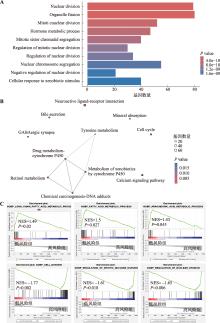
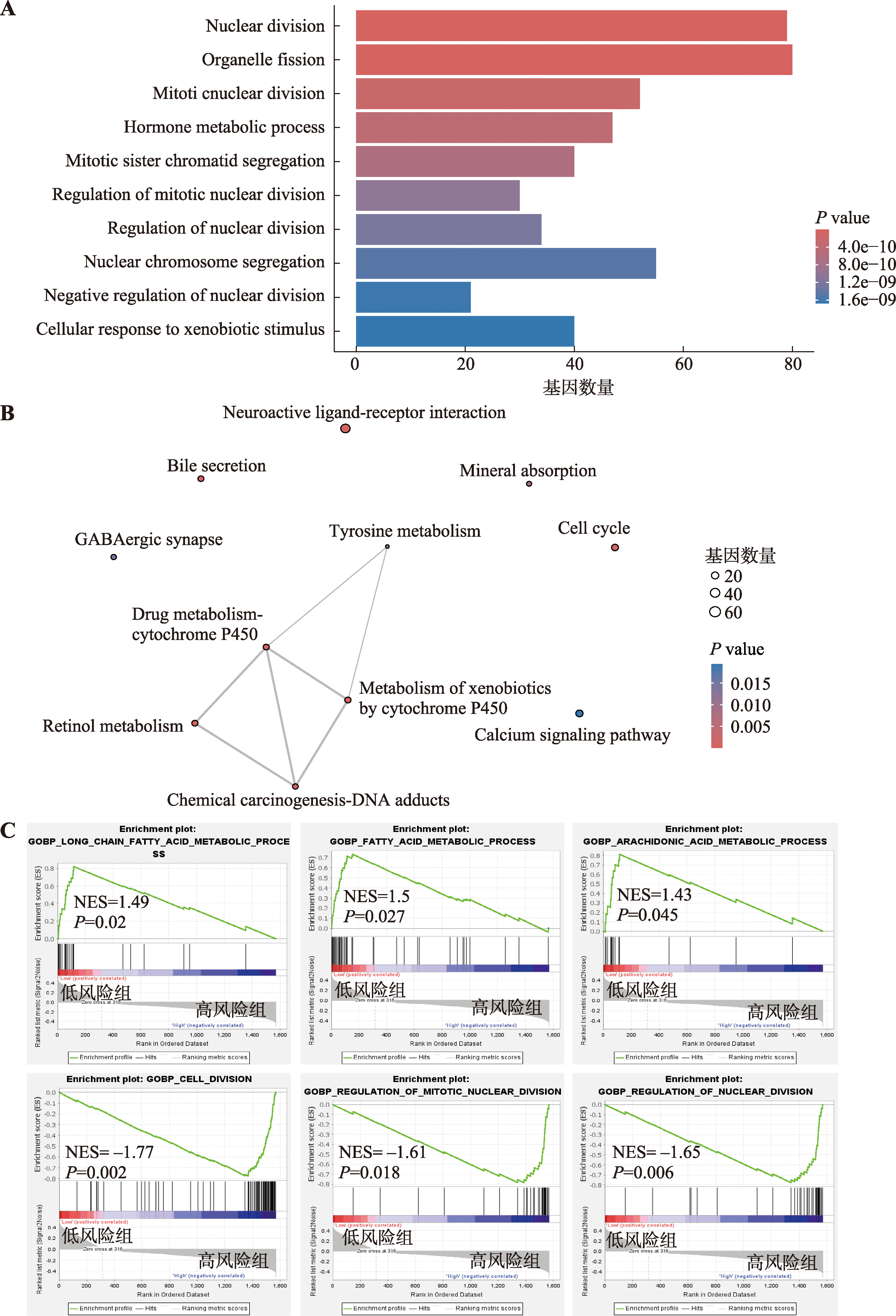
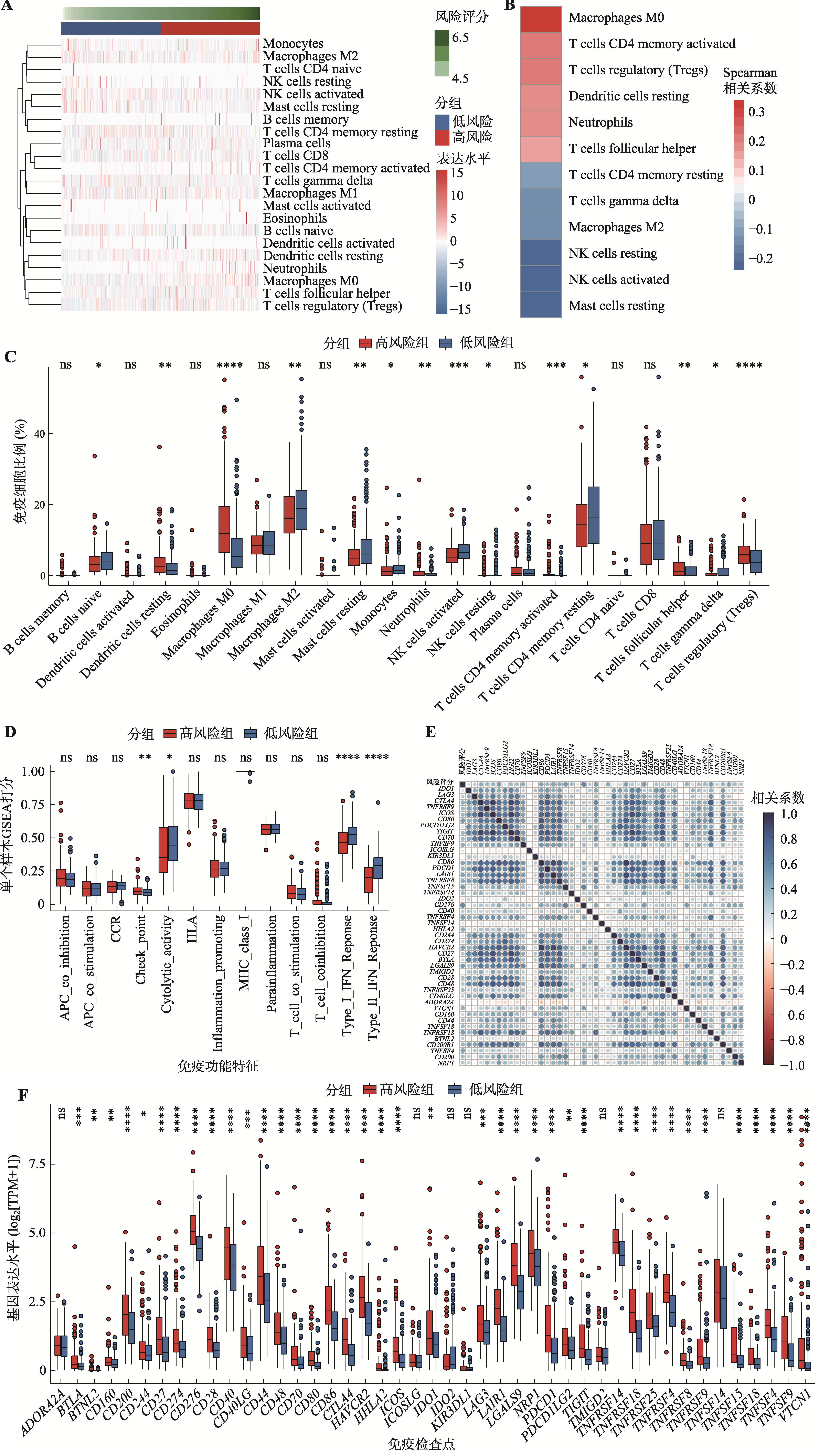
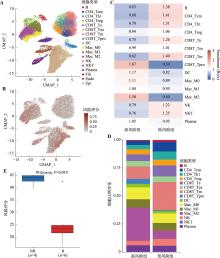
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (7): 768-785.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.25-007
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Potential value of anoikis transcriptional signatures in predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
Furong Cheng1,2( ), Wenyu Song2, Pengbo Cao2, Gangqiao Zhou1,2(
), Wenyu Song2, Pengbo Cao2, Gangqiao Zhou1,2( )
)
- 1. College of Life Science, Hebei University, Baoding 071002, China
2. State Key Lab of Medical Proteomics, National Center for Protein Sciences at Beijing, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Academy of Military Sciences, Beijing 100850, China
-
Received:2025-01-06Revised:2025-03-17Online:2025-03-26Published:2025-03-26 -
Contact:Gangqiao Zhou E-mail:1578877852@qq.com;zhougq114@126.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(82002573);National Natural Science Foundation of China(82172707);National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFA0504301)
Cite this article
