遗传 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 29-41.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-206
收稿日期:2022-09-22
修回日期:2022-10-29
出版日期:2023-01-20
发布日期:2022-11-04
通讯作者:
汤文学
E-mail:beipingzeng1120@163.com;beipingzeng1120@163.com;hongen_xu@zzu.edu.cn;hongen_xu@zzu.edu.cn;twx@zzu.edu.cn
作者简介:曾焙枰,硕士研究生,专业方向:遗传性耳聋分子诊断。E-mail: 基金资助:
Beiping Zeng1( ), Hongen Xu2(
), Hongen Xu2( ), Lu Mao2, Wenxue Tang3(
), Lu Mao2, Wenxue Tang3( )
)
Received:2022-09-22
Revised:2022-10-29
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2022-11-04
Contact:
Tang Wenxue
E-mail:beipingzeng1120@163.com;beipingzeng1120@163.com;hongen_xu@zzu.edu.cn;hongen_xu@zzu.edu.cn;twx@zzu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
遗传性耳聋是人类最常见的感觉障碍之一,具有高度遗传异质性。目前常用的遗传性耳聋分子诊断方法包括基因芯片、Sanger测序、靶向富集测序和全外显子组测序等,诊断率可达33.5%~56.67%,但还有相当一部分患者不能进行及时有效的分子病因诊断。考虑到患者家庭的经济负担及目前全外显子组/全基因组测序仍相对昂贵,根据患者情况提供包含多种检测手段的梯级诊断策略至关重要。因此,本文对遗传性耳聋分子诊断现状以及梯级检测在遗传性耳聋分子诊断中的应用进行综述,以期为诊断策略的选择提供参考。
曾焙枰, 许红恩, 毛璐, 汤文学. 遗传性耳聋分子诊断及梯级检测策略应用[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(1): 29-41.
Beiping Zeng, Hongen Xu, Lu Mao, Wenxue Tang. Molecular diagnosis of hereditary deafness and application of stepwise testing strategy[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(1): 29-41.
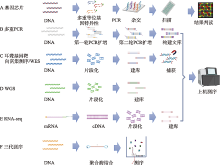
图1
高通量检测技术示意图 A:基因芯片技术。针对不同耳聋基因突变位点设计带有不同标签的上游探针和下游带荧光标记的通用引物,进行多重等位基因特异性引物延伸PCR。PCR产物变性后,与固定有标签互补寡核苷酸序列的芯片杂交,通过激光扫描检测出突变位点。B: 多重PCR技术。第一轮PCR中使用的引物包含位点特异性引物及通用序列,第二轮PCR中使用的引物包含通用接头序列及通用序列对应引物。第二轮PCR产物经过纯化后可直接进行测序。C: 耳聋基因靶向富集测序和全外显子组测序。将基因组DNA片段化及末端修复后加上接头序列构建文库,然后采用芯片杂交捕获或液相捕获等方法对目标基因区域进行富集并测序,全外显子组测序需要对全部外显子区域进行捕获并测序。D:全基因组测序。先将基因组进行DNA片段化处理,文库构建完成后直接测序,无需捕获步骤。E:RNA-seq。mRNA逆转录为cDNA后,片段化、建库及测序。F:三代测序。基因组DNA片段化后,连接接头序列构建文库,纯化后上机测序。"

表1
高通量检测技术在遗传性耳聋分子诊断中的应用"
| 技术 | 代表性研究 | 主要进展 | 优点 | 局限性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因芯片 | Li等[ | 首次利用基因芯片检测 | 自动化、微型性,是进行耳聋基因分子诊断最快捷的方法之一 | 只涵盖4个耳聋基因的热点突变,携带罕见突变的患者不能得到明确诊断 |
| He等[ | 在2500个新生儿中,检测到101名(4.04%)为阳性 | |||
| Dai等[ | 在180 469名新生儿中,检测到8136名(4.508%)为阳性 | |||
| 耳聋基因靶 向富集测序 | Smith等[ | 首次发表了耳聋基因靶向富集测序对听力损失患者进行分子诊断的研究 | 低成本、个性化、易解释,在各大研究机构和公司广泛应用 | 随着耳聋新基因的发现,基因panel需要持续更新;基因panel通常无法涵盖内含子区域及基因调控区域的突变 |
| Tang等[ | 提出了一种基于cDNA探针捕获已知耳聋基因外显子,并进行高通量测序从而实现耳聋分子诊断的方法 | |||
| Sloan-Heggen等[ | 1119名听力损失患者,诊断率为39% | |||
| Cabanillas等[ | 50名听力损失患者,诊断率为42% | |||
| Yuan等[ | 433名耳聋患者,诊断率为52.19% | |||
| 全外显子 组测序 | Zazo Seco等[ | 200名耳聋患者,诊断率为33.5% | 较全基因组测序更经济高效;能获得编码区测序覆盖度更深、准确性更高的数据;可获得与表型相关的大部分遗传变异 | 鉴定内含子或基因调控区域突变的能力不足;检出结构重排、CNV和串联重复等变异的能力有所欠缺 |
| Sheppard等[ | 43例听力损失儿童患者,诊断率为37.2% | |||
| Feng等[ | 33个听力损失家系,诊断率为48.5% | |||
| Downie等[ | 106名中度至重度听力损失婴儿,诊断率为56% | |||
| 全基因 组测序 | Vuckovic等[ | 确定了21个与年龄性听力损失相关的基因 | 检测全面,能够识别非编码区域中的变异,可分析结构变异;无目标基因捕获步骤,上机测序更快速便捷 | 成本昂贵;数据分析和变异解读存在一定挑战,比如与同源基因相关的轻中度遗传性耳聋的变异分析(STRC基因) |
| Le Nabec等[ | 在9名携带GJB2单杂合突变的DFNB1患者中,发现4名患者携带GJB2的另一个变异 | |||
| 三代测序 | Dai等[ | 在3名未诊断的内耳畸形(IP-III)患者中,发现2名患者携带POU3F4基因的结构变异 | 真正实现了单分子测序;超长的测序读长,利于分析结构变异;可直接检测碱基修饰;可应用于转录组研究 | 精确度较低,测序深度有限;成本昂贵,还达不到广泛应用的条件 |

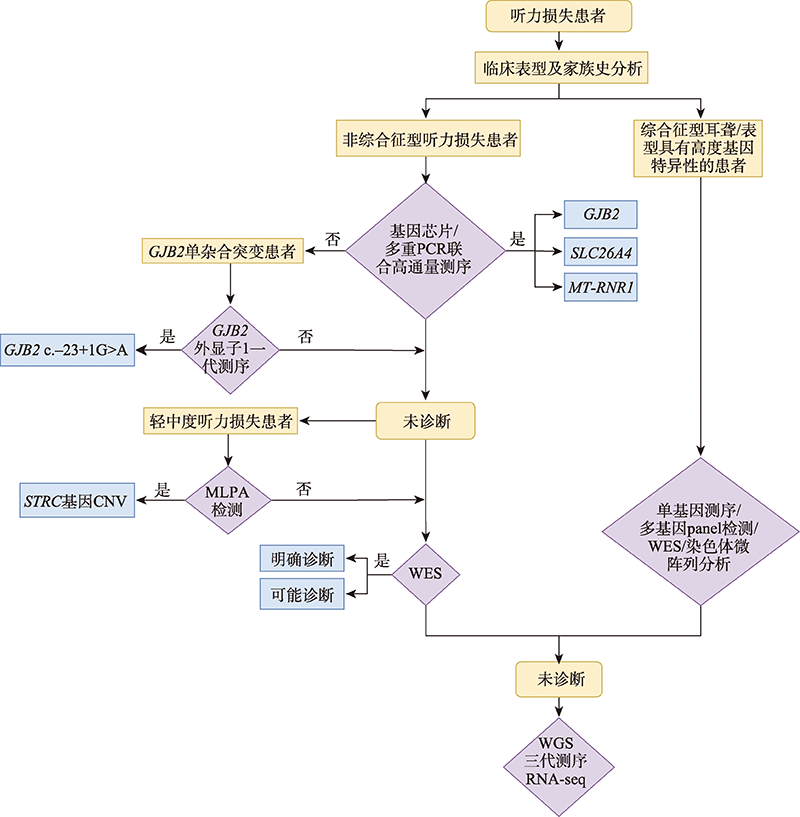
图2
听力损失患者分子诊断的梯级检测策略图 橙色框表示患者类型,紫色框表示基因检测方法,蓝色框表示诊断结果。对于非综合征型听力损失患者,经基因芯片或多重PCR联合高通量测序检测的患者可归类为常见耳聋基因GJB2、SLC26A4或MT-RNR1诊断,对GJB2单杂合突变患者进行GJB2外显子1的一代测序主要是检测c.-23+1G>A的突变情况,需要对轻中度听力损失患者进行MLPA检测以确定STRC基因的CNV情况,应用以上方法未诊断患者可进行WES确定遗传病因。对于综合征型耳聋或表型具有高度基因特异性的患者,可直接进行单基因测序、多基因panel检测、WES或染色体微阵列分析等检测。经以上检测仍然为阴性的样本,可利用WGS、RNA-seq或三代测序等手段探索潜在遗传病因。"
| [1] | Deafness and hearing loss.World Health Organization. Page publishing date: April, 2021. Reference date: July, 2022. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss. |
| [2] | Marazita ML, Ploughman LM, Rawlings B, Remington E, Arnos KS, Nance WE. Genetic epidemiological studies of early-onset deafness in the U.S. school-age population. Am J Med Genet, 1993, 46(5): 486-491. |
