遗传 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (10): 871-885.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-167
万羽鑫( ), 朱欣雨, 赵宇, 孙娜, 江天彤妃(
), 朱欣雨, 赵宇, 孙娜, 江天彤妃( ), 徐娟(
), 徐娟( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-11
修回日期:2024-09-21
出版日期:2024-09-26
发布日期:2024-09-26
通讯作者:
江天彤妃,博士,讲师,研究方向:癌症免疫生物信息学。E-mail: jttf@hrbmu.edu.cn;作者简介:万羽鑫,本科生,专业方向:生物信息学。E-mail: wyuxin0228@163.com
基金资助:
Yuxin Wan( ), Xinyu Zhu, Yu Zhao, Na Sun, Tiantongfei Jiang(
), Xinyu Zhu, Yu Zhao, Na Sun, Tiantongfei Jiang( ), Juan Xu(
), Juan Xu( )
)
Received:2024-06-11
Revised:2024-09-21
Published:2024-09-26
Online:2024-09-26
Supported by:摘要:
肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)中T细胞亚群的组成和肿瘤特异的T细胞互作促进了乳腺癌异质性的形成。此外,肿瘤的异常代谢通常与T细胞的抗肿瘤免疫功能失调关联密切,识别影响免疫细胞互作的关键代谢基因能够为乳腺癌治疗提供潜在靶点。本研究利用乳腺癌单细胞转录组数据,重点研究了乳腺癌发展过程中肿瘤特异性T细胞亚群及其互作子网,进一步评估肿瘤特异性激活的T细胞亚群的代谢通路活性。结果显示,肠促胰岛素的合成、分泌和失活的代谢通路以及果糖分解代谢通路显著影响了多个T细胞亚群的互作。整合肿瘤中T细胞显著上调以及影响互作的代谢通路,依此筛选出核心T细胞互作相关的异常代谢基因,并进一步构建乳腺癌风险评估模型。利用异常代谢显著相关预后基因表达谱与药物IC50值预测靶向药物,最终获得潜在靶向药物GSK-J4、PX-12等。本研究整合分析乳腺癌微环境中T细胞互作的重塑与代谢通路异常在癌症恶性进展中的作用,为新型乳腺癌抗癌疗法提供线索。
万羽鑫, 朱欣雨, 赵宇, 孙娜, 江天彤妃, 徐娟. 计算解析异常代谢对乳腺癌微环境重塑的调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(10): 871-885.
Yuxin Wan, Xinyu Zhu, Yu Zhao, Na Sun, Tiantongfei Jiang, Juan Xu. Computational dissection of the regulatory mechanisms of aberrant metabolism in remodeling the microenvironment of breast cancer[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(10): 871-885.
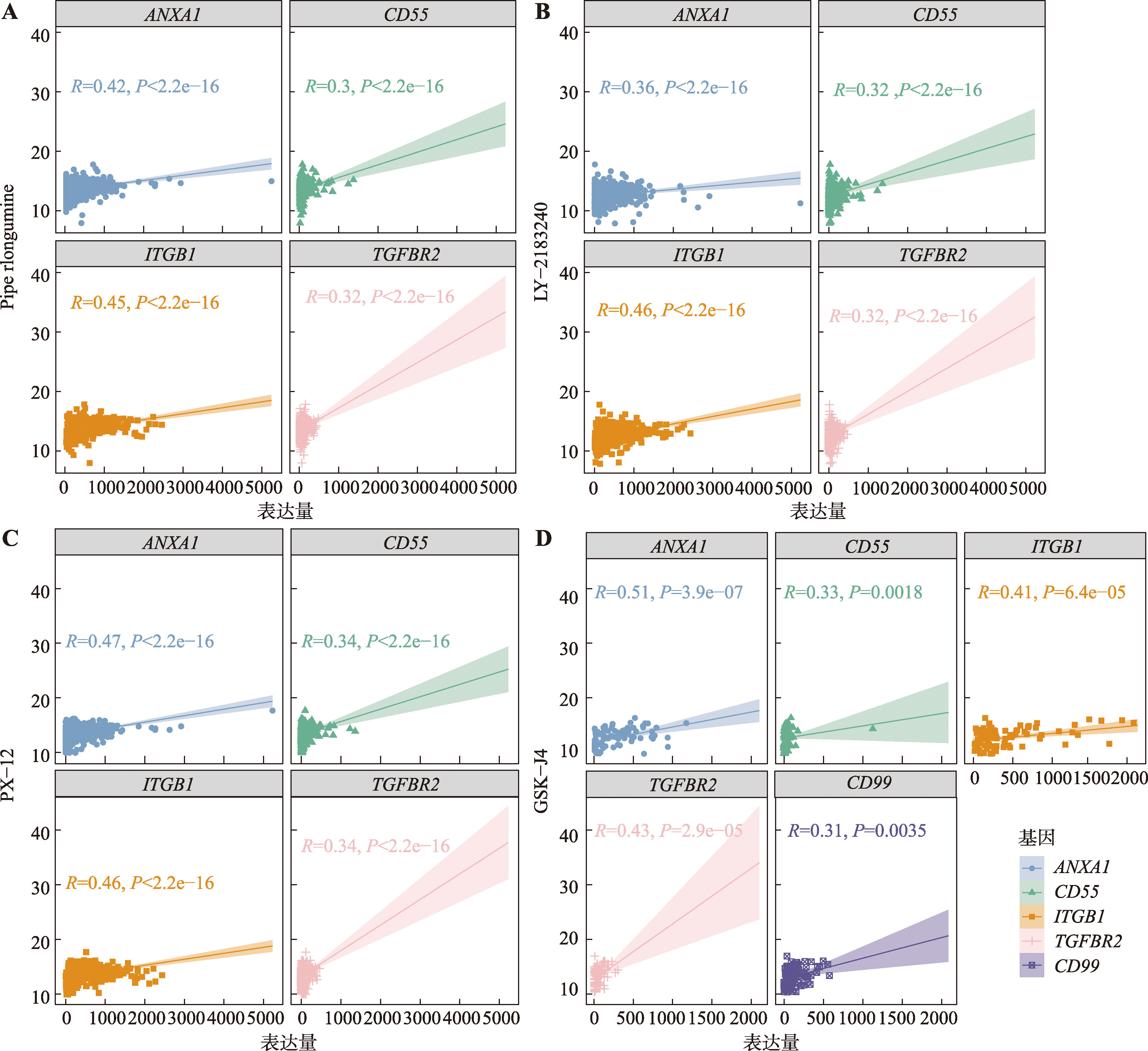
图9
基于药物IC50值与关键预后因子表达的相关性分析筛选潜在靶向药物 A:Piperlongumine与关键预后因子的相关性分析。ITGB1(R=0.45)、ANXA1(R=0.42)、TGFBR2(R=0.32)、CD55(R=0.3)。B:LY-2183240与关键预后因子的相关性分析。ITGB1(R=0.46)、ANXA1(R=0.36)、TGFBR2(R=0.32)、CD55(R=0.32)。C:PX-12与关键预后因子的相关性分析。ITGB1(R=0.46)、ANXA1(R=0.47)、TGFBR2(R=0.34)、CD55(R=0.34)。D:GSK-J4与关键预后因子的相关性分析。ITGB1(R=0.41)、ANXA1(R=0.51)、TGFBR2(R=0.43)、CD55(R=0.33)、CD99(R=0.31)。"
| [1] | Makhoul I, Atiq M, Alwbari A, Kieber-Emmons T. Breast cancer immunotherapy: an update. Breast Cancer (Auckl), 2018, 12: 1178223418774802. |
| [2] |
Arnold M, Morgan E, Rumgay H, Mafra A, Singh D, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Gralow JR, Cardoso F, Siesling S, Soerjomataram I. Current and future burden of breast cancer: global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast, 2022, 66: 15-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2022.08.010 pmid: 36084384 |