Furong Cheng, Wenyu Song, Pengbo Cao, Gangqiao Zhou. Potential value of anoikis transcriptional signatures in predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(7): 768-785.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Huang DQ, Mathurin P, Cortez-Pinto H, Loomba R. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: trends, projections and risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(1): 37-49.
pmid: 36258033 |
| [2] |
Balitzer DJ, Greenland NY. The utility of next-generation sequencing in challenging liver FNA biopsies. Cancer Cytopathol, 2024, 132(11): 714-722.
pmid: 39097802 |
| [3] |
Watanabe T, Bertoletti A, Tanoto TA. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis virus infection. J Viral Hepat, 2010, 17(7): 453-458.
pmid: 20487259 |
| [4] |
Ando S, Perkins CM, Sajiki Y, Chastain C, Valanparambil RM, Wieland A, Hudson WH, Hashimoto M, Ramalingam SS, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R, Araki K. mTOR regulates T cell exhaustion and PD-1-targeted immunotherapy response during chronic viral infection. J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(2): e160025.
pmid: 36378537 |
| [5] |
Chakraborty E, Sarkar D. Emerging therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(11): 2798.
pmid: 35681776 |
| [6] |
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet, 2018, 391(10127): 1301-1314.
pmid: 29307467 |
| [7] |
Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013, 1833(12): 3481-3498.
pmid: 23830918 |
| [8] | Yang Y, Wang BS, Wang XM, Zhang Y, Wang MR, Jia XM. Screening and identification of anoikis-resistant gene UBCH7 in esophageal cancer cells. Hereditas (Beijing), 2012, 34(2): 190-197. |
| 杨扬, 王博石, 汪晓敏, 张钰, 王明荣, 贾雪梅. 食管癌细胞抗失巢凋亡基因UBCH7的发现与鉴定. 遗传, 2012, 34(2): 190-197. | |
| [9] |
de Sousa Mesquita AP, de Araújo Lopes S, Pernambuco Filho PCA, Nader HB, Lopes CC. Acquisition of anoikis resistance promotes alterations in the Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and matrix remodeling in endothelial cells. Apoptosis, 2017, 22(9): 1116-1137.
pmid: 28653224 |
| [10] |
Simpson CD, Anyiwe K, Schimmer AD. Anoikis resistance and tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett, 2008, 272(2): 177-185.
pmid: 18579285 |
| [11] |
Chiarugi P, Giannoni E. Anoikis: a necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Pharmacol, 2008, 76(11): 1352-1364.
