Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (10): 1004-1016.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-144
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Related genes and characteristic analysis of trophoblast cells during early embryo developmental cessation
Yue Zhang1, Ying Feng2, Fang Ma1,3( )
)
- 1. Gynecologic and Pediatric Diseases and Birth Defects of Ministry of Education, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China
2. West China School of Basic Medical Sciences & Forensic Medicine, Chengdu 610041, China;
3. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China
-
Received:2020-08-08Revised:2020-10-02Online:2020-10-20Published:2020-10-15 -
Contact:Ma Fang E-mail:mafangmed@126.com -
Supported by:Supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China No(31771662);the National Science and Technology Major Project No(2018YFC1002803-3)
Cite this article
Yue Zhang, Ying Feng, Fang Ma. Related genes and characteristic analysis of trophoblast cells during early embryo developmental cessation[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(10): 1004-1016.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Clinic information of the patients (clinical samples involved in transcriptome sequencing)"
| 序号 | 临床诊断 | 年龄(岁) | 孕产次 | 孕周(d) | 是否可探胎心 | β-HCG(mIU/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 人工流产 | 24 | G2P0+1 | 42 | 胎芽不清 | - |
| 2 | 人工流产 | 34 | G4P0+3 | 43 | 胎芽不清 | - |
| 3 | 人工流产 | 29 | G3P1+1 | 49 | 可见胎心搏动 | - |
| 4 | 人工流产 | 31 | G2P1 | 47 | 可见胎心搏动 | - |
| 5 | 人工流产 | 28 | - | 51 | 可见胎心搏动 | - |
| 6 | 胚胎停育 | 30 | 55 | 未见胎心 | 11,951.4 | |
| 7 | 胚胎停育 | 36 | G2P1 | 50 | 未见胎心 | 12,612.1 |
| 8 | 胚胎停育 | 27 | G1P0 | 57 | 未见胎心 | 69,220 |
| 9 | 胚胎停育 | 27 | G1P0 | 80 | 未见胎心 | - |
| 10 | 胚胎停育 | 33 | G1P0 | 59 | 未见胎心 | 32,594.4 |
Table 2
Primer sequences used in quantitative real-time (qRT-PCR) validation"
| 序列 | 类型 | 基因名称 | 上游序列(5?→3?) | 下游序列(5?→3?) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | mRNA | C1QC | ATCCTGGGAAAAATGGCCCC | GAGGACCGCGTTGAATCTGA |
| 2 | VSIG4 | TCCAGCAGGCAAAGTACCAG | GTTTCTGGACACGGAGCTCA | |
| 3 | SPP1 | GATGACCATGTGGACAGCCA | AACCACACTATCACCTCGGC | |
| 4 | CD36 | GACCGAGGAAGCCACTTTGA | TAAGCAGGTCTCCAACTGGC | |
| 5 | NCKAP1L | TGTCTTCCACTCCCGAATGC | TGCAGTGGACAAAGTGAGCA | |
| 6 | FGD2 | TGCTACGCATTCCTCACTGG | ATAGAGCACGAGGGGGTCAT | |
| 7 | LILRB5 | ACCCTGCTGTGTCAGTCATG | GTAGGACCTGATTGCGCTGT | |
| 8 | FOLR2 | GCACCACAAGACAAAGCCAG | CAGGTTGGGTGAGCACTCAT | |
| 9 | DPPA3 | CCAGGGTCTCCACAAATGCT | ATTTCCCTGAGGACTGCTGC | |
| 10 | MX1 | TCGGAGGCTACAGGAAGACT | TTTGCGATGTCCACTTCGGA | |
| 11 | lncRNA | CLRN1-AS1 | GAAAGTCTGAAGCCAGGCCT | CTTTGGGCTTGCACAGTCAC |
| 12 | AC104809.4 | CGTGGGCTCGTCTAAGTGTT | GCACTGAGCTGTTTGCAGTC | |