| [3] | Chen YL, Chang MC, Cheng WF. Metronomic chemotherapy and immunotherapy in cancer treatment. Cancer Lett, 2017, 400: 282-292. |
| [4] | Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, Campone M, Blackwell KL, André F, Winer EP, Janni W, Verma S, Conte P, Arteaga CL, Cameron DA, Petrakova K, Hart LL, Villanueva C, Chan A, Jakobsen E, Nusch A, Burdaeva O, Grischke EM, Alba E, Wist E, Marschner N, Favret AM, Yardley D, Bachelot T, Tseng LM, Blau S, Xuan FJ, Souami F, Miller M, Germa C, Hirawat S, O'Shaughnessy J. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med, 2016, 375(18): 1738-1748. |
| [5] |
Zhang Q, Gu ML. Single-cell sequencing and its application in breast cancer. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(3): 250-268.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-268 pmid: 32217511 |
| 张强, 顾明亮. 单细胞测序技术及其在乳腺癌研究中的应用. 遗传, 2020, 42(3): 250-268. | |
| [6] |
Savas P, Virassamy B, Ye CZ, Salim A, Mintoff CP, Caramia F, Salgado R, Byrne DJ, Teo ZL, Dushyanthen S, Byrne A, Wein L, Luen SJ, Poliness C, Nightingale SS, Skandarajah AS, Gyorki DE, Thornton CM, Beavis PA, Fox SB, Kathleen Cuningham Foundation Consortium for Research into Familial Breast Cancer (kConFab), Darcy PK, Speed TP, Mackay LK, Neeson PJ, Loi S. Single-cell profiling of breast cancer T cells reveals a tissue-resident memory subset associated with improved prognosis. Nat Med, 2018, 24(7): 986-993.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0078-7 pmid: 29942092 |
| [7] |
Tietscher S, Wagner J, Anzeneder T, Langwieder C, Rees M, Sobottka B, de Souza N, Bodenmiller B. A comprehensive single-cell map of T cell exhaustion-associated immune environments in human breast cancer. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 98.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35238-w pmid: 36609566 |
| [8] | Ding SN, Qiao N, Zhu QC, Tong YW, Wang SY, Chen XS, Tian Q, Xiao YC, Shen KW. Single-cell atlas reveals a distinct immune profile fostered by T cell-B cell crosstalk in triple negative breast cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2023, 43(6): 661-684. |
