遗传 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 144-155.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-302
收稿日期:2022-10-13
修回日期:2023-01-30
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2023-02-03
作者简介:王澜,硕士,研究实习员,研究方向:代谢生物钟与心血管疾病。E-mail: 基金资助:
Lan Wang( ), Fan Zeng, Rongfeng Huang, Shu Lin, Zhihui Zhang, Min-Dian Li(
), Fan Zeng, Rongfeng Huang, Shu Lin, Zhihui Zhang, Min-Dian Li( )
)
Received:2022-10-13
Revised:2023-01-30
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2023-02-03
Supported by:摘要:
脂肪组织的神经支配与调节在能量代谢稳态的维持中发挥重要作用。神经肽Y (neuropeptide Y, NPY)及其脂肪细胞受体信号通路促进高脂饮食诱导的肥胖,其中NPY受体1 (NPY receptor Y1, NPY1R)与受体2(NPY2R)是主要的NPY外周受体。NPY受体4 (NPY4R)也在脂肪组织表达,然而尚不清楚其是否参与肥胖的发生发展机制。本研究建立了NPY及其受体的免疫荧光成像技术和脂肪细胞回复性表达Npy4r小鼠。根据对不同部位脂肪组织的荧光显微术观察,发现NPY在肩胛间棕色脂肪和皮下脂肪的围绕血管区域以点状形式表达,NPY系统的各受体在脂肪组织的空间分布上具有明显的组织特异性:NPY1R在棕色脂肪、主动脉周围脂肪和性腺脂肪较为富集,NPY2R在棕色脂肪和主动脉周围脂肪较为富集,NPY4R在棕色脂肪与性腺脂肪较为富集。继而通过比较脂肪细胞回复性表达Npy4r小鼠与全身Npy4r基因静默小鼠在高脂喂食下的体重与糖代谢,发现脂肪细胞Npy4r促进高脂饮食诱导的肥胖(P < 0.0001)。本研究明确了NPY及其受体NPY1R、NPY2R和NPY4R在不同部位脂肪组织的蛋白水平与分布,进而用脂肪细胞特异性地回复表达小鼠模型揭示脂肪细胞Npy4r具有促进高脂饮食诱导肥胖的作用。
王澜, 曾帆, 黄荣凤, 林树, 张志辉, 李旻典. 脂肪细胞Npy4r促进高脂饮食诱导肥胖[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(2): 144-155.
Lan Wang, Fan Zeng, Rongfeng Huang, Shu Lin, Zhihui Zhang, Min-Dian Li. Adipocyte reconstitution of Npy4r gene in Npy4r silenced mice promotes diet-induced obesity[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(2): 144-155.
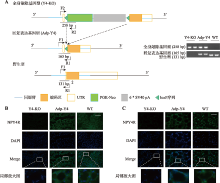
图5
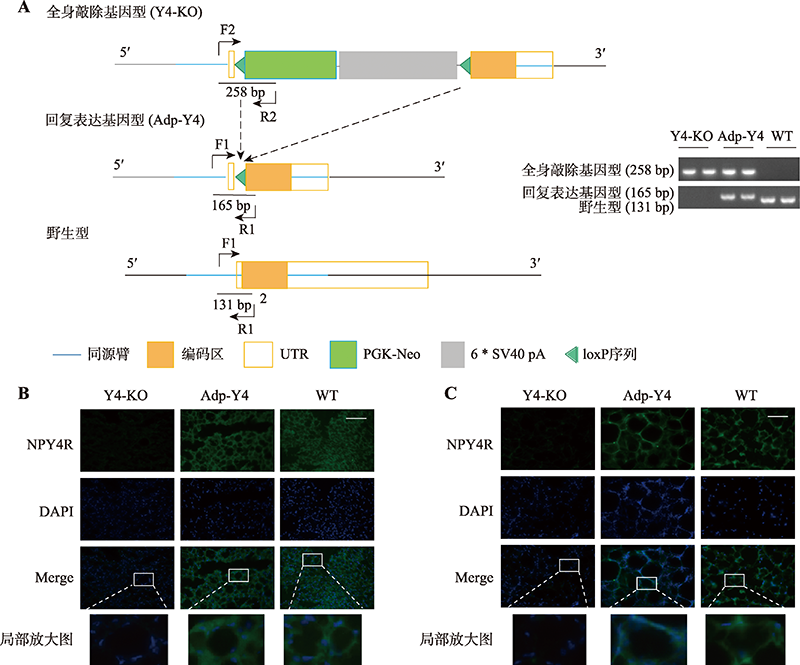
脂肪细胞Npy4r基因回复表达小鼠的构建 A:左图为Y4-KO小鼠以及脂肪细胞回复表达小鼠Adp-Y4构建原理;右图为PCR分析小鼠皮下脂肪组织DNA鉴定Y4-KO小鼠(Y4-KO,258 bp)、脂肪细胞特异性突变小鼠未发生Cre-loxP位点剪接的细胞(Y4-KO,258 bp)和发生Cre-loxP位点剪接的脂肪细胞(Adp-Y4,165 bp)、野生型小鼠(非同窝小鼠,Wild-type,WT,131 bp)。B和C:Y4-KO、Adp-Y4和WT小鼠的脂肪组织NPY4R免疫荧光图。肩胛间棕色脂肪(B)和性腺脂肪(C),WT小鼠为非高脂喂养的非同窝小鼠,EGFP标记显示为绿色;DAPI 染细胞核,显示为蓝色;曝光时间200 ms,标尺:100 μm。"
| [1] |
Cypess AM. Reassessing human adipose tissue. N Engl J Med, 2022, 386(8): 768-779.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2032804 |
| [2] |
Zeng F, Wang L, Wan XQ, Huang RF, Zhang ZH, Li MD. Targeting leptin-positive adipocytes by expressing the Cre recombinase transgene under the endogenous leptin gene. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 950-957.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-236 pmid: 36384730 |
|
曾帆, 王澜, 万小勤, 黄荣凤, 张志辉, 李旻典. 瘦素基因启动的新型脂肪细胞表达Cre工具小鼠的构建. 遗传, 2022, 44(10): 950-957.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-236 pmid: 36384730 |
|
| [3] |
