Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 409-424.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-008
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
The mechanism of circadian clock and its influence on animal circannual rhythm
Yang Yang1( ), Mingxing Chu1(
), Mingxing Chu1( ), Qiuyue Liu2(
), Qiuyue Liu2( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Institute of Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100193, China
2. Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Innovation Academy for Seed Design, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
-
Received:2023-01-09Revised:2023-04-14Online:2023-05-20Published:2023-04-24 -
Contact:Chu Mingxing,Liu Qiuyue E-mail:yy176362@163.com;qyliu@genetics.ac.cn;mxchu@263.net -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(32172704);Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of China(CAAS-ZDRW202106);Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of China(ASTIP-IAS13);China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA(CARS-38);Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA24030205)
Cite this article
Yang Yang, Mingxing Chu, Qiuyue Liu. The mechanism of circadian clock and its influence on animal circannual rhythm[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(5): 409-424.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | Shui K.Systematic study of the regulatory mechanism and function of circadian rhythm [Dissertation]. Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2020. |
| 税珂.近日节律的调控机理与功能的系统生物学研究[学位论文]. 华中科技大学, 2020. | |
| [2] |
Roenneberg T, Merrow M. The circadian clock and human health. Curr Biol, 2016, 26(10): R432-R443.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.04.011 |
| [3] | Virshup DM, Forger DB. After hours keeps clock researchers CRYing Overtime. Cell, 2007, 129(5): 857-859. |
| [4] |
Lowrey PL, Takahashi JS. Mammalian circadian biology: elucidating genome-wide levels of temporal organization. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet, 2004, 5: 407-441.
pmid: 15485355 |
| [5] |
Musiek ES, Holtzman DM. Mechanisms linking circadian clocks, sleep, and neurodegeneration. Science, 2016, 354(6315): 1004-1008.
pmid: 27885006 |
| [6] |
Huang RC. The discoveries of molecular mechanisms for the circadian rhythm: the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Biomed J, 2018, 41(1): 5-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2018.02.003 |
| [7] |
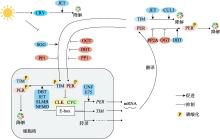
Peschel N, Chen KF, Szabo G, Stanewsky R. Light-dependent interactions between the Drosophila circadian clock factors cryptochrome, jetlag, and timeless. Curr Biol, 2009, 19(3): 241-247.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.12.042 |
| [8] |
Kivimäe S, Saez L, Young MW. Activating PER repressor through a DBT-directed phosphorylation switch. PLoS Biol, 2008, 6(7): e183.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060183 |
| [9] |
Kloss B, Rothenfluh A, Young MW, Saez L. Phosphorylation of period is influenced by cycling physical associations of double-time, period, and timeless in the Drosophila clock. Neuron, 2001, 30(3): 699-706.
doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00320-8 pmid: 11430804 |
| [10] |
Emery P, So WV, Kaneko M, Hall JC, Rosbash M. CRY, a Drosophila clock and light-regulated cryptochrome, is a major contributor to circadian rhythm resetting and photosensitivity. Cell, 1998, 95(5): 669-679.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81637-2 pmid: 9845369 |
| [11] |
Krishnan B, Levine JD, Lynch MK, Dowse HB, Funes P, Hall JC, Hardin PE, Dryer SE. A new role for cryptochrome in a Drosophila circadian oscillator. Nature, 2001, 411(6835): 313-317.
doi: 10.1038/35077094 |
| [12] |
Jaumouillé E, Machado Almeida P, Stähli P, Koch R, Nagoshi E. Transcriptional regulation via nuclear receptor crosstalk required for the Drosophila circadian clock. Curr Biol, 2015, 25(11): 1502-1508.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.04.017 pmid: 26004759 |
| [13] | Lu H, Li YC, Huang XS. Mechanistic studies of post-translational modifications on the proteasome. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol, 2021, 37(6): 710-719. |
| 卢慧, 李衍常, 黄学石. 蛋白酶体翻译后修饰功能机制研究. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2021, 37(6): 710-719. | |
| [14] |
Edery I, Zwiebel LJ, Dembinska ME, Rosbash M. Temporal phosphorylation of the Drosophila period protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1994, 91(6): 2260-2264.
pmid: 8134384 |
| [15] |
Price JL, Blau J, Rothenfluh A, Abodeely M, Kloss B, Young MW. Double-time is a novel Drosophila clock gene that regulates PERIOD protein accumulation. Cell, 1998, 94(1): 83-95.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81224-6 pmid: 9674430 |
| [16] |
Fang YS, Sathyanarayanan S, Sehgal A. Post-translational regulation of the Drosophila circadian clock requires protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). Genes Dev, 2007, 21(12): 1506-1518.
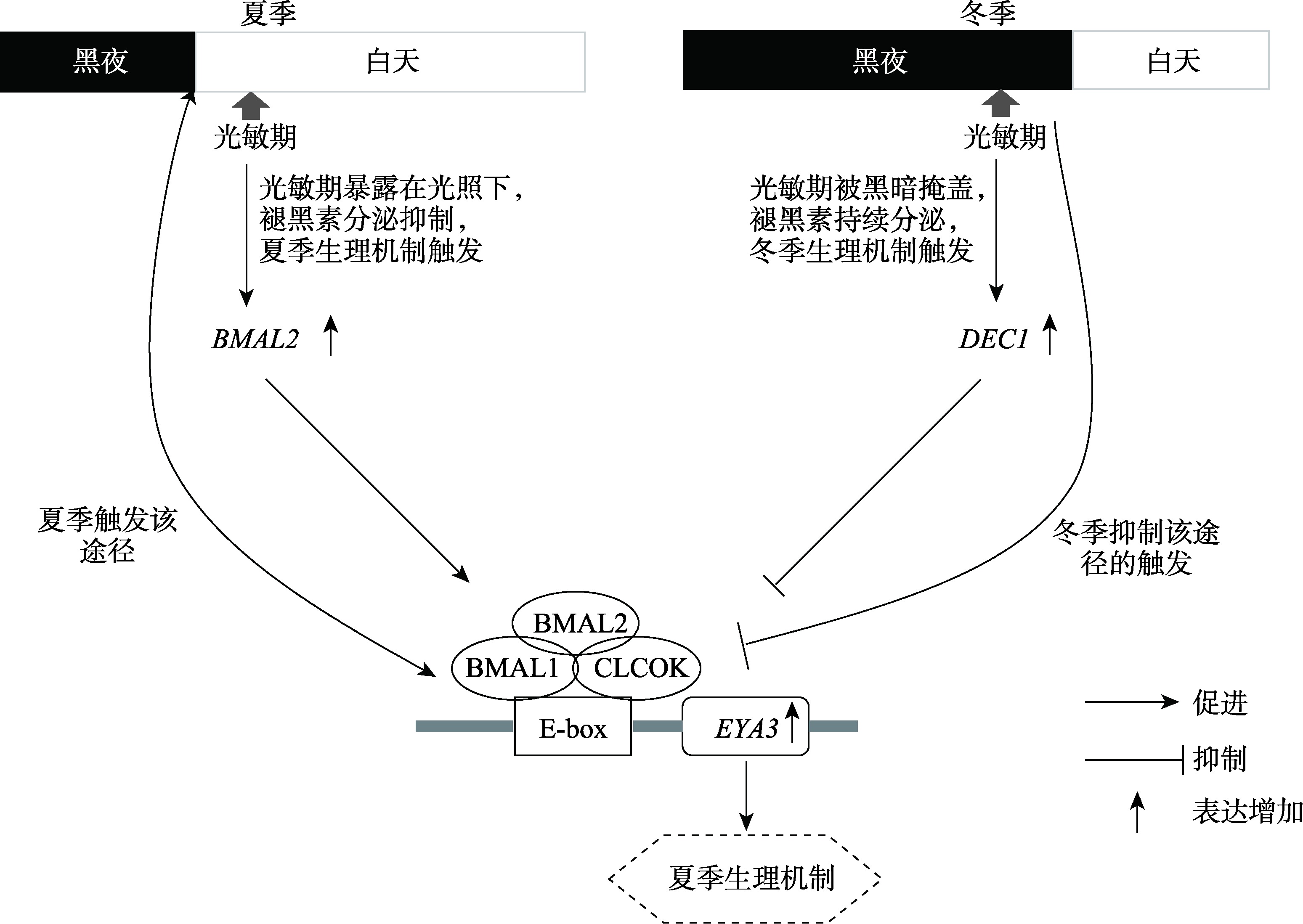
doi: 10.1101/gad.1541607 |
| [17] |
Grima B, Dognon A, Lamouroux A, Chélot E, Rouyer F. CULLIN-3 controls TIMELESS oscillations in the Drosophila circadian clock. PLoS Biol, 2012, 10(8): e1001367.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001367 |
| [18] |
Koh K, Zheng XZ, Sehgal A. JETLAG resets the Drosophila circadian clock by promoting light-induced degradation of TIMELESS. Science, 2006, 312(5781): 1809-1812.