| [9] | Yao CB, Zhou X, Chen CS, Lei QY. The regulatory mechanisms and functional roles of the Hippo signaling pathway in breast cancer. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(7): 617-629. |
| 姚传波, 周鑫, 陈策实, 雷群英. Hippo信号通路在乳腺癌中的调控机制及作用. 遗传, 2017, 39(7): 617-629. | |
| [10] | Chang CH, Qiu J, O'Sullivan D, Buck MD, Noguchi T, Curtis JD, Chen QY, Gindin M, Gubin MM, van der Windt GJW, Tonc E, Schreiber RD, Pearce EJ, Pearce EL. Metabolic competition in the tumor microenvironment is a driver of cancer progression. Cell, 2015, 162(6): 1229-1241. |
| [11] |
Balaban S, Shearer RF, Lee LS, van Geldermalsen M, Schreuder M, Shtein HC, Cairns R, Thomas KC, Fazakerley DJ, Grewal T, Holst J, Saunders DN, Hoy AJ. Adipocyte lipolysis links obesity to breast cancer growth: adipocyte-derived fatty acids drive breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. Cancer Metab, 2017, 5: 1.
doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0163-7 pmid: 28101337 |
| [12] | Liu X, Hartman CL, Li LY, Albert CJ, Si FS, Gao AQ, Huang L, Zhao YJ, Lin WL, Hsueh EC, Shen LZ, Shao QX, Hoft DF, Ford DA, Peng GY. Reprogramming lipid metabolism prevents effector T cell senescence and enhances tumor immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med, 2021, 13(587): eaaz6314. |
| [13] |
Grum-Schwensen B, Klingelhöfer J, Beck M, Bonefeld CM, Hamerlik P, Guldberg P, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E, Ambartsumian N. S100A4-neutralizing antibody suppresses spontaneous tumor progression, pre-metastatic niche formation and alters T-cell polarization balance. BMC Cancer, 2015, 15: 44.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1034-2 pmid: 25884510 |
| [14] |
Stuart T, Butler A, Hoffman P, Hafemeister C, Papalexi E, Mauck WM, Hao YH, Stoeckius M, Smibert P, Satija R. Comprehensive integration of single-cell data. Cell, 2019, 177(7): 1888-1902.e21.
doi: S0092-8674(19)30559-8 pmid: 31178118 |
| [15] | Zhao Y, Xu H, Zhang MZ, Li L. Single-cell RNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq reveal intratumoral heterogeneity and tumor microenvironment characteristics in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 881345. |
| [16] |
Korsunsky I, Millard N, Fan J, Slowikowski K, Zhang F, Wei K, Baglaenko Y, Brenner M, Loh PR, Raychaudhuri S. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat Methods, 2019, 16(12): 1289-1296.
doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0619-0 pmid: 31740819 |
| [17] |
Farrel A, Li P, Veenbergen S, Patel K, Maris JM, Leonard WJ. ROGUE: an R shiny app for RNA sequencing analysis and biomarker discovery. BMC Bioinformatics, 2023, 24(1): 303.
doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05420-y pmid: 37516886 |
| [18] |
Jin SQ, Guerrero-Juarez CF, Zhang LH, Chang I, Ramos R, Kuan CH, Myung P, Plikus MV, Nie Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1088.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21246-9 pmid: 33597522 |
| [19] | Liang LL, Yu J, Li J, Li N, Liu J, Xiu L, Zeng J, Wang TT, Wu LY. Integration of scRNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq to analyse the heterogeneity of ovarian cancer immune cells and establish a molecular risk model. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 711020. |
| [20] | Shang SL, Liu ML, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Clendenen TV, Krogh V, Hallmans G, Lu WB. Partially linear single index cox regression model in nested case-control studies. Comput Stat Data Anal, 2013, 67: 199-212. |
| [21] | Xu F, Li L, Jiang LM, Zhang J. Identification of key genes and immune infiltration in multiple myeloma by bioinformatics analysis. Hematology, 2023, 28(1): 2264517. |
| [22] |
Yang XP, Su XL, Wang ZR, Yu Y, Wu ZP, Zhang DK. ULBP2 is a biomarker related to prognosis and immunity in colon cancer. Mol Cell Biochem, 2023, 478(10): 2207-2219.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04647-2 pmid: 36633827 |
| [23] |
Wang MH, Huang JF, Liu YY, Ma L, Potash JB, Han SZ. COMBAT: a combined association test for genes using summary statistics. Genetics, 2017, 207(3): 883-891.
doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300257 pmid: 28878002 |
| [24] |
Lira-Junior R, Holmström SB, Clark R, Zwicker S, Majster M, Johannsen G, Axtelius B, Åkerman S, Svensson M, Klinge B, Boström EA. S100A12 expression is modulated during monocyte differentiation and reflects periodontitis severity. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 86.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00086 pmid: 32082330 |
| [25] | Wang L, Wei Q, Zhang M, Chen LZ, Li ZN, Zhou CY, He M, Wei MJ, Zhao L. Identification of the prognostic value of immune gene signature and infiltrating immune cells for esophageal cancer patients. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 87: 106795. |
| [26] |
Yeong J, Lim JCT, Lee B, Li HH, Chia N, Ong CCH, Lye WK, Putti TC, Dent R, Lim E, Thike AA, Tan PH, Iqbal J. High densities of tumor-associated plasma cells predict improved prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1209.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01209 pmid: 29899747 |
| [27] | Onieva JL, Xiao QY, Berciano-Guerrero MÁ, Laborda-Illanes A, de Andrea C, Chaves P, Piñeiro P, Garrido-Aranda A, Gallego E, Sojo B, Gálvez L, Chica-Parrado R, Prieto D, Pérez-Ruiz E, Farngren A, Lozano MJ, Álvarez M, Jiménez P, Sánchez-Muñoz A, Oliver J, Cobo M, Alba E, Barragán I. High IGKC-expressing intratumoral plasma cells predict response to immune checkpoint blockade. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(16): 9124. |
| [28] | Chen X, Iliopoulos D, Zhang Q, Tang QZ, Greenblatt MB, Hatziapostolou M, Lim E, Tam WL, Ni M, Chen YW, Mai JH, Shen HF, Hu DZ, Adoro S, Hu B, Song M, Tan C, Landis MD, Ferrari M, Shin SJ, Brown M, Chang JC, Liu XS, Glimcher LH. XBP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by controlling the HIF1α pathway. Nature, 2014, 508(7494): 103-107. |
| [29] |
Xiao J, McGill JR, Nasir A, Lekan A, Johnson B, Wilkins DJ, Pearson GW, Tanner K, Goodarzi H, Glasgow E, Schlegel R, Agarwal S. Identifying drivers of breast cancer metastasis in progressively invasive subpopulations of zebrafish-xenografted MDA-MB-231. Mol Biomed, 2022, 3(1): 16.