Duerrschmid C, He YL, Wang CM, Li C, Bournat JC, Romere C, Saha PK, Lee ME, Phillips KJ, Jain M, Jia P, Zhao ZM, Farias M, Wu Q, Milewicz DM, Sutton VR, Moore DD, Butte NF, Krashes MJ, Xu Y, Chopra AR. Asprosin is a centrally acting orexigenic hormone. Nat Med, 2017, 23(12): 1444-1453.
doi: 10.1038/nm.4432 pmid: 29106398 |
| [4] |
Li MD, Vera NB, Yang YF, Zhang BC, Ni WM, Ziso- Qejvanaj E, Ding S, Zhang KS, Yin RN, Wang SM, Zhou X, Fang EX, Xu T, Erion DM, Yang XY. Adipocyte OGT governs diet-induced hyperphagia and obesity. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 5103.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07461-x |
| [5] |
Zeng WW, Pirzgalska RM, Pereira MMA, Kubasova N, Barateiro A, Seixas E, Lu YH, Kozlova A, Voss H, Martins GG, Friedman JM, Domingos AI. Sympathetic neuro- adipose connections mediate leptin-driven lipolysis. Cell, 2015, 163(1): 84-94.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.055 |
| [6] |
Chi JY, Wu ZH, Choi CHJ, Nguyen L, Tegegne S, Ackerman SE, Crane A, Marchildon F, Tessier-Lavigne M, Cohen P. Three-Dimensional adipose tissue imaging reveals regional variation in beige fat biogenesis and PRDM16-dependent sympathetic neurite density. Cell Metab, 2018, 27(1): 226-236.e3.
doi: S1550-4131(17)30724-6 pmid: 29320703 |
| [7] |
Jiang HC, Ding XF, Cao Y, Wang HH, Zeng WW. Dense intra-adipose sympathetic arborizations are essential for cold-induced beiging of mouse white adipose tissue. Cell Metab, 2017, 26(4): 686-692.e3.
doi: S1550-4131(17)30501-6 pmid: 28918935 |
| [8] |
Zeng X, Ye MC, Resch JM, Jedrychowski MP, Hu B, Lowell BB, Ginty DD, Spiegelman BM. Innervation of thermogenic adipose tissue via a calsyntenin 3beta-S100b axis. Nature, 2019, 569(7755): 229-235.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1156-9 |
| [9] |
Wang Y, Leung VH, Zhang YX, Nudell VS, Loud M, Servin-Vences MR, Yang D, Wang K, Moya-Garzon MD, Li VL, Long JZ, Patapoutian A, Ye L. The role of somatosensory innervation of adipose tissues. Nature, 2022, 609(7927): 569-574.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05137-7 |
| [10] |
Myers MG Jr, Affinati AH, Richardson N, Schwartz MW. Central nervous system regulation of organismal energy and glucose homeostasis. Nat Metab, 2021, 3(6): 737-750.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00408-5 pmid: 34158655 |
| [11] |
Rossi MA, Stuber GD. Overlapping brain circuits for homeostatic and hedonic feeding. Cell Metab, 2018, 27(1): 42-56.
doi: S1550-4131(17)30609-5 pmid: 29107504 |
| [12] |
Loh K, Herzog H, Shi YC. Regulation of energy homeostasis by the NPY system. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 26(3): 125-135.
doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.01.003 |
| [13] |
Yan CX, Zeng TS, Lee KL, Nobis M, Loh K, Gou LN, Xia ZF, Gao ZM, Bensellam M, Hughes W, Lau J, Zhang L, Ip CK, Enriquez R, Gao H, Wang QP, Wu Q, Haigh JJ, Laybutt DR, Timpson P, Herzog H, Shi YC. Peripheral- specific Y1 receptor antagonism increases thermogenesis and protects against diet-induced obesity. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2622.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22925-3 |
| [14] |
Kuo LE, Kitlinska JB, Tilan JU, Li LJ, Baker SB, Johnson MD, Lee EW, Burnett MS, Fricke ST, Kvetnansky R, Herzog H, Zukowska Z. Neuropeptide Y acts directly in the periphery on fat tissue and mediates stress-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nat Med, 2007, 13(7): 803-811.
doi: 10.1038/nm1611 pmid: 17603492 |
| [15] |
Shi YC, Lin S, Castillo L, Aljanova A, Enriquez RF, Nguyen AD, Baldock PA, Zhang L, Bijker MS, Macia L, Yulyaningsih E, Zhang H, Lau J, Sainsbury A, Herzog H. Peripheral-specific y 2 receptor knockdown protects mice from high-fat diet-induced obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2011, 19(11): 2137-2148.
doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.99 |
| [16] |
Rangwala SM, D'Aquino K, Zhang YM, Bader L, Edwards W, Zheng SM, Eckardt A, Lacombe A, Pick R, Moreno V, Kang LJ, Jian WY, Arnoult E, Case M, Jenkinson C, Chi E, Swanson RV, Kievit P, Grove K, Macielag M, Erion MD, SinhaRoy R, Leonard JN. A long-acting PYY(3-36) analog mediates robust anorectic efficacy with minimal emesis in nonhuman primates. Cell Metab, 2019, 29(4): 837-843.e5.
doi: S1550-4131(19)30017-8 pmid: 30773465 |
| [17] |
Sainsbury A, Schwarzer C, Couzens M, Jenkins A, Oakes SR, Ormandy CJ, Herzog H. Y4 receptor knockout rescues fertility in ob/ob mice. Genes Dev, 2002, 16(9): 1077-1088.
doi: 10.1101/gad.979102 |
| [18] |
Lin S, Shi YC, Yulyaningsih E, Aljanova A, Zhang L, Macia L, Nguyen AD, Lin EJ, During MJ, Herzog H, Sainsbury A. Critical role of arcuate Y4 receptors and the melanocortin system in pancreatic polypeptide-induced reduction in food intake in mice. PLoS One, 2009, 4(12): e8488.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008488 |
| [19] |
Sainsbury A, Bergen HT, Boey D, Bamming D, Cooney GJ, Lin S, Couzens M, Stroth N, Lee NJ, Lindner D, Singewald N, Karl T, Duffy L, Enriquez R, Slack K, Sperk G, Herzog H. Y2Y 4 receptor double knockout protects against obesity due to a high-fat diet or Y 1 receptor deficiency in mice. Diabetes, 2006, 55(1): 19-26.
pmid: 16380472 |
| [20] |
Eguchi J, Wang X, Yu ST, Kershaw EE, Chiu PC, Dushay J, Estall JL, Klein U, Maratos-Flier E, Rosen ED.Transcriptional control of adipose lipid handling by IRF4. Cell Metab, 2011, 13(3): 249-259.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.005 pmid: 21356515 |
| [21] |
Kong XX, Banks A, Liu TM, Kazak L, Rao RR, Cohen P, Wang X, Yu ST, Lo JC, Tseng YH, Cypess AM, Xue RD, Kleiner S, Kang S, Spiegelman BM, Rosen ED. IRF4 is a key thermogenic transcriptional partner of PGC-1alpha. Cell, 2014, 158(1): 69-83.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.049 |
| [22] |
Virtue S, Vidal-Puig A. GTTs and ITTs in mice: simple tests, complex answers. Nat Metab, 2021, 3(7): 883-886.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00414-7 pmid: 34117483 |
| [23] |
Shin H, Ma YY, Chanturiya T, Cao Q, Wang YL, Kadegowda AKG, Jackson R, Rumore D, Xue BZ, Shi H, Gavrilova O, Yu LQ. Lipolysis in brown adipocytes is not essential for cold-induced thermogenesis in mice. Cell Metab, 2017, 26(5): 764-777.e5.