doi: 10.1126/science.1124951 |
| [19] |
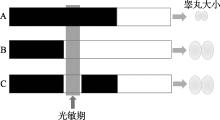
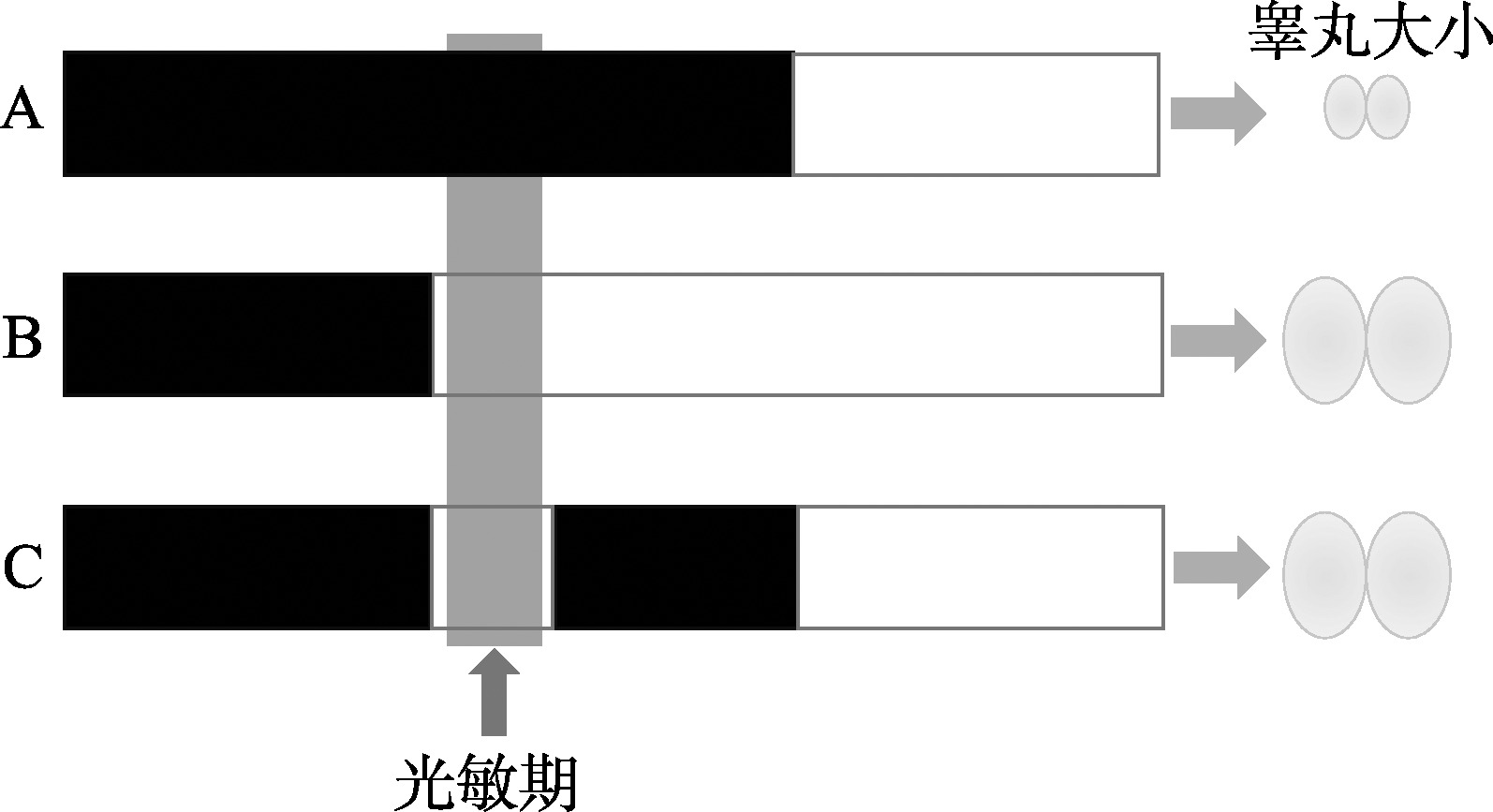
Li MD, Ruan HB, Hughes ME, Lee JS, Singh JP, Jones SP, Nitabach MN, Yang XY. O-GlcNAc signaling entrains the circadian clock by inhibiting BMAL1/CLOCK ubiquitination. Cell Metab, 2013, 17(2): 303-310.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.12.015 |
| [20] |
Kaasik K, Kivimäe S, Allen JJ, Chalkley RJ, Huang Y, Baer K, Kissel H, Burlingame AL, Shokat KM, Ptáček LJ, Fu YH. Glucose sensor O-GlcNAcylation coordinates with phosphorylation to regulate circadian clock. Cell Metab, 17(2): 291-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.12.017 |
| [21] |
Kim EY, Jeong EH, Park S, Jeong HJ, Edery I, Cho JW. A role for O-GlcNAcylation in setting circadian clock speed. Genes Dev, 2012, 26(5): 490-502.