pmid: 18708031 |
| [12] |
Tajbakhsh A, Rivandi M, Abedini S, Pasdar A, Sahebkar A. Regulators and mechanisms of anoikis in triple- negative breast cancer (TNBC): a review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2019, 140: 17-27.
pmid: 31154235 |
| [13] |
Candia J, Bayarsaikhan E, Tandon M, Budhu A, Forgues M, Tovuu LO, Tudev U, Lack J, Chao A, Chinburen J, Wang XW. The genomic landscape of mongolian hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 4383.
pmid: 32873799 |
| [14] |
Gui MH, Huang SL, Li SZ, Chen YY, Cheng FR, Liu YL, Wang JA, Wang YT, Guo R, Lu YM, Cao PB, Zhou GQ. Integrative single-cell transcriptomic analyses reveal the cellular ontological and functional heterogeneities of primary and metastatic liver tumors. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 206.
pmid: 38414027 |
| [15] |
Xie PY, Guo L, Yu Q, Zhao YF, Yu MC, Wang H, Wu MY, Xu WX, Xu M, Zhu XD, Xu YF, Xiao YS, Huang C, Zhou J, Fan J, Hung MC, Sun HC, Ye QH, Zhang B, Li H. ACE2 enhances sensitivity to PD-L1 blockade by inhibiting macrophage-induced immunosuppression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res, 2025, 85(2): 299-313.
pmid: 39495239 |
| [16] |
Diao XY, Guo C, Li SQ. Identification of a novel anoikis-related gene signature to predict prognosis and tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac Cancer, 2023, 14(3): 320-330.
pmid: 36507553 |
| [17] |
Chen YT, Huang WR, Ouyang J, Wang JX, Xie ZW. Identification of anoikis-related subgroups and prognosis model in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2862.
pmid: 36769187 |
| [18] |
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu YF, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47.
pmid: 25605792 |
| [19] | Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw, 2010, 33(1): 1-22. [DOI] |
| [20] |
Peng T, Sun F, Yang JC, Cai MH, Huai MX, Pan JX, Zhang FY, Xu LM. Novel lactylation-related signature to predict prognosis for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol, 2024, 30(19): 2575-2602.
pmid: 38817665 |
| [21] |
Steyerberg EW, Vergouwe Y. Towards better clinical prediction models: seven steps for development and an ABCD for validation. Eur Heart J, 2014, 35(29): 1925-1931.
pmid: 24898551 |
| [22] |
Blanche P, Dartigues JF, Jacqmin-Gadda H. Estimating and comparing time-dependent areas under receiver operating characteristic curves for censored event times with competing risks. Stat Med, 2013, 32(30): 5381-5397.
pmid: 24027076 |
| [23] |
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(43): 15545-15550.
pmid: 16199517 |
| [24] |
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng WG, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M, Alizadeh AA. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods, 2015, 12(5): 453-457.
pmid: 25822800 |
| [25] |
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013, 14: 7.
pmid: 23323831 |
| [26] |
He Y, Jiang ZH, Chen C, Wang XS. Classification of triple-negative breast cancers based on Immunogenomic profiling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 327.
pmid: 30594216 |
| [27] |
Ma PJ, Amemiya HM, He LL, Gandhi SJ, Nicol R, Bhattacharyya RP, Smillie CS, Hung DT. Bacterial droplet- based single-cell RNA-seq reveals antibiotic-associated heterogeneous cellular states. Cell, 2023, 186(4): 877-891.
pmid: 36708705 |
| [28] |
Zhang L, Yu X, Zheng LT, Zhang YY, Li YS, Fang Q, Gao RR, Kang BX, Zhang QM, Huang JY, Konno H, Guo XY, Ye YJ, Gao SY, Wang S, Hu XD, Ren XW, Shen ZL, Ouyang WJ, Zhang ZM. Lineage tracking reveals dynamic relationships of T cells in colorectal cancer. Nature, 2018, 564(7735): 268-272.