| 13 | LINC01136 | ACCTCAGAGGCTACCCACAT | AGAAGAAATCCAGGGGCTGC | |
| 14 | USP27X-AS1 | TGCAACCAGAGGAACTGCAA | AGGTGGACCTATGGGCTTCT |
Table 3
KEGG enrichment analysis of differential mRNAs (the top 10 signaling pathways with the highest confidence)"
| 通路二级分类(B类) | 通路 | P值 | q值 | 通路号 | 富集到的基因 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
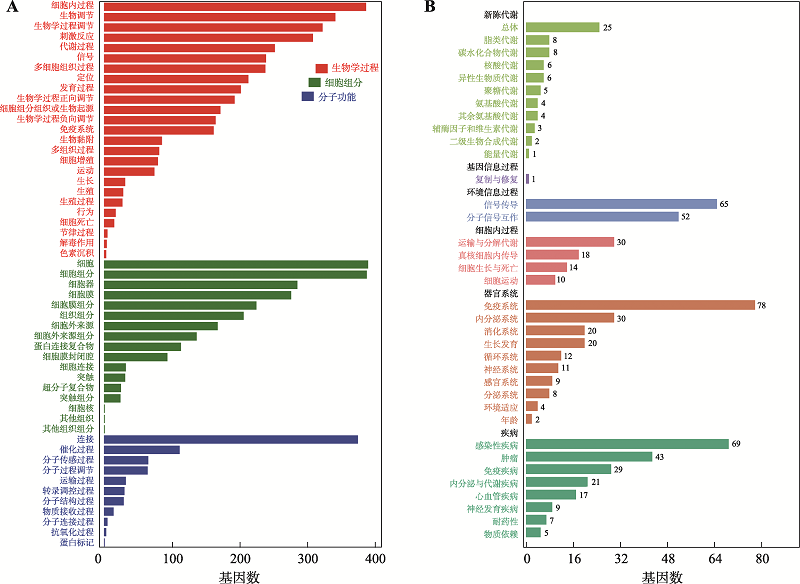
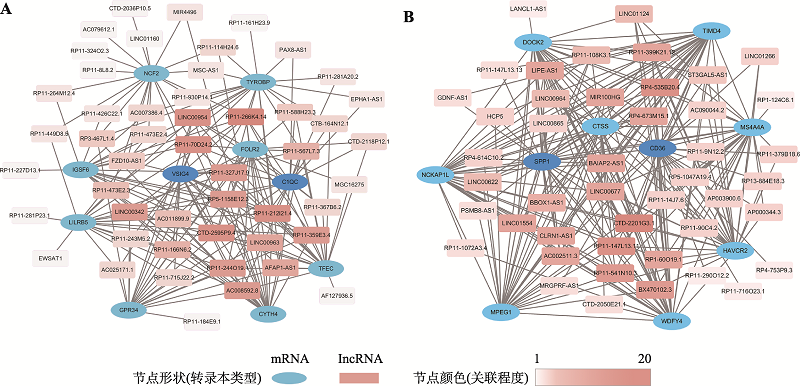
| 免疫系统 (immune system) | 补体及凝血级联反应(complement and coagulation cascades) | 3.70E-07 | 9.07E-05 | ko04610 | C7、CLU、F13A1、VSIG4、C1QC、ITGB2、ITGAM、C3AR1、C1QB、C1QA、C5AR1、CFD、CR1 |
| 信号分子与相互作用 (signaling molecules and interaction) | 细胞外基质 (cell adhesion molecules) | 3.78E-07 | 1.16E-03 | ko04514 | ITGAL、SPP1、CD4、PTPRC、SIGLEC1、NRCAM、MAG、CD36、LRRC4、VTCN1、ITGB2、NFASC、ITGAM、HLA-DOA、HLA-DRA、HLA-C、HLA-G、HLA-A、HLA-B |
| 运输和分解代谢 (transport and catabolism) | 吞噬体 (phagosome) | 2.54E-06 | 2.07E-04 | ko04145 | MSR1、CORO1A、COMP、NCF2、CD36、TLR2、FCGR2A、FCGR1A、PLA2R1、ITGB2、CTSS、CYBB、ITGAM、CD14、HLA-DOA、HLA-DRA、HLA-C、HLA-G、HLA-A、HLA-B、MRC1、RAB7B |
| 感染性疾病 (infectious diseases) | 金黄色葡萄球菌感染 (Staphylococcus aureus infection) | 3.84E-06 | 2.35E-04 | ko05150 | ITGAL、FCGR2A、FCGR1A、C1QC、ITGB2、ITGAM、FPR2、FPR1、C3AR1、C1QB、C1QA、C5AR1、CFD、HLA-DOA、HLA-DRA |
| 感染性疾病 (infectious diseases) | 阿米巴病 (amoebiasis) | 6.45E-06 | 3.16E-04 | ko05146 | GNA15、LAMB4、LAMA1、TLR2、PLCB2、ITGB2、CXCL1、PRKCB、ITGAM、CD14、PIK3CD、RAB7B |
| 免疫系统 (immune system) | 血小板激活 (platelet activation) | 1.59E-05 | 6.48E-04 | ko04611 | LCP2、PTGS1、P2RX1、PLCB2、PIK3R5、FCGR2A、FCER1G、PTGIR、GUCY1A3、SYK、PIK3CD、RASGRP1、PLCG2 |
| 感染性疾病 (infectious diseases) | 肺结核 (tuberculosis) | 3.59E-05 | 1.16E-03 | ko05152 | CD74、CORO1A、LSP1、TLR2、FCGR2A、FCGR1A、PLA2R1、FCER1G、ITGB2、CTSS、SYK、ITGAM、CD14、TLR1、CR1、HLA-DOA、HLA-DRA、MRC1 |
| 免疫系统 (immune system) | FcγR 介导的吞噬作用 (Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis) | 2.01E-04 | 2.07E-04 | ko04666 | WAS、PTPRC、HCK、DOCK2、BIN1、FCGR2A、FCGR1A、PLPP3、SYK、PRKCB、PIK3CD、PLCG2 |
| 生长发育 (development) | 破骨细胞分化 (osteoclast differentiation) | 0.000123966 | 3.37E-03 | ko04380 | TYROBP、LCP2、SPI1、TREM2、LILRB1、LILRB5、NCF2、FCGR2A、FCGR1A、SYK、PIK3CD、CSF1、PLCG2、LILRA6 |
| 感染性疾病 (infectious diseases) | 疟疾 (malaria) | 0.000277305 | 6.79E-03 | ko05144 | ITGAL、COMP、CCL2、CD36、TLR2、ITGB2、CR1 |
| [1] |
Staud F, Karahoda R . Trophoblast: The central unit of fetal growth, protection and programming. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2018,105:35-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.09.016 pmid: 30266525 |
| [2] |
Moser G, Windsperger K, Pollheimer J, de Sousa Lopes SC, Huppertz B,. Human trophoblast invasion: new and unexpected routes and functions. Histochem Cell Biol, 2018,150(4):361-370.
doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1699-0 pmid: 30046889 |