| [3] | Morton CC, Nance WE. Newborn hearing screening-a silent revolution. N Engl J Med, 2006, 354(20): 2151- 2164. |
| [4] | Brownstein Z, Bhonker Y, Avraham KB. High-throughput sequencing to decipher the genetic heterogeneity of deafness. Genome Biol, 2012, 13(5): 245. |
| [5] | Dai P, Yuan YY eds. Diagnosis and genetic counseling of deafness. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2017. |
| 戴朴, 袁永一 编著. 耳聋基因诊断与遗传咨询. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. | |
| [6] | Yang T, Guo L, Wang LH, Yu XY. Diagnosis, intervention, and prevention of genetic hearing loss. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1130: 73-92. |
| [7] | Yan D, Tekin M, Blanton SH, Liu XZ. Next-generation sequencing in genetic hearing loss. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers, 2013, 17(8): 581-587. |
| [8] | Xu YF, Ren LF, Yang Y. Nonsyndromic hereditary deafness genes research progress and related databases. Hereditas(Beijing), 2002, 24(1): 65-71. |
| 徐悦凡, 任鲁风, 杨宇. 非综合征型遗传性耳聋基因的研究进展及相关网络资源. 遗传, 2002, 24(1): 65-71. | |
| [9] | Alford RL, Arnos KS, Fox M, Lin JW, Palmer CG, Pandya A, Rehm HL, Robin NH, Scott DA, Yoshinaga-Itano C, ACMG Working Group on Update of Genetics Evaluation Guidelines for the Etiologic Diagnosis of Congenital Hearing Loss, Professional Practice and Guidelines Committee. American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guideline for the clinical evaluation and etiologic diagnosis of hearing loss. Genet Med, 2014, 16(4): 347-355. |
| [10] | Du W, Wang QJ, Zhu YM, Wang YL, Guo YF. Associations between GJB2, mitochondrial 12S rRNA, SLC26A4 mutations, and hearing loss among three ethnicities. Biomed Res Int, 2014, 2014: 746838. |
| [11] | Yuan YY, You YW, Huang DL, Cui JH, Wang Y, Wang Q, Yu F, Kang DY, Yuan HJ, Han DY, Dai P. Comprehensive molecular etiology analysis of nonsyndromic hearing impairment from typical areas in China. J Transl Med, 2009, 7: 79. |
| [12] | Dai P, Huang LH, Wang GJ, Gao X, Qu CY, Chen XW, Ma FR, Zhang J, Xing WL, Xi SY, Ma BR, Pan Y, Cheng XH, Duan H, Yuan YY, Zhao LP, Chang L, Gao RZ, Liu HH, Zhang W, Huang SS, Kang DY, Liang W, Zhang K, Jiang H, Guo YL, Zhou Y, Zhang WX, Lyu F, Jin YN, Zhou Z, Lu HL, Zhang X, Liu P, Ke J, Hao JS, Huang HM, Jiang D, Ni X, Long M, Zhang L, Qiao J, Morton CC, Liu XZ, Cheng J, Han DM. Concurrent hearing and genetic screening of 180,469 neonates with follow-up in Beijing, China. Am J Hum Genet, 2019, 105(4): 803-812. |
| [13] | He XH, Li XZ, Guo YQ, Zhao Y, Dong H, Dong J, Zhong L, Shi ZY, Zhang YY, Soliman M, Song CH, Zhao ZJ. Newborn screening of genetic mutations in common deafness genes with bloodspot-based gene chip array. Am J Audiol, 2018, 27(1): 57-66. |
| [14] | Green GE, Scott DA, McDonald JM, Woodworth GG, Sheffield VC, Smith RJ. Carrier rates in the midwestern United States for GJB2 mutations causing inherited deafness. JAMA, 1999, 281(23): 2211-2216. |
| [15] | Kenneson A, Van Naarden Braun K, Boyle C. GJB2 (connexin 26) variants and nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss: a HuGE review. Genet Med, 2002, 4(4): 258-274. |
| [16] | Liu YH, Ke XM, Qi Y, Li W, Zhu P. Connexin 26 gene (GJB2): prevalence of mutations in the Chinese population. J Hum Genet, 2002, 47(12): 688-690. |
| [17] | Li Q, Dai P, Huang DL, Zhang J, Wang GJ, Zhu QW, Liu X, Han DY. Prevalence of GJB 2 mutations in Uigur and Han ethnic populations with deafness in Xinjiang region of China. Natl Med J China, 2007, 87(42): 2977-2981. |
| 李琦, 戴朴, 黄德亮, 张劲, 王国建, 朱庆文, 刘新, 韩东一. 新疆地区维吾尔族和汉族非综合征性耳聋GJB2基因突变研究. 中华医学杂志, 2007, 87(42): 2977-2981. | |
| [18] | Yu F, Han DY, Dai P, Kang DY, Zhang X, Liu X, Zhu QW, Yuan YY, Sun Q, Xue DD, Li M, Liu J, Yuan HJ, Yang ZY. Mutation of GJB2 gene in nonsyndromic hearing impairment patients: analysis of 1190 cases. Natl Med J China, 2007, 87(40): 2814-2819. |