doi: S1550-4131(17)30553-3 pmid: 28988822 |
| [24] | Zhao QW, Pan DN. Progress on the epigenetic regulation of adipose tissue thermogenesis. Hereditas (Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 867-880. |
| 赵清雯, 潘东宁. 表观遗传修饰对脂肪组织产热的调控进展. 遗传, 2022, 44(10): 867-880. | |
| [25] |
Tang Y, He Y, Li C, Mu WJ, Zou Y, Liu CH, Qian SW, Zhang FC, Pan JB, Wang YN, Huang HY, Pan DN, Yang PY, Mei J, Zeng R, Tang QQ. RPS3A positively regulates the mitochondrial function of human periaortic adipose tissue and is associated with coronary artery diseases. Cell Discov, 2018, 4: 52.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-018-0041-2 pmid: 30131868 |
| [26] | Koronowski KB, Kinouchi K, Welz PS, Smith JG, Zinna VM, Shi JJ, Samad M, Chen SW, Magnan CN, Kinchen JM, Li W, Baldi P, Benitah SA, Sassone-Corsi P. Defining the independence of the liver circadian clock. Cell, 2019, 177(6): 1448-1462.e14. |
| [27] |
Welz PS, Zinna VM, Symeonidi A, Koronowski KB, Kinouchi K, Smith JG, Guillén IM, Castellanos A, Furrow S, Aragón F, Crainiciuc G, Prats N, Caballero JM, Hidalgo A, Sassone-Corsi P, Benitah SA. BMAL1-driven tissue clocks respond independently to light to maintain homeostasis. Cell, 2019, 177(6): 1436-1447.e12.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.009 |
| [28] |
Tang TT, Tan QX, Han S, Diemar A, Löbner K, Wang HY, Schüß C, Behr V, Mörl K, Wang M, Chu XJ, Yi CY, Keller M, Kofoed J, Reedtz-Runge S, Kaiser A, Beck-Sickinger AG, Zhao Q, Wu B. Receptor-specific recognition of NPY peptides revealed by structures of NPY receptors. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(18): eabm1232.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm1232 |
| [29] |
Wang L, Pydi SP, Zhu L, Barella LF, Cui YH, Gavrilova O, Bence KK, Vernochet C, Wess J. Adipocyte G(i) signaling is essential for maintaining whole-body glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 2995.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16756-x pmid: 32532984 |
| [1] | 曾帆, 王澜, 万小勤, 黄荣凤, 张志辉, 李旻典. 瘦素基因启动的新型脂肪细胞表达Cre工具小鼠的构建[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(10): 950-957. |
| [2] | 赵清雯, 潘东宁. 表观遗传修饰对脂肪组织产热的调控进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(10): 867-880. |
| [3] | 杜坤, 毛初阳, 任安勇, 吴雪梅, 李庆玲, 陈婷婷, 陈仕毅, 赖松家. 家兔前体脂肪细胞分化不同时期基因表达谱分析[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(3): 309-320. |
| [4] | 黄鑫,陈永强,徐国良,彭淑红. 脂肪组织DNA甲基化与糖尿病和肥胖的发生发展[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(2): 98-110. |
| [5] | 李欢, 冯晋川, 李贵林, 王讯, 李明洲, 刘海峰. Lnc-RAP3对小鼠3T3-L1前脂肪细胞分化的影响[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(9): 758-766. |
| [6] | 张潇飞,宋鹤,刘静,张文建,闫晓红,李辉,王宁. 鸡miR-17-92基因簇靶基因ZFPM2的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(4): 333-345. |
| [7] | 张君, 张望强, 丁毓磊, 许彭, 王婷婷, 徐文静, 陆环, 刘宗智, 谢建新. 腹部脂肪组织APN基因DNA甲基化及mRNA表达与维吾尔族T2DM的相关性[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(3): 269-275. |
| [8] | 郭云涛, 苗向阳. 调控褐色脂肪细胞分化的microRNAs[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(3): 240-249. |
| [9] | 张进威, 罗毅, 王宇豪, 何刘军, 李明洲, 王讯. MicroRNA调控动物脂肪细胞分化研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(12): 1175-1184. |
| [10] | 王丽,那威,王宇祥,王彦博,王宁,王启贵,李玉茂,李辉. 鸡PPARγ基因的表达特性及其对脂肪细胞增殖分化的影响[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(4): 454-464. |
| [11] | 郭云学,莫德林,陈瑶生,张悦,张云,肖书奇,刘小红. PI3K/AKT抑制剂渥曼青霉素对猪前体脂肪细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(10): 1282-1290. |
| [12] | 郭玉姣,唐国庆,李学伟,朱砺,李明洲. 猪脂肪组织中IGF2和IGFBP3基因表达的发育性变化及其品种差异[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(5): 602-606. |
| [13] | 白亮,庞卫军,杨公社. Sirt1: 一种新的脂肪细胞和肌细胞调控因子[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(11): 1462-1466. |
| [14] | 王辰,王沥,杨泽. 蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸酶1B(PTP1B)与2型糖尿病及肥胖的关系[J]. 遗传, 2004, 26(6): 941-946. |
| [15] | 孙玉茹,杨泽. 核转录因子PPARγ2的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2003, 25(6): 713-717. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
