遗传 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 46-62.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-224
陈昱颖1,2( ), 张倩3(
), 张倩3( ), 桂梦会4, 冯岚2, 曹鹏博2, 周钢桥1,2,4(
), 桂梦会4, 冯岚2, 曹鹏博2, 周钢桥1,2,4( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-23
修回日期:2023-11-08
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-12-05
通讯作者:
周钢桥
E-mail:529897537@qq.com;15111174004@163.com;zhougq114@126.com
作者简介:陈昱颖,硕士研究生,专业方向:基础医学。E-mail: 基金资助:
Yuying Chen1,2( ), Qian Zhang3(
), Qian Zhang3( ), Menghui Gui4, Lan Feng2, Pengbo Cao2, Gangqiao Zhou1,2,4(
), Menghui Gui4, Lan Feng2, Pengbo Cao2, Gangqiao Zhou1,2,4( )
)
Received:2023-08-23
Revised:2023-11-08
Published:2024-01-20
Online:2023-12-05
Contact:
Gangqiao Zhou
E-mail:529897537@qq.com;15111174004@163.com;zhougq114@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)是原发性肝癌的主要类型,是一种早期无明显症状、易发生转移、存活率低的恶性肿瘤。多聚嘧啶区结合蛋白1 (polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1,PTBP1)是一种重要的RNA结合蛋白,可诱导促癌剪接事件的发生。虽然PTBP1在肝癌细胞中的促癌功能已被证实,但是其介导的促癌可变剪接事件及作用机制尚未得到完全解析。本文利用免疫共沉淀联合质谱分析发现与PTBP1结合的蛋白复合体显著富集于编码成纤维细胞生长因子受体2 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 2,FGFR2)的基因可变剪接调控过程。通过RNA免疫共沉淀和定量PCR实验,证实PTBP1可显著下调肝癌细胞中FGFR2-IIIb异构体的水平,上调FGFR2-IIIc异构体的水平,促进FGFR2-IIIb向FGFR2-IIIc的异构体转换。随后,通过CCK-8、transwell和平板克隆实验,在肝癌细胞系HepG2和Huh7中评价了FGFR2-IIIb和FGFR2-IIIc的肿瘤生物学功能。结果显示FGFR2-IIIb发挥抑癌功能,而FGFR2-IIIc发挥促癌功能。机制研究证实,FGFR2-IIIb向FGFR2-IIIc异构体的转换显著促进肝癌细胞的上皮-间充质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transformation,EMT)及FGFR下游ERK和AKT信号通路的活化。本研究揭示了PTBP1促进肝癌进展的分子调控机制,为肝癌的防治提供了新的理论依据。
陈昱颖, 张倩, 桂梦会, 冯岚, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. PTBP1通过调控FGFR2的可变剪接促进肝癌的发展[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(1): 46-62.