| 于飞, 韩东一, 戴朴, 康东洋, 张昕, 刘新, 朱庆文, 袁永一, 孙勍, 薛丹丹, 李梅, 刘军, 袁慧军, 杨伟炎. 1190例非综合征性耳聋患者GJB2基因突变序列分析. 中华医学杂志, 2007, 87(40): 2814-2819. | |
| [19] | Dai P, Yu F, Han B, Liu XZ, Wang GJ, Li Q, Yuan Y, Liu X, Huang DL, Kang DY, Zhang X, Yuan HJ, Yao K, Hao JS, He J, He Y, Wang YQ, Ye Q, Yu YJ, Lin HY, Liu LJ, Deng W, Zhu XH, You YW, Cui JH, Hou NS, Xu XH, Zhang J, Tang L, Song RD, Lin YJ, Sun SZ, Zhang RN, Wu H, Ma YB, Zhu SX, Wu BL, Han DY, Wong LJC. GJB 2 mutation spectrum in 2,063 Chinese patients with nonsyndromic hearing impairment. J Transl Med, 2009, 7: 26. |
| [20] | Yuan YY, Yu F, Wang GJ, Huang SS, Yu RL, Zhang X, Huang DL, Han DY, Dai P. Prevalence of the GJB2 IVS1+1G >A mutation in Chinese hearing loss patients with monoallelic pathogenic mutation in the coding region of GJB2. J Transl Med, 2010, 8: 127. |
| [21] | Park HJ, Shaukat S, Liu XZ, Hahn SH, Naz S, Ghosh M, Kim HN, Moon SK, Abe S, Tukamoto K, Riazuddin S, Kabra M, Erdenetungalag R, Radnaabazar J, Khan S, Pandya A, Usami SI, Nance WE, Wilcox ER, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ. Origins and frequencies of SLC26A4 (PDS) mutations in east and south Asians: global implications for the epidemiology of deafness. J Med Genet, 2003, 40(4): 242-248. |
| [22] | Guo YF, Liu XW, Guan J, Han MK, Wang DY, Zhao YL, Rao SQ, Wang QJ. GJB2, SLC26A4 and mitochondrial DNA A1555G mutations in prelingual deafness in Northern Chinese subjects. Acta Otolaryngol, 2008, 128(3): 297-303. |
| [23] | Dai P, Stewart AK, Chebib F, Hsu A, Rozenfeld J, Huang DL, Kang DY, Lip V, Fang H, Shao H, Liu X, Yu F, Yuan HJ, Kenna M, Miller DT, Shen YP, Yang WY, Zelikovic I, Platt OS, Han DY, Alper SL, Wu BL. Distinct and novel SLC26A4/Pendrin mutations in Chinese and U.S. patients with nonsyndromic hearing loss. Physiol Genomics, 2009, 38(3): 281-290. |
| [24] | Yuan YY, Guo WW, Tang J, Zhang GZ, Wang GJ, Han MY, Zhang X, Yang SM, He DZZ, Dai P. Molecular epidemiology and functional assessment of novel allelic variants of SLC26A4 in non-syndromic hearing loss patients with enlarged vestibular aqueduct in China. PLoS One, 2012, 7(11): e49984. |
| [25] | Yuan YY, Li Q, Su Y, Lin QF, Gao X, Liu HK, Huang SS, Kang DY, Todd NW, Mattox D, Zhang JG, Lin X, Dai P. Comprehensive genetic testing of Chinese SNHL patients and variants interpretation using ACMG guidelines and ethnically matched normal controls. Eur J Hum Genet, 2020, 28(2): 231-243. |
| [26] | Igumnova V, Veidemane L, Viksna A, Capligina V, Zole E, Ranka R. The prevalence of mitochondrial mutations associated with aminoglycoside-induced deafness in ethnic Latvian population: the appraisal of the evidence. J Hum Genet, 2019, 64(3): 199-206. |
| [27] | Shearer AE, Kolbe DL, Azaiez H, Sloan CM, Frees KL, Weaver AE, Clark ET, Nishimura CJ, Black-Ziegelbein EA, Smith RJH. Copy number variants are a common cause of non-syndromic hearing loss. Genome Med, 2014, 6(5): 37. |
| [28] | Hoppman N, Aypar U, Brodersen P, Brown N, Wilson J, Babovic-Vuksanovic D.Genetic testing for hearing loss in the United States should include deletion/duplication analysis for the deafness/infertility locus at 15q15.3. Mol Cytogenet, 2013, 6(1): 19. |
| [29] | Ji HT, Lu JQ, Wang JJ, Li HW, Lin X. Combined examination of sequence and copy number variations in human deafness genes improves diagnosis for cases of genetic deafness. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord, 2014, 14: 9. |
| [30] | Austin-Tse CA, Mandelker DL, Oza AM, Mason-Suares H, Rehm HL, Amr SS. Analysis of intragenic USH2A copy number variation unveils broad spectrum of unique and recurrent variants. Eur J Med Genet, 2018, 61(10): 621- 626. |