doi: 10.1101/gad.182378.111 |
| [22] |
Zhang R, Du J, Zhao X, Wei L, Zhao Z. Regulation of circadian behavioural output via clock-responsive miR-276b. Insect Mol Biol, 2021, 30(1): 81-89.
doi: 10.1111/imb.12679 pmid: 33131172 |
| [23] |
Xia XJ, Fu XN, Du J, Wu BB, Zhao XG, Zhu JS, Zhao ZW.Regulation of circadian rhythm and sleep by miR-375-timeless interaction in Drosophila. FASEB J, 2020, 34(12): 16536-16551.
doi: 10.1096/fj.202001107R pmid: 33078445 |
| [24] | Chen X, Rosbash M. Mir-276a strengthens Drosophila circadian rhythms by regulating timeless expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(21): E2965-E2972. |
| [25] |
Zhang Y, Lamba P, Guo PY, Emery P. MiR-124 regulates the phase of Drosophila circadian locomotor behavior. J Neurosci, 2016, 36(6): 2007-2013.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3286-15.2016 pmid: 26865623 |
| [26] |
Garaulet DL, Sun KL, Li WH, Wen JY, Panzarino AM, O'Neil JL, Hiesinger PR, Young MW, Lai EC.MiR-124 regulates diverse aspects of rhythmic behavior in Drosophila. J Neurosci, 2016, 36(12): 3414-3421.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3287-15.2016 pmid: 27013671 |
| [27] |
Liu ZX, Selby CP, Yang YY, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Cao XM, Eynullazada K, Sancar A. Circadian regulation of c-MYC in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(35): 21609-21617.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2011225117 pmid: 32817420 |
| [28] |
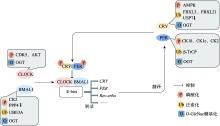
Griffin EA Jr, Staknis D, Weitz CJ. Light-independent role of CRY1 and CRY2 in the mammalian circadian clock. Science, 1999, 286(5440): 768-771.
pmid: 10531061 |
| [29] |
Kume K, Zylka MJ, Sriram S, Shearman LP, Weaver DR, Jin X, Maywood ES, Hastings MH, Reppert SM. mCRY1 and mCRY2 are essential components of the negative limb of the circadian clock feedback loop. Cell, 1999, 98(2): 193-205.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81014-4 pmid: 10428031 |
| [30] |
Preitner N, Damiola F, Lopez-Molina L, Zakany J, Duboule D, Albrecht U, Schibler U. The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell, 2002, 110(2): 251-260.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00825-5 pmid: 12150932 |
| [31] |
Vitaterna MH, Selby CP, Todo T, Niwa H, Thompson C, Fruechte EM, Hitomi K, Thresher RJ, Ishikawa T, Miyazaki J, Takahashi JS, Sancar A.Differential regulation of mammalian period genes and circadian rhythmicity by cryptochromes 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96(21): 12114-12119.
pmid: 10518585 |
| [32] |
Matsuo T, Yamaguchi S, Mitsui S, Emi A, Shimoda F, Okamura H. Control mechanism of the circadian clock for timing of cell division in vivo. Science, 2003, 302(5643): 255-259.
pmid: 12934012 |
| [33] |
Kondratov RV, Shamanna RK, Kondratova AA, Gorbacheva VY, Antoch MP. Dual role of the CLOCK/ BMAL1 circadian complex in transcriptional regulation. FASEB J, 2006, 20(3): 530-532.
pmid: 16507766 |
| [34] |
Liu AC, Welsh DK, Ko CH, Tran HG, Zhang EE, Priest AA, Buhr ED, Singer O, Meeker K, Verma IM, Doyle FJ 3rd, Takahashi JS, Kay SA. Intercellular coupling confers robustness against mutations in the SCN circadian clock network. Cell, 2007, 129(3): 605-616.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.047 pmid: 17482552 |
| [35] |
Etchegaray JP, Lee C, Wade PA, Reppert SM. Rhythmic histone acetylation underlies transcription in the mammalian circadian clock. Nature, 2003, 421(6919): 177-182.
doi: 10.1038/nature01314 |
| [36] |
Crumbley C, Burris TP. Direct regulation of CLOCK expression by REV-ERB. PLoS One, 2011, 6(3): e17290.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017290 |
| [37] |
Dierickx P, Zhu K, Carpenter BJ, Jiang CJ, Vermunt MW, Xiao Y, Luongo TS, Yamamoto T, Martí-Pàmies Í, Mia S, Latimer M, Diwan A, Zhao JJ, Hauck AK, Krusen B, Nguyen HCB, Blobel GA, Kelly DP, Pei LM, Baur JA, Young ME, Lazar MA. Circadian REV-ERBs repress E4bp4 to activate NAMPT-dependent NAD+ biosynthesis and sustain cardiac function. Nat Cardiovasc Res, 2022, 1(1): 45-58.
doi: 10.1038/s44161-021-00001-9 |
| [38] |
Yamajuku D, Shibata Y, Kitazawa M, Katakura T, Urata H, Kojima T, Takayasu S, Nakata O, Hashimoto S. Cellular DBP and E4BP4 proteins are critical for determining the period length of the circadian oscillator. FEBS Lett, 2011, 585(14): 2217-2222.
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.05.038 pmid: 21635892 |
| [39] |
Ohno T, Onishi Y, Ishida N.A novel E4BP 4 element drives circadian expression of mPeriod2. Nucleic Acids Res, 2007, 35(2): 648-655.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl868 |
| [40] |
Yoshitane H, Asano Y, Sagami A, Sakai S, Suzuki Y, Okamura H, Iwasaki W, Ozaki H, Fukada Y. Functional D-box sequences reset the circadian clock and drive mRNA rhythms. Commun Biol, 2019, 2: 300.
doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0522-3 pmid: 31925105 |
| [41] |
Chen K, Cheng HH, Zhou RJ. Molecular mechanisms and functions of autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Hereditas (Beijing), 2012, 34(1): 5-18.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2012.00005 |
|
陈科, 程汉华, 周荣家. 自噬与泛素化蛋白降解途径的分子机制及其功能. 遗传, 2012, 34(1): 5-18.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2012.00005 |
|
| [42] |
St John PC, Hirota T, Kay SA, Doyle FJ 3rd. Spatiotemporal separation of PER and CRY posttranslational regulation in the mammalian circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(5): 2040-2045.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323618111 pmid: 24449901 |
| [43] |
Lee C, Etchegaray JP, Cagampang FR, Loudon AS, Reppert SM. Posttranslational mechanisms regulate the mammalian circadian clock. Cell, 2001, 107(7): 855-867.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00610-9 pmid: 11779462 |
| [44] |
Busino L, Bassermann F, Maiolica A, Lee C, Nolan PM, Godinho SIH, Draetta GF, Pagano M. SCFFbxl3 controls the oscillation of the circadian clock by directing the degradation of cryptochrome proteins. Science, 2007, 316(5826): 900-904.