| [3] |
Baines KJ, Renaud SJ . Transcription factors that regulate trophoblast development and function. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci, 2017,145:39-88.
doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.12.003 pmid: 28110754 |
| [4] |
Harris LK, Jones CJ, Aplin JD . Adhesion molecules in human trophoblast - a review. II. extravillous trophoblast. Placenta, 2009,30(4):299-304.
doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2008.12.003 |
| [5] |
Chung TW, Park MJ, Kim HS, Choi HJ, Ha KT . Integrin αVβ3 and αVβ5 are required for leukemia inhibitory factor-mediated the adhesion of trophoblast cells to the endometrial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016,469(4):936-940.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.103 pmid: 26723254 |
| [6] |
Huppertz B . Traditional and new routes of trophoblast invasion and their implications for pregnancy diseases. Int J Mol Sci, 2019,21(1):289.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21010289 |
| [7] |
Malik A, Pal R, Gupta SK . Interdependence of JAK-STAT and MAPK signaling pathways during EGF-mediated HTR-8/SVneo cell invasion. PLoS One, 2017,12(5):e0178269.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178269 pmid: 28542650 |
| [8] |
Huang ZY, Li SW, Fan W, Ma QH . Transforming growth factor β1 promotes invasion of human JEG-3 trophoblast cells via TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget, 2017,8(20):33560-33570.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16826 pmid: 28432277 |
| [9] |
Chitu V, Stanley ER . Regulation of embryonic and postnatal development by the CSF-1 receptor. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2017,123:229-275.
doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.10.004 pmid: 28236968 |
| [10] |
Ding JL, Yin TL, Yan NN, Cheng YX, Yang J . FasL on decidual macrophages mediates trophoblast apoptosis: A potential cause of recurrent miscarriage. Int J Mol Med, 2019,43(6):2376-2386.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4146 pmid: 30942389 |
| [11] |
Shaik R, Ramakrishna W . Genes and Co-Expression modules common to drought and bacterial stress responses in arabidopsis and rice. PLoS One, 2013,8(10):e77261.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077261 pmid: 24130868 |
| [12] |
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK,. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics, 2010,26(1):139-140.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616 pmid: 19910308 |
| [13] |
Takeshita A, Kusakabe KT, Hiyama M, Kuniyoshi N, Kondo T, Kano K, Kiso Y, Okada T . Dynamics and reproductive effects of complement factors in the spontaneous abortion model of CBA/J×DBA/2 mice. Immunobiology, 2014,219(5):385-391.
doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.01.001 |
| [14] |
Huang J, Qin H, Yang YH, Chen XY, Zhang JM, Laird S, Wang CC, Chan TF, Li TC . A comparison of transcriptomic profiles in endometrium during window of implantation between women with unexplained recurrent implantation failure and recurrent miscarriage. Reproduction, 2017,153(6):749-758.
doi: 10.1530/REP-16-0574 pmid: 28283674 |
| [15] |
Yurdakan G, Ekem TE, Bahadir B, Gun BD, Kuzey GM, Ozdamar SO . Expression of adhesion molecules in first trimester spontaneous abortions and their role in abortion pathogenesis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand, 2008,87(7):775-782.
doi: 10.1080/00016340802177412 pmid: 18607815 |
| [16] |
Soylu Karapınar O, Benk Şilfeler D, Dolapçıoğlu K, Keskin Kurt R, Beyazıt A . The effect of molar pregnancies on platelet parameters. J Obstet Gynaecol, 2016,36(7):912-915.
doi: 10.1080/01443615.2016.1174823 pmid: 27183899 |
| [17] |
Girardi G, Salmon JB . The role of complement in pregnancy and fetal loss. Autoimmunity, 2003,36(1):19-26.
doi: 10.1080/0891693031000067322 pmid: 12765467 |
| [18] |
Kouser L, Madhukaran SP, Shastri A, Saraon A, Ferluga J, Al-Mozaini M, Kishore U . Emerging and novel functions of complement protein C1q. Front Immunol, 2015,6:317.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00317 pmid: 26175731 |
| [19] | Liu FL, Zhou J, Zhang W, Wang H . Epigenetic regulation and related diseases during placental development. Hereditas (Beijing), 2017,39(4):263-275. |
| 刘福林, 周瑾, 张蔚, 汪晖 . 胎盘发育过程中的表观遗传学改变及其相关疾病. 遗传, 2017,39(4):263-275. | |
| [20] | Lai XM, Wang YX . Trophoblastic invasion and its regulatory factors. Chin J Birth Heal Hered, 2007,15(3):1-3. |
| 赖雪梅, 王应雄 . 滋养层侵袭力及其调控因素. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2007,15(3):1-3. | |
| [21] |
Burton GJ, Jauniaux E . Pathophysiology of placental- derived fetal growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2018,218(2S):S745-S761.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.11.577 pmid: 29422210 |
| [22] |
James-Allan LB, Whitley GS, Leslie K, Wallace A, Cartwright JE . Decidual cell regulation of trophoblast is altered in pregnancies at risk of pre-eclampsia. J Mol Endocrinol, 2018.
pmid: 32580159 |
| [23] |
Zadrozna M, Nowak B, Marcinek A, Duc J . Villous trophoblast cell turnover in placentas from preterm pregnancy and pregnancy complicated by intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). Folia Biol (Krakow), 2009,58(1-2):79-83.
doi: 10.3409/fb58_1-2.79-83 |
| [24] |
Check JH, Aly J, Chang E . Improving the chance of successful implantation-Part I-Embryo attachment to the endometrium and adequate trophoblast invasion. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol, 2016,43(6):787-791.
pmid: 29944223 |
| [25] |
Burton GJ, Jauniaux E . The cytotrophoblastic shell and complications of pregnancy. Placenta, 2017,60:134-139.
doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2017.06.007 pmid: 28651899 |
| [26] |
Yang WM, Lu ZY, Zhi ZF, Liu LL, Deng LJ, Jiang XL, Pang LH . High-throughput transcriptome-Seq and small RNA-Seq reveal novel functional genes and microRNAs for early embryonic arrest in humans. Gene, 2019,697:19-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.12.084 pmid: 30776465 |
| [27] |
Pan HT, Ding HG, Fang M, Yu B, Cheng Y, Tan YJ, Fu QQ, Lu BB, Cai HG, Jin X, Xia XQ, Zhang T . Proteomics and bioinformatics analysis of altered protein expression in the placental villous tissue from early recurrent miscarriage patients. Placenta, 2018,61:1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2017.11.001 pmid: 29277264 |
| [28] |
Atanasova MA, Konova EI, Aleksovska TA, Todorova KN, Georgieva MN, Lukanov TH . Anti-fibrillin-1 autoantibodies in normal pregnancy and recurrent pregnancy loss. Autoimmun Rev, 2011,10(3):131-136.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.09.003 |
| [29] |
Vogt L, Schmitz N, Kurrer MO, Bauer M, Hinton HI, Behnke S, Gatto D, Sebbel P, Beerli RR, Sonderegger I, Kopf M, Saudan P, Bachmann MF . VSIG4, a B7 family-related protein, is a negative regulator of T cell activation. J Clin Invest, 2006,116(10):2817-2826.