Yuying Chen, Qian Zhang, Menghui Gui, Lan Feng, Pengbo Cao, Gangqiao Zhou. PTBP1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing the oncogenic splicing switch of FGFR2[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(1): 46-62.
表1
与PTBP1相互作用的蛋白质所参与的信号通路及生物学过程"
| 显著富集的信号通路及生物学 过程 | 富集的蛋白质数量 | 错误发现率 | 信号通路显著富集的蛋白质 |
|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA splicing-major pathway | 23 | 9.12E-20 | CPSF7、CSTF1、EIF4A3、FUS、HNRNPA1、HNRNPC、HNRNPD、HNRNPH2、HSPA8、NUDT21、PCBP1、PCBP2、POLR2A、POLR2B、PRPF19、PTBP1、PUF60、SF1、SF3B4、SNRNP40、SNW1、U2AF2、YBX1 |
| Processing of capped intron- containing pre-mRNA | 25 | 9.12E-20 | CPSF7、CSTF1、EIF4A3、FUS、HNRNPA1、HNRNPC、HNRNPD、HNRNPH2、HSPA8、NUDT21、NXF1、PCBP1、PCBP2、POLDIP3、POLR2A、POLR2B、PRPF19、PTBP1、PUF60、SF1、SF3B4、SNRNP40SNW1、U2AF2、YBX1 |
| rRNA processing in the nucleus and cytosol | 15 | 6.05E-10 | DDX21、EBNA1BP2、FBL、GNL3、NOP2、PES1、RPL10、RPL18、RPL28、RPL3、RPL36A、RPL4、RPL6、RPLP0、RRP1 |
| Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol | 14 | 2.71E-09 | DDX21、EBNA1BP2、FBL、GNL3、PES1、RPL10、RPL18、RPL28、RPL3、RPL36A、RPL4、RPL6、RPLP0、RRP1 |
| FGFR2 alternative splicing | 7 | 1.02E-07 | HNRNPA1、POLR2A、POLR2B、PTBP1、RBFOX2、TIA1、TIAL1 |
| L13a-mediated translational silencing of ceruloplasmin expression | 10 | 2.93E-07 | EIF2S2、EIF2S3、RPL10、RPL18、RPL28、RPL3、RPL36A、RPL4、RPL6、RPLP0 |
| GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit | 10 | 2.93E-07 | EIF2S2、EIF2S3、RPL10、RPL18、RPL28、RPL3、RPL36A、RPL4、RPL6、RPLP0 |
| Influenza infection | 11 | 3.79E-07 | EIF2AK2、POLR2A、POLR2B、RPL10、RPL18、RPL28、RPL3、RPL36A、RPL4、RPL6、RPLP0 |
| Influenza viral RNA transcription and replication | 10 | 9.28E-07 | POLR2A、POLR2B、RPL10、RPL18、RPL28、RPL3、RPL36A、RPL4、RPL6、RPLP0 |
图2