doi: 10.1126/science.1141194 pmid: 17463251 |
| [45] |
Dardente H, Mendoza J, Fustin JM, Challet E, Hazlerigg DG. Implication of the F-Box protein FBXL21 in circadian pacemaker function in mammals. PLoS One, 2008, 3(10): e3530.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003530 |
| [46] |
Lamia KA, Sachdeva UM, DiTacchio L, Williams EC, Alvarez JG, Egan DF, Vasquez DS, Juguilon H, Panda S, Shaw RJ, Thompson CB, Evans RM. AMPK regulates the circadian clock by cryptochrome phosphorylation and degradation. Science, 2009, 326(5951): 437-440.
doi: 10.1126/science.1172156 pmid: 19833968 |
| [47] |
Schmalen I, Reischl S, Wallach T, Klemz R, Grudziecki A, Prabu JR, Benda C, Kramer A, Wolf E. Interaction of circadian clock proteins CRY1 and PER2 is modulated by zinc binding and disulfide bond formation. Cell, 2014, 157(5): 1203-1215.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.057 pmid: 24855952 |
| [48] | Berthier A, Vinod M, Porez G, Steenackers A, Alexandre J, Yamakawa N, Gheeraert C, Ploton M, Maréchal X, Dubois-Chevalier J, Hovasse A, Schaeffer-Reiss C, Cianférani S, Rolando C, Bray F, Duez H, Eeckhoute J, Lefebvre T, Staels B, Lefebvre P. Combinatorial regulation of hepatic cytoplasmic signaling and nuclear transcripttional events by the OGT/REV-ERBα complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(47): E11033-E11042. |
| [49] |
Chen R, D'Alessandro M, Lee C. MiRNAs are required for generating a time delay critical for the circadian oscillator. Curr Biol, 2013, 23(20): 1959-1968.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.08.005 pmid: 24094851 |
| [50] | Yoo SH, Kojima S, Shimomura K, Koike N, Buhr ED, Furukawa T, Ko CH, Gloston G, Ayoub C, Nohara K, Reyes BA, Tsuchiya Y, Yoo OJ, Yagita K, Lee C, Chen Z, Yamazaki S, Green CB, Takahashi JS. Period 2 3'-UTR and microRNA-24 regulate circadian rhythms by repressing PERIOD2 protein accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(42): E8855-E8864. |
| [51] |
Zhou L, Miller C, Miraglia LJ, Romero A, Mure LS, Panda S, Kay SA. A genome-wide microRNA screen identifies the microRNA-183/96/182 cluster as a modulator of circadian rhythms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(1): e2020454118.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2020454118 |
| [52] | Bu Y, Yoshida A, Chitnis N, Altman BJ, Tameire F, Oran A, Gennaro V, Armeson KE, McMahon SB, Wertheim GB, Dang CV, Ruggero D, Koumenis C, Fuchs SY, Diehl JA.A PERK-miR-211 axis suppresses circadian regulators and protein synthesis to promote cancer cell survival. Nat Cell Biol, 2018, 20(1): 104-115. |
| [53] |
Cha S, Wang JY, Lee SM, Tan Z, Zhao Q, Bai D.Clock-modified mesenchymal stromal cells therapy rescues molecular circadian oscillation and age-related bone loss via miR142 -3 p/Bmal1/YAP signaling axis. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 111.
doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00908-7 pmid: 35279674 |
| [54] |
Gao Q, Zhou L, Yang SY, Cao JM. A novel role of microRNA17-5p in the modulation of circadian rhythm. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 30070.
doi: 10.1038/srep30070 |
| [55] |
Cheng QY, Fan XY, Liu YT, Xu LR, Dong PJ, Song LW, Qian RZ. MiR-455-5p regulates circadian rhythms by accelerating the degradation of clock mRNA. IUBMB Life, 2022, 74(3): 245-258.
doi: 10.1002/iub.v74.3 |
| [56] |
Guh YJ, Tamai TK, Yoshimura T. The underlying mechanisms of vertebrate seasonal reproduction. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, 2019, 95(7): 343-357.
doi: 10.2183/pjab.95.025 |
| [57] |
Koštál V, Štětina T, Poupardin R, Korbelová J, Bruce AW. Conceptual framework of the eco-physiological phases of insect diapause development justified by transcriptomic profiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(32): 8532-8537.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707281114 pmid: 28720705 |
| [58] | Ren S. Mechanism of summer diapause induction of Delia antiqua (Diptera: Anthomyiidae) [Dissertation]. Chongqing University, 2018. |
| 任爽. 葱蝇Delia antiqua(Diptera: Anthomyiidae)夏滞育诱导机理研究[学位论文]. 重庆大学, 2018. | |
| [59] |
Saeed MM, Tougeron K, Raza ABM, Afzal M, Aqueel A, Le Goff GJ, Renoz F, Pirotte J, Hance T. Transgenerational phenotypic plasticity of diapause induction and related fitness cost in a commercial strain of the parasitoid Aphidius ervi Haliday. Insect Sci, 2021, 28(3): 780-792.
doi: 10.1111/ins.v28.3 |
| [60] |
Abrieux A, Xue YB, Cai Y, Lewald KM, Nguyen HN, Zhang Y, Chiu JC. EYES ABSENT and TIMELESS integrate photoperiodic and temperature cues to regulate seasonal physiology in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(26): 15293-15304.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2004262117 pmid: 32541062 |
| [61] |
Ikeno T, Tanaka SI, Numata H, Goto SG. Photoperiodic diapause under the control of circadian clock genes in an insect. BMC Biol, 2010, 8: 116.
doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-116 pmid: 20815865 |
| [62] |
Yamashita O. Diapause hormone of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: structure, gene expression and function. J Insect Physiol, 1996, 42(7): 669-679.
doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(96)00003-0 |
| [63] |
Xu WH, Denlinger DL. Molecular characterization of prothoracicotropic hormone and diapause hormone in Heliothis virescens during diapause, and a new role for diapause hormone. Insect Mol Biol, 2003, 12(5): 509-516.
pmid: 12974956 |
| [64] |
Jindra M, Palli SR, Riddiford LM. The juvenile hormone signaling pathway in insect development. Annu Rev Entomol, 2013, 58: 181-204.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-120811-153700 pmid: 22994547 |
| [65] |
Ma HY, Li YY, Li L, Tan Y, Pang BP. Juvenile hormone regulates the reproductive diapause through Methoprene- tolerant gene in Galeruca daurica. Insect Mol Biol, 2021, 30(4): 446-458.
doi: 10.1111/imb.12710 pmid: 33949026 |
| [66] |
Batz ZA, Brent CS, Marias MR, Sugijanto J, Armbruster PA.Juvenile hormone III but not 20-hydroxyecdysone regulates the embryonic diapause of aedes albopictus. Front Physiol, 2019, 10: 1352.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01352 pmid: 31708801 |
| [67] |
Dong YC, Chen ZZ, Clarke AR, Niu CY. Changes in energy metabolism trigger pupal diapause transition of bactrocera minax after 20-hydroxyecdysone application. Front Physiol, 2019, 10: 1288.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01288 |
| [68] |
Thrun LA, Moenter SM, O'Callaghan D, Woodfill CJ, Karsch FJ. Circannual alterations in the circadian rhythm of melatonin secretion. J Biol Rhythms, 1995, 10(1): 42-54.