doi: 10.1172/JCI25673 pmid: 17016562 |
| [30] |
Helmy KY, Katschke KJ, Gorgani NN, Kljavin NM, Elliott JM, Diehl L, Scales SJ, Ghilardi N, van Lookeren Campagne M,. CRIg: A macrophage complement receptor required for phagocytosis of circulating pathogens. Cell, 2006,124(5):915-927.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.12.039 pmid: 16530040 |
| [31] |
Kim DD, Miwa T, Kimura Y, Schwendener RA, van Lookeren Campagne M, Song WC,. Deficiency of decay- accelerating factor and complement receptor 1-related gene/protein y on murine platelets leads to complement- dependent clearance by the macrophage phagocytic receptor CRIg. Blood, 2008,112(4):1109-1119.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-01-134304 pmid: 18524992 |
| [32] |
Mascarell L, Airouche S, Berjont N, Gary C, Gueguen C, Fourcad G, Bellier B, Togbe D, Ryffel B, Klatzmann D, Baron-Bodo V, Moingeon P . The regulatory dendritic cell marker C1q is a potent inhibitor of allergic inflammation. Mucosal Immunol, 2016,10(3):695-704.
doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.87 pmid: 27731323 |
| [33] |
Girardi G . Complement inhibition keeps mothers calm and avoids fetal rejection. Immunol Invest, 2008,37(5):645-659.
doi: 10.1080/08820130802191615 pmid: 18716942 |
| [34] |
Girardi G, Prohászka Z, Bulla R, Tedesco F, Scherjon S . Complement activation in animal and human pregnancies as a model for immunological recognition. Mol Immunol, 2011,48(14):1621-1630
doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.04.011 |
| [35] |
Teirilä L, Heikkinen-Eloranta J, Kotimaa J, Meri S, Lokki AI . Regulation of the complement system and immunological tolerance in pregnancy. Semin Immunol, 2019,45:101337.
doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2019.101337 pmid: 31757607 |
| [36] | Sun J, Jin L . Trophinin, tastin, bystin complex binds to embryo initiation. Chin J Birth Heal Hered, 2005,13(5):113-114. |
| 孙虹, 靳镭 . Trophinin, tastin, bystin复合体与胚胎起始黏附. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2005,13(5):113-114. | |
| [37] |
Oz HS, Ebersole JL, de Villiers WJS,. The macrophage pattern recognition scavenger receptors SR-A and CD36 protect against microbial induced pregnancy loss. Inflamm Res, 2011,60(1):93-97.
doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0241-1 |
| [38] | Silverstein RL, Febbraio M . CD36, a scavenger receptor involved in immunity, metabolism, angiogenesis, behavior. SciSignal, 2009, 2(72): re3. |
| [39] |
Abumrad NA, Goldberg IJ . CD36 actions in the heart: Lipids, calcium, inflammation, repair and more? Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016,1861(10):1442-1449.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.03.015 pmid: 27004753 |
| [40] |
Wang JC, Li YS . CD36 tango in cancer: signaling pathways and functions. Theranostics, 2019,9(17):4893-4908.
doi: 10.7150/thno.36037 pmid: 31410189 |
| [41] |
Johnson GA, Burghardt RC, Bazer FW, Spencer TE . Osteopontin: Roles in implantation and placentation. Biol Reprod, 2003,69(5):1458-1471.
doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.020651 pmid: 12890718 |
| [42] | Yu QB, Wang YX . Cell adhesion molecules to the embryo implantatio. Chin J Birth Heal Hered, 2005,13(1):6-8. |
| 余秋波, 王应雄 . 细胞粘附分子与胚胎着床. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2005,13(1):6-8. | |
| [43] |
Nardo LG, Nikas G, Makrigiannakis A . Molecules in blastocyst implantation. Role of matrix metalloproteinases, cytokines and growth factors. J Reprod Med, 2003,48(3):137-147.