| [31] | Marková SP, Brožková DŠ, Laššuthová P, Mészárosová A, Krůtová M, Neupauerová J, Rašková D, Trková M, Staněk D, Seeman P. STRC gene mutations, mainly large deletions, are a very important cause of early-onset hereditary hearing loss in the Czech population. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers, 2018, 22(2): 127-134. |
| [32] | Shearer AE, Kolbe DL, Azaiez H, Sloan CM, Frees KL, Weaver AE, Clark ET, Nishimura CJ, Black-Ziegelbein EA, Smith RJH. Copy number variants are a common cause of non-syndromic hearing loss. Genome Med, 2014, 6(5): 37. |
| [33] | Plevova P, Paprskarova M, Tvrda P, Turska P, Slavkovsky R, Mrazkova E. STRC deletion is a frequent cause of slight to moderate congenital hearing impairment in the Czech Republic. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(10): e393-e400. |
| [34] | Yokota Y, Moteki H, Nishio SY, Yamaguchi T, Wakui K, Kobayashi Y, Ohyama K, Miyazaki H, Matsuoka R, Abe S, Kumakawa K, Takahashi M, Sakaguchi H, Uehara N, Ishino T, Kosho T, Fukushima Y, Usami SI. Frequency and clinical features of hearing loss caused by STRC deletions. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 4408. |
| [35] | Kim BJ, Oh DY, Han JH, Oh J, Kim MY, Park HR, Seok J, Cho SD, Lee SY, Kim Y, Carandang M, Kwon IS, Lee S, Jang JH, Choung YH, Lee S, Lee H, Hwang SM, Choi BY. Significant Mendelian genetic contribution to pediatric mild-to-moderate hearing loss and its comprehensive diagnostic approach. Genet Med, 2020, 22(6): 1119-1128. |
| [36] | Best S, Wou K, Vora N, Van der Veyver IB, Wapner R, Chitty LS. Promises, pitfalls and practicalities of prenatal whole exome sequencing. Prenat Diagn, 2018, 38(1): 10-19. |
| [37] | Sloan-Heggen CM, Bierer AO, Shearer AE, Kolbe DL, Nishimura CJ, Frees KL, Ephraim SS, Shibata SB, Booth KT, Campbell CA, Ranum PT, Weaver AE, Black-Ziegelbein EA, Wang DH, Azaiez H, Smith RJH. Comprehensive genetic testing in the clinical evaluation of 1119 patients with hearing loss. Hum Genet, 2016, 135(4): 441-450. |
| [38] | Yuan HJ, Lu Y. Application of next generation sequencing in gene identification and genetic diagnosis of hereditary hearing loss. Hereditas(Beijing), 2014, 36(11): 1112-1120. |
| 袁慧军, 卢宇. 新一代测序技术在遗传性耳聋基因研究及诊断中的应用. 遗传, 2014, 36(11): 1112-1120. | |
| [39] | Wang CC, Yuan HJ. Application and progress of high- throughput sequencing technologies in the research of hereditary hearing loss. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(3): 208-219. |
| 王翠翠, 袁慧军. 高通量测序技术在遗传性耳聋研究中的应用及研究进展. 遗传, 2017, 39(3): 208-219. | |
| [40] | Zazo Seco C, Wesdorp M, Feenstra I, Pfundt R, Hehir-Kwa JY, Lelieveld SH, Castelein S, Gilissen C, de Wijs IJ, Admiraal RJ, Pennings RJ, Kunst HP, van de Kamp JM, Tamminga S, Houweling AC, Plomp AS, Maas SM, de Koning Gans PA, Kant SG, de Geus CM, Frints SG, Vanhoutte EK, van Dooren MF, van den Boogaard MJH, Scheffer H, Nelen M, Kremer H, Hoefsloot L, Schraders M, Yntema HG. The diagnostic yield of whole-exome sequencing targeting a gene panel for hearing impairment in The Netherlands. Eur J Hum Genet, 2017, 25(3): 308-314. |
| [41] | Shearer AE, Smith RJH. Massively parallel sequencing for genetic diagnosis of hearing loss: the new standard of care. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 153(2): 175-182. |
| [42] | Downie L, Halliday J, Burt R, Lunke S, Lynch E, Martyn M, Poulakis Z, Gaff C, Sung V, Wake M, Hunter MF, Saunders K, Rose E, Lewis S, Jarmolowicz A, Phelan D, Rehm HL, Melbourne Genomics Health Alliance, Amor DJ. Exome sequencing in infants with congenital hearing impairment: a population-based cohort study. Eur J Hum Genet, 2020, 28(5): 587-596. |