doi: 10.1177/074873049501000104 |
| [69] |
Karsch FJ, Bittman EL, Foster DL, Goodman RL, Legan SJ, Robinson JE. Neuroendocrine basis of seasonal reproduction. Recent Prog Horm Res, 1984, 40: 185-232.
pmid: 6385166 |
| [70] | Butler MP, Turner KW, Park JH, Schoomer EE, Zucker I, Gorman MR. Seasonal regulation of reproduction: altered role of melatonin under naturalistic conditions in hamsters. Proc Biol Sci, 2010, 277(1695): 2867-2874. |
| [71] |
Casao A, Cebrián I, Asumpção ME, Pérez-Pé R, Abecia JA, Forcada F, Cebrián-Pérez JA, Muiño-Blanco T. Seasonal variations of melatonin in ram seminal plasma are correlated to those of testosterone and antioxidant enzymes. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2010, 8: 59.
doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-8-59 |
| [72] |
Weems PW, Goodman RL, Lehman MN. Neural mechanisms controlling seasonal reproduction: principles derived from the sheep model and its comparison with hamsters. Front Neuroendocrinol, 2015, 37: 43-51.
doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.12.002 |
| [73] |
Ralph MR, Foster RG, Davis FC, Menaker M. Transplanted suprachiasmatic nucleus determines circadian period. Science, 1990, 247(4945): 975-978.
doi: 10.1126/science.2305266 pmid: 2305266 |
| [74] |
Xu P, Berto S, Kulkarni A, Jeong B, Joseph C, Cox KH, Greenberg ME, Kim TK, Konopka G, Takahashi JS. NPAS4 regulates the transcriptional response of the suprachiasmatic nucleus to light and circadian behavior. Neuron, 2021, 109(20): 3268-3282.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.07.026 pmid: 34416169 |
| [75] |
Pandi-Perumal SR, Srinivasan V, Maestroni GJM, Cardinali DP, Poeggeler B, Hardeland R. Melatonin: nature's most versatile biological signal? FEBS J, 2006, 273(13): 2813-2838.
doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05322.x pmid: 16817850 |
| [76] |
Brainard GC, Hanifin JP, Greeson JM, Byrne B, Glickman G, Gerner E, Rollag MD. Action spectrum for melatonin regulation in humans: evidence for a novel circadian photoreceptor. J Neurosci, 2001, 21(16): 6405-6412.
pmid: 11487664 |
| [77] | Xia Q, Liu QY, Wang XY, Hu WP, Li CY, He XY, Chu MX, Di R. The molecular mechanism of sheep seasonal breeding and artificial regulatory techniques for estrus and mating in anestrus. Hereditas (Beijing), 2018, 40(5): 369-377. |
| 夏青, 刘秋月, 王翔宇, 胡文萍, 李春艳, 贺小云, 储明星, 狄冉. 绵羊季节性繁殖分子机制及休情季节诱导绵羊发情配种技术. 遗传, 2018, 40(5): 369-377. | |
| [78] |
Kang SW, Thayananuphat A, Bakken T, El Halawani ME. Dopamine-melatonin neurons in the avian hypothalamus controlling seasonal reproduction. Neuroscience, 2007, 150(1): 223-233.
pmid: 17935892 |
| [79] |
Johnston JD, Tournier BB, Andersson H, Masson-Pévet M, Lincoln GA, Hazlerigg DG. Multiple effects of melatonin on rhythmic clock gene expression in the mammalian pars tuberalis. Endocrinology, 2006, 147(2): 959-965.
doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1100 pmid: 16269454 |
| [80] |