doi: 10.1186/s43556-022-00080-5 pmid: 35614362 |
| [30] | Nishimura T, Végvári Á, Nakamura H, Fujii K, Sakai H, Naruki S, Furuya N, Saji H. Cancer cell immunity-related protein co-expression networks are associated with early-stage solid-predominant lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol, 2024, 14: 1273780. |
| [31] |
Jankauskas SS, Wong DWL, Bucala R, Djudjaj S, Boor P. Evolving complexity of MIF signaling. Cell Signal, 2019, 57: 76-88.
doi: S0898-6568(19)30015-4 pmid: 30682543 |
| [32] | Fey RM, Nichols RA, Tran TT, Vandenbark AA, Kulkarni RP. MIF and CD74 as emerging biomarkers for immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancers (Basel), 2024, 16(9): 1773. |
| [33] |
Puchalska P, Crawford PA. Multi-dimensional roles of ketone bodies in fuel metabolism, signaling, and therapeutics. Cell Metab, 2017, 25(2): 262-284.
doi: S1550-4131(16)30655-6 pmid: 28178565 |
| [34] | Chang CF, Diers AR, Hogg N. Cancer cell metabolism and the modulating effects of nitric oxide. Free Radic Biol Med, 2015, 79: 324-336. |
| [35] | Yuan HR, Wu XJ, Wu QL, Chatoff A, Megill E, Gao JJ, Huang TF, Duan TT, Yang KL, Jin CY, Yuan FE, Wang S, Zhao LJ, Zinn PO, Abdullah KG, Zhao YM, Snyder NW, Rich JN. Lysine catabolism reprograms tumour immunity through histone crotonylation. Nature, 2023, 617(7962): 818-826. |
| [36] | Luo YZ, Tian WW, Lu XQ, Zhang C, Xie JD, Deng XP, Xie Y, Yang SH, Du W, He RF, Wei WD. Prognosis stratification in breast cancer and characterization of immunosuppressive microenvironment through a pyrimidine metabolism-related signature. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1056680. |
| [37] | Chen L, Zhang YH, Wang SP, Zhang YH, Huang T, Cai YD. Prediction and analysis of essential genes using the enrichments of gene ontology and KEGG pathways. PLoS One, 2017, 12(9): e0184129. |
| [38] |
Maciolek JA, Alex Pasternak J, Wilson HL. Metabolism of activated T lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol, 2014, 27: 60-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.01.006 pmid: 24556090 |
| [39] |
Fellows E, Gil-Parrado S, Jenne DE, Kurschus FC. Natural killer cell-derived human granzyme H induces an alternative, caspase-independent cell-death program. Blood, 2007, 110(2): 544-552.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-051649 pmid: 17409270 |
| [40] |
Fan D, Zeng C, Wang SM, Han J, Zhu LL, Zhao HD, Zhang YQ, Lu JG, Xu Y. Forkhead box P3 promotes breast cancer cell apoptosis by regulating programmed cell death 4 expression. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(6): 292.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12155 pmid: 33101486 |
| [41] | Wang YL, Gao GP, Wu Y, Wang YQ, Wu XR, Zhou Q. S100A4 silencing facilitates corneal wound healing after alkali burns by promoting autophagy via blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2020, 61(11): 19. |
| [42] | Tian QQ, Liu XY, Li A, Wu HJ, Xie YN, Zhang HM, Wu FJ, Chen YT, Bai CC, Zhang XM. LINC01936 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of lung squamous cell carcinoma probably by EMT signaling and immune infiltration. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e16447. |
| [43] | Zhu TY, Hong LL, Ling ZQ. Oncofetal protein IGF2BPs in human cancer: functions, mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biomark Res, 2023, 11(1): 62. |
| [44] | Geidl-Flueck B, Gerber PA. Insights into the hexose liver metabolism-glucose versus fructose. Nutrients, 2017, 9(9): 1026. |
| [45] |
Liu L, Zhang LL, Li CL, Qiu ZD, Kuang TR, Wu ZK, Deng WH. Effects of hormones on intestinal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14(1): 105.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03336-1 pmid: 37101229 |
| [46] |
Yan NN, Xu L, Wu XB, Zhang L, Fei XC, Cao YL, Zhang FC. GSKJ4, an H3K27me3 demethylase inhibitor, effectively suppresses the breast cancer stem cells. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 359(2): 405-414.
