Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 300-312.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-379
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Recent advances on the role of glia in physiological behaviors: insights from Drosophila melanogaster
Mengxiao Wang( ), Margaret S. Ho(
), Margaret S. Ho( )
)
- School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China
-
Received:2021-11-04Revised:2022-03-20Online:2022-04-20Published:2022-04-01 -
Contact:S. Ho Margaret E-mail:wangmx1@shanghaitech.edu.cn;margareth@shanghaitech.edu.cn -
Supported by:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(31871039);Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos(32170962);Shanghai High-end Foreigner Expert Program No(#21WZ2502300);Start-up fund of ShanghaiTech University
Cite this article
Mengxiao Wang, Margaret S. Ho. Recent advances on the role of glia in physiological behaviors: insights from Drosophila melanogaster[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(4): 300-312.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
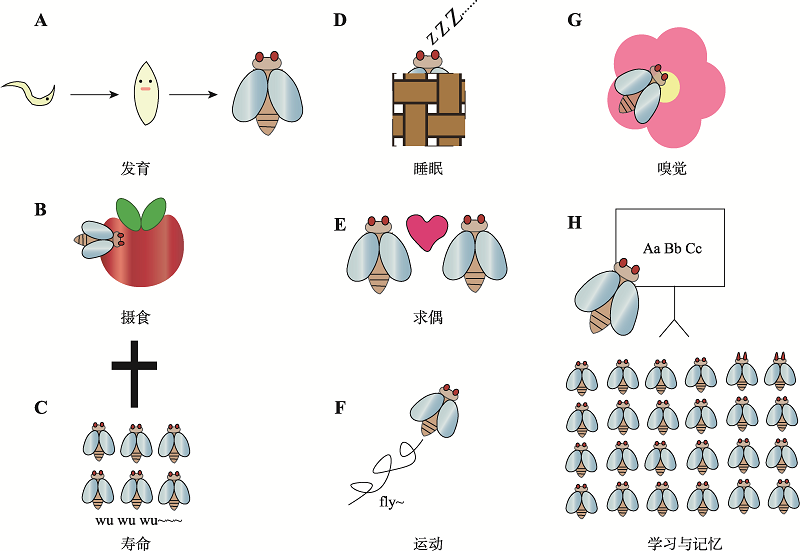
Glia regulate Drosophila physiological behaviors"
| 生理行为 | 胶质细胞类型 | 调控方式 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 发育 | 神经束膜胶质细胞 | Ebony突变影响组胺释放从而调控神经元的发育 | [ |
| 星形胶质细胞 | 胶质细胞释放或接收嘌呤能信号影响神经元或其他细胞的发育 | [ | |
| 总胶质细胞 | dSmurf调节Fasciclin蛋白的稳定性影响磨菇体神经元的发育 | [ | |
| Slimb和Ago介导GCM泛素化调控胶质细胞增殖分化,进一步调控神经系统发育 | [ | ||
| 皮层胶质细胞 | 胶质细胞对dILP的营养依赖型表达诱导神经母细胞增殖分化 | [ | |
| 营养代谢 | 神经束膜胶质细胞 亚神经束膜胶质细胞 | 周围神经胶质细胞形成血脑屏障,其上的转运蛋白参与运输海藻糖葡萄糖,调控机体营养代谢 | [ |
| 胶质细胞内的糖酵解提供能量以维持神经元的正常功能 | [ | ||
| 胶质细胞形成的血脑屏障上23种氨基酸转运蛋白参与运输氨基酸 | [ | ||
| 寿命 | 总胶质细胞 | 胶质细胞中EDTP的下调抑制了polyQ聚集,延长果蝇的寿命 | [ |
| 胶质细胞中载脂蛋白D的同源物Lazarillo缺失,缩短果蝇的寿命 | [ | ||
| 睡眠 | 总胶质细胞 | 胶质细胞GABA 转氨酶增加引起果蝇失眠 | [ |
| 胶质细胞中的淀粉样前体蛋白调节果蝇睡眠 | [ | ||
| 胶质细胞内的钙储存增加和Serca受干扰会扰乱果蝇的睡眠节律 | [ | ||
| 神经束膜胶质细胞 亚神经束膜胶质细胞 | 阻断胶质细胞内的囊泡运输可促进果蝇睡眠 | [ | |
| 星形胶质细胞 | 果蝇星形胶质细胞中Eiger的敲低减少了果蝇睡眠 | [ | |
| 总胶质细胞 | 胶质细胞上保幼激素受体Methoprene-tolerant(Met)通过作用于MB的α/β lobe维持成年果蝇睡眠 | [ | |
| 细胞凋亡 | 鞘胶质细胞 | MMP-1诱导胶质细胞清除受损伤的轴突 | [ |
| 胶质细胞表达吞噬受体Draper吞噬轴突碎片 | [ | ||
| 胶质细胞中Shark被敲降,抑制胶质细胞对凋亡神经元的清除 | [ | ||