FGFR2-IIIb抑制肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭 A:在HepG2和MHCC97H细胞中敲低FGFR2-IIIb后通过Western blot实验检测其表达水平;B:通过CCK-8实验检测敲低FGFR2-IIIb对HepG2和MHCC97H细胞生长能力的影响;C:通过平板克隆形成实验检测敲低FGFR2-IIIb对HepG2和MHCC97H细胞克隆形成能力的影响;D:通过transwell实验检测敲低FGFR2-IIIb对HepG2和MHCC97H细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响;E:在HepG2和Huh7细胞中过表达FGFR2-IIIb后通过Western blot实验检测其表达水平;F:通过CCK-8实验检测过表达FGFR2-IIIb对HepG2和Huh7细胞生长能力的影响;G:通过克隆形成实验检测过表达FGFR2-IIIb对HepG2和Huh7细胞克隆形成能力的影响;H:通过transwell实验检测过表达FGFR2-IIIb对HepG2和Huh7细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响。所有数据均以平均值±标准差来表示,每组实验设置3个重复孔。组间差异采用Student′s t检验确定显著性;ns表示P>0.05,*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01,***表示P<0.001。"
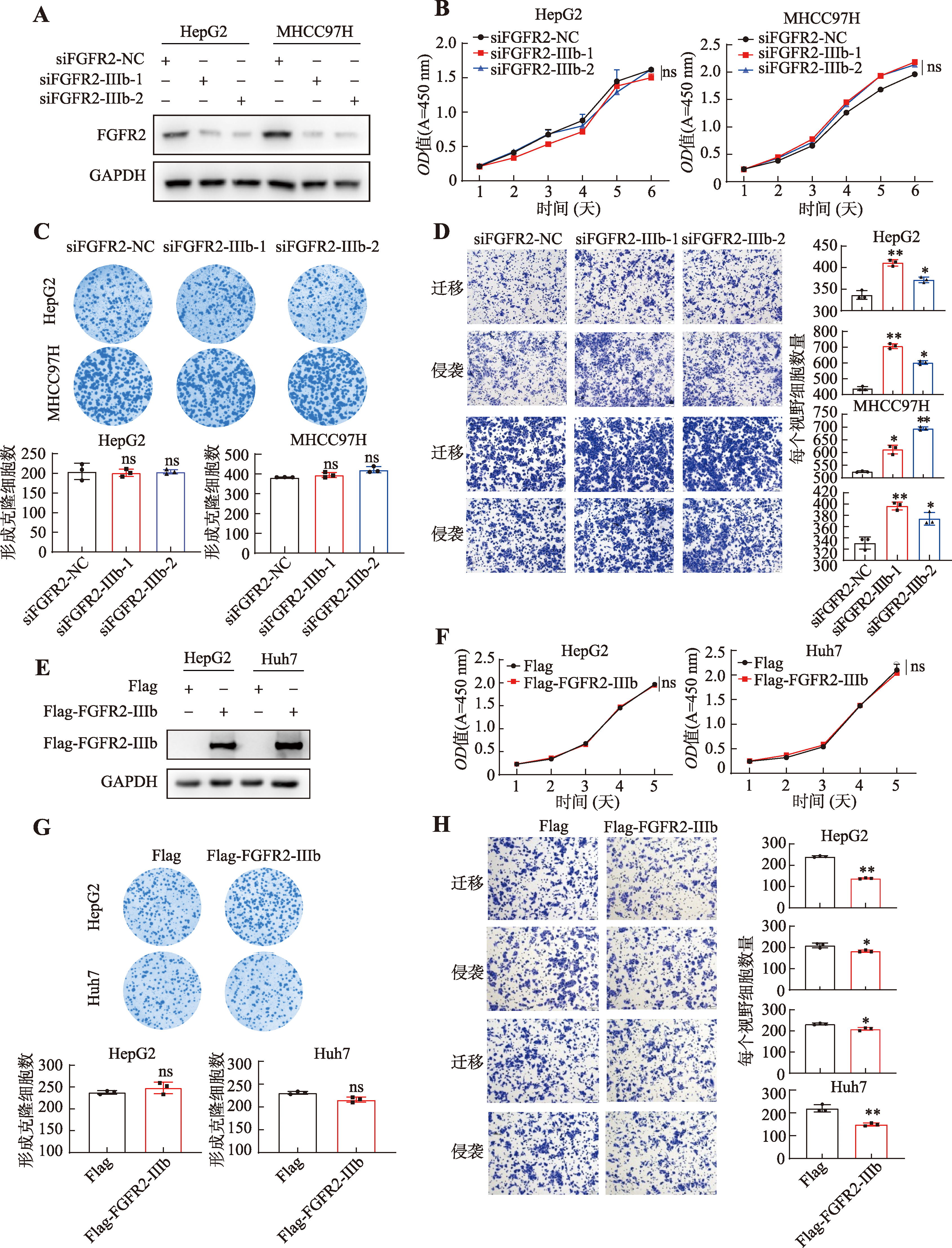
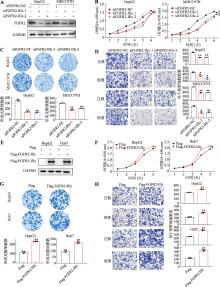
图3
FGFR2-IIIc促进肝癌细胞的生长、迁移和侵袭 A:在HepG2和MHCC97H细胞中敲低FGFR2-IIIc后通过Western blot实验检测其表达水平;B:通过CCK-8实验检测敲低FGFR2-IIIc对HepG2和MHCC97H细胞生长能力的影响;C:通过平板克隆形成实验检测敲低FGFR2-IIIc对HepG2和MHCC97H细胞克隆形成能力的影响;D:通过transwell实验检测敲低FGFR2-IIIc对HepG2和MHCC97H细胞迁移、侵袭能力的影响;E:在HepG2和Huh7细胞中过表达FGFR2-IIIc后通过Western blot实验检测其表达水平;F:通过CCK-8实验检测过表达FGFR2-IIIc对HepG2和Huh7细胞生长能力的影响;G:通过平板克隆形成实验检测过表达FGFR2-IIIc对HepG2和Huh7细胞克隆形成能力的影响;H:通过transwell实验检测过表达FGFR2-IIIc对HepG2和Huh7细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响。所有数据均以平均值±标准差来表示,每组实验设置3个重复孔。组间差异采用Student′s t检验确定显著性;*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01,***表示P<0.001。"

图4
FGFR2-IIIb/IIIc异构体转化对肝癌细胞中EMT标志分子表达水平的影响 A:通过qRT-PCR实验检测HepG2和MHCC97H细胞中敲低FGFR2-IIIb对上皮细胞标记分子(CDH1和KRT19)以及间充质细胞标记分子(CDH2和VIM)表达水平的影响;B:通过Western blot实验检测HepG2和MHCC97H细胞中敲低FGFR2-IIIb对上皮细胞标记分子CDH1以及间充质细胞标记分子(CDH2和VIM)表达水平的影响;C:通过qRT-PCR实验检测HepG2和MHCC97H细胞中敲低FGFR2-IIIc对EMT标志分子表达水平的影响;D:通过Western blot实验检测HepG2和MHCC97H细胞中敲低FGFR2-IIIc对EMT标志分子表达水平的影响;E:通过qRT-PCR检测HepG2和Huh7细胞中过表达FGFR2-IIIb对EMT标志分子表达水平的影响;F:通过Western blot检测HepG2和Huh7细胞中过表达FGFR2-IIIb对EMT标志分子表达水平的影响;G:通过qRT-PCR检测HepG2和Huh7细胞中过表达FGFR2-IIIc对EMT标志分子表达水平的影响;H:通过Western blot检测HepG2和Huh7细胞中过表达FGFR2-IIIc对EMT标志分子表达水平的影响。