| [43] | Bademci G, Foster J, Mahdieh N, Bonyadi M, Duman D, Cengiz FB, Menendez I, Diaz-Horta O, Shirkavand A, Zeinali S, Subasioglu A, Tokgoz-Yilmaz S, Huesca-Hernandez F, de la Luz Arenas-Sordo M, Dominguez-Aburto J, Hernandez-Zamora E, Montenegro P, Paredes R, Moreta G, Vinueza R, Villegas F, Mendoza-Benitez S, Guo SR, Bozan N, Tos T, Incesulu A, Sennaroglu G, Blanton SH, Ozturkmen-Akay H, Yildirim-Baylan M, Tekin M. Comprehensive analysis via exome sequencing uncovers genetic etiology in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness in a large multiethnic cohort. Genet Med, 2016, 18(4): 364-371. |
| [44] | Zou SF, Mei XS, Yang WQ, Zhu RF, Yang T, Hu HY. Whole-exome sequencing identifies rare pathogenic and candidate variants in sporadic Chinese Han deaf patients. Clin Genet, 2020, 97(2): 352-356. |
| [45] | Sheppard S, Biswas S, Li MH, Jayaraman V, Slack I, Romasko EJ, Sasson A, Brunton J, Rajagopalan R, Sarmady M, Abrudan JL, Jairam S, DeChene ET, Ying X, Choi J, Wilkens A, Raible SE, Scarano MI, Santani A, Pennington JW, Luo MJ, Conlin LK, Devkota B, Dulik MC, Spinner NB, Krantz ID. Utility and limitations of exome sequencing as a genetic diagnostic tool for children with hearing loss. Genet Med, 2018, 20(12): 1663-1676. |
| [46] | Sang SS, Ling J, Liu XZ, Mei LY, Cai XZ, Li TX, Li W, Li M, Wen J, Liu XL, Liu J, Liu YL, Chen HS, He CF, Feng Y. Proband whole-exome sequencing identified genes responsible for autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss in 33 Chinese nuclear families. Front Genet, 2019, 10: 639. |
| [47] | Bademci G, Foster J, Mahdieh N, Bonyadi M, Duman D, Cengiz FB, Menendez I, Diaz-Horta O, Shirkavand A, Zeinali S, Subasioglu A, Tokgoz-Yilmaz S, Huesca- Hernandez F, de la Luz Arenas-Sordo M, Dominguez- Aburto J, Hernandez-Zamora E, Montenegro P, Paredes R, Moreta G, Vinueza R, Villegas F, Mendoza-Benitez S, Guo SR, Bozan N, Tos T, Incesulu A, Sennaroglu G, Blanton SH, Ozturkmen-Akay H, Yildirim-Baylan M, Tekin M. Comprehensive analysis via exome sequencing uncovers genetic etiology in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness in a large multiethnic cohort. Genet Med, 2016, 18(4): 364-371. |
| [48] | Guan QN, Balciuniene J, Cao KJ, Fan ZQ, Biswas S, Wilkens A, Gallo DJ, Bedoukian E, Tarpinian J, Jayaraman P, Sarmady M, Dulik M, Santani A, Spinner N, Abou Tayoun AN, Krantz ID, Conlin LK, Luo MJ. AUDIOME: a tiered exome sequencing-based comprehensive gene panel for the diagnosis of heterogeneous nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Genet Med, 2018, 20(12): 1600-1608. |
| [49] | Baux D, Vaché C, Blanchet C, Willems M, Baudoin C, Moclyn M, Faugère V, Touraine R, Isidor B, Dupin- Deguine D, Nizon M, Vincent M, Mercier S, Calais C, Garcia-Garcia G, Azher Z, Lambert L, Perdomo-Trujillo Y, Giuliano F, Claustres M, Koenig M, Mondain M, Roux AF. Combined genetic approaches yield a 48% diagnostic rate in a large cohort of French hearing-impaired patients. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 16783. |
| [50] | Budde BS, Aly MA, Mohamed MR, Breß A, Altmüller J, Motameny S, Kawalia A, Thiele H, Konrad K, Becker C, Toliat MR, Nürnberg G, Sayed EAF, Mohamed ES, Pfister M, Nürnberg P. Comprehensive molecular analysis of 61 Egyptian families with hereditary nonsyndromic hearing loss. Clin Genet, 2020, 98(1): 32-42. |
| [51] | Wang J, Xiang JL, Chen LS, Luo HY, Xu XH, Li N, Cui CM, Xu JJ, Song NN, Peng JG, Peng ZY. Molecular diagnosis of non-syndromic hearing loss patients using a stepwise approach. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 4036. |
| [52] | Li M, Mei LY, He CF, Chen HS, Cai XZ, Liu YL, Tian RY, Tian Q, Song J, Jiang L, Liu C, Wu H, Li TX, Liu J, Li XM, Yi YF, Yan D, Blanton SH, Hu ZM, Liu XZ, Li JD, Ling J, Feng Y. Extrusion pump ABCC1 was first linked with nonsyndromic hearing loss in humans by stepwise genetic analysis. Genet Med, 2019, 21(12): 2744-2754. |