| 鞘胶质细胞 | 果蝇胚胎中枢神经系统中胶质细胞参与清除凋亡细胞 | [ | |
| 中线胶质细胞 | 胶质细胞与神经元之间的接触激活 EGFR/RAS/MAPK通路特异性拮抗因子HID的活性,使发育过程中Midline glia存活 | [ | |
| 求偶 | 总胶质细胞 | Spinster在神经胶质细胞中表达被阻断影响神经元程序性死亡,使雌果蝇拒绝雄果蝇的求偶行为 | [ |
| 运动 | 总胶质细胞 | 神经束膜与胶质细胞中dEAAT1被敲除会显著降低果蝇活力 | [ |
| 胶质细胞和肌肉细胞的TDP-43功能障碍导致果蝇出现ALS的行为表型 | [ | ||
| 胶质细胞分泌Sema2a,使果蝇行走出现异常 | [ | ||
| 胶质细胞中hAtx1突变导致果蝇出现运动功能障碍 | [ | ||
| 胶质细胞中Draper缺失导致果蝇出现运动功能障碍 | [ | ||
| 胶质细胞中谷氨酸/GABA/谷氨酰胺循环相关基因的转录调节控制果蝇的运动活动 | [ | ||
| 嗅觉 | 总胶质细胞 | 果蝇嗅觉系统中乙酰胆碱介导胶质细胞与神经元之间的信息传递 | [ |
| 星形胶质细胞 | 星形胶质细胞通过调节ORN-PN突触强度来调节果蝇的嗅觉行为 | [ | |
| 学习记忆 | 总胶质细胞 | 胶质细胞中EAAT1过表达可以挽救果蝇长时间记忆随年龄增长而下降的相关损伤 | [ |
| Klg定位于神经元和神经胶质之间的连接处,对其进行敲降会影响果蝇的长时间记忆 | [ |
| [1] |
Allen NJ, Lyons DA. Glia as architects of central nervous system formation and function. Science, 2018, 362(6411):181-185.
doi: 10.1126/science.aat0473 |
| [2] |
Zwarts L, Van Eijs F, Callaerts P. Glia in Drosophila behavior. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol, 2015, 201(9):879-893.
doi: 10.1007/s00359-014-0952-9 |
| [3] |
Freeman MR, Doherty J. Glial cell biology in Drosophila and vertebrates. Trends Neurosci, 2006, 29(2):82-90.
pmid: 16377000 |
| [4] |
Yildirim K, Petri J, Kottmeier R, Klämbt C. Drosophila glia: few cell types and many conserved functions. Glia, 2019, 67(1):5-26.
doi: 10.1002/glia.23459 pmid: 30443934 |
| [5] |
Allen NJ, Barres BA. Neuroscience: glia-more than just brain glue. Nature, 2009, 457(7230):675-677.
doi: 10.1038/457675a |
| [6] |
Awasaki T, Lee T. New tools for the analysis of glial cell biology inDrosophila. Glia, 2011, 59(9):1377-1386.
doi: 10.1002/glia.21133 |
| [7] |
Stork T, Engelen D, Krudewig A, Silies M, Bainton RJ, Klämbt C. Organization and function of the blood-brain barrier in Drosophila. J Neurosci, 2008, 28(3):587-597.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4367-07.2008 |
| [8] |
Sanuki R. Drosophila models of traumatic brain injury. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2020, 25(1):168-178.
doi: 10.2741/4801 |
| [9] |
Tix S, Eule E, Fischbach KF, Benzer S. Glia in the chiasms and medulla of the Drosophila melanogaster optic lobes. Cell Tissue Res, 1997, 289(3):397-409.