Von Gall C, Garabette ML, Kell CA, Frenzel S, Dehghani F, Schumm-Draeger PM, Weaver DR, Korf HW, Hastings MH, Stehle JH. Rhythmic gene expression in pituitary depends on heterologous sensitization by the neurohormone melatonin. Nat Neurosci, 2002, 5(3): 234-238.
pmid: 11836530 |
| [81] |
Dardente H, Lomet D, Robert V, Decourt C, Beltramo M, Pellicer-Rubio MT. Seasonal breeding in mammals: from basic science to applications and back. Theriogenology, 2016, 86(1): 324-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.04.045 pmid: 27173960 |
| [82] |
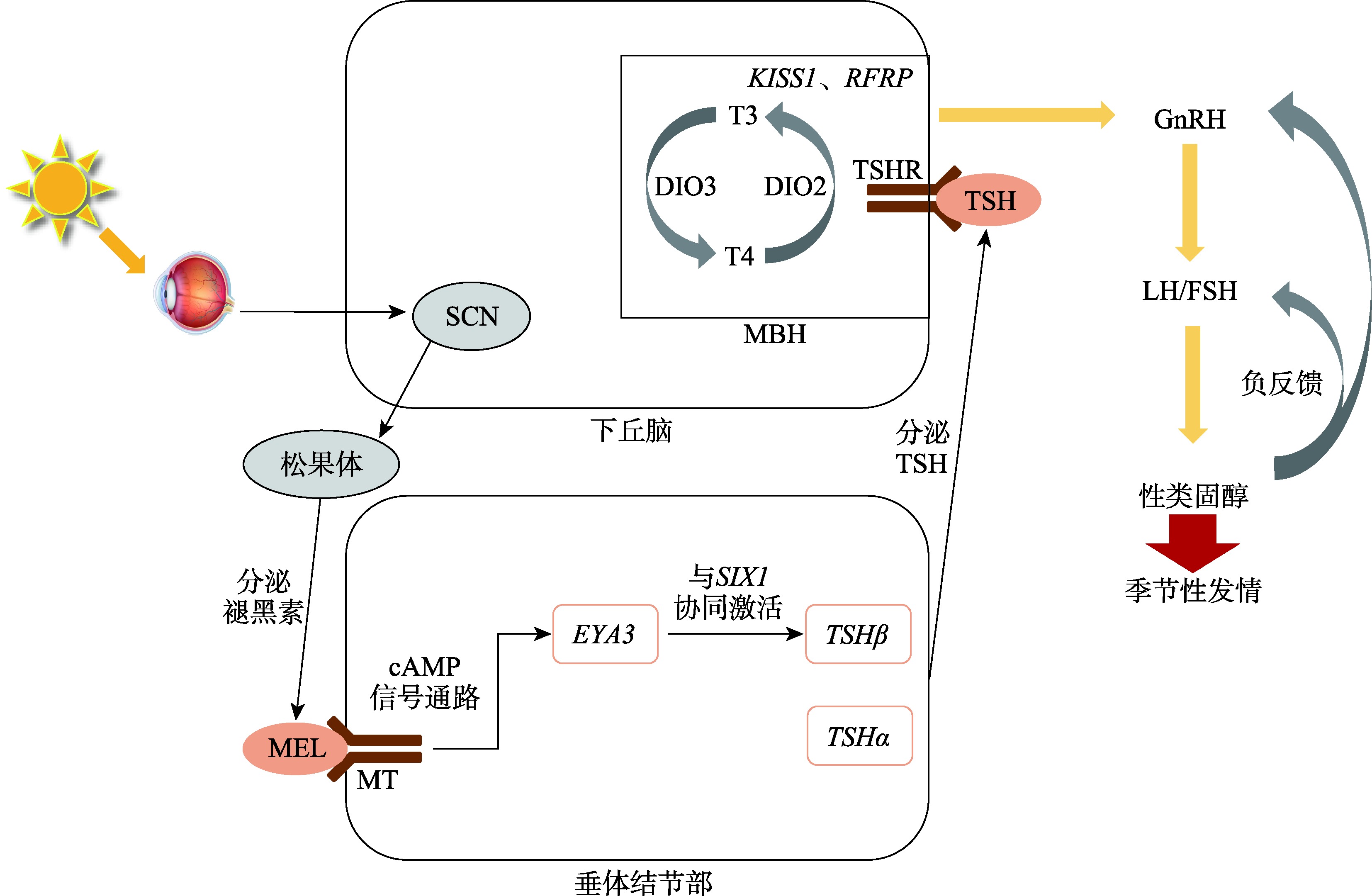
Hanon EA, Lincoln GA, Fustin JM, Dardente H, Masson-Pévet M, Morgan PJ, Hazlerigg DG. Ancestral TSH mechanism signals summer in a photoperiodic mammal. Curr Biol, 2008, 18(15): 1147-1152.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.06.076 pmid: 18674911 |
| [83] |
Ono H, Hoshino Y, Yasuo S, Watanabe M, Nakane Y, Murai A, Ebihara S, Korf HW, Yoshimura T. Involvement of thyrotropin in photoperiodic signal transduction in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(47): 18238-18242.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808952105 pmid: 19015516 |
| [84] |
Dupré SM, Miedzinska K, Duval CV, Yu L, Goodman RL, Lincoln GA, Davis JR, McNeilly AS, Burt DD, Loudon AS. Identification of EYA3 and TAC1 as long-day signals in the sheep pituitary. Curr Biol, 2010, 20(9): 829-835.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.02.066 pmid: 20434341 |
| [85] |
Henson JR, Carter SN, Freeman DA. Exogenous T-elicits long day-like alterations in testis size and the RFamides Kisspeptin and gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone in short-day Siberian hamsters. J Biol Rhythms, 2013, 28(3): 193-200.
doi: 10.1177/0748730413487974 |
| [86] |
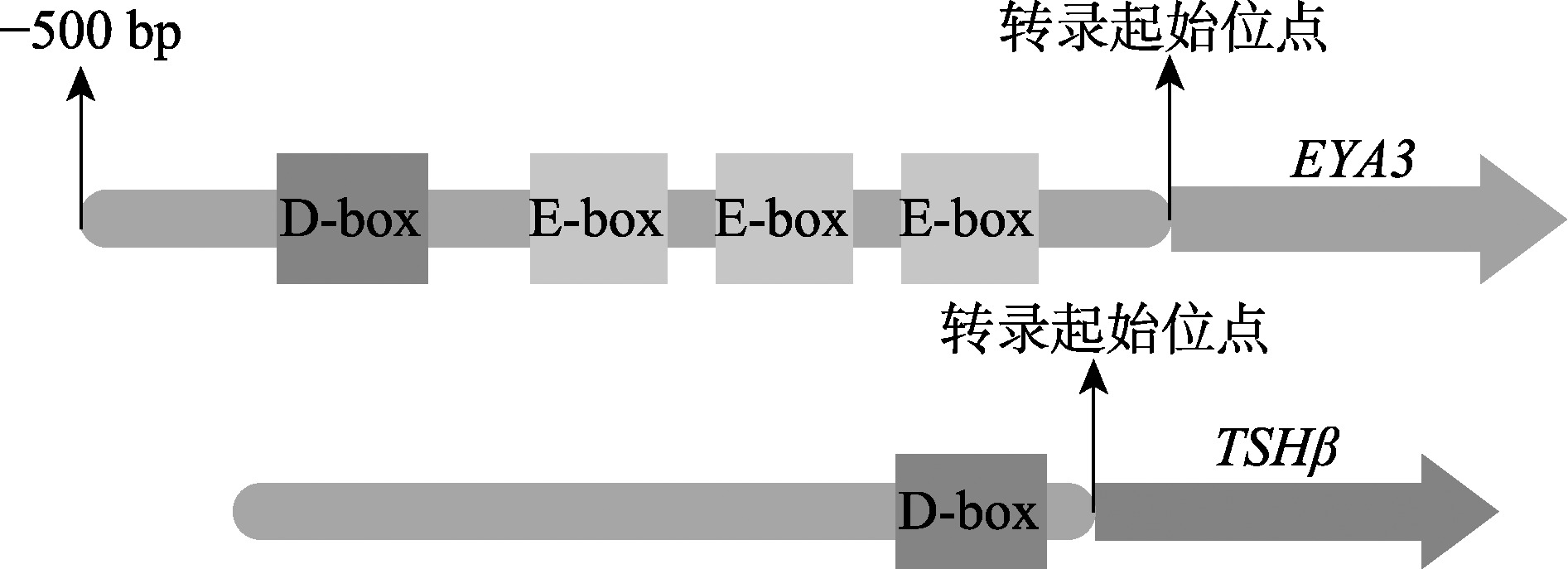
Masumoto KH, Ukai-Tadenuma M, Kasukawa T, Nagano M, Uno KD, Tsujino K, Horikawa K, Shigeyoshi Y, Ueda HR. Acute induction of Eya3 by late-night light stimulation triggers TSHβ expression in photoperiodism. Curr Biol, 2010, 20(24): 2199-2206.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.11.038 pmid: 21129973 |
| [87] | Castle-Miller J, Bates DO, Tortonese DJ. Mechanisms regulating angiogenesis underlie seasonal control of pituitary function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(12): E2514-E2523. |
| [88] |
Carcangiu V, Vacca GM, Mura MC, Dettori ML, Pazzola M, Luridiana S, Bini PP. Relationship between MTNR1A melatonin receptor gene polymorphism and seasonal reproduction in different goat breeds. Anim Reprod Sci, 2009, 110(1-2): 71-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2007.12.014 pmid: 18243602 |
| [89] |
Huang DW, Wang JX, Liu QY, Chu MX, Di R, He JN, Cao GL, Fang L, Feng T, Li N. Analysis on DNA sequence of TSHB gene and its association with reproductive seasonality in goats. Mol Biol Rep, 2013, 40(2): 1893-1904.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2245-0 pmid: 23076536 |
| [90] |
He XY, Zhang ZB, Liu QY, Chu MX. Polymorphisms of the melatonin receptor 1A gene that affects the reproductive seasonality and litter size in Small Tail Han sheep. Reprod Domest Anim, 2019, 54(10): 1400-1410.
