旭方,廖婉琴,周天鸿. 斑马鱼胚胎发育中细胞凋亡的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(8): 1009-1014. |
| [13] | 王振兴,王璞,姚玲,曾智东,徐汉福,段军,王根洪,夏庆友. 家蚕细胞凋亡相关基因BmICAD的克隆、序列和功能分析及其在精巢中特异表达的初步研究[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(7): 838-844. |
| [14] | 张文燕,张菁,钱远槐,曾庆韬. 黑腹果蝇种组五种核型的报道[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(5): 545-550. |
| [15] | 李艳凤,张强,朱大海. 泛素介导的蛋白质降解与肿瘤发生[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(12): 1591-1591~1596. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