pmid: 12698769 |
| [44] |
Gonzalez I, Munita R, Agirre E, Dittmer TA, Gysling K, Misteli T, Luco RF . A lncRNA regulates alternative splicing via establishment of a splicing-specific chromatin signature . Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2015,22(5):370-376.
doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3005 pmid: 25849144 |
| [45] |
Lieberman J . Tapping the RNA world for therapeutics. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2018,25(5):357-364.
doi: 10.1038/s41594-018-0054-4 pmid: 29662218 |
| [46] |
Pérez-Palacios R, Fauque P, Teissandier A, Bourc'his D. Deciphering the early mouse embryo transcriptome by Low-Input RNA-Seq. Methods Mol Biol, 2021,2214:189-205.
pmid: 32944911 |
| [47] |
Svensson V, Natarajan KN, Ly LH, Miragaia RJ, Labalette C, Macaulay IC, Cvejic A, Teichmann SA . Power analysis of single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments. Nat Methods, 2017,14(4):381-387.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4220 pmid: 28263961 |
| [1] | Kun Du, Chuyang Mao, Anyong Ren, Xuemei Wu, Qingling Li, Tingting Chen, Shiyi Chen, Songjia Lai. Analysis of gene expression profiles at different stages during preadipocyte differentiation in rabbits [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(3): 309-320. |
| [2] | Ting Zheng, Mailin Gan, Linyuan Shen, Lili Niu, Zongyi Guo, Jinyong Wang, Shunhua Zhang, Li Zhu. circRNA on animal skeletal muscle development regulation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(12): 1178-1191. |
| [3] | Qichao Yu,Bin Song,Xuanxuan Zou,Ling Wang,Dequan Liu,Bo Li,Kun Ma. Analysis of normal tissues adjacent to the tumour-specific expressed genes in breast cancer [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(7): 625-633. |
| [4] | Xuanshi Liu, Wei Li. Mining and characterization of preterm birth related genes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(5): 413-421. |
| [5] | Tianpei Shi,Li Zhang. Application of whole transcriptomics in animal husbandry [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(3): 193-205. |
| [6] | Jinchuan Wei,Tianyi Xu,Jing Wu,Xiaofeng Song. Molecular mechanisms of recursive splicing events in long introns of eukaryotes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(2): 89-97. |
| [7] | Yu Zhang,Suying Bai,Yue Ma. Comparative analysis on the transcriptomes of the prostates of muskrats at breeding stage and non-breeding stage [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(6): 488-495. |
| [8] | Wanlong Huang,Xiuxiu Zhang,Ai Li,Xiangyang Miao. Identification of differentially expressed genes between subcutaneous and intramuscular adipose tissue of Large White pig using RNA-seq [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(6): 501-511. |
| [9] | Yanfeng Fu, Yanhong Zhou, Aiguo Wang, Lan Li, Honglin Liu, Bixia Li, Shouwen Ren. Tissue expression of EphB2 and RNA-seq analysis during embryo im-plantation in Meishan pigs [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(12): 1243-1248. |
| [10] | Lu Wen, Fuchou Tang. Recent progress in single-cell RNA-Seq analysis [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(11): 1069-1076. |
| [11] | Xiangmei Jiang, Yanfang Wu, Fuming Xiao, Zhenyu Xiong, Haining Xu. Transcriptome analysis for leaves of five chemical types in Cinna-momum camphora [J]. HEREDITAS, 2014, 36(1): 58-68. |
| [12] | HOU Zhi-Wei WANG Yun GAO Hong HOU Sheng-Wei. The principle of dRNA-seq and its applications in prokaryotic tran-scriptome analyses [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(8): 983-991. |
| [13] | LIU Hong-Liang, ZHENG Li-Ming, LIU Qing-Qing, QUAN Fu-Sheng, ZHANG Yong. Studies on the transcriptomes of non-model organisms [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(8): 955-970. |
| [14] | CHEN Hao, JIANG Gui-Xiong, LONG Hong-Xu, TAN Xiao-Feng. Analysis of oil synthesis metabolism pathways based on transcrip-tomechanges in tung oil tree’s seeds during three different develop-ment stages [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(12): 1403-1414. |
| [15] | GUO Hao, ZHU Yun-Ping, LI Dong, HE Fu-Chu. Identification, modeling and simulation of key pathways underlying certain cancers [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(8): 809-819. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||