所有数据均以平均值±标准差来表示,每组实验设置3个重复孔。组间差异采用Student′s t检验确定显著性;ns表示P>0.05,*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01,***表示P<0.001。"
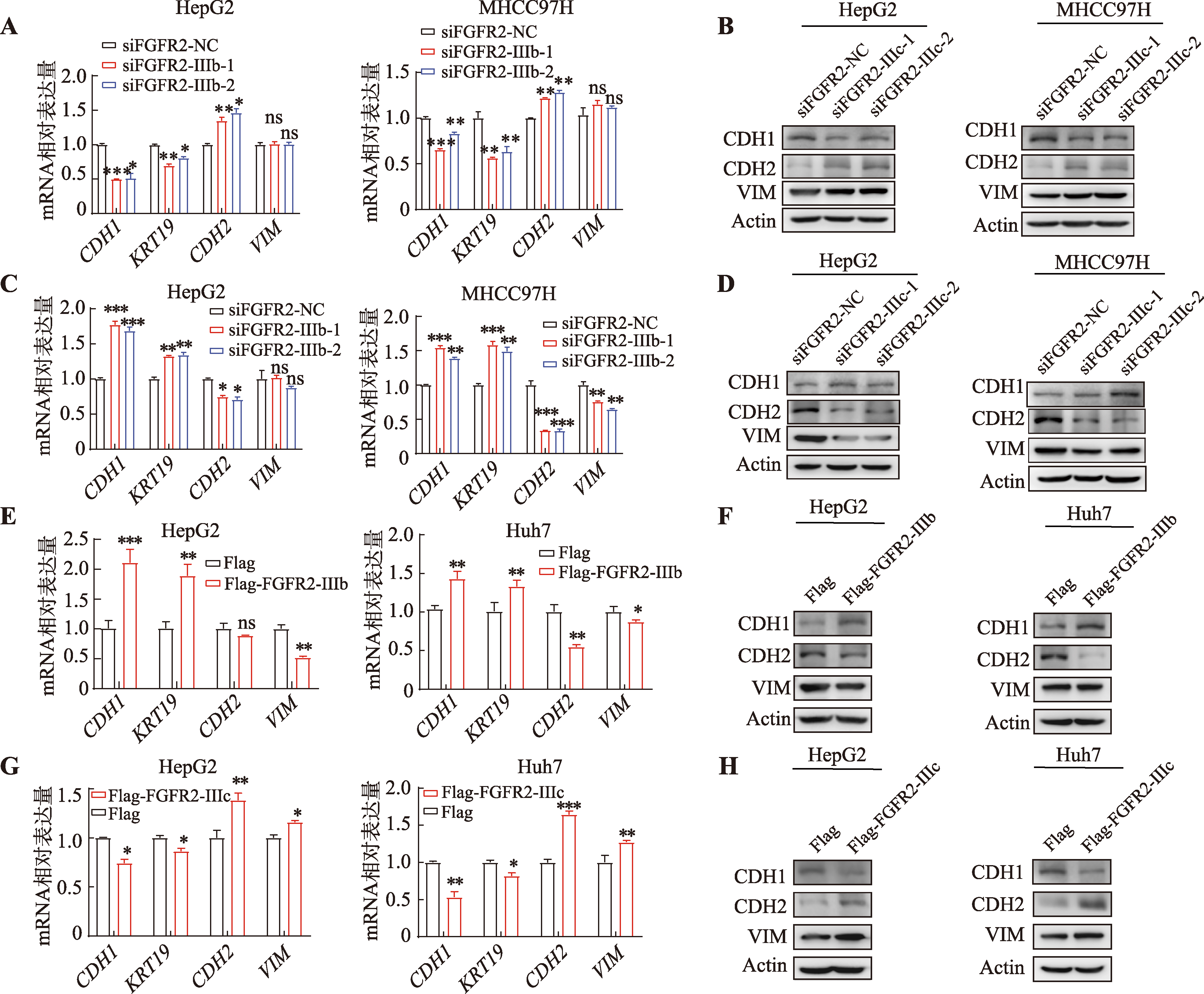
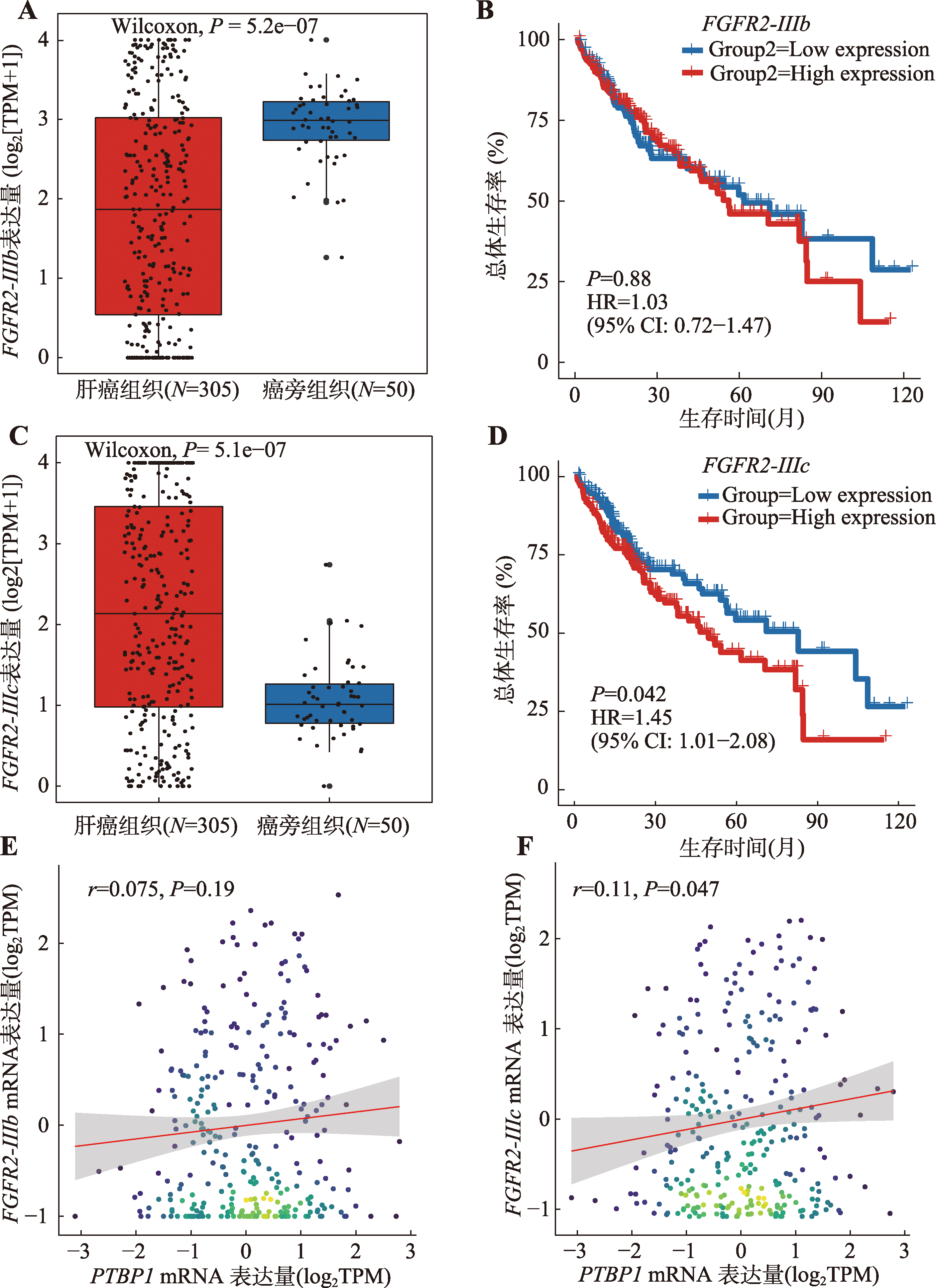
图6
FGFR2-IIIb/IIIc在肝癌中的异构体比例变化及预后价值 A:FGFR2-IIIb在TCGA肝癌组织和癌旁组织中的表达水平,采用秩和检验计算组间差异;B:FGFR2-IIIb高表达及低表达(以中值分组)的肝癌患者的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线图;C:FGFR2-IIIc在TCGA肝癌组织和癌旁组织中的表达水平,采用秩和检验计算组间差异;D:FGFR2-IIIc高表达及低表达(以中值分组)高表达及低表达(以中值分组)的肝癌患者的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线图。使用survival包绘制Kaplan-Meier生存曲线,采用Cox比例风险回归模型进行单变量生存分析,计算HR和P值,P<0.05被认为有统计学意义。E:TCGA-LIHC数据集中PTBP1 mRNA(TPM:transcript per million)表达水平与FGFR2-IIIb mRNA(TPM)表达水平的相关性散点图;F:TCGA-LIHC数据集中PTBP1 mRNA(TPM)表达水平与FGFR2-IIIc mRNA(TPM)表达水平的相关性散点图。采用Pearson方法计算相关性系数,P<0.05被认为有统计学意义。"
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v71.3 |
| [2] | Qiu HB, Cao SM, Xu RH. Cancer incidence, mortality, and burden in China: a time-trend analysis and comparison with the United States and United Kingdom based on the global epidemiological data released in 2020. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2021, 41(10): 1037-1048. |
| [3] |
Steyerberg EW, Vergouwe Y. Towards better clinical prediction models: seven steps for development and an ABCD for validation. Eur Heart J, 2014, 35(29): 1925-1931.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu207 pmid: 24898551 |
| [4] |
Guan Z, Cheng W, Huang D, Wei A. High MYBL2 expression and transcription regulatory activity is associated with poor overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Res Transl Med, 2018, 66(1): 27-32.