pmid: 30479382 |
| [29] |
Wu TZ, Hu EQ, Xu SB, Chen MJ, Guo PF, Dai ZH, Feng TZ, Zhou L, Tang WL, Zhan L, Fu XC, Liu SS, Bo XC, Yu GC. ClusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation (Camb), 2021, 2(3): 100141.
pmid: 34557778 |
| [30] |
Bian J, Xiong WJ, Yang ZG, Li MZ, Song DM, Zhang YL, Liu CY. Identification and prognostic biomarkers among ZDHHC4/12/18/24, and APT2 in lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 522.
pmid: 38177255 |
| [31] |
Li L, Shao CY, Liu ZT, Wu XL, Yang JH, Wan HT. Comparative efficacy of Honghua class injections for treating acute ischemic stroke: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1010533.
pmid: 36249799 |
| [32] |
Torgovnick A, Schumacher B. DNA repair mechanisms in cancer development and therapy. Front Genet, 2015, 6: 157.
pmid: 25954303 |
| [33] |
Xiao F, Liu XH, Chen Y, Dai HZ. Tumor-suppressing STF cDNA 3 overexpression suppresses renal fibrosis by alleviating anoikis resistance and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2021, 46(5): 588-600.
pmid: 34284400 |
| [34] |
Wang K, Jiang XL, Jiang Y, Liu J, Du YT, Zhang ZC, Li YL, Zhao XH, Li JP, Zhang R. EZH2-H3K27me3- mediated silencing of mir-139-5p inhibits cellular senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating TOP2A. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42(1): 320.
pmid: 38008711 |
| [35] |
Li R, Yan XJ, Zhong WH, Zheng J, Li XJ, Liang JL, Hu ZY, Liu HY, Chen GH, Yang Y, Zhang JW, Qu EZ, Liu W. Stratifin promotes the malignant progression of HCC via binding and hyperactivating AKT signaling. Cancer Lett, 2024, 592: 216761.
pmid: 38490326 |
| [36] |
Trefts E, Gannon M, Wasserman DH. The liver. Curr Biol, 2017, 27(21): R1147-R1151.
pmid: 29112863 |
| [37] |
Badmus OO, Hillhouse SA, Anderson CD, Hinds TD, Stec DE. Molecular mechanisms of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): functional analysis of lipid metabolism pathways. Clin Sci (Lond), 2022, 136(18): 1347-1366.
pmid: 36148775 |
| [38] |
Herrera FG, Ronet C, Ochoa de Olza M, Barras D, Crespo I, Andreatta M, Corria-Osorio J, Spill A, Benedetti F, Genolet R, Orcurto A, Imbimbo M, Ghisoni E, Navarro Rodrigo B, Berthold DR, Sarivalasis A, Zaman K, Duran R, Dromain C, Prior J, Schaefer N, Bourhis J, Dimopoulou G, Tsourti Z, Messemaker M, Smith T, Warren SE, Foukas P, Rusakiewicz S, Pittet MJ, Zimmermann S, Sempoux C, Dafni U, Harari A, Kandalaft LE, Carmona SJ, Dangaj Laniti D, Irving M, Coukos G. Low-dose radiotherapy reverses tumor immune desertification and resistance to immunotherapy. Cancer Discov, 2022, 12(1): 108-133.
pmid: 34479871 |
| [39] |
Lei X, de Groot DC, Welters MJP, de Wit T, Schrama E, van Eenennaam H, Santegoets SJ, Oosenbrug T, van der Veen A, Vos JL, Zuur CL, Jacobs H, van der Burg SH, Borst J, Xiao YL. CD4+ T cells produce IFN-I to license cDC1s for induction of cytotoxic T-cell activity in human tumors. Cell Mol Immunol, 2024, 21(4): 374-392.