pmid: 9232819 |
| [10] |
Purice MD, Ray A, Münzel EJ, Pope BJ, Park DJ, Speese SD, Logan MA. A novelDrosophila injury model reveals severed axons are cleared through a Draper/MMP-1 signaling cascade. eLife, 2017, 6:e23611.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.23611 |
| [11] |
Rival T, Soustelle L, Strambi C, Besson MT, Iché M, Birman S. Decreasing glutamate buffering capacity triggers oxidative stress and neuropil degeneration in the Drosophila brain. Curr Biol, 2004, 14(7):599-605.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.03.039 |
| [12] |
Truman JW. Metamorphosis of the central nervous system of Drosophila. J Neurobiol, 1990, 21(7):1072-1084.
pmid: 1979610 |
| [13] |
Brehme KS. The effect of adult body color mutations upon the larva of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1941, 27(6):254-261
doi: 10.1073/pnas.27.6.254 |
| [14] |
Meinertzhagen IA, O'Neil SD. Synaptic organization of columnar elements in the lamina of the wild type in Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol, 1991, 305(2):232-263.
pmid: 1902848 |
| [15] |
Richardt A, Rybak J, Störtkuhl KF, Meinertzhagen IA, Hovemann BT. Ebony protein in the Drosophila nervous system: optic neuropile expression in glial cells. J Comp Neurol, 2002, 452(1):93-102.
pmid: 12205712 |
| [1] | Shan He, Jian Zhao, Xiaofeng Song. Effects of N6-methyladenosine modification on the function of the female reproductive system [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(6): 472-487. |
| [2] | Feifei Li, Yanmin Hao, Minlong Cui, Chunlan Piao. Cloning and functional analysis of RADIALIS-like 1 gene from Antirrhinum majus [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(6): 526-535. |
| [3] | Chaofan Xing, Mintao Wang, Lei Wang, Xin Shen. Progress on the mechanism of left-right asymmetrical patterning in bilaterians [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(6): 488-500. |
| [4] | Lingling Wu, Xiaoyu Zhang, Xiao Li, Jianjun Jin, Gongshe Yang, Xin’e Shi. miR-196b-5p promotes myoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(5): 435-446. |
| [5] | Xiaokang Shang, Simeng Zhang, Junjun Ni. Research progress of cathepsin B in brain aging and Alzheimer’s diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(3): 212-220. |
| [6] | Shuyu Mao, Changrui Zhao, Chang Liu. The nuclear receptor REV-ERBα integrates circadian clock and energy metabolism [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(2): 99-114. |
| [7] | Mengxuan Xu, Ming Zhou. Advances of RNA polymerase IV in controlling DNA methylation and development in plants [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(7): 567-580. |
| [8] | Sinan Luan, Lele Liu, Jiayuan Zhou, Nurasya Imam, Minlong Cui, Chunlan Piao. Functional analysis of flower development related gene SvGLOBOSA from Senecio vulgaris [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 521-530. |
| [9] | Yuan Zhang, Yuting Zhao, Lenan Zhuang, Jin He. Transcriptional regulation of transcriptional Mediator complexes in cardiovascular development and disease [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(5): 383-397. |
| [10] | Huan Zhao, Bin Zhou. Pancreatic beta cells regeneration [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(5): 370-382. |
| [11] | Yizhun Zeng, Tao Zhang, Ying Xu. Rapid assessment of circadian behavior in mice [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(4): 346-357. |
| [12] | Cuiling Wang, Xinyi Liu, Yahui Wang, Zheng Zhang, Zhidong Wang, Gangqiao Zhou. MCM2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells by reducing the p53 signaling pathway [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(3): 230-244. |
| [13] | Hui Qu, Yi Liu, Yawen Chen, Hui Wang. Alteration of imprinted genes and offspring organ development caused by environmental factors [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(2): 107-116. |
| [14] | Haoqiang Zhao, Xiaofei Wang, Shaopei Gao. Progress on the functional role of oleosin gene family in plants [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1128-1140. |
| [15] | Ke Mao, Ziqiu Meng, Yongbiao Zhang. Progress on the regulation of neural crest and the genetics in craniofacial development [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1089-1102. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||