doi: 10.1111/rda.13538 pmid: 31355975 |
| [91] |
Simonneaux V. A Kiss to drive rhythms in reproduction. Eur J Neurosci, 2020, 51(1): 509-530.
doi: 10.1111/ejn.14287 pmid: 30472752 |
| [92] |
Woller A, Gonze D. The bird circadian clock: insights from a computational model. J Biol Rhythms, 2013, 28(6): 390-402.
doi: 10.1177/0748730413512454 |
| [93] |
Siopes TD, Wilson WO. Extraocular modification of photoreception in intact and pinealectomized coturnix. Poult Sci, 1974, 53(6): 2035-2041.
doi: 10.3382/ps.0532035 |
| [94] |
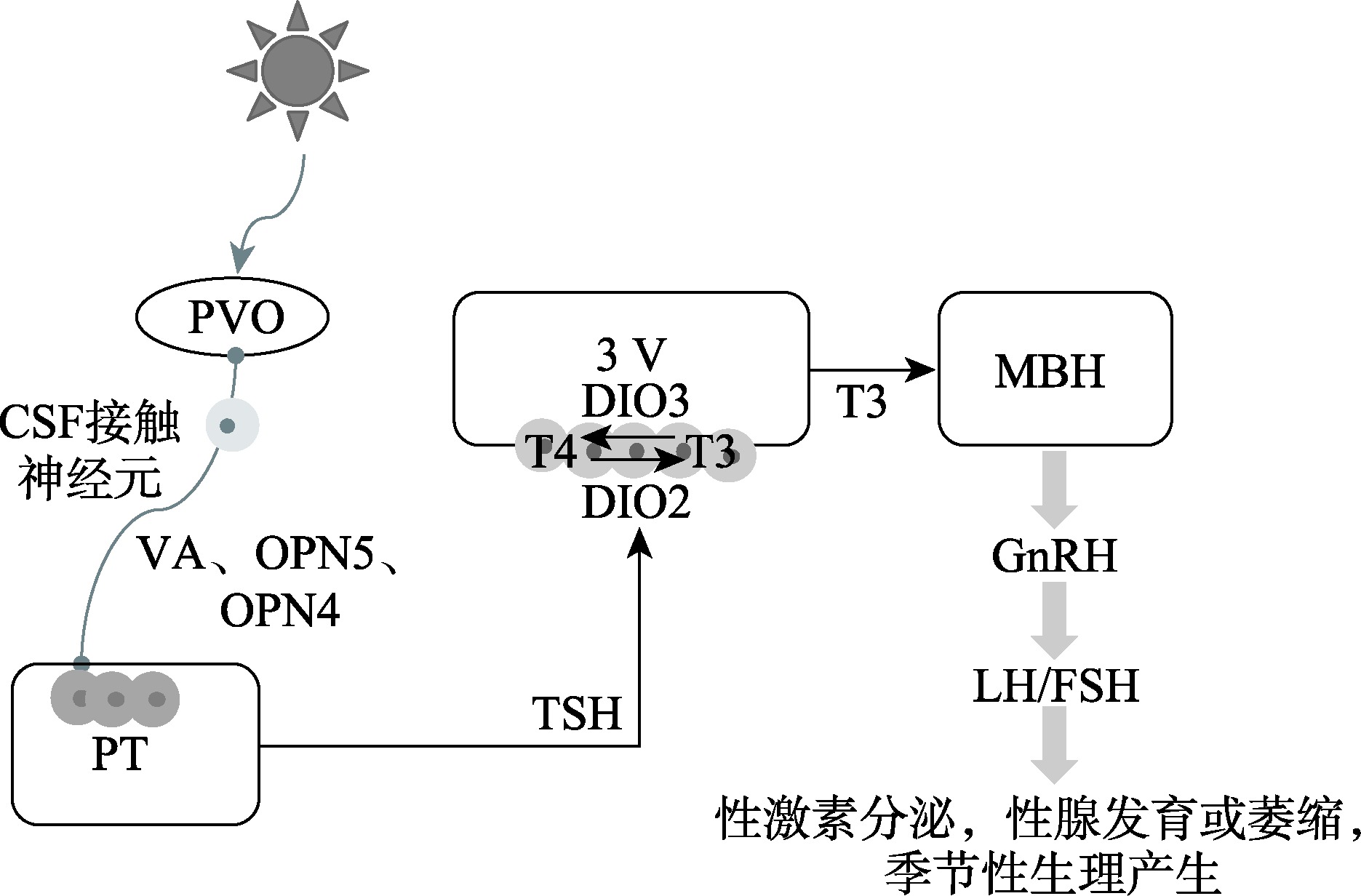
Halford S, Pires SS, Turton M, Zheng L, González- Menéndez I, Davies WL, Peirson SN, García-Fernández JM, Hankins MW, Foster RG. VA opsin-based photoreceptors in the hypothalamus of birds. Curr Biol, 2009, 19(16): 1396-1402.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.066 pmid: 19664923 |
| [95] |
Nakane Y, Ikegami K, Ono H, Yamamoto N, Yoshida S, Hirunagi K, Ebihara S, Kubo Y, Yoshimura T. A mammalian neural tissue opsin (Opsin 5) is a deep brain photoreceptor in birds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(34): 15264-15268.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006393107 pmid: 20679218 |
| [96] |
Chaurasia SS, Rollag MD, Jiang G, Hayes WP, Haque R, Natesan A, Zatz M, Tosini G, Liu C, Korf HW, Iuvone PM, Provencio I. Molecular cloning, localization and circadian expression of chicken melanopsin (Opn4): differential regulation of expression in pineal and retinal cell types. J Neurochem, 2005, 92(1): 158-170.
pmid: 15606905 |
| [97] |
Di R, He JN, Song SH, Tian DM, Liu QY, Liang XJ, Ma Q, Sun M, Wang JD, Zhao WM, Cao GL, Wang JX, Yang ZM, Ge Y, Chu MX. Characterization and comparative profiling of ovarian microRNAs during ovine anestrus and the breeding season. BMC Genom, 2014, 15(1): 899.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-899 |
| [98] |
Tamai TK, Yoshimura T. Molecular and neuroendocrine mechanisms of avian seasonal reproduction. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 1001: 125-136.
doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-3975-1_8 pmid: 28980233 |
| [99] |
Pittendrigh CS. Circadian surfaces and the diversity of possible roles of circadian organization in photoperiodic induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1972, 69(9): 2734-2737.
pmid: 4506793 |
| [100] |
Lincoln G, Messager S, Andersson H, Hazlerigg D. Temporal expression of seven clock genes in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and the pars tuberalis of the sheep: evidence for an internal coincidence timer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(21): 13890-13895.