pmid: 38383773 |
| [40] |
Constant DA, Van Winkle JA, VanderHoek E, Dekker SE, Sofia MA, Regner E, Modiano N, Tsikitis VL, Nice TJ. Transcriptional and cytotoxic responses of human intestinal organoids to IFN types I, II, and III. Immunohorizons, 2022, 6(7): 416-429.
pmid: 35790340 |
| [41] |
Leblond MM, Tillé L, Nassiri S, Gilfillan CB, Imbratta C, Schmittnaegel M, Ries CH, Speiser DE, Verdeil G. CD40 agonist restores the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 therapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer in an IFN I/II-mediated manner. Cancer Immunol Res, 2020, 8(9): 1180-1192.
pmid: 32661095 |
| [42] |
Xie M, Lin ZY, Ji XY, Luo XY, Zhang ZR, Sun MY, Chen XP, Zhang BX, Liang HF, Liu DF, Feng YY, Wang YJ, Li YW, Liu BF, Huang WJ, Xia LM. FGF19/FGFR4-mediated elevation of ETV4 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by upregulating PD-L1 and CCL2. J Hepatol, 2023, 79(1): 109-125.
pmid: 36907560 |
| [43] |
Han ZJ, Li YB, Yang LX, Cheng HJ, Liu X, Chen H. Roles of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. Molecules, 2021, 27(1): 137.
pmid: 35011369 |
| [44] |
Nyalali AMK, Leonard AU, Xu YX, Li HY, Zhou JL, Zhang XR, Rugambwa TK, Shi XH, Li F. CD147: an integral and potential molecule to abrogate hallmarks of cancer. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1238051.
pmid: 38023152 |
| [45] |
Knutti N, Huber O, Friedrich K. CD147 (EMMPRIN) controls malignant properties of breast cancer cells by interdependent signaling of Wnt and JAK/STAT pathways. Mol Cell Biochem, 2019, 451(1-2): 197-209.
pmid: 30022447 |
| [46] |
Yang H, Chen BL. CD147 in ovarian and other cancers. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2013, 23(1): 2-8.
pmid: 23221648 |
| [47] |
Raeisi M, Zehtabi M, Velaei K, Fayyazpour P, Aghaei N, Mehdizadeh A. Anoikis in cancer: the role of lipid signaling. Cell Biol Int, 2022, 46(11): 1717-1728.
pmid: 36030535 |
| [48] |
Yang QX, Zhong S, He L, Jia XJ, Tang H, Cheng ST, Ren JH, Yu HB, Zhou L, Zhou HZ, Ren F, Hu ZW, Gong R, Huang AL, Chen J. PBK overexpression promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via activating ETV4-uPAR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett, 2019, 452: 90-102.
pmid: 30914208 |
| [49] |
Peng XL, Ji MY, Yang ZR, Song J, Dong WG. Tumor suppressor function of ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50 through β-catenin/E-cadherin pathway in human hepatocellular cancer. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(8): 1306-1313.
pmid: 23483729 |
| [50] |
Yang Y, Zheng J, Wang MC, Zhang J, Tian T, Wang ZH, Yuan SX, Liu L, Zhu P, Gu FM, Fu SY, Shan YF, Pan ZY, Zhou WP. NQO1 promotes an aggressive phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma via amplifying ERK-NRF2 signaling. Cancer Sci, 2021, 112(2): 641-654.
pmid: 33222332 |
| [51] |
Khan SU, Fatima K, Malik F. Understanding the cell survival mechanism of anoikis-resistant cancer cells during different steps of metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2022, 39(5): 715-726.
pmid: 35829806 |
| [52] |
Sattari Fard F, Jalilzadeh N, Mehdizadeh A, Sajjadian F, Velaei K. Understanding and targeting anoikis in metastasis for cancer therapies. Cell Biol Int, 2023, 47(4): 683-698.
pmid: 36453448 |
| [53] |
Yang JN, Zhang Y, Cheng SS, Xu YN, Wu MX, Gu SJ, Xu SL, Wu YS, Wang C, Wang Y. Anoikis-related signature predicts prognosis and characterizes immune landscape of ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell Int, 2024, 24(1): 53.