doi: S2452-3186(17)30049-1 pmid: 29274707 |
| [5] | Tang R, Wu JC, Zheng LM, Li ZR, Zhou KL, Zhang ZS, Xu DF, Chen C. Long noncoding RNA RUSC1-AS-N indicates poor prognosis and increases cell viability in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(2): 388-396. |
| [6] |
Cheung HC, Hai T, Zhu W, Baggerly KA, Tsavachidis S, Krahe R, Cote GJ. Splicing factors PTBP1 and PTBP2 promote proliferation and migration of glioma cell lines. Brain, 2009, 132(Pt 8): 2277-2288.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awp153 pmid: 19506066 |
| [7] |
Takahashi H, Nishimura J, Kagawa Y, Kano Y, Takahashi Y, Wu X, Hiraki M, Hamabe A, Konno M, Haraguchi N, Takemasa I, Mizushima T, Ishii M, Mimori K, Ishii H, Doki Y, Mori M, Yamamoto H. Significance of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 expression in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther, 2015, 14(7): 1705-1716.
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0142 pmid: 25904505 |
| [8] |
Ferrarese R, Harsh GR 4th, Yadav AK, Bug E, Maticzka D, Reichardt W, Dombrowski SM, Miller TE, Masilamani AP, Dai FP, Kim H, Hadler M, Scholtens DM, Yu ILY, Beck J, Srinivasasainagendra V, Costa F, Baxan N, Pfeifer D, von Elverfeldt D, Backofen R, Weyerbrock A, Duarte CW, He XL, Prinz M, Chandler JP, Vogel H, Chakravarti A, Rich JN, Carro MS, Bredel M,. Lineage-specific splicing of a brain-enriched alternative exon promotes glioblastoma progression. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(7): 2861-2876.
doi: 10.1172/JCI68836 pmid: 24865424 |
| [9] |
Kang H, Heo S, Shin JJ, Ji E, Tak H, Ahn S, Lee KJ, Lee EK, Kim W. A miR-194/PTBP1/CCND3 axis regulates tumor growth in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pathol, 2019, 249(3): 395-408.