pmid: 12374857 |
| [101] |
Ikegami K, Yoshimura T. Circadian clocks and the measurement of daylength in seasonal reproduction. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2012, 349(1): 76-81.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.06.040 pmid: 21767603 |
| [102] | Si FL.Cloning and expression of the DaHSP23 gene during diapause in the maggot, Delia antiqua [Dissertation]. Chongqing Normal University, 2011. |
| 司风玲.葱蝇HSP23基因的克隆及在滞育时期的表达[学位论文]. 重庆师范大学, 2011. | |
| [103] |
Pegoraro M, Gesto JS, Kyriacou CP, Tauber E. Role for circadian clock genes in seasonal timing: testing the Bünning hypothesis. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10(9): e1004603.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004603 |
| [104] |
Ueda H, Tamaki S, Miki T, Uryu O, Kamae Y, Nose M, Shinohara T, Tomioka K. Cryptochrome genes mediate photoperiodic responses in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis. Physiol Entomol, 2018, 43(4): 285-294.
doi: 10.1111/phen.2018.43.issue-4 |
| [105] | Cui WZ, Qiu JF, Dai TM, Chen Z, Li JL, Liu K, Wang YJ, Sima YH, Xu SQ. Circadian clock gene Period contributes to diapause via GABAeric-diapause hormone pathway in Bombyx mori. Biology (Basel), 2021, 10(9): 842. |
| [106] |
Coomans CP, Ramkisoensing A, Meijer JH. The suprachiasmatic nuclei as a seasonal clock. Front Neuroendocrinol, 2015, 37: 29-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.11.002 |
| [107] |
Nishiwaki-Ohkawa T, Yoshimura T. Molecular basis for regulating seasonal reproduction in vertebrates. J Endocrinol, 2016, 229(3): R117-R127.
doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0066 |
| [108] | Bittman EL, Bartness TJ, Goldman BD, DeVries GJ. Suprachiasmatic and paraventricular control of photoperiodism in Siberian hamsters. Am J Physiol, 1991, 260(<W>1 Pt 2):R90-R101. |
| [109] |
Maurel D, Boissin-Agasse L, Roch G, Herbuté S, Boissin J. Suprachiasmatic nucleus lesions abolish photoperiod- induced changes in the testis function and GnRH immunoreactivity in the mink, a short-day breeder. Neuroendocrinology, 1991, 54(2): 103-110.
pmid: 1766547 |
| [110] |
Dardente H, Wyse CA, Birnie MJ, Dupré SM, Loudon ASI, Lincoln GA, Hazlerigg DG. A molecular switch for photoperiod responsiveness in mammals. Curr Biol, 2010, 20(24): 2193-2198.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.10.048 pmid: 21129971 |
| [111] | Shi GS.The roles of FBXL3 in regulating circadian clock[Dissertation]. Nanjing University, 2014. |
| 时广森.FBXL3对近日节律作用机制的研究[学位论文]. 南京大学, 2014. | |
| [112] |
Wood SH, Hindle MM, Mizoro Y, Cheng Y, Saer BRC, Miedzinska K, Christian HC, Begley N, McNeilly J, McNeilly AS, Meddle SL, Burt DW, Loudon ASI. Circadian clock mechanism driving mammalian photoperiodism. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 4291.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18061-z pmid: 32855407 |
| [113] | Yang Y, Zhong YJ, Jiang Y, Chu MX, Liu QY. FBXL3 gene expression and correlation analysis between its polymorphism and seasonal estrus in sheep (Ovis aries). J Agric Biotechnol, 2022, 30(1): 75-84. |
| 杨阳, 钟英杰, 姜雨, 储明星, 刘秋月. 绵羊FBXL3基因表达及其多态性与季节性发情的相关性分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2022, 30(1): 75-84 | |
| [114] |
Naval-Sanchez M, Nguyen Q, McWilliam S, Porto-Neto LR, Tellam R, Vuocolo T, Reverter A, Perez-Enciso M, Brauning R, Clarke S, McCulloch A, Zamani W, Naderi S, Rezaei HR, Pompanon F, Taberlet P, Worley KC, Gibbs RA, Muzny DM, Jhangiani SN, Cockett N, Daetwyler H, Kijas J. Sheep genome functional annotation reveals proximal regulatory elements contributed to the evolution of modern breeds. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 859.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02809-1 pmid: 29491421 |
| [1] | Xiangyi Wei, Dongchun Hu, Zupeng Gao, Congjing Feng. JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its regulation on insect immunity [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(3): 229-236. |
| [2] | Chengan Lv, Ruoran Wang, Zhuo-Xian Meng. Molecular mechanism of islet β-cell functional alternations during type 2 diabetes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 840-852. |
| [3] | Shanshan Gao, Jinliang Li, Jiani Yang, Tong Zhou, Rui Liu, Xiaoping Wang, Li Yu. Progresses on adaptive evolution of gliding and flying ability in mammals [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(1): 46-58. |
| [4] | Lian Ren, Xiushan Wu, Yongqing Li. The mechanism underlying histone deacetylases regulating cardiac hypertrophy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(6): 536-547. |
| [5] | Xiaomin Liu, Minglong Yuan. Progress in innate immunity-related genes in insects [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(6): 451-466. |
| [6] | Xiaoling Tong,Chunyan Fang,Tingting Gai,Jin Shi,Cheng Lu,Fangyin Dai. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in insects [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(4): 266-278. |
| [7] | Xianci Xue,Li Yu. Advances on polyphenism in insects [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(9): 798-809. |
| [8] | Jia Li,Yunhua Liu,Yu Zhang,Chen Chen,Xia Yu,Shunwu Yu. Drought stress modulates diurnal oscillations of circadian clock and drought-responsive genes in Oryza sativa L. [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(9): 837-846. |
| [9] | Min Yue, Yu Yang, Gaili Guo, Ximing Qin. Genetic and epigeneticregulations of mammalian circadian rhythms [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(12): 1122-1137. |
| [10] | Fang Yang, Baoyun Zhang, Guangde Feng, Wei Xiang, Yunxia Ma, Hang Chen, Mingxing Chu, Pingqing Wang. A mechanistic review of how hypoxic mircroenvironment regulates mammalian ovulation [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2016, 38(2): 109-117. |
| [11] | Guilin Li, Lili Niu, Haifeng Liu, Jiazhong Guo. Structure and function of insulin-like growth factor acid-labile subunits in mammalian homologues [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(12): 1185-1193. |
| [12] | Yuancheng Lu, Xiaohui Wu. Research progresses in animal cryptochromes [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(9): 864-870. |
| [13] | Xiaohua Yang, Huafeng Zhang, Jianghua Lai. Alcohol dependence mediated by monoamine neurotransmitters in the central nervous system [J]. HEREDITAS, 2014, 36(1): 11-20. |
| [14] | XU Chen-Lu, SUN Xiao-Mei, ZHANG Shou-Gong. Mechanism on differential gene expression and heterosis formation [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(6): 714-726. |
| [15] | LI Ze-Qin LI Jing-Xiao ZHANG Gen-Fa. Expression regulation of plant ascorbate peroxidase and its tolerance to abiotic stresses [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(1): 45-54. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||