pmid: 38310291 |
| [54] |
Shi JX, Peng B, Zhou X, Wang CH, Xu R, Lu T, Chang XY, Shen ZP, Wang KY, Xu CY, Zhang LY. An anoikis- based gene signature for predicting prognosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma and revealing immune infiltration. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2023, 149(13): 12089-12102.
pmid: 37421452 |
| [55] |
Chen J, Sun MJ, Chen CQ, Kang MY, Qian B, Sun J, Ma XP, Zhou JF, Huang L, Jiang B, Fang YJ. Construction of a novel anoikis-related prognostic model and analysis of its correlation with infiltration of immune cells in neuroblastoma. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1135617.
pmid: 37081871 |
| [56] |
Chen Y, Lin QX, Xu YT, Qian FJ, Lin CJ, Zhao WY, Huang JR, Tian L, Gu DN. An anoikis-related gene signature predicts prognosis and reveals immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1158605.
pmid: 37182175 |
| [57] |
Fang WZ, Chen Z. Identification of anoikis related subtypes and construction of prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 2023, 69(9): 219-228.
pmid: 37807308 |
| [58] |
Savarese-Brenner B, Heugl M, Rath B, Schweizer C, Obermayr E, Stickler S, Hamilton G. MUC1 and CD147 are promising markers for the detection of circulating tumor cells in small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res, 2022, 42(1): 429-439.
pmid: 34969753 |
| [59] |
Shigematsu Y, Kanda H, Takahashi Y, Takeuchi K, Inamura K. Relationships between tumor CD147 expression, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and oncostatin M in hepatocellular carcinoma. Virchows Arch, 2024, doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03939-w.
pmid: 39395054 |
| [1] | Rui He, Xiujuan Zheng, Ningning Wang, Xuying Li, Mingqi Li, Shijing Nian, Kewei Wang. Identification of PANoptosis-related lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatics and construction of a prognostic model [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(4): 456-475. |
| [2] | Yuying Chen, Qian Zhang, Menghui Gui, Lan Feng, Pengbo Cao, Gangqiao Zhou. PTBP1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing the oncogenic splicing switch of FGFR2 [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(1): 46-62. |
| [3] | Min Cheng, Jing Zhang, Pengbo Cao, Gangqiao Zhou. Prognostic and predictive value of the hypoxia-associated long non-coding RNA signature in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(2): 153-167. |
| [4] | Changgui Lei, Xueyuan Jia, Wenjing Sun. Establish six-gene prognostic model for glioblastoma based on multi-omics data of TCGA database [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(7): 665-679. |
| [5] | Hongbo Luo, Pengbo Cao, Gangqiao Zhou. Prognostic and predictive value of a DNA methylation-driven transcriptional signature in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(8): 775-787. |
| [6] | Lingyun Sun, Xingyu Li, Zhiwei Sun. Progress of epigenetics and its therapeutic application in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(6): 517-527. |
| [7] | SU Hong SI Xiao-Yu TANG Wen-Ru LUO Ying. The regulation of anoikis in tumor invasion and metastasis [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(1): 10-16. |
| [8] | YANG Yang, WANG Bo-Shi, WANG Xiao-Min, ZHANG Yu, WANG Ming-Rong, JIA Xue-Mei. Screening and identification of anoikis-resistant gene UBCH7 in esophageal cancer cells [J]. HEREDITAS, 2012, 34(2): 190-197. |
| [9] | HUANG Xue-Wen, ZHAO Qi, CHEN Dao-Zhen, ZHANG Li-Shan. Mutations in the D-Loop Region of Mitochondrial DNA and the ROS Level in the Tissue of Hepatocellular Carcinoma [J]. HEREDITAS, 2005, 27(1): 14-20. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||