doi: 10.1002/path.v249.3 |
| [10] |
Wu DG, He XT, Wang WJ, Hu XT, Wang KF, Wang MH. Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 induces proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and stemness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via post-transcriptional regulation of BMI1 and CTNNB1. Mol Oncol, 2020, 14(9): 2332-2351.
doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12683 pmid: 32239639 |
| [11] |
Li T, Jin XZ, Dong JR, Deng HB. Long noncoding RNA ARSR is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. J Gene Med, 2020, 22(10): e3241.
doi: 10.1002/jgm.v22.10 |
| [12] |
Wei L, Wang XW, Lv LY, Liu JB, Xing HX, Song YM, Xie MY, Lei TS, Zhang NS, Yang M. The emerging role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 147.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1086-z pmid: 31651347 |
| [13] |
Gao G, Dai C, Yu X, Yin XB, Zhou F. Long noncoding RNA LINC00324 exerts protumorigenic effects on liver cancer stem cells by upregulating fas ligand via PU box binding protein. FASEB J, 2020, 34(4): 5800-5817.
doi: 10.1096/fj.201902705RR pmid: 32128906 |
| [14] |
Khadirnaikar S, Chatterjee A, Kumar P, Shukla S. A greedy algorithm-based stem cell lncRNA signature identifies a novel subgroup of lung adenocarcinoma patients with poor pognosis. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 1203.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01203 pmid: 32850350 |
| [15] |
Lu GM, Rong YX, Liang ZJ, Hunag DL, Ma YF, Luo ZZ, Wu FX, Liu XH, Liu Y, Mo S, Qi ZQ, Li HM. Multiomics global landscape of stemness-related gene clusters in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 310.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01823-3 |
| [16] |
Sun LK, Wang L, Chen TX, Shi Y, Yao BW, Liu ZK, Wang YF, Li Q, Liu RK, Niu YS, Tu KS, Liu QG. LncRNA RUNX1-IT1 which is downregulated by hypoxia-driven histone deacetylase 3 represses proliferation and cancer stem-like properties in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(2): 95.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2274-x pmid: 32024815 |
| [17] |
Shen LH, Lei SJ, Zhang B, Li SG, Huang LY, Czachor A, Breitzig M, Gao YM, Huang MY, Mo XM, Zheng Q, Sun HX, Wang F. Skipping of exon 10 in Axl pre-mRNA regulated by PTBP1 mediates invasion and metastasis process of liver cancer cells. Theranostics, 2020, 10(13): 5719-5735.
doi: 10.7150/thno.42010 |
| [18] |
He ZT, Ni QH, Li XC, Zhao MY, Mo QG, Duo YS. PTBP1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating the skipping of exon 9 in NUMB pre-mRNA. Heliyon, 2023, 9(6): e17387.
doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17387 |
| [19] |
Guo JC, Yang YJ, Zheng JF, Zhang JQ, Guo M, Yang X, Jiang XL, Xiang L, Li Y, Ping H, Zhuo L. Silencing of long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway via the upregulation of HOXA11 and thereby inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and self-renewal of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells. Exp Mol Med, 2019, 51(11): 1-20.
doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0343-y pmid: 31704909 |
| [20] |
Amann T, Bataille F, Spruss T, Dettmer K, Wild P, Liedtke C, Mühlbauer M, Kiefer P, Oefner PJ, Trautwein C, Bosserhoff AK, Hellerbrand C. Reduced expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2IIIb in hepatocellular carcinoma induces a more aggressive growth. Am J Pathol, 2010, 176(3): 1433-1442.
doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090356 pmid: 20093481 |
| [21] |
Yang H, Jiang Z, Wang S, Zhao YB, Song XM, Xiao YF, Yang SM. Long non-coding small nucleolar RNA host genes in digestive cancers. Cancer Med, 2019, 8(18): 7693-7704.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.v8.18 |
| [22] |
Zhu QY, Yang HJ, Cheng P, Han Q. Bioinformatic analysis of the prognostic value of the lncRNAs encoding snoRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biofactors, 2019, 45(2): 244-252.
doi: 10.1002/biof.1478 pmid: 30537372 |
| [23] |
Adamczyk-Gruszka O, Horecka-Lewitowicz A, Gruszka J, Wawszczak-Kasza M, Strzelecka A, Lewitowicz P. FGFR-2 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial cancer. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(18): 5416.
doi: 10.3390/jcm11185416 |
| [24] |
Maehara O, Suda G, Natsuizaka M, Shigesawa T, Kanbe G, Kimura M, Sugiyama M, Mizokami M, Nakai M, Sho T, Morikawa K, Ogawa K, Ohashi S, Kagawa S, Kinugasa H, Naganuma S, Okubo N, Ohnishi S, Takeda H, Sakamoto N. FGFR2 maintains cancer cell differentiation via AKT signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, 22(5-6): 372-380.
doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.1939638 |
| [25] |
Czaplinska D, Turczyk L, Grudowska A, Mieszkowska M, Lipinska AD, Skladanowski AC, Zaczek AJ, Romanska HM, Sadej R. Phosphorylation of RSK2 at Tyr 529 by FGFR2-p38 enhances human mammary epithelial cells migration. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1843(11): 2461-2470.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.06.022 pmid: 25014166 |
| [26] |
Cai SY, Yang YM, Jia BH, Wu ZH, Zhang JG, Shen JX, Qiu GX. Transcriptome-wide sequencing reveals molecules and pathways involved in neurofibromatosis type I combined with spinal deformities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2020, 45(9): E489-E498.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003338 |
| [27] |
Chaffee BR, Hoang TV, Leonard MR, Bruney DG, Wagner BD, Dowd JR, Leone G, Ostrowski MC, Robinson ML. FGFR and PTEN signaling interact during lens development to regulate cell survival. Dev Biol, 2016, 410(2): 150-163.
doi: S0012-1606(15)30127-5 pmid: 26764128 |
| [28] |
Nagaraju GP., Dariya B, Kasa P, Peela S, El-Rayes BF. Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86(Pt 3): 622-632.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.07.017 |
| [29] |
Yang Y, Ren PW, Liu XF, Sun XY, Zhang CF, Du XJ, Xing BC. PPP1R26 drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression by controlling glycolysis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 101.
doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02302-8 pmid: 35292107 |
| [30] | Zhao JX, Wang F, Xu ZR, Fan YM. The epigenetic effect on pre-mRNA alternative splicing. Hereditas (Beijing), 2014, 36(3): 248-255. |
| 赵金璇, 王芳, 徐峥嵘, 范怡梅. 表观遗传调控pre-mRNA的选择性剪接. 遗传, 2014, 36(3): 248-255. | |
| [31] |
Liao RG, Jung J, Tchaicha J, Wilkerson MD, Sivachenko A, Beauchamp EM, Liu QS, Pugh TJ, Pedamallu CS, Hayes DN, Gray NS, Getz G, Wong KK, Haddad RI, Meyerson M, Hammerman PS. Inhibitor-sensitive FGFR2 and FGFR3 mutations in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(16): 5195-5205.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3950 pmid: 23786770 |
| [32] |
Taniguchi K, Sakai M, Sugito N, Kumazaki M, Shinohara H, Yamada N, Nakayama T, Ueda H, Nakagawa Y, Ito Y, Futamura M, Uno B, Otsuki Y, Yoshida K, Uchiyama K, Akao Y. PTBP1-associated microRNA-1 and -133b suppress the Warburg effect in colorectal tumors. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(14): 18940-18952.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8005 pmid: 26980745 |
| [33] |
Xie RH, Chen X, Chen ZY, Huang M, Dong W, Gu P, Zhang JT, Zhou QH, Dong W, Han JL, Wang XS, Li H, Huang J, Lin TX. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 promotes lymphatic metastasis and proliferation of bladder cancer via alternative splicing of MEIS2 and PKM. Cancer Lett, 2019, 449: 31-44.
doi: S0304-3835(19)30071-0 pmid: 30742945 |
| [34] |
Kuranaga Y, Sugito N, Shinohara H, Tsujino T, Taniguchi K, Komura K, Ito Y, Soga T, Akao Y. SRSF3, a splicer of the PKM gene, regulates cell growth and maintenance of cancer-specific energy metabolism in colon cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(10): 3012.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19103012 |
| [35] |
Miao H, Wu F, Li Y, Qin CY, Zhao YY, Xie MF, Dai HY, Yao H, Cai HY, Wang QH, Song X, Li L. MALAT1 modulates alternative splicing by cooperating with the splicing factors PTBP1 and PSF. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(51): eabq7289.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq7289 |
| [36] |
Teles SP, Oliveira P, Ferreira M, Carvalho J, Ferreira P, Oliveira C. Integrated analysis of structural variation and RNA expression of FGFR2 and its splicing modulator ESRP1 highlight the ESRP1(amp)-FGFR2(norm)-FGFR2- IIIc(high) axis in diffuse gastric cancer. Cancers (Basel), 2019, 12(1): 70.
doi: 10.3390/cancers12010070 |
| [37] |
Warzecha CC, Shen SH, Xing Y, Carstens RP. The epithelial splicing factors ESRP1 and ESRP2 positively and negatively regulate diverse types of alternative splicing events. RNA Biol, 2009, 6(5): 546-562.
doi: 10.4161/rna.6.5.9606 pmid: 19829082 |
| [38] |
Jones RB, Carstens RP, Luo Y, McKeehan WL. 5′- and 3′-terminal nucleotides in the FGFR2 ISAR splicing element core have overlapping roles in exon IIIb activation and exon IIIc repression. Nucleic Acids Res, 2001, 29(17): 3557-3565.