| [53] | Sakuma N, Moteki H, Takahashi M, Nishio SY, Arai Y, Yamashita Y, Oridate N, Usami SI. An effective screening strategy for deafness in combination with a next-generation sequencing platform: a consecutive analysis. J Hum Genet, 2016, 61(3): 253-261. |
| [54] | Li CX, Pan Q, Guo YG, Li Y, Gao HF, Zhang D, Hu H, Xing WL, Mitchelson K, Xia K, Dai P, Cheng J. Construction of a multiplex allele-specific PCR-based universal array (ASPUA) and its application to hearing loss screening. Hum Mutat, 2008, 29(2): 306-314. |
| [55] | Onda Y, Takahagi K, Shimizu M, Inoue K, Mochida K. Multiplex PCR targeted amplicon sequencing (MTA-Seq): simple, flexible, and versatile SNP genotyping by highly multiplexed PCR amplicon sequencing. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9: 201. |
| [56] | Tian YA, Xu HE, Liu DH, Zhang JL, Yang ZG, Zhang S, Liu HF, Li RJ, Tian YT, Zeng BP, Li T, Lin QY, Wang HL, Li XH, Lu W, Shi Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Jiang C, Xu Y, Chen B, Liu J, Tang WX. Increased diagnosis of enlarged vestibular aqueduct by multiplex PCR enrichment and next-generation sequencing of the SLC26A4 gene. Mol Genet Genomic Med, 2021, 9(8): e1734. |
| [57] | Yang HY, Luo HY, Zhang GW, Zhang JQ, Peng ZY, Xiang JL. A multiplex PCR amplicon sequencing assay to screen genetic hearing loss variants in newborns. BMC Med Genomics, 2021, 14(1): 61. |
| [58] | Shearer AE, DeLuca AP, Hildebrand MS, Taylor KR, Gurrola J, Scherer S, Scheetz TE, Smith RJH. Comprehensive genetic testing for hereditary hearing loss using massively parallel sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(49): 21104-21109. |
| [59] | Tang WX, Qian D, Ahmad S, Mattox D, Todd NW, Han H, Huang ST, Li YH, Wang YF, Li HW, Lin X. A low-cost exon capture method suitable for large-scale screening of genetic deafness by the massively-parallel sequencing approach. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers, 2012, 16(6): 536-542. |
| [60] | Cabanillas R, Diñeiro M, Cifuentes GA, Castillo D, Pruneda PC, Álvarez R, Sánchez-Durán N, Capín R, Plasencia A, Viejo-Díaz M, García-González N, Hernando I, Llorente JL, Repáraz-Andrade A, Torreira-Banzas C, Rosell J, Govea N, Gómez-Martínez JR, Núñez-Batalla F, Garrote JA, Mazón-Gutiérrez Á, Costales M, Isidoro- García M, García-Berrocal B, Ordóñez GR, Cadiñanos J. Comprehensive genomic diagnosis of non-syndromic and syndromic hereditary hearing loss in Spanish patients. BMC Med Genomics, 2018, 11(1): 58. |
| [61] | Botstein D, Risch N. Discovering genotypes underlying human phenotypes: past successes for mendelian disease, future approaches for complex disease. Nat Genet, 2003, 33 Suppl: 228-237. |
| [62] | Rabbani B, Mahdieh N, Hosomichi K, Nakaoka H, Inoue I. Next-generation sequencing: impact of exome sequencing in characterizing Mendelian disorders. J Hum Genet, 2012, 57(10): 621-632. |
| [63] | Choi M, Scholl UI, Ji WZ, Liu TW, Tikhonova IR, Zumbo P, Nayir A, Bakkaloğlu A, Ozen S, Sanjad S, Nelson- Williams C, Farhi A, Mane S, Lifton RP. Genetic diagnosis by whole exome capture and massively parallel DNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(45): 19096-19101. |
| [64] | Singleton AB. Exome sequencing: a transformative technology. Lancet Neurol, 2011, 10(10): 942-946. |