doi: S0014-4827(17)30435-4 pmid: 28823831 |
| [47] |
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Shimokawa Y, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Aritake K, Urade Y, Goda Y. Characterization of four new designer drugs, 5-chloro-NNEI, NNEI indazole analog, α-PHPP and α-POP, with 11 newly distributed designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Sci Int, 2014, 243: 1-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2014.03.013 pmid: 24769262 |
| [48] | Sadeghirizi A, Yazdanparast R, Aghazadeh S. Combating trastuzumab resistance by targeting thioredoxin-1/PTEN interaction. Tumour Biol, 2015, 37(5): 6737-6747. |
| [49] | Sadeghi L, Wright APH. GSK-J4 Inhibition of KDM6B histone demethylase blocks adhesion of mantle cell lymphoma cells to stromal cells by modulating NF-κB signaling. Cells, 2023, 12(15): 2010. |
| [50] |
Lhuissier E, Aury-Landas J, Allas L, Boittin M, Boumediene K, Baugé C. Antiproliferative effect of the histone demethylase inhibitor GSK-J4 in chondrosarcomas. IUBMB Life, 2019, 71(11): 1711-1719.
doi: 10.1002/iub.2110 pmid: 31241814 |
| [51] |
Dias AS, Almeida CR, Helguero LA, Duarte IF. Metabolic crosstalk in the breast cancer microenvironment. Eur J Cancer, 2019, 121: 154-171.
doi: S0959-8049(19)30502-7 pmid: 31581056 |
| [52] |
Yu FL, Quan F, Xu JY, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zhang JY, Lan YJ, Yuan HT, Zhang HY, Cheng SJ, Xiao Y, Li X. Breast cancer prognosis signature: linking risk stratification to disease subtypes. Brief Bioinform, 2019, 20(6): 2130-2140.
doi: 10.1093/bib/bby073 pmid: 30184043 |
| [1] | 章子怡, 王棨临, 张俊有, 段迎迎, 刘家欣, 刘赵硕, 李春燕. 多组学数据驱动的机器学习模型在乳腺癌生存及治疗响应预测中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(10): 820-832. |
| [2] | 马春辉, 胡海旭, 张丽娟, 刘毅, 刘天懿. 用于循环肿瘤细胞定量分析的CK19数字PCR检测方法的建立及性能验证[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(3): 250-260. |
| [3] | 常栋, 刘享享, 刘睿, 孙建伟. FSCN1在乳腺癌发生发展中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(2): 115-127. |
| [4] | 张强, 顾明亮. 单细胞测序技术及其在乳腺癌研究中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(3): 250-268. |
| [5] | 王昕源, 张雨, 杨楠, 程禾, 孙玉洁. DNMT3a通过提升基因内部甲基化介导紫杉醇诱导的LINE-1异常表达[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(1): 100-111. |
| [6] | 禹奇超,宋彬,邹轩轩,王岭,刘德权,李波,马昆. 乳腺癌癌旁组织特异性表达基因分析[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(7): 625-633. |
| [7] | 余同露,蔡栋梁,朱根凤,叶晓娟,闵太善,陈红岩,卢大儒,陈浩明. CSN4基因干扰对乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(4): 318-326. |
| [8] | 姚传波, 周鑫, 陈策实, 雷群英. Hippo信号通路在乳腺癌中的调控机制及作用[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(7): 617-629. |
| [9] | 李泰明, 蓝文俊, 黄灿, 张春, 刘晓玫. 近红外荧光蛋白标记乳腺癌细胞外泌体的构建及鉴定[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(5): 427-435. |
| [10] | 吴新刚,彭姝彬,黄谦. 乳腺癌耐药蛋白基因的转录调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(12): 1529-1536. |
| [11] | 程龙,黄翠芬,叶棋浓. 乳腺癌中雌激素受体α表达水平调节的分子机制[J]. 遗传, 2010, 32(3): 191-197. |
| [12] | 王靖,李彦辉,郭政,朱晶,马文财,彭春方,刘庆. 根据蛋白质互作网络预测乳腺癌相关蛋白质的细致功能[J]. 遗传, 2007, 29(9): 1061-1066. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