pmid: 11522825 |
| [39] |
Simarro M, Mauger D, Rhee K, Pujana MA, Kedersha NL, Yamasaki S, Cusick ME, Vidal M, Garcia-Blanco MA, Anderson P. Fas-activated serine/threonine phosphoprotein (FAST) is a regulator of alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(27): 11370-11375.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704964104 pmid: 17592127 |
| [40] |
Hovhannisyan RH, Warzecha CC, Carstens RP. Characterization of sequences and mechanisms through which ISE/ISS-3 regulates FGFR2 splicing. Nucleic Acids Res, 2006, 34(1): 373-385.
pmid: 16410617 |
| [41] |
Yoshino M, Ishiwata T, Watanabe M, Matsunobu T, Komine O, Ono Y, Yamamoto T, Fujii T, Matsumoto K, Tokunaga A, Naito Z. Expression and roles of keratinocyte growth factor and its receptor in esophageal cancer cells. Int J Oncol, 2007, 31(4): 721-728.
pmid: 17786302 |
| [42] |
Ishiwata T, Friess H, Büchler MW, Lopez ME, Korc M. Characterization of keratinocyte growth factor and receptor expression in human pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol, 1998, 153(1): 213-222.
doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65562-9 pmid: 9665482 |
| [43] |
Kurban G, Ishiwata T, Kudo M, Yokoyama M, Sugisaki Y, Naito Z. Expression of keratinocyte growth factor receptor (KGFR/FGFR2 IIIb) in human uterine cervical cancer. Oncol Rep, 2004, 11(5): 987-991.
pmid: 15069536 |
| [44] |
Yamayoshi T, Nagayasu T, Matsumoto K, Abo T, Hishikawa Y, Koji T. Expression of keratinocyte growth factor/fibroblast growth factor-7 and its receptor in human lung cancer: correlation with tumour proliferative activity and patient prognosis. J Pathol, 2004, 204(1): 110-118.
pmid: 15307144 |
| [45] |
Cho K, Ishiwata T, Uchida E, Nakazawa N, Korc M, Naito Z, Tajiri T. Enhanced expression of keratinocyte growth factor and its receptor correlates with venous invasion in pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol, 2007, 170(6): 1964-1974.
pmid: 17525264 |
| [46] |
Zhang Y, Wang H, Toratani S, Sato JD, Kan M, McKeehan WL, Okamoto T. Growth inhibition by keratinocyte growth factor receptor of human salivary adenocarcinoma cells through induction of differentiation and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98(20): 11336-11340.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.191377098 pmid: 11562460 |
| [47] |
Matsubara A, Kan M, Feng S, McKeehan WL.Inhibition of growth of malignant rat prostate tumor cells by restoration of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2. Cancer Res, 1998, 58(7): 1509-1514.
pmid: 9537256 |
| [48] |
Ricol D, Cappellen D, El Marjou A, Gil-Diez-de-Medina S, Girault JM, Yoshida T, Ferry G, Tucker G, Poupon MF, Chopin D, Thiery JP, Radvanyi F. Tumour suppressive properties of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2-IIIb in human bladder cancer. Oncogene, 1999, 18(51): 7234-7243.
pmid: 10602477 |
| [49] |
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2006, 7(2): 131-142.
doi: 10.1038/nrm1835 |
| [50] |
Warzecha CC, Carstens RP. Complex changes in alternative pre-mRNA splicing play a central role in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Semin Cancer Biol, 2012, 22(5-6): 417-427.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.04.003 pmid: 22548723 |
| [51] |
Mittal V. Epithelial mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol, 2018, 13: 395-412.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-043854 pmid: 29414248 |
| [52] |
Carstens RP, Eaton JV, Krigman HR, Walther PJ, Garcia-Blanco MA. Alternative splicing of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGF-R2) in human prostate cancer. Oncogene, 1997, 15(25): 3059-3065.
pmid: 9444954 |
| [53] |
Zhao Q, Caballero OL, Davis ID, Jonasch E, Tamboli P, Yung WK, Weinstein JN, Kenna Shaw for TCGA research network, Strausberg RL, Yao J. Tumor-specific isoform switch of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 underlies the mesenchymal and malignant phenotypes of clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(9): 2460-2472.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3708 pmid: 23444225 |
| [54] |
Huynh H, Ngo VC, Fargnoli J, Ayers M, Soo KC, Koong HN, Thng CH, Ong HS, Chung A, Chow P, Pollock P, Byron S, Tran E. Brivanib alaninate, a dual inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, induces growth inhibition in mouse models of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14(19): 6146-6153.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0509 pmid: 18829493 |
| [1] | 程敏, 张静, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. 缺氧相关长链非编码RNA作为肝癌预后预测标志物的潜在价值[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(2): 153-167. |
| [2] | 冷奇颖, 郑嘉辉, 徐海冬, PatriciaAdu-Asiamah, 张颖, 杜炳旺, 张丽. 鸡胰岛素降解酶基因环状转录本克隆及其表达规律[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(12): 1129-1137. |
| [3] | 罗艳,王瑛. 茄子SmU2AF基因的可变剪接[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(11): 1499-1505. |
| [4] | 许先国,吴俊杰,洪小珍,朱发明,严力行. 鉴定9个新的RHD基因mRNA可变剪接体[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(10): 1213-1218. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