| [65] | Lionel AC, Costain G, Monfared N, Walker S, Reuter MS, Hosseini SM, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Merico D, Jobling R, Nalpathamkalam T, Pellecchia G, Sung WWL, Wang ZZ, Bikangaga P, Boelman C, Carter MT, Cordeiro D, Cytrynbaum C, Dell SD, Dhir P, Dowling JJ, Heon E, Hewson S, Hiraki L, Inbar-Feigenberg M, Klatt R, Kronick J, Laxer RM, Licht C, MacDonald H, Mercimek- Andrews S, Mendoza-Londono R, Piscione T, Schneider R, Schulze A, Silverman E, Siriwardena K, Snead OC, Sondheimer N, Sutherland J, Vincent A, Wasserman JD, Weksberg R, Shuman C, Carew C, Szego MJ, Hayeems RZ, Basran R, Stavropoulos DJ, Ray PN, Bowdin S, Meyn MS, Cohn RD, Scherer SW, Marshall CR. Improved diagnostic yield compared with targeted gene sequencing panels suggests a role for whole-genome sequencing as a first-tier genetic test. Genet Med, 2018, 20(4): 435-443. |
| [66] | Franchini LF, Pollard KS. Human evolution: the non-coding revolution. BMC Biol, 2017, 15(1): 89. |
| [67] | Check E. It's the junk that makes us human. Nature, 2006, 444(7116): 130-131. |
| [68] | Khan AO, Becirovic E, Betz C, Neuhaus C, Altmüller J, Riedmayr LM, Motameny S, Nürnberg G, Nürnberg P, Bolz HJ. A deep intronic CLRN1 (USH3A) founder mutation generates an aberrant exon and underlies severe Usher syndrome on the Arabian Peninsula. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 1411. |
| [69] | Farnaes L, Hildreth A, Sweeney NM, Clark MM, Chowdhury S, Nahas S, Cakici JA, Benson W, Kaplan RH, Kronick R, Bainbridge MN, Friedman J, Gold JJ, Ding Y, Veeraraghavan N, Dimmock D, Kingsmore SF. Rapid whole-genome sequencing decreases infant morbidity and cost of hospitalization. Npj Genom Med, 2018, 3: 10. |
| [70] | Vuckovic D, Mezzavilla M, Cocca M, Morgan A, Brumat M, Catamo E, Concas MP, Biino G, Franze A, Ambrosetti U, Pirastu M, Gasparini P, Girotto G. Whole-genome sequencing reveals new insights into age-related hearing loss: cumulative effects, pleiotropy and the role of selection. Eur J Hum Genet, 2018, 26(8): 1167-1179. |
| [71] | Le Nabec A, Collobert M, Le Maréchal C, Marianowski R, Férec C, Moisan S. Whole-genome sequencing improves the diagnosis of DFNB1 monoallelic patients. Genes (Basel), 2021, 12(8): 1267. |
| [72] | Mikheyev AS, Tin MMY. A first look at the Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencer. Mol Ecol Resour, 2014, 14(6): 1097-1102. |
| [73] | Lin B, Hui JA, Mao HJ. Nanopore technology and its applications in gene sequencing. Biosensors (Basel), 2021, 11(7): 214. |
| [74] | Oikonomopoulos S, Wang YC, Djambazian H, Badescu D, Ragoussis J. Benchmarking of the Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencing for quantitative and qualitative assessment of cDNA populations. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 31602. |
| [75] | Liu S, Wang H, Leigh D, Cram DS, Wang L, Yao YQ. Third-generation sequencing: any future opportunities for PGT? J Assist Reprod Genet, 2021, 38(2): 357-364. |
| [76] | Roberts RJ, Carneiro MO, Schatz MC. The advantages of SMRT sequencing. Genome Biol, 2013, 14(7): 405. |
| [77] | Midha MK, Wu MC, Chiu KP. Long-read sequencing in deciphering human genetics to a greater depth. Hum Genet, 2019, 138(11-12): 1201-1215. |
| [78] | Au CH, Ho DN, Ip BBK, Wan TSK, Ng MHL, Chiu EKW, Chan TL, Ma ESK. Rapid detection of chromosomal translocation and precise breakpoint characterization in acute myeloid leukemia by nanopore long-read sequencing. Cancer Genet, 2019, 239: 22-25. |
| [79] | Chow JFC, Cheng HHY, Lau EYL, Yeung WSB, Ng EHY. High-resolution mapping of reciprocal translocation breakpoints using long-read sequencing. MethodsX, 2019, 6: 2499-2503. |
| [80] | Merker JD, Wenger AM, Sneddon T, Grove M, Zappala Z, Fresard L, Waggott D, Utiramerur S, Hou YL, Smith KS, Montgomery SB, Wheeler M, Buchan JG, Lambert CC, Eng KS, Hickey L, Korlach J, Ford J, Ashley EA. Long-read genome sequencing identifies causal structural variation in a Mendelian disease. Genet Med, 2018, 20(1): 159-163. |
| [81] | Simpson JT, Workman RE, Zuzarte PC, David M, Dursi LJ, Timp W. Detecting DNA cytosine methylation using nanopore sequencing. Nat Methods, 2017, 14(4): 407-410. |
| [82] | Liu Q, Georgieva DC, Egli D, Wang K. NanoMod: a computational tool to detect DNA modifications using Nanopore long-read sequencing data. Bmc Genomics, 2019, (Suppl 1): 7820. |
| [83] | Jeck WR, Lee J, Robinson H, Le LP, Iafrate AJ, Nardi V. A nanopore sequencing-based assay for rapid detection of gene fusions. J Mol Diagn, 2019, 21(1): 58-69. |
| [84] | Sharon D, Tilgner H, Grubert F, Snyder M. A single- molecule long-read survey of the human transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol, 2013, 31(11): 1009-1014. |
| [85] | Jiang Y, Wu LH, Huang SS, Li PD, Gao B, Yuan YY, Zhang SW, Yu GL, Gao Y, Wu H, Dai P. Study of complex structural variations of X-linked deafness-2 based on single-molecule sequencing. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(6): BSR20203740. |
| [86] | Cummings BB, Marshall JL, Tukiainen T, Lek M, Donkervoort S, Foley AR, Bolduc V, Waddell LB, Sandaradura SA, O'Grady GL, Estrella E, Reddy HM, Zhao FM, Weisburd B, Karczewski KJ, O'Donnell-Luria AH, Birnbaum D, Sarkozy A, Hu Y, Gonorazky H, Claeys K, Joshi H, Bournazos A, Oates EC, Ghaoui R, Davis MR, Laing NG, Topf A, Genotype-Tissue Expression Consortium, Kang PB, Beggs AH, North KN, Straub V, Dowling JJ, Muntoni F, Clarke NF, Cooper ST, Bönnemann CG, MacArthur DG. Improving genetic diagnosis in Mendelian disease with transcriptome sequencing. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(386): eaal5209. |
| [87] | Gonorazky HD, Naumenko S, Ramani AK, Nelakuditi V, Mashouri P, Wang PQ, Kao D, Ohri K, Viththiyapaskaran S, Tarnopolsky MA, Mathews KD, Moore SA, Osorio AN, Villanova D, Kemaladewi DU, Cohn RD, Brudno M, Dowling JJ. Expanding the boundaries of RNA sequencing as a diagnostic tool for rare Mendelian disease. Am J Hum Genet, 2019, 104(3): 466-483. |
| [88] | Frésard L, Smail C, Ferraro NM, Teran NA, Li X, Smith KS, Bonner D, Kernohan KD, Marwaha S, Zappala Z, Balliu B, Davis JR, Liu BX, Prybol CJ, Kohler JN, Zastrow DB, Reuter CM, Fisk DG, Grove ME, Davidson JM, Hartley T, Joshi R, Strober BJ, Utiramerur S, Undiagnosed Diseases Network, Care4Rare Canada Consortium, Lind L, Ingelsson E, Battle A, Bejerano G, Bernstein JA, Ashley EA, Boycott KM, Merker JD, Wheeler MT, Montgomery SB. Identification of rare-disease genes using blood transcriptome sequencing and large control cohorts. Nat Med, 2019, 25(6): 911-919. |
| [89] | Yu XY, Lin Y, Xu J, Che TJ, Li L, Yang T, Wu H. Molecular epidemiology of Chinese Han deaf patients with bi-allelic and mono-allelic GJB2 mutations. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2020, 15(1): 29. |
| [1] | 谢春梅, 武海萍, 马雪萍, 周国华. 用于临床新型冠状病毒核酸检测的分子诊断新技术[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(9): 870-881. |
| [2] | 鲁有望,王昆华. 结直肠癌原发与配对转移肿瘤遗传异质性研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(6): 482-490. |
| [3] | 王翠翠,袁慧军. 高通量测序技术在遗传性耳聋研究中的应用及研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(3): 208-219. |
| [4] | 赵跃, 张宏, 夏雪山. 下一代半导体测序技术在遗传性心肌病分子诊断中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(7): 635-644. |
| [5] | 许飞,王慧君,马端. 表观遗传学——耳聋研究的新视野[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(3): 253-259. |
| [6] | 卜枫啸,彭聿,王树辉,潘琼,胡正茂,龚惠勇,张静,邬玲仟,梁德生,潘乾,冯永,夏昆,夏家辉,. 定位于5q31-5q32的DFNA52的20个候选基因的突变筛查[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(1): 43-49. |
| [7] | 陈静,杨淑芝,刘军,韩冰,王国建,张昕,康东洋,戴朴,杨伟炎,袁慧军. Waardenburg综合征Ⅱ型患者MITF基因突变分析[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(4): 433-438. |
| [8] | 任新鸾,李联祥,韩淑萍,蔡杰,张宏义,马常义. 家族性支气管哮喘的遗传方式分析[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(9): 1067-1070. |
| [9] | 王秋菊,杨伟炎,吴子明,郭维维,李庆忠,仇春燕. X连锁隐性遗传聋哑(deaf-mute)家系的遗传学特征分析[J]. 遗传, 2004, 26(5): 579-583. |
| [10] | 钱得胜. 情感性障碍的遗传异质性研究啊[J]. 遗传, 1994, 16(4): 1